First Report of Rickettsia conorii in Hyalomma kumari Ticks
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
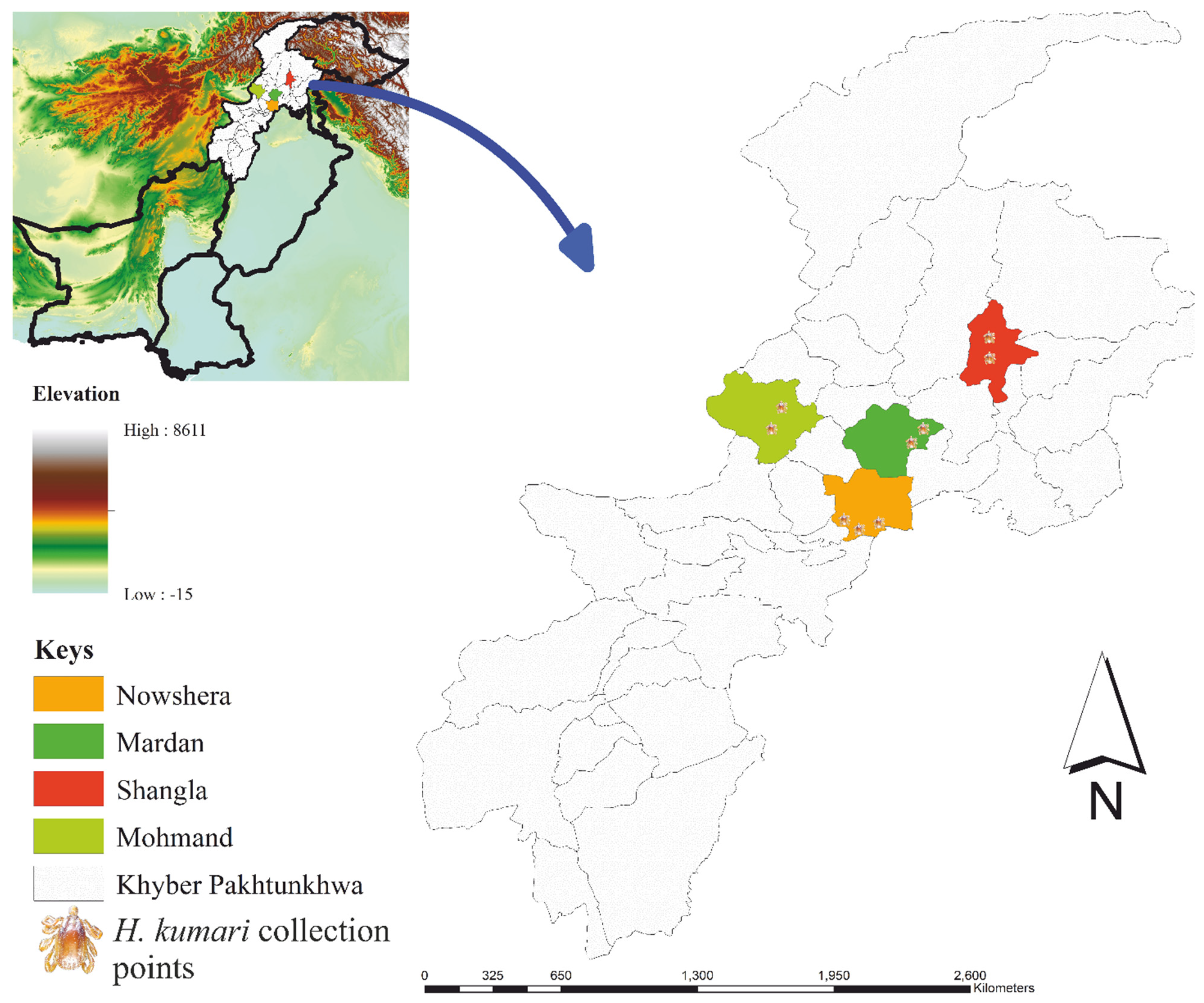
2.1. Hosts and Spatial Survey of Ticks
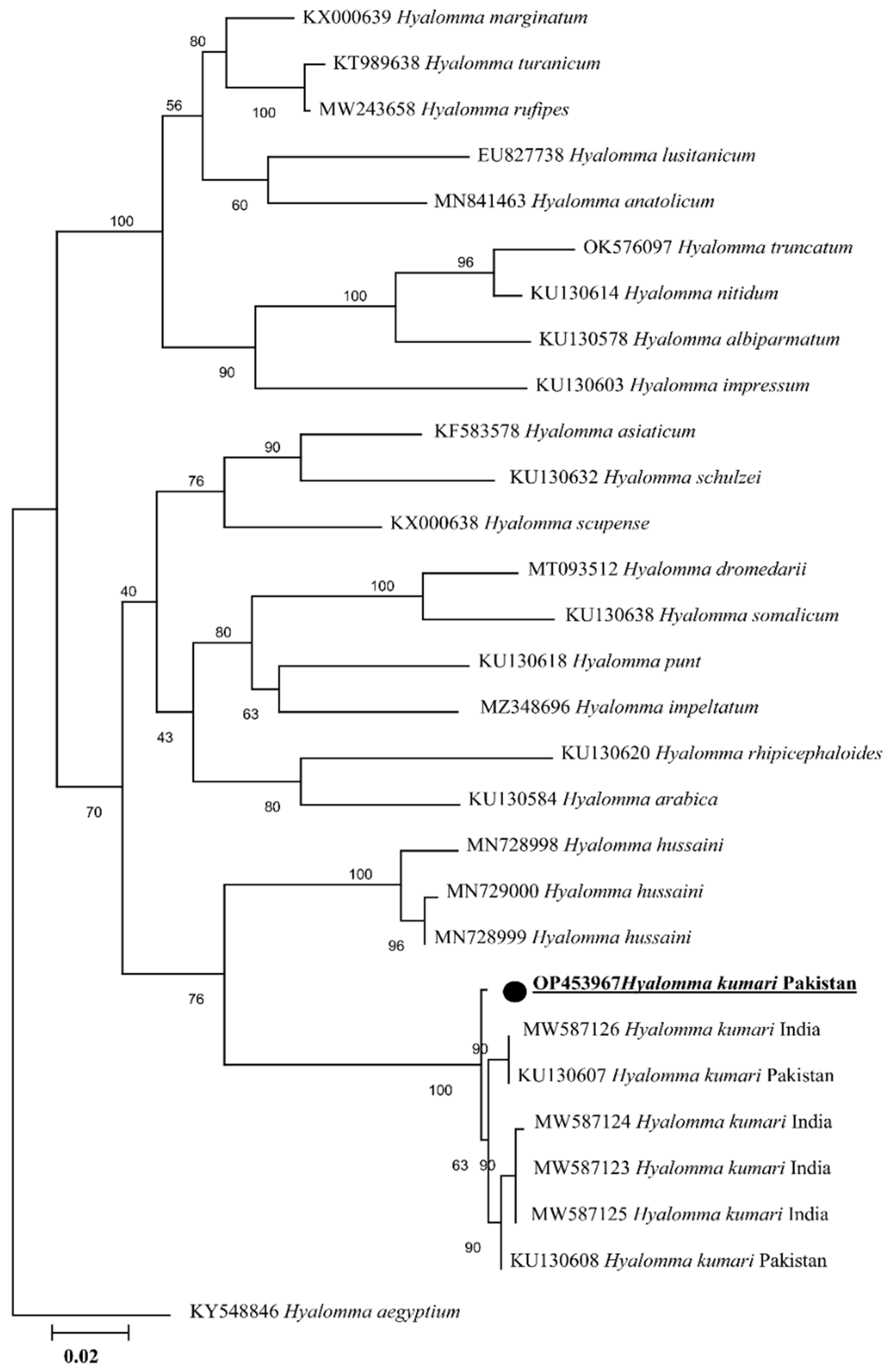
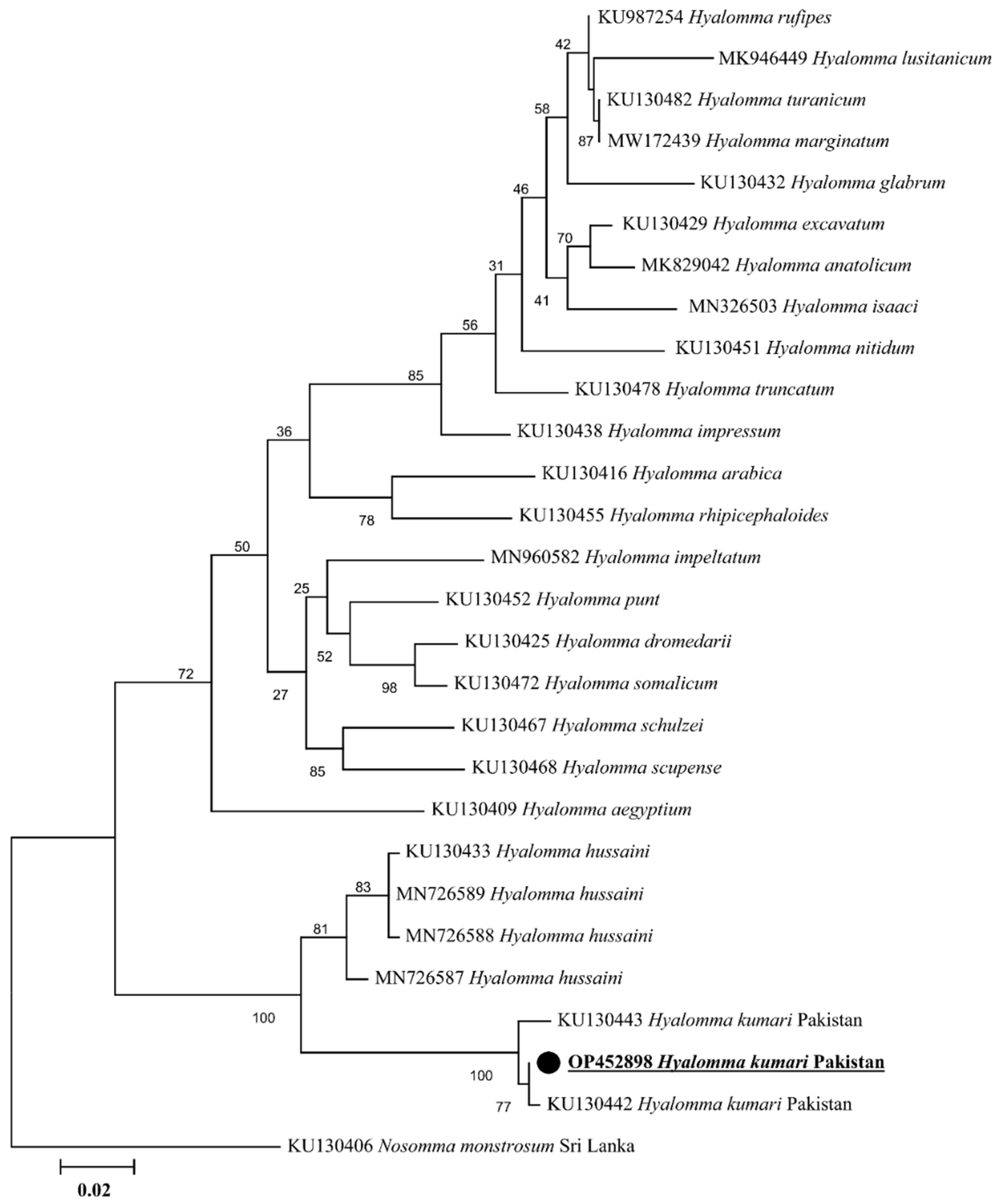
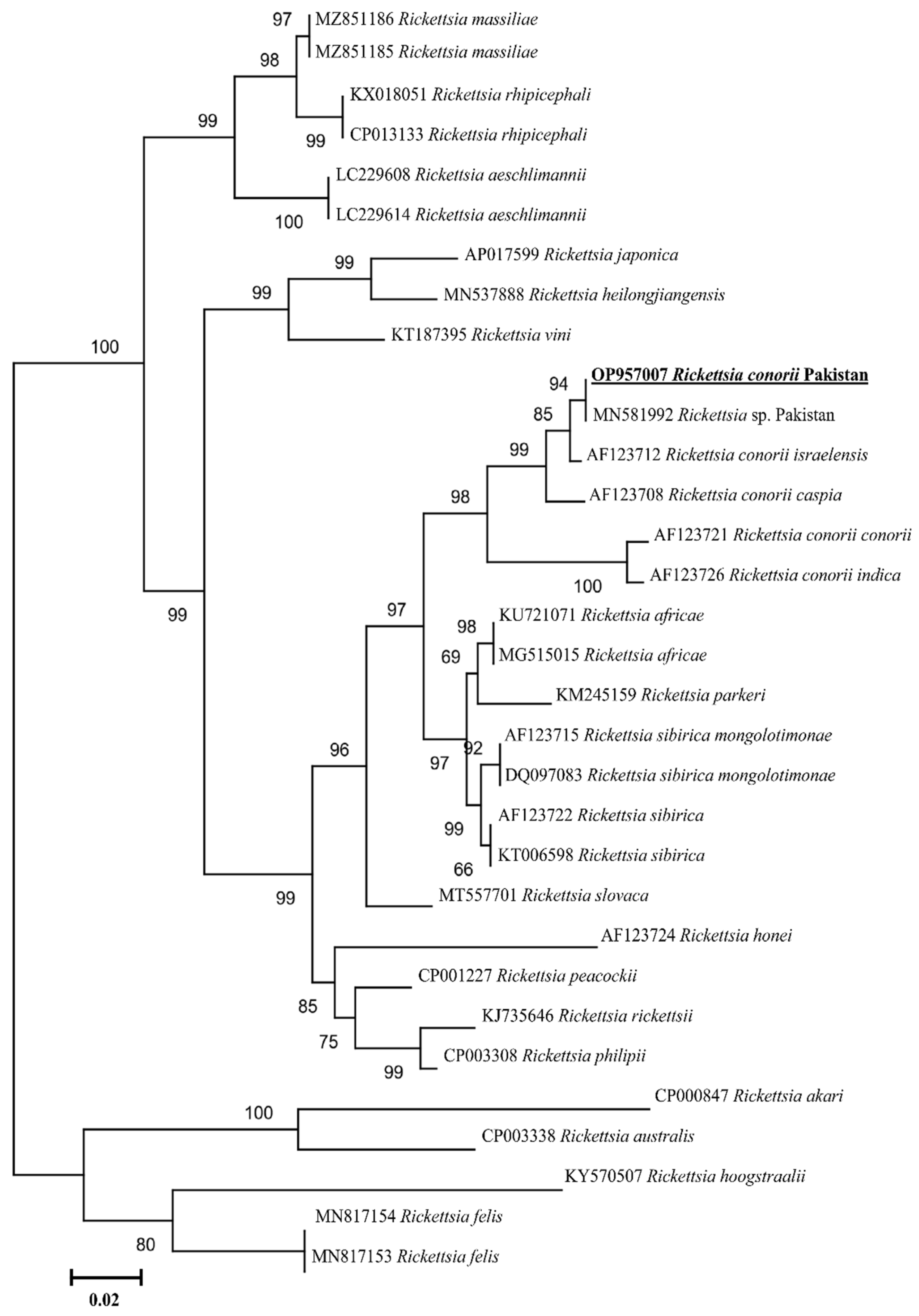
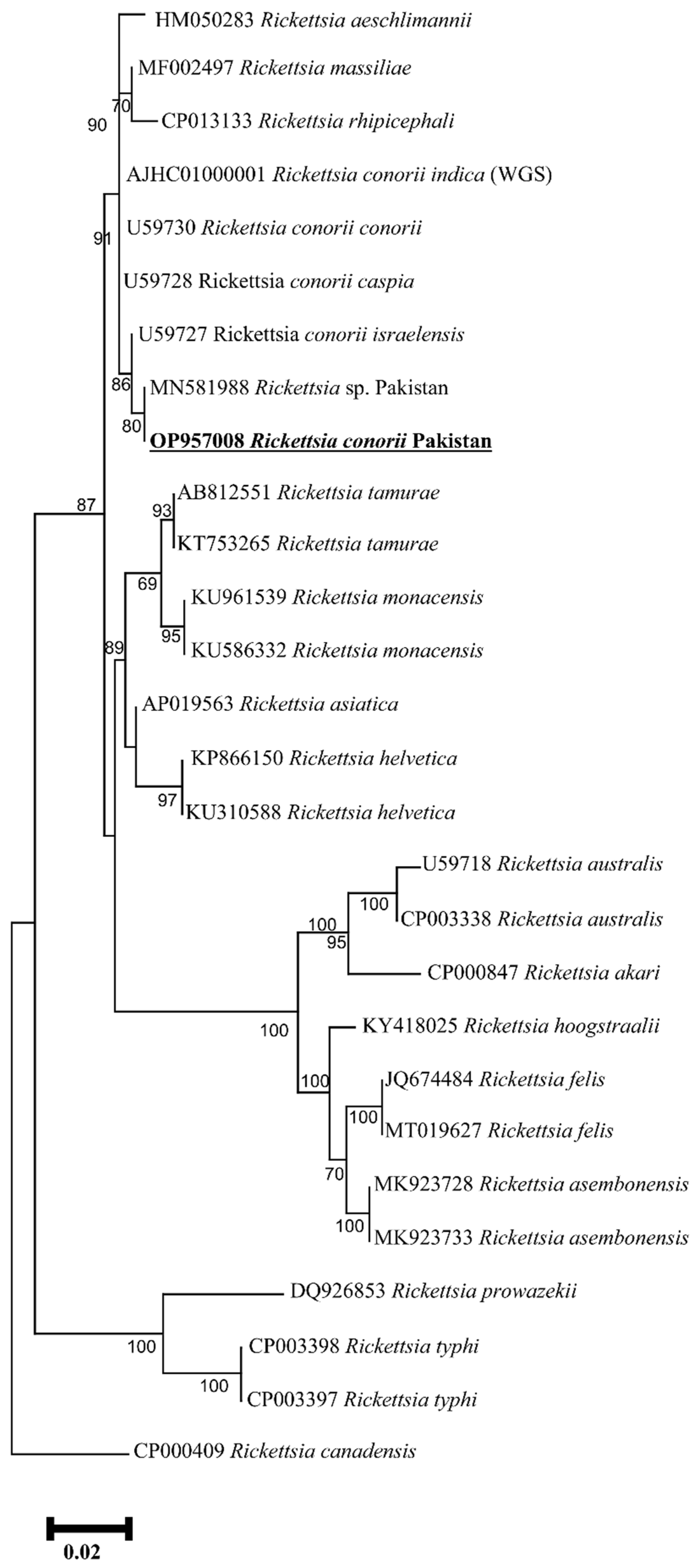
2.2. Sequence and Phylogenetic Analyses of Tick
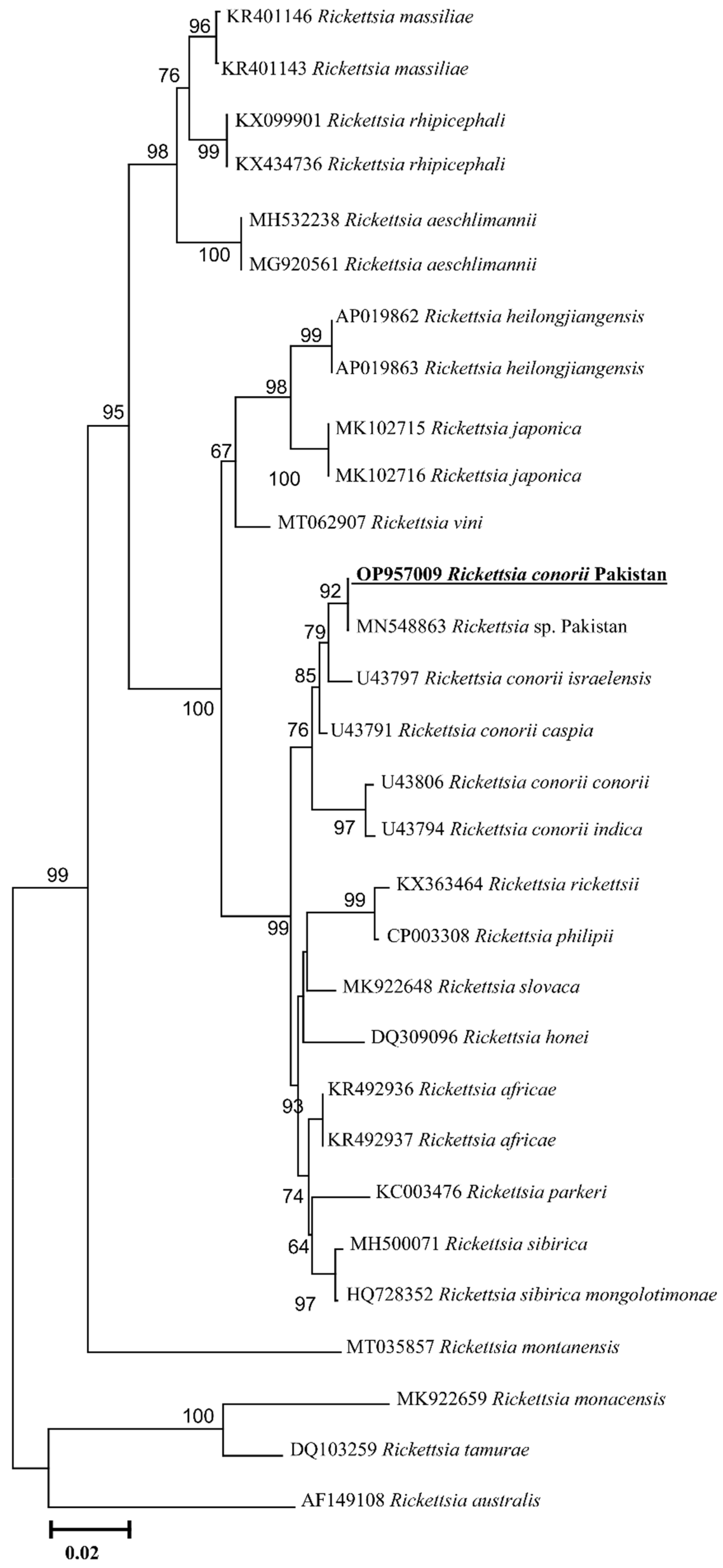
2.3. Rickettsia spp. Prevalence and Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Area and Tick Collection
4.2. Collection, Preservation and Morphological Identification
4.3. DNA Extraction and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
| Organisms and Genes | Primers Sequences (5′-3′) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Annealing Temperature | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ticks | ||||
| 16S rRNA | F-CCGGTCTGAACTCAG R-CAATGATTTTTTAAA | 460 | 54 °C | [36] |
| cox I | F-GGAACAATATATTTAATTTTTGG R 5-ATCTATCCCTACTGTAAATATATG | 801 | 55 °C | [46] |
| ITS-2 | F-CCATCGATGTGAAYTGCAGGACA R-GTGAATTCTATGCTTAAATTCAGGGGGT | 900 | 55 °C | [57] |
| Rickettsia | ||||
| gltA | F-GCAAGTATCGGTGAGGATGTAAT R-GCTTCCTAAAATTCAATAAATCAGGAT | 401 | 56 °C | [58] |
| ompA | F-ATGGCGAATATTTCTCCAAAA R-GTTCCGTTAATGGCAGCATCT | 532 | 55 °C | [59] |
| ompB | F-CCGCAGGGTTGGTAACTGC R-CCTTTTAGATTACCGCCTAA | 862 | 50 °C | [60] |
4.4. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analyses
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sands, A.F.; Apanaskevich, D.A.; Matthee, S.; Horak, I.G.; Harrison, A.; Karim, S.; Mohammad, M.K.; Mumcuoglu, K.Y.; Rajakaruna, R.S.; Santos-Silva, M.M.; et al. Effects of tectonics and large scale climatic changes on the evolutionary history of Hyalomma ticks. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2017, 114, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Khan, M.A.; Zahid, H.; Yaseen, P.M.; Qayash Khan, M.; Nawab, J.; Ur Rehman, Z.; Ateeq, M.; Khan, S.; Ibrahim, M. Seasonal dynamics, record of ticks infesting humans, wild and domestic animals and molecular phylogeny of Rhipicephalus microplus in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Pakistan. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, W.I. The aetiology, pathogenesis and control of theileriosis in domestic animals. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2015, 34, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, K.; Numan, M.; Alouffi, A.; Almutairi, M.M.; Zahid, H.; Khan, M.; Islam, Z.U.; Kamil, A.; Safi, S.Z.; Ahmed, H.; et al. Molecular Characterization and Assessment of Risk Factors Associated with Theileria annulata Infection. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.; Ma, M.; Moreau, E.; Liu, J.; Lu, B.; Bai, Q.; Luo, J.; Jorgensen, W.; Chauvin, A.; Yin, H. A new ovine Babesia species transmitted by Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum. Exp. Parasitol. 2009, 122, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubdar, N.; Oshaghi, M.A.; Rafinejad, J.; Pourmand, M.R.; Maleki-Ravasan, N.; Salehi-Vaziri, M.; Telmadarraiy, Z.; Karimian, F.; Koosha, M.; Rahimi-Foroushani, A.; et al. Effect of meteorological factors on Hyalomma species composition and their host preference, seasonal prevalence and infection status to Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever in Iran. J. Arthropod Borne Dis. 2019, 13, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasi, K.K.; von Arnim, F.; Schulz, A.; Rehman, A.; Chudhary, A.; Oneeb, M.; Sas, M.A.; Jamil, T.; Maksimov, P.; Sauter-Louis, C.; et al. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus in ticks collected from livestock in Balochistan, Pakistan. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomar, A.M.; Portillo, A.; Mazuelas, D.; Roncero, L.; Arizaga, J.; Crespo, A.; Gutiérrez, Ó.; Márquez, F.J.; Cuadrado, J.F.; Eiros, J.M.; et al. Molecular analysis of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus and Rickettsia in Hyalomma marginatum ticks removed from patients (Spain) and birds (Spain and Morocco), 2009–2015. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmone, A.A.; Petney, T.N.; Robbins, R.G. Ixodidae (Acari: Ixodoidea): Descriptions and redescriptions of all known species from 1758 to December 31, 2019. Zootaxa 2020, 4871, 1–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, M.N.; Hoogstraal, H. The Hyalomma ticks (Ixodoidea, Ixodidae) of Pakistan, India, and Ceylon, with keys to subgenera and species. Acarologia 1964, 6, 257–286. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, V.C. Ixodid ticks (Acarina, Ixodidae) of West Pakistan; University of Maryland: College Park, MD, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, S.; Budachetri, K.; Mukherjee, N.; Williams, J.; Kausar, A.; Hassan, M.J.; Adamson, S.; Dowd, S.E.; Apanskevich, D.; Arijo, A.; et al. A study of ticks and tick-borne livestock pathogens in Pakistan. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, 0005681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, N.; Shabbir, R.M.K.; Ahmed, H.; Afzal, M.S.; Ullah, S.; Ali, A.; Irum, S.; Naqvi, S.K.H.; Yin, J.; Cao, J. Prevalence of dierent tick species on livestock and associated equines and canine from dierent agro-ecological zones of Pakistan. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 9, 10899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamran, K.; Ali, A.; Villagra, C.; Siddiqui, S.; Alouffi, A.S.; Iqbal, A. A cross-sectional study of hard ticks (acari: Ixodidae) on horse farms to assess the risk factors associated with tick-borne diseases. Zoonoses Public Health 2021, 68, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, S.; Khan, M.; Alouffi, A.; Almutairi, M.M.; Ullah, S.; Numan, M.; Islam, N.; Khan, Z.; Aiman, O.; Zaman Safi, S.; et al. Spatio-temporal patterns of ticks and molecular survey of Anaplasma marginale, with notes on their phylogeny. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apanaskevich, D.A.; Horak, I.G.; Geevarghese, G. The genus Hyalomma Koch, 1844. VIII. Redescription of three Hyalommina Schulze, 1919 species (Acari: Ixodidae) from South Asia with notes on their biology. Zootaxa 2009, 2050, 3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Peña, A. Climate, niche, ticks, and models: What they are and how we should interpret them. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 103, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirosh-Levy, S.; Gottlieb, Y.; Apanaskevich, D.A.; Mumcuoglu, K.Y.; Steinman, A. Species distribution and seasonal dynamics of equine tick infestation in two Mediterranean climate niches in Israel. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government of Pakistan (GOP). 2020–2022. Pakistan Economic Survey. Ministry of Finance. Available online: www.finance.gov.pk (accessed on 7 April 2022).
- Apanaskevich, D.A.; Horak, I.G. The genus Hyalomma. XI. Redescription of all parasitic stages of H. (Euhyalomma) asiaticum (Acari: Ixodidae) and notes on its biology. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2010, 52, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apanaskevich, D.A.; Filippova, N.A.; Horak, I.G. The genus Hyalomma Koch, 1844. X. Redescription of all parasitic stages of H. (Euhyalomma) scupense Schulze, 1919 (= H. detritum Schulze) (Acari: Ixodidae) and notes on its biology. Folia Parasitol. 2010, 57, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Shehla, S.; Alouffi, A.; Kashif Obaid, M.; Zeb Khan, A.; Almutairi, M.M.; Numan, M.; Aiman, O.; Alam, S.; Ullah, S.; et al. Molecular survey and genetic characterization of Anaplasma marginale in ticks collected from livestock hosts in Pakistan. Animals 2022, 12, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, H.R.; Pilgrim, J.; Wybouw, N.; Parker, J.; Pirro, S.; Hunter-Barnett, S.; Campbell, P.M.; Blow, F.; Darby, A.C.; Hurst, G.D.; et al. Genomic diversity across the Rickettsia and ‘Candidatus Megaira’genera and proposal of genus status for the Torix group. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinerman, G.; Baneth, G.; Mumcuoglu, K.Y.; van Straten, M.; Berlin, D.; Apanaskevich, D.A.; Abdeen, Z.; Nasereddin, A.; Harrus, S. Molecular detection of Rickettsia africae, Rickettsia aeschlimannii, and Rickettsia sibirica mongolitimonae in camels and Hyalomma spp. ticks from Israel. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2013, 13, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, M.; Rymaszewska, A. Expansion of tick-borne rickettsioses in the world. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, M.L.; Killmaster, L.F.; Zemtsova, G.E. Domestic dogs (Canis familiaris) as reservoir hosts for Rickettsia conorii. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parola, P.; Paddock, C.D.; Socolovschi, C.; Labruna, M.B.; Mediannikov, O.; Kernif, T.; Abdad, M.Y.; Stenos, J.; Bitam, I.; Fournier, P.E.; et al. Update on tick-borne rickettsioses around the world: A geographic approach. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 657–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, R.G.; Wisseman JR, C.L. Tick-borne Rickettsia of the spotted fever group in west Pakistan: Ii. Serological classification of isolates from west Pakistan and Thailand: Evidence for two new species. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1973, 97, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, G.S.; Évora, P.M.; Mangold, A.J.; Jittapalapong, S.; Rodriguez-Mallon, A.; Guzmán, P.E.; Bechara, G.H.; Camargo-Mathias, M.I. Molecular, biological, and morphometric comparisons between different geographical populations of Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato (Acari: Ixodidae). Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 215, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Pena, A.; D’Amico, G.; Palomar, A.M.; Dupraz, M.; Fonville, M.; Heylen, D.; Habela, M.A.; Hornok, S.; Lempereur, L.; Madder, M.; et al. A comparative test of ixodid tick identification by a network of European researchers. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2017, 8, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Islam, N.; Khan, A.; Islam, Z.U.; Muñoz-Leal, S.; Labruna, M.B.; Ali, A. New records of Amblyomma gervaisi from Pakistan, with detection of a reptile-associated Borrelia sp. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 102047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanduma, E.G.; Mwacharo, J.M.; Mwaura, S.; Njuguna, J.N.; Nzuki, I.; Kinyanjui, P.W.; Githaka, N.; Heyne, H.; Hanotte, O.; Skilton, R.A.; et al. Multi-locus genotyping reveals absence of genetic structure in field populations of the brown ear tick (Rhipicephalus appendiculatus) in Kenya. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, P.H.C.; Barcelos, R.M.; Klein, R.C.; Vidigal, P.M.P.; Montandon, C.E.; Fabres-Klein, M.H.; Dergam, J.A.; Mafra, C. Sequencing and comparative analysis of the Amblyomma sculptum mitogenome. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 247, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronstein, O.; Kroh, A.; Haring, E. Mind the gap! The mitochondrial control region and its power as a phylogenetic marker in echinoids. BMC Evol. Biol. 2018, 18, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numan, M.; Islam, N.; Adnan, M.; Safi, Z.S.; Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Labruna, M.B.; Ali, A. First genetic report of Ixodes kashmiricus and associated Rickettsia sp. Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangold, A.J.; Bargues, M.D.; Mas-Coma, S. Mitochondrial 16S rDNA sequences and phylogenetic relationships of species of Rhipicephalus and other tick genera among Metastriata (Acari: Ixodidae). Parasitol. Res. 1998, 84, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonenshine, D.E. Range expansion of tick disease vectors in North America: Implications for spread of tick-borne disease. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, R.; Krüger, R.F.; Peterson, A.T.; de Melo, L.F.; Vicenzi, N.; Jiménez-García, D. Climate change implications for the distribution of the babesiosis and anaplasmosis tick vector, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, R.P. Description of the immature stages of Hyalomma (Hyalommina) kumari Sharif, 1928 (Acarina: Ixodidae) and redescription of the adults, with notes on its hosts and distribution. Parasitology 1970, 61, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Shehla, S.; Zahid, H.; Ullah, F.; Zeb, I.; Ahmed, H.; da Silva Vaz, I., Jr.; Tanaka, T. Molecular survey and spatial distribution of Rickettsia spp. in ticks infesting free-ranging wild animals in Pakistan (2017–2021). Pathogens 2022, 11, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Zahid, H.; Zeb, I.; Tufail, M.; Khan, S.; Haroon, M.; Bilal, M.; Hussain, M.; Alouffi, A.S.; Muñoz-Leal, S.; et al. Risk factors associated with tick infestations on equids in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan, with notes on Rickettsia massiliae detection. Parasit. Vectors 2021, 14, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, B.R.; Kumar, N.; Kant, R.; Deval, H.; Singh, R.; Pandey, A.K.; Behera, S.P.; Bondre, V.P. Abundance of ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) and presence of Rickettsia and Anaplasma in ticks infesting domestic animals from northern India. J. Med. Entomol. 2021, 58, 1370–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Feng, C.; Yuan, X.; Jia, G.; Deng, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; et al. Assessment of four DNA fragments (COI, 16S rDNA, ITS2, 12S rDNA) for species identification of the Ixodida (Acari: Ixodida). Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beati, L.; Klompen, H. Phylogeography of ticks (Acari: Ixodida). Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2019, 64, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiman, O.; Ullah, S.; Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Nijhof, A.M.; Ali, A. First report of Nosomma monstrosum ticks infesting Asian water buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) in Pakistan. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 101899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitimia, L.; Lin, R.Q.; Cosoroaba, I.; Wu, X.Y.; Song, H.Q.; Yuan, Z.G.; Zhu, X.Q. Genetic characterization of ticks from southwestern Romania by sequences of mitochondrial coxI and nad5 genes. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2010, 52, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, I.; Ullah, S.; Alouffi, A.; Almutairi, M.M.; Khan, M.; Numan, M.; Sher Safi, Z.; Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Tanaka, T.; Ali1, A. Description of male, redescription of female, host record, and phylogenetic position of Haemaphysalis danieli. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byaruhanga, C.; Collins, N.E.; Knobel, D.; Kabasa, W.; Oosthuizen, M.C. Endemic status of tick-borne infections and tick species diversity among transhumant zebu cattle in Karamoja region, Uganda: Support for control approaches. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Reports 2015, 1, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parola, P.; Raoult, D. Ticks and tickborne bacterial diseases in humans: An emerging infectious threat. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 897–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutailler, S.; Valiente Moro, C.; Vaumourin, E.; Michelet, L.; Tran, F.H.; Devillers, E.; Cosson, J.F.; Gasqui, P.; Van, V.T.; Mavingui, P.; et al. Co-infection of ticks: The rule rather than the exception. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, 0004539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakheit, M.A.; Latif, A.A.; Vatansever, Z.; Seitzer, U.; Ahmed, J. The huge risks due to Hyalomma ticks. In Arthropods as Vectors of Emerging Diseases; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 167–194. [Google Scholar]
- Sentausa, E.; El Karkouri, K.; Robert, C.; Raoult, D.; Fournier, P.E. Genome sequence of Rickettsia conorii subsp. indica, the agent of Indian tick typhus. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 3288–3289. [Google Scholar]
- Kimita, G.; Mutai, B.; Nyanjom, S.G.; Wamunyokoli, F.; Waitumbi, J. Phylogenetic variants of Rickettsia africae, and incidental identification of” Candidatus Rickettsia moyalensis” in Kenya. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. Dis. 2016, 10, 0004788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Fournier, P.E.; Eremeeva, M.; Raoult, D. Proposal to create subspecies of Rickettsia conorii based on multi-locus sequence typing and an emended description of Rickettsia conorii. BMC Microbiol. 2005, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devendra, C. Small ruminants: Imperatives for productivity enhancement improved livelihoods and rural growth-a review. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 14, 1483–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.E.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Marrelli, M.T.; Souza, L.F.; Marques, R.C.; Labruna, M.B.; Matioli, S.R.; Tonon, A.P.; Ribolla, P.E.M.; Marinotti, O.; Schumaker, T.T.S. Taxonomic and phylogenetic relationships between neotropical species of ticks from genus Amblyomma (Acari: Ixodidae) inferred from second internal transcribed spacer sequences of rDNA. J. Med. Entomol. 2007, 44, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labruna, M.B.; Whitworth, T.; Bouyer, D.H.; McBride, J.; Camargo, L.M.A.; Camargo, E.P.; Popov, V.; Walker, D.H. Rickettsia bellii and Rickettsia amblyommii in Amblyomma ticks from the state of Rondônia, Western Amazon, Brazil. J. Med. Entomol. 2004, 41, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regnery, R.L.; Spruill, C.L.; Plikaytis, B. Genotypic identification of rickettsiae and estimation of intraspecies sequence divergence for portions of two rickettsial genes. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 1576–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, V.; Raoult, D. Phylogenetic analysis of members of the genus Rickettsia using the gene encoding the outer-membrane protein rOmpB (ompB). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.; Biosciences, I.; Carlsbad, C.J.G.B.B. BioEdit: An important software for molecular biology. GERF Bull. Biosci. 2011, 2, 60–61. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
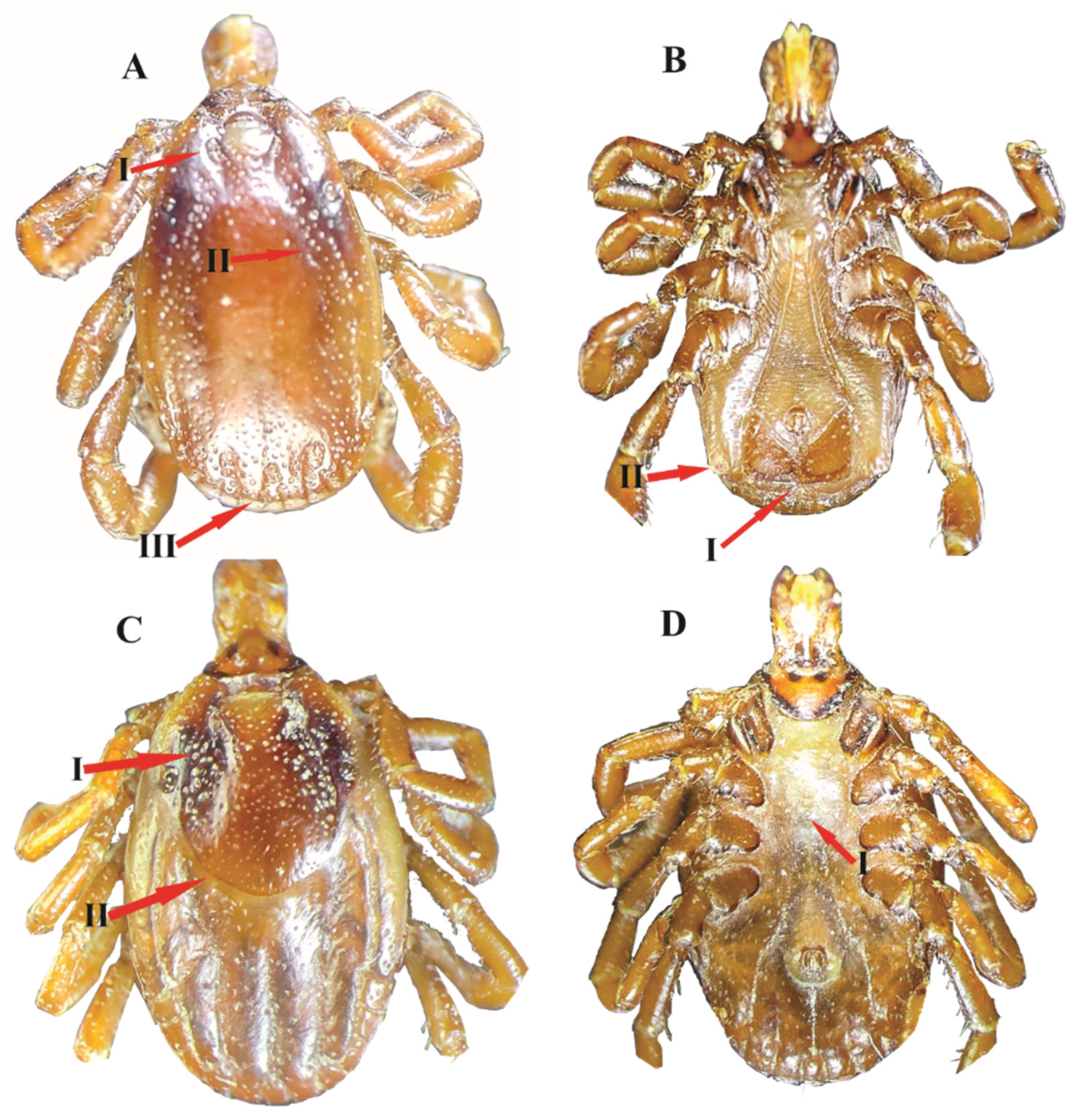
| Districts | Hosts | Host Gender | No. of Ticks | Tick Life Stages | Molecularly Analyzed Ticks | Rickettsia Positive (%) | p-Value * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | Male | Nymph | |||||||
| Nowshera | Goat | male | 27 | 13 | 10 | 4 | 11 F, 9 M, 4 N | 1 F, 1 M, 1 N (12.5) | 0.0058 |
| female | 39 | 20 | 13 | 6 | |||||
| Sheep | male | 23 | 11 | 9 | 3 | ||||
| female | 29 | 14 | 12 | 3 | |||||
| Mardan | Goat | male | 20 | 10 | 8 | 2 | 8 F, 6 M, 5 N | 1 F, 1 N (10.5) | |
| female | 24 | 12 | 11 | 1 | |||||
| Sheep | male | 15 | 8 | 6 | 1 | ||||
| female | 21 | 11 | 8 | 2 | |||||
| Shangla | Goat | male | 22 | 13 | 6 | 3 | 10 F, 5 M, 3 N | 1 M (5.5) | |
| female | 28 | 16 | 11 | 1 | |||||
| Sheep | male | 18 | 9 | 7 | 2 | ||||
| female | 23 | 10 | 8 | 5 | |||||
| Mohmand | Goat | male | 29 | 15 | 12 | 2 | 9 F, 9 M, 4 N | 1 F, 1 M (9.1) | |
| female | 35 | 14 | 13 | 8 | |||||
| Sheep | male | 25 | 15 | 8 | 2 | ||||
| female | 31 | 13 | 16 | 2 | |||||
| Total | 409 | 204 | 158 | 47 | 38 F, 29 M, 16 N | 3 F, 3 M, 2 N (9.6) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ullah, S.; Alouffi, A.; Almutairi, M.M.; Islam, N.; Rehman, G.; Ul Islam, Z.; Ahmed, H.; Júnior, I.d.S.V.; Labruna, M.B.; Tanaka, T.; et al. First Report of Rickettsia conorii in Hyalomma kumari Ticks. Animals 2023, 13, 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091488
Ullah S, Alouffi A, Almutairi MM, Islam N, Rehman G, Ul Islam Z, Ahmed H, Júnior IdSV, Labruna MB, Tanaka T, et al. First Report of Rickettsia conorii in Hyalomma kumari Ticks. Animals. 2023; 13(9):1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091488
Chicago/Turabian StyleUllah, Shafi, Abdulaziz Alouffi, Mashal M. Almutairi, Nabila Islam, Gauhar Rehman, Zia Ul Islam, Haroon Ahmed, Itabajara da Silva Vaz Júnior, Marcelo B. Labruna, Tetsuya Tanaka, and et al. 2023. "First Report of Rickettsia conorii in Hyalomma kumari Ticks" Animals 13, no. 9: 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091488
APA StyleUllah, S., Alouffi, A., Almutairi, M. M., Islam, N., Rehman, G., Ul Islam, Z., Ahmed, H., Júnior, I. d. S. V., Labruna, M. B., Tanaka, T., & Ali, A. (2023). First Report of Rickettsia conorii in Hyalomma kumari Ticks. Animals, 13(9), 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091488









