Seasonal-Spatial Distribution Variations and Predictions of Loliolus beka and Loliolus uyii in the East China Sea Region: Implications from Climate Change Scenarios
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
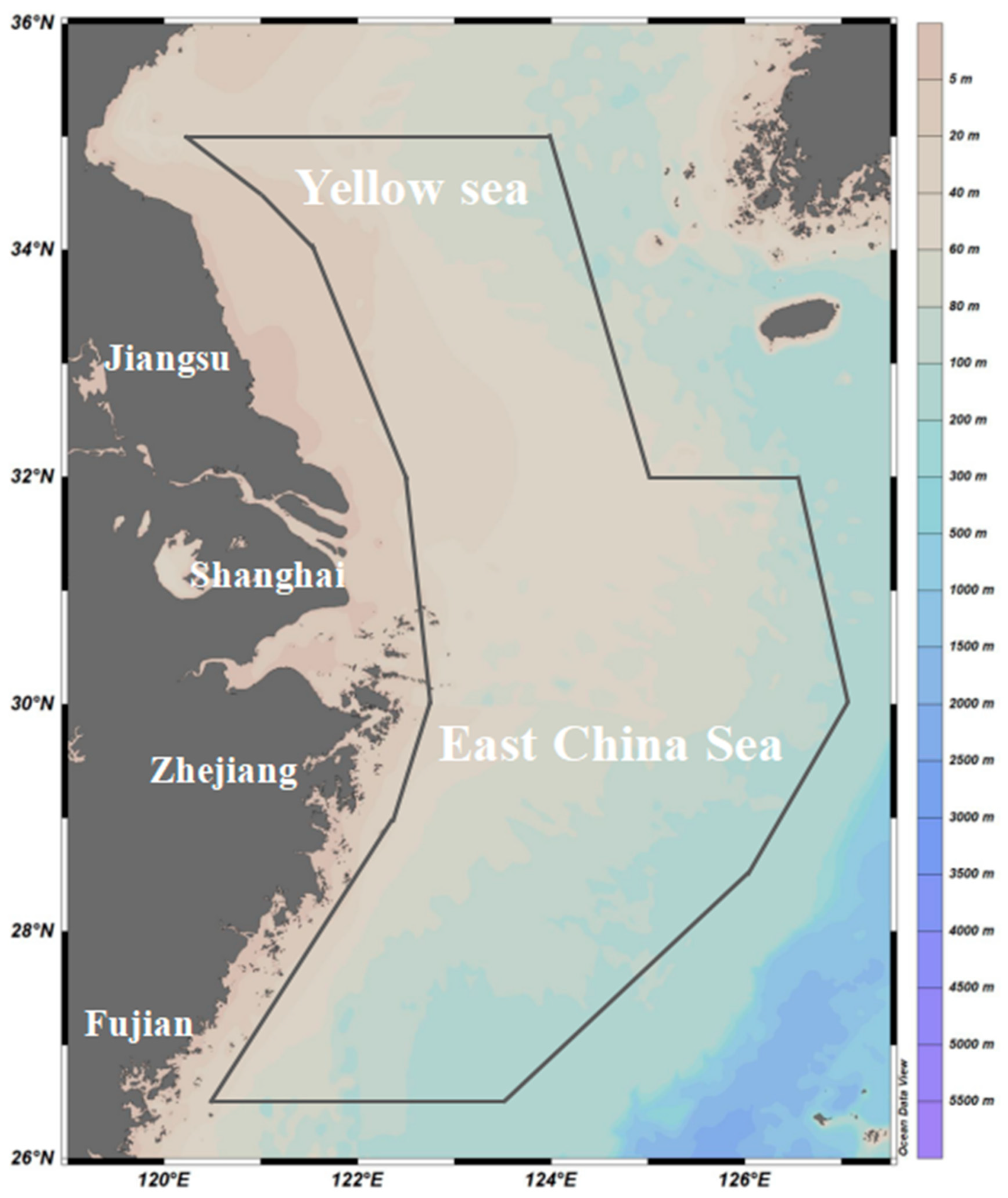
2.1. Data Source and In Situ Surveys
2.2. Introduce and Define SSP1-2.6, SSP2-4.5 and SSP5-8.5
2.3. sdmTMB Model
2.4. Model Construction and Variable Selection
2.5. Predictive Power
2.6. Prediction of Habitat Spatial Distribution
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
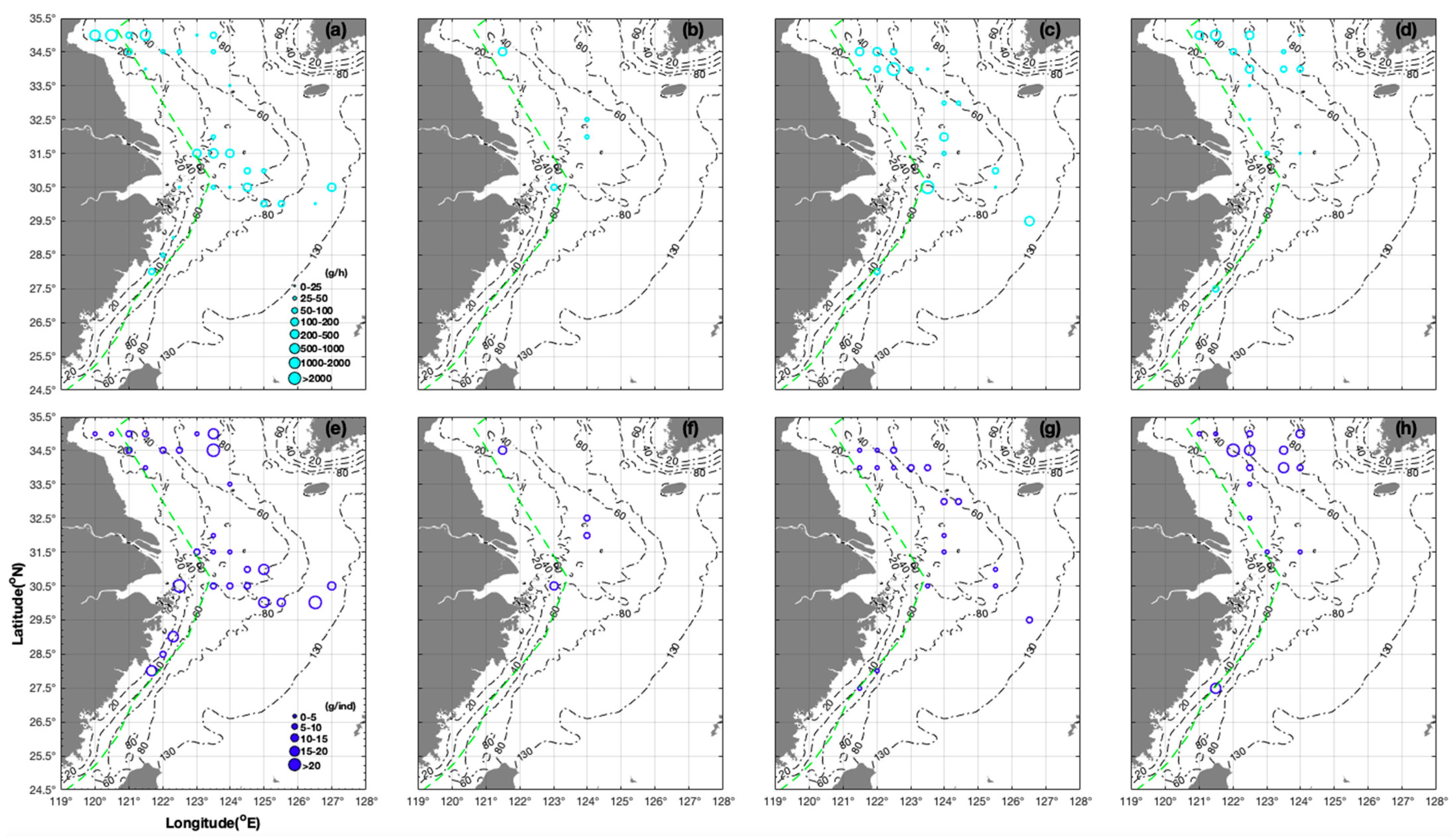
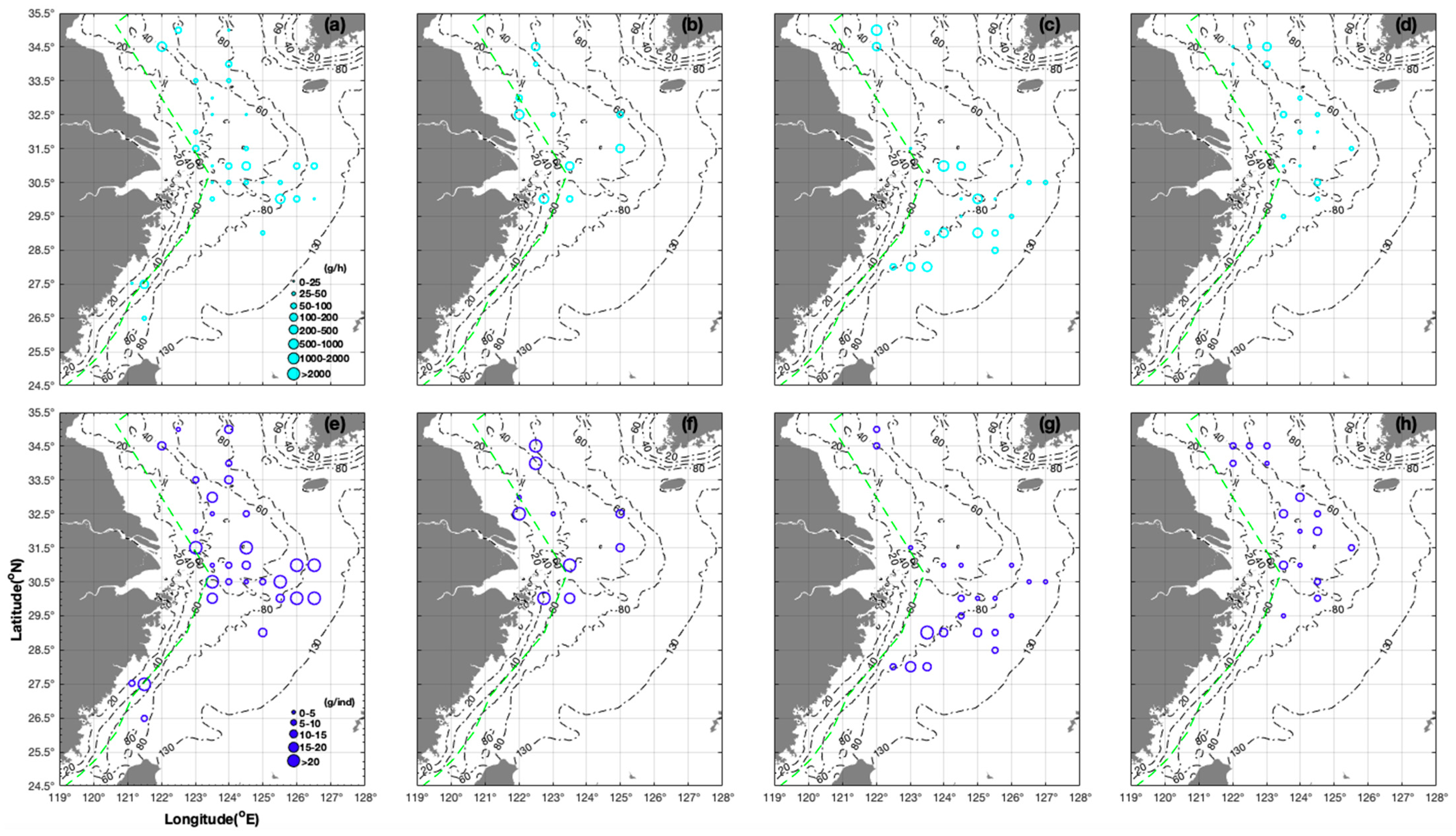
3.1. Seasonal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics
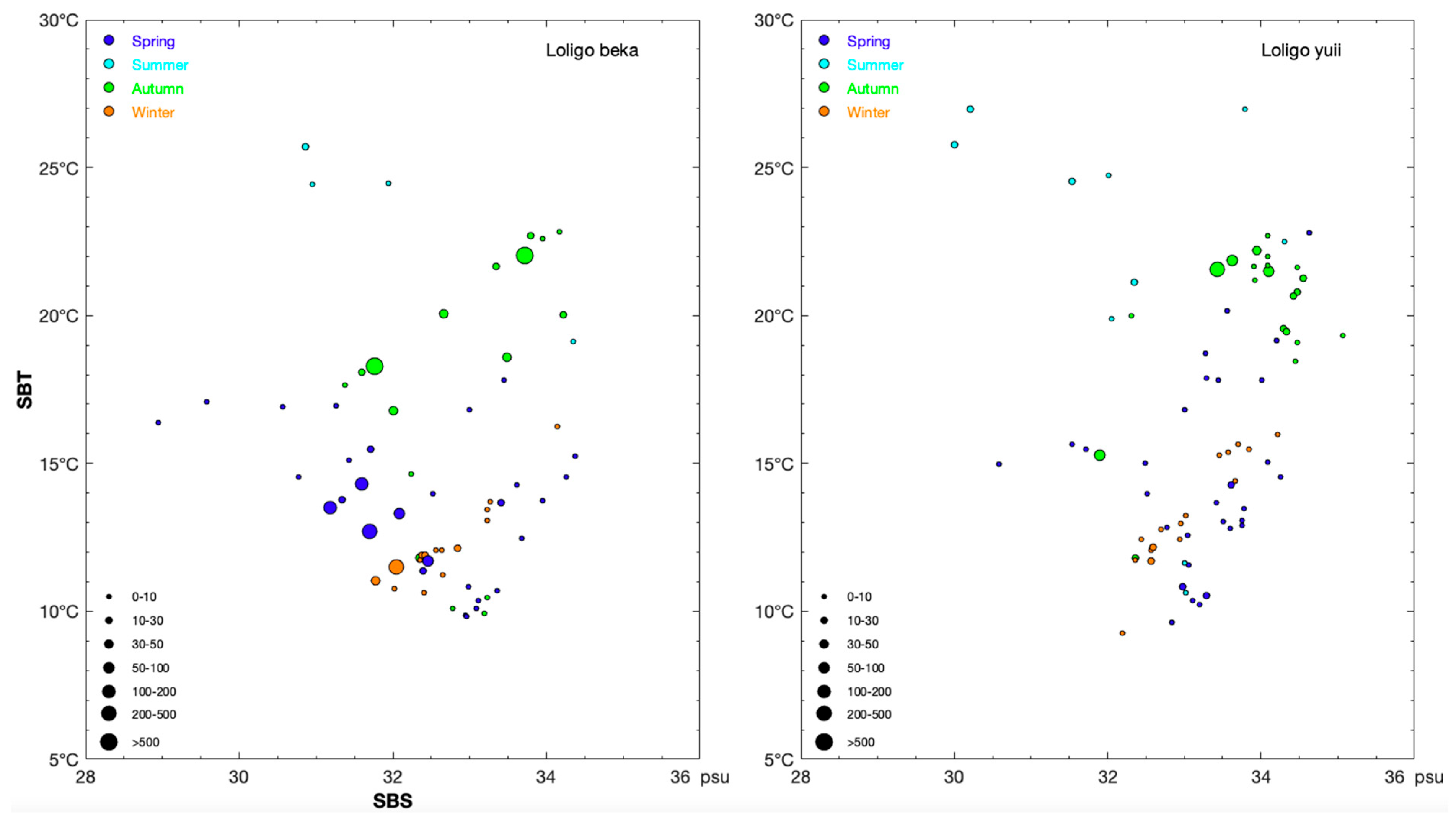
3.2. Environmental Variables and Most Suitable Habitat Range
3.3. Environment Variable Filtering, Response Curves, and Merged Spatial Distribution of Models
3.4. Future Scenario Forecasting
4. Discussion
4.1. Models Evaluation and Predictive Effects of Data-Pool Model
4.2. The Life History Characteristics and Seasonal–Spatial Distribution
4.3. Fisheries Management Strategies to Address Impacts of Climate Change on Species Distributions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.M. A study on food and trophic levels of Bohai Sea invertebrates. Mod. Fish. Inf. 2001, 16, 8–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Zhou, C.Q.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, L.; Yang, G.; Chen, W. A rapid, low-cost deep learning system to classify squid species and evaluate freshness based on digital images. Fish. Res. 2020, 221, 105376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Liu, Y. Quantity distribution and population composition of Loliolus beka in the East China Sea. In Proceedings of the 26th Fisheries Academic Exchange Conferences of the Southern China Fisheries Academic Forum, Chongqing, China, 28–30 October 2010; pp. 221–225. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Xu, C.; Ma, C.; Ye, S.; Zhuang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xie, S.; Shen, C. Population aggregation characteristics of the main dominant species of nekton in Minnan Fishing Ground. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 4818–4826. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Qu, J.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, J. Variation of community structure of cephalopods in spring and autumn along the coast of Zhejiang Province. J. Fish. China 2020, 44, 1317–1328. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Climate Change Center of China Meteorological Administration (Ed.) China Climate Change Blue Book 2023; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2023; 110p. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Doney, S.; Ruckelshaus, M.; Duffy, E.; Barry, J.; Chan, F.; English, C.A.; Galindo, H.M.; Grebmeier, J.M.; Hollowed, A.B.; Knowlton, N.; et al. Climate change impacts on marine ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 11–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Fu, C.; Wang, B.; Li, J.; Ren, Y.; Wan, R. Variability of coastal cephalopods in overexploited China Seas under climate change with implications on fisheries management. Fish. Res. 2018, 208, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, N.; Awata, S.; Munehara, H. Seasonal occurrence and sexual maturation of Japanese pygmy squid (Idiosepius paradoxus) at the northern limits of their distribution. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 66, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hare, S.R.; Mantua, N.J. Empirical evidence for North Pacific regime shifts in 1977 and 1989. Prog. Oceanogr. 2000, 47, 103–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.W.; Dong, Z.Y.; Chi, C.F.; Ding, F. Reproductive and spawning habits of Sepiella maindroni off Zhejiang, China. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2010, 41, 39–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shang, S.; Hong, H.; Shang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C. On the potential relationship of fishing ground position shift with the variability of sea surface temperature in the Taiwan Strait in summers of 1997 and 1998. Mar. Sci. 2002, 26, 27–30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hong, H.; Shang, S.; Zhang, C.; Huang, B.; Hu, J.; Huang, J.; Lu, Z. Evidence of ecosystem response to the interannual environmental variability in the Taiwan Strait. Haiyang Xuebao 2005, 27, 63–69. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dulvy, N.; Rogers, S.; Jennings, S.; Stelzenmüller, V.; Skjoldal, H.R. Climate change and deepening of the North Sea fish assemblage: A biotic indicator of warming seas. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 45, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, G.; Valavanis, V.; Guerra, A.; Jereb, P.; Orsi-Relini, L.; Bellido, J.; Katara, I.; Piatkowski, U.; Pereira, J.; Balguerias, E. A review of cephalopod—Environment interactions in European Seas. In Essential Fish Habitat Mapping in the Mediterranean; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 49–70. [Google Scholar]
- Engler, J.O.; Stiels, D.; Schidelko, K.; Strubbe, D.; Quillfeldt, P.; Brambilla, M. Avian SDMs: Current state, challenges, and opportunities. J. Avian Biol. 2017, 48, 1483–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, N.M.; Nelson, W.A.; Costello, M.J.; Sutherland, J.E.; Lundquist, C.J. A systematic review of marine-based species distribution models (SDMs) with recommendations for best practice. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, B.; Delsol, R.; Hugueny, B.; Meynard, C.N.; Barhoumi, C.; Barbet-Massin, M.; Bellard, C. Without quality presence–absence data, discrimination metrics such as TSS can be misleading measures of model performance. J. Biogeogr. 2018, 45, 1994–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, C.H.; Elith, J.; Hijmans, R.J.; NSDM Group. The influence of spatial errors in species occurrence data used in distribution models. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 45, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y. Unveiling unselective fishing in China: A nationwide meta–analysis of multispecies fisheries. Fish Fish. 2023, 24, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Zuo, Z.; Huang, L.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhong, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, A.; Zhang, H.; et al. Marine oriented multimodal intelligent computing: Challenges, progress and prospects. J. Image Graph. 2022, 27, 2589–2610. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Seasonal and spatial distribution characteristics of Sepia esculenta in the East China Sea Region: Transfer of the central distribution from 29° N to 28° N. Animals 2024, 14, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, F.; Wu, H.; Cheng, J. Seasonal distribution of the early life stages of the small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) and its dynamic controls adjacent to the Changjiang River Estuary. Fish. Oceanogr. 2023, 32, 390–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, H.; Song, X.; Otaki, T.; Yang, L.; Cheng, J. Larval spatiotemporal distribution of six fish species: Implications for sustainable fisheries management in the East China Sea. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Liu, Z.; Song, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Otaki, T.; Shen, J.; Komatsu, T.; Cheng, J. Tidal variations of fish larvae measured using a 15-day continuous ichthyoplankton survey in Subei Shoal: Management implications for the red-Crowned Crane (Grus japonensis) population in Yancheng Nature Reserve. Animals 2023, 13, 3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, E.J.; Barnett, L.A.; Anderson, S.C.; Commander, C.; Essington, T. Incorporating non-stationary spatial variability into dynamic species distribution models. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2022, 79, 2422–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C. Modeling of individual tree mortality and analysis of influence factor in Mongolian Oak stand based on generalized linear mixed effect model. For. Res. 2020, 33, 105–113. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cameletti, M.; Lindgren, F.; Simpson, D.; Rue, H. Spatio-temporal modeling of particulate matter concentration through the SPDE approach. AStA Adv. Stat. Anal. 2013, 97, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, F.; Bolin, D.; Rue, H. The SPDE approach for Gaussian and non-Gaussian fields: 10 years and still running. Spat. Stat. 2022, 50, 100599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenmakers, E.-J.; Farrell, S. AIC model selection using Akaike weights. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2004, 11, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, M.W. Cross-validation methods. J. Math. Psychol. 2000, 44, 108–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bürkner, P.-C.; Gabry, J.; Vehtari, A. Approximate leave-future-out cross-validation for Bayesian time series models. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2020, 90, 2499–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ling, C.X. Using AUC and accuracy in evaluating learning algorithms. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2005, 17, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Jurman, G. The advantages of the Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) over F1 score and accuracy in binary classification evaluation. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Gu, H.; Huang, X.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y. Machine learning models for predicting in-hospital death in patients with acute new ischemic stroke based on unbalanced data. Chin. J. Stroke 2021, 16, 779–786. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- O’neill, B.C.; Kriegler, E.; Riahi, K.; Ebi, K.; Hallegatte, S.; Carter, T.; Mathur, R.; Vuuren, D. A new scenario framework for climate change research: The concept of shared socioeconomic pathways. Clim. Chang. 2014, 122, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assis, J.; Fernández Bejarano, S.J.; Salazar, V.W.; Schepers, L.; Gouvêa, L.; Fragkopoulou, E.; Leclercq, F.; Vanhoorne, B.; Tyberghein, L.; Serrão, E.A.; et al. Bio-ORACLE v3.0. Pushing marine data layers to the CMIP6 Earth System Models of climate change research. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2024, 33, e13813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorson, J.T.; Barnes, C.L.; Friedman, S.T.; Morano, J.; Siple, M. Spatially varying coefficients can improve parsimony and descriptive power for species distribution models. Ecography 2023, 5, e06510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.P.; Brotons, L.; Bustamante, J.; Seoane, J. The application of predictive modelling of species distribution to biodiversity conservation. Divers. Distrib. 2007, 13, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, P.B.; Ver Hoef, J.M.; Mcclintock, B.; Johnson, D.; Brost, B. A GLMM approach for combining multiple relative abundance surfaces. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2022, 13, 2236–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, J.; Zhang, C.; Xu, B.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y. Relationship between catch distribution of Portunid crab (Charybdis bimaculata) and environmental factors based on three species distribution models in Haizhou Bay. J. Fish. China 2018, 42, 889–901. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Boivin, N.L.; Zeder, M.A.; Fuller, D.Q.; Crowther, A.; Larson, G.; Erlandson, J.M.; Denham, T.; Petraglia, M.D. Ecological consequences of human niche construction: Examining long-term anthropogenic shaping of global species distributions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 6388–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Gu, D.; Wu, N.; Meng, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, H. Study on resources present situation of Loliolus beka in Tianjin Sea area. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2018, 22, 232–233+237. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Jin, X.; Gorfine, H.; Wu, Q.; Shan, X. Modeling the oceanographic impacts on the spatial distribution of common cephalopods during autumn in the Yellow Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.S.; Zhao, X.Y.; Meng, T.X.; Cui, Y. Living Resources and Their Habitat in the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2005. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Chen, G.; Chen, Z. Forecasting fishing ground of calamary in the northern South China Sea according to habitat suitability index. South China Fish. Sci. 2017, 13, 11–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Weiskopf, S.R.; Rubenstein, M.A.; Crozier, L.G.; Gaichas, S.; Griffis, R.; Halofsky, J.E.; Hyde, K.J.W.; Morelli, T.L.; Morisette, R.C. Climate change effects on biodiversity, ecosystems, ecosystem services, and natural resource management in the United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 137782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, T.; Li, A.; Dai, F.; Li, D.; Liu, S.; Zhuang, Z. Survey and analysis of the autumnal cephalopod distribution in the Yellow Sea during 2006–2013. J. Fish. Sci. China 2016, 23, 955–964. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe, J. Accounting for the effect of temperature on squid growth in nature: From hypothesis to practice. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2004, 55, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodhouse, P.G.K.; Pierce, G.J.; Nichols, O.C.; Sauer, W.H.H.; Arkhipkin, A.I.; Laptikhovsky, V.; Lipinski, M.R.; Ramos, J.E.; Gras, M.; Kidokoro, H.; et al. Environmental effects on cephalopod population dynamics: Implications for management of fisheries. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2014, 67, 99–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brierley, A.S.; Kingsford, M.J. Impacts of climate change on marine organisms and ecosystems. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, R602–R614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, R.A.; Crick, H.Q.; Learmonth, J.A.; Maclean, I.; Thomas, C.; Bairlein, F.; Forchhammer, M.; Francis, C.; Gill, J.; Godley, B. Travelling through a warming world: Climate change and migratory species. Endanger. Species Res. 2009, 7, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Loliolus beka | Loliolus uyii | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |
| Mean CPUEw at all stations | 28.03 | 1.95 | 84.65 | 14.03 | 12.51 | 10.43 | 26.74 | 6.21 |
| Mean CPUEw at collection stations | 136.31 | 68.34 | 597.25 | 103.85 | 58.79 | 146.01 | 161.70 | 43.11 |
| Value range of CPUEw | 2.90–1042.76 | 29.16–147.60 | 4.80–7196.00 | 13.60–755.20 | 8.00–277.20 | 45.50–496.80 | 10.47–809.41 | 9.84–101.50 |
| Mean CPUEn at all stations | 6.37 | 0.18 | 26.12 | 2.91 | 1.07 | 0.70 | 4.79 | 0.89 |
| Mean CPUEn at collection stations | 30.95 | 6.40 | 184.27 | 21.52 | 5.05 | 9.79 | 29.00 | 6.15 |
| value range of CPUEn | 1.00–256.55 | 3.60–12.00 | 1.50–2380.00 | 1.00–208.00 | 1.00–21.05 | 2.00–24.00 | 1.50–225.88 | 1.97–16.00 |
| Mean AIW | 10.63 | 10.33 | 4.29 | 11.29 | 14.95 | 19.54 | 7.80 | 7.92 |
| Value range of AIW | 1.24–40.88 | 6.50–14.40 | 0.80–8.00 | 2.00–51.05 | 1.30–36.46 | 3.50–40.03 | 1.70–28.90 | 2.50–12.34 |
| Groups classified by AIW | Station number | |||||||
| 0–5 | 7 | 12 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 9 | 4 | |
| 5–10 | 12 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 9 | 7 | 7 | |
| 10–15 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 5 | |
| 15–20 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||
| >20 | 3 | 1 | 9 | 5 | 1 | |||
| Factor | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loliolus beka | ||||
| Depth (m) | 19.00–101.00 | 15.00–60.00 | 14.00–102.00 | 32.00–78.00 |
| SST (°C) | 13.23–17.91 | 25.76–28.90 | 18.00–22.69 | 10.58–16.11 |
| SBT (°C) | 9.85–17.83 | 19.13–25.70 | 9.92–22.83 | 10.62–16.26 |
| SSS (‰) | 28.80–33.50 | 29.88–31.93 | 30.49–33.71 | 31.50–34.06 |
| SBS (‰) | 28.95–34.38 | 30.86–34.35 | 31.37–34.22 | 31.77–34.14 |
| SSDO (mg/L) | 7.84–8.61 | 4.92–7.20 | 8.00–8.84 | |
| SBDO (mg/L) | 7.76–9.18 | 3.55–4.30 | 7.97–8.55 | |
| Loliolus uyii | ||||
| Depth (m) | 35.00–90.00 | 16.00–68.00 | 35.00–107.00 | 19.00–70.00 |
| SST (°C) | 13.17–24.81 | 25.03–29.26 | 18.97–23.22 | 9.14–15.94 |
| SBT (°C) | 9.64–22.79 | 10.64–26.97 | 11.79–22.70 | 9.26–15.97 |
| SSS (‰) | 30.58–34.41 | 29.81–33.20 | 31.87–34.12 | 32.08–34.18 |
| SBS (‰) | 30.58–34.62 | 30.00–34.30 | 31.90–35.07 | 32.19–34.22 |
| SSDO (mg/L) | 7.84–8.57 | 4.51–6.97 | 8.02–8.76 | |
| SBDO (mg/L) | 7.76–9.23 | 3.56–6.47 | 8.01–8.68 | |
| Category | Formula (Fixed Effects) | Random Effects a | AIC | Sum of Log-Likelihoods b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loliolus uyii | y ~ 1 c | off | 370.70 | - |
| y ~ 1 | on | 370.47 | −185.85 | |
| y ~ s(Depth) d | on | 367.66 | −183.91 | |
| y ~ s(Depth) + s(SST) | on | 370.25 | −185.20 | |
| y ~ s(Depth) + s(SST) + s(SSS) | on | - | - | |
| Loliolusbeka | y ~ 1 | off | 394.14 | - |
| y ~ 1 | on | 351.74 | −214.12 | |
| y ~ s(SSS) | on | 352.95 | −170.47 | |
| y ~ s(Depth) + s(SSS) | on | - | - | |
| y ~ s(Depth) + s(SSS) + s(SST) | on | 326.32 | −160.38 | |
| Data-pool | y ~ 1 | off | 559.22 | - |
| y ~ 1 | on | 524.04 | −299.67 | |
| y ~ s(Depth) | on | 517.49 | −258.47 | |
| y ~ s(SST) | on | 509.34 | −269.97 | |
| y ~ s(SSS) | on | 527.77 | −262.01 | |
| y ~ s(SST) + s(SSS) | on | 507.52 | −215.41 | |
| y ~ s(Depth) + s(SST) | on | 493.47 | −187.55 | |
| y ~ s(Depth) + s(SSS) | on | - | - | |
| y ~ s(SSS) + s(SST) | on | 500.65 | −215.41 | |
| y ~ s(Depth) + s(SSS) + s(SST) | on | - | - |
| Method | Evaluation Index | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | Brier Score | Matthews Correlation Coefficient | |
| Prediction-pool | 0.7741 | 0.1580 | 0.2402 |
| Data-pool | 0.8597 | 0.1292 | 0.3879 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, M.; Feng, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Song, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Yang, L. Seasonal-Spatial Distribution Variations and Predictions of Loliolus beka and Loliolus uyii in the East China Sea Region: Implications from Climate Change Scenarios. Animals 2024, 14, 2070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142070
Xu M, Feng W, Liu Z, Li Z, Song X, Zhang H, Zhang C, Yang L. Seasonal-Spatial Distribution Variations and Predictions of Loliolus beka and Loliolus uyii in the East China Sea Region: Implications from Climate Change Scenarios. Animals. 2024; 14(14):2070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142070
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Min, Wangjue Feng, Zunlei Liu, Zhiguo Li, Xiaojing Song, Hui Zhang, Chongliang Zhang, and Linlin Yang. 2024. "Seasonal-Spatial Distribution Variations and Predictions of Loliolus beka and Loliolus uyii in the East China Sea Region: Implications from Climate Change Scenarios" Animals 14, no. 14: 2070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142070
APA StyleXu, M., Feng, W., Liu, Z., Li, Z., Song, X., Zhang, H., Zhang, C., & Yang, L. (2024). Seasonal-Spatial Distribution Variations and Predictions of Loliolus beka and Loliolus uyii in the East China Sea Region: Implications from Climate Change Scenarios. Animals, 14(14), 2070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142070






