DNA Content in Embryonic Extracellular Vesicles Is Independent of the Apoptotic Rate in Bovine Embryos Produced In Vitro
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Vitro Embryo Production
2.2. In Vitro Fertilization Production
2.3. Parthenogenesis Production
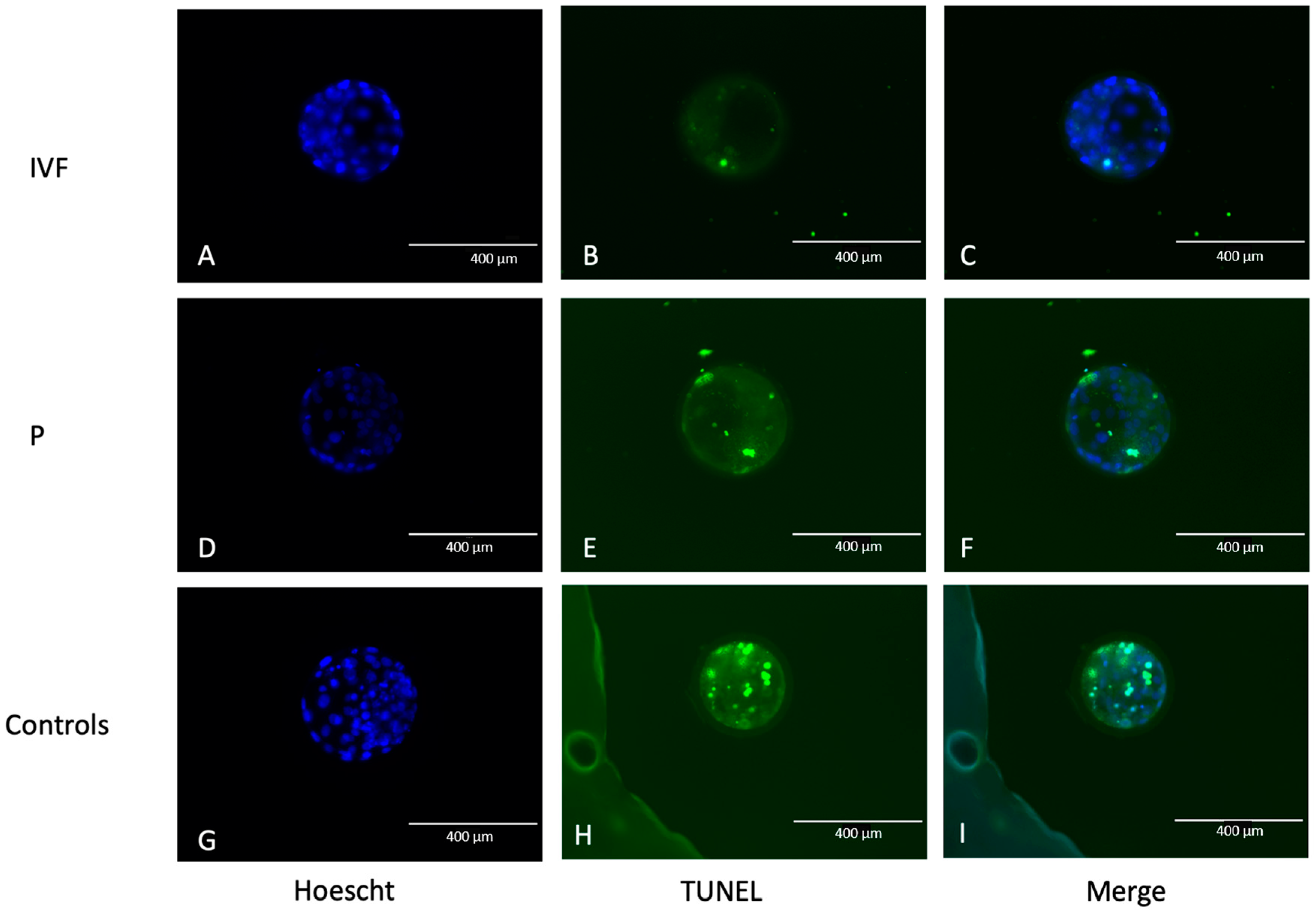
2.4. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT) dUTP Nick-End Labeling (TUNEL)
2.5. Extracellular Vesicle Concentration and Characterization
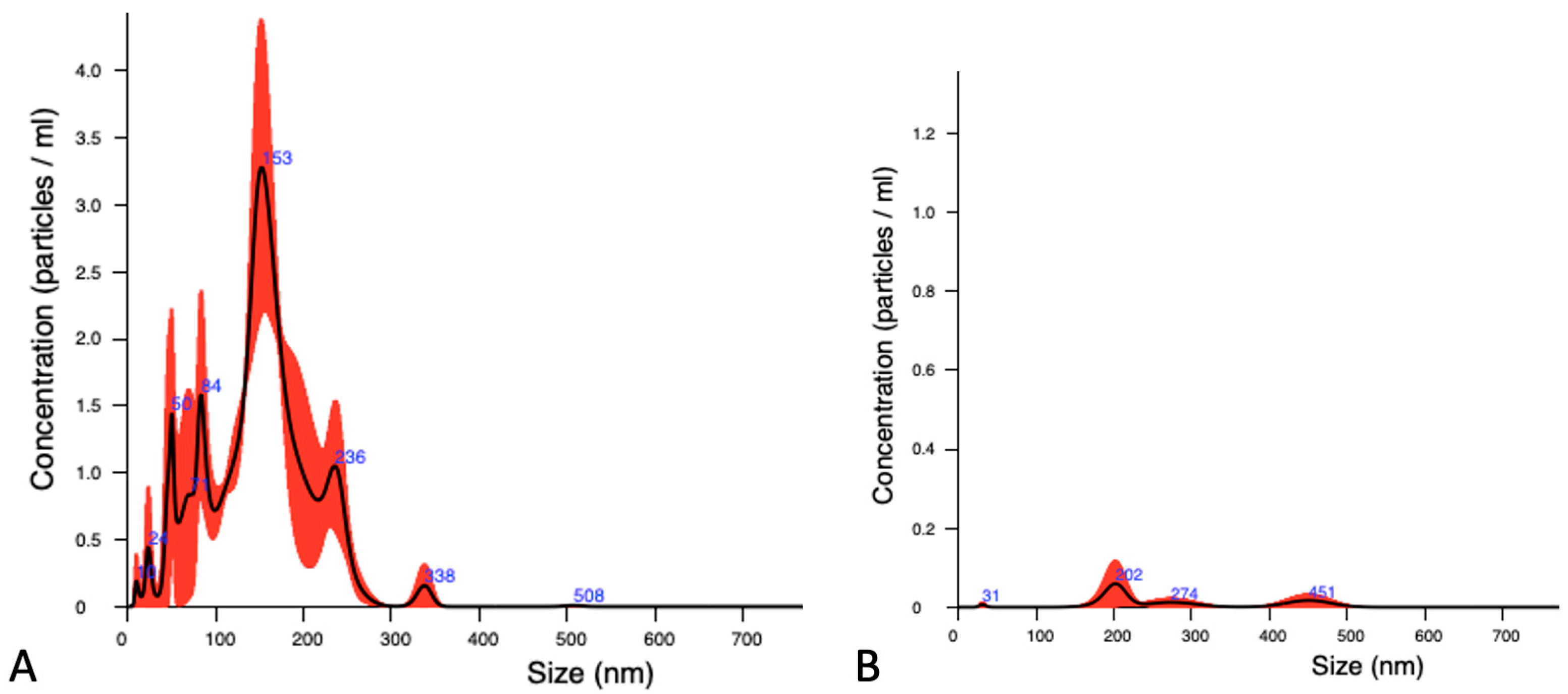
2.5.1. Nano-Tracking Analysis
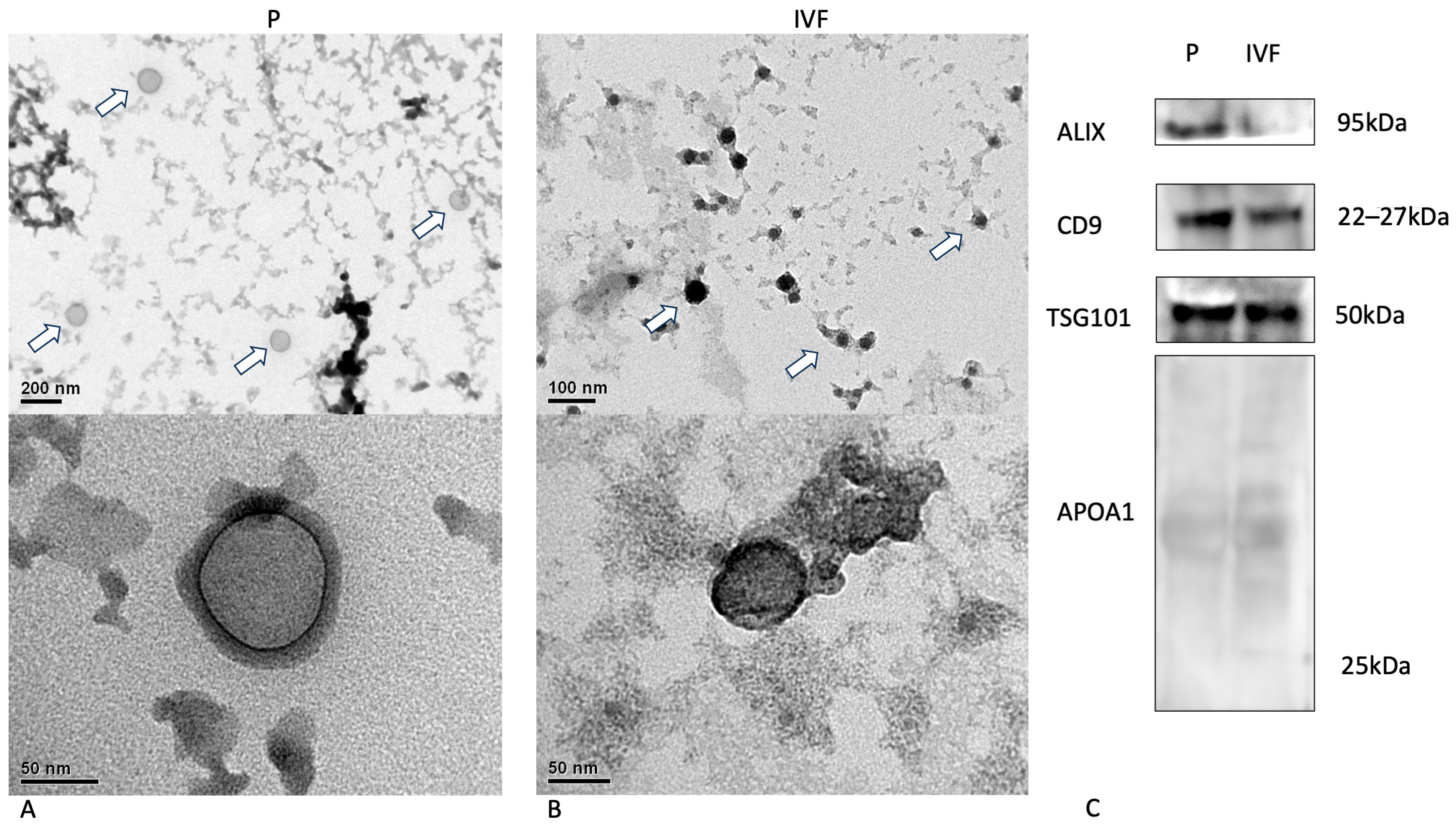
2.5.2. Western Blot
2.5.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy
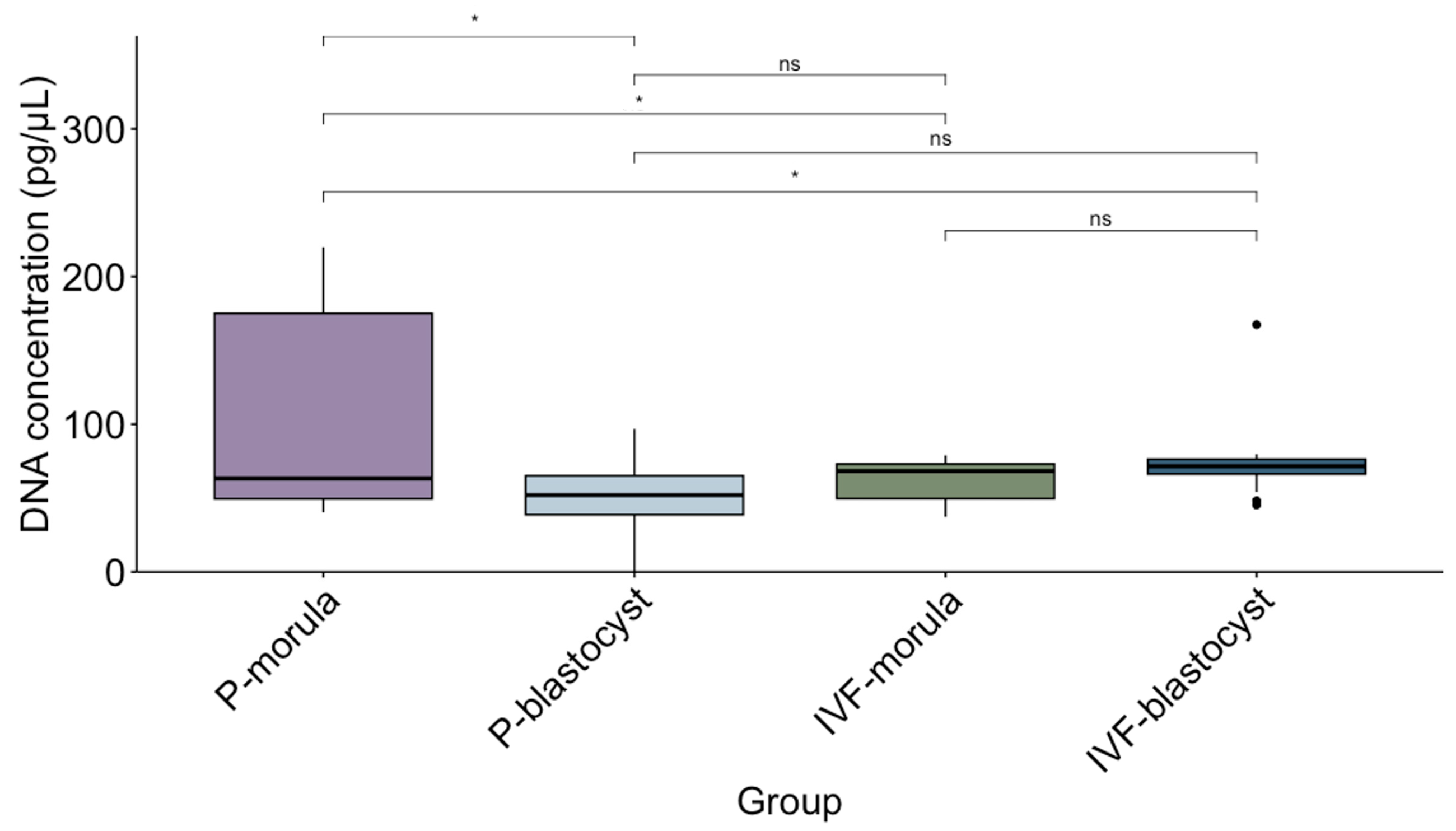
2.6. DNA Quantification in EVs
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Embryos with Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT) dUTP Nick-End Labeling (TUNEL) Dye and Apoptosis Determination
3.2. Characterization of EVs Released by Parthenogenesis and IVF Bovine Embryos
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caby, M.P.; Lankar, D.; Vincendeau-Scherrer, C.; Raposo, G.; Bonnerot, C. Exosomal-like vesicles are present in human blood plasma. Int. Immunol. 2005, 17, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisitkun, T.; Shen, R.F.; Knepper, M.A. Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human urine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13368–13373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumeda, N.; Ogawa, Y.; Akimoto, Y.; Kawakami, H.; Tsujimoto, M.; Yanoshita, R. Characterization of Membrane Integrity and Morphological Stability of Human Salivary Exosomes. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Admyre, C.; Johansson, S.M.; Qazi, K.R.; Filén, J.J.; Lahesmaa, R.; Norman, M.; Neve, E.P.; Scheynius, A.; Gabrielsson, S. Exosomes with immune modulatory features are present in human breast milk. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asea, A.; Jean-Pierre, C.; Kaur, P.; Rao, P.; Linhares, I.M.; Skupski, D.; Witkin, S.S. Heat shock protein-containing exosomes in mid-trimester amniotic fluids. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2008, 79, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A.; Yoshida-Court, K.; Solley, T.N.; Mikkelson, M.; Yeung, C.L.A.; Nick, A.; Lu, K.; Klopp, A.H. Extracellular vesicles derived from ascitic fluid enhance growth and migration of ovarian cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilella, F.; Moreno-Moya, J.M.; Balaguer, N.; Grasso, A.; Herrero, M.; Martínez, S.; Marcilla, A.; Simón, C. Hsa-miR-30d, secreted by the human endometrium, is taken up by the pre-implantation embryo and might modify its transcriptome. Development 2015, 142, 3210–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masyuk, A.I.; Huang, B.Q.; Ward, C.J.; Gradilone, S.A.; Banales, J.M.; Masyuk, T.V.; Radtke, B.; Splinter, P.L.; LaRusso, N.F. Biliary exosomes influence cholangiocyte regulatory mechanisms and proliferation through interaction with primary cilia. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 299, G990–G999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellisho, E.A.; Velásquez, A.E.; Nuñez, M.J.; Cabezas, J.G.; Cueto, J.A.; Fader, C.; Castro, F.O.; Rodríguez-Álvarez, L. Identification and characteristics of extracellular vesicles from bovine blastocysts produced in vitro. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistelli, M.; Falcieri, E. Apoptotic Bodies: Particular Extracellular Vesicles Involved in Intercellular Communication. Biology 2020, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akers, J.C.; Gonda, D.; Kim, R.; Carter, B.S.; Chen, C.C. Biogenesis of extracellular vesicles (EV): Exosomes, microvesicles, retrovirus-like vesicles, and apoptotic bodies. J. Neurooncol. 2013, 113, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- György, B.; Szabó, T.G.; Pásztói, M.; Pál, Z.; Misják, P.; Aradi, B.; László, V.; Pállinger, E.; Pap, E.; Kittel, A.; et al. Membrane vesicles, current state-of-the-art: Emerging role of extracellular vesicles. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 2667–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocucci, E.; Racchetti, G.; Meldolesi, J. Shedding microvesicles: Artefacts no more. Trends Cell Biol. 2009, 19, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Verrilli, M.A.; Picou, F.; Court, F.A. Schwann cell-derived exosomes enhance axonal regeneration in the peripheral nervous system. Glia 2013, 61, 1795–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.E. Extracellular Vesicles and Metastasis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2020, 10, a037275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathan, M.; Fonseka, P.; Chitti, S.V.; Kang, T.; Sanwlani, R.; Van Deun, J.; Hendrix, A.; Mathivanan, S. Vesiclepedia 2019: A compendium of RNA, proteins, lipids and metabolites in extracellular vesicles. Nucleic Acids Res 2019, 47, D516–D519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, C.A.; Hardy, J.; Schott, J.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatischeff, I. Extracellular Vesicle-DNA: The Next Liquid Biopsy Biomarker for Early Cancer Diagnosis? Cancers 2023, 15, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, C.; Wong, Y.S.; Gutierrez-Reinoso, M.A.; Velásquez, A.E.; Melo-Báez, B.; Cabezas, J.; Caamaño, D.; Navarrete, F.; Castro, F.O.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, L.l. Embryo-maternal communication mediated by extracellular vesicles in the early stages of embryonic development is modified by in vitro conditions. Theriogenology 2024, 214, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, C.; Velásquez, A.E.; Gutierrez-Reinoso, M.A.; Wong, Y.S.; Melo-Baez, B.; Cabezas, J.; Caamaño, D.; Navarrete, F.; Rojas, D.; Riadi, G.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Pre-Hatching Bovine Embryos Produced In Vitro and In Vivo Alter the Expression of IFNtau-Stimulated Genes in Bovine Endometrial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, K.; Nõmm, M.; Lättekivi, F.; Ressaissi, Y.; Godakumara, K.; Lavrits, A.; Midekessa, G.; Viil, J.; Bæk, R.; Jørgensen, M.M.; et al. Individually cultured bovine embryos produce extracellular vesicles that have the potential to be used as non-invasive embryo quality markers. Theriogenology 2020, 149, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavani, K.C.; Hendrix, A.; Van Den Broeck, W.; Couck, L.; Szymanska, K.; Lin, X.; De Koster, J.; Van Soom, A.; Leemans, B. Isolation and Characterization of Functionally Active Extracellular Vesicles from Culture Medium Conditioned by Bovine Embryos In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellisho, E.A.; Briones, M.A.; Velásquez, A.E.; Cabezas, J.; Castro, F.O.; Rodríguez-Álvarez, L. Extracellular vesicles secreted during blastulation show viability of bovine embryos. Reproduction 2019, 158, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomini, E.; Vago, R.; Sanchez, A.M.; Podini, P.; Zarovni, N.; Murdica, V.; Rizzo, R.; Bortolotti, D.; Candiani, M.; Viganò, P. Secretome of in vitro cultured human embryos contains extracellular vesicles that are uptaken by the maternal side. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, M.; Kale, V. Extracellular vesicles: Mediators of embryo-maternal crosstalk during pregnancy and a new weapon to fight against infertility. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 99, 151125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadeldin, I.M.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, Y.B.; Lee, B.C. Improvement of cloned embryos development by co-culturing with parthenotes: A possible role of exosomes/microvesicles for embryos paracrine communication. Cell Reprogram 2014, 16, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallinger, E.; Bognar, Z.; Bodis, J.; Csabai, T.; Farkas, N.; Godony, K.; Varnagy, A.; Buzas, E.; Szekeres-Bartho, J. A simple and rapid flow cytometry-based assay to identify a competent embryo prior to embryo transfer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, B.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Shi, C.; Xu, Y.; Dong, J.; Wang, C.; Lai, W.; et al. Derivation of Pluripotent Stem Cells with In Vivo Embryonic and Extraembryonic Potency. Cell 2017, 169, 243–257.e225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimadomo, D.; Capalbo, A.; Ubaldi, F.M.; Scarica, C.; Palagiano, A.; Canipari, R.; Rienzi, L. The Impact of Biopsy on Human Embryo Developmental Potential during Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 7193075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belandres, D.; Shamonki, M.; Arrach, N. Current status of spent embryo media research for preimplantation genetic testing. J. Assist Reprod Genet 2019, 36, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, E.R.; McGillivray, B.C.; Wicker, S.M.; Peek, J.C.; Shelling, A.N.; Stone, P.; Chamley, L.W.; Cree, L.M. Characterizing nuclear and mitochondrial DNA in spent embryo culture media: Genetic contamination identified. Fertil. Steril. 2017, 107, 220–228.e225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzanowska, J.; Semira, C.; Costa-Silva, B. DNA in extracellular vesicles: Biological and clinical aspects. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 1701–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasquez, A.E.; Castro, F.O.; Veraguas, D.; Cox, J.F.; Lara, E.; Briones, M.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, L. Splitting of IVP bovine blastocyst affects morphology and gene expression of resulting demi-embryos during in vitro culture and in vivo elongation. Zygote 2016, 24, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.E.; Sung, K.J.; Sung, Y.H.; Pack, C.G.; Jung, M.K.; Han, B.; et al. Exosomal PD-L1 promotes tumor growth through immune escape in non-small cell lung cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crasta, D.N.; Nair, R.; Kumari, S.; Dutta, R.; Adiga, S.K.; Zhao, Y.; Kannan, N.; Kalthur, G. Haploid Parthenogenetic Embryos Exhibit Unique Stress Response to pH, Osmotic and Oxidative Stress. Reprod. Sci. 2023, 30, 2137–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo-Baez, B.; Wong, Y.S.; Aguilera, C.J.; Cabezas, J.; Mançanares, A.C.F.; Riadi, G.; Castro, F.O.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, L. MicroRNAs from Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Bovine Embryos as Early Biomarkers of Developmental Competence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifkar, A.; Hur, Y.H.; Sanchez, J.C.; Cerione, R.A.; Antonyak, M.A. New insights into extracellular vesicle biogenesis and function. J. Cell Sci. 2019, 132, jcs222406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlert, C.; Melo, S.A.; Protopopov, A.; Tang, J.; Seth, S.; Koch, M.; Zhang, J.; Weitz, J.; Chin, L.; Futreal, A.; et al. Identification of double-stranded genomic DNA spanning all chromosomes with mutated KRAS and p53 DNA in the serum exosomes of patients with pancreatic cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 3869–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Okada, R.; Nagao, K.; Kawamata, Y.; Hanyu, A.; Yoshimoto, S.; Takasugi, M.; Watanabe, S.; Kanemaki, M.T.; Obuse, C.; et al. Exosomes maintain cellular homeostasis by excreting harmful DNA from cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoda, Y.; Ogata, T.; Nagasawa, S.; Kumazu, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Yamada, T.; Oshima, T. The impact of muscle mass loss after esophagectomy for esophageal cancer on prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boelens, M.C.; Wu, T.J.; Nabet, B.Y.; Xu, B.; Qiu, Y.; Yoon, T.; Azzam, D.J.; Twyman-Saint Victor, C.; Wiemann, B.Z.; Ishwaran, H.; et al. Exosome transfer from stromal to breast cancer cells regulates therapy resistance pathways. Cell 2014, 159, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veraguas, D.; Aguilera, C.; Henriquez, C.; Velasquez, A.E.; Melo-Baez, B.; Silva-Ibañez, P.; Castro, F.O.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, L. Evaluation of extracellular vesicles and gDNA from culture medium as a possible indicator of developmental competence in human embryos. Zygote 2021, 29, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caamaño, D.J.; Cabezas, Y.S.; Wong, C.J.; Aguilera, D.; Veraguas, B.; Melo-Báez, D.; Sanhueza, F.O.C.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, A.L. Short Communication: Pre-implantation bovine embryos secrete small extracellular vesicles that contain embryonic DNA useful for genetic analysis. Embryo Technol. Newsl. 2022, 40, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Yang, D.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, K.; Zhang, C.; Chen, B.; Zou, W.; Hao, Y.; Ding, D.; Yu, Z.; et al. Application of Two Blastocyst Biopsy Strategies in Preimplantation Genetic Testing Treatment and Assessment of Their Effects. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 852620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouillet, S.; Martinez, G.; Coutton, C.; Hamamah, S. Is cell-free DNA in spent embryo culture medium an alternative to embryo biopsy for preimplantation genetic testing? A systematic review. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2020, 40, 779–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stigliani, S.; Anserini, P.; Venturini, P.L.; Scaruffi, P. Mitochondrial DNA content in embryo culture medium is significantly associated with human embryo fragmentation. Hum. Reprod. 2013, 28, 2652–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haouzi, D.; Hamamah, S. Pertinence of apoptosis markers for the improvement of in vitro fertilization (IVF). Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 1905–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, G.; Chaveiro, A.; Santos, P.; Marques, A.; Jin, H.S.; Moreira da Silva, F. Influence of apoptosis in bovine embryo’s development. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2010, 45, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, K.D.; Agarwal, A.; Nagy, Z.P. Preimplantation genetic screening: Does it help or hinder IVF treatment and what is the role of the embryo? J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2011, 28, 833–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Group | n | EVs | DNA-Positive EVs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size, nm (x; IQR) | Concentration of Particles/mL (x; IQR) | Size, nm (x; IQR) | Concentration of Particles/mL (x; IQR) | ||
| Morula-P | 18 | 143.0; 28.0 a | 12.0; 4.8 × 109 a | 457.8; 96.2 | 2.8; 3.9 × 108 |
| Blasto-P | 8 | 141.0; 12.0 a | 11.1; 7.71 × 109 a | 513.2; 52.2 | 3.6; 3.4 × 108 |
| Morula-IVF | 18 | 150.6; 21.1 b | 6.0; 3.40 × 109 b | 478.7; 198.0 | 2.5; 1.7 × 108 |
| Blasto-IVF | 22 | 154.5; 18.2 b | 6.5; 3.85 × 109 b | 437.5; 169.9 | 2.3; 2.7 × 108 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caamaño, D.; Cabezas, J.; Aguilera, C.; Martinez, I.; Wong, Y.S.; Sagredo, D.S.; Ibañez, B.; Rodriguez, S.; Castro, F.O.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, L. DNA Content in Embryonic Extracellular Vesicles Is Independent of the Apoptotic Rate in Bovine Embryos Produced In Vitro. Animals 2024, 14, 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14071041
Caamaño D, Cabezas J, Aguilera C, Martinez I, Wong YS, Sagredo DS, Ibañez B, Rodriguez S, Castro FO, Rodriguez-Alvarez L. DNA Content in Embryonic Extracellular Vesicles Is Independent of the Apoptotic Rate in Bovine Embryos Produced In Vitro. Animals. 2024; 14(7):1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14071041
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaamaño, Diego, Joel Cabezas, Constanza Aguilera, Ioanna Martinez, Yat Sen Wong, Daniela Sanhueza Sagredo, Belén Ibañez, Sebastián Rodriguez, Fidel Ovidio Castro, and Lleretny Rodriguez-Alvarez. 2024. "DNA Content in Embryonic Extracellular Vesicles Is Independent of the Apoptotic Rate in Bovine Embryos Produced In Vitro" Animals 14, no. 7: 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14071041
APA StyleCaamaño, D., Cabezas, J., Aguilera, C., Martinez, I., Wong, Y. S., Sagredo, D. S., Ibañez, B., Rodriguez, S., Castro, F. O., & Rodriguez-Alvarez, L. (2024). DNA Content in Embryonic Extracellular Vesicles Is Independent of the Apoptotic Rate in Bovine Embryos Produced In Vitro. Animals, 14(7), 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14071041







