Improved Antibody Detection for Canine Leptospirosis: ELISAs Modified Using Local Leptospiral Serovar Isolates from Asymptomatic Dogs
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Cultures and Growth Conditions
2.2. Serum Samples and Groups of Dogs
2.3. Detection of Leptospira in Sera Using a Genus-Specific Nested PCR Assay
2.4. A Preliminary Study Using the Microscopic Agglutination Test (MAT)
2.5. Leptospiral Protein Preparations for Modified ELISAs
2.5.1. Whole-Cell Protein Using Sonicated Leptospiral Preparations
2.5.2. Total Membrane Protein Fraction Obtained Using Lysis Buffer
2.5.3. Outer Membrane Protein Isolation Using Triton X-114
2.6. Confirmation of Protein Components via SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
2.7. Indirect Immunoglobulin G (IgG) ELISAs
2.7.1. Optimisation of Indirect ELISAs and Cut-Off OD Values
2.7.2. IgG Antibody Detection
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Detection of Leptospira in Serum via Nested PCR
3.2. Antibody Titres in the Microscopic Agglutination Test
3.3. The Protein Components Confirmed via SDS-PAGE and Western Blot Analysis Using Serum from a Dog with Leptospirosis
3.4. Determination of the Optimal OD Cut-Off Values for Indirect ELISAs
3.5. Detection of Antibody Levels via the Modified ELISAs
3.6. Diagnostic Performance of All Modified ELISAs
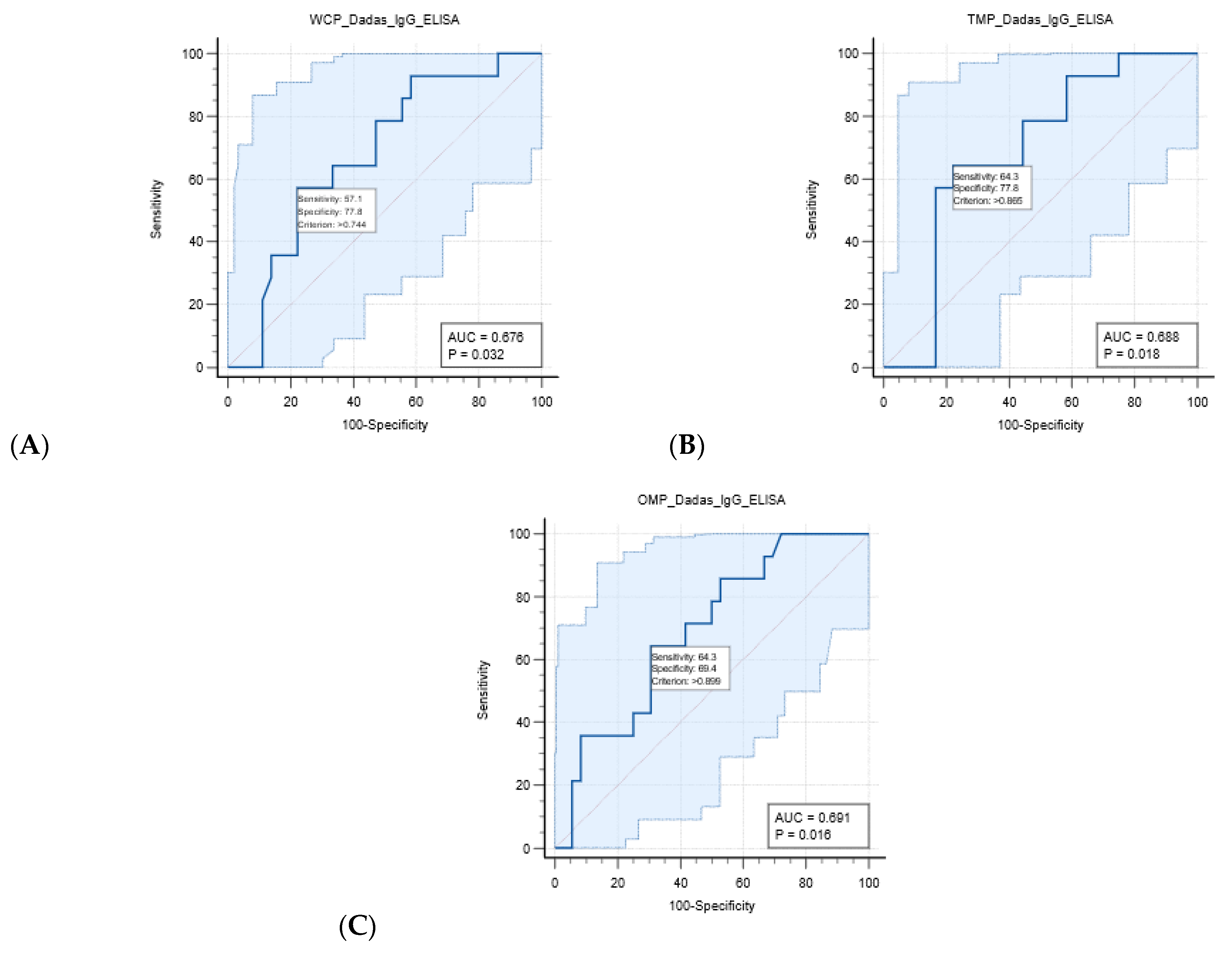
3.7. Receiver–Operator Curve (ROC) Analysis, Correlation Analysis, and Agreement Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adler, B.; de la Peña Moctezuma, A. Leptospira and Leptospirosis. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.; Hagan, J.E.; Calcagno, J.; Kane, M.; Torgerson, P.; Martinez-Silveira, M.S.; Stein, C.; Abela-Ridder, B.; Ko, A.I. Global Morbidity and Mortality of Leptospirosis: A Systematic Review. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangkanakul, W.; Smits, H.L.; Jatanasen, S.; Ashford, D.A. Leptospirosis: An Emerging Health Problem in Thailand. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2005, 36, 281–288. [Google Scholar]
- Wuthiekanun, V.; Sirisukkarn, N.; Daengsupa, P.; Sakaraserane, P.; Sangkakam, A.; Chierakul, W.; Smythe, L.D.; Symonds, M.L.; Dohnt, M.F.; Slack, A.T.; et al. Clinical Diagnosis and Geographic Distribution of Leptospirosis, Thailand. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, G.M.; Picardeau, M. A Century of Leptospira Strain Typing. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2009, 9, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.S.; Matthias, M.A.; Vinetz, J.M.; Fouts, D.E. Leptospiral Pathogenomics. Pathogens 2014, 3, 280–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arent, Z.; Pardyak, L.; Dubniewicz, K.; Płachno, B.; Kotula-Balak, M. Leptospira Taxonomy: Then and Now. Med. Weter. 2022, 78, 2022–6694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kmety, E.; Dikken, H. Classification of the Species Leptospira interrogans and History of Its Serovars; University Press Groningen: Groningen, The Netherlands, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Feresu, S.B.; Ann Bolin, C.; van de Kemp, H.; Korver, H. Identification of a Serogroup Bataviae Leptospira Strain Isolated from an Ox in Zimbabwe. Zentralbl Bakteriol 1999, 289, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourhy, P.; Collet, L.; Clément, S.; Huerre, M.; Ave, P.; Giry, C.; Pettinelli, F.; Picardeau, M. Isolation and Characterization of New Leptospira Genotypes from Patients in Mayotte (Indian Ocean). PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benacer, D.; Zain, S.N.M.; Sim, S.Z.; Khalid, M.K.N.M.; Galloway, R.L.; Souris, M.; Thong, K.L. Determination of Leptospira borgpetersenii Serovar Javanica and Leptospira interrogans Serovar Bataviae as the Persistent Leptospira Serovars Circulating in the Urban Rat Populations in Peninsular Malaysia. Parasit Vectors 2016, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Zhang, W.; Ding, Y.; Wu, D.; Dai, Z.; Xu, L.; Cao, Y. Preliminary Characterization of Dog Derived Pathogenic Strains of Leptospira interrogans Serovar Australis in Nanchang of Jiangxi Province, China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 607115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.A.; Khor, K.H.; Khairani-Bejo, S.; Lau, S.F.; Mazlan, M.; Roslan, A.; Goh, S.H. Detection and Characterization of Leptospira spp. In Dogs Diagnosed with Kidney and/or Liver Disease in Selangor, Malaysia. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2021, 33, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narkkul, U.; Thaipadungpanit, J.; Srisawat, N.; Rudge, J.W.; Thongdee, M.; Pawarana, R.; Pan-Ngum, W. Human, Animal, Water Source Interactions and Leptospirosis in Thailand. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eric Klaasen, H.L.; Adler, B. Recent Advances in Canine Leptospirosis: Focus on Vaccine Development. Vet. Med. 2015, 6, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Colocho, R.A.B.; Pereira, C.R.; Lage, A.P.; Heinemann, M.B.; Dorneles, E.M.S. Canine Leptospirosis in Stray and Sheltered Dogs: A Systematic Review. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2022, 23, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeyam, T.; Tablerk, P.; Petchanok, B.; Pichpol, D.; Padungtod, P. Seroprevalence and Risk Factors Associated with Leptospirosis in Dogs. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2006, 37, 148–153. [Google Scholar]
- Niwetpathomwat, A.; Assarasakorn, S. Preliminary Investigation of Canine Leptospirosis in a Rural Area of Thailand. Med. Weter. 2007, 63, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Jittapalapong, S.; Sittisan, P.; Sakpuaram, T.; Kabeya, H.; Maruyama, S.; Inpankaew, T. Coinfection of Leptospira spp. and Toxoplasma Gondii among Stray Dogs in Bangkok, Thailand. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2009, 40, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pumipuntu, N.; Suwannarong, K. Seroprevalence of Leptospira spp. in Cattle and Dogs in Mahasarakham Province, Thailand. J. Health Res. 2016, 30, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngasaman, R.; Saechan, V.; Prachantasena, S.; Yingkajorn, M.; Sretrirutchai, S. Investigation of Leptospira Infection in Stray Animals in Songkhla, Thailand: Leptospirosis Risk Reduction in Human. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2020, 20, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubel, D.; Seijo, A.; Cernigoi, B.; Viale, A.; Wisnivesky-Colli, C. Leptospira interrogans in a Canine Population of Greater Buenos Aires: Variables Associated with Seropositivity. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica 1997, 2, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez Hernández, M.; Martínez Sánchez, R.; Posada Fernández, P.; Bustelo Aguila, J.; Carrera Nodal, O.; Fleite, F.B.; García, I.V.; Sánchez Sibello, A. Leptospirosis in Children in Ciego De Avila Province, Cuba. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 1999, 32, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Patil, D.; Dahake, R.; Roy, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Chowdhary, A.; Deshmukh, R. Prevalence of Leptospirosis among Dogs and Rodents and Their Possible Role in Human Leptospirosis from Mumbai, India. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 32, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelu, M.; Muñoz-Zanzi, C.; Higgins, B.; Galloway, R. Seroepidemiology of Leptospirosis in Dogs from Rural and Slum Communities of Los Rios Region, Chile. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurilung, A.; Chanchaithong, P.; Lugsomya, K.; Niyomtham, W.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Prapasarakul, N. Molecular Detection and Isolation of Pathogenic Leptospira from Asymptomatic Humans, Domestic Animals and Water Sources in Nan Province, a Rural Area of Thailand. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 115, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurilung, A.; Keeratipusana, C.; Suriyaphol, P.; Hampson, D.J.; Prapasarakul, N. Genomic Analysis of Leptospira interrogans Serovar Paidjan and Dadas Isolates from Carrier Dogs and Comparative Genomic Analysis to Detect Genes under Positive Selection. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonsilp, S.; Thaipadungpanit, J.; Amornchai, P.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Bailey, M.S.; Holden, M.T.G.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, X.; Koizumi, N.; Taylor, K.; et al. A Single Multilocus Sequence Typing (Mlst) Scheme for Seven Pathogenic Leptospira Species. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voronina, O.L.; Kunda, M.S.; Aksenova, E.I.; Ryzhova, N.N.; Semenov, A.N.; Petrov, E.M.; Didenko, L.V.; Lunin, V.G.; Ananyina, Y.V.; Gintsburg, A.L. The Characteristics of Ubiquitous and Unique Leptospira Strains from the Collection of Russian Centre for Leptospirosis. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 649034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kurilung, A.; Perreten, V.; Prapasarakul, N. Comparative Genomic Analysis and a Novel Set of Missense Mutation of the Leptospira Weilii Serogroup Mini from the Urine of Asymptomatic Dogs in Thailand. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 731937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amran, F.; Khalid, M.K.N.M.; Mohamad, S.; Ripen, A.M.; Ahmad, N.; Goris, M.G.A.; Muhammad, A.H.; Halim, N.A.N. Draft Genome Sequence of Leptospira interrogans Serovar Bataviae Strain Lepimr 22 Isolated from a Rodent in Johor, Malaysia. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00956-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altheimer, K.; Jongwattanapisan, P.; Luengyosluechakul, S.; Pusoonthornthum, R.; Prapasarakul, N.; Kurilung, A.; Broens, E.M.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Goris, M.G.A.; Ahmed, A.A.; et al. Leptospira Infection and Shedding in Dogs in Thailand. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonciew, P.; Kurilung, A.; Altheimer, K.; Hartmann, K.; Prapasarakul, N. Draft Genome Sequence of Leptospira interrogans Serovar Bataviae Strain D64, Isolated from the Urine of an Asymptomatic Dog in Pathum Thani, Thailand. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, e00361-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramli, S.R.; Bunk, B.; Spröer, C.; Geffers, R.; Jarek, M.; Bhuju, S.; Goris, M.; Mustakim, S.; Pessler, F. Complete Genome Sequencing of Leptospira interrogans Isolates from Malaysia Reveals Massive Genome Rearrangement but High Conservation of Virulence-Associated Genes. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevejo, R.T.; Rigau-Pérez, J.G.; Ashford, D.A.; McClure, E.M.; Jarquín-González, C.; Amador, J.J.; Reyes, J.O.d.L.; Gonzalez, A.; Zaki, S.R.; Shieh, W.; et al. Epidemic Leptospirosis Associated with Pulmonary Hemorrhage-Nicaragua, 1995. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 178, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, D.; La Scola, B. Laboratory Diagnosis of Leptospirosis: A Challenge. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2013, 46, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leptospirosis–Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals, 8th ed. 2021. Available online: https://www.woah.org/en/what-we-do/standards/codes-and-manuals/terrestrial-manual-online-access/ (accessed on 8 October 2021).
- Pinto, G.V.; Senthilkumar, K.; Rai, P.; Kabekkodu, S.P.; Karunasagar, I.; Kumar, B.K. Current Methods for the Diagnosis of Leptospirosis: Issues and Challenges. J. Microbiol. Methods 2022, 195, 106438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gökmen, T.G.; Soyal, A.; Kalayci, Y.; Önlen, C.; Köksal, F. Comparison of 16s Rrna-Pcr-Rflp, Lipl32-Pcr and Ompl1-Pcr Methods in the Diagnosis of Leptospirosis. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2016, 58, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwancharoen, D.; Chaisakdanugull, Y.; Thanapongtharm, W.; Yoshida, S. Serological Survey of Leptospirosis in Livestock in Thailand. Epidemiol. Infect. 2013, 141, 2269–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dara, C.; Anunnatsiri, S.; Kessomboon, P.; Laha, T.; Brameld, S.; Saisongkorh, W.; Sripa, B.; Suttiprapa, S. Leptospira spp. Seroprevalence of Co-Infection with Opisthorchis Viverrini Infection in Northeast, Thailand. Suranaree J. Sci. Technol. 2022, 29, 070029. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.S.; Pillai, R.M.; Mukhopadhyay, H.K.; Antony, P.X.; Thanislass, J.; Srinivas, V.M.V.; Vishnupriya, S. Seroepidemiology of Canine Leptospirosis by Ielisa and Mat. Vet. World 2013, 6, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-orry, W.; Arahou, M.; Hassikou, R.; Mennane, Z. A Review of Laboratory Diagnosis and Treatment of Leptospirosis. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 8, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, J.E.; Reagan, K.L.; Nally, J.E.; Galloway, R.L.; Haake, D.A. Role of Diagnostics in Epidemiology, Management, Surveillance, and Control of Leptospirosis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonsilp, S.; Thaipadungpanit, J.; Amornchai, P.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Chierakul, W.; Limmathurotsakul, D.; Day, N.P.; Peacock, S.J. Molecular Detection and Speciation of Pathogenic Leptospira spp. In Blood from Patients with Culture-Negative Leptospirosis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goris, M.G.; Hartskeerl, R.A. Leptospirosis Serodiagnosis by the Microscopic Agglutination Test. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2014, 32, 12E-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, B.; Murphy, A.M.; Locarnini, S.A.; Faine, S. Detection of Specific Anti-Leptospiral Immunoglobulins M and G in Human Serum by Solid-Phase Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1980, 11, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerreiro, H.; Croda, J.; Flannery, B.; Mazel, M.; Matsunaga, J.; Reis, M.G.; Levett, P.N.; Ko, A.I.; Haake, D.A. Leptospiral Proteins Recognized During the Humoral Immune Response to Leptospirosis in Humans. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 4958–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haake, D.A.; Chao, G.; Zuerner, R.L.; Barnett, J.K.; Barnett, D.; Mazel, M.; Matsunaga, J.; Levett, P.N.; Bolin, C.A. The Leptospiral Major Outer Membrane Protein Lipl32 Is a Lipoprotein Expressed During Mammalian Infection. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 2276–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, R.F.A.A.; Fleitas, O.; Rodriguez, I.; Beltran, J.F.; Falcon, R.; Almaguer, T.; TH, S. Triton X-100 Vs. Triton X-114: Isolation of Outer Membrane Proteins from Leptospira spp. J. Vet. Sci. 2017, 1, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Thoduvayil, S.; Dhandapani, G.; Brahma, R.; Balaya, R.D.A.; Mangalaparthi, K.K.; Patel, K.; Kumar, M.; Tennyson, J.; Satheeshkumar, P.K.; Kulkarni, M.J.; et al. Triton X-114 Fractionated Subcellular Proteome of Leptospira interrogans Shows Selective Enrichment of Pathogenic and Outer Membrane Proteins in the Detergent Fraction. Proteomics 2020, 20, e2000170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneewatchararangsri, S.; Reamtong, O.; Kalambaheti, T.; Pumirat, P.; Vanaporn, M.; Limmathurotsakul, D.; Thavornkuno, C. Development of Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Human Leptospirosis Serodiagnosis Using Leptospira Secretome Antigen. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2017, 48, 576–584. [Google Scholar]
- Sathiyamoorthy, A.; Selvaraju, G.; Palanivel, K.M.; Srinivasan, A.P. Development of Indirect Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Diagnosis of Canine Leptospirosis. Vet. World 2017, 10, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araghian, A.; Elmi, A.; Farahbakhsh, M.; Hosseini, S.; Faezi, S. Seroepidemiology of Leptospirosis in Guilan Province, Northern Iran: Comparison between Mat and Igm-Elisa Techniques. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2018, 12, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Morales, M.A.; Selmi, M.; Ludovisi, A.; Amati, M.; Fiorentino, E.; Breviglieri, L.; Poglayen, G.; Pozio, E. Hunting Dogs as Sentinel Animals for Monitoring Infections with Trichinella spp. in Wildlife. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottschalk, M.; Altman, E.; Charland, N.; De Lasalle, F.; Dubreuil, J.D. Evaluation of a Saline Boiled Extract, Capsular Polysaccharides and Long-Chain Lipopolysaccharides of Actinobacillus Pleuropneumoniae Serotype 1 as Antigens for the Serodiagnosis of Swine Pleuropneumonia. Vet. Microbiol. 1994, 42, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribotta, M.J.; Higgins, R.; Gottschalk, M.; Lallier, R. Development of an Indirect Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for the Detection of Leptospiral Antibodies in Dogs. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2000, 64, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, P.C.; Leung, A.S.; Lau, S.K.; Chong, K.T.; Yuen, K.Y. Use of Recombinant Mitogillin for Serodiagnosis of Aspergillus Fumigatus-Associated Diseases. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 4598–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.; Yan, W.; Xiang, H.; He, H.; Yang, M.; Ijaz, M.; Useh, N.; Hsieh, C.-L.; McDonough, P.L.; McDonough, S.P.; et al. Recombinant Antigens Rlipl21, Rloa22, Rlipl32 and Rligacon4-8 for Serological Diagnosis of Leptospirosis by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays in Dogs. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, B.; Marassi, C.D.; Libonati, H.; Narduche, L.; Lilenbaum, W.; Bourhy, P. Diagnostic Accuracy of an in-House Elisa Using the Intermediate Species Leptospira Fainei as Antigen for Diagnosis of Acute Leptospirosis in Dogs. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 50, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizer, J.; Velineni, S.; Weber, A.; Krecic, M.; Meeus, P. Evaluation of 3 Serological Tests for Early Detection of Leptospira-Specific Antibodies in Experimentally Infected Dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, M.; Kawaoka, Y.; Naiki, M.; Yanagawa, R. Isolation of Antigenically Active Components from Leptospiral Serovar-Specific Lipopolysaccharide Antigen by Alkaline Treatment. Microbiol. Immunol. 1981, 25, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, E.; Takase, H.; Naiki, M.; Yanagawa, R. Purification, Characterization and Serological Properties of a Glycolipid Antigen Reactive with a Serovar-Specific Monoclonal Antibody against Leptospira interrogans Serovar Canicola. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1987, 133, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinco, M.; Banfi, E.; Panfili, E. Leptospiral Lipopolysaccharide Presence in the Outer Envelope: Electrophoretic Evidence and Immunological Specificity. Zentralblatt Für Bakteriol. Mikrobiol. Und Hyg. A 1988, 269, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surujballi, O.; Mallory, M. An Indirect Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay for the Detection of Bovine Antibodies to Multiple Leptospira Serovars. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2004, 68, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cariou, C.; Herbet, G.; Ripart, P.; Martin-Cagnon, N.; Bouvet, J.; Schneider, M.; Guiot, A.-L.; Cupillard, L. Development of Antibody Elisa Specific of Leptospira interrogans Serovar Grippotyphosa, Canicola, and Icterohaemorrhagiae to Monitor Vaccine Immunogenicity. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2020, 219, 109960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripattanakul, S.; Prapong, T.; Kamlangdee, A.; Katzenmeier, G.; Haltrich, D.; Hongprayoon, R.; Prapong, S. Leptospira borgpetersenii Leucine-Rich Repeat Proteins and Derived Peptides in an Indirect Elisa Development for the Diagnosis of Canine Leptospiral Infections. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibyan, L.; Avashia, N. Polymerase Chain Reaction. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Rothman, R.E. Pcr-Based Diagnostics for Infectious Diseases: Uses, Limitations, and Future Applications in Acute-Care Settings. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2004, 4, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirathaworn, C.; Inwattana, R.; Poovorawan, Y.; Suwancharoen, D. Interpretation of Microscopic Agglutination Test for Leptospirosis Diagnosis and Seroprevalence. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4 (Suppl. 1), S162–S164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, E.A.; Heseltine, J.C.; Creevy, K.E. The Evaluation of the Diagnostic Value of a Pcr Assay When Compared to a Serologic Micro-Agglutination Test for Canine Leptospirosis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 815103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-W.; Tilley, D.H.; Canal, E.; Guevara, C.; Maves, R.; Hall, E.; Halsey, E.S.; Zhang, Z.; Ching, W.-M.; Kochel, T.J. Detection of Leptospira-Specific Antibodies Using a Recombinant Antigen-Based Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 89, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Souza, M.A.; Castro, J.; Tavares, T.; Soares, P.; Santos, M.; Ganda, M.; Gomes, D.O.; Lima, A.M.C. Comparison of Microscopic Agglutination Test and Indirect Elisa in the Diagnosis of Bovine Leptospirosis. Biosci. J. 2014, 30, 833–838. [Google Scholar]
- Ooteman, M.C.; Vago, A.R.; Koury, M.C. Evaluation of Mat, Igm Elisa and Pcr Methods for the Diagnosis of Human Leptospirosis. J. Microbiol. Methods 2006, 65, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, L.R.; Mahadeviah, S.N.; Balamurugan, V.; Kini, K.R. Evaluation of an in-House Lipl32 Polymerase Chain Reaction for Diagnosis of Leptospirosis and Its Correlation with Various Serological Diagnostic Techniques. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 36, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, N.; Affendy, N.B.; Masri, S.N.; Yuhana, M.Y.; Than, L.T.L.; Sekawi, Z.; Neela, V.K. Combined Pcr and Mat Improves the Early Diagnosis of the Biphasic Illness Leptospirosis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.; Mittal, V.; Singh, P.; Singh, A. Evaluation of Taqman Based Real-Time Pcr Assay Targeting Lipl32 Gene for Leptospirosis in Serologically Positive Human Urine Samples from North India. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 39, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajani, M.D.; Ashford, D.A.; Bragg, S.L.; Woods, C.W.; Aye, T.; Spiegel, R.A.; Plikaytis, B.D.; Perkins, B.A.; Phelan, M.; Levett, P.N.; et al. Evaluation of Four Commercially Available Rapid Serologic Tests for Diagnosis of Leptospirosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater Reliability: The Kappa Statistic. Biochem. Med. 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulla, S.; Chakraborty, T.; Patel, M.; Pandya, H.P.; Dadhaniya, V.; Vaghela, G. Diagnosis of Leptospirosis and Comparison of Elisa and Mat Techniques. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2006, 49, 468–470. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasundara, D.; Gamage, C.; Senavirathna, I.; Warnasekara, J.; Matthias, M.A.; Vinetz, J.M.; Agampodi, S. Optimizing the Microscopic Agglutination Test (Mat) Panel for the Diagnosis of Leptospirosis in a Low Resource, Hyper-Endemic Setting with Varied Microgeographic Variation in Reactivity. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Levine, M.; Guptill-Yoran, C.; Johnson, A.J.; von Kamecke, P.; Moore, G.E. Regional and Temporal Variations of Leptospira Seropositivity in Dogs in the United States, 2000–2010. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2014, 28, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertasio, C.; Boniotti, M.B.; Lucchese, L.; Ceglie, L.; Bellinati, L.; Mazzucato, M.; Furlanello, T.; D’Incau, M.; Natale, A.K. Detection of New Leptospira Genotypes Infecting Symptomatic Dogs: Is a New Vaccine Formulation Needed? Pathogens 2020, 9, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Azevedo, M.I.N.; Aymée, L.; Borges, A.; Lilenbaum, W. Molecular Epidemiology of Pathogenic Leptospira spp. Infecting Dogs in Latin America. Animals 2023, 13, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, A.I.; Goarant, C.; Picardeau, M. Leptospira: The Dawn of the Molecular Genetics Era for an Emerging Zoonotic Pathogen. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauretti-Ferreira, F.; Silva, P.L.D.; Alcântara, N.M.; Silva, B.F.; Grabher, I.; Souza, G.O.; Nakajima, E.; Akamatsu, M.A.; Vasconcellos, S.A.; Abreu, P.A.E.; et al. New Strategies for Leptospira Vaccine Development Based on Lps Removal. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthias, M.A.; Lubar, A.A.; Acharige, S.S.L.; Chaiboonma, K.L.; Pilau, N.N.; Marroquin, A.S.; Jayasundara, D.; Agampodi, S.; Vinetz, J.M. Culture-Independent Detection and Identification of Leptospira Serovars. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0247522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.; Stull, J.W.; Moore, G.E. Potential Drivers for the Re-Emergence of Canine Leptospirosis in the United States and Canada. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Serovars/Isolates | MAT | ELISA |
|---|---|---|
| 24 representative reference isolates (belonging to 24 serovars) | ||
| Australis | Used | - |
| Aumtumnalis | Used | - |
| Ballum | Used | - |
| Bataviae | Used | - |
| Canicola | Used | Used |
| Cellidoni | Used | - |
| Cynopteri | Used | - |
| Djasiman | Used | - |
| Grippotyphosa | Used | Used |
| Hebdonadis | Used | - |
| Icterohaemorrhagiae | Used | Used |
| Javanica | Used | - |
| Louisaina | Used | - |
| Manhao | Used | - |
| Mini | Used | - |
| Panama | Used | - |
| Pomona | Used | Used |
| Pyrogenes | Used | - |
| Ranarum | Used | - |
| Sarmin | Used | - |
| Sejroe | Used | - |
| Shermani | Used | - |
| Tarasovi | Used | - |
| Semaranga | Used | - |
| 5 local Thai isolates (belonging to 4 serovars) | ||
| Paidjan strain CUDO5 | Used | Used |
| Dadas strain CUDO8 | Used | Used |
| Bataviae strain D64 | Used | Used |
| Mini strain CUDO6 | Used | Used |
| Mini strain CUD13 | Used | Used |
| Groups | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 | Group 5 | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infected Dogs from Nan Province That Were Confirmed as Infected via Positive PCR and Isolation | Unvaccinated Dogs from Nan Province | Vaccinated Dogs from Non-Endemic Areas | Unvaccinated Dogs from Non-Endemic Areas | Unvaccinated Puppies from Non-Endemic Areas | |||
| Number of samples | 6 | 21 | 23 * | 89 ** | 108 | 13 | 260 |
| 112 | |||||||
| Area | Endemic area: Nan Province | Endemic area: Nan Province | Non-endemic area: Bangkok, Samut Prakan, and Chonburi provinces | Non-endemic area: Bangkok, Samut Prakan, and Chonburi provinces | Non-endemic area: Bangkok, Samut Prakan, and Chonburi provinces | - | |
| Age | >1 year | >1 year | >1 year | >1 year | Two months | - | |
| Vaccination status | No vaccination | No vaccination | Complete vaccination | No vaccination | No vaccination | - | |
| Methods (Nested PCR, Isolation, and MAT assays) | |||||||
| Nested PCR from urine | 6 (6/6; 100%) | 0 (0/21; 0%) | N/A | N/A | N/A | 6 (6/27; 22%) | |
| Isolation from urine | 4 (4/6; 67%) | 0 (0/21; 0%) | N/A | N/A | N/A | 4 (4/27; 15%) | |
| Nested PCR from sera | 6 (6/6; 100%) | 0 (0/21; 0%) | 0 (0/112; 0%) | 0 (0/108; 0%) | 0 (0/13; 0%) | 6 (6/260; 2%) | |
| MAT from sera | 0 (0/6; 0%) | 0 (0/21; 0%) | 0 (0/23; 0%) | N/A | N/A | N/A | 14 (14/50; 28%) |
| Methods (modified ELISAs), protein preparation, and local isolates of serovars used in the ELISAs | |||||||
| WCP-Dadas/IgG-ELISA | 6 (6/6; 100%) | 14 (14/21; 67%) | 12 (12/23; 52%) | 25 (25/89; 28%) | 0 (0/108; 0%) | 0 (0/13; 0%) | 57 (57/260; 22%) |
| 37 (37/112; 33%) | |||||||
| TMP-Dadas/IgG-ELISA | 6 (6/6; 100%) | 13 (13/21; 62%) | 6 (6/23; 26%) | 12 (12/89; 13%) | 0 (0/108; 0%) | 0 (0/13; 0%) | 37 (37/260; 14%) |
| 18 (18/112; 16%) | |||||||
| OMP-Dadas/IgG-ELISA | 6 (6/6; 100%) | 15 (10/21; 48%) | 0 (0/23; 0%) | 0 (0/89; 0%) | 0 (0/108; 0%) | 0 (0/13; 0%) | 21 (21/260; 8%) |
| 0 (0/112; 0%) | |||||||
| Groups | Number | MAT | Serovars and Serological Titres in MAT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hebdonadis | Sejroe | Shermani | Paidjan (CUDO5) | ||||
| Isolation and PCR-confirmed infected dogs from Nan Province (Group 1) | 6 | 0 (0/6; 0%) | - | - | - | - | |
| Unvaccinated dogs from Nan Province (Group 2) | 21 | 11 (11/21; 52%) | 1 * | 1 | 9 * | 1 | |
| 1:20 | 1:80 | 4 | 5 | ||||
| 1:20 | 1:40 | ||||||
| Vaccinated dogs from Bangkok (Group 3) | 23 | 3 (3/23; 13%) | - | - | 3 | - | |
| 1:20 | |||||||
| Total | 50 | 14 (28%) | 1 | 1 | 12 | 1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boonciew, P.; Saisongkorh, W.; Brameld, S.; Thongpin, M.; Kurilung, A.; Krangvichian, P.; Niyomtham, W.; Patarakul, K.; Phichitraslip, T.; Hampson, D.J.; et al. Improved Antibody Detection for Canine Leptospirosis: ELISAs Modified Using Local Leptospiral Serovar Isolates from Asymptomatic Dogs. Animals 2024, 14, 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060893
Boonciew P, Saisongkorh W, Brameld S, Thongpin M, Kurilung A, Krangvichian P, Niyomtham W, Patarakul K, Phichitraslip T, Hampson DJ, et al. Improved Antibody Detection for Canine Leptospirosis: ELISAs Modified Using Local Leptospiral Serovar Isolates from Asymptomatic Dogs. Animals. 2024; 14(6):893. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060893
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoonciew, Pannawich, Watcharee Saisongkorh, Suppalak Brameld, Matsaya Thongpin, Alongkorn Kurilung, Pratomporn Krangvichian, Waree Niyomtham, Kanitha Patarakul, Thanmaporn Phichitraslip, David J. Hampson, and et al. 2024. "Improved Antibody Detection for Canine Leptospirosis: ELISAs Modified Using Local Leptospiral Serovar Isolates from Asymptomatic Dogs" Animals 14, no. 6: 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060893
APA StyleBoonciew, P., Saisongkorh, W., Brameld, S., Thongpin, M., Kurilung, A., Krangvichian, P., Niyomtham, W., Patarakul, K., Phichitraslip, T., Hampson, D. J., & Prapasarakul, N. (2024). Improved Antibody Detection for Canine Leptospirosis: ELISAs Modified Using Local Leptospiral Serovar Isolates from Asymptomatic Dogs. Animals, 14(6), 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060893







