A Comprehensive Analysis of CSN1S2 I and II Transcripts Reveals Significant Genetic Diversity and Allele-Specific Exon Skipping in Ragusana and Amiatina Donkeys
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Donkey Breeds
2.2. mRNA Samples
2.3. DNA Samples
2.4. Primer Design, RT-PCR Conditions for Amplification, and Cloning of the Donkey CSN1S2 I and CSN1S2 II cDNAs
2.5. Screening of Clones by PCR and Sequencing
2.6. Genomic DNA Sequencing
2.7. Genotyping of Donkey at CSN1S2 I Locus by XbaI PCR-RFLP
2.8. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of the Transcripts
3.1.1. CSN1S2 I
3.1.2. CSN1S2 II
3.2. Analysis of Genetic Diversity
3.2.1. CSN1S2 I and CSN1S2 II cDNA Polymorphisms Detection
3.2.2. DNA Sequences: Detection of a Point Mutation in the Splice Acceptor Site of CSN1S2 I Exon 17
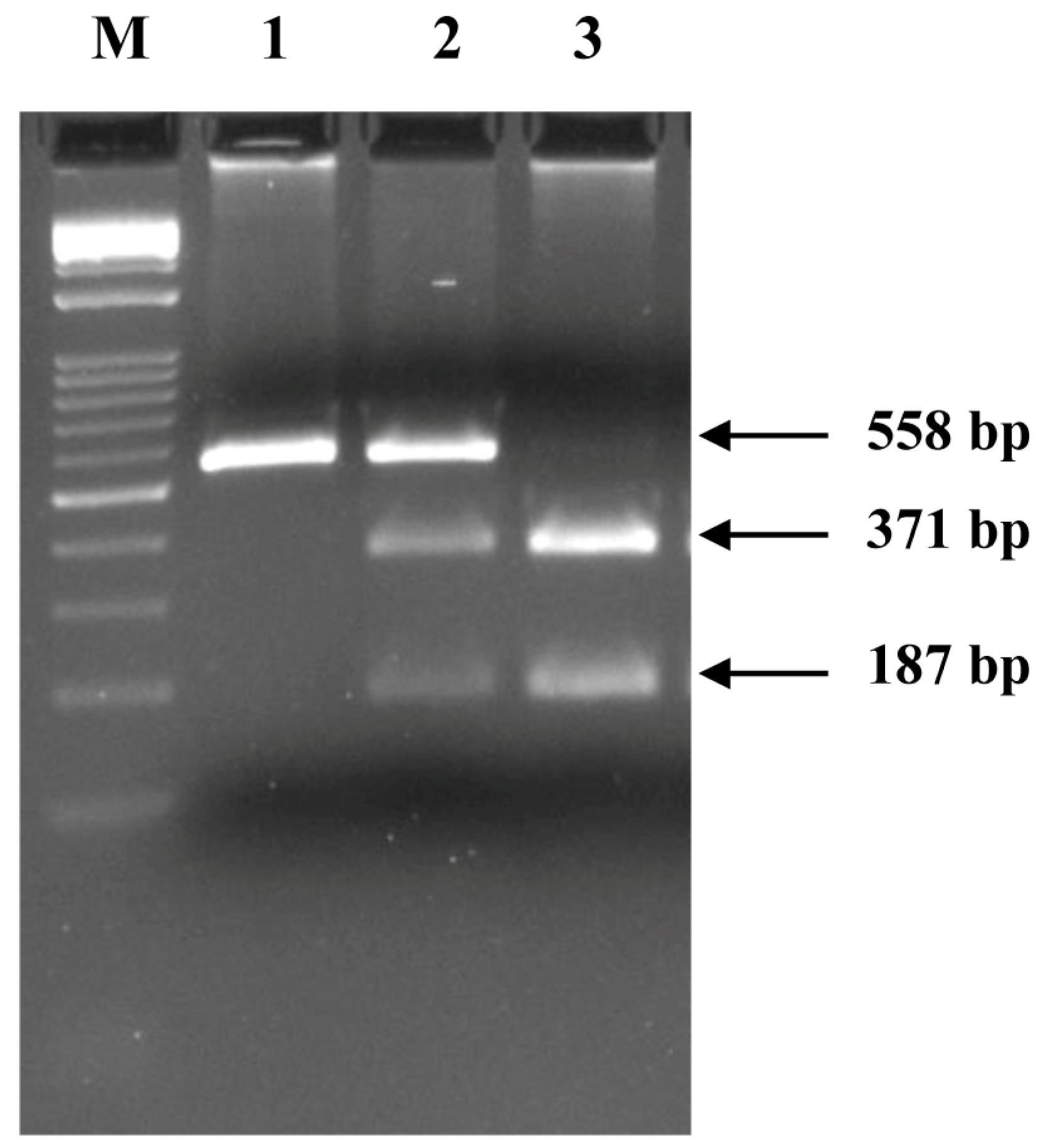
3.2.3. Genotyping of the SNP FM946022.1: c.375-1G>A in the Donkey CSN1S2 I Gene
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bordonaro, S.; Dimauro, C.; Criscione, A.; Marletta, D.; Macciotta, N.P.P. The mathematical modeling of the lactation curve for dairy traits of the donkey (Equus asinus). J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 4005–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colli, L.; Perrotta, G.; Negrini, R.; Bomba, L.; Bigi, D.; Zambonelli, P.; Verini Supplizi, A.; Liotta, L.; Ajmone-Marsan, P. Detecting population structure and recent demographic history in endangered livestock breeds: The case of the Italian autochthonous donkeys. Anim. Genet. 2013, 44, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maryniak, N.Z.; Sancho, A.I.; Hansen, E.B.; Bøgh, K.L. Alternatives to cow’s milk-based infant formulas in the prevention and management of cow’s milk allergy. Foods 2022, 11, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faccia, M.; D’Alessandro, A.G.; Summer, A.; Hailu, Y. Milk products from minor dairy species: A review. Animals 2020, 10, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierska, K.; Kalinowska-Lis, U. Milk proteins—Their biological activities and use in cosmetics and dermatology. Molecules 2021, 26, 3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, G.; Mauriello, R.; Garro, G.; Auzino, B.; Iannaccone, M.; Costanzo, A.; Chianese, L.; Pauciullo, A. Casein composition and differential translational efficiency of casein transcripts in donkey’s milk. J. Dairy Res. 2019, 86, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auzino, B.; Miranda, G.; Henry, C.; Krupova, Z.; Martini, M.; Salari, F.; Cosenza, G.; Ciampolini, R.; Martin, P. Top-Down proteomics based on LC-MS combined with cDNA sequencing to characterize multiple proteoforms of Amiata donkey milk proteins. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianese, L.; Calabrese, M.G.; Ferranti, P.; Mauriello, R.; Garro, G.; De Simone, C.; Quarto, M.; Addeo, F.; Cosenza, G.; Ramunno, L. Proteomic characterization of donkey milk “caseome”. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 4834–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianese, L.; De Simone, C.; Ferranti, P.; Mauriello, R.; Costanzo, A.; Quarto, M.; Garro, G.; Picariello, G.; Mamone, G.; Ramunno, L. Occurrence of qualitative and quantitative polymorphism at donkey beta-Lactoglobulin II locus. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 1273–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, G.; Ciampolini, R.; Iannaccone, M.; Gallo, D.; Auzino, B.; Pauciullo, A. Sequence variation and detection of a functional promoter polymorphism in the lysozyme c-type gene from Ragusano and Grigio Siciliano donkeys. Anim. Genet. 2018, 49, 270–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, G.; Patrice, M.; Garro, G.; Gallo, D.; Barbara, A.; Roberta, C.; Alfredo, P. A novel allelic donkey β-Lg I protein isoform generated by a non-AUG translation initiation codon is associated with a non-synonymous SNP. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 4158–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, G.; Pauciullo, A.; Annunziata, A.L.; Rando, A.; Chianese, L.; Marletta, D.; Iannolino, G.; Nicodemo, D.; Berardino, D.D.; Ramunno, L. Identification and characterization of the donkey CSN1S2 I and II cDNAs. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 9, e40. [Google Scholar]
- Criscione, A.; Cunsolo, V.; Tumino, S.; Di Francesco, A.; Bordonaro, S.; Muccilli, V.; Saletti, R.; Marletta, D. Polymorphism at donkey β-lactoglobulin II locus: Identification and characterization of a new genetic variant with a very low expression. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrouin, M.; Mollé, D.; Fauquant, J.; Ballestra, F.; Maubois, J.-L.; Léonil, J. New genetic variants identified in donkey’s milk whey proteins. J. Protein Chem. 2000, 19, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdil, F.; Bulut, H.; Işık, R. Genetic diversity of κ-casein (CSN3) and lactoferrin (LTF) genes in the endangered Turkish donkey (Equus asinus) populations. Arch. Anim. Breed. 2019, 62, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunsolo, V.; Saletti, R.; Muccilli, V.; Gallina, S.; Di Francesco, A.; Foti, S. Proteins and bioactive peptides from donkey milk: The molecular basis for its reduced allergenic properties. Food Research International 2017, 99, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saletti, R.; Muccilli, V.; Cunsolo, V.; Fontanini, D.; Capocchi, A.; Foti, S. MS-based characterization of αs2-casein isoforms in donkey’s milk. J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 47, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malacarne, M.; Criscione, A.; Franceschi, P.; Bordonaro, S.; Formaggioni, P.; Marletta, D.; Summer, A. New insights into chemical and mineral composition of donkey milk throughout nine months of lactation. Animals 2019, 9, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargentini, C.; Tocci, R.; Martini, A.; Bozzi, R. Morphological characterization of Amiata donkey through Multivariate analyses. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2018, 47, e20170310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijnkels, M. Multispecies comparison of the casein gene loci and evolution of casein gene family. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2002, 7, 327–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauciullo, A.; Versace, C.; Gaspa, G.; Letaief, N.; Bedhiaf-Romdhani, S.; Fulgione, A.; Cosenza, G. Sequencing and Characterization of αs2-Casein Gene (CSN1S2) in the Old-World Camels Have Proven Genetic Variations Useful for the Understanding of Species Diversification. Animals 2023, 13, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenen, M.; Dijkhof, R.; Verstege, A.; Van der Poel, J. The complete sequence of the gene encoding bovine α2-casein. Gene 1993, 123, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryskaliyeva, A.; Henry, C.; Miranda, G.; Faye, B.; Konuspayeva, G.; Martin, P. Alternative splicing events expand molecular diversity of camel CSN1S2 increasing its ability to generate potentially bioactive peptides. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosenza, G.; Iannaccone, M.; Pico, B.A.; Ramunno, L.; Capparelli, R. The SNP g. 1311T> C associated with the absence of β-casein in goat milk influences CSN2 promoter activity. Anim. Genet. 2016, 47, 615–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramunno, L.; Cosenza, G.; Rando, A.; Pauciullo, A.; Illario, R.; Gallo, D.; Di Berardino, D.; Masina, P. Comparative analysis of gene sequence of goat CSN1S1 F and N alleles and characterization of CSN1S1 transcript variants in mammary gland. Gene 2005, 345, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramunno, L.; Longobardi, E.; Pappalardo, M.; Rando, A.; Di Gregorio, P.; Cosenza, G.; Mariani, P.; Pastore, N.; Masina, P. An allele associated with a non-detectable amount of αs2 casein in goat milk. Anim. Genet. 2001, 32, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Jeong, S. 3’UTR diversity: Expanding repertoire of RNA alterations in human mRNAs. Mol. Cells 2023, 46, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, E.; Mallén, A.; Hueso, M. Dynamic variations of 3′UTR length reprogram the mRNA regulatory landscape. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferranti, P.; Chianese, L.; Malorni, A.; Migliaccio, F.; Stingo, V.; Addeo, F. Copresence of deleted protein species generates structural heterogeneity of ovine αs1-casein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferranti, P.; Lilla, S.; Chianese, L.; Addeo, F. Alternative nonallelic deletion is constitutive of ruminant α s1-casein. J. Protein Chem. 1999, 18, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milenkovic, D.; Martin, P.; Guérin, G.; Leroux, C. A specific pattern of splicing for the horse α S1-Casein mRNA and partial genomic characterization of the relevant locus. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2002, 34, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Martin, P.; Brignon, G.; Furet, J.; Leroux, C. The gene encoding αs1-casein is expressed in human mammary epithelial cells during lactation. Le Lait 1996, 76, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisnard, M.; Hue, D.; Bouniol, C.; Mercier, J.C.; Gaye, P. Multiple mRNA species code for two non-allelic forms of ovine αs2-casein. Eur. J. Biochem. 1991, 201, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.; Szymanowska, M.; Zwierzchowski, L.; Leroux, C. The impact of genetic polymorphisms on the protein composition of ruminant milks. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2002, 42, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramunno, L.; Cosenza, G.; Pappalardo, M.; Longobardi, E.; Gallo, D.; Pastore, N.; Di Gregorio, P.; Rando, A. Characterization of two new alleles at the goat CSN1S2 locus. Anim. Genet. 2001, 32, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, G.; Gallo, D.; Auzino, B.; Gaspa, G.; Pauciullo, A. Complete CSN1S2 Characterization, Novel Allele Identification and Association With Milk Fatty Acid Composition in River Buffalo. Front. Genet. 2021, 11, 622494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, G.; Pauciullo, A.; Feligini, M.; Coletta, A.; Colimoro, L.; Di Berardino, D.; Ramunno, L. A point mutation in the splice donor site of intron 7 in the αs2-casein encoding gene of the Mediterranean River buffalo results in an allele-specific exon skipping. Anim. Genet. 2009, 40, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouniol, C.; Printz, C.; Mercier, J.-C. Bovine αs2-casein D is generated by exon VIII skipping. Gene 1993, 128, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, J.; Koudelka, T.; Keppler, J.K.; Tholey, A.; Schwarz, K.; Thaller, G.; Tetens, J. Characterization of an equine α-S2-casein variant due to a 1.3 kb deletion spanning two coding exons. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieslak, J.; Pawlak, P.; Wodas, L.; Borowska, A.; Stachowiak, A.; Puppel, K.; Kuczynska, B.; Luczak, M.; Marczak, L.; Mackowski, M. Characterization of equine CSN1S2 variants considering genetics, transcriptomics, and proteomics. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balteanu, V.A.; Carsai, T.C.; Vlaic, A. Identification of an intronic regulatory mutation at the buffalo α S1-casein gene that triggers the skipping of exon 6. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 4311–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pascale, S.; Caira, S.; Garro, G.; Mauriello, R.; Scaloni, A.; Cosenza, G.; Chianese, L. Proteomic characterisation and phylogenetic derivation of ovine αS1-CN B and αS1-CN G genetic variants. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 131, 105387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambra, I.J.; Chianese, L.; Ferranti, P.; Erhardt, G. Short communication: Molecular genetic characterization of ovine alpha(S1)-casein allele H caused by alternative splicing. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 792–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenasi, T.; Rogelj, I.; Dovc, P. Characterization of equine cDNA sequences for αS1-, β-and κ-casein. J. Dairy Res. 2003, 70, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauciullo, A.; Gauly, M.; Cosenza, G.; Wagner, H.; Erhardt, G. Lama glama αS1-casein: Identification of new polymorphisms in the CSN1S1 gene. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, L.; Beattie, C. The sequence of porcine αs1-casein cDNA: Evidence for protein variants generated by altered RNA splicing. Anim. Genet. 1992, 23, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Cosenza, G.; Nicolae, I.; Bota, A.; Guo, Y.; Di Stasio, L.; Pauciullo, A. Transcript analysis at DGAT1 reveals different mRNA profiles in river buffaloes with extreme phenotypes for milk fat. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 8265–8276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, J.; Jagannathan, V.; Drögemüller, C.; Rieder, S.; Leeb, T.; Thaller, G.; Tetens, J. Genetic variability of the equine casein genes. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 5486–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambra, I.; Erhardt, G. Molecular genetic characterization of ovine CSN1S2 variants C and D reveal further important variability within CSN1S2. Anim. Genet. 2012, 43, 642–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell Jr, H.; Jimenez-Flores, R.; Bleck, G.; Brown, E.; Butler, J.; Creamer, L.; Hicks, C.; Hollar, C.; Ng-Kwai-Hang, K.; Swaisgood, H. Nomenclature of the proteins of cows’ milk—Sixth revision. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 1641–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, G.; Albarella, S.; D’Anza, E.; Iannuzzi, A.; Selvaggi, M.; Pugliano, M.; Galli, T.; Saralli, G.; Ciotola, F.; Peretti, V. A New AS-PCR Method to Detect CSN2 01 Allele, Genotyping at Ca-Sensitive Caseins Loci and Milk Traits Association Studies in Autochthonous Lazio Goats. Animals 2023, 13, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Gerlando, R.; Tortorici, L.; Sardina, M.T.; Monteleone, G.; Mastrangelo, S.; Portolano, B. Molecular Characterisation of κ–Casein Gene in Girgentana Dairy Goat Breed and Identification of Two New Alleles. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 14, 3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzola, M.; Vacca, G.M.; Noce, A.; Porcedda, M.; Onnis, M.; Manca, N.; Dettori, M.L. Exploring the genotype at CSN3 gene, milk composition, coagulation and cheese-yield traits of the sardo-modicana, an autochthonous cattle breed from the Sardinia Region, Italy. Animals 2020, 10, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostou, M.; Chung, C.; McGann, E.; Verheijen, B.; Kou, Y.; Chen, L.; Vermulst, M. Transcription errors in aging and disease. Transl. Med. Aging 2021, 5, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, C.; Gout, J.-F.P.; Vermulst, M. Genome-wide surveillance of transcription errors in eukaryotic organisms. JoVE (J. Vis. Exp.) 2018, 139, e57731. [Google Scholar]
- Mohr, U.; Koczan, D.; Linder, D.; Hobom, G.; Erhardt, G. A single point mutation results in A allele-specific exon skipping in the bovine αs1-casein mRNA. Gene 1994, 143, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, G.; Iannaccone, M.; Auzino, B.; Macciotta, N.; Kovitvadhi, A.; Nicolae, I.; Pauciullo, A. Remarkable genetic diversity detected at river buffalo prolactin receptor (PRLR) gene and association studies with milk fatty acid composition. Anim. Genet. 2018, 49, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosenza, G.; Iannaccone, M.; Pico, A.B.; Gallo, D.; Capparelli, R.; Pauciullo, A. Molecular characterisation, genetic variability and detection of a functional polymorphism influencing the promoter activity of OXT gene in goat and sheep. J. Dairy Res. 2017, 84, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pauciullo, A.; Versace, C.; Miretti, S.; Giambra, I.; Gaspa, G.; Letaief, N.; Cosenza, G. Genetic variability among and within domestic Old and New World camels at the α-lactalbumin gene (LALBA) reveals new alleles and polymorphisms responsible for differential expression. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 1068–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J. Origin of major histocompatibility complex polymorphism: The trans-species hypothesis. Hum. Immunol. 1987, 19, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachos, F.E. Mammalian phylogenetics: A short overview of recent advances. In Mammals of Europe-Past, Present, and Future; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 31–48. [Google Scholar]

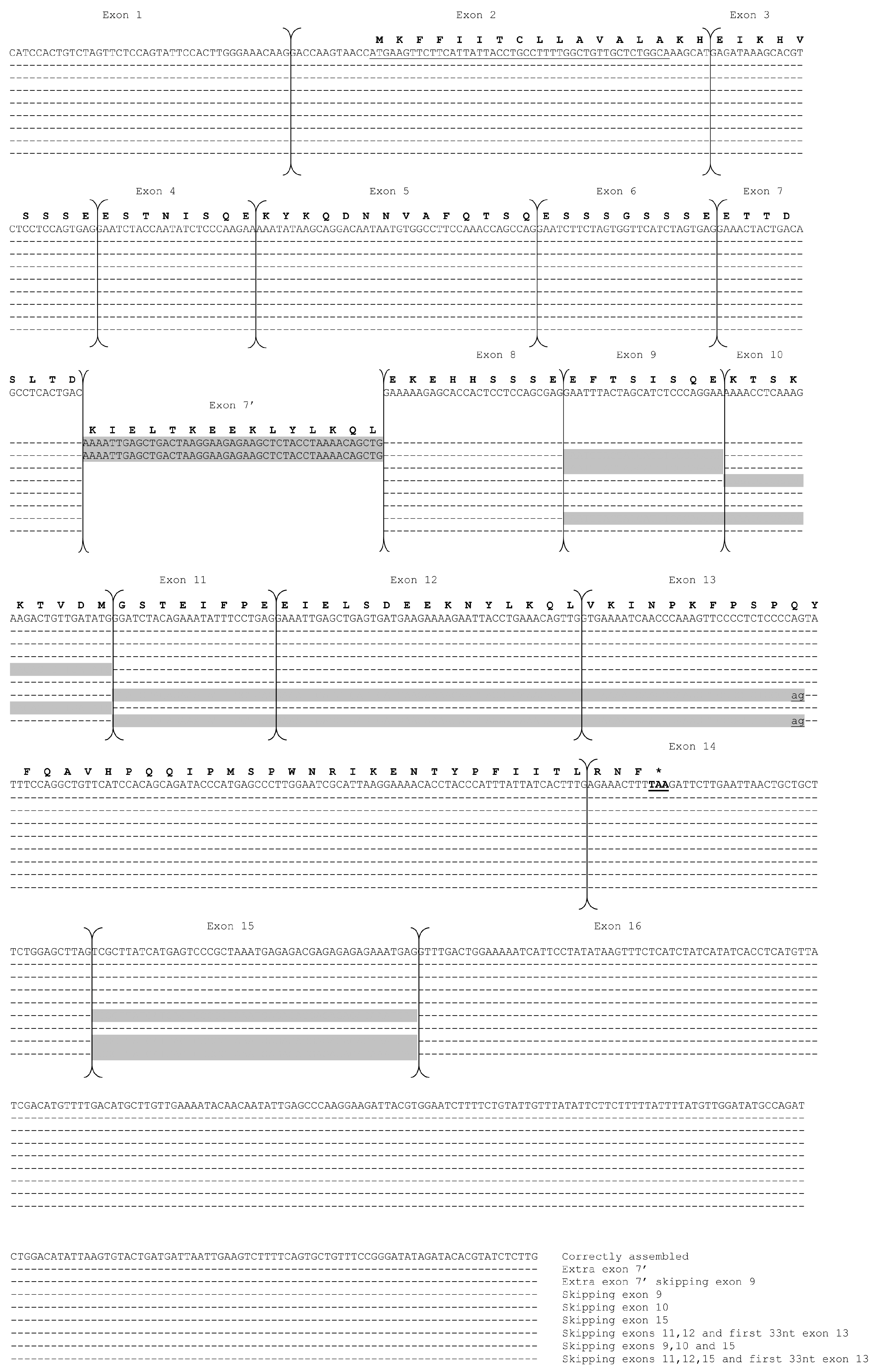
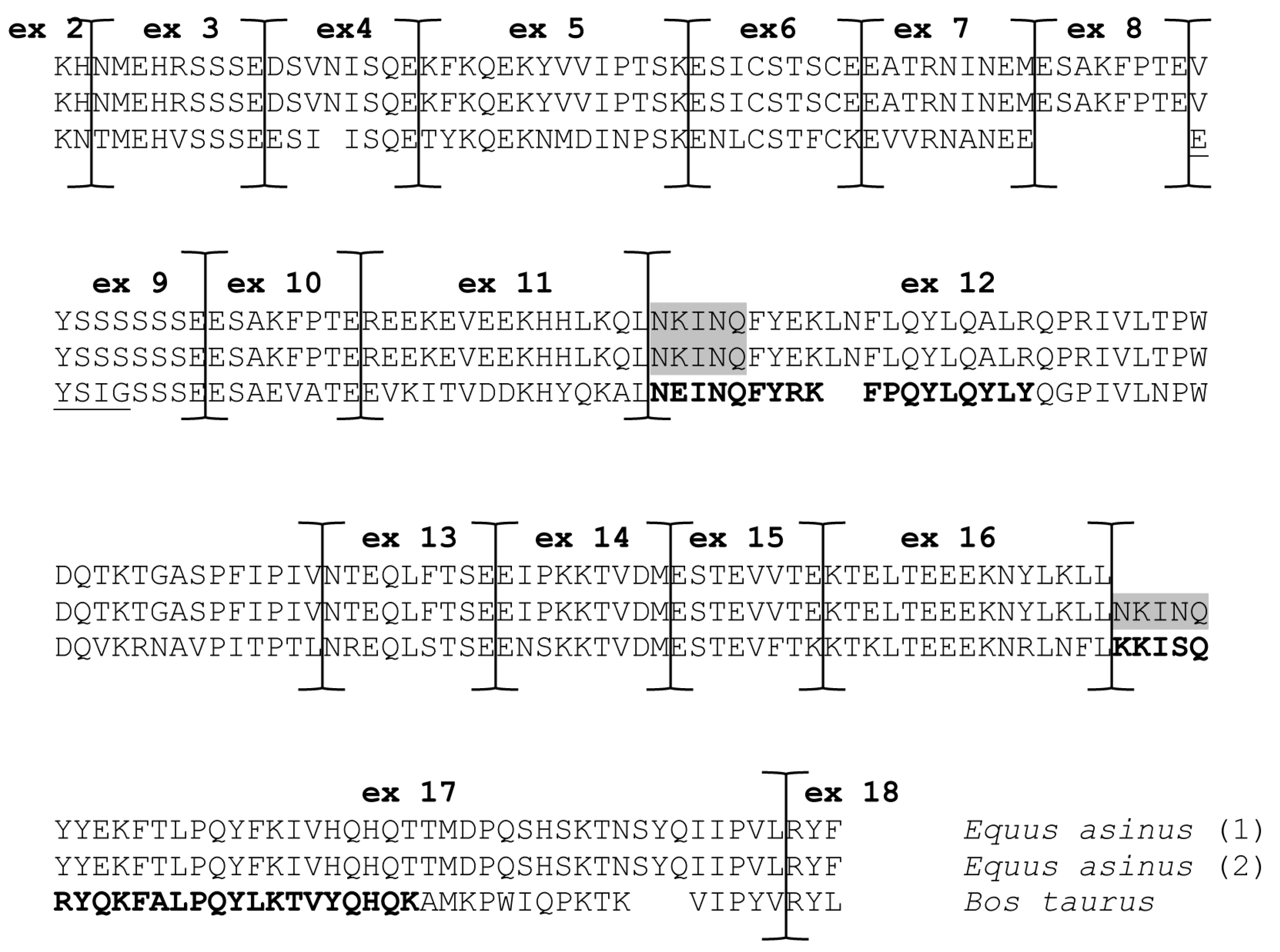
| Present Work | Auzino et al. [7] | Saletti et al. [17] Cunsolo et al. [16] | Deduced Mature Protein Size (aa) | Theoretical Mw | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correctly assembled | - | Correctly assembled | 221 | 26,030.19 | |
| Alternative skipping | Lacking exon 11 | - | - | 206 | 24,116.04 |
| Insertion exon 12′ | - | - | 143 | 16,617.68 | |
| - | Lacking exon 3 and 3′ end of exon 17 | - | 205 | 24,145.24 | |
| Lacking exons 4, 5, 6, and 3′ end of exon 17 | Lacking exons 4, 5, 6, and 3′ end of exon 17 | Lacking exons 4, 5, 6, and 3′ end of exon 17 | 183 | 21,713.42 | |
| Lacking 3′ end of exon 17 | Lacking 3′ end of exon 17 | Lacking 3′ end of exon 17 | 214 | 25,203.33 | |
| Lacking exons 4, 5, and 6 | Lacking exons 4, 5, and 6 | - | 190 | 22,540.28 | |
| - | Lacking exons 4, 5, 6, and 13 | - | 181 | 21,490.19 | |
| - | Lacking exon 6 and 3′ end of exon 17 | - | 205 | 24,263.32 | |
| Lacking exons 4, 5, 6, and 5′ of exon 17 | - | Lacking exons 4, 5, 6, and 5′ of exon 17 | 185 | 21,942.60 | |
| Lacking 5′ of exon 17 | - | Lacking 5′ of exon 17 | 216 | 25,432.52 |
| Present Work | Auzino et al. [7] | Deduced Mature Protein Size (aa) | Theoretical Mw | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correctly assembled with or without exon 15 | 142 | 16,377.88 | ||
| Alternative skipping | Insertion exon 7′ | 157 | 18,236.13 | |
| Lacking exon 9 and insertion exon 7′ | 149 | 17,314.17 | ||
| Lacking exon 3 and insertion exon 7′ | 148 | 17,239.06 | ||
| Lacking exons 3, 9, and insertion exon 7′ | 140 | 16,317.10 | ||
| Lacking exons 3, 11, 12, first 33nt exon 13, and insertion exon 7′ | 114 | 13,308.63 | ||
| Lacking exon 9 | 134 | 15,455.92 | ||
| Lacking exon 10 | 133 | 15,358.65 | ||
| Lacking exons 11, 12, and first 33nt exon 13 with or without exon 15 | 108 | 12,447.45 | ||
| Lacking exons 9, 10, and 15 | 125 | 14,436.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cosenza, G.; Pauciullo, A. A Comprehensive Analysis of CSN1S2 I and II Transcripts Reveals Significant Genetic Diversity and Allele-Specific Exon Skipping in Ragusana and Amiatina Donkeys. Animals 2024, 14, 2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14202918
Cosenza G, Pauciullo A. A Comprehensive Analysis of CSN1S2 I and II Transcripts Reveals Significant Genetic Diversity and Allele-Specific Exon Skipping in Ragusana and Amiatina Donkeys. Animals. 2024; 14(20):2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14202918
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosenza, Gianfranco, and Alfredo Pauciullo. 2024. "A Comprehensive Analysis of CSN1S2 I and II Transcripts Reveals Significant Genetic Diversity and Allele-Specific Exon Skipping in Ragusana and Amiatina Donkeys" Animals 14, no. 20: 2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14202918
APA StyleCosenza, G., & Pauciullo, A. (2024). A Comprehensive Analysis of CSN1S2 I and II Transcripts Reveals Significant Genetic Diversity and Allele-Specific Exon Skipping in Ragusana and Amiatina Donkeys. Animals, 14(20), 2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14202918






