GFI-YOLOv8: Sika Deer Posture Recognition Target Detection Method Based on YOLOv8
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
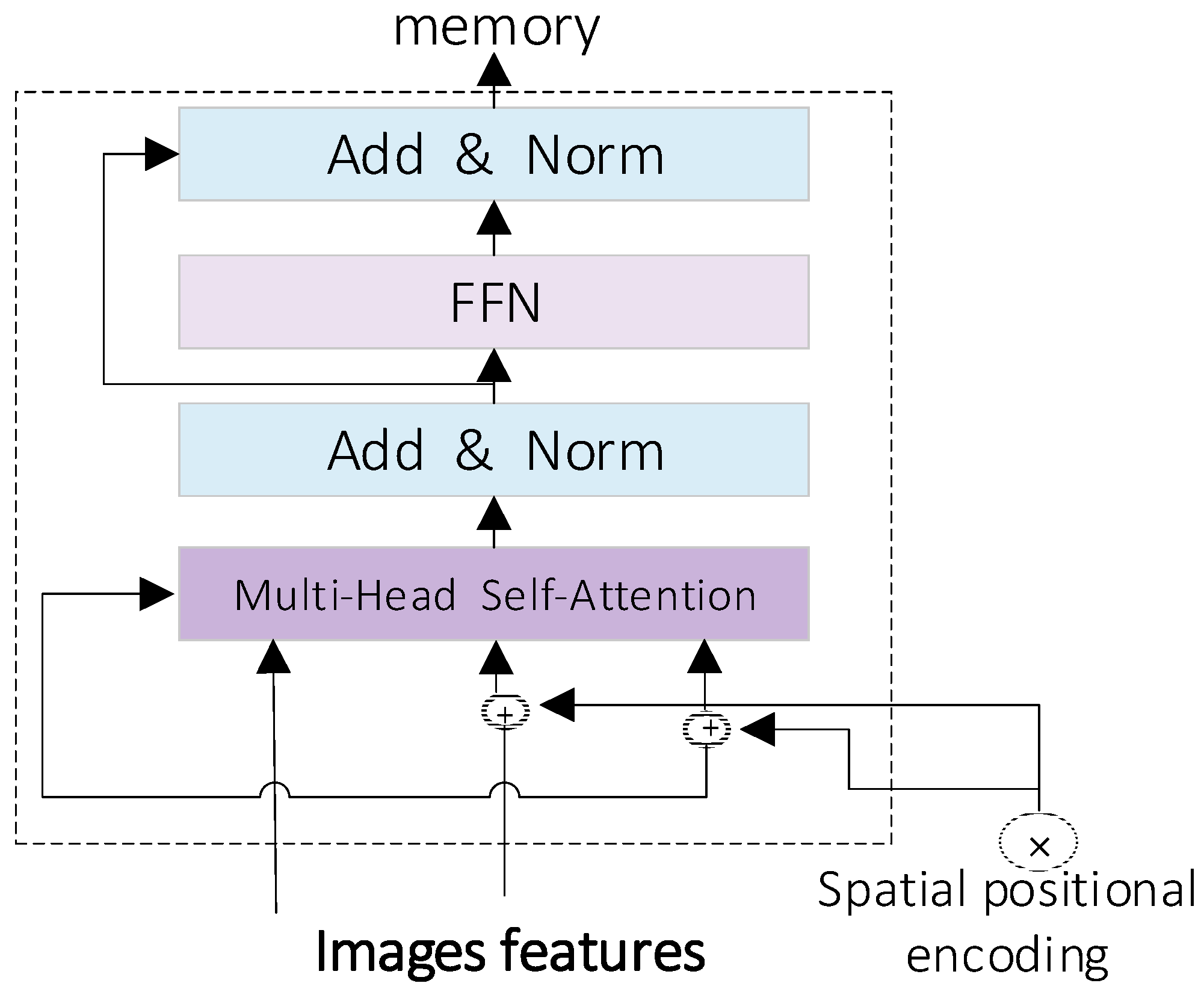
- In this paper, Iterative Attentive Feature Fusion (iAFF) [15] is introduced into the C2f structure to form the C2f_iAFF. The original Spatial Pyramid Pooling Fast (SPPF) module is replaced with the attention-based intra-scale feature interaction module (AIFI) [16] module. This enhancement aims to improve the model’s performance in object detection and recognition by iteratively fusing features at different scales. It focuses on processing advanced image features through a self-attention mechanism.
- (2)
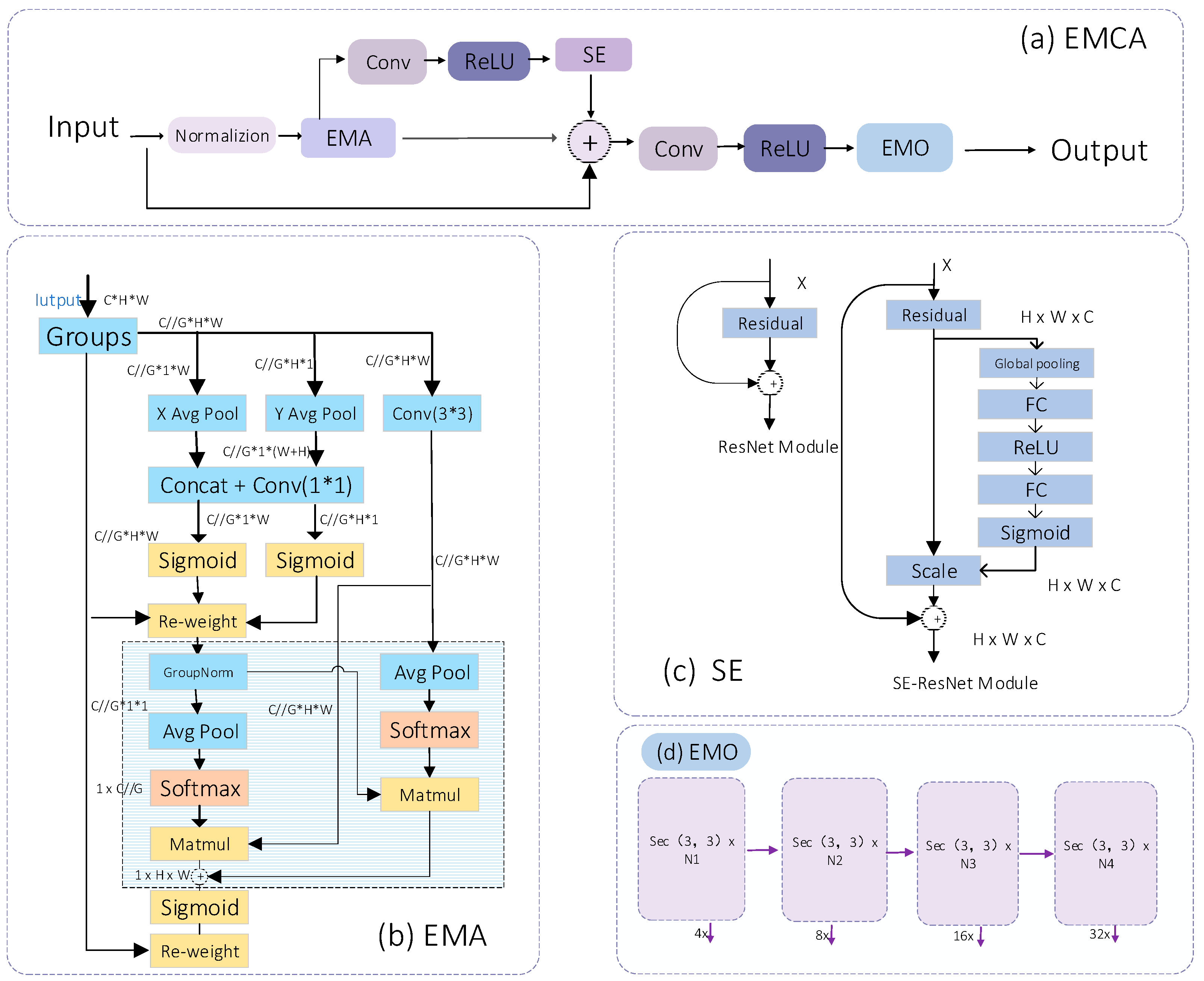
- This paper proposes a new attention mechanism module, which is combined with the CSP-Net structure to form a new down-sampling network module called CSA. The proposed EMCA module is the core component of CSA, enhancing the depth and diversity of feature extraction through an improved multi-branch structure. This module offers a more comprehensive feature description and boosts the model’s generalization ability.
- (3)
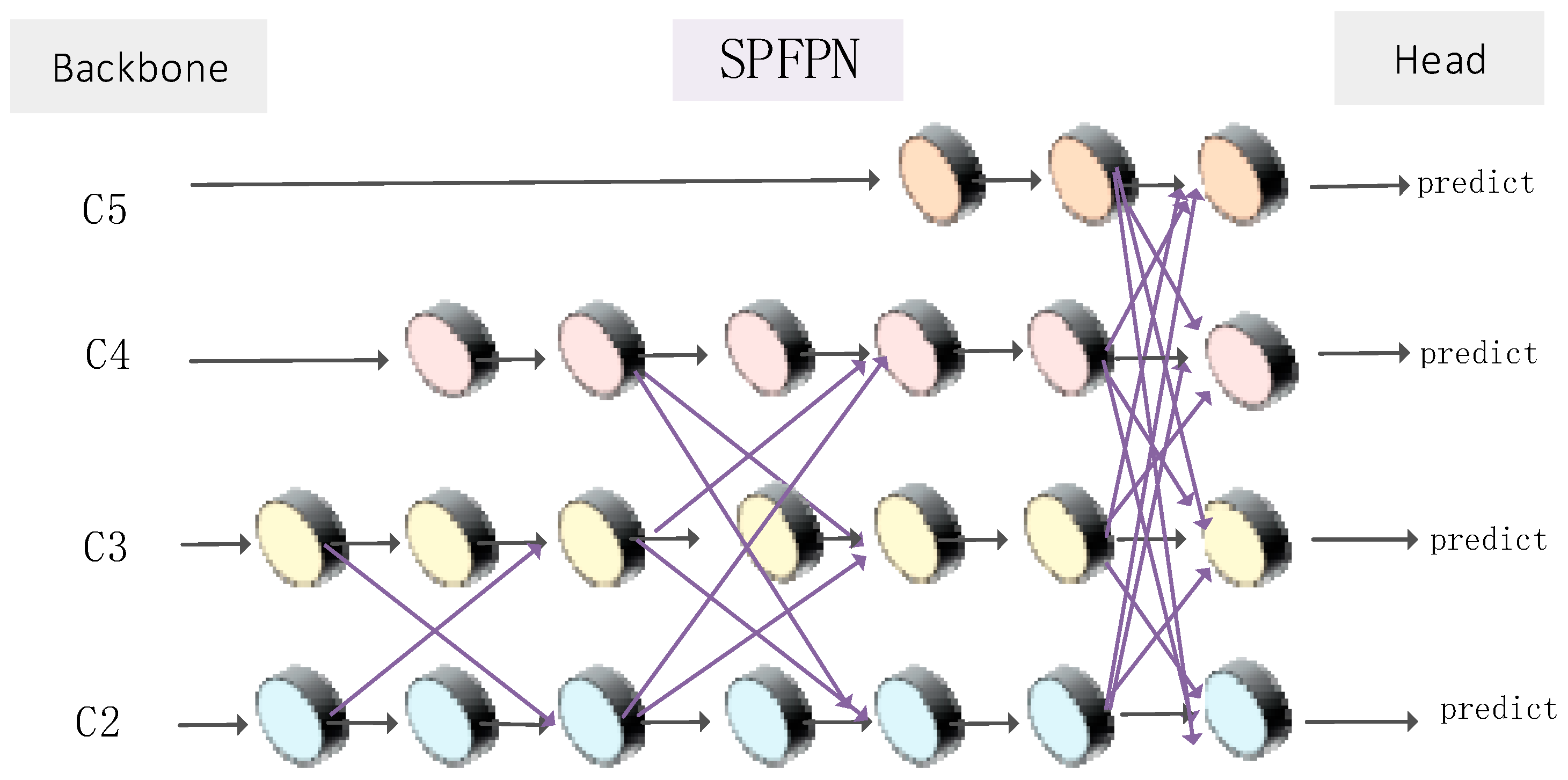
- We replaced the original YOLOv8 detection head with a new detection head module called DETECT_SPFPN. This change introduced a new contrast space generalized feature pyramid network (SPFPN) that enhances the concept of the feature pyramid network (FPN) for object detection. The SPFPN efficiently integrates multi-scale features, essential for capturing high-level semantics and low-level spatial details. To optimize performance under computing resources, feature maps of different scales utilize different channel dimensions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.1.1. Data Acquisition
2.1.2. Dataset Production
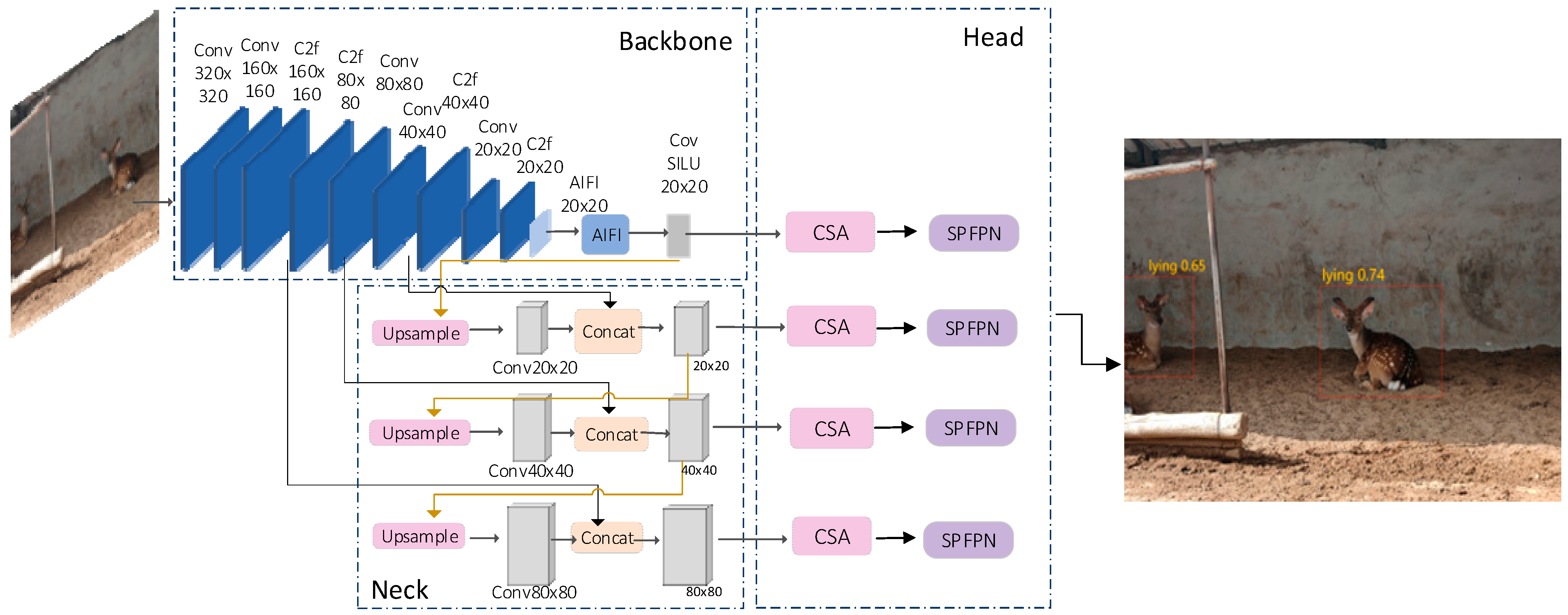
2.2. The Proposed Improved GFI-YOLOv8
2.2.1. Modification of Backbone Network Structure
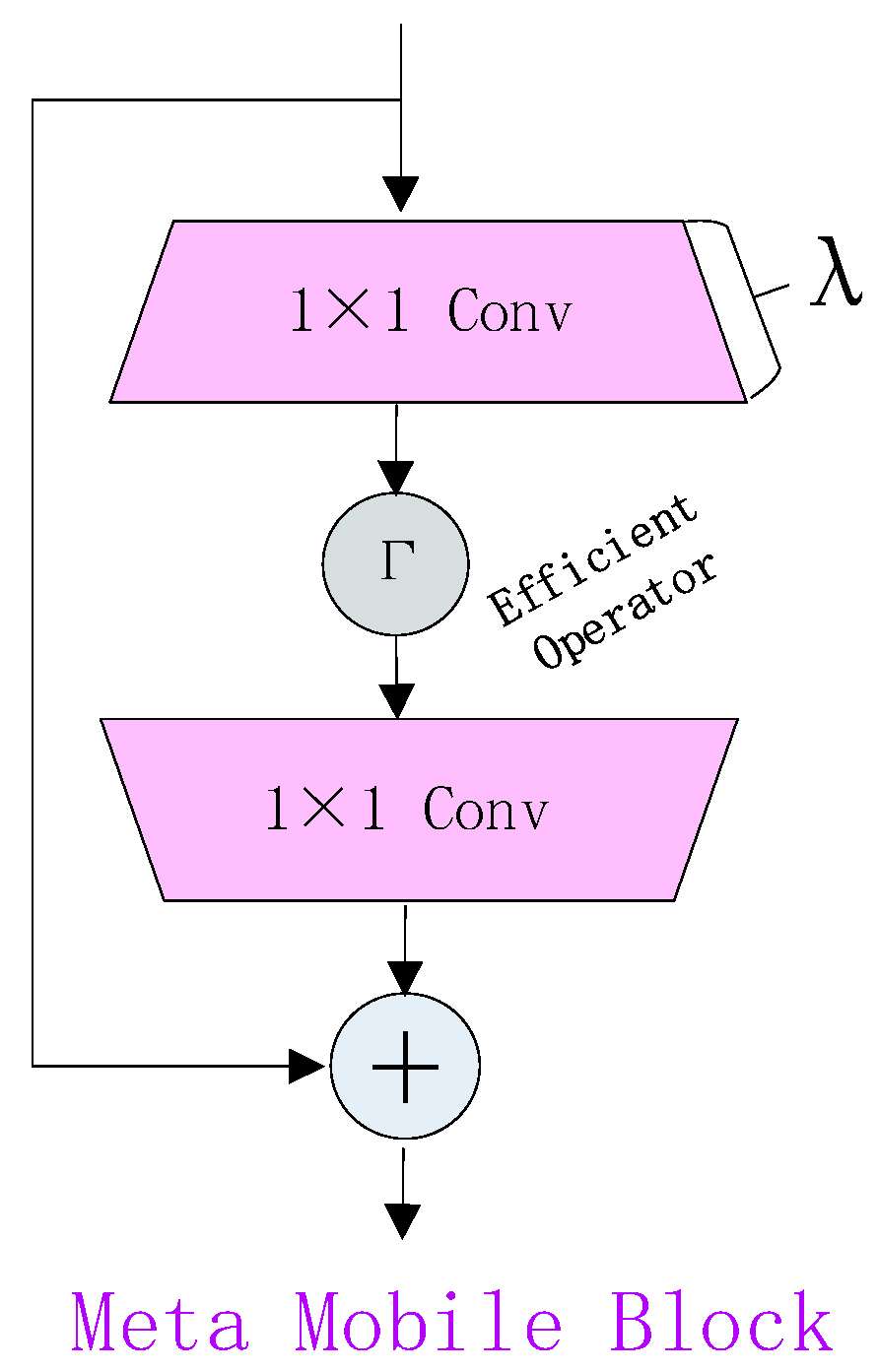
2.2.2. Improved Convolutional Neural Network Module and Attention Mechanism Module
EMCA Module
CSA Module
2.2.3. Improved Detection Head Derect Module: SPFPN
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
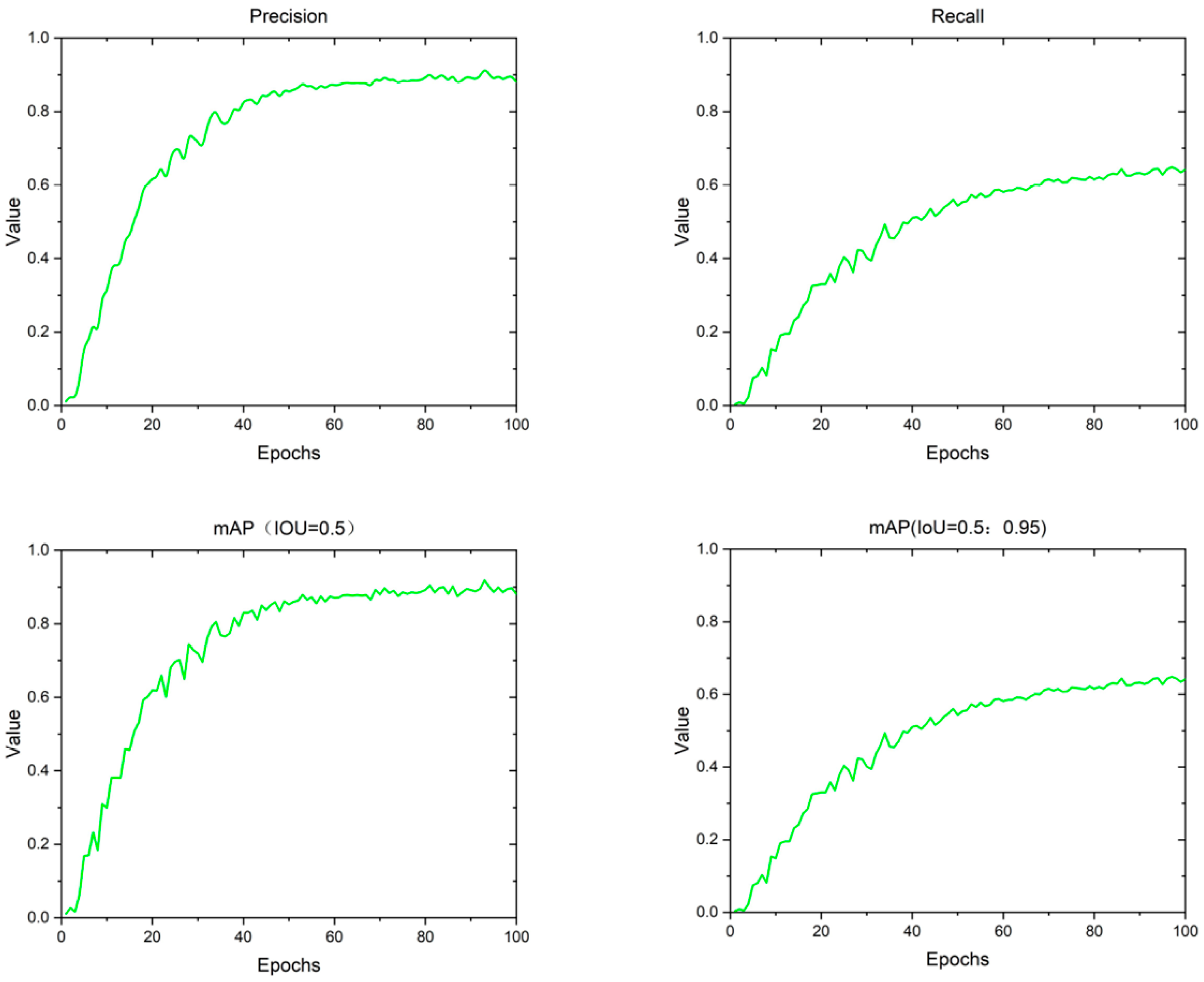
3.1. Evaluation Indicators
3.2. Experimental Details
3.2.1. Comparative Experiments of Different Attention Mechanisms
3.2.2. Comparison of Different Feature Extraction Backbone Networks in Head Networks
3.2.3. Comparison of Different Improved C2f Networks
3.3. Ablation Experiment
Comparative Experiments on the Performance of Different Network Models
3.4. Heat Map Visualization Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, Y.; Liu, Z.T. Rare animal—Sika deer and its research. Biol. Bull. 2005, 40, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, J. Environmental requirements and optimization strategies for sika deer breeding. Anim. Husb. Environ. 2023, 24, 38–39. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.W.; Yan, C.L.; Wu, W.; Li, J. Application of Microfluidic Chip Technology in Food Safety Sensing. Sensors 2020, 20, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.N. Breeding and product utilization of artificially bred sika deer. Anim. Husb. Vet. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2017, 33, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, C.; Jiang, L.X.; Xiao, Y.; Deng, L.M.; Han, Z.Z. Detection and Analysis of Behavior Trajectory for Sea Cucumbers Based on Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 18832–18840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.M.; Han, Z.Z. Image features and DUS testing traits for peanut pod variety identification and pedigree analysis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 2572–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.L.; Truman, M.; Sukkarieh, S. Cattle segmentation and contour extraction based on Mask R-CNN for precision livestock farming. Computer. Electron. Agric. 2019, 165, 104958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hua, Z.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xu, X.; Song, H. E-YOLO: Recognition of estrus cow based on improved YOLOv8n model. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 122212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Xuan, K.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J. AD-YOLOv5: An object detection approach for key parts of sika deer based on deep learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 217, 108610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.M.; Pu, J.Y.; Mu, J. Pig-Posture Recognition Based on Computer Vision: Dataset and Exploration. Animals 2021, 11, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Li, B.; Du, Y.; Jiao, F.; Song, X.; Liu, Z. Deep learning strategies with CReToNeXt-YOLOv5 for advanced pig face emotion detection. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gong, H.; Deng, M.; Li, S.; Hu, T.; Sun, Y.; Mu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Tyasi, T.L. Sika Deer Behavior Recognition Based on Machine Vision. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 73, 4953–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, Y.; Han, M.; Song, L.; Shang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Song, H. Using a CNN-LSTM for basic behaviors detection of a single dairy cow in a complex environment. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 182, 106016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, F.; Shen, W.; Gu, Z. Research on Automatic Recognition of Dairy Cow Daily Behaviors Based on Deep Learning. Animals 2024, 14, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Gieseke, F.; Oehmcke, S.; Wu, Y.; Barnard, K. Attentional Feature Fusion. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lv, W.; Xu, S.; Wei, J.; Wang, G.; Dang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. DETRs Beat YOLOs on Real-time Object Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2304.08069. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, F. Images of Deer for SVM classifier. 2020. Available online: https://kaggle.com (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Qiu, J. Ultralytics YOLO, version 8.0.0; [Computer software]. 2023. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zh-moginov, A.; Chen, L.-C. Mobilenetv2: Invertedresiduals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. arXiv 2023, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y.M.; Wu, Y.-H.; Chen, P.-Y.; Hsieh, J.-W.; Yeh, I.-H. CSPNet: A New Backbone that can Enhance Learning Capability of CNN. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, D.; He, S.; Zhang, G.; Luo, M.; Guo, H.; Zhan, J.; Huang, Z. Efficient Multi-Scale Attention Module with Cross-Spatial Learning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.13563. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1612.0314. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Lei, J.; Zhu, Z.; Cheng, S.; Feng, Z.; Liang, R. AFPN: Asymptotic Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Oahu, HI, USA, 1–4 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Ji, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Y. High-Resolution Feature Pyramid Network for Small Object Detection On Drone View. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Rethinking Mobile Block for Efficient Attention-based Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.01146. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Albanie, S.; Sun, G.; Wu, E. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1709.01507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Song, T.; Yang, D.; Ye, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L. AKConv: Convolutional Kernel with Arbitrary Sampled Shapes and Arbitrary Number of Parameters. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.11587. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Yeh, I.-H.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv9: Learning What You Want to Learn Using Programmable Gradient Information. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.13616. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. YOLOv10: Real-Time End-to-End Object Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14458. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-based Localization. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 336–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
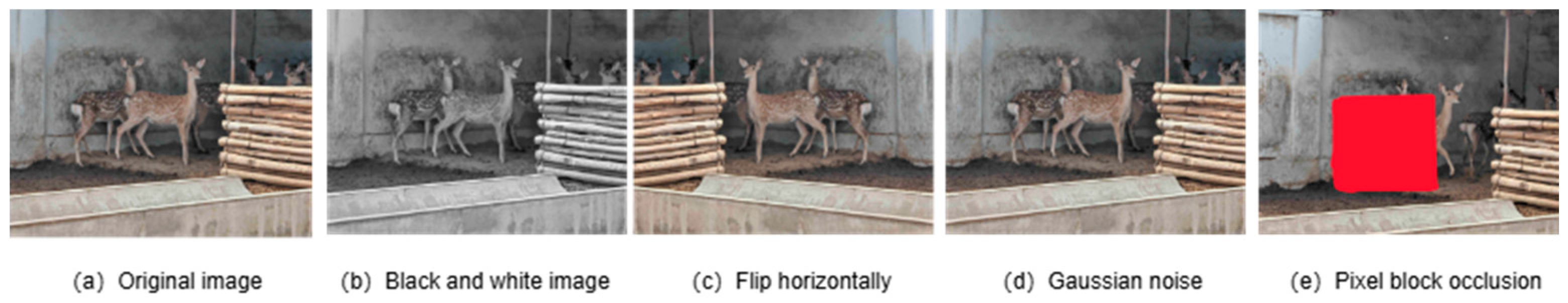






| Posture Category | The Name of the Pose | Pose Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Standing | Standing | Sika deer have at least three legs standing on the ground at the same time |
| Lying | Lying | The abdomen of the body is in contact with the ground, and the hooves and legs are not used to support the body |
| Eating | Eating | The mouth of the sika deer touches the ground, or the sika deer is standing next to the trough, or the small sika deer is feeding on its mother’s milk |
| Attacking | Bumping, kicking, Chasing | The act of striking another deer’s body or antlers with its horns, sika deer kicking or kicking the other body with its front foot, or before or after a fight |
| Environment Configuration | Parameter |
|---|---|
| Operating system | Windows10 |
| CPU | Intel(R) Core(TM) i9-10920X CPU @ 3.50GHz |
| GPU | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 |
| Development environment | PyCharm 2023.2.5 |
| Language | Python 3.9.6 |
| Framework | PyTorch 2.0.1 |
| Operating platform | CUDA 11.8 |
| Methods | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95 (%) | Para (M) | GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | 85.6 | 81.6 | 85.6 | 65 | 30.06 | 8.1 |
| EMA | 90.5 | 80.4 | 89.2 | 66.8 | 30.06 | 8.1 |
| iRMB | 90.3 | 85.2 | 90.1 | 67 | 33.56 | 8.3 |
| SE | 88.7 | 83.4 | 86.4 | 67.8 | 31.45 | 8.3 |
| EMCA | 91.3 | 85.4 | 84.6 | 68.8 | 30.51 | 8.4 |
| Methods | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95(%) | Para (M) | GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | 85.6 | 81.6 | 85.6 | 65 | 30.06 | 8.1 |
| YOLOv8n + CSPS | 90.1 | 84.1 | 90.3 | 67.8 | 29.83 | 8.1 |
| CSPS + EMA | 89.3 | 84.2 | 89.6 | 67.3 | 29.91 | 8.2 |
| CSPS + iRMB | 85.1 | 84.6 | 88.5 | 67.4 | 32.79 | 8.9 |
| CSA | 90.3 | 86.4 | 86.5 | 68.5 | 33.54 | 8.1 |
| Methods | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95 (%) | Para (M) | GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2f_EMA | 87.3 | 81.8 | 86.3 | 62.7 | 29.91 | 8.1 |
| C2f_iRMB | 84.2 | 83.1 | 86.3 | 63.6 | 29.83 | 8.1 |
| C2f_AKConv | 86.1 | 80.4 | 85.6 | 65.4 | 23.67 | 8.2 |
| C2f_Faster | 83.5 | 81.9 | 86.8 | 62.7 | 32.79 | 8.0 |
| C2f_EMCA | 87.8 | 81.7 | 87.5 | 64.7 | 33.54 | 8.1 |
| C2f_iAFF | 88.7 | 83.4 | 89.8 | 66.2 | 30.52 | 8.1 |
| NO. | C2f_iAFF | AIFI | CSA | SPFPN | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95 (%) | Para (M) | GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | √ | 88.7 | 83.4 | 89.8 | 66.2 | 30.52 | 8.1 | |||
| 2 | √ | 89.1 | 83.4 | 89.6 | 67.6 | 31.2 | 8.4 | |||
| 3 | √ | 90.3 | 86.4 | 86.5 | 68.5 | 33.54 | 8.1 | |||
| 4 | √ | 87.6 | 82.6 | 83.1 | 65.1 | 8.8 | 30.5 | |||
| 5 | √ | √ | 88.4 | 83.7 | 84.7 | 64.8 | 8.4 | 29.7 | ||
| 6 | √ | √ | √ | 89.8 | 83.4 | 88.5 | 66.1 | 8.9 | 32.7 | |
| 7 | √ | √ | √ | 90.9 | 84.0 | 87.4 | 65.6 | 19.6 | 48.8 | |
| 8 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 91.6 | 82.4 | 91.1 | 68.3 | 51.74 | 20.3 |
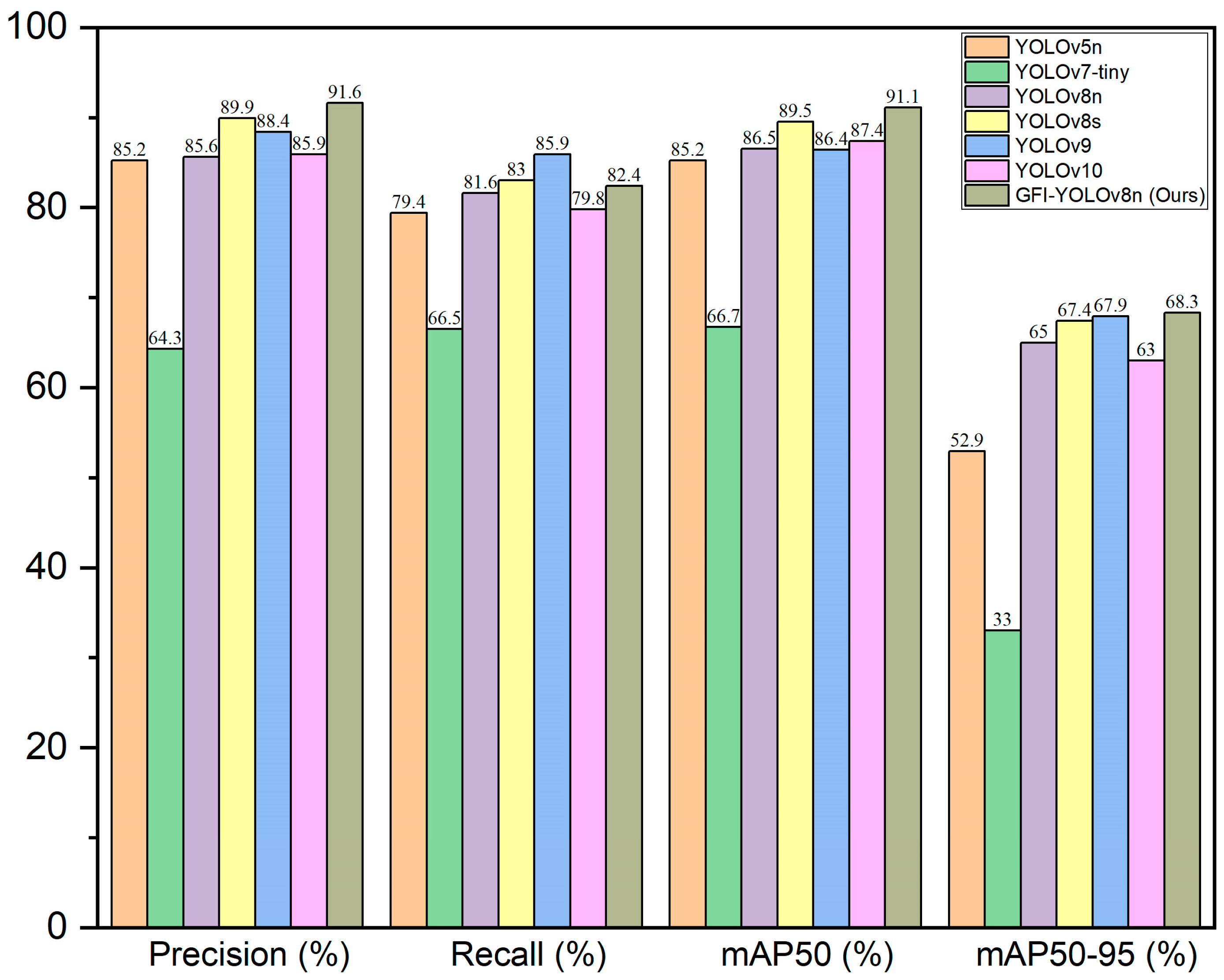
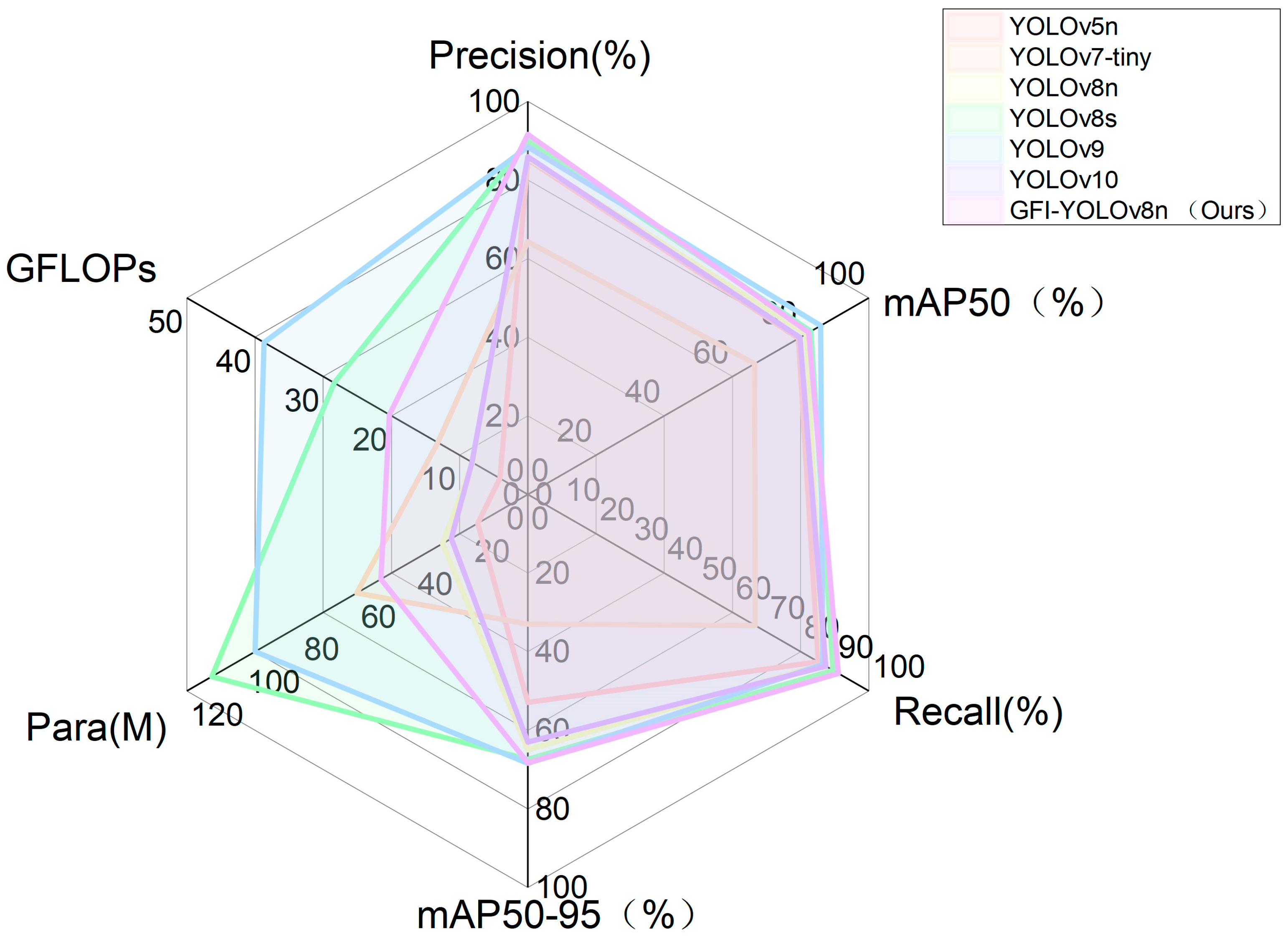
| Methods | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95 (%) | Para (M) | GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5n | 85.2 | 79.4 | 85.2 | 52.9 | 17.64 | 4.1 |
| YOLOv7-tiny | 64.3 | 66.5 | 66.7 | 33 | 60.22 | 13.2 |
| YOLOv8n | 85.6 | 81.6 | 86.5 | 65 | 30.06 | 8.1 |
| YOLOv8s | 89.9 | 83 | 89.5 | 67.4 | 111.27 | 28.4 |
| YOLOv9 | 88.4 | 85.9 | 86.4 | 67.9 | 96.01 | 38.7 |
| YOLOv10 | 85.9 | 79.8 | 87.4 | 63 | 26.95 | 8.2 |
| GFI-YOLOv8n (Ours) | 91.6 | 82.4 | 91.1 | 68.3 | 51.74 | 20.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, H.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhu, H.; Luo, L.; Li, H.; Hu, T.; Guo, Y.; Mu, Y. GFI-YOLOv8: Sika Deer Posture Recognition Target Detection Method Based on YOLOv8. Animals 2024, 14, 2640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14182640
Gong H, Liu J, Li Z, Zhu H, Luo L, Li H, Hu T, Guo Y, Mu Y. GFI-YOLOv8: Sika Deer Posture Recognition Target Detection Method Based on YOLOv8. Animals. 2024; 14(18):2640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14182640
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, He, Jingyi Liu, Zhipeng Li, Hang Zhu, Lan Luo, Haoxu Li, Tianli Hu, Ying Guo, and Ye Mu. 2024. "GFI-YOLOv8: Sika Deer Posture Recognition Target Detection Method Based on YOLOv8" Animals 14, no. 18: 2640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14182640
APA StyleGong, H., Liu, J., Li, Z., Zhu, H., Luo, L., Li, H., Hu, T., Guo, Y., & Mu, Y. (2024). GFI-YOLOv8: Sika Deer Posture Recognition Target Detection Method Based on YOLOv8. Animals, 14(18), 2640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14182640






