Evaluation of Post-Surgical Recovery in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) by Assessing Behavior, Heart Rate, and Wound Healing
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Condition, Research Ethics and Procedures
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Behavior Monitoring
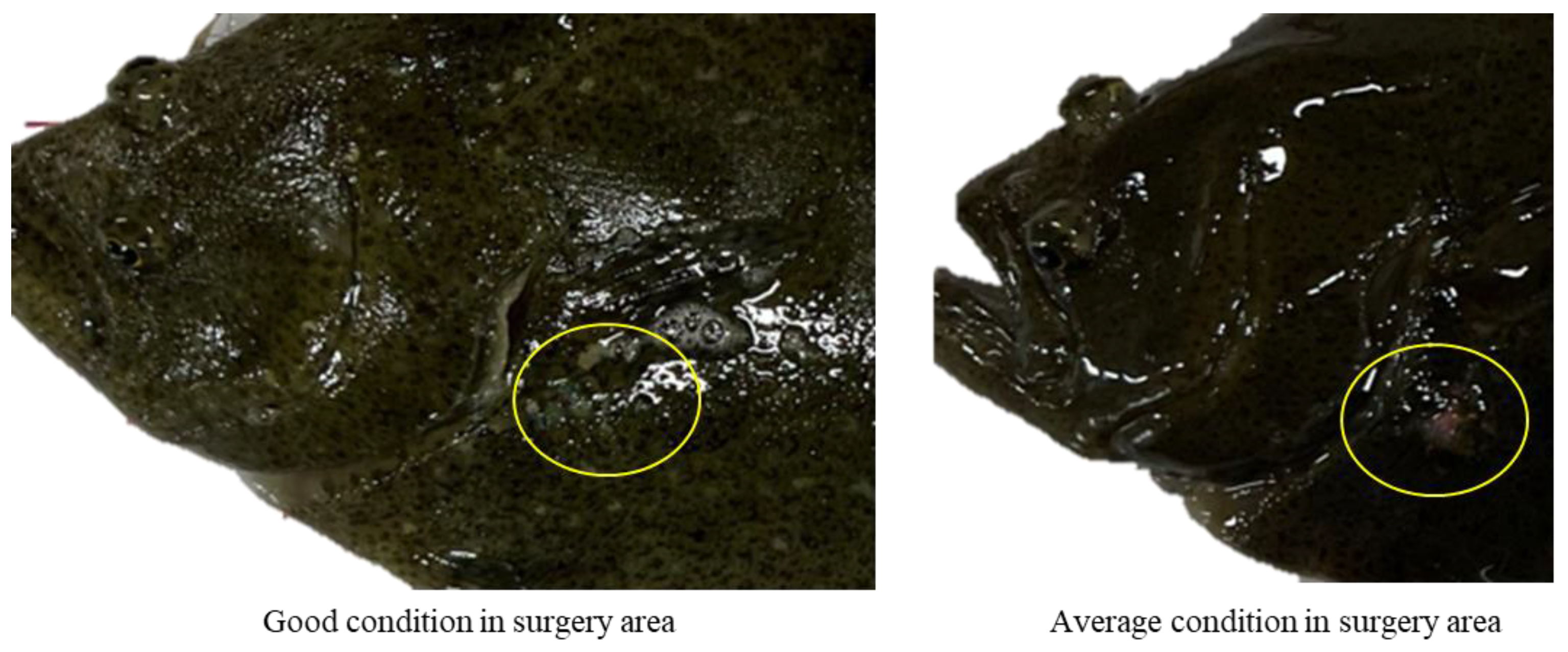
3.2. Degree of Wound Healing
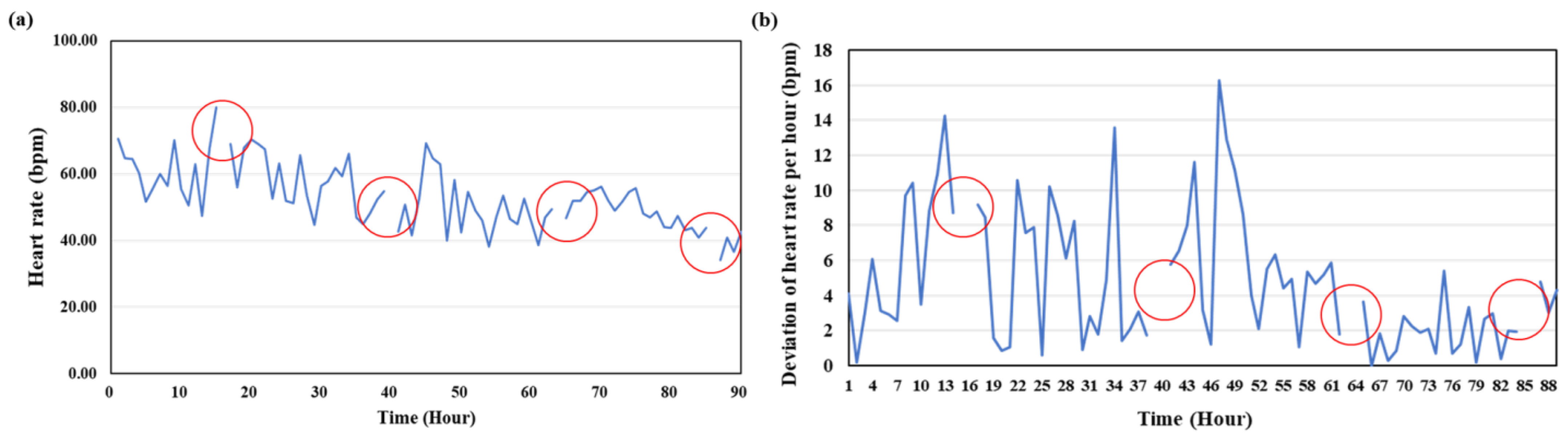
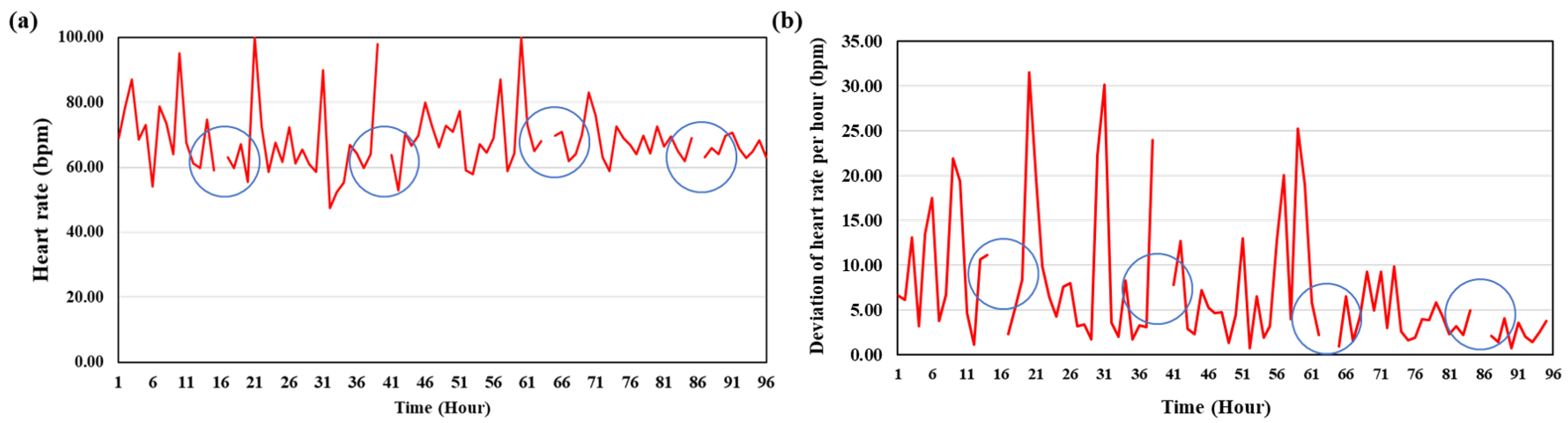
3.3. Heart Rate
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klinard, N.V.; Halfyard, E.A.; Fisk, A.T.; Stewart, T.J.; Johnson, T.B. Effects of surgically implanted acoustic tags on body condition, growth, and survival in a small, laterally compressed forage fish. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2018, 147, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussey, N.E.; Kessel, S.T.; Aarestrup, K.; Cooke, S.J.; Cowley, P.D.; Fisk, A.T.; Harcourt, R.G.; Holland, K.N.; Iverson, S.J.; Kocik, J.F.; et al. Aquatic animal telemetry: A panoramic window into the underwater world. Science 2015, 348, 1255642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macaulay, G.; Warren-Myers, F.; Barrett, L.T.; Oppedal, F.; Føre, M.; Dempster, T. Tag use to monitor fish behaviour in aquaculture: A review of benefits, problems and solutions. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 1565–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anras, M.B.; Bodaly, R.A.; McNicol, R. Use of an acoustic beam actograph to assess the effects of external tagging procedure on lake whitefish swimming activity. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1998, 127, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, J.; Hissmann, K.; Fricke, H. A method for deployment of externally attached sonic fish tags from a manned submersible and their effects on coelacanths. Mar. Biol. 1997, 128, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikardsen, A.H.; Diserub, O.H.; Elliott, J.M.; Dempson, J.B.; Sturlaugsson, J.; Jensen, A.J. The marine temperature and depth preferences of Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus) and sea trout (Salmo trutta), as recorded by data storage tags. Fish. Oceanogr. 2007, 16, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.W.; Diamond, S.L.; Stunz, G.W. External attachment of acoustic tags to deepwater reef fishes: An alternate approach when internal implantation affects experimental design. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2015, 144, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, V.; Silva, D.; Martinho, F.; Antunes, C.; Ramos, S.; Freitas, V. Assessing the effects of internal and external acoustic tagging methods on European flounder Platichthys flesus. Fish. Res. 2018, 206, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runde, B.J.; Buckel, J.A.; Bacheler, N.M.; Tharp, R.M.; Rudershausen, P.J.; Harms, C.A.; Ben-Horin, T. Evaluation of six methods for external attachment of electronic tags to fish: Assessment of tag retention, growth and fish welfare. J. Fish Biol. 2022, 101, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westhoff, J.T.; Sievert, N.A. Mortality and growth of crayfish internally tagged with PIT tags. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2013, 33, 878–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brijs, J.; Sandblom, E.; Axelsson, M.; Sundell, K.; Sundh, H.; Huyben, D.; Broströmd, R.; Kiessling, A.; Berg, C.; Gräns, A. The final countdown: Continuous physiological welfare evaluation of farmed fish during common aquaculture practices before and during harvest. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brijs, J.; Sandblom, E.; Rosengren, M.; Sundell, K.; Berg, C.; Axelsson, M.; Gräns, A. Prospects and pitfalls of using heart rate bio-loggers to assess the welfare of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2019, 509, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, M.N.; Røn, Ø.; Hagen, P.P.; McGurk, C. Monitoring fish welfare using heart rate bio-loggers in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.): An insight into the surgical recovery. Aquaculture 2022, 555, 738211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, I.; Kim, T. Monitoring the effect of water temperature on the heart rate of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) using a bio-logger. Aquaculture 2023, 575, 739739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Føre, M.; Svendsen, E.; Økland, F.; Gräns, A.; Alfredsen, J.A.; Finstad, B.; Hedger, R.D.; Uglem, I. Heart rate and swimming activity as indicators of post-surgical recovery time of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Anim. Biotelemetry 2021, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, W.M.; Burch, R.L. The Principles of Humane Experimental Technique; Methuen & Co Ltd.: London, UK, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, M.L.; Myers, M.S.; Burke, B.J.; O’Neill, S.M. Effects of surgically-implanted transmitters on survival and feeding behavior of adult English sole. In Aquatic Telemetry: Advances and Applications, Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Fish Telemetry Held in Europe, Ustica, Italy, 9–13 June 2003; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2005; pp. 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Tierney, K.B.; Farrell, A.P. The relationships between fish health, metabolic rate, swimming performance and recovery in return-run sockeye salmon, Oncorhynchus nerka (Walbaum). J. Fish Dis. 2004, 11, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeck, B.; Gudefin, A.; Romans, P.; Loubet, J.; Lenfant, P. Effects of intracoelomic tagging procedure on white seabream (Diplodus sargus) behavior and survival. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 440, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, C.J.; Deeming, D.C.; Wellby, I.; Soulsbury, C.D.; Eady, P.E. Effects of surgically implanted tags and translocation on the movements of common bream Abramis brama (L.). Fish. Res. 2015, 167, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hvas, M.; Folkedal, O.; Oppedal, F. Heart rates of Atlantic salmon Salmo salar during a critical swim speed test and subsequent recovery. J. Fish Biol. 2021, 98, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonyan, A.; Kraus, R.T.; Faust, M.D.; Vandergoot, C.S.; Cooke, S.J.; Cook, H.A.; Hayden, T.A.; Krueger, C.C. Estimating incision healing rate for surgically implanted acoustic transmitters from recaptured fish. Anim. Biotelemetry 2017, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.M.; Alves, C.; Silva, F.O.; Bedore, A.G.; Pompeu, P.S. Effect of anesthetic, tag size, and surgeon experience on postsurgical recovering after implantation of electronic tags in a neotropical fish: Prochilodus lineatus (Valenciennes, 1837) (Characiformes: Prochilodontidae). Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rożyński, M.; Kapusta, A.; Demska-Zakęś, K.; Hopko, M.; Sikora, A.; Zakęś, Z. The effects of surgically implanted dummy tags on the survival, growth performance, and physiology of pikeperch (Sander lucioperca). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabrizio, M.C.; Pessutti, J.P. Long-term effects and recovery from surgical implantation of dummy transmitters in two marine fishes. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 351, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoo, O.B.; Ivanina, A.V.; Ullstad, C.; Beniash, E.; Sokolova, I.M. Interactive effects of elevated temperature and CO2 levels on metabolism and oxidative stress in two common marine bivalves (Crassostrea virginica and Mercenaria mercenaria). Comp. Biochem. Phys. A 2013, 164, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, F.E.J. The effect of environmental factors on the physiology of fish. In Fish Physiology; Hoar, W.S., Randall, D.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971; Volume 6, pp. 1–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, L.B.; Wahli, T.; McGurk, C.; Eriksen, T.B.; Obach, A.; Waagbø, R.; Handler, A.; Tafalla, C. Effect of temperature and diet on wound healing in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 41, 1527–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIA (National Information Society Agency). Guidelines for Building and Utilizing Artificial Intelligence Data. 2021. Available online: https://aihub.or.kr/ (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Kawabe, R.; Nashimoto, K.; Hiraishi, T.; Naito, Y.; Sato, K. A new device for monitoring the activity of freely swimming flatfish, Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish. Sci. 2003, 69, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, P.W. Is tilting behaviour at low swimming speeds unique to negatively buoyant fish? Observations on steelhead trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, and bluegill, Lepomis macrochirus. J. Fish Biol. 1993, 43, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirri, R.; Mandrioli, L.; Zamparo, S.; Errani, F.; Volpe, E.; Tura, G.; Barbé, T.; Ciulli, S. Swim bladder disorders in Koi Carp (Cyprinus carpio). Animals 2020, 10, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIFS (National Institute of Fisheries Science). Olive Flounder Farming Standards Manual; NIFS: Busan, Republic of Korea, 2016; pp. 1–103.
- Shirakashi, S.; Nishioka, T.; Ogawa, K. Neoheterobothrium hirame (Monogenea) alters the feeding behavior of juvenile olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish. Sci. 2009, 75, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vornanen, M. The temperature dependence of electrical excitability in fish hearts. J. Exp. Bio. 2016, 219, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, T.J. Modulation of the immune system of fish by their environment. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2008, 25, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bly, J.E.; Clem, L.W. Temperature and teleost immune functions. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 1992, 2, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Code | Classification of Abnormal Types | Explanation | Causes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Normal behavior |
| NIA [29] Kawabe et al. [30] | |
| B |
|
| Kawabe et al. [30] | |
| C | Tilted swimming |
|
| Webb [31] Sirri [32] |
| D | Raising the mouth |
|
| NIA [29] |
| E | Slow swimming at the water surface |
|
| NIA [29] NIFS [33] |
| F | Turning |
|
| NIA [29] |
| G | Rubbing |
|
| NIA [29] |
| Postsurgical Ranking | Description |
|---|---|
| Good | Incision closed |
| All sutures retained (applies to one week post-surgery only) | |
| No signs of infection | |
| Average | Incision not fully closed |
| Most sutures retained (applies to one week post-surgery only) | |
| No signs of infection | |
| Poor | Large incision opening |
| Most sutures lost (applies to one week post-surgery only) | |
| Signs of infection and necrotic tissue around the incision site |
| Time (d) | Average Swimming Time (s) | Average Swimming Frequency (Off the Bottom) | Average Swimming Frequency (When Attached to the Bottom) | Abnormal Behavior (Type-Frequency) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8.59 ± 5.14 | 5.88 ± 5.63 | 9.5 ± 4.12 | - |
| 2 | 8.20 ± 4.23 | 5.67 ± 5.41 | 7.9 ± 5.62 | C-1 |
| 3 | 8.62 ± 4.75 | 6.08 ± 5.69 | 7.1 ± 7.72 | - |
| 4 | 8.25 ± 5.12 | 5.58 ± 4.33 | 9.7 ± 4.33 | - |
| 5 | 9.79 ± 5.22 | 5.42 ± 4.12 | 6.0 ± 5.20 | - |
| 6 | 10.00 ± 5.84 | 6.00 ± 5.98 | 6.7 ± 4.13 | - |
| 7 | 9.96 ± 4.60 | 5.83 ± 4.13 | 5.2 ± 5.21 | - |
| Average | 9.06 ± 4.99 | 5.78 ± 5.04 | 7.45 ± 5.19 |
| Time (d) | Average Swimming Time (s) | Average Swimming Frequency (Off the Bottom) | Average Swimming Frequency (When Attached to the Bottom) | Abnormal Behavior (Type-Frequency) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15.90 ± 7.87 | 13.50 ± 7.15 | 7.00 ± 3.53 | C-2 |
| 2 | 11.63 ± 7.28 | 14.00 ± 8.88 | 9.13 ± 6.91 | C-1 |
| 3 | 9.01 ± 4.48 | 11.79 ± 7.88 | 14.50 ± 7.12 | - |
| 4 | 8.65 ± 5.65 | 5.23 ± 5.31 | 6.10 ± 7.04 | - |
| 5 | 8.00 ± 4.39 | 5.21 ± 4.04 | 7.00 ± 7.64 | - |
| 6 | 7.93 ± 4.63 | 5.33 ± 5.24 | 5.71 ± 5.60 | - |
| 7 | 7.96 ± 4.79 | 5.04 ± 4.80 | 5.50 ± 5.53 | - |
| Average | 9.99 ± 5.58 | 9.02 ± 6.19 | 8.45 ± 6.19 |
| Time (d) | Average Swimming Time (s) | Average Swimming Frequency (Off the Bottom) | Average Swimming Frequency (When Attached to the Bottom) | Abnormal Behavior (Type-Frequency) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 14.45 ± 13.62 | 9.67 ± 7.50 | 12.78 ± 8.77 | C-10 |
| 2 | 25.08 ± 16.65 | 11.75 ± 5.60 | 18.42 ± 12.10 | C-5 |
| 3 | 9.21 ± 5.15 | 10.42 ± 6.95 | 24.88 ± 13.99 | C-10 |
| 4 | 6.47 ± 1.80 | 8.92 ± 4.93 | 26.75 ± 11.01 | C-1 |
| 5 | 6.68 ± 1.61 | 8.25 ± 4.41 | 25.54 ± 11.57 | - |
| 6 | 7.05 ± 1.78 | 9.17 ± 6.06 | 22.38 ± 15.56 | - |
| 7 | 6.81 ± 1.83 | 7.83 ± 4.97 | 24.04 ± 16.44 | - |
| Average | 10.82 ± 6.06 | 9.43 ± 5.77 | 22.11 ± 12.78 |
| Experiment 1 | Experiment 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Good | 10 | 9 |
| Average | - | 1 |
| Poor | 0 | 0 |
| Time (d) | Experiment 1 (bpm) | Experiment 2 (bpm) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 61.03 ± 8.48 | 67.54 ± 11.86 |
| 2 | 52.41 ± 8.98 | 70.14 ± 11.88 |
| 3 | 50.0 ± 4.3 | 68.07 ± 5.35 |
| 4 | 43.64 ± 6.38 | 71.08 ± 5.95 |
| 5 | 46.20 ± 6.66 | 66.08 ± 9.16 |
| 6 | 43.27 ± 8.26 | 68.43 ± 7.61 |
| 7 | 46.86 ± 7.73 | 67.10 ± 8.24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koo, M.; Jeong, M.-K.; Kwon, I. Evaluation of Post-Surgical Recovery in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) by Assessing Behavior, Heart Rate, and Wound Healing. Animals 2024, 14, 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14030363
Koo M, Jeong M-K, Kwon I. Evaluation of Post-Surgical Recovery in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) by Assessing Behavior, Heart Rate, and Wound Healing. Animals. 2024; 14(3):363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14030363
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoo, Myungsung, Man-Ki Jeong, and Inyeong Kwon. 2024. "Evaluation of Post-Surgical Recovery in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) by Assessing Behavior, Heart Rate, and Wound Healing" Animals 14, no. 3: 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14030363
APA StyleKoo, M., Jeong, M.-K., & Kwon, I. (2024). Evaluation of Post-Surgical Recovery in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) by Assessing Behavior, Heart Rate, and Wound Healing. Animals, 14(3), 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14030363






