Seroprevalence and Risk Factors of Chlamydia Infection in Cattle in Shanxi Province, North China
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval
2.2. Study Sites
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Serological Tests
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elwell, C.; Mirrashidi, K.; Engel, J. Chlamydia cell biology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiwattanarungruengpaisan, S.; Thongdee, M.; Anuntakarun, S.; Payungporn, S.; Arya, N.; Punchukrang, A.; Ramasoota, P.; Singhakaew, S.; Atithep, T.; Sariya, L. A new species of Chlamydia isolated from Siamese crocodiles (Crocodylus siamensis). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhold, P.; Sachse, K.; Kaltenboeck, B. Chlamydiaceae in cattle: Commensals, trigger organisms, or pathogens? Vet. J. 2011, 189, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borel, N.; Thoma, R.; Spaeni, P.; Weilenmann, R.; Teankum, K.; Brugnera, E.; Zimmermann, D.R.; Vaughan, L.; Pospischil, A. Chlamydia-related abortions in cattle from Graubunden, Switzerland. Vet. Pathol. 2006, 43, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struthers, J.D.; Lim, A.; Ferguson, S.; Lee, J.K.; Chako, C.; Okwumabua, O.; Cuneo, M.; Valle, A.M.; Brower, A. Meningoencephalitis, vasculitis, and abortions caused by Chlamydia pecorum in a herd of cattle. Vet. Pathol. 2021, 58, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, A.; Elsasser, T.H.; Rahman Kh, S.; Chowdhury, E.U.; Kaltenboeck, B. Asymptomatic endemic Chlamydia pecorum infections reduce growth rates in calves by up to 48 percent. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabell, E. Bovine abortion: Aetiology and investigations. Pract. 2007, 29, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein-Zadeh, N.G.; Ardalan, M. Evaluation of the potential effects of abortion on the productive performance of Iranian Holstein dairy cows. Anim. Sci. J. 2011, 82, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.W.; Meng, Q.F.; Cong, W.; Shan, X.F.; Wang, C.F.; Qian, A.D. Herd-level prevalence and associated risk factors for Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum, Chlamydia abortus and bovine viral diarrhoea virus in commercial dairy and beef cattle in eastern, northern and northeastern China. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 4211–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.; Quigley, B.L.; Timms, P. Seventy years of Chlamydia vaccine research-limitations of the past and directions for the future. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodolakis, A.; Yousef Mohamad, K. Zoonotic potential of Chlamydophila. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheelhouse, N.; Longbottom, D. Endemic and emerging chlamydial infections of animals and their zoonotic implications. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2012, 59, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Qin, S.; Lou, Z.; Ning, H.; Sun, X. Seroprevalence and risk factors of Chlamydia infection in domestic rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) in China. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 460473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.H.; Zhao, F.R.; Xia, H.Y.; Xu, M.J.; Huang, S.Y.; Song, H.Q.; Zhu, X.Q. Seroprevalence of chlamydial infection in dairy cattle in Guangzhou, southern China. Ir. Vet. J. 2013, 66, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasova, M.; Damaso, A.; Prakashbabu, B.C.; Gibbons, J.; Wheelhouse, N.; Longbottom, D.; Van Winden, S.; Green, M.; Guitian, J. Herd-level prevalence of selected endemic infectious diseases of dairy cows in Great Britain. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 9215–9233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffold, J.; Henning, K.; Bachmann, R.; Hotzel, H.; Melzer, F. The prevalence of Chlamydiae of bulls from six bull studs in Germany. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2007, 102, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didkowska, A.; Klich, D.; Hapanowicz, A.; Orłowska, B.; Gałązka, M.; Rzewuska, M.; Olech, W.; Anusz, K. Pathogens with potential impact on reproduction in captive and free-ranging European bison (Bison bonasus) in Poland-a serological survey. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cao, X.; Fu, B.; Chao, Y.; Cai, J.; Zhou, J. Identification and characterization of Chlamydia abortus isolates from yaks in Qinghai, China. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 658519. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, S.Y.; Huang, S.Y.; Yin, M.Y.; Tan, Q.D.; Liu, G.X.; Zhou, D.H.; Zhu, X.Q.; Zhou, J.Z.; Qian, A.D. Seroprevalence and risk factors of Chlamydia abortus infection in free-ranging white yaks in China. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumer, S.; Greub, G.; Waldvogel, A.; Hässig, M.; Thoma, R.; Tschuor, A.; Pospischil, A.; Borel, N. Waddlia, Parachlamydia and Chlamydiaceae in bovine abortion. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 152, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, M.D.C.; Fort, M.; Bettermann, S.; Entrocassi, C.; Costamagna, S.R.; Sachse, K.; Rodríguez Fermepin, M. Detection of Chlamydia abortus in bovine reproductive losses in the province of La Pampa, Argentina. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2018, 50, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.X.; Li, R.C.; Liu, G.H.; Cong, W.; Song, H.Q.; Yu, X.L.; Zhu, X.Q. High seroprevalence of Chlamydia infection in sows in Hunan province, subtropical China. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2014, 46, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndengu, M.; Matope, G.; Tivapasi, M.; Scacchia, M.; Bonfini, B.; Pfukenyi, D.M.; de Garine-Wichatitsky, M. Seroprevalence of chlamydiosis in cattle and selected wildlife species at a wildlife/livestock interface area of Zimbabwe. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2018, 50, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halánová, M.; Petrová, L.; Halán, M.; Trbolová, A.; Babinská, I.; Weissová, T. Impact of way of life and environment on the prevalence of Chlamydia felis in cats as potentional sources of infection for humans. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2019, 26, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkallah, M.; Jribi, H.; Ben Slima, A.; Gharbi, Y.; Mallek, Z.; Gautier, M.; Fendri, I.; Gdoura, R. Molecular prevalence of Chlamydia and Chlamydia-like bacteria in Tunisian domestic ruminant farms and their influencing risk factors. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, e329–e338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, J.; Degraves, F.J.; Kim, T.; Kaltenboeck, B. High prevalence of natural Chlamydophila species infection in calves. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 5664–5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Ladino, J.; Koochesfahani, K.M.; Zaharik, M.L.; Shen, C.; Brunham, R.C. A live and inactivated Chlamydia trachomatis mouse pneumonitis strain induces the maturation of dendritic cells that are phenotypically and immunologically distinct. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 1568–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longbottom, D.; Sait, M.; Livingstone, M.; Laroucau, K.; Sachse, K.; Harris, S.R.; Thomson, N.R.; Seth-Smith, H.M.B. Genomic evidence that the live Chlamydia abortus vaccine strain 1B is not attenuated and has the potential to cause disease. Vaccine 2018, 36, 3593–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.F.; Li, F.; Zheng, W.B.; Liu, G.H. Seroprevalence and risk factors of Chlamydia abortus infection in goats in Hunan Province, subtropical China. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2018, 18, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tian, T.; Yao, N.Q.; Chen, Z.Y.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.H.; Shi, J.F.; Li, J.M.; Shi, K.; Du, R. A meta-analysis of bovine Chlamydia prevalence in cattle in China from 1989 to 2020. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2022, 22, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhold, P.; Hartmann, H.; Constable, P.D. Characterisation of acid-base abnormalities in pigs experimentally infected with Chlamydia suis. Vet. J. 2010, 184, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermann, C.; Rüttger, A.; Schubert, E.; Schrödl, W.; Sachse, K.; Reinhold, P. Infection, disease, and transmission dynamics in calves after experimental and natural challenge with a bovine Chlamydia psittaci isolate. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, W.; Kaltenboeck, B.; Sachse, K.; Yang, Y.; Lu, G.; Zhang, J.; Luan, L.; You, J.; Huang, K.; et al. Chlamydia pecorum is the endemic intestinal species in cattle while C. gallinacea, C. psittaci and C. pneumoniae associate with sporadic systemic infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 193, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orjuela, A.G.; Reyes Castañeda, L.J.; Tobón, J.C.; Parra Arango, J.L.; Guzmán-Barragán, B. Seroprevalence of antibodies to Chlamydia abortus and risk factors in cattle from Villavicencio, Colombia. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year | Resident Population | Rural | Primary Industry |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 34.91 | 13.08 | 4.24 |
| 2019 | 34.97 | 13.53 | 4.62 |
| 2018 | 35.02 | 14.06 | 4.78 |
| 2017 | 35.10 | 14.54 | 5.00 |
| 2016 | 35.14 | 15.02 | 5.22 |
| 2015 | 35.19 | 15.53 | 5.50 |
| 2014 | 35.28 | 16.12 | 5.95 |
| 2013 | 35.35 | 16.66 | 5.92 |
| 2012 | 35.48 | 17.27 | 6.09 |
| 2011 | 35.62 | 17.88 | 6.50 |
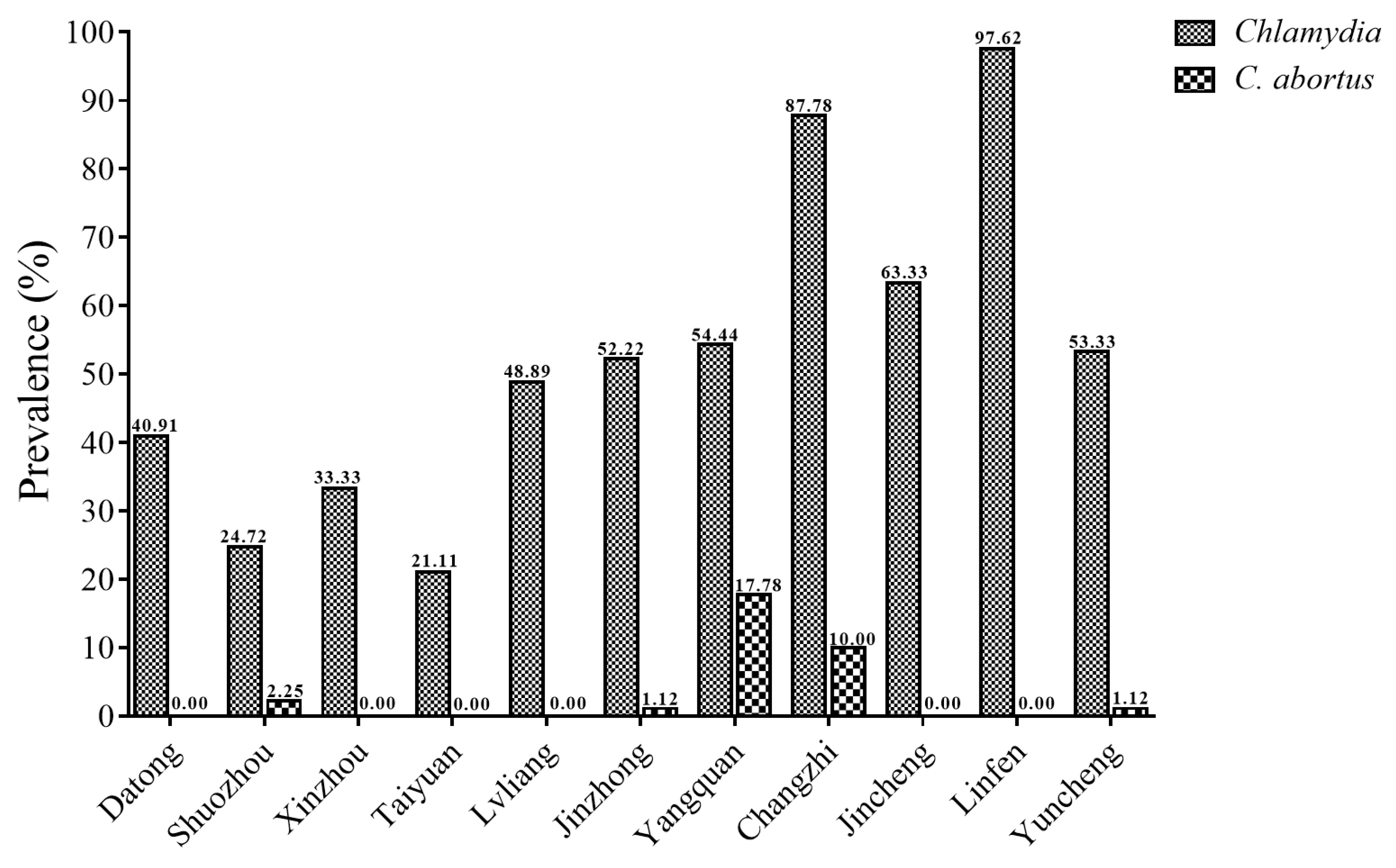
| Location | City | No. Examined | Chlamydia No. of Positive (%) | C. abortus No. of Positive (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern Shanxi | Datong | 88 | 36 (40.91) | 0 (0.00) |
| Shuozhou | 89 | 22 (24.72) | 2 (2.25) | |
| Xinzhou | 90 | 30 (33.33) | 0 (0.00) | |
| Central Shanxi | Taiyuan | 90 | 19 (21.11) | 0 (0.00) |
| Lvliang | 90 | 44 (48.89) | 0 (0.00) | |
| Jinzhong | 90 | 47 (52.22) | 1 (1.12) | |
| Yangquan | 90 | 49 (54.44) | 16 (17.78) | |
| Southern Shanxi | Changzhi | 90 | 79 (87.78) | 9 (10.00) |
| Jincheng | 90 | 57 (63.33) | 0 (0.00) | |
| Linfen | 84 | 82 (97.62) | 0 (0.00) | |
| Yuncheng | 90 | 48 (53.33) | 1 (1.12) | |
| Total | 981 | 513 (52.29) | 29 (2.96) |
| Variable | Categories | No. Examined | No. Positive | Antibody Titers | Prevalence % (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:16 | 1:64 | |||||||
| Location | Northern Shanxi | 267 | 88 | 83 | 5 | 32.96 (27.32–38.60) | <0.01 | Reference |
| Central Shanxi | 360 | 159 | 123 | 36 | 44.17 (39.04–49.30) | 1.61 (1.16–2.24) | ||
| Southern Shanxi | 354 | 266 | 202 | 64 | 75.14 (70.64–79.64) | 6.15 (4.33–8.73) | ||
| Management pattern | Household animal farm | 567 | 278 | 237 | 41 | 49.03 (44.92–53.14) | <0.01 | 1.09 (0.71–1.66) |
| Animal farming cooperative | 100 | 47 | 43 | 4 | 47.00 (37.22–56.78) | Reference | ||
| Large-scale animal farming company | 314 | 188 | 128 | 60 | 59.87 (54.45–65.29) | 1.68 (1.07–2.65) | ||
| Total | 981 | 513 | 408 | 105 | 52.29 (49.17–55.42) | |||
| Variable | Categories | No. Examined | No. Positive | Prevalence % (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Northern Shanxi | 267 | 2 | 0.75 (0–1.78) | <0.05 | Reference |
| Central Shanxi | 360 | 17 | 4.72 (2.53–6.91) | 6.57 (1.50–28.67) | ||
| Southern Shanxi | 354 | 10 | 2.82 (1.10–4.55) | 3.85 (0.84–17.73) | ||
| Management pattern | Household animal farm | 567 | 17 | 3.00 (1.59–4.40) | 0.14 | Reference |
| Animal farming cooperative | 100 | 0 | 0.00 | |||
| Large-scale animal farming company | 314 | 12 | 3.82 (1.70–5.94) | 1.29 (0.61–2.73) | ||
| Total | 981 | 29 | 2.96 (1.90–4.02) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.-J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C.-X.; Zheng, W.-B.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Lei, Y.-P.; Gao, W.-W. Seroprevalence and Risk Factors of Chlamydia Infection in Cattle in Shanxi Province, North China. Animals 2023, 13, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13020252
Wu X-J, Gao J, Zhang Q, Li C-X, Zheng W-B, Liu Q, Zhu X-Q, Lei Y-P, Gao W-W. Seroprevalence and Risk Factors of Chlamydia Infection in Cattle in Shanxi Province, North China. Animals. 2023; 13(2):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13020252
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xiao-Jing, Jin Gao, Qian Zhang, Chen-Xu Li, Wen-Bin Zheng, Qing Liu, Xing-Quan Zhu, Yu-Ping Lei, and Wen-Wei Gao. 2023. "Seroprevalence and Risk Factors of Chlamydia Infection in Cattle in Shanxi Province, North China" Animals 13, no. 2: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13020252
APA StyleWu, X.-J., Gao, J., Zhang, Q., Li, C.-X., Zheng, W.-B., Liu, Q., Zhu, X.-Q., Lei, Y.-P., & Gao, W.-W. (2023). Seroprevalence and Risk Factors of Chlamydia Infection in Cattle in Shanxi Province, North China. Animals, 13(2), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13020252






