Patterns of Tadpole β Diversity in Temperate Montane Streams
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
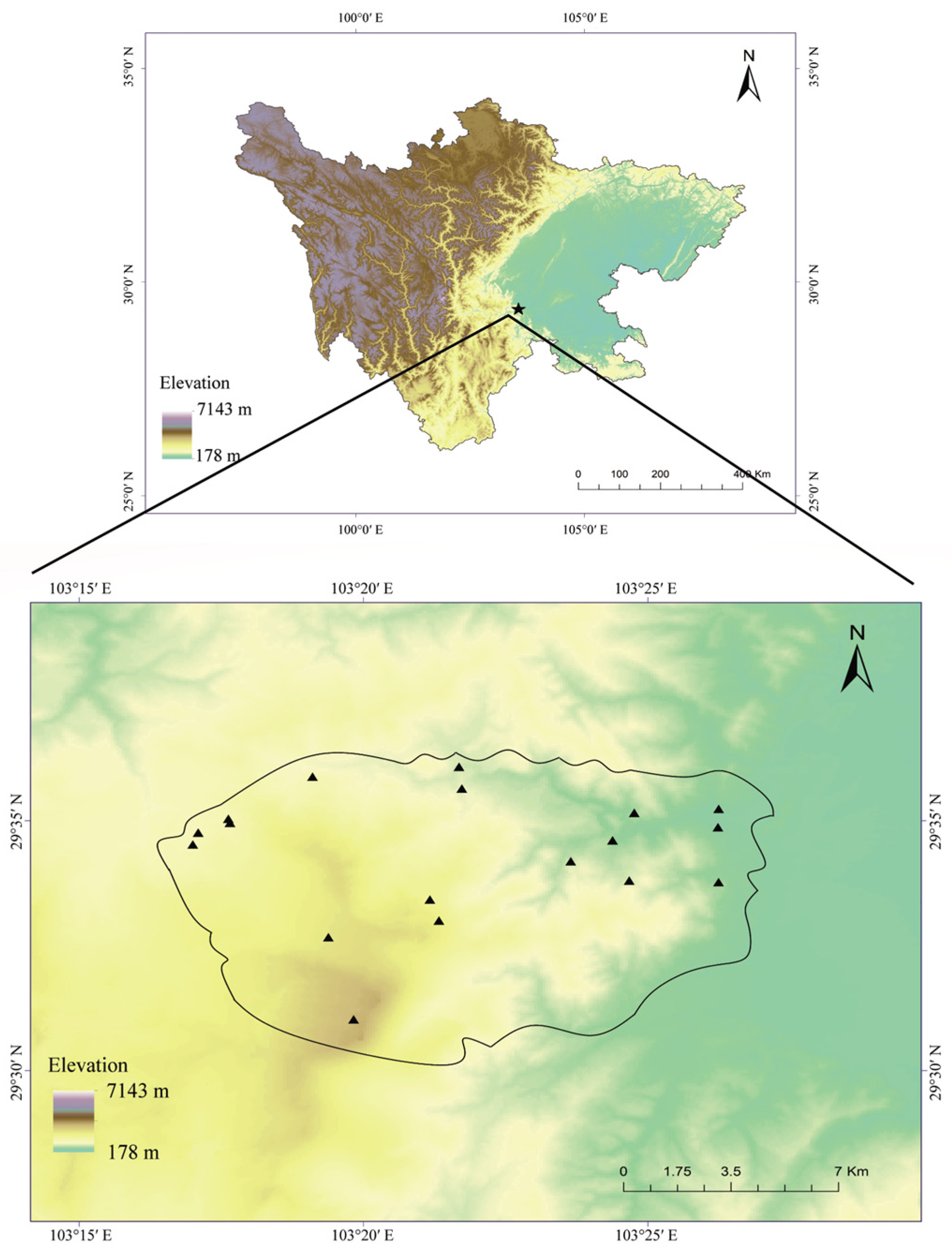
2.1. Study Area and Transects Selection
2.2. Tadpole Sampling
2.3. Environment Variables
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
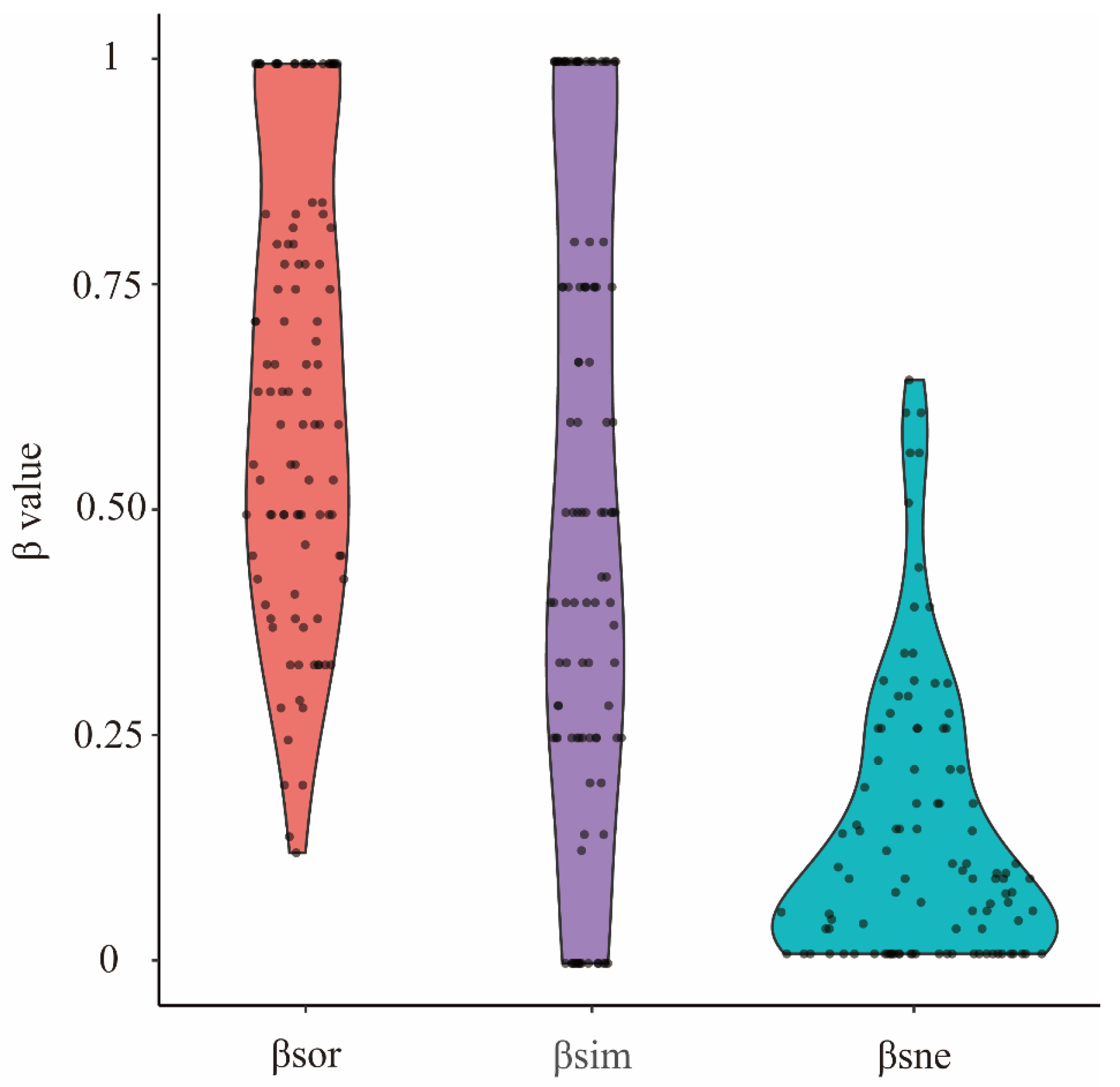
3.1. β Diversity and Its Components
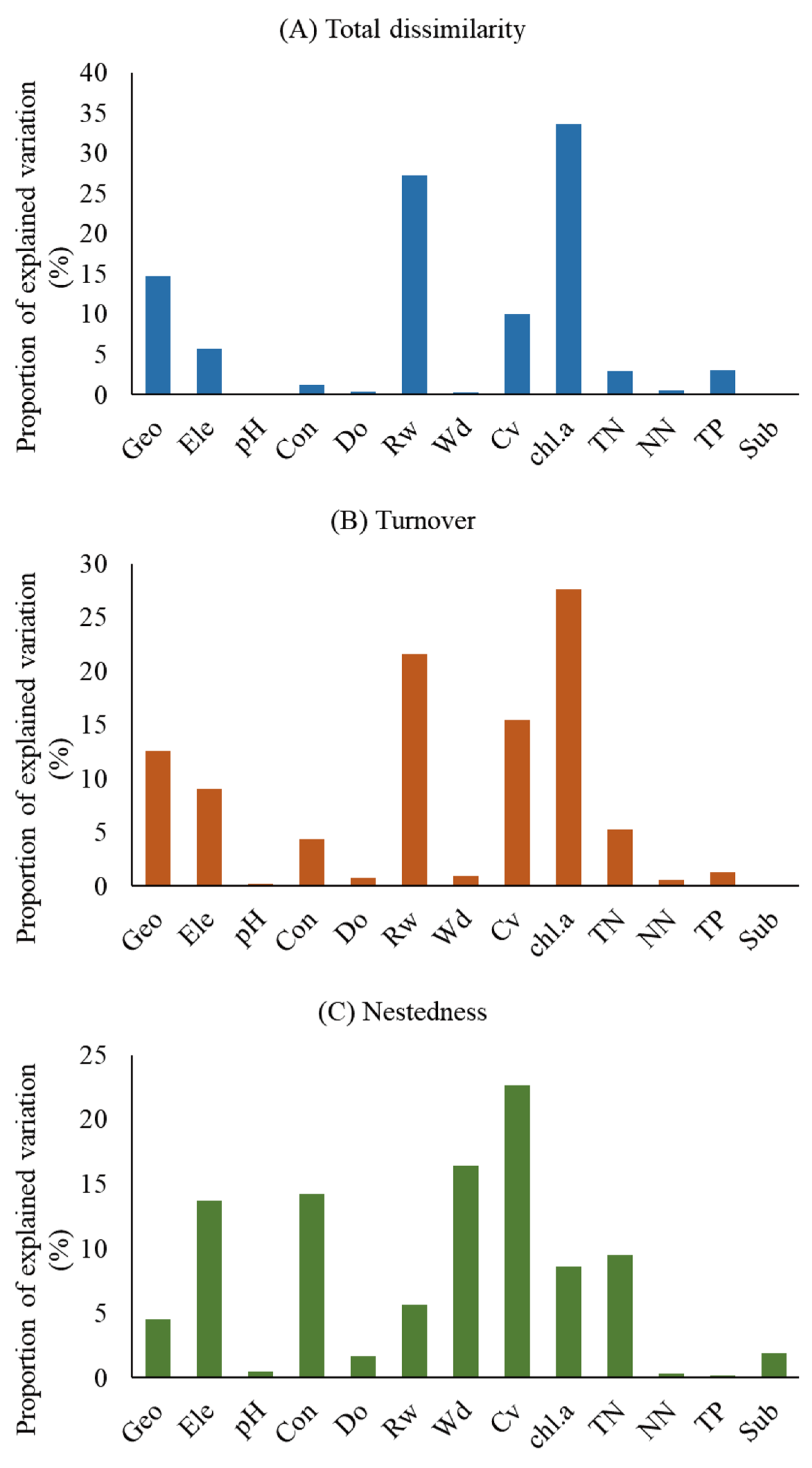
3.2. The Influencing Factors of β Diversity and Its Components
3.3. Relative Contribution of Independent Factors to Tadpole β Diversity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chase, J.M.; Blowes, S.A.; Knight, T.M.; Gerstner, K.; May, F. Ecosystem decay exacerbates biodiversity loss with habitat loss. Nature 2020, 584, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Fang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, S.; He, S.; Qi, W.; Bao, C.; Ma, H.; Fan, Y.; et al. Global impacts of future urban expansion on terrestrial vertebrate diversity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, R.H. Vegetation of the Siskiyou Mountains, Oregon and California. Ecol. Monogr. 1960, 30, 279–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; De Cáceres, M. Beta diversity as the variance of community data: Dissimilarity coefficients and partitioning. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, H.; Ricklefs, R.E. A latitudinal gradient in large-scale beta diversity for vascular plants in North America. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Soininen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Yang, X.; Shen, J. Patterns of elevational beta diversity in micro- and macroorganisms. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2012, 21, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Crist, T.O.; Chase, J.M.; Vellend, M.; Inouye, B.D.; Freestone, A.L.; Sanders, N.J.; Cornell, H.V.; Comita, L.S.; Davies, K.F.; et al. Navigating the multiple meanings of β diversity: A roadmap for the practicing ecologist. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baselga, A. The relationship between species replacement, dissimilarity derived from nestedness, and nestedness. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2012, 21, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouillot, D.; De Bortoli, J.; Leprieur, F.; Parravicini, V.; Kulbicki, M.; Bellwood, D.R. The challenge of delineating biogeographical regions: Nestedness matters for Indo-Pacific coral reef fishes. J. Biogeogr. 2013, 40, 2228–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socolar, J.B.; Gilroy, J.J.; Kunin, W.E.; Edwards, D.P. How Should Beta-Diversity Inform Biodiversity Conservation? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, A. Partitioning the turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2010, 19, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, P.S.; Cunningham, S.A.; Manning, A.D.; Gibb, H.; Lindenmayer, D.B.; Didham, R.K. The spatial scaling of beta diversity. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2013, 22, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, A.S.; Isbell, F.; Seidl, R. β-diversity, community assembly, and ecosystem functioning. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2018, 33, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponisio, L.C.; M’Gonigle, L.K.; Kremen, C. On-farm habitat restoration counters biotic homogenization in intensively managed agriculture. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Bao, Y.; Yu, M.; Xu, G.; Ding, P. Biodiversity Research: Nestedness for different reasons: The distributions of birds, lizards and small mammals on islands of an inundated lake. Divers. Distrib. 2010, 16, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeler, D.G. Revealing a conservation challenge through partitioned long-term beta diversity: Increasing turnover and decreasing nestedness of boreal lake metacommunities. Divers. Distrib. 2013, 19, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P. Interpreting the replacement and richness difference components of beta diversity. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2014, 23, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.C.; Cardoso, P.; Gomes, P. Determining the relative roles of species replacement and species richness differences in generating beta-diversity patterns. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2012, 21, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.; Baselga, A.; Ding, P. Revealing Beta-Diversity Patterns of Breeding Bird and Lizard Communities on Inundated Land-Bridge Islands by Separating the Turnover and Nestedness Components. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, M.; Yang, S.; Jiang, J.; Hu, J. Multiple β-diversity patterns and the underlying mechanisms across amphibian communities along a subtropical elevational gradient. Divers. Distrib. 2022, 28, 2489–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koleff, P.; Lennon, J.J.; Gaston, K.J. Are there latitudinal gradients in species turnover? Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2003, 12, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, R.D.; Willig, M.R. Geographical Ecology at the Community Level: Perspectives on the Diversity of New World Bats. Ecology 2002, 83, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, L.A.; Singer, M.S.; Lill, J.T.; Stireman, J.O.; Gentry, G.L.; Marquis, R.J.; Ricklefs, R.E.; Greeney, H.F.; Wagner, D.L.; Morais, H.C.; et al. Host specificity of Lepidoptera in tropical and temperate forests. Nature 2007, 448, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, H.; Badgley, C.; Fox, D.L. The latitudinal gradient of beta diversity in relation to climate and topography for mammals in North America. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2009, 18, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Fang, J.; Chi, X.; Feng, J.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Zheng, C.; et al. Patterns of plant beta-diversity along elevational and latitudinal gradients in mountain forests of China. Ecography 2012, 35, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, K.J.; Davies, R.G.; Orme, C.D.L.; Olson, V.A.; Thomas, G.H.; Ding, T.-S.; Rasmussen, P.C.; Lennon, J.J.; Bennett, P.M.; Owens, I.P.; et al. Spatial turnover in the global avifauna. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahbek, C.; Borregaard, M.K.; Colwell, R.K.; Dalsgaard, B.; Holt, B.G.; Morueta-Holme, N.; Nogues-Bravo, D.; Whittaker, R.J.; Fjeldså, J. Humboldt’s enigma: What causes global patterns of mountain biodiversity? Science 2019, 365, 1108–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Körner, C. Why are there global gradients in species richness? mountains might hold the answer. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2000, 15, 513–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condit, R.; Pitman, N.; Leigh, E.G.; Chave, J.; Terborgh, J.; Foster, R.B.; Núñez, P.; Aguilar, S.; Valencia, R.; Villa, G.; et al. Beta-Diversity in Tropical Forest Trees. Science 2002, 295, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Sanders, N.J.; Liu, J.; Jin, T.; Zhou, H.; Lu, R.; Ding, P.; Si, X. β diversity among ant communities on fragmented habitat islands: The roles of species trait, phylogeny and abundance. Ecography 2021, 44, 1568–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamonjisoa, N.; Natuhara, Y. Contrasting effects of functionally distinct tadpole species on nutrient cycling and litter breakdown in a tropical rainforest stream. Freshw. Biol. 2018, 63, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauß, A.; Reeve, E.; Randrianiaina, R.-D.; Vences, M.; Glos, J. The world’s richest tadpole communities show functional redundancy and low functional diversity: Ecological data on Madagascar’s stream-dwelling amphibian larvae. BMC Ecol. 2010, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.B.; Zhao, C.L.; Liao, C.L.; Zou, B.; Xu, D.; Zhu, W.; Zhao, T.; Jiang, J.P. Spatial and temporal patterns of amphibian species richness on Tianping Mountain, Hunan Province, China. Zool. Res. 2020, 41, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, W.; Feng, J.; Su, S.; Zhao, T. Microhabitat features determine the tadpole diversity in mountainous streams. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Guo, C.-P.; Tang, K.; Jiang, J.-p.; Hu, J. Amphibian diversity and conservation along an elevational gradient on mount Emei, southwestern China. Amphib. Reptile Conserv. 2020, 14, 46–56. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.Q.; Ohsawa, M. Altitudinal distribution of evergreen broad-leaved trees and their leaf-size pattern on a humid subtropical mountain, Mt. Emei, Sichuan, China. Plant Ecol. 1999, 145, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Su, S.; Feng, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, W.; Fan, W.; Lan, J.; Zhao, T. Functional and phylogenetic analyses of tadpole community assembly in temperate montane streams. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, T.d.S.; dos Santos, T.G.; Rossa-Feres, D.d.C.; Haddad, C.F.B. Spatial and temporal distribution of tadpole assemblages (Amphibia, Anura) in a seasonal dry tropical forest of southeastern Brazil. Hydrobiologia 2011, 673, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, D.; Smith, G.; Rettig, J. Effects of age and group size on habitat selection and activity level in Xenopus Laevis tadpoles. Trans. Neb. Acad. Sci. 2000, 26, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Negovetic, S.; Anholt, B.R.; Semlitsch, R.D.; Reyer, H.-U. Specific Responses of Sexual and Hybridogenetic European Waterfrog Tadpoles to Temperature. Ecology 2001, 82, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, A.; Orme, D.; Villeger, S.; De Bortoli, J.; Leprieur, F.; Logez, M.; Henriques-Silva, R. Betapart: Partitioning beta diversity into turnover and nestedness componts. R Package Version 1.5.4. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=betapart (accessed on 20 May 2023).
- Khatiwada, J.R.; Zhao, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Xie, F.; Cannatella, D.C.; Jiang, J. Amphibian Community Structure along Elevation Gradients in Eastern Nepal Himalaya. BMC Ecol. 2019, 19, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrell, F.E., Jr. HMISC: Harrell Miscellaneous. R Package Version 4.1-1. 2018. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=Hmisc (accessed on 21 March 2022).
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, B.; Simpson, G.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, H.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.3-0. 2015. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/web/packages/vegan/index.html (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- Hijmans, R.J.; Karney, C.; Williams, E.; Vennes, C. Geosphere: Spherical Trigonometry. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=geosphere (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Bartoń, K. MuMIn: Multi-Model Inference. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/MuMIn/index.html (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Legendre, P.; Lapointe, F.-J.; Casgrain, P. Modeling Brain Evolution from Behavior: A Permutational Regression Approach. Evolution 1994, 48, 1487–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mac Nally, R. Multiple regression and inference in ecology and conservation biology: Further comments on identifying important predictor variables. Biodivers. Conserv. 2002, 11, 1397–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 12 January 2022).
- Bishop, T.R.; Robertson, M.P.; van Rensburg, B.J.; Parr, C.L. Contrasting species and functional beta diversity in montane ant assemblages. J. Biogeogr. 2015, 42, 1776–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, P.G.; Lobo, J.M.; Hensen, M.C.; Vaz-De-Mello, F.Z.; Hernández, M.I.M. Turnover and nestedness in subtropical dung beetle assemblages along an elevational gradient. Divers. Distrib. 2018, 24, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, D.; Liu, J.; Jin, T.; Ding, P. Spatial patterns and influencing factors of ground ant species diversity on the land-bridge islands in the Thousand Island Lake, China. Biodivers. Sci. 2019, 27, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, K.; Messyasz, B.; Xu, Y.; Gao, M.; Li, Y.; Wu, N. Functional and taxonomic beta diversity of butterfly assemblages in an archipelago: Relative importance of island characteristics, climate, and spatial factors. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, I.R.; Sandel, B.; Tsirogiannis, C.; Morueta-Holme, N.; Svenning, J.; Enquist, B.J.; Kraft, N.J. Temperature shapes opposing latitudinal gradients of plant taxonomic and phylogenetic β diversity. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-B.; Lü, X.-T.; Yao, J.; Wang, Z.-W.; Deng, Y.; Cheng, W.-X.; Zhou, J.-Z.; Han, X.-G. Habitat-specific patterns and drivers of bacterial β-diversity in China’s drylands. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1345–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennon, J.J.; Koleff, P.; Greenwood, J.J.D.; Gaston, K.J. The geographical structure of British bird distributions: Diversity, spatial turnover and scale. J. Anim. Ecol. 2001, 70, 966–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-D.; Qian, H.; Jin, Y.; Xiao, K.-Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, Q.-F. Geographic patterns of taxonomic and phylogenetic β-diversity of aquatic angiosperms in China. Plant Divers. 2023, 45, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astorga, A.; Death, R.G.; Death, F.; Paavola, R.; Chakraborty, M.; Muotka, T. Habitat heterogeneity drives the geographical distribution of beta diversity: The case of New Zealand stream invertebrates. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 2693–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Ding, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Quan, Q.; Guo, K.; Tian, L.; Hu, H.; Gibson, L. Birds in the Himalayas: What drives beta diversity patterns along an elevational gradient? Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 11704–11716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.-C.; Ding, Z.-F.; Li, C.-L.; Hu, Y.-M.; Zhou, Z.-X.; Lie, G.-W.; Niu, X.-N.; Huang, W.-B.; Hu, H.-J.; Si, X.-F.; et al. Patterns and drivers of avian taxonomic and phylogenetic beta diversity in China vary across geographical backgrounds and dispersal abilities. Zool. Res. 2023, 45, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, R.A.; Poff, N.L.; Kondratieff, B.C. Aquatic insect β-diversity is not dependent on elevation in Southern Rocky Mountain streams. Freshw. Biol. 2015, 61, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Delgado, E.O.; Winemiller, K.O.; Villa-Navarro, F.A. Local environmental factors influence beta-diversity patterns of tropical fish assemblages more than spatial factors. Ecology 2020, 101, e02940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legendre, P.; Mi, X.; Ren, H.; Ma, K.; Yu, M.; Sun, I.-F.; He, F. Partitioning beta diversity in a subtropical broad-leaved forest of China. Ecology 2009, 90, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soininen, J.; Heino, J.; Wang, J. A meta-analysis of nestedness and turnover components of beta diversity across organisms and ecosystems. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2018, 27, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosindell, J.; Hubbell, S.P.; Etienne, R.S. The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography at Age Ten. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2011, 26, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Fan, L.; Xu, Z.; Wen, Z.; Cai, T.; Feijo, A.; Hu, J.; Lei, F.; Yang, Q.; Qiao, H. A multi-faceted comparative perspective on elevational beta-diversity: The patterns and their causes. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 288, 20210343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Distance Matrixes | Total Dissimilarity | Turnover | Nestedness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geography | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.952 |
| Elevation | 0.010 | 0.008 | 0.962 |
| Environment | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.959 |
| Components | Total Dissimilarity | Turnover | Nestedness |
|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.41 | 0.40 | 0.22 |
| p | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.31 |
| Geo | 0.33 | 0.39 | 0.78 |
| Ele | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.23 |
| pH | 0.96 | 0.86 | 0.61 |
| Con | 0.68 | 0.38 | 0.20 |
| Do | 0.58 | 0.62 | 0.83 |
| Rw | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.29 |
| Wd | 0.82 | 0.39 | 0.04 |
| Cv | 0.41 | 0.13 | 0.09 |
| chl.a | 0.14 | 0.23 | 0.81 |
| TN | 0.39 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| NN | 0.66 | 0.65 | 0.79 |
| TP | 0.29 | 0.45 | 0.96 |
| Sub | 0.88 | 0.78 | 0.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, D.; Sun, Z.; Tao, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, T. Patterns of Tadpole β Diversity in Temperate Montane Streams. Animals 2024, 14, 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14081240
Kang D, Sun Z, Tao J, Huang Y, Zhao T. Patterns of Tadpole β Diversity in Temperate Montane Streams. Animals. 2024; 14(8):1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14081240
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Da, Zijian Sun, Jiacheng Tao, Yan Huang, and Tian Zhao. 2024. "Patterns of Tadpole β Diversity in Temperate Montane Streams" Animals 14, no. 8: 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14081240
APA StyleKang, D., Sun, Z., Tao, J., Huang, Y., & Zhao, T. (2024). Patterns of Tadpole β Diversity in Temperate Montane Streams. Animals, 14(8), 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14081240






