Genetic Characterization of Avian Paramyxovirus Isolated from Wild Waterfowl in Korea between 2015 and 2021
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.2. Virus Isolation and Detection
2.3. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. Host Species Identification
2.5. Accession Number
3. Results
3.1. Virus Detection and Identification
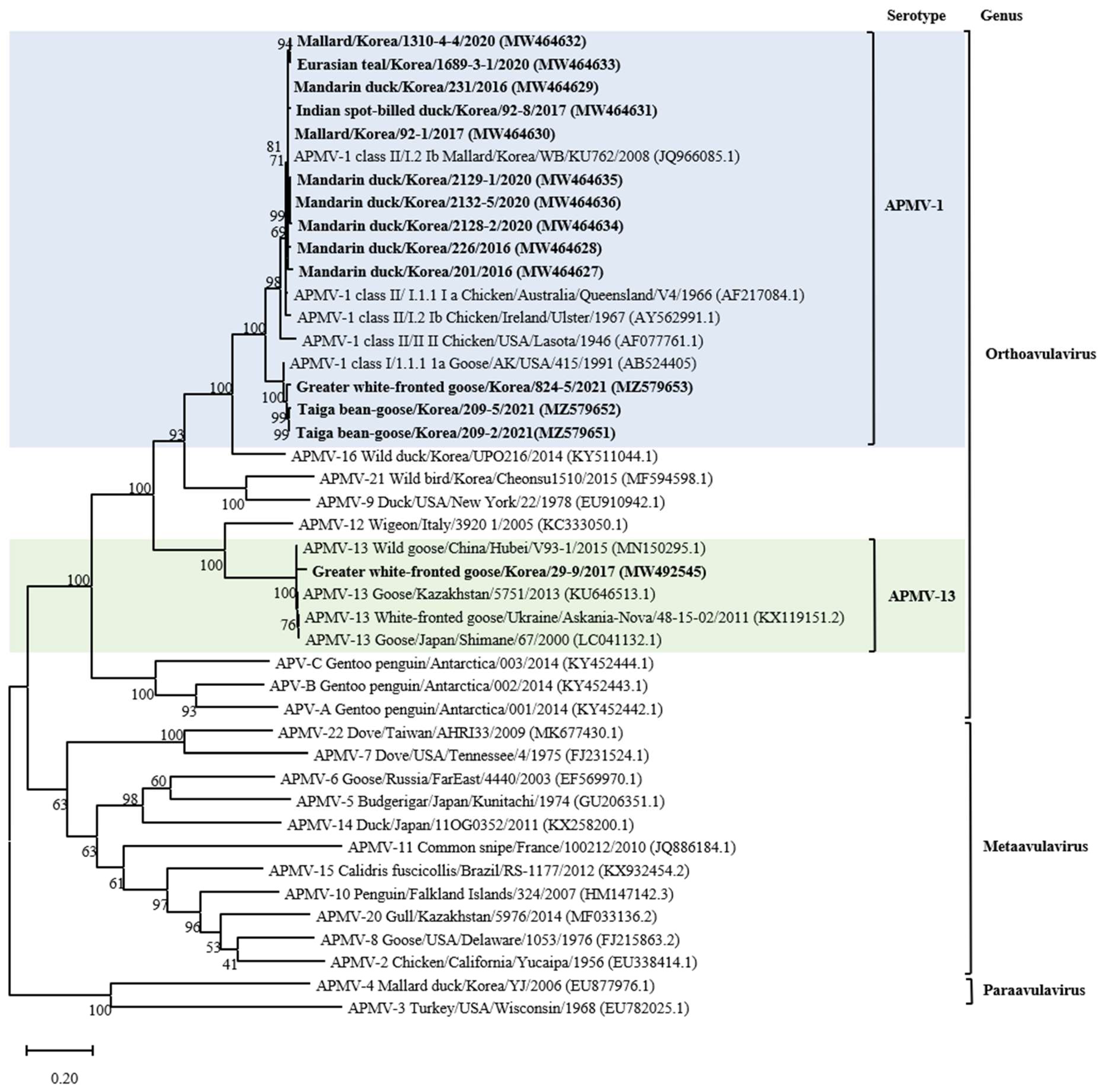
3.2. Genetic Characterization of AMPV-1
3.3. Genetic Characterization of AMPV-13
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahman, A.U.; Habib, M.; Shabbir, M.Z. Adaptation of Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) in Feral Birds and their Potential Role in Interspecies Transmission. Open Virol. J. 2018, 12, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.P.; Chang, C.Y.; Lee, F.; Chiou, C.J.; Tsai, H.J. Phylogenetic analysis of avian paramyxoviruses 1 isolated in Taiwan from 2010 to 2018 and evidence for their intercontinental dispersal by migratory birds. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 82, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogoi, P.; Ganar, K.; Kumar, S. Avian Paramyxovirus: A Brief Review. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, D.J. Newcastle disease and other avian paramyxoviruses. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2000, 19, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OIE. Newcastle Disease (Infection with Newcastle Disease Virus), Chapter 3.3.14. Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals; World Organization for Animal Health: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Umali, D.V.; Ito, H.; Suzuki, T.; Shirota, K.; Katoh, H.; Ito, T. Molecular epidemiology of Newcastle disease virus isolates from vaccinated commercial poultry farms in non-epidemic areas of Japan. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, Y.D.; Liu, X.X.; Mu, J.Q.; Li, J.J.; Yu, X.B.; Chang, J.; Bi, Y.; Stoeger, T.; Wajid, A.; Muzyka, D.; et al. The Emergence of Avian Orthoavulavirus 13 in Wild Migratory Waterfowl in China Revealed the Existence of Diversified Trailer Region Sequences and HN Gene Lengths within this Serotype. Viruses 2019, 11, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goraichuk, I.; Poonam, S.; Dimitrov, K.; Stegniy, B.; Muzyka, D.; Pantin-Jackwood, M.; Gerilovych, A.; Solodiankin, O.; Bolotin, V.; Rula, O.; et al. Phylogenetic analysis of the complete genome of the APMV-13 isolate from Ukraine. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 45, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamendin, K.; Kydyrmanov, A.; Seidalina, A.; Asanova, S.; Sayatov, M.; Kasymbekov, E.; Khan, E.; Daulbayeva, K.; Harrison, S.M.; Carr, I.M.; et al. Complete Genome Sequence of a Novel Avian Paramyxovirus (APMV-13) Isolated from a Wild Bird in Kazakhstan. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00167-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, E.; Ito, H.; Tomioka, Y.; Ito, T. Characterization of novel avian paramyxovirus strain APMV/Shimane67 isolated from migratory wild geese in Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2015, 77, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajid, A.; Mayahi, V.; Yin, R.; Ain, Q.; Mohiuddin, A.; Khalid, F.; Rehim, A.; Manan, A.; Baksh, M. Genomic and biological characteristics of Avian Orthoavulavirus-1 strains isolated from multiple wild birds and backyard chickens in Pakistan. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.F.; Zhang, P.Z.; Liu, X.X.; Chen, Y.Y.; Tao, Z.; Ai, L.L.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Xue, C.; et al. Dispersal and Transmission of Avian Paramyxovirus Serotype 4 among Wild Birds and Domestic Poultry. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidanovic, D.; Sekler, M.; Asanin, R.; Milic, N.; Nisavic, J.; Petrovic, T.; Savić, V. Characterization of velogenic Newcastle disease viruses isolated from dead wild birds in Serbia during 2007. J. Wildl. Dis. 2011, 47, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snoeck, C.J.; Marinelli, M.; Charpentier, E.; Sausy, A.; Conzemius, T.; Losch, S.; Muller, C.P. Characterization of newcastle disease viruses in wild and domestic birds in Luxembourg from 2006 to 2008. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khulape, S.A.; Gaikwad, S.S.; Chellappa, M.M.; Mishra, B.P.; Dey, S. Genetic characterization and pathogenicity assessment of Newcastle disease virus isolated from wild peacock. Virus Genes 2014, 49, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lycett, S.J.; Duchatel, F.; Digard, P. A brief history of bird flu. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, B.D.; Fuller, R.A.; Watkins, D.; Rogers, D.I.; Clemens, R.S.; Newman, M.; Woehler, E.J.; Weller, D.R. Revision of the East Asian-Australasian Flyway Population Estimates for 37 Listed Migratory Shorebird Species; BirdLife Australia: Melbourne, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hanna, A.; Banks, J.; Marston, D.A.; Ellis, R.J.; Brookes, S.M.; Brown, I.H. Genetic Characterization of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (H5N8) Virus from Domestic Ducks, England, November 2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, I.P.; Bae, Y.J.; Lee, S.B.; Mo, J.S.; Oh, K.H.; Shin, J.H.; Kang, H.M.; Lee, Y.J. Review of Avian Influenza Outbreaks in South Korea from 1996 to 2014. Avian Dis. 2016, 60 (Suppl. 1), 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.J.; Lee, I.W.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, Y.I.; Kwon, H.I.; Park, S.J.; Nguyen, H.D.; Kim, S.M.; Kwon, J.J.; Choi, W.S.; et al. Genetic characterization of novel, highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) H5N6 viruses isolated in birds, South Korea, November 2016. Euro Surveill. 2017, 22, 30434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kye, S.J.; Park, C.K.; Sung, H.W. Genetic diversity of avian paramyxovirus type 4 isolates from wild ducks in Korea from 2006 to 2011. Virus Genes 2013, 46, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, E.K.; Song, B.M.; Lee, H.S.; Choi, K.S. A Novel Avian Paramyxovirus (Putative Serotype 15) Isolated from Wild Birds. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Jang, M.J.; Kwon, H.M.; Sung, H.W. Genetic Diversity of Avian Paramyxovirus Type 6 Isolated from Wild Ducks in the Republic of Korea. J. Wildl. Dis. 2018, 54, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Kim, Y.; An, I.; Wang, S.J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, K.S.; Im, S.P.; Min, W.; Oem, J.K.; et al. Complete genome sequence of a novel avian paramyxovirus isolated from wild birds in South Korea. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.N.; Cheon, S.H.; Lee, E.K.; Heo, G.B.; Bae, Y.C.; Joh, S.J.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, Y.J. Pathogenesis and genetic characteristics of novel reassortant low-pathogenic avian influenza H7 viruses isolated from migratory birds in the Republic of Korea in the winter of 2016–2017. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, Y.G.; Lee, Y.N.; Lee, D.H.; Shin, J.I.; Lee, J.H.; Chung, D.H.; Lee, E.K.; Heo, G.B.; Sagong, M.; Kye, S.J.; et al. Multiple Reassortants of H5N8 Clade 2.3.4.4b Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Viruses Detected in South Korea during the Winter of 2020–2021. Viruses 2021, 13, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.N.; Lee, D.H.; Cheon, S.H.; Park, Y.R.; Baek, Y.G.; Si, Y.J.; Kye, S.J.; Lee, E.K.; Heo, G.B.; Bae, Y.C.; et al. Genetic characteristics and pathogenesis of H5 low pathogenic avian influenza viruses from wild birds and domestic ducks in South Korea. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.S.; Bashiruddin, J.B.; Alexander, D.J. Deduced Amino-Acid-Sequences at the Fusion Protein Cleavage Site of Newcastle-Disease Viruses Showing Variation in Antigenicity and Pathogenicity. Arch. Virol. 1993, 128, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, P.J.; Dimitrov, K.M.; Williams-Coplin, D.; Peterson, M.P.; Pantin-Jackwood, M.J.; Swayne, D.E.; Suarez, D.L.; Afonso, C.L. International Biological Engagement Programs Facilitate Newcastle Disease Epidemiological Studies. Front. Public Health 2015, 3, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Kang, H.M.; Jeong, O.M.; Kim, M.C.; Kwon, J.S.; Kwon, J.H.; Kim, C.B.; Lee, J.B.; et al. DNA barcoding techniques for avian influenza virus surveillance in migratory bird habitats. J. Wildl. Dis. 2010, 46, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, M.S.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, Y.N.; Park, J.K.; Yuk, S.-S.; Lee, J.-B.; Park, S.-Y.; Choi, I.-S.; et al. Exchange of Newcastle disease viruses in Korea: The relatedness of isolates between wild birds, live bird markets, poultry farms and neighboring countries. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, K.M.; Abolnik, C.; Afonso, C.L.; Albina, E.; Bahl, J.; Berg, M.; Briand, F.X.; Brown, I.H.; Choi, K.S.; Chvala, I.; et al. Updated unified phylogenetic classification system and revised nomenclature for Newcastle disease virus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 74, 103917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzyka, D.; Pantin-Jackwood, M.; Stegniy, B.; Rula, O.; Bolotin, V.; Stegniy, A.; Gerilovych, A.; Shutchenko, P.; Stegniy, M.; Koshelev, V.; et al. Wild Bird Surveillance for Avian Paramyxoviruses in the Azov-Black Sea Region of Ukraine (2006 to 2011) Reveals Epidemiological Connections with Europe and Africa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5427–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, L.M.; King, D.J.; Curry, P.E.; Suarez, D.L.; Swayne, D.E.; Stallknecht, D.E.; Slemons, R.D.; Pedersen, J.C.; Senne, D.A.; Winker, K.; et al. Phylogenetic diversity among low-virulence newcastle disease viruses from waterfowl and shorebirds and comparison of genotype distributions to those of poultry-origin isolates. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12641–12653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goraichuk, I.; Sharma, P.; Stegniy, B.; Muzyka, D.; Pantin-Jackwood, M.J.; Gerilovych, A.; Solodiankin, O.; Bolotin, V.; Miller, P.J.; Dimitrov, K.M.; et al. Complete Genome Sequence of an Avian Paramyxovirus Representative of Putative New Serotype 13. Genome Annouc. 2016, 4, e00729-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, E.; Ito, T.; Ito, H. Completion of full length genome sequence of novel avian paramyxovirus strain APMV/Shimane67 isolated from migratory wild geese in Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2016, 78, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.W.; Wang, X.Q.; Wu, S.; Hu, S.L.; Peng, Y.; Xue, F.; Liu, X. Surveillance for avirulent Newcastle disease viruses in domestic ducks (Anas platyrhynchos and Cairina moschata) at live bird markets in Eastern China and characterization of the viruses isolated. Avian Pathol. 2009, 38, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellor, K.C.; Meyer, A.; Elkholly, D.A.; Fournie, G.; Long, P.T.; Inui, K.; Padungtod, P.; Gilbert, M.; Newman, S.H.; Vergne, T.; et al. Comparative Epidemiology of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus H5N1 and H5N6 in Vietnamese Live Bird Markets: Spatiotemporal Patterns of Distribution and Risk Factors. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, C.L. Not so fast on recombination analysis of Newcastle disease virus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 9303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, J.T.; Dimitrov, K.M.; Afonso, C.L.; Ramey, A.M.; Bahl, J. Global phylodynamic analysis of avian paramyxovirus-1 provides evidence of inter-host transmission and intercontinental spatial diffusion. BMC Evol. Biol. 2019, 19, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.J.; Vijaykrishna, D.; Ellis, T.M.; Dyrting, K.C.; Leung, Y.H.; Bahl, J.; Wong, C.W.; Kai, H.; Chow, M.K.W.; Duan, L.; et al. Characterization of avian influenza viruses A (H5N1) from wild birds, Hong Kong, 2004–2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.J.; Campbell, G.; Manvell, R.J.; Collins, M.S.; Parsons, G.; McNulty, M.S. Characterisation of an antigenically unusual virus responsible for two outbreaks of Newcastle disease in the Republic of Ireland in 1990. Vet. Rec. 1992, 130, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, A.R.; Kattenbelt, J.A.; Selleck, P.; Hansson, E.; Della-Porta, A.; Westbury, H.A. Virulent Newcastle disease in Australia: Molecular epidemiological analysis of viruses isolated prior to and during the outbreaks of 1998–2000. Virus Res. 2001, 77, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shengqing, Y.; Kishida, N.; Ito, H.; Kida, H.; Otsuki, K.; Kawaoka, Y.; Ito, T. Generation of velogenic Newcastle disease viruses from a nonpathogenic waterfowl isolate by passaging in chickens. Virology 2002, 301, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, C.; Rehman, Z.U.; Liu, K.; Qiu, X.; Tan, L.; Sun, Y.; Liao, Y.; Song, C.; Yu, S.; Ding, Z.; et al. Potential of genotype VII Newcastle disease viruses to cause differential infections in chickens and ducks. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1851–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, P.J.; King, D.J.; Afonso, C.L.; Suarez, D.L. Antigenic differences among Newcastle disease virus strains of different genotypes used in vaccine formulation affect viral shedding after a virulent challenge. Vaccine 2007, 25, 7238–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H.; Park, J.K.; Yuk, S.S.; Erdene-Ochir, T.O.; Kwon, J.H.; Lee, J.B.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, I.S.; Lee, S.W.; Song, C.S. Complete genome sequence of a natural reassortant H9N2 avian influenza virus found in bean goose (Anser fabalis): Direct evidence for virus exchange between Korea and China via wild birds. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 26, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No. | Isolate | Abbreviation | Year | Location | Species | Virus | Class | Sub-Genotype (Current/ Former) | Fusion Gene Cleavage Site (112–117) | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mandarin duck/Korea/201/2016 | 201 | 2016 | Chungnam | Mandarin duck (Aix galericulata) | APMV-1 | II | I.2/Ib | GKQGR↓L | MW464627 |
| 2 | Mandarin duck/Korea/226/2016 | 226 | 2016 | Chungnam | Mandarin duck (Aix galericulata) | APMV-1 | II | I.2/Ib | GKQGR↓L | MW464628 |
| 3 | Mandarin duck/Korea/231/2016 | 231 | 2016 | Chungnam | Mandarin duck (Aix galericulata) | APMV-1 | II | I.2/Ib | GKQGR↓L | MW464629 |
| 4 | Mallard/Korea/92-1/2017 | 92-1 | 2017 | Jeonbuk | Mallard (Anas platyrhynchos) | APMV-1 | II | I.2/Ib | GKQGR↓L | MW464630 |
| 5 | Indian spot-billed duck/Korea/92-8/2017 | 92-8 | 2017 | Jeonbuk | Indian spot-billed duck (Anas poecilorhyncha) | APMV-1 | II | I.2/Ib | GKQGR↓L | MW464631 |
| 6 | Mallard/Korea/1310-4-4/2020 | 1310-4-4 | 2020 | Chungnam | Mallard (Anas platyrhynchos) | APMV-1 | II | I.2/Ib | GKQGR↓L | MW464632 |
| 7 | Eurasian teal/Korea/1689-3-1/2020 | 1689-3-1 | 2020 | Chungnam | Eurasian teal (Anas crecca) | APMV-1 | II | I.2/Ib | GKQGR↓L | MW464633 |
| 8 | Mandarin duck/Korea/2128-2/2020 | 2128-2 | 2020 | Jeonbuk | Mandarin duck (Aix galericulata) | APMV-1 | II | I.2/Ib | EKQGR↓L | MW464634 |
| 9 | Mandarin duck/Korea/2129-1/2020 | 2129-1 | 2020 | Jeonbuk | Mandarin duck (Aix galericulata) | APMV-1 | II | I.2/Ib | EKQGR↓L | MW464635 |
| 10 | Mandarin duck/Korea/2132-5/2020 | 2132-5 | 2020 | Jeonbuk | Mandarin duck (Aix galericulata) | APMV-1 | II | I.2/Ib | EKQGR↓L | MW464636 |
| 11 | Taiga bean-goose/Korea/209-2/2021 | 209-2 | 2021 | Jeonbuk | Taiga bean-goose (Anser fabalis) | APMV-1 | I | 1.2/1c | ERQER↓L | MZ579651 |
| 12 | Taiga bean-goose/Korea/209-5/2021 | 209-5 | 2021 | Jeonbuk | Taiga bean-goose (Anser fabalis) | APMV-1 | I | 1.2/1c | ERQER↓L | MZ579652 |
| 13 | Greater white-fronted goose/Korea/824-5/2021 | 824-5 | 2021 | Chungnam | Greater white-fronted goose (Anser albifrons) | APMV-1 | I | 1.2/1c | ERQER↓L | MZ579653 |
| 14 | Greater white-fronted goose/Korea/29-9/2017 | 29-9 | 2017 | Jeonbuk | Greater white-fronted goose (Anser albifrons) | APMV-13 | - | - | VRENR↓L | MW492545 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.-J.; Park, J.-Y.; Shang, K.; Zhang, J.-F.; Choi, Y.-R.; Kim, S.-W.; Cha, S.-Y.; Kang, M.; Wei, B.; Jang, H.-K. Genetic Characterization of Avian Paramyxovirus Isolated from Wild Waterfowl in Korea between 2015 and 2021. Animals 2024, 14, 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14050780
Lee Y-J, Park J-Y, Shang K, Zhang J-F, Choi Y-R, Kim S-W, Cha S-Y, Kang M, Wei B, Jang H-K. Genetic Characterization of Avian Paramyxovirus Isolated from Wild Waterfowl in Korea between 2015 and 2021. Animals. 2024; 14(5):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14050780
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Yea-Jin, Jong-Yeol Park, Ke Shang, Jun-Feng Zhang, Yu-Ri Choi, Sang-Won Kim, Se-Yeoun Cha, Min Kang, Bai Wei, and Hyung-Kwan Jang. 2024. "Genetic Characterization of Avian Paramyxovirus Isolated from Wild Waterfowl in Korea between 2015 and 2021" Animals 14, no. 5: 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14050780
APA StyleLee, Y.-J., Park, J.-Y., Shang, K., Zhang, J.-F., Choi, Y.-R., Kim, S.-W., Cha, S.-Y., Kang, M., Wei, B., & Jang, H.-K. (2024). Genetic Characterization of Avian Paramyxovirus Isolated from Wild Waterfowl in Korea between 2015 and 2021. Animals, 14(5), 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14050780





