The Substitution of Fishmeal with Yeast Culture in the Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) Diet: Growth, Serum Biochemical Indices, and Intestinal and Hepatopancreatic Histology
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Experimental Plan
2.4. Sample Collection
2.5. Measurement and Methods
2.5.1. Growth Performance and Physical Indices
2.5.2. Composition of the Whole-Body and Diet
2.5.3. Serum Biochemical Indices
2.5.4. Nutrient Retention
2.5.5. Intestinal Digestive Enzyme and Intracellular Enzyme Activity
2.5.6. Intestinal and Hepatopancreas Histology
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance and Physical Indices
3.2. Whole-Body Composition and Nutrient Utilization
3.3. Serum Biochemical Indices
3.4. Intestinal Digestive Enzyme and Intracellular Enzyme Activity
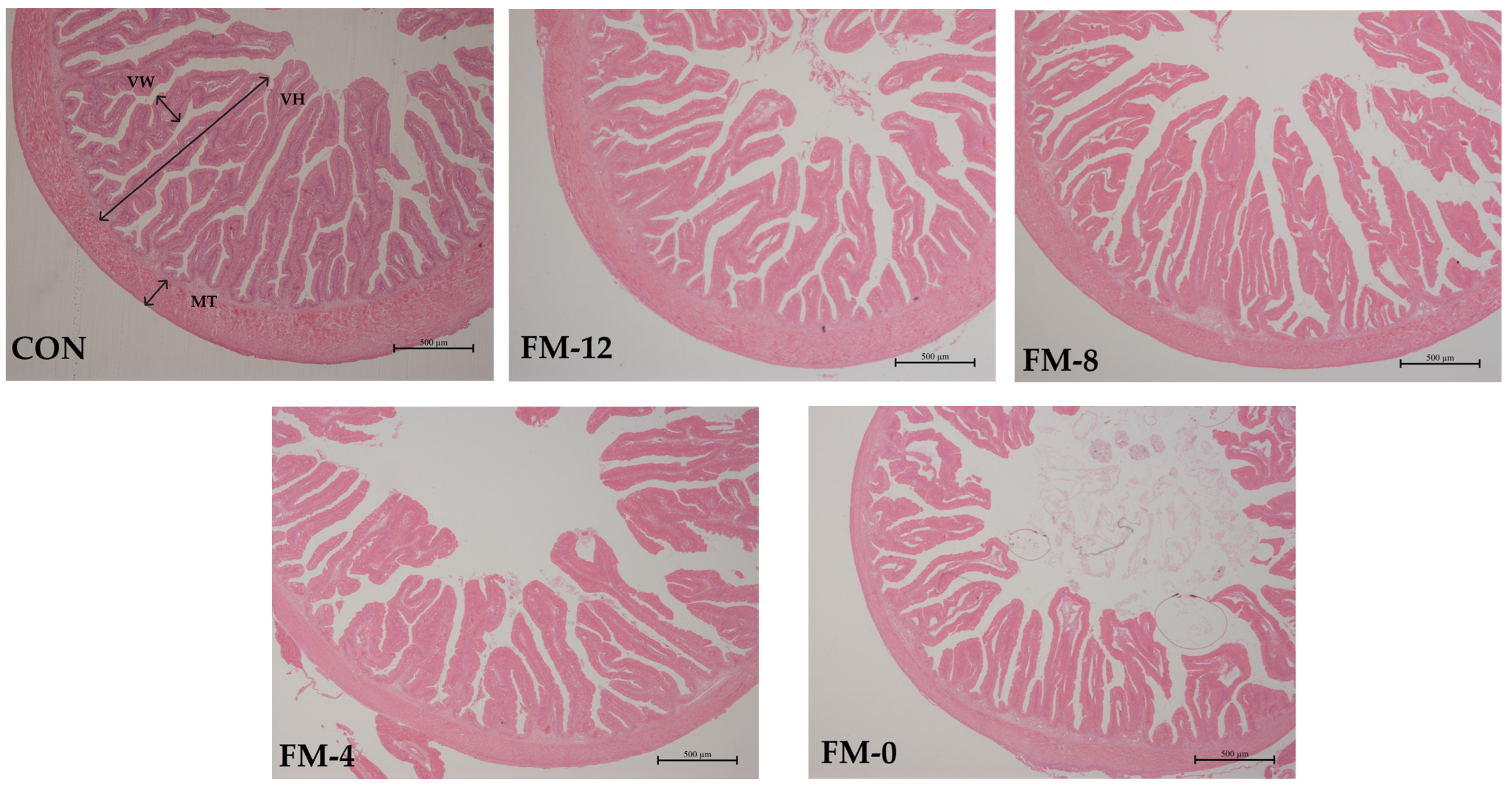
3.5. Intestinal Morphology
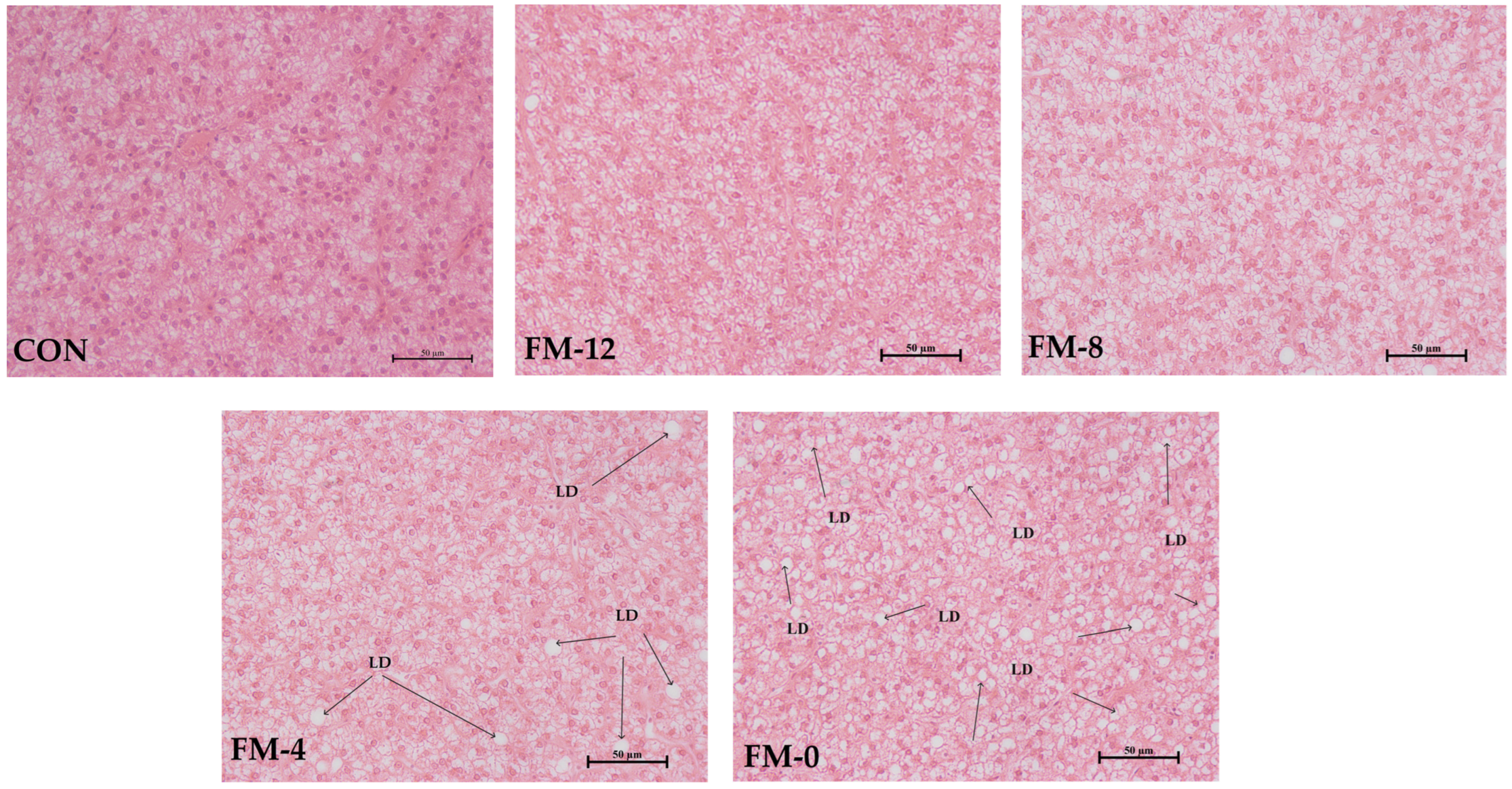
3.6. Hepatopancreas Morphology
4. Discussion
4.1. Growth Indices
4.2. Serum Biochemical and Immune Indices
4.3. Intestinal Digestive Enzyme and Intestinal Morphology
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, H.F.; Li, X.Q.; Cao, K.L.; Leng, X.J. Effects of replacing fishmeal with the mixture of cottonseed protein concentrate and Clostridium autoethanogenum protein on the growth, nutrient utilization, serum biochemical indices, intestinal and hepatopancreas histology of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Animals 2023, 13, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlader, S.; Sumi, K.R.; Sarkar, S.; Billah, S.M.; Ali, M.L.; Howlader, J.; Shahjahan, M. Effects of dietary replacement of fish meal by soybean meal on growth, feed utilization, and health condition of stinging catfish, Heteropneustes fossilis. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 30, 103601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santigosa, E.; Sáenz de Rodrigáñez, M.Á.; Rodiles, A.; Barroso, F.G.; Alarcón, F.J. Effect of diets containing a purified soybean trypsin inhibitor on growth performance, digestive proteases and intestinal histology in juvenile sea bream (Sparus aurata L.). Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, e187–e198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.C.; Liao, Y.L.; Song, Y.Y.; Wang, J.H.; Deng, X.Y.; Luan, L.Y.; An, N.; Zhou, W.H.; Liang, T.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; et al. Dietary yeast culture alleviates intestinal-hepatic damage related to TLR2-MyD88-NF-κB signaling pathway and antioxidant capability in Pseudobagrus ussuriensis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 130, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttle, L.G.; Burrells, A.C.; Good, J.E.; Williams, P.D.; Southgate, P.J.; Burrells, C. The binding of soybean agglutinin (SBA) to the intestinal epithelium of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar and rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, fed high levels of soybean meal. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2001, 80, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, Z.J.; Zhang, W.C.; Zheng, J.C.; Gong, Y.; Cui, K.; Mai, K.S.; Ai, Q.H. Effects of fishmeal substitution by four fermented soybean meals on growth, antioxidant capacity and inflammation responses of turbot juveniles (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Aquaculture 2022, 560, 738414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yao, W.X.; Sun, Z.C.; Liu, J.Y.; Dang, J.Y.; Li, X.Q.; Leng, X.J. Effects of yeast culture substituting fishmeal on growth, nonspecific immunity, intestinal, and hepatopancreatic histology of Litopenaeus vannamei. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 2022, 53, 1155–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayiku, S.; Shen, J.F.; Tan, B.P.; Dong, X.H.; Liu, H.Y. Effects of reducing dietary fishmeal with yeast supplementations on Litopenaeus vannamei growth, immune response and disease resistance against Vibrio harveyi. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 239, 126554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Q.; Xia, R.; Zhang, Q.S.; Xie, Y.D.; Ran, C.; Yang, Y.L.; Zhou, W.H.; Chu, F.W.; Zhang, X.M.; Wang, Y.; et al. Partially replacing dietary fish meal by Saccharomyces cerevisiae culture improve growth performance, immunity, disease resistance, composition and function of intestinal microbiota in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 125, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xv, Z.C.; Zhong, Y.F.; Wei, Y.X.; Zhang, T.T.; Zhou, W.H.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Chen, Y.J.; Lin, S.M. Yeast culture supplementation alters the performance and health status of juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) fed a high-plant protein diet. Aquac. Nutr. 2021, 27, 2637–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Y.; Cao, S.P.; Zou, T.; Han, D.; Liu, H.K.; Jin, J.Y.; Yang, Y.X.; Zhou, X.M.; Xie, S.Q.; Zhou, W.H. Effects of dietary yeast culture on growth performance, immune response and disease resistance of gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio CAS III). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 82, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Trinh, L.T.; Chau, D.T.; Baruah, K.; Lundh, T.; Kiessling, A. Spent brewer’s yeast as a replacement for fishmeal in diets for giant freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii), reared in either clear water or a biofloc environment. Aquac. Nutr. 2019, 25, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Pan, T.T.; Jin, M.; Ma, H.N.; Liang, C.; Ren, Z.L.; Zhou, W.H.; Zhou, Z.G.; Zhou, Q.C. Effect of dietary yeast culture supplementation on growth performance, nonspecific immunity and intestinal health of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. J. Fish. China 2019, 43, 1080–1091. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Communities International, 18th ed.; AOAC: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.Z.; Wang, S.D.; Qin, C.J.; Li, M. Dietary inulin benefits on growth, digestive ability and intestinal microbiota in yellow catfish exposed to ammonia. Aquacult. Rep. 2023, 32, 101724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.Y.; Xu, J.M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.J.; Chen, N.S.; Li, S.L. Dietary protein hydrolysate effects on growth, digestive enzymes activity, and expression of genes related to amino acid transport and metabolism of larval snakehead (Channa argus). Aquaculture 2023, 563, 738896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, Z.L.; Niu, J. Growth performance, intestinal histomorphology, body composition, hematological and antioxidant parameters of Oncorhynchus mykiss were not detrimentally affected by replacement of fish meal with concentrated dephenolization cottonseed protein. Aquacult. Rep. 2021, 19, 100557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayiku, S.; Shen, J.F.; Tan, B.P.; Dong, X.H.; Liu, H.Y. Effects of dietary yeast culture on shrimp growth, immune response, intestinal health and disease resistance against Vibrio harveyi. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 102, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.H.; Xu, X.Y.; Duan, Z.P.; Sun, Z.C.; Liu, J.Y.; Li, X.Q.; Leng, X.J. Effects of replacing fishmeal with yeast culture on growth performance, serum biochemical indices and intestinal morphology of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 33, 5182–5192. [Google Scholar]
- Ozório, R.O.A.; Turini, B.G.S.; Môro, G.V.; Oliveira, L.S.T.; Portz, L.; Cyrino, J.E.P. Growth, nitrogen gain and indispensable amino acid retention of pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus, Holmberg 1887) fed different brewers yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) levels. Aquac. Nutr. 2010, 16, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Xu, S.X.; Feng, L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, W.D.; Wu, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, X.Q. Lysine and methionine supplementation ameliorates high inclusion of soybean meal inducing intestinal oxidative injury and digestive and antioxidant capacity decrease of yellow catfish. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 44, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaylord, T.G.; Barrows, F.T.; Teague, A.M.; Johansen, K.A.; Overturf, K.E.; Shepherd, B. Supplementation of taurine and methionine to all-plant protein diets for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2007, 269, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lai, H.; Li, Q.; Gong, S.Y.; Wang, R.X. Effects of dietary taurine on growth, immunity and hyperammonemia in juvenile yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco fed all-plant protein diets. Aquaculture 2016, 450, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y. Effect of Three Microecologicalagents on Growth Performance, Physiological Function and Intestinal Mucosa of Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Master’s Thesis, Suzhou University, Suzhou, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, M.; Xiong, J.; Zhou, Q.C.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, X.X.; Sun, P. Dietary yeast hydrolysate and brewer′s yeast supplementation could enhance growth performance, innate immunity capacity and ammonia nitrogen stress resistance ability of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 82, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrahari, S.; Pandey, K.C.; Gopal, K. Biochemical alteration induced by monocrotophos in the blood plasma of fish, Channa punctatus (Bloch). Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 2007, 88, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhzadeh, N.; Tayefi-Nasrabadi, H.; Khani Oushani, A.; Najafi Enferadi, M.H. Effects of Haematococcus pluvialis supplementation on antioxidant system and metabolism in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvez, S.; Raisuddin, S. Protein carbonyls: Novel biomarkers of exposure to oxidative stress-inducing pesticides in freshwater fish Channa punctata (Bloch). Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 20, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.Y.; Ren, Y.K.; Li, Y.; Fan, M.C.; Qian, H.F.; Wang, L.; Wu, G.C.; Zhang, H.; Qi, X.G.; Xue, M.J.; et al. Physiological functionalities and mechanisms of β-glucans. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Deng, J.M.; Tan, B.P. Effects of dietary β-glucan on growth rate, antioxidant status, immune response, and resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila in genetic improvement of farmed tilapia (GIFT, Oreochromis niloticus). Aquacult. Rep. 2023, 29, 101480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.L.; Limbu, S.M.; Lv, H.B.; Ma, Q.; Chen, L.Q.; Zhang, M.L.; Du, Z.Y. The comparisons in protective mechanisms and efficiencies among dietary α-lipoic acid, β-glucan and l-carnitine on Nile tilapia infected by Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhang, X.; Chang, E.H.; Wan, W.L.; Xu, J.; Zhao, C.Z.; Miao, S.Y. Effects of dietary Saccharomyces cerevisiae and β-glucan on the growth performance, antioxidant capacity and immunity response in Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Aquac. Nutr. 2021, 27, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.Y.; Feng, L.; Jiang, W.D.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Kuang, S.Y.; Tang, L.; Zhou, X.Q. Mannan oligosaccharides improved growth performance and antioxidant capacity in the intestine of on-growing grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Aquacult. Rep. 2020, 17, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Ma, H.M.; Mai, K.S.; Zhang, W.B.; Bai, N.; Wang, X.J. Effects of dietary β-glucan, mannan oligosaccharide and their combinations on growth performance, immunity and resistance against Vibrio splendidus of sea cucumber, Apostichopus japonicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Elala, N.; Marzouk, M.; Moustafa, M. Use of different Saccharomyces cerevisiae biotic forms as immune-modulator and growth promoter for Oreochromis niloticus challenged with some fish pathogens. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2013, 1, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrecillas, S.; Montero, D.; Izquierdo, M. Improved health and growth of fish fed mannan oligosaccharides: Potential mode of action. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 36, 525–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chang, H.M.; Han, D.X.; Lu, S.X.; Lv, W.H.; Guo, K.; Wang, C.A.; Li, S.W.; Han, S.C.; Liu, H.B. Effects of dietary chrysophyte (Poterioochromonas malhamensis) rich in beta-glucan on the growth performance, intestinal health, lipid metabolism, immune gene expression, and disease resistance against Aeromonas salmonicida in juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2022, 561, 738589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magouz, F.I.; Salem, M.F.; Emara, A.E.; Hassan, M.M.; Dawood, M.A. A mixture of β-Glucan and Mannanoligosaccharide ameliorated the growth rate, digestive enzyme activity, intestinal morphometry, and immunity of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Ann. Anim. Sci. 2021, 21, 1027–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, N.; Zhang, W.B.; Mai, K.S.; Wang, X.J.; Xu, W.; Ma, H.M. Effects of discontinuous administration of β-glucan and glycyrrhizin on the growth and immunity of white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2010, 306, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.J. Ruminal microbiology, biotechnology, and ruminant nutrition: Progress and problems. J. Anim. Sci. 1994, 72, 2992–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ayiku, S.; Liu, H.Y.; Tan, B.P.; Dong, X.H.; Chi, S.Y.; Yang, Q.H.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, W.H. Dietary yeast culture facilitates the growth, immune response, digestive enzyme activity, intestinal microbiota and disease resistance against Vibrio harveyi of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀ × Epinephelus lanceolatus♂). Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 2484–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar, D.; Zambonino, J.; Cahu, C.; Gatesoupe, F.J.; Vázquez-Juárez, R.; Lésel, R. Effect of live yeast incorporation in compound diet on digestive enzyme activity in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larvae. Aquaculture 2002, 204, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Q.; Fu, X.B.; Lü, Y.; Deng, Q.; Jiang, X.G.; Sheng, Z.Y. Relationship between plasma D-lactate and intestinal damage after severe injuries in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 7, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.X.; Qiao, G.X.; Cao, J.M.; Huang, Y.H.; Wang, G.X.; Chen, B.; Chen, X.Y.; Mo, W.Y. Dietary supplementation of N-carbamylglutamate and effects on growth, intestinal enzyme activities, immunological and antioxidant abilities of juvenile yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Aquac. Nutr. 2019, 25, 1250–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.Q.; Ye, Y.T.; Cai, C.F.; Wu, P.; Huang, Y.W.; Wu, T.; Lin, X.X.; Luo, Q.G.; Zhang, B.T.; Xiao, P.Z. Effect of diet oxidized fish oil on the intestinal structure and permeability of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2016, 40, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.X.; Guo, H.Y.; Zhu, K.C.; Liu, B.S.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, D.C. Effects of exogenous taurine supplementation on the growth, antioxidant capacity, intestine immunity, and resistance against Streptococcus agalactiae in juvenile golden pompano (Trachinotus ovatus) fed with a low-fishmeal diet. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1036821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ingredients 1 | CON | YC-12 | YC-8 | YC-4 | YC-0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fishmeal | 160 | 120 | 80 | 40 | 0 |
| Yeast culture | 0 | 53.5 | 107 | 160.5 | 214 |
| Soybean meal | 230 | 230 | 230 | 230 | 230 |
| Soybean protein concentrate | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 |
| Wheat flour | 286 | 268.8 | 251.7 | 234.5 | 217.3 |
| Corn gluten meal | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Chicken meal | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Meat meal | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Fish oil | 0 | 3.7 | 7.3 | 11 | 14.7 |
| Soybean oil | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 |
| Soybean lecithin | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Ca(H2PO4)2 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Vitamin and mineral premix 2,3 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Total | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| Proximate composition (g/kg) | |||||
| Moisture | 95.3 | 80.3 | 76.6 | 73.2 | 88.1 |
| Crude protein | 384.9 | 388.5 | 387.0 | 392.8 | 387.7 |
| Crude lipid | 74.8 | 73.1 | 68.1 | 67.9 | 69.0 |
| Crude ash | 75.1 | 74.3 | 72.0 | 66.8 | 65.5 |
| Items | Yeast Culture | Fishmeal |
|---|---|---|
| Proximate composition (air-dried basis) | ||
| Crude protein | 550.0 | 672.2 |
| Crude lipid | 16.4 | 104.0 |
| Crude ash | 65.3 | 149.5 |
| Phosphorus | 7.4 | 28.5 |
| Essential amino acids (dry-matter basis) | ||
| Lysine | 33.7 | 50.6 |
| Methionine | 7.4 | 19.4 |
| Arginine | 40.2 | 38.9 |
| Histidine | 16.3 | 16.0 |
| Isoleucine | 24.5 | 30.8 |
| Leucine | 44.1 | 50.0 |
| Phenylalanine | 29.6 | 27.5 |
| Threonine | 24.8 | 28.1 |
| Tryptophan | 6.7 | 7.6 |
| Valine | 25.8 | 34.8 |
| Non-essential amino acids (dry-matter basis) | ||
| Aspartic acid | 55.3 | 62 |
| Serine | 25.9 | 29.2 |
| Glutamic acid | 96.2 | 89.5 |
| Glycine | 23.1 | 37.4 |
| Alanine | 25.8 | 44.2 |
| Cysteine | 3.5 | 6.1 |
| Proline | 37.5 | 28.4 |
| Tyrosine | 20.2 | 23.8 |
| Total amino acids | 540.6 | 624.3 |
| Items | CON | YC-12 | YC-8 | YC-4 | YC-0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IBW (g) | 3.08 ± 0.04 | 3.05 ± 0.05 | 3.08 ± 0.08 | 3.08 ± 0.09 | 3.03 ± 0.07 |
| FBW (g) | 19.13 ± 0.35 a | 18.46 ± 0.59 ab | 16.57 ± 1.18 bc | 15.75 ± 1.00 c | 14.91 ± 0.69 c |
| WG (%) | 524.45 ± 8.88 a | 505.17 ± 9.34 a | 437.25 ± 34.98 b | 412.54 ± 36.49 b | 386.86 ± 20.46 b |
| FCR | 1.37 ± 0.04 c | 1.43 ± 0.07 bc | 1.59 ± 0.14 bc | 1.67 ± 0.06 ab | 1.87 ± 0.15 a |
| FI (g/fish) | 22.08 | 22.08 | 22.08 | 22.08 | 22.08 |
| SGR (%/d) | 3.27 ± 0.03 a | 3.21 ± 0.03 ab | 3.00 ± 0.11 bc | 2.92 ± 0.13 c | 2.82 ± 0.08 c |
| SR (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| K (g/cm3) | 1.59 ± 0.06 | 1.61 ± 0.11 | 1.68 ± 0.05 | 1.66 ± 0.04 | 1.68 ± 0.05 |
| VSI (%) | 7.32 ± 0.78 | 7.49 ± 0.60 | 8.12 ± 0.80 | 8.09 ± 0.29 | 7.88 ± 0.34 |
| HSI (%) | 1.31 ± 0.20 | 1.30 ± 0.11 | 1.31 ± 0.07 | 1.37 ± 0.28 | 1.12 ± 0.02 |
| Items | CON | YC-12 | YC-8 | YC-4 | YC-0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | 732.4 ± 4.7 | 730.4 ± 7.2 | 739.7 ± 11.4 | 743.1 ± 11.1 | 747.9 ± 7.8 |
| Crude ash | 35.1 ± 1.6 | 36.8 ± 4.3 | 34.2 ± 1.8 | 35.4 ± 3.7 | 35.8 ± 2.9 |
| Crude lipid | 56.1 ± 5.9 a | 53.6 ± 5.3 ab | 59.1 ± 3.7 a | 49.8 ± 3.8 ab | 44.2 ± 1.3 b |
| Crude protein | 142.3 ± 2.3 | 142.8 ± 4.4 | 137.7 ± 3.6 | 141.5 ± 1.1 | 138.1 ± 2.8 |
| PER | 2.00 ± 0.06 a | 1.85 ± 0.09 a | 1.50 ± 0.03 b | 1.53 ± 0.05 b | 1.39 ± 0.11 b |
| PR (%) | 29.38 ± 0.84 a | 27.31 ± 1.32 a | 22.52 ± 1.87 b | 21.59 ± 1.64 b | 21.05 ± 2.25 b |
| LR (%) | 60.69 ± 1.65 a | 56.95 ± 2.65 a | 57.78 ± 1.37 a | 49.36 ± 1.72 b | 42.47 ± 4.18 c |
| Items | CON | YC-12 | YC-8 | YC-4 | YC-0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AST (U/mL) | 2.25 ± 0.22 b | 2.29 ± 0.33 b | 2.52 ± 0.01 ab | 2.60 ± 0.22 ab | 3.11 ± 0.63 a |
| ALT (U/mL) | 1.58 ± 0.18 b | 1.71 ± 0.39 ab | 1.82 ± 0.09 ab | 1.98 ± 0.12 ab | 2.10 ± 0.09 a |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.63 ± 0.04 | 1.61 ± 0.07 | 1.45 ± 0.14 | 1.42 ± 0.09 | 1.58 ± 0.08 |
| GLU (g/L) | 1.56 ± 0.11 | 1.51 ± 0.09 | 1.48 ± 0.12 | 1.45 ± 0.06 | 1.44 ± 0.02 |
| TCHO (mmol/L) | 3.21 ± 0.44 a | 3.11 ± 0.14 a | 2.74 ± 0.22 ab | 2.35 ± 0.67 ab | 1.77 ± 0.48 b |
| TP (g/L) | 35.73 ± 0.48 | 36.03 ± 3.80 | 35.73 ± 5.20 | 34.16 ± 2.11 | 34.10 ± 3.60 |
| MDA (nmol/mL) | 4.04 ± 0.13 a | 2.33 ± 0.79 b | 2.70 ± 0.31 b | 3.14 ± 0.81 ab | 3.89 ± 0.23 a |
| CAT (U/mL) | 8.06 ± 0.22 b | 9.92 ± 0.61 a | 9.67 ± 1.28 a | 8.91 ± 0.63 ab | 8.63 ± 0.28 ab |
| SOD (U/mL) | 101.14 ± 5.61 b | 117.37 ± 3.15 a | 122.52 ± 6.96 a | 115.88 ± 5.64 a | 113.34 ± 10.36 ab |
| C3 (μg/mL) | 60.03 ± 13.45 b | 78.17 ± 1.76 a | 82.33 ± 7.68 a | 70.68 ± 6.11 ab | 61.36 ± 2.89 ab |
| IgM (μg/mL) | 19.58 ± 3.57 c | 24.77 ± 0.61 ab | 28.26 ± 1.01 a | 22.05 ± 3.40 bc | 21.00 ± 1.41 bc |
| AKP (U/L) | 40.32 ± 1.22 a | 50.67 ± 3.64 b | 53.26 ± 0.61 b | 49.91 ± 6.17 b | 46.70 ± 1.98 ab |
| D-LA (μmol/L) | 6.42 ± 0.08 b | 3.93 ± 0.40 c | 6.63 ± 0.42 b | 7.68 ± 0.20 b | 13.59 ± 1.58 a |
| Items | CON | YC-12 | YC-8 | YC-4 | YC-0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amylase (U/mg prot) | 0.25 ± 0.02 | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.28 ± 0.04 | 0.30 ± 0.04 | 0.28 ± 0.01 |
| Trypsin (U/mg prot) | 3542.81 ± 50.97 b | 4382.74 ± 350.65 a | 4677.12 ± 303.35 a | 4223.82 ± 46.24 ab | 3975.84 ± 129.93 ab |
| Lipase (U/mg prot) | 142.33 ± 13.35 | 142.94 ± 21.33 | 163.03 ± 14.00 | 147.95 ± 11.76 | 158.02 ± 1.82 |
| DAO (U/mg prot) | 11.11 ± 1.63 b | 11.64 ± 2.18 ab | 13.65 ± 1.21 ab | 14.21 ± 0.69 a | 14.28 ± 1.52 a |
| Items (μm) | CON | YC-12 | YC-8 | YC-4 | YC-0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Villus height | 1766.1 ± 139.5 a | 1759.8 ± 119.2 a | 1703.4 ± 250.1 a | 1477.7 ± 196.3 b | 1183.3 ± 138.8 c |
| Villus width | 306.0 ± 24.7 a | 306.3 ± 31.7 a | 307.1 ± 49.1 a | 272.8 ± 43.3 ab | 252.0 ± 25.4 b |
| Muscular thickness | 307.7 ± 43.7 | 293.1 ± 29.3 | 258.7 ± 60.5 | 259.2 ± 28.3 | 264.1 ± 22.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, H.; Li, X.; Guo, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Leng, X. The Substitution of Fishmeal with Yeast Culture in the Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) Diet: Growth, Serum Biochemical Indices, and Intestinal and Hepatopancreatic Histology. Animals 2024, 14, 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060869
Huang H, Li X, Guo B, Zhang Y, Yang X, Liu Y, Leng X. The Substitution of Fishmeal with Yeast Culture in the Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) Diet: Growth, Serum Biochemical Indices, and Intestinal and Hepatopancreatic Histology. Animals. 2024; 14(6):869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060869
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Hongfei, Xiaoqin Li, Beibei Guo, Yugui Zhang, Xu Yang, Yan Liu, and Xiangjun Leng. 2024. "The Substitution of Fishmeal with Yeast Culture in the Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) Diet: Growth, Serum Biochemical Indices, and Intestinal and Hepatopancreatic Histology" Animals 14, no. 6: 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060869
APA StyleHuang, H., Li, X., Guo, B., Zhang, Y., Yang, X., Liu, Y., & Leng, X. (2024). The Substitution of Fishmeal with Yeast Culture in the Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) Diet: Growth, Serum Biochemical Indices, and Intestinal and Hepatopancreatic Histology. Animals, 14(6), 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060869





