Fish Gut Microbiome Analysis Provides Insight into Differences in Physiology and Behavior of Invasive Nile Tilapia and Indigenous Fish in a Large Subtropical River in China
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
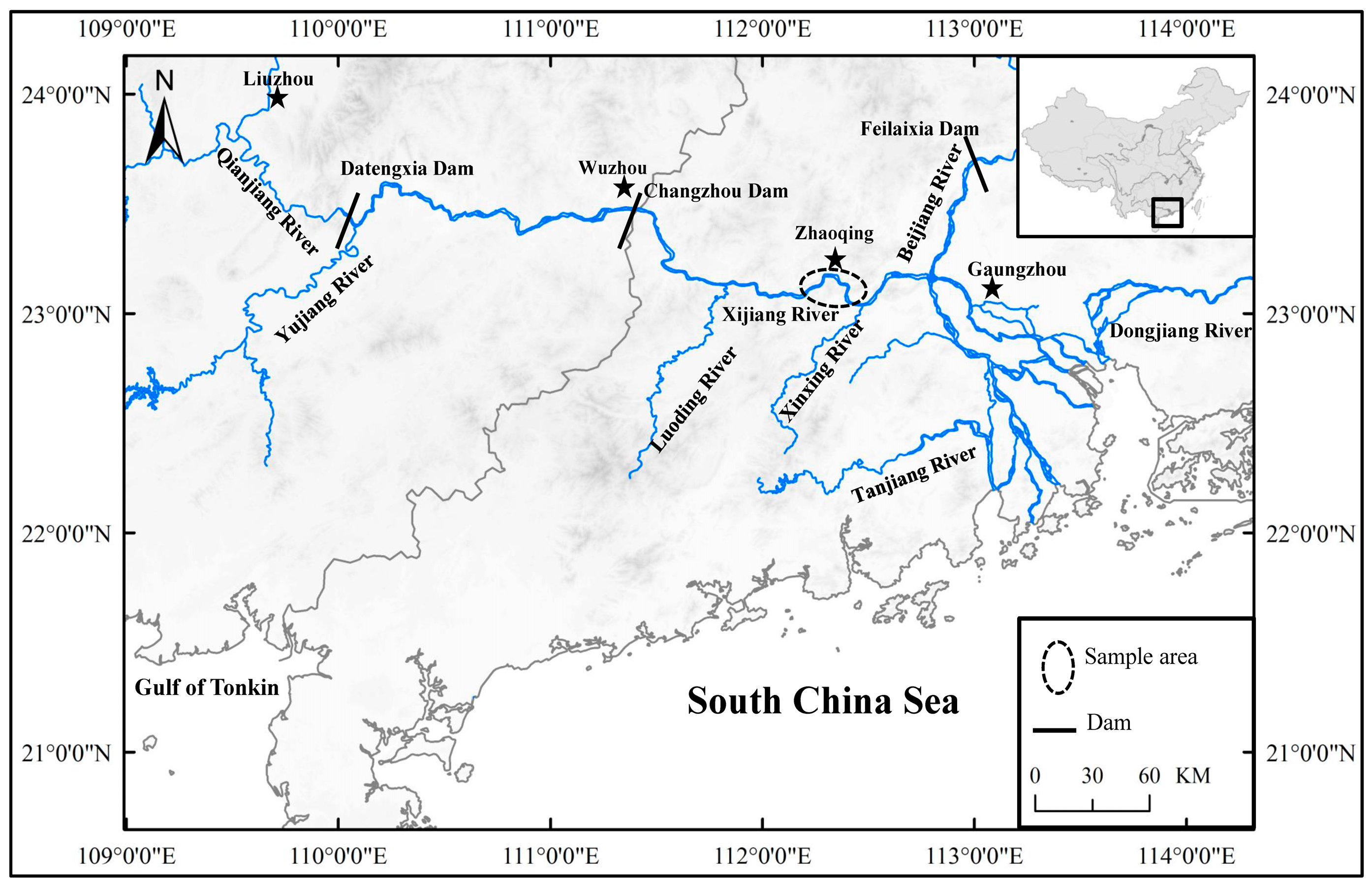
2.1. Fish Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and Amplification
2.3. Bioinformatic and Statistical Analysis
2.4. Habitat Niche Breadth Analysis
3. Results
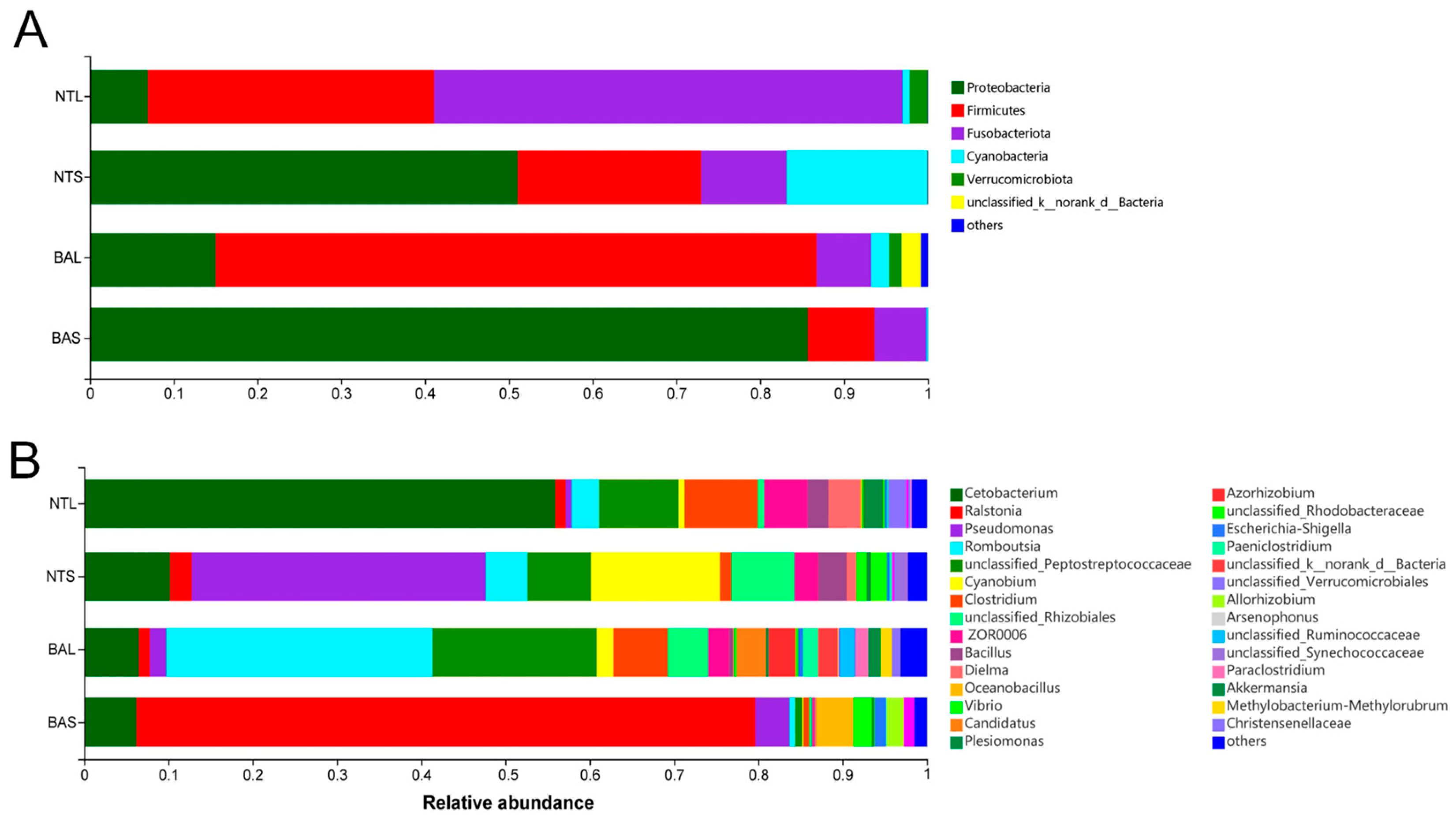
3.1. Differences between Invasive and Indigenous Fish in Gut Microbiome Composition
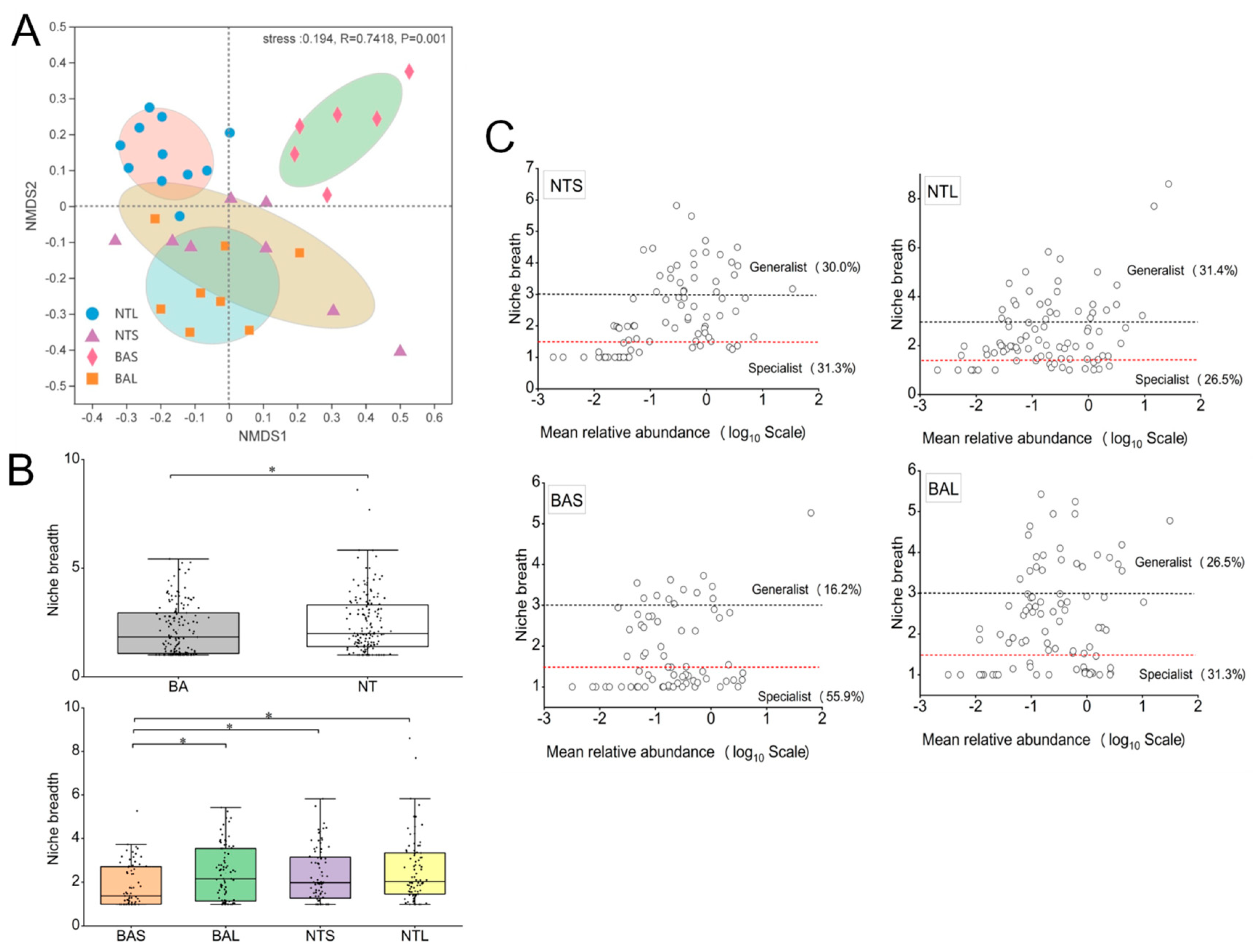
3.2. Partitioning the Gut Microbial Community into Generalists and Specialists
3.3. Microbial Populations in Response to Fish Interspecific and Intraspecific Differences
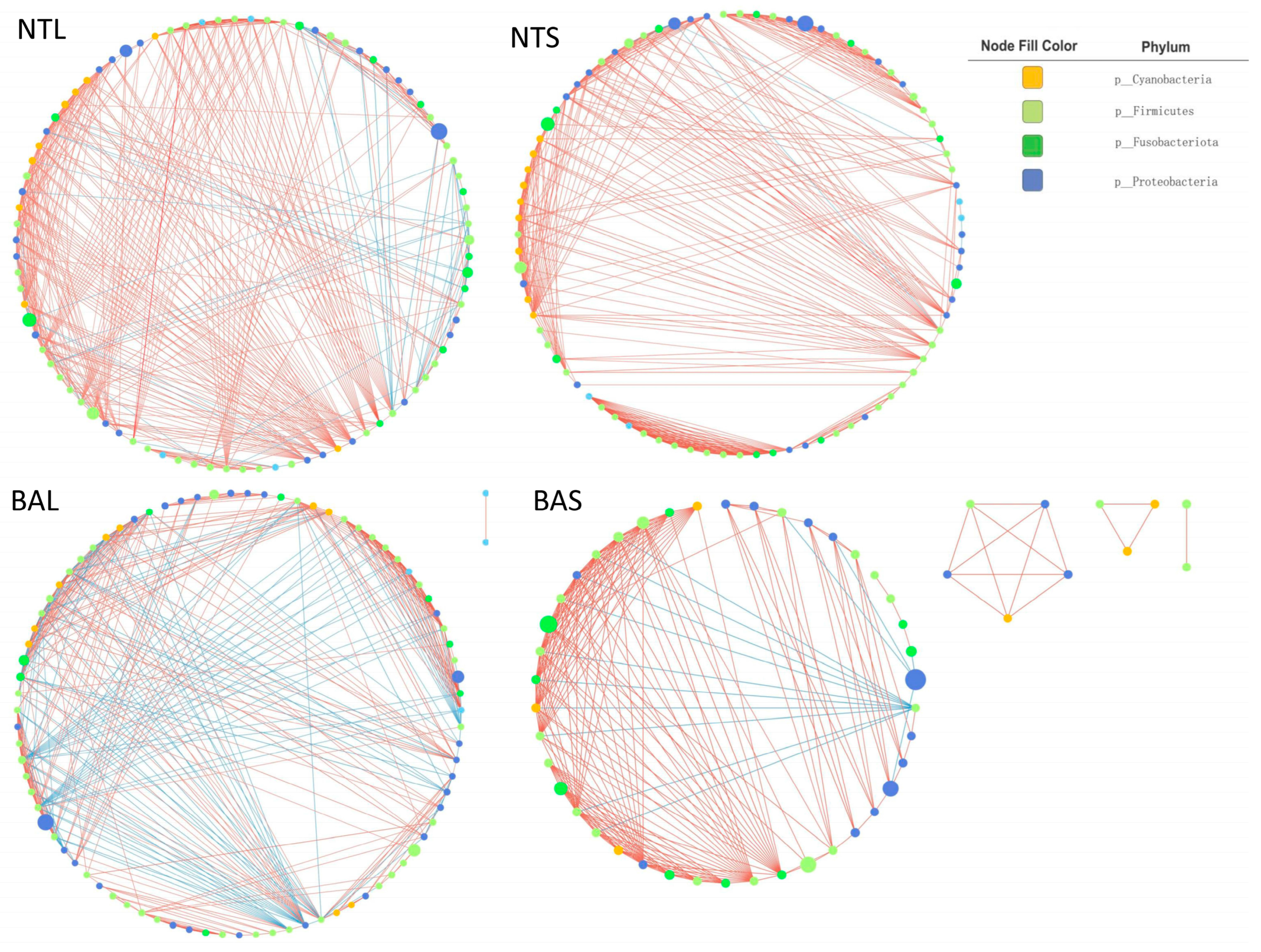
3.4. Network Analysis and Topological Roles of the Gut Microbiome among Different Groups
3.5. Functional Prediction of Gut Microbiome Digestion-Related Bacteria Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, D.E.; Ma, G.M.; Zhu, Y.J.; Xu, M.; Luo, D.; Li, Y.Y.; Wei, H.; Mu, X.D.; Luo, J.R.; Hu, Y.C. The impacts of invasive Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) on the fisheries in the main rivers of Guangdong Province, China. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2015, 59, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.W.; Valentine, M.M.; Valentine, J.F. Competitive interactions between invasive Niletilapia and native fish: The potential for altered trophic exchange and modification of food webs. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canonico, G.C.; Arthington, A.; McCrary, J.K.; Thieme, M.L. The effects of introduced tilapias on native biodiversity. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Fresh. Ecosyst. 2005, 15, 463–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.E.; Mu, X.D.; Xu, M.; Luo, D.; Wei, H.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Luo, J.R.; Hu, Y.C. Identification of wild tilapia species in the main rivers of south China using mitochondrial control region sequence and morphology. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2016, 65, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M.S.; Slack, W.T.; Woodley, C.M. The occurrence of non indigenous Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus) in coastal Mississippi: Ties to aquaculture and thermal effluent. Wetlands 2005, 25, 112e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.E.; Yu, F.D.; Yang, Y.X.; Xu, M.; Wei, H.; Luo, D.; Mu, X.D.; Hu, Y.C. Tilapia fisheries in Guangdong Province, China: Socio-economic benefits, and threats on native ecosystems and economics. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2019, 26, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xie, Y.F.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhong, P.; Liu, Z.W. The effect of tilapia on water quality. Ecol. Sci. 2008, 27, 494–498. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.; Liu, Z.W. Effects of tilapia on periphyton and phytoplankton. Ecol. Sci. 2010, 29, 147–151. [Google Scholar]
- Ley, R.E.; Hamady, M.; Lozupone, C.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ramey, R.R.; Bircher, J.S.; Schlegel, M.L.; Tucker, T.A.; Schrenzel, M.D.; Knight, R. Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science 2008, 320, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulski, T.; Kozłowski, K.; Ciesielski, S. Habitat and seasonality shape the structure of tench (Tinca tinca L.) gut microbiome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H.; Lamer, J.T.; Wang, J.; Wei, W.; Fu, L.; Tang, M.; Wang, C.; Lu, G. Gut microbiomes of bigheaded carps and hybrids provide insights into invasion: A hologenome perspective. Evol. Appl. 2021, 14, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, S.; Prewer, E.; Kutz, S.; Leclerc, L.M.; Vilaca, S.T.; Kyle, C.J. Geography, seasonality, and host-associated population structure influence the fecal microbiome of a genetically depauparate Arctic mammal. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 13202–13217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Li, X. Gut Microbiome Analyses of Wild Migratory Freshwater Fish (Megalobrama terminalis) Through Geographic Isolation. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 858454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Xing, W.; Li, T.; Xue, M.; Ma, Z.; Jiang, N.; Luo, L. Comparative study on the effects of different feeding habits and diets on intestinal microbiota in Acipenser baeri Brandt and Huso huso. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Amberg, J.; Chapman, D.; Gaikowski, M.; Liu, W.T. Fish gut microbiota analysis differentiates physiology and behavior of invasive Asian carp and indigenous American fish. ISME J. 2014, 8, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokou, F.; Sasson, G.; Friedman, J.; Eyal, S.; Ovadia, O.; Harpaz, S.; Cnaani, A.; Mizrahi, I. Core gut microbial communities are maintained by beneficial interactions and strain variability in fish. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 2456–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, L.K.; Williams, C.V.; Junge, R.E.; Mahefarisoa, K.L.; Rajaonarivelo, T.; Rakotondrainibe, H.; O’connell, T.M.; Drea, C.M. A role for gut microbiota in host niche differentiation. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1675–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereded, N.K.; Curto, M.; Domig, K.J.; Abebe, G.B.; Fanta, S.W.; Waidbacher, H.; Meimberg, H. Metabarcoding Analyses of Gut Microbiota of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) from Lake Awassa and Lake Chamo, Ethiopia. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giatsis, C.; Sipkema, D.; Smidt, H.; Heilig, H.; Benvenuti, G.; Verreth, J.; Verdegem, M. The impact of rearing environment on the development of gut microbiota in tilapia larvae. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, srep18206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.M.; Chen, J.Z.; Meng, S.L.; Song, C.; Qiu, L.P.; Hu, G.D.; Xu, P. Characterization of microbial communities in intensive GIFT tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) pond systems during the peak period of breeding. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parata, L.; Mazumder, D.; Sammut, J.; Egan, S. Diet type influences the gut microbiome and nutrient assimilation of Genetically Improved Farmed Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Chen, W. The gut microbiome composition and degradation enzymes activity of black Amur bream (Megalobrama terminalis) in response to breeding migratory behavior. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 5150–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Insights Into Energy Accumulation and Allocation Strategy of Reproductive Migration of Black Amur Bream (Megalobrama terminalis) in the Pearl River Basin, China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 848228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mago, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; Mcmurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.; Westcott, S.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Villot, C.; Renaud, D.; Skidmore, A.; Chevaux, E.; Steele, M.; Guan, L.L. Linking perturbations to temporal changes in diversity, stability, and compositions of neonatal calf gut microbiota: Prediction of diarrhea. ISME J. 2020, 14, 2223–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessen, J.V.D. Modulation of cytokine patterns and microbiome during pregnancy in IBD. Gut 2020, 69, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E. Fast algorithm for detecting community structure in networks. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 69, 066133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y. Balance between community assembly processes mediates species coexistence in agricultural soil microbiomes across eastern China. ISME J. 2020, 14, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, S.N.; Kolasa, J.; Cottenie, K. Contrasts between habitat generalists and specialists: An empirical extension to the basic metacommunity framework. Ecology 2009, 90, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Székely, A.J.; Langenheder, S. The importance of species sorting differs between habitat generalists and specialists in bacterial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 87, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Li, X.; Yan, M.; Lu, J.; Qiu, Q.; Chen, J. Comparable ecological processes govern the temporal succession of gut bacteria and microeukaryotes as shrimp aged. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 80, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, D.; Raab, N.; Pinto, Y.; Rothschild, D.; Zanir, G.; Godneva, A.; Mellul, N.; Futorian, D.; Gal, D.; Leviatan, S. Diversity and functional landscapes in the microbiota of animals in the wild. Science 2021, 372, eabb5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, S. Gut microbiomes of Cyprinid fishes exhibit host-species symbiosis along gut trait and diet. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 936601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, H.; Franzosa, E.A.; Mclver, L.J.; Banerjee, S.; Sirota-Madi, A.; Kostic, A.D.; Clish, C.B.; Vlamakis, H.; Xavier, R.J.; Huttenhower, C. Predictive metabolomic profiling of microbial communities using amplicon or metagenomic sequences. Nat. Communi. 2019, 10, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.F.; Wu, Y.Q.; Zhao, Y.T.; Lin, L.; Du, Y.; Li, P.; Li, H.; Ji, X. The invasive red-eared slider turtle is more successful than the native Chinese three-keeled pond turtle: Evidence from the gut microbiota. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, B.D.; Farrell, J.M.; Leydet, B. Use of next generation sequencing to compare simple habitat and species level differences in the gut microbiota of an invasive and native freshwater fish species. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrndorff, S.; Alemu, T.; Alemneh, T.; Nielsen, J.L. The Microbiome of Animals: Implications for Conservation Biology. Int. J. Genom. 2016, 2016, 5304028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, S.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Li, X. Individual dietary specialization reduces intraspecific competition, rather than feeding activity, in black amur bream (Megalobrama terminalis). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, J.Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.H.; Qu, Y.F. Comparative study on gut microbiota in three Anura frogs from a mountain stream. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e8854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Li, C.; Yan, Q. Comparative study on the gut microbiota of four economically important Asian carp species. Sci. China Life Sci. 2018, 61, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereded, N.K.; Abebe, G.B.; Fanta, S.W.; Curto, M.; Waidbacher, H.; Meimberg, H.; Domig, K.J. The gut bacterial microbiome of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) from lakes across an altitudinal gradient. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wu, H.; Li, D.; Zeng, W.; Huang, J.; Wu, Z. Comparison of gut microbiome in the Chinese mud snail (Cipangopaludina chinensis) and the invasive golden apple snail (Pomacea canaliculata). PeerJ 2022, 10, e13245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngblut, N.D.; Reischer, G.H.; Walters, W.; Schuster, N.; Walzer, C.; Stalder, G.; Ley, R.E.; Farnleitner, A.H. Host diet and evolutionary history explain different aspects of gut microbiome diversity among vertebrate clades. Nat. Communi. 2019, 10, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascompte, J. Networks in ecology. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2007, 8, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Deng, Y.; Luo, F.; He, Z.; Tu, Q.; Zhi, X. Functional molecular ecological networks. mBio 2010, 1, e1016910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, S.; Fan, S.; Xu, Y.; Tian, X. Profiling intestinal microbiota of Metaplax longipes and Helice japonica and their co-occurrence relationships with habitat microbes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.M.; Benbow, M.E. Species interactions and competition. Nat. Educ. Knowl. 2013, 4, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Pastore, A.I.; Barabas, G.; Bimler, M.D.; Mayfield, M.M.; Miller, T.E. The evolution of niche overlap and competitive differences. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Mi, T.; He, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhen, Y.; Yu, Z. Active bacterial and archaeal communities in coastal sediments: Biogeography pattern, assembly process and co-occurrence relationship. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 142252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucker, R.M.; Bordenstein, S.R. Speciation by symbiosis. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, G.; Zhu, L. Research Progress of the Gut Microbiome in Hybrid Fish. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, F.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) invasions disrupt the functional patterns of fish community in a large subtropical river in China. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2019, 26, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracida-Juárez, C.A.; Ioannou, C.C.; Genner, M.J. Competitive dominance and broad environmental tolerance favour invasive success of Nile tilapia. Hydrobiologia 2022, 849, 1161–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.E.; Luo, D.; Xu, M.; Ma, G.M.; Mu, X.D.; Luo, J.R.; Hu, Y.C. Species diversity defends against the invasion of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2014, 414, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.E.; Yu, F.D.; Hu, Y.C.; Wang, J.W.; Xu, M.; Mu, X.D.; Yang, Y.X.; Luo, D.; Wei, H.; Shen, Z.X.; et al. The Species Composition and Distribution Patterns of Non-Native Fishes in the Main Rivers of South China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Estimators | BAS–Mean | BAS–sd | BAL–Mean | BAL–sd | NTS–Mean | NTS–sd | NTL–Mean | NTL–sd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ace | 29.98 b | 6.68 | 47.87 a | 5.193 | 40.86 a | 7.57 | 44.51 a | 5.09 |
| Chao1 | 29 b | 4.13 | 47.75 a | 5.312 | 41.17 a | 6.59 | 44.48 a | 5.24 |
| PD | 3.854 b | 0.3967 | 4.658 a | 0.5548 | 4.027 a | 1.21 | 4.439 a | 0.7405 |
| Shannon | 0.9917 b | 0.1346 | 2.368 a | 0.474 | 2.056 a | 0.678 | 2.13 a | 0.4143 |
| Networks Estimators | BAS | BAL | NTS | NTL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of nodes | 52 | 85 | 84 | 87 |
| Number of edges | 224 | 429 | 422 | 467 |
| Avg. number of neighbors | 8.615 | 10.313 | 10.048 | 10.736 |
| Network diameter | 6 | 7 | 8 | 8 |
| Characteristics path length | 1.849 | 2.862 | 2.212 | 2.747 |
| Clustering coefficient | 0.354 | 0.636 | 0.341 | 0.506 |
| Network density | 0.084 | 0.126 | 0.061 | 0.125 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Kou, C.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, S. Fish Gut Microbiome Analysis Provides Insight into Differences in Physiology and Behavior of Invasive Nile Tilapia and Indigenous Fish in a Large Subtropical River in China. Animals 2023, 13, 2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13152413
Liu Y, Kou C, Li Y, Li J, Zhu S. Fish Gut Microbiome Analysis Provides Insight into Differences in Physiology and Behavior of Invasive Nile Tilapia and Indigenous Fish in a Large Subtropical River in China. Animals. 2023; 13(15):2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13152413
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yaqiu, Chunni Kou, Yuefei Li, Jie Li, and Shuli Zhu. 2023. "Fish Gut Microbiome Analysis Provides Insight into Differences in Physiology and Behavior of Invasive Nile Tilapia and Indigenous Fish in a Large Subtropical River in China" Animals 13, no. 15: 2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13152413
APA StyleLiu, Y., Kou, C., Li, Y., Li, J., & Zhu, S. (2023). Fish Gut Microbiome Analysis Provides Insight into Differences in Physiology and Behavior of Invasive Nile Tilapia and Indigenous Fish in a Large Subtropical River in China. Animals, 13(15), 2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13152413






