Plasma and Synovial Fluid Cell-Free DNA Concentrations Following Induction of Osteoarthritis in Horses
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
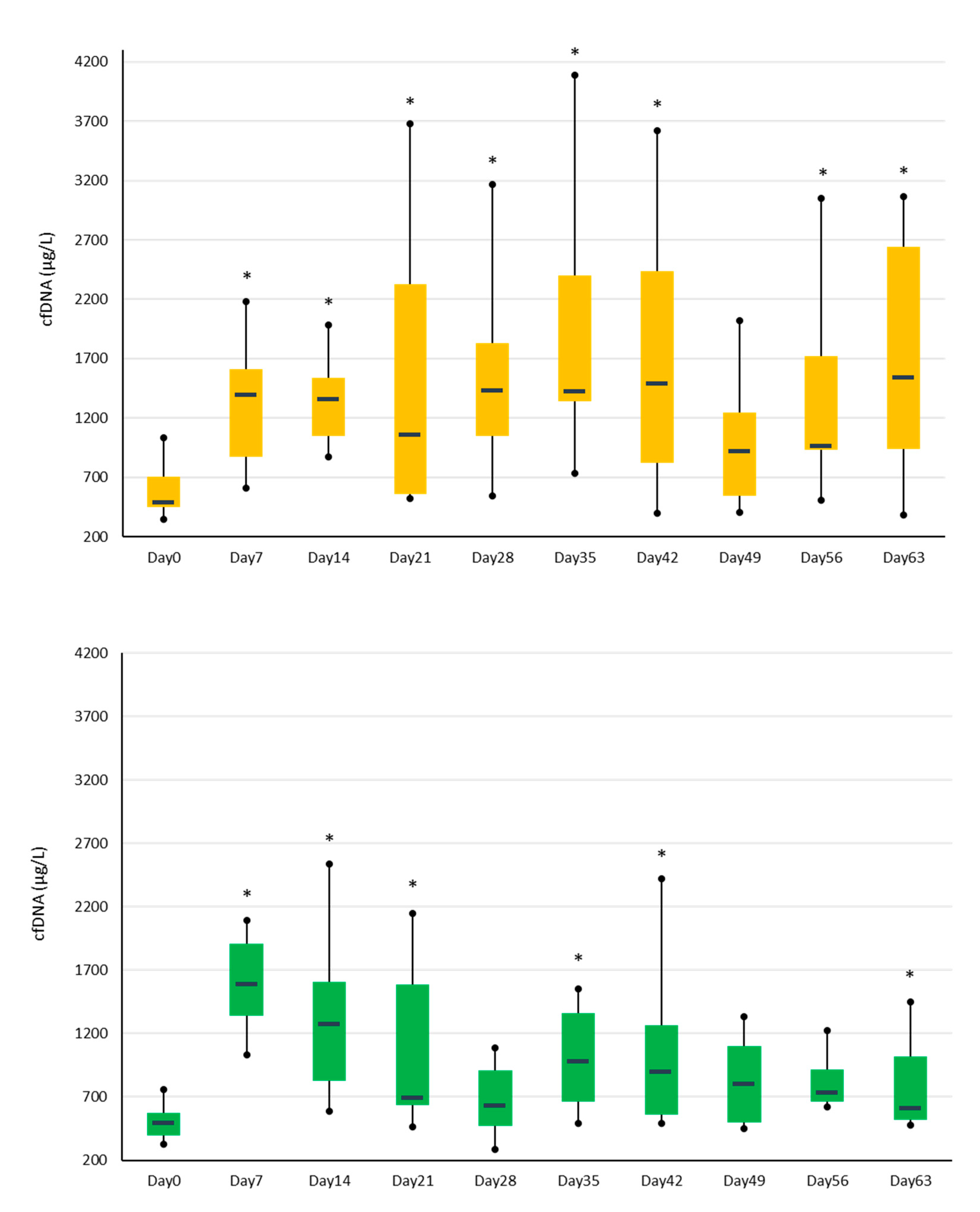
3.1. Synovial Fluid cfDNA
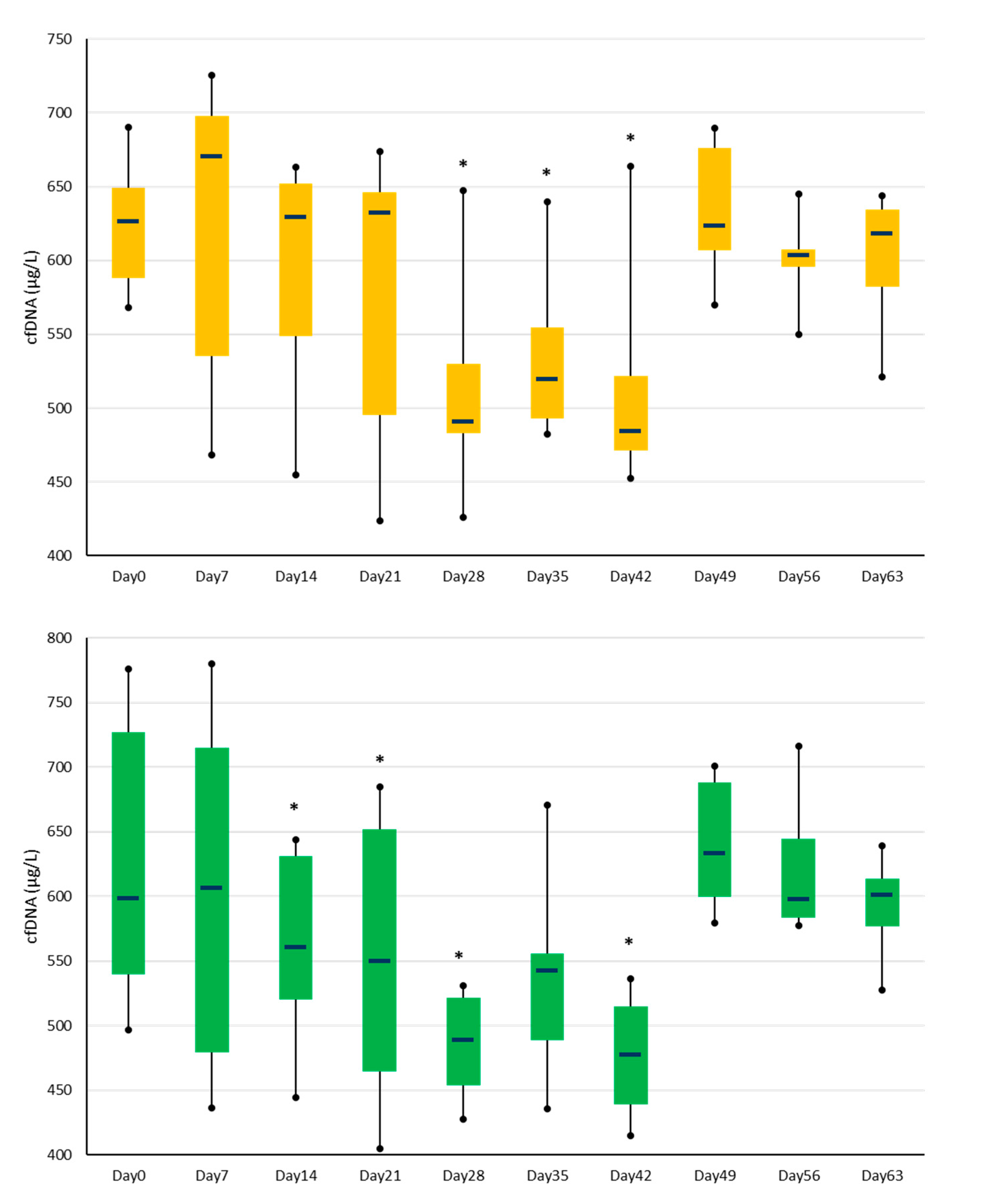
3.2. Plasma cfDNA
3.3. Clinical Parameters
3.4. Assay Precision
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeffcott, L.; Rossdale, P.; Freestone, J.; Frank, C.; Towers-Clark, P. An assessment of wastage in Thoroughbred racing from conception to 4 years of age. Equine Vet. J. 1982, 14, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasashima, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Smith, R.; Goodship, A.; Kuwano, A.; Ueno, T.; Hirano, S. Prevalence of superficial digital flexor tendonitis and suspensory desmitis in Japanese Thoroughbred flat racehorses in 1999. Equine Vet. J. 2004, 36, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.; Parkin, T.; Riggs, C.; Morgan, K. Descriptive analysis of retirement of Thoroughbred racehorses due to tendon injuries at the Hong Kong Jockey Club (1992–2004). Equine Vet. J. 2007, 39, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Harkins, L.; Hammond, C.; Wood, J. Racehorse injuries, clinical problems and fatalities recorded on British racecourses from flat racing and National Hunt racing during 1996, 1997 and 1998. Equine Vet. J. 2001, 33, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossdale, P.; Hopes, R.; Digby, N. Epidemiological study of wastage among racehorses 1982 and 1983. Vet. Rec. 1985, 116, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, J.; Genovese, R. Principles and practices of joint disease treatment. In Diagnosis and Management of Lameness in the Horse; Ross, M.W., Dyson, S.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2003; pp. 746–764. [Google Scholar]
- Clegg, P.; Booth, T. Drugs used to treat osteoarthritis in the horse. In Pract. 2000, 22, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlwraith, C.W. From arthroscopy to gene therapy—30 years of looking in joints. In Proceedings of the 51st Annual Convention of the American Association of Equine Practitioners, Seattle, Washington, DC, USA, 3–7 December 2005; pp. 65–113. [Google Scholar]
- Kraus, V.B.; Burnett, B.; Coindreau, J.; Cottrell, S.; Eyre, D.; Gendreau, M.; Gardiner, J.; Garnero, P.; Hardin, J.; Henrotin, Y. Application of biomarkers in the development of drugs intended for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2011, 19, 515–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawcak, C.; Frisbie, D.; Werpy, N.; Park, R.; McIlwraith, C. Effects of exercise vs experimental osteoarthritis on imaging outcomes. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawcak, C.E.; McIlwraith, C.W.; Norrdin, R.W.; Park, R.D.; Steyn, P.S. Clinical effects of exercise on subchondral bone of carpal and metacarpophalangeal joints in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2000, 61, 1252–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twardock, A. Equine bone scintigraphic uptake patterns related to age, breed, and occupation. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2001, 17, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, S.L.; Gavin, P. Physical principles and technical considerations for equine computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2001, 17, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmander, L.S. Markers of cartilage metabolism in arthrosis. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1991, 62, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmander, L.S. Markers of altered metabolism in osteoarthritis. J. Rheumatol.-Suppl. 2004, 31, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Frisbie, D.; Al-Sobayil, F.; Billinghurst, R.; Kawcak, C.; McIlwraith, C. Changes in synovial fluid and serum biomarkers with exercise and early osteoarthritis in horses. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 1196–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisbie, D.; Ray, C.; Ionescu, M.; Poole, A.; Chapman, P.; McIlwraith, C. Measurement of synovial fluid and serum concentrations of the 846 epitope of chondroitin sulfate and of carboxy propeptides of type II procollagen for diagnosis of osteochondral fragmentation in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1999, 60, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bertone, A.; Palmer, J.; Jones, J. Synovial fluid cytokines and eicosanoids as markers of joint disease in horses. Vet. Surg. 2001, 30, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laverty, S. What biomarkers are telling us and the challenges ahead. In Proceedings of the Havemeyer Foundation Monograph Series No. 22—Equine Musculoskeletal Biomarkers, Steamboat Springs, CO, USA, 28 September–2 October 2009; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- McIlwraith, C. Use of synovial fluid and serum biomarkers in equine bone and joint disease: A review. Equine Vet. J. 2005, 37, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlwraith, C.W.; Billinghurst, R.C.; Frisbie, D.D. Current and future diagnostic means to better characterize osteoarthritis in the horse—Routine synovial fluid analysis and synovial fluid and serum markers. AAEP Proc. 2001, 47, 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Trumble, T.N.; Trotter, G.W.; Oxford, J.R.T.; McIlwraith, C.W.; Cammarata, S.; Goodnight, J.L.; Billinghurst, R.C.; Frisbie, D.D. Synovial fluid gelatinase concentrations and matrix metalloproteinase and cytokine expression in naturally occurring joint disease in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2001, 62, 1467–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Weeren, P.R.; Firth, E.C. Future tools for early diagnosis and monitoring of musculoskeletal injury: Biomarkers and CT. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2008, 24, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisbie, D.; Mc Ilwraith, C.; Arthur, R.; Blea, J.; Baker, V.; Billinghurst, R. Serum biomarker levels for musculoskeletal disease in two-and three-year-old racing thoroughbred horses: A prospective study of 130 horses. Equine Vet. J. 2010, 42, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, D.J.; Nevitt, M.; Losina, E.; Kraus, V. Biomarkers for osteoarthritis: Current position and steps towards further validation. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 28, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, V.B. Osteoarthritis year 2010 in review: Biochemical markers. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2011, 19, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotz, M.; Martel-Pelletier, J.; Christiansen, C.; Brandi, M.L.; Bruyère, O.; Chapurlat, R.; Collette, J.; Cooper, C.; Giacovelli, G.; Kanis, J.A. Republished: Value of biomarkers in osteoarthritis: Current status and perspectives. Postgrad. Med. J. 2014, 90, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitbach, S.; Tug, S.; Simon, P. Circulating cell-free DNA an up-coming molecular marker in exercise physiology. Sports Med. 2012, 42, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, P. Les acides nucleiques du plasma sanguin chez 1 homme. CR Seances Soc. Biol. Fil. 1948, 142, 241–243. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.P.-Y.; Chia, R.-H.; Wu, T.-L.; Tsao, K.-C.; Sun, C.-F.; Wu, J.T. Elevated cell-free serum DNA detected in patients with myocardial infarction. Clin. Chim. Acta 2003, 327, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koffler, D.; Agnello, V.; Winchester, R.; Kunkel, H.G. The occurrence of single-stranded DNA in the serum of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and other diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 1973, 52, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, S.; Shapiro, B.; Sklaroff, D.; Yaros, M. Free DNA in the serum of cancer patients and the effect of therapy. Cancer Res. 1977, 37, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jahr, S.; Hentze, H.; Englisch, S.; Hardt, D.; Fackelmayer, F.O.; Hesch, R.-D.; Knippers, R. DNA fragments in the blood plasma of cancer patients: Quantitations and evidence for their origin from apoptotic and necrotic cells. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 1659–1665. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, D.M.W.; Forman, M.; Kisseberth, W.; Lehman, A.; Kelbick, N.; Harper, P.; Rush, L. Quantification of plasma DNA as a prognostic indicator in canine lymphoid neoplasia. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2007, 5, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.; Hennecke, S.; Bornemann-Kolatzki, K.; Urnovitz, H.B.; Neumann, S.; Ströbel, P.; Kaup, F.-J.; Brenig, B.; Schütz, E. Genome aberrations in canine mammary carcinomas and their detection in cell-free plasma DNA. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzuelli, J.A.; Dias-Junior, C.A.; Izidoro-Toledo, T.C.; Gerlach, R.F.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Circulating cell-free DNA levels in plasma increase with severity in experimental acute pulmonary thromboembolism. Clin. Chim. Acta 2009, 409, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leon, P.M.M.; Campos, V.F.; Dellagostin, O.A.; Deschamps, J.C.; Seixas, F.K.; Collares, T. Equine fetal sex determination using circulating cell-free fetal DNA (ccffDNA). Theriogenology 2012, 77, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadivar, A.; Tafti, R.D.; Khoei, H.H.; Nasirabadi, M.H.; Esfandabadi, N.S.; Cheraghi, N.; Davoodian, N. Developing a nested real-time PCR assay for determining equine fetal sex prenatally. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2016, 40, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmer, S.F.; Luethy, D.; Abraham, M.; Stefanovski, D.; Hurcombe, S.D. Utility of cell-free DNA concentrations and illness severity scores to predict survival in critically ill neonatal foals. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0242635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ren, J.; Luo, N.; Guo, H.; Zheng, Y.; Li, J.; Tang, F.; Wen, L.; Peng, J. Comprehensive DNA methylation analysis of tissue of origin of plasma cell-free DNA by methylated CpG tandem amplification and sequencing (MCTA-Seq). Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, J.; Magenheim, J.; Neiman, D.; Zemmour, H.; Loyfer, N.; Korach, A.; Samet, Y.; Maoz, M.; Druid, H.; Arner, P. Comprehensive human cell-type methylation atlas reveals origins of circulating cell-free DNA in health and disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aucamp, J.; Bronkhorst, A.J.; Badenhorst, C.P.; Pretorius, P.J. The diverse origins of circulating cell-free DNA in the human body: A critical re-evaluation of the literature. Biol. Rev. 2018, 93, 1649–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kananen, L.; Hurme, M.; Bürkle, A.; Moreno-Villanueva, M.; Bernhardt, J.; Debacq-Chainiaux, F.; Grubeck-Loebenstein, B.; Malavolta, M.; Basso, A.; Piacenza, F. Circulating cell-free DNA in health and disease—The relationship to health behaviours, ageing phenotypes and metabolomics. GeroScience 2022, 45, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustanovich, A.; Schwartz, R.; Peretz, T.; Grinshpun, A. Life and death of circulating cell-free DNA. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Vaart, M.; Pretorius, P.J. Circulating Dna. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1137, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.-Y.; von Mühlenen, I.; Li, Y.; Kang, A.; Gupta, A.K.; Tyndall, A.; Holzgreve, W.; Hahn, S.; Hasler, P. Increased concentrations of antibody-bound circulatory cell-free DNA in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 1609–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, A.; Zangemeister-Wittke, U.; Stahel, R.A. Circulating DNA: A new diagnostic gold mine? Cancer Treat. Rev. 2002, 28, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, S.A.; Revach, M.; Ehrlich, G.E.; Adler, R.; Petersen, V.; Shapiro, B. DNA in synovial fluid and the circulation of patients with arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1981, 24, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Yoshida, K.; Hashiramoto, A.; Matsui, K. Cell-Free DNA in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atamaniuk, J.; Stuhlmeier, K.M.; Vidotto, C.; Tschan, H.; Dossenbach-Glaninger, A.; Mueller, M.M. Effects of ultra-marathon on circulating DNA and mRNA expression of pro-and anti-apoptotic genes in mononuclear cells. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 104, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atamaniuk, J.; Vidotto, C.; Kinzlbauer, M.; Bachl, N.; Tiran, B.; Tschan, H. Cell-free plasma DNA and purine nucleotide degradation markers following weightlifting exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 110, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atamaniuk, J.; Vidotto, C.; Tschan, H.; Bachl, N.; Stuhlmeier, K.M.; Müller, M.M. Increased concentrations of cell-free plasma DNA after exhaustive exercise. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 1668–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiter, T.; Fragasso, A.; Hudemann, J.; Nieß, A.M.; Simon, P. Short-term treadmill running as a model for studying cell-free DNA kinetics in vivo. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatouros, I.G.; Destouni, A.; Margonis, K.; Jamurtas, A.Z.; Vrettou, C.; Kouretas, D.; Mastorakos, G.; Mitrakou, A.; Taxildaris, K.; Kanavakis, E. Cell-free plasma DNA as a novel marker of aseptic inflammation severity related to exercise overtraining. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 1820–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatouros, I.G.; Jamurtas, A.Z.; Nikolaidis, M.G.; Destouni, A.; Michailidis, Y.; Vrettou, C.; Douroudos, I.I.; Avloniti, A.; Chatzinikolaou, A.; Taxildaris, K. Time of sampling is crucial for measurement of cell-free plasma DNA following acute aseptic inflammation induced by exercise. Clin. Biochem. 2010, 43, 1368–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, N.; Helmig, S.; Taenny, P.; Petry, J.; Schmidt, S.; Simon, P. Circulating, cell-free DNA as a marker for exercise load in intermittent sports. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmig, S.; Frühbeis, C.; Krämer-Albers, E.-M.; Simon, P.; Tug, S. Release of bulk cell free DNA during physical exercise occurs independent of extracellular vesicles. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 115, 2271–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, C.; Gee, E.; Bolwell, C. Horse Production. In Livestock Production in New Zealand: The Complete Guide to Dairy Cattle, Beef Cattle, Sheep, Deer, Goats, Pigs and Poultry.; Stafford, K., Ed.; Massey University Press: Auckland, New Zealand, 2017; p. 304. [Google Scholar]
- Frisbie, D.; Kawcak, C.; Baxter, G.; Trotter, G.; Powers, B.; Lassen, E.; McIlwraith, C. Effects of 6alpha-methylprednisolone acetate on an equine osteochondral fragment exercise model. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1998, 59, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar]
- Frisbie, D.; Kawcak, C.; Trotter, G.; Powers, B.; Walton, R.; McIlwraith, C. Effects of triamcinolone acetonide on an in vivo equine osteochondral fragment exercise model. Equine Vet. J. 1997, 29, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisbie, D.; Ghivizzani, S.; Robbins, P.; Evans, C.H.; McIlwraith, C. Treatment of experimental equine osteoarthritis by in vivo delivery of the equine interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene. Gene Ther. 2002, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, T.D. Guide for Veterinary Service and Judging of Equestrian Events, 3rd ed.; American Association of Equine Practitioners: Golden, CO, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Panizzi, L.; Vignes, M.; Dittmer, K.; Waterland, M.; Rogers, C.; Sano, H.; McIlwraith, C.; Pemberton, S.; Owen, M.; Riley, C. Infrared spectroscopy of serum fails to identify early biomarker changes in an equine model of traumatic osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. Open 2022, 4, 100297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldshtein, H.; Hausmann, M.J.; Douvdevani, A. A rapid direct fluorescent assay for cell-free DNA quantification in biological fluids. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2009, 46, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenvey, C.; Caraguel, C.; Howarth, G.; Riley, C. Identification of periparturient mare and foal associated predictors of post parturient immunoglobulin A concentrations in T horoughbred foals. Equine Vet. J. 2012, 44, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Boom, R.; Van De Lest, C.; Bull, S.; Brama, P.; Van Weeren, P.R.; Barneveld, A. Influence of repeated arthrocentesis and exercise on synovial fluid concentrations of nitric oxide, prostaglandin E2 and glycosaminoglycans in healthy equine joints. Equine Vet. J. 2005, 37, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemelä, T.M.; Tulamo, R.-M.; Carmona, J.U.; López, C. Evaluation of the effect of experimentally induced cartilage defect and intra-articular hyaluronan on synovial fluid biomarkers in intercarpal joints of horses. Acta Vet. Scand. 2019, 61, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emlen, W.; Mannik, M. Effect of DNA size and strandedness on the in vivo clearance and organ localization of DNA. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1984, 56, 185. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, I.; Burchell, R.; Worth, A.; Burton, S.; Gedye, K.; Clark, K.; Crosse, K.; Jack, M.; Odom, T.; De Grey, S. Kinetics of Plasma Cell-Free DNA and Creatine Kinase in a Canine Model of Tissue Injury. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayless, R.L.; Cooper, B.L.; Sheats, M.K. Investigation of plasma cell-free DNA as a potential biomarker in horses. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig 2022, 34, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- te Moller, N.C.; van Weeren, P.R. How exercise influences equine joint homeostasis. Vet. J. 2017, 222, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, H.; Cave, N.; Bridges, J.; Gedye, K.; Hill, K. Plasma NT-pro BNP and Cell-Free DNA Concentrations after Prolonged Strenuous Exercise in Working Farm Dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benesova, L.; Belsanova, B.; Suchanek, S.; Kopeckova, M.; Minarikova, P.; Lipska, L.; Levy, M.; Visokai, V.; Zavoral, M.; Minarik, M. Mutation-based detection and monitoring of cell-free tumor DNA in peripheral blood of cancer patients. Anal. Biochem. 2013, 433, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mattos-Arruda, L.; Cortes, J.; Santarpia, L.; Vivancos, A.; Tabernero, J.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Seoane, J. Circulating tumour cells and cell-free DNA as tools for managing breast cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, D.L.; Cave, N.J.; Gedye, K.R.; Bridges, J.P. Investigation of cell-free DNA in canine plasma and its relation to disease. Vet. Q. 2016, 36, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykgraaf, S.; Dechant, J.E.; Johns, J.L.; Christopher, M.M.; Bolt, D.M.; Snyder, J.R. Effect of intrathecal amikacin administration and repeated centesis on digital flexor tendon sheath synovial fluid in horses. Vet. Surg. 2007, 36, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steel, C.M. Equine synovial fluid analysis. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2008, 24, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilyeva, I.; Bespalov, V.; Von, J.; Semenov, A.; Tochilnikov, G.; Romanov, V.; Alvovsky, I.; Baranenko, D. Cell-free DNA Plasma levels differ in age-specific pattern in healthy rats and castrates with testosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia. Int. J. Genom. 2019, 2019, 8173630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.Y.; Hahn, S.; Kiefer, V.; Holzgreve, W. Is the quantity of circulatory cell-free DNA in human plasma and serum samples associated with gender, age and frequency of blood donations? Ann. Hematol. 2007, 86, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jylhävä, J.; Nevalainen, T.; Marttila, S.; Jylhä, M.; Hervonen, A.; Hurme, M. Characterization of the role of distinct plasma cell-free DNA species in age-associated inflammation and frailty. Aging Cell 2013, 12, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panizzi, L.; Dittmer, K.E.; Vignes, M.; Doucet, J.S.; Gedye, K.; Waterland, M.R.; Rogers, C.W.; Sano, H.; McIlwraith, C.W.; Riley, C.B. Plasma and Synovial Fluid Cell-Free DNA Concentrations Following Induction of Osteoarthritis in Horses. Animals 2023, 13, 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061053
Panizzi L, Dittmer KE, Vignes M, Doucet JS, Gedye K, Waterland MR, Rogers CW, Sano H, McIlwraith CW, Riley CB. Plasma and Synovial Fluid Cell-Free DNA Concentrations Following Induction of Osteoarthritis in Horses. Animals. 2023; 13(6):1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061053
Chicago/Turabian StylePanizzi, Luca, Keren E. Dittmer, Matthieu Vignes, Jennie S. Doucet, Kristene Gedye, Mark R. Waterland, Chris W. Rogers, Hiroki Sano, C. Wayne McIlwraith, and Christopher B. Riley. 2023. "Plasma and Synovial Fluid Cell-Free DNA Concentrations Following Induction of Osteoarthritis in Horses" Animals 13, no. 6: 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061053
APA StylePanizzi, L., Dittmer, K. E., Vignes, M., Doucet, J. S., Gedye, K., Waterland, M. R., Rogers, C. W., Sano, H., McIlwraith, C. W., & Riley, C. B. (2023). Plasma and Synovial Fluid Cell-Free DNA Concentrations Following Induction of Osteoarthritis in Horses. Animals, 13(6), 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061053




