Tissue Distributions and Toxic Effects of Hexavalent Chromium in Laboratory-Exposed Periwinkle (Littorina littorea Linnaeus)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Organism
2.2. Laboratory Exposure of Periwinkles to Hexavalent Chromium
2.3. Determination of Levels of Chromium in Periwinkle Tissues
2.4. Determination of Condition Index (CI)
2.5. Determination of Proximate Compositions of Periwinkle Tissues
2.6. Histopathological Analyses of the Soft Tissue
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Mortality Rate
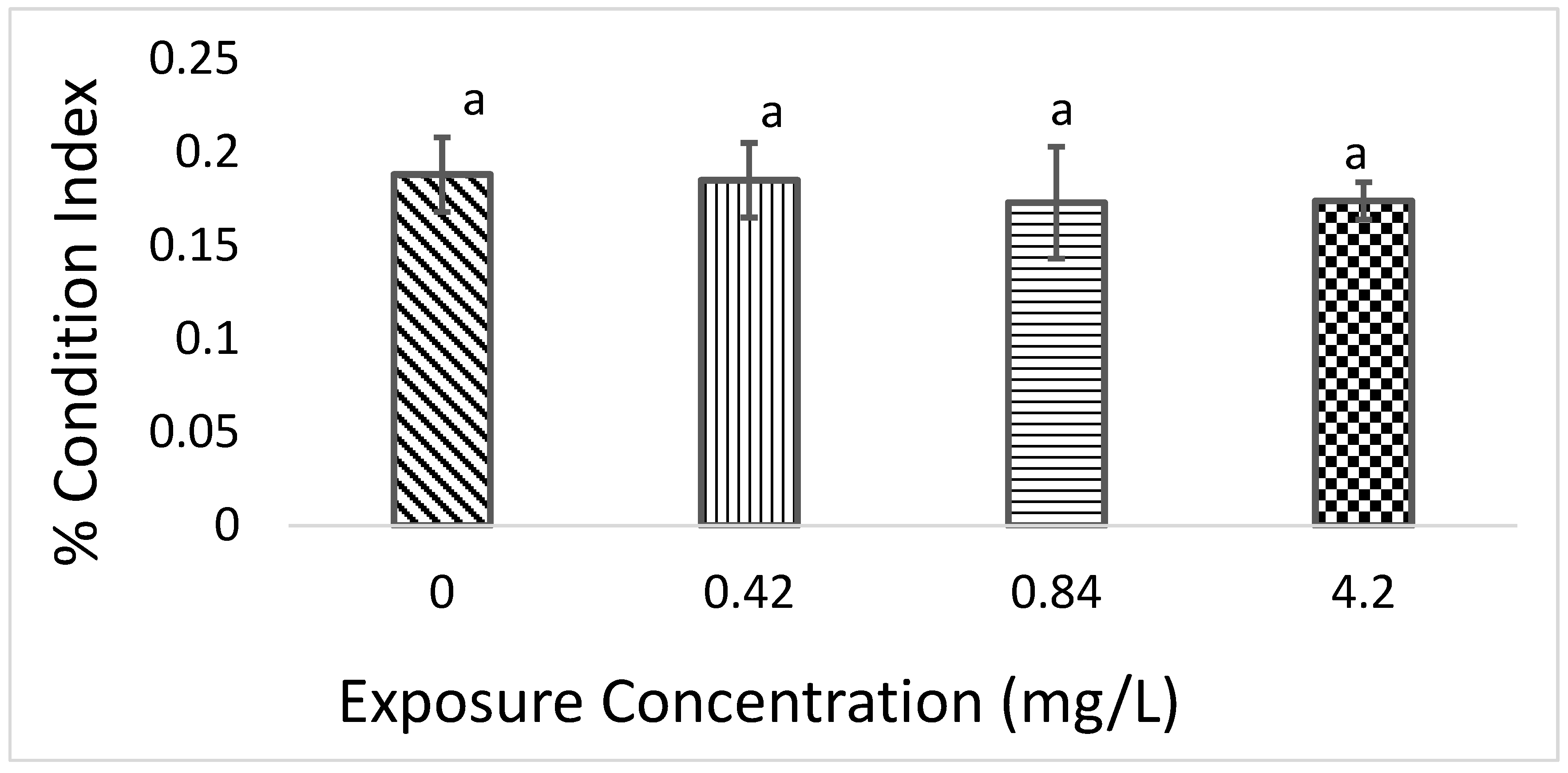
3.2. Condition Index (CI)
3.3. Tissue Accumulation of Total Chromium in L. littorea Exposed to Sublethal Concentrations
3.4. Proximate Compositions of the Tissues
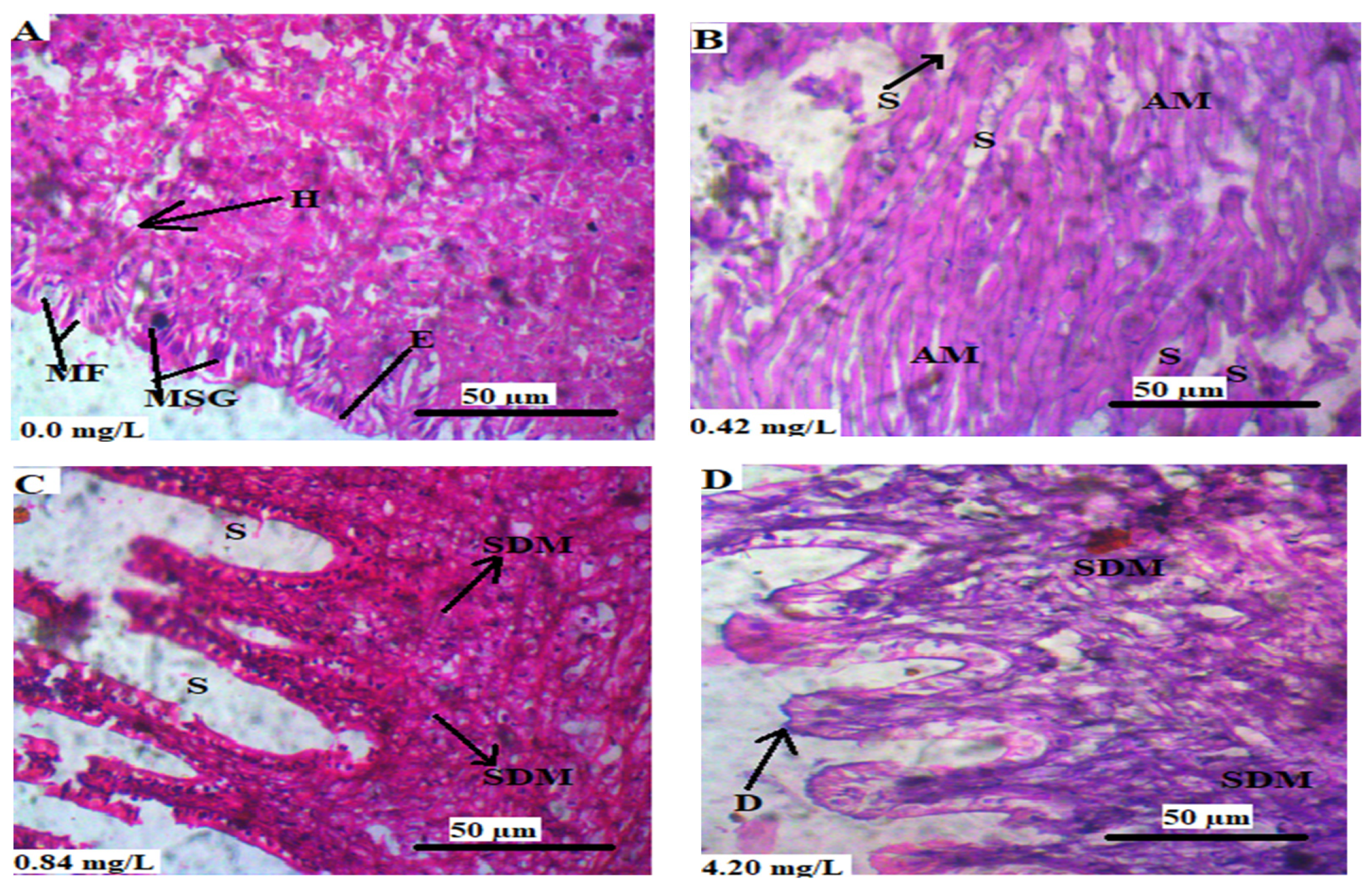
3.5. Histopathology of the Soft Tissues of L. littorea
3.5.1. Brain
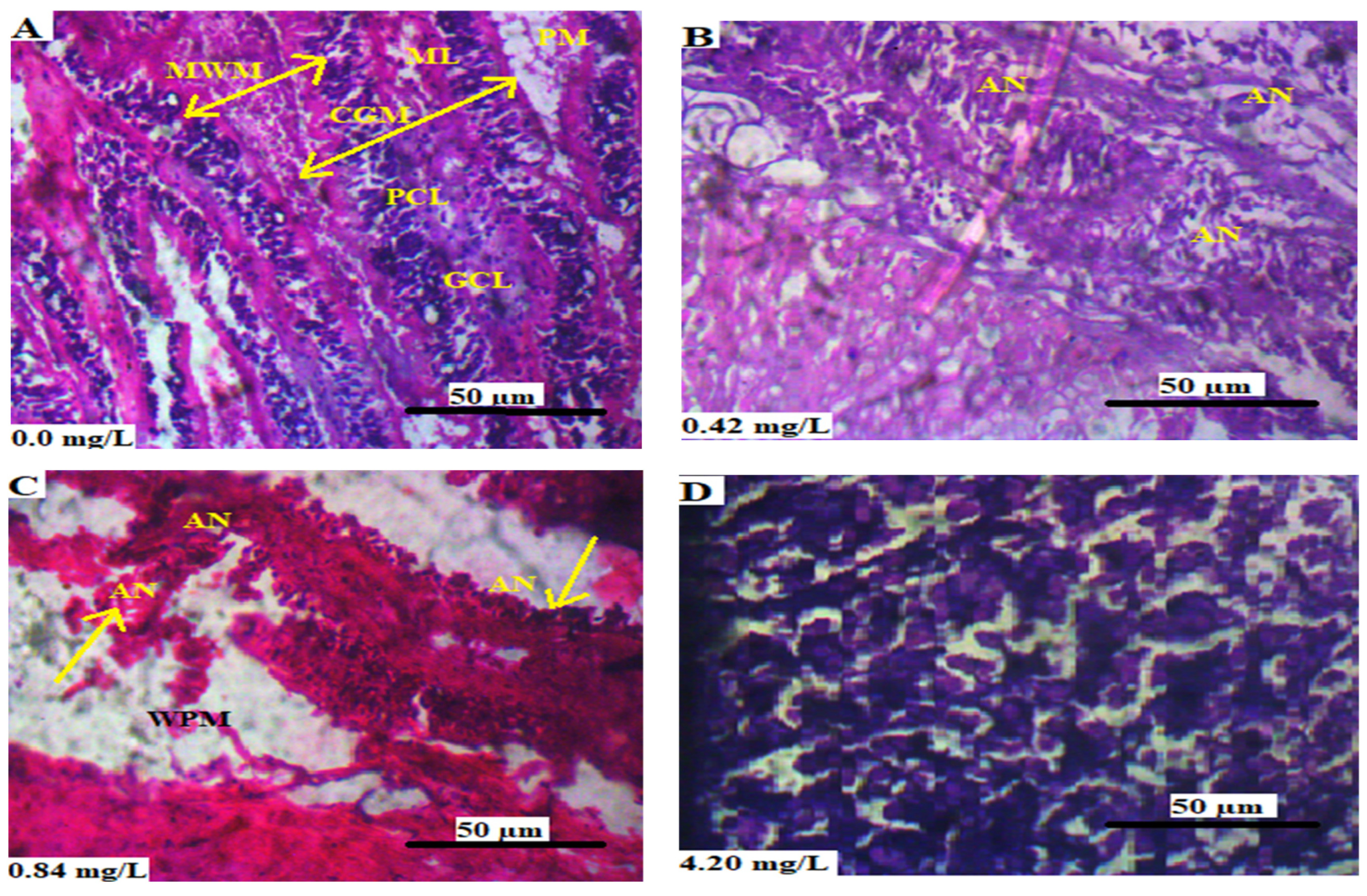
3.5.2. Gills
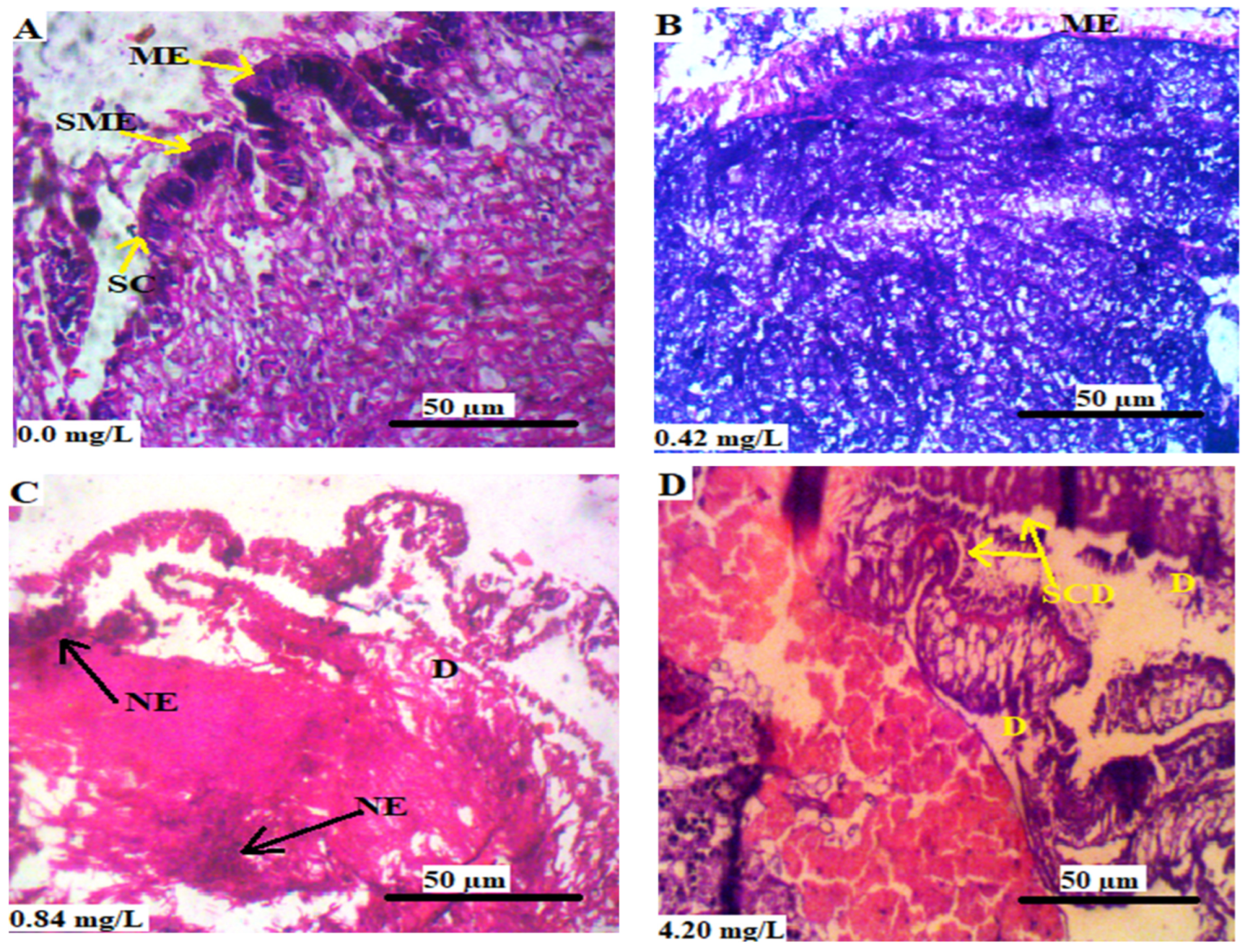
3.5.3. Mantle
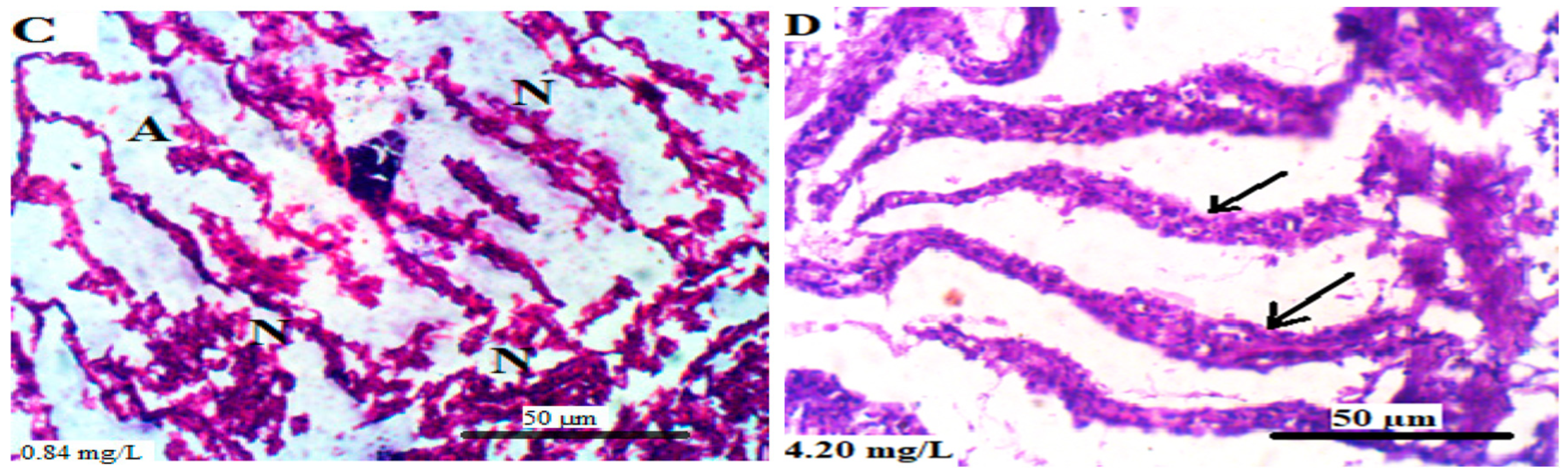
3.5.4. Intestine
3.5.5. Foot
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stohs, S.J.; Bagchi, D.; Hassoun, E.; Bagchi, M. Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of chromium and cadmium ions. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2001, 20, 201–213. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, C.C.; Gómez, M.E.B.; Zavala, A.H. Hexavalent chromium: Regulation and health effects. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2021, 65, 126729. [Google Scholar]
- Topcuoğlu, S.; Kırbaşoğlu, Ç.; Güngör, N. Heavy metals in organisms and sediments from Turkish Coast of the Black Sea, 1997–1998. Environ. Int. 2002, 27, 521–526. [Google Scholar]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological Profile for Chromium. 2012. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp7.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Shekhawat, K.; Chatterjee, S.; Joshi, B. Chromium toxicity and its health hazards. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 3, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, C.A.M.; Cardoso, P.C.S.; Cunha, L.A.; Gomes, C.F.; Ribeiro Junior, R.F.G.; Pinheiro, R.H.; Costa, M.H.P.; Burbano, R.R. Mutagenic effects of potassium dichromate as evaluated by means of animal and plant bioindicators. In Vivo 2015, 29, 729–735. [Google Scholar]
- IARC. Lista de Classificações da IARC. 2018. Available online: http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/latest_classif.php (accessed on 26 August 2023).
- Singh, P.; Itankar, N.; Patil, Y. Biomanagement of hexavalent chromium: Current trends and promising perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111547. [Google Scholar]
- National Toxicological Program. Reports on Carcinogens: Hexavalent Chromium Compounds. 2021. Available online: https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/sites/default/files/ntp/roc/content/profiles/chromiumhexavalentcompounds.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Onchoke, K.K.; Sasu, S.A. Determination of Hexavalent Chromium (Cr (VI)) concentrations via ion chromatography and UV-Vis spectrophotometry in samples collected from Nacogdoches wastewater treatment plant, East Texas (USA). Adv. Environ. Chem. 2016, 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Miyake, Y.; Tokumura, M.; Iwazaki, Y.; Wang, Q.; Amagai, T.; Horii, Y.; Otsuka, H.; Tanikawa, N.; Kobayashi, T.; Oguchi, M. Determination of hexavalent chromium concentration in industrial waste incinerator stack gas by using a modified ion chromatography with post-column derivatization method. J. Chromatogr. A. 2017, 1502, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zewdu, F.; Amare, M. Determination of the level of hexavalent, trivalent, and total chromium in the discharged effluent of Bahir Dar tannery using ICP-OES and UV–Visible spectrometry. Cogent Chem. 2018, 4, 1534566. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhary, P.; Yadav, A.; Singh, R.; Chandra, R.; Singh, D.P.; Raj, A.; Bharagava, R.N. Stress response of Triticum aestivum L. and Brassica juncea L. against heavy metals growing at distillery and tannery wastewater contaminated site. Chemosphere 2018, 206, 122–131. [Google Scholar]
- Sardiña, P.; Leahy, P.; Metzeling, L.; Stevenson, G.; Hinwood, A. Emerging and legacy contaminants across land-use gradients and the risk to aquatic ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133842. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, S.; Fowler, S.W.; Behbehani, M. An assessment of microplastic inputs into the aquatic environment from wastewater streams. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111538. [Google Scholar]
- Arunachalam, K.D.; Annamalai, S.K.; Kuruva, J.K. In vivo evaluation of hexavalent chromium induced DNA damage by alkaline comet assay and oxidative stress in Catla catla. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 9, 470–482. [Google Scholar]
- Nagpure, N.S.; Srivastava, R.; Kumar, R.; Kushwaha, B.; Srivastava, S.K.; Kumar, P.; Dabas, A. Assessment of genotoxic and mutagenic potential of hexavalent chromium in the freshwater fish Labeo rohita (Hamilton, 1822). Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 38, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, J.A.D.N.; Cunha, L.A.D.; Costa, M.H.P.D.; Reis, H.S.D.; Aguiar, A.C.D.S.; Oliveira-Bahia, V.R.L.; Burbano, R.M.R.; Rocha, C.A.M.D. Mutagenic and histopathological effects of hexavalent chromium in tadpoles of Lithobates catesbeianus (Shaw, 1802) (Anura, Ranidae). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 400–407. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando, V.A.; Weerasena, J.; Lakraj, G.P.; Perera, I.C.; Dangalle, C.D.; Handunnetti, S.; Wijesinghe, M.R. Lethal and sub-lethal effects on the Asian common toad Duttaphrynus melanostictus from exposure to hexavalent chromium. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 177, 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.W.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, D.C.; Lim, H.J.; Kang, J.C. Toxic effects on oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, stress, and immune responses in juvenile olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus, exposed to waterborne hexavalent chromium. Biology 2022, 11, 766. [Google Scholar]
- Chaâbane, M.; Bejaoui, S.; Trabelsi, W.; Telahigue, K.; Chetoui, I.; Chalghaf, M.; Zeghal, N.; Soudani, N. The potential toxic effects of hexavalent chromium on oxidative stress biomarkers and fatty acids profile in soft tissues of Venus verrucosa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 196, 110562. [Google Scholar]
- Ogungbenle, H.N.; Omowole, B.M. Chemical, functional and amino acid composition of periwinkle (Tympanotonus fuscatus var radula) meat. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2012, 13, 128–132. [Google Scholar]
- Nwaka, S.U.; Udoh, J.P. Evaluation of Nutritional Profile of Periwinkle (Tympanotonus fuscatus) from Ekeuku Market, Owerri, Imo State. J. Aquat. Sci. 2022, 37, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Noventa, S.; Pavoni, B.; Galloway, T.S. Periwinkle (Littorina littorea) as a sentinel species: A field study integrating chemical and biological analyses. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2634–2640. [Google Scholar]
- Ololade, I.A.; Lajide, L.; Olumekun, V.O.; Ololade, O.O.; Ejelonu, B.C. Influence of diffuse and chronic metal pollution in water and sediments on edible seafoods within Ondo oil-polluted coastal region, Nigeria. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2011, 46, 898–908. [Google Scholar]
- Ayanda, I.O.; Ekhator, U.I.; Bello, O.A. Determination of selected heavy metal and analysis of proximate composition in some fish species from Ogun River, Southwestern Nigeria. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02512. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazala, G.; Sultana, S.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Mahboob, S. The effect of profenofos on the nutritive composition of major carp for estimating maximum allowable toxicant concentration of the pesticide. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Adeyemi, J.A.; Deaton, L.E. The effect of cadmium exposure on digestive enzymes in the Eastern oyster Crassostrea virginica. J. Shellfish Res. 2012, 31, 631–634. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, C.; Bourgeault, A.; Gourlay-Francé, C.; Palais, F.; Geffard, A.; Vincent-Hubert, F. Seasonal and PAH impact on DNA strand-break levels in gills of transplanted zebra mussels. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 92, 18–26. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Association of Official Analytical Chemist, Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, ML, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Adeyemi, J.A.; Olise, C.C.; Bamidele, O.S.; Akinola, B.K. Effect of ultraviolet photoxidation of cypermethrin on the activities of phosphatases and digestive enzymes, and intestinal histopathology in African cat fish, Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822). J. Exp. Zool. 2020, 333, 543–549. [Google Scholar]
- Jindal, R.; Handa, K. Hexavalent chromium-induced toxic effects on the antioxidant levels, histopathological alterations and expression of Nrf2 and MT2 genes in the branchial tissue of Ctenopharyngodon idellus. Chemosphere 2019, 230, 144–156. [Google Scholar]
- Aliu, C.; Ajayi, O.O.; Olawuyi, T.S.; Gbadamosi, O.K.; Barbosa, F.; Adedire, C.O.; Adeyemi, J.A. Tissue accumulation, cytotoxicity, oxidative stress, and immunotoxicity in African catfish, Clarias gariepinus exposed to sublethal concentrations of hexavalent chromium. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehr, S.; Kosfeld, V.; Schlechtriem, C. Bioaccumulation assessment of nanomaterials using freshwater invertebrate species. Environ. Sci. Europe. 2021, 33, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Shahjahan, M.; Taslima, K.; Rahman, M.S.; Al-Emran, M.; Alam, S.I.; Faggio, C. Effects of heavy metals on fish physiology—A review. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134519. [Google Scholar]
- Gundacker, C. Comparison of heavy metal bioaccumulation in freshwater molluscs of urban river habitats in Vienna. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 110, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Vernon, E.L.; Jha, A.N.; Ferreira, M.F.; Slomberg, D.L.; Malard, V.; Grisolia, C.; Payet, M.; Turner, A. Bioaccumulation, release and genotoxicity of stainless steel particles in marine bivalve molluscs. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134914. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, R.A.F.; Valentin, J.L.; Figueiredo, G.M.; Hegaret, H. Responses of the common periwinkle Littorina littorea to exposure to the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum. J. Mollus. Stud. 2015, 81, 308–311. [Google Scholar]
- Świacka, K.; Michnowska, A.; Maculewicz, J.; Caban, M.; Smolarz, K. Toxic effects of NSAIDs in non-target species: A review from the perspective of the aquatic environment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 115891. [Google Scholar]
- Gorbi, S.; Baldini, C.; Regoli, F. Seasonal variability of metallothioneins, cytochrome P450, bile metabolites and oxyradical metabolism in the European eel Anguilla anguilla L.(Anguillidae) and striped mullet Mugil cephalus L. (Mugilidae). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2005, 49, 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Xin, T.; Wan, B.; Xia, B.; Zhong, L.; Zou, Z. The metabolism and detoxification effects of lead exposure on Aleurolyphus ovatus (Acari: Acaridae) via transcriptome analysis. Chemosphere 2023, 333, 138886. [Google Scholar]
- Velma, V.; Tchounwou, P.B. Chromium-induced biochemical, genotoxic and histopathologic effects in liver and kidney of goldfish, Carassius auratus. Mutat. Res. 2010, 698, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Domingues, I.; Oliveira, R.; Lourenço, J.; Grisolia, C.K.; Mendo, S.; Soares, A.M.V.M. Biomarkers as a tool to assess effects of chromium (VI): Comparison of responses in zebrafish early life stages and adults. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 152, 338–345. [Google Scholar]
- Byrd, K.; Fakoya, K.; Akintola, S.; Westlund, L.; Isa, S.; Cohen, P. The Role of Small-Scale Fisheries in Nigeria’s Food System. WorldFish Technical Report. 2022. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12348/5270 (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Karbalaei, S.; Karami, A.; Ebrahimi, M.; Jahromi, M.F.; Ismail, A.; Liang, J.B.; Simpson, S.L.; Ismail, S.N.S.; Goh, Y.M. Changes in nutritional parameters in diploid and triploid African catfish Clarias gariepinus following chlorpyrifos exposure. Aquat. Biol. 2017, 26, 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Sohail, M.; Khan, M.N.; Chaudhry, A.S.; Qureshi, N.A. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and analysis of mineral element alongside proximate composition in foot, gills and mantle of freshwater mussels (Anodonta anatina). Rendiconti Lincei 2016, 27, 687–696. [Google Scholar]
- Jeyanthi, V.; Paul, J.A.J.; Selvi, B.K.; Karmegam, N. Comparative study of biochemical responses in three species of earthworms exposed to pesticide and metal contaminated soil. Environ. Process. 2016, 3, 167–178. [Google Scholar]
- Maurya, P.K.; Malik, D.S.; Yadav, K.K.; Gupta, N.; Kumar, S. Haematological and histological changes in fish Heteropneustes fossilis exposed to pesticides from industrial waste water. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2019, 25, 1251–1278. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, S.A. Histopathology and heavy metal bioaccumulation in some tissues of Luciobarbus xanthopterus collected from Tigris River of Baghdad, Iraq. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2020, 46, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Velma, V.; Vutukuru, S.S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Ecotoxicology of hexavalent chromium in freshwater fish: A critical review. Rev. Environ. Health. 2009, 24, 129–145. [Google Scholar]
- Muthukumaravel, K.; Rajaraman, P. A study on the toxicity of chromium on the histology of gill and liver of freshwater fish Labeo rohita. J. Pure Appl. Zool. 2013, 1, 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- Bakshi, A.; Panigrahi, A.K. A comprehensive review on chromium induced alterations in fresh water fishes. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 440–447. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, S.; Antunes, S.C.; Nunes, B.; Correia, A.T. Histological alterations in gills and liver of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) after exposure to the antibiotic oxytetracycline. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 53, 164–176. [Google Scholar]


| Concentration of Cr6+ (mg/L) | Percentage Mortality (Inactive) of L. littorea per Day | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 96 h | |
| Control | 0.00 ± 0.0 a | 0.00 ± 0.0 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| 3.5 | 15.00 ± 5.7 b | 15.00 ± 5.8 b | 52.50 ± 5.0 b | 55.00 ± 5.8 b |
| 7.0 | 22.50 ± 5.0 b,c | 35.00 ± 17.3 c | 52.50 ± 5.0 b | 65.00± 5.8 c |
| 10.5 | 32.50 ± 9.5 c,d | 45.00 ± 17.3 c | 70.00 ± 11.5 c | 75.00± 5.8 d |
| 14.0 | 35.00 ± 5.8 c,d | 67.50 ± 5.00 d | 75.00 ± 5.8 c | 85.00 ± 5.8 e |
| 17.5 | 35.00 ± 5.8 c,d | 85.00 ± 5.8 e | 85.00 ± 5.8 d | 85.00 ± 5.0 e |
| 21.0 | 45.00 ± 17.6 d | 95.00 ± 5.8 e | 95.00 ± 5.8 e | 95.00 ± 5.8 f |
| Exposure Concentration (mg/L) | Tissue Accumulation (µg/g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain | Foot | Gills | Intestine | Mantle | |
| Control | 0.67 ± 0.03 a,C | 0.30 ± 0.03 a,A | 0.40 ± 0.08 a,A,B | 0.57 ± 0.05 a,B | 0.46 ± 0.05 a,A,B |
| 0.42 | 0.78 ± 0.05 a,C | 0.45 ± 0.06 a,b,A,B | 0.41 ± 0.09 a,A | 0.64 ± 0.05 a,B,C | 0.58 ± 0.05 a,A,B |
| 0.8 | 0.74 ± 0.02 a,C | 0.39 ± 0.05 a,b,A | 0.48 ± 0.14 a,A,B | 0.66 ± 0.04 a,B,C | 0.57 ± 0.02 a,A,B,C |
| 4.2 | 0.70 ± 0.06 a,B | 0.48 ± 0.05 b,A | 0.46 ± 0.05 a,A | 0.69 ± 0.06 a,B | 0.54 ± 0.06 a,A,B |
| Body Part | Conc. (mg/L) | Protein (%) | Carbohydrate (%) | Lipid (%) | Fiber (%) | Moisture (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain | Control | 29.89 ± 1.69 c | 4.74 ± 0.86 a | 1.32 ± 0.02 a,b | 6.05 ± 0.18 c | 58.00 ± 1.00 a |
| 0.42 | 22.63 ± 0.32 b | 7.19 ± 0.23 b | 2.63 ± 0.29 c | 3.55 ± 0.10 a | 64.00 ± 0.00 b | |
| 0.8 | 22.66 ± 0.57 b | 8.12 ± 0.73 b,c | 1.39 ± 0.04 b | 3.82 ± 0.18 a | 64.00 ± 0.00 b | |
| 4.2 | 19.38 ± 0.02 a | 9.50 ± 1.66 c | 1.08 ± 0.02 a | 4.37 ± 0.16 b | 65.66 ± 1.53 b | |
| Foot | Control | 22.68 ± 0.28 c | 12.85 ± 0.87 a | 1.71 ± 0.58 a | 2.42 ± 0.25 a | 60.33 ± 1.15 a,b |
| 0.42 | 20.94 ± 0.25 b | 11.72 ± 0.52 a | 2.90 ± 0.06 b | 2.78 ± 0.14 a,b | 61.66 ± 0.58 b | |
| 0.8 | 21.18 ± 1.22 b | 14.07 ± 0.23 b | 1.56 ± 0.01 a | 3.51 ± 0.80 b | 59.66 ± 1.15 a | |
| 4.2 | 19.18 ± 0.49 a | 14.00 ± 0.36 b | 1.96 ± 0.01 a | 5.86 ± 0.51 c | 59.00 ± 0.00 a | |
| Gills | Control | 32.15 ± 0.30 c | 4.50 ± 0.50 b | 1.96 ± 0.00 a | 2.39 ± 0.38 a | 59.00 ± 0.00 a |
| 0.42 | 25.56 ± 0.40 b | 2.42 ± 0.40 a | 9.85 ± 0.00 d | 3.17 ± 0.36 a,b | 59.00 ± 0.00 a | |
| 0.8 | 25.42 ± 0.18 b | 4.36 ± 0.56 b | 7.43 ± 0.38 c | 3.80 ± 0.33 b | 59.00 ± 0.00 a | |
| 4.2 | 15.36 ± 0.06 a | 9.36 ± 0.50 c | 5.74 ± 0.19 b | 2.54 ± 0.54 a | 67.00 ± 0.00 b | |
| Intestine | Control | 28.12 ± 0.59 c | 7.90 ± 0.57 a | 1.88 ± 0.21 a | 3.10 ± 0.55 a | 59.00 ± 0.00 a,b |
| 0.42 | 27.91 ± 0.91 c | 6.72 ± 0.88 a | 2.41 ± 0.01 a | 6.29 ±2.28 a,b | 56.66 ± 4.04 a | |
| 0.8 | 21.11 ± 0.06 b | 9.58 ± 0.11 b | 3.62 ± 0.05 b | 5.03 ± 1.33 a,b | 60.66 ± 1.15 a,b | |
| 4.2 | 10.61 ± 0.22 a | 10.70 ± 0.71 b | 7.39 ± 1.12 c | 8.30 ± 2.28 b | 63.00 ± 1.00 b | |
| Mantle | Control | 18.16 ± 0.24 a | 11.51 ± 0.94 b | 4.81 ± 0.69 a | 2.51 ± 0.50 a | 63.00 ± 0.00 b |
| 0.42 | 17.66 ± 0.12 a | 11.33 ± 0.33 b | 9.22 ± 0.55 b | 2.79 ± 0.30 a | 59.00 ± 0.00 a | |
| 0.8 | 17.90 ± 0.42 a | 10.56 ± 0.30 b | 9.54 ± 0.58 b,c | 3.01 ± 0.67 a | 59.00 ± 0.00 a | |
| 4.2 | 18.86 ± 1.02 a | 8.30 ± 1.57 a | 10.31 ± 0.00 c | 3.53 ± 0.55 a | 59.00 ± 0.00 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salami, O.S.; Adeyemi, J.A.; Olawuyi, T.S.; Barbosa, F., Jr.; Adedire, C.O. Tissue Distributions and Toxic Effects of Hexavalent Chromium in Laboratory-Exposed Periwinkle (Littorina littorea Linnaeus). Animals 2023, 13, 3412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13213412
Salami OS, Adeyemi JA, Olawuyi TS, Barbosa F Jr., Adedire CO. Tissue Distributions and Toxic Effects of Hexavalent Chromium in Laboratory-Exposed Periwinkle (Littorina littorea Linnaeus). Animals. 2023; 13(21):3412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13213412
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalami, Olufemi S., Joseph A. Adeyemi, Toluwase S. Olawuyi, Fernando Barbosa, Jr., and Chris O. Adedire. 2023. "Tissue Distributions and Toxic Effects of Hexavalent Chromium in Laboratory-Exposed Periwinkle (Littorina littorea Linnaeus)" Animals 13, no. 21: 3412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13213412
APA StyleSalami, O. S., Adeyemi, J. A., Olawuyi, T. S., Barbosa, F., Jr., & Adedire, C. O. (2023). Tissue Distributions and Toxic Effects of Hexavalent Chromium in Laboratory-Exposed Periwinkle (Littorina littorea Linnaeus). Animals, 13(21), 3412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13213412






