Ethogram of the Chinese Giant Salamander during the Breeding Period Based on the PAE Coding System
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Observation Subjects
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Behavior Coding
3. Results
3.1. Posture Coding
3.2. Action Coding
3.3. Environmental Coding
3.4. Reproductive Ethogram and PAE Coding System
- (1)
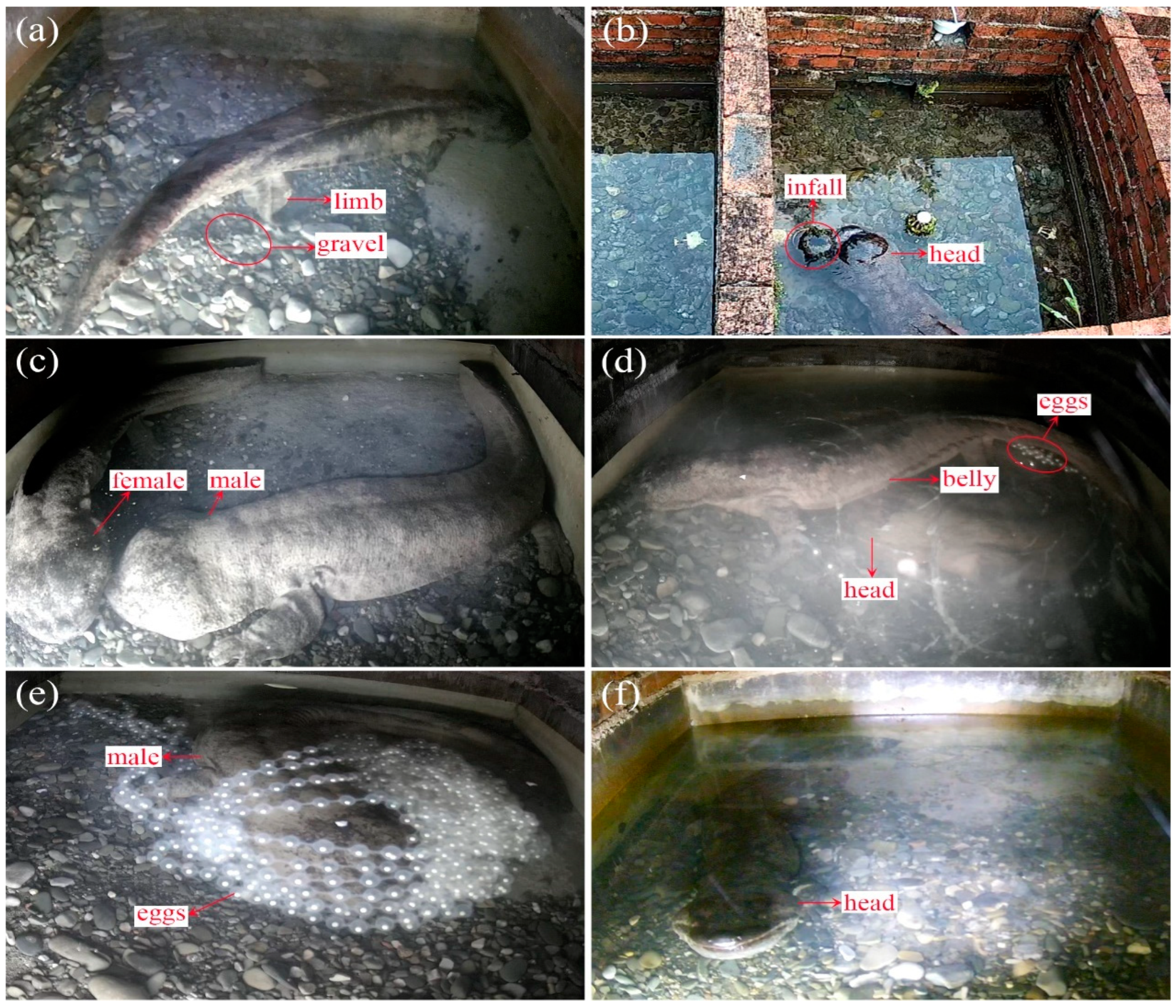
- Sand pushing: The male pushed gravel outward from the cave’s bottom with his head (Figure 2a), limbs, body, and tail.
- (2)
- Showering: The male crawled towards the water inlet, and different parts of their body, including the head, trunk, tail, bending, and head lifting, were continuously showered by the flowing water (Figure 2b).
- (3)
- Courtship: The male displayed an array of behaviors aimed at attracting and stimulating the female, such as knocking bellies side-by-side, riding, kissing (Figure 2c), following, etc.
- (4)
- (5)
- (6)
- Locomotion: The daily displacement behavior of A. davidianus, such as chasing, swimming, retreating, etc.
- (7)
- Ingestion: A. davidianus’s daily foraging behavior includes catching and swallowing.
- (8)
- Resting: A. davidianus maintains the same posture with its whole body in a relaxed state, such as bent resting, head-exposed resting, and lying resting.
- (9)
- Miscellaneous: At various stages, A. davidianus may exhibit behaviors such as vigilance, turning over, and breathing (Figure 2f).
4. Discussion
4.1. Reproductive Behavior of A. davidianus
4.2. PAE Coding System and Ethogram
4.3. The Ecological Law of Reproductive Behavior
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Behaviors | Males | Females | Time (Mth) | Number | PAE Code | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | A | E | |||||
| Sand-pushing behavior | |||||||
| Head pushing | + | 7–8 | 1 | 7 | 2, 3, 4, 15, 17, 18 | 1, 4, 5, 9 | |
| Limbs pushing | +++ | 7–8 | 2 | 7, 8 | 15, 17, 18, 21, 27 | 1, 4, 5, 9 | |
| Trunk pushing | + | 7–8 | 3 | 3, 7 | 14, 15, 16, 18, 21, 23, 27 | 1, 4, 5, 9 | |
| Tail pushing | + | 7–8 | 4 | 7, 8 | 15, 17, 18, 21, 27, 29, 30 | 1, 4, 5, 9 | |
| Showering behavior | |||||||
| Head showering | ++ | + | 7–8 | 5 | 2 | 3, 4, 15, 17 | 3, 5, 9 |
| Trunk showering | ++ | + | 7–8 | 6 | 2, 7 | 15, 17, 18, 21, 24 | 3, 5, 9 |
| Tail showering | ++ | + | 7–8 | 7 | 2 | 15, 17, 29, 32, 33 | 3, 5, 9 |
| Bend showering | + | + | 7–8 | 8 | 5, 7 | 15, 17, 18, 21 | 3, 5, 9 |
| Rising-head showering | + | + | 7–8 | 9 | 3, 4 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 14, 17 | 3, 5, 9 |
| Courtship behavior | |||||||
| Side-by-side | +++ | +++ | 7–8 | 10 | 2, 3 | 4, 14, 15, 17, 24 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 9, 10 |
| Knocking bellies | ++ | 7–8 | 11 | 7 | 2, 3, 4, 15, 17, 18, 19 | 1, 5, 9, 10 | |
| Riding | + | 7–8 | 12 | 3, 7 | 1, 4, 14, 16, 18 | 1, 5, 9, 10 | |
| Following | + | 7–8 | 13 | 7 | 3, 4, 5, 15, 17, 18 | 1, 5, 9, 10 | |
| Rolling over | + | 7–8 | 14 | 3, 6 | 14, 16, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 26 | 1, 5, 9, 10 | |
| Kissing | + | + | 7–8 | 15 | 2, 7 | 3, 4, 6, 15, 17, 18 | 1, 2, 5, 9, 10 |
| Inviting | ++ | 7–8 | 16 | 7 | 3, 4, 15, 17, 18 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 9, 10 | |
| Cohabiting | +++ | +++ | 7–8 | 17 | 1, 2 | 15, 17 | 1, 5, 9, 10 |
| Cloacal sniffing | ++ | 7–8 | 18 | 7 | 2, 3, 4, 6, 15, 17, 18 | 1, 5, 9, 10 | |
| Oviposition behavior | |||||||
| Riding | ++ | + | 8 | 19 | 3, 7 | 1, 4, 14, 16, 18 | 1, 5, 9, 10 |
| Kissing | + | + | 8 | 20 | 2, 7 | 3, 4, 6, 15, 17, 18 | 1, 5, 9, 10 |
| Knocking bellies | ++ | 8 | 21 | 7 | 2, 3, 4, 15, 17, 18, 19 | 1, 5, 9, 10 | |
| Intertwining | ++ | ++ | 8 | 22 | 5, 7 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 17, 18, 19, 21, 27, 29 | 1, 5, 9, 10 |
| Ovulating | + | 8 | 23 | 2, 3, 7 | 15, 17, 18, 21, 24, 25 | 1, 5, 9, 10 | |
| Ejaculating | + | 8 | 24 | 3, 7 | 15, 17, 18, 21, 24 | 1, 5, 9, 10 | |
| Fondling | + | 8 | 25 | 5, 7 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 15, 17, 18, 29, 31, 33 | 1, 5, 9, 10 | |
| Entwining eggs | ++ | 8 | 26 | 5, 7 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 17, 18, 21 | 1, 5, 9, 10 | |
| Detaining | + | 8 | 27 | 3, 7 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 10, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18 | 1, 2, 5, 9, 10 | |
| Cloacal sniffing | + | 8 | 28 | 7 | 2, 3, 4, 6, 15, 17, 18 | 1, 5, 9, 10 | |
| Vigilance | ++ | 8 | 29 | 3 | 4, 14, 17, 24 | 1, 2, 5, 9, 10 | |
| Parental care | |||||||
| Tail fanning | +++ | 8–10 | 30 | 3 | 4, 14, 16, 24, 29, 30 | 1, 5, 9, 10, 11 | |
| Agitating | ++ | 8–10 | 31 | 3, 7 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18 | 1, 5, 9, 10, 11 | |
| Shaking | + | 8–10 | 32 | 3, 7 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 14, 16, 18, 21, 23, 24, 28 | 1, 5, 9, 10, 11 | |
| Eggs eating | + | 8–10 | 33 | 3 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 17 | 1, 5, 9, 10, 11 | |
| Locomotive behavior | |||||||
| Chasing | + | + | 7–10 | 34 | 7, 9 | 4, 15, 17, 18 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 9, 10 |
| Following | + | + | 7–10 | 35 | 7 | 3, 4, 5, 15, 17, 18 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 9, 10 |
| Retreating | + | + | 7–10 | 36 | 7 | 2, 3, 15, 17, 18, 19 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 9, 10 |
| Swimming | + | + | 7–10 | 37 | 9 | 4, 15, 17, 18, 30 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 9, 10 |
| Ingestive behavior | |||||||
| Capturing | + | + | 7–10 | 38 | 10 | 1, 4, 9, 10, 12, 14, 17 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 9, 10 |
| Swallowing | + | + | 7–10 | 39 | 2, 3 | 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 9, 10 |
| Resting behavior | |||||||
| Resting with bending | ++ | ++ | 7–10 | 40 | 1, 2, 5 | 2, 15, 17, 21 | 1, 5, 9, 10 |
| Resting with head-exposed | + | + | 7–10 | 41 | 3, 4 | 1, 4, 14, 15, 17 | 1, 5, 9, 10 |
| Resting with lying | +++ | +++ | 7–10 | 42 | 1, 2 | 2, 4, 15, 17, 24 | 1, 5, 9, 10 |
| Miscellaneous behavior | |||||||
| Vigilance | ++ | ++ | 7–10 | 43 | 3 | 4, 14, 17, 24 | 1, 2, 5, 9, 10 |
| Rolling over | + | + | 7–10 | 44 | 3, 6 | 14, 16, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 26 | 1, 5, 9, 10 |
| Breathing | ++ | ++ | 7–10 | 45 | 3, 4 | 1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 14, 17, 24 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 9, 10 |
References
- Lorenz, K.Z. The fashionable fallacy of dispensing with description. Sci. Nat. 1973, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinbergen, N. On aims and methods of ethology. Z. Tierpsychol. 1963, 20, 410–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, P.N. Handbook of Ethological Methods; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.G. Behavior coding and ethogram of the Pere David’s deer. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2000, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell, S.M.; Poulin, A. Equid play ethogram. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2002, 78, 263–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settle, R.A.; Ettling, J.A.; Wanner, M.D.; Schuette, C.D.; Briggler, J.T.; Mathis, A. Quantitative Behavioral Analysis of First Successful Captive Breeding of Endangered Ozark Hellbenders. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 6, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.K.; Okada, S.; Fukuda, Y. From embryos to larvae: Seven-month-long paternal care by male Japanese giant salamander. J. Zool. 2017, 302, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Shu, G.; Huang, F.; He, L.; Li, C.; Xie, F. Courtship behaviour and male sexual competition of the Taliang crocodile newt, Liangshantriton taliangensis. Amphibia-Reptilia 2018, 39, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, A.; Pomchote, P.; Jamin, A. First reproduction of Panha’s crocodile newt Tylototriton panhai in captivity, with a description of the courtship behaviour, eggs and larval development. Herpetol. Bull. 2022, 159, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Z.L.; Zhang, H.H.; Ma, J.Z.; Wei, Q.G. PAE coding ethogram in breeding of semi-free-ranging Amur tiger (Panthera tigris altaica). Chin. J. Ecol. 2015, 34, 736–743. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Lü, X.; Wang, X.; Kou, W.; Miu, G.; Yuan, H. Behavioral ethogram and posture-act-environment coding system of Capricornis sumatraensis. Biodivers. Sci. 2021, 29, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.B.; Huang, Y.; Dong, X.; Li, J.G.; Zhou, C.Q. Ethogram and PAE coding system of Rostratula benghalensis in breeding period. Sichuan J. Zool. 2017, 36, 412–419. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.Z.; Chen, J.Z.; Fan, R.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, K.; Zhang, X.M.; Zeng, Q.; Lei, G.C. Ethogram and PAE (Posture-Act-Environment) coding system of Scaly-Sided Merganser during winter. Chin. J. Wildl. 2023, 44, 106–117. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Li, S.; Suo, L.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. An Ethogram of the Toad-headed Lizard Phrynocephalus vlangalii during the Breeding Season. Asian Herpetol. Res. 2011, 2, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wei, Y.L.; Wu, L.; Zheng, B.Y.; Li, J.H. PAE coding system-based ethogram of Yangtze finless porpoise (Neophocaena phocaenoides asiaeorientalis) in a semi-natural environment. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2015, 35, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.B.; Yan, W.B.; Yang, D.G. PAE coding system-based ethogram of Schicothorax wangchiachit. J. Fish. Sci. China 2018, 25, 294–300. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard, E. On a new gigantic salamander (Sieboldia Davidiana, Blanch.) from Western China. Ann. Maga. Nat. Hist. 1871, 8, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bòulenger, E.G. On a new giant salamander, living in the society’s gardens. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1924, 94, 173–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Lu, C.-Q.; Yi, M.-R.; Dai, N.-H.; Weng, X.-D.; Di, M.-X.; Peng, Y.; Tang, Y.; Shan, Q.-H.; Wang, K.; et al. Discovery of a wild, genetically pure Chinese giant salamander creates new conservation opportunities. Zool. Res. 2022, 43, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.A.; Xu, J.C.; Song, H.; Yi, H.R.; Li, J.Q.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Yang, D.C.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.J. A New Species of the Giant Salamander of the Genus Andrias from Qimeng, Anhui, China (Amphibia: Cryptorchiidae). Chin. J. Zool. 2023, 58, 651–657. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.J.; Wang, X.M.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.H.; Huang, S. Advances in conservation biology of Chinese giant salamander. Biodivers. Sci. 2002, 10, 291–297. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Cunningham, A.A.; Wei, G.; Yang, J.; Liang, Z.Q.; Wang, J.; Wu, M.Y.; Yan, F.; Xiao, H.B.; Harrison, X.A.; et al. Determining threatened species distributions in the face of limited data: Spatial conservation prioritization for the Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus). Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 3098–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Zhang, K.J.; Wang, Z.H.; Ding, Y.Z.; Wu, W.; Huang, S. The decline of the Chinese giant salamander Andrias davidianus and implications for its conservation. Oryx 2004, 38, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.Q.; Zhang, S.H.; Wang, C.R.; Wei, Q.W.; Wu, Y.A. Present situation of natural resources and protection recommendations of Andrias davidianus. Freshw. Fish. 2013, 43, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, G.; Geng, B.; Zhao, E. Andrias davidianus. In The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- National Forestry and Grassland Administration of China. Official Release of the Updated List of Wild Animals under Special State Protection in China. Available online: http://www.forestry.gov.cn/main/586/20210208/095403793167571.html (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- Zhang, H.X.; Wang, K.F.; Quan, Q.Z.; Fan, W.D.; Fang, S.M. Productive ecology and behavior of Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus). J. Shaanxi Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2006, 34, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, G.; Wu, F. The activity rhythm and reproductive behaviors of Andrias davidianus. Chin. J. Zool. 2010, 45, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q.H.; Tong, F.; Song, Y.J.; Wang, H.; Du, M.L.; Ji, H.B. Observation of the breeding behavior of the Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus) using a digital monitoring system. Animals 2018, 8, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.H.; Fu, L.; Jiang, W.S.; Zhou, L.Q.; Cao, W.; Tian, H.; Chen, R.G. Effects of water quality on the reproductive behavior and capacity of Andrias davidianus under tourism disturbance. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.G. Showering and Courtship Behavior and PAE Coding of Andrias davidianus during Early Reproductive Period. Master’s Thesis, The Shanxi Normal University, Xi’an, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, M.L.; Hu, L.J.; Shi, H.T.; Lin, L. Ethogram and PAE Coding System of Captive Beale’s Eyed Turtle (Sacalia bealei). Sichuan J. Zool. 2023, 43, 209–302. [Google Scholar]
- Flannigan, G.; Stookey, J. Day-time time budgets of pregnant mares housed in tie stalls: A comparison of draft versus light mares. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2002, 78, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, J.; Taguchi, Y.; Dixon, J.; Kuwabara, K.; Takahashi, M.K. Preoviposition paternal care in a fully aquatic giant salamander: Nest cleaning by a den master. J. Zool. 2019, 307, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.G.; Wang, Q.Z.; Liang, G. The washing behavior and its significance for male adult Andrias davidianus in the pre-reproductive period. Chin. J. Zool. 2013, 48, 529–533. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.X.; Wang, W.J.; Jiang, H.; Yang, A.S.; Bai, H.Q.; Wu, Z.C. Comparative experiments on the growth rate of male and female Andrias davidianus. J. Hydroecol. 2007, 27, 31–32. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, S.; Fukuda, Y.; Takahashi, M.K. Paternal care behaviors of Japanese giant salamander Andrias japonicus in natural populations. J. Ethol. 2015, 33, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, S.; Jachowski, C.M.B.; Diaz, L.; Williams, L.A. Shelter Guarding Behavior of the Eastern Hellbender (Cryptobranchus alleganiensis alleganiensis) in North Carolina Streams. Southeast. Nat. 2020, 19, 742–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.Y.; Nui, K.F.; Luen, T.C.; Mouyu, Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.G.; Yang, Y.Q. Behavior coding and ethogram of Guizhou snub-nosed monkey (Rhinopithecus brelichi). Sichuan J. Zool. 2014, 33, 815–828. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.D.; Li, Y.; Hunag, J.Y.; Bai, W.K.; Zhou, S.Q.; Li, Y.H.; Zhou, C. Behavior coding and ethogram of the sambar (Rusa unicolor) in field environment. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2018, 38, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, K.Q.; Shubin, N.H. Earliest known crown-group salamanders. Nature 2003, 422, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L.; Luo, L.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.F.; Zhai, X.L.; Xue, Y. Advance on the artificial breeding technologies of Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus). Chin. Fish. Qual. Stand. 2018, 8, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q.H. Habitat characteristics of Andrias davidianus in Zhangjiajie of China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 20, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.L.; Jang, F.J.; Wang, B.L. Investigation on natural breeding habits of Chinese giant salamander. J. Hydroecol. 2000, 112, 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y.R.; Zheng, H.X. Natural breeding cycle of the giant salamander (Andrias davidianus). J. Henan Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 1994, 22, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Kobara, J.; Ashikaga, K. The Study about Protection of the Japanese Giant Salamander in Hiroshima Prefecture. J. Jpn. Assoc. Zoos Aquar. 1980, 22, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Browne, R.K.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Okada, S.; Hime, P.; McMillan, A.; Wu, M.; Diaz, R.; McGinnity, D.; Briggler, J.T. The giant salamanders (Cryptobranchidae): Part B. Biogeography, ecology and reproduction. Amphib. Reptile Conserv. 2014, 5, 30–50. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Aravena, M.; Gonzalez-Mendez, A.; Estay, S.A.; Gaitán-Espitia, J.D.; Barria-Oyarzo, I.; Bartheld, J.L.; Bacigalupe, L.D. Impact of global warming at the range margins: Phenotypic plasticity and behavioral thermoregulation will buffer an endemic amphibian. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 4467–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.X.; Wang, K.F.; Quan, Q.Z.; Fang, S.M.; Jing, Y.L. The research on ecological breeding engineering technology of the Chinese giant salamander in Qinling Mountain area. Freshw. Fish 2003, 33, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Mou, H.M.; Li, Y.; Yao, J.J.; Ma, S. A review: Current research on biology of Chinese giant salamander. Fish. Sci. 2011, 30, 513–516. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.C. New technology of mass reproduction of Andrias davidianus. Hebei Fish. 2004, 135, 33–34+41. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.M. A probe into the spawning season of Andrias davidianus. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2003, 27, 211–213. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q.H.; Liu, Q.B.; Liu, Y.; Luo, H.; Tang, C.C. Preliminary study on ecological conditions in breeding den of Chinese giant salamander. Chin. J. Zool. 2007, 42, 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.X.; Shen, J.Z.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Q.J.; Kouba, A.; Willard, S.T. Water temperature of ecological-imitated breeding of parent Andrias davidianus in Qinba Mountains. J. Hydroecol. 2012, 33, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.Y.; Xiao, H.B.; Lin, X.Z.; Yang, Y.Q. Preliminary report on improving the oxytocin rate of Andrias davidianus under artificial ecological conditions. Freshw. Fish. 1993, 23, 11–12. [Google Scholar]

| Posture | Definition | Code |
|---|---|---|
| Lying | The limbs are bent and tightened, so the whole body is pressed against the cave’s bottom. | 1 |
| Groveling | The forelimbs are slightly upright, the torso and tail are close to the cave’s bottom, and there is a small distance between the head and the cave’s bottom; the top of the head has not emerged from the water. | 2 |
| Bracing | The forelimbs, or hind limbs, are extended, causing the head and trunk to maintain a certain distance from the cave’s bottom. | 3 |
| Head exposing | The head emerges above the water’s surface. | 4 |
| Bending | The head, torso, and tail form an arc. | 5 |
| Flipping | A. davidianus tips over from the side of his body. | 6 |
| Crawling | A. davidianus displaces its body by swaying its limbs back and forth. | 7 |
| Digging | A. davidianus repeatedly glides its four limbs along the ground and alternately planes the bottom surface back and forth. | 8 |
| Swimming | A. davidianus paddles in the water with its front and hind limbs, propelling its body forward. | 9 |
| Leaping | A. davidianus made a forward leap. | 10 |
| Body Position | Action | Code |
|---|---|---|
| Head | Rising head | 1 |
| Lowering head | 2 | |
| Head swing | 3 | |
| Extending forward | 4 | |
| Torsion head | 5 | |
| Mouth | Kissing | 6 |
| Inhaling | 7 | |
| Exhaling | 8 | |
| Opening mouth | 9 | |
| Closing mouth | 10 | |
| Swallowing | 11 | |
| Biting | 12 | |
| Holding | 13 | |
| Limbs | Forelegs stand | 14 |
| Forelegs bend | 15 | |
| Hindlegs stand | 16 | |
| Hindlegs bend | 17 | |
| Swing back-forth | 18 | |
| Swing left-right | 19 | |
| Unilateral straight brace | 20 | |
| Trunk | Bending | 21 |
| Hunch-up | 22 | |
| Tilting | 23 | |
| Stretching | 24 | |
| Trembling | 25 | |
| Turning | 26 | |
| Twisting | 27 | |
| Wobbling | 28 | |
| Tall | Contorting | 29 |
| Swing | 30 | |
| Upwarping | 31 | |
| Extending | 32 | |
| Leaning | 33 |
| Environment | Abiotic | Biotic | Code | Attribute |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cave | √ | 1 | Area (0.8~1.5) m2 Height (0.30~0.38) m | |
| Cave mouth | √ | 2 | Width (0.25~0.35) m High (0.30~0.35) m | |
| Stream | √ | 3 | Length (20~22) m Width (0.9~1.5) m | |
| Bottom material | √ | 4 | Sand, pebbles | |
| Waterbody | √ | 5 | Water depth (0.3~0.4) m WT (16.9~22.8) °C DO (5.50~9.25) mg/L pH 6.58~7.70 | |
| Island | √ | 6 | Substrate: sand, pebbles Vegetation covers 30% | |
| Creek bank | √ | 7 | The slope of both sides 60~90° | |
| Bait | √ | √ | 8 | Live fish/fish pieces/chicken embryos |
| Adult male | √ | 9 | 7–11 years old Weight (6.9~12.6) kg Body length (1.03~1.28) m | |
| Adult female | √ | 10 | ||
| Eggs | √ | 11 | Bead-like |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tian, H.; Luo, Q. Ethogram of the Chinese Giant Salamander during the Breeding Period Based on the PAE Coding System. Animals 2023, 13, 3632. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233632
Luo S, Wang P, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Tian H, Luo Q. Ethogram of the Chinese Giant Salamander during the Breeding Period Based on the PAE Coding System. Animals. 2023; 13(23):3632. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233632
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Shouliang, Pei Wang, Yifang Zhang, Ziteng Wang, He Tian, and Qinghua Luo. 2023. "Ethogram of the Chinese Giant Salamander during the Breeding Period Based on the PAE Coding System" Animals 13, no. 23: 3632. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233632
APA StyleLuo, S., Wang, P., Zhang, Y., Wang, Z., Tian, H., & Luo, Q. (2023). Ethogram of the Chinese Giant Salamander during the Breeding Period Based on the PAE Coding System. Animals, 13(23), 3632. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233632





