Neutral and Selective Processes Shape MHC Diversity in Roe Deer in Slovenia
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Study Area and Sampling
2.3. DNA Extraction and MHC Genotyping by Sequencing
2.4. MHC Diversity
2.4.1. Sequence Diversity
2.4.2. Clusters/Populations Genetic Parameters and Molecular Variance
2.4.3. Clustering of DRB Exon 2 Alleles
2.4.4. Detecting Signatures of Recombination and Selection in MHC DRB Exon 2 Alleles in Roe Deer
2.5. Determination of Genetic Variability among Groups and Clusters Based on Neutral Microsatellite Loci
3. Results
3.1. Diversity of MHC DRB Alleles
3.2. Clusters/Populations Genetic Parameters and Molecular Variance
3.3. Recombination and Natural Selection in MHC DRB Alleles in Roe Deer
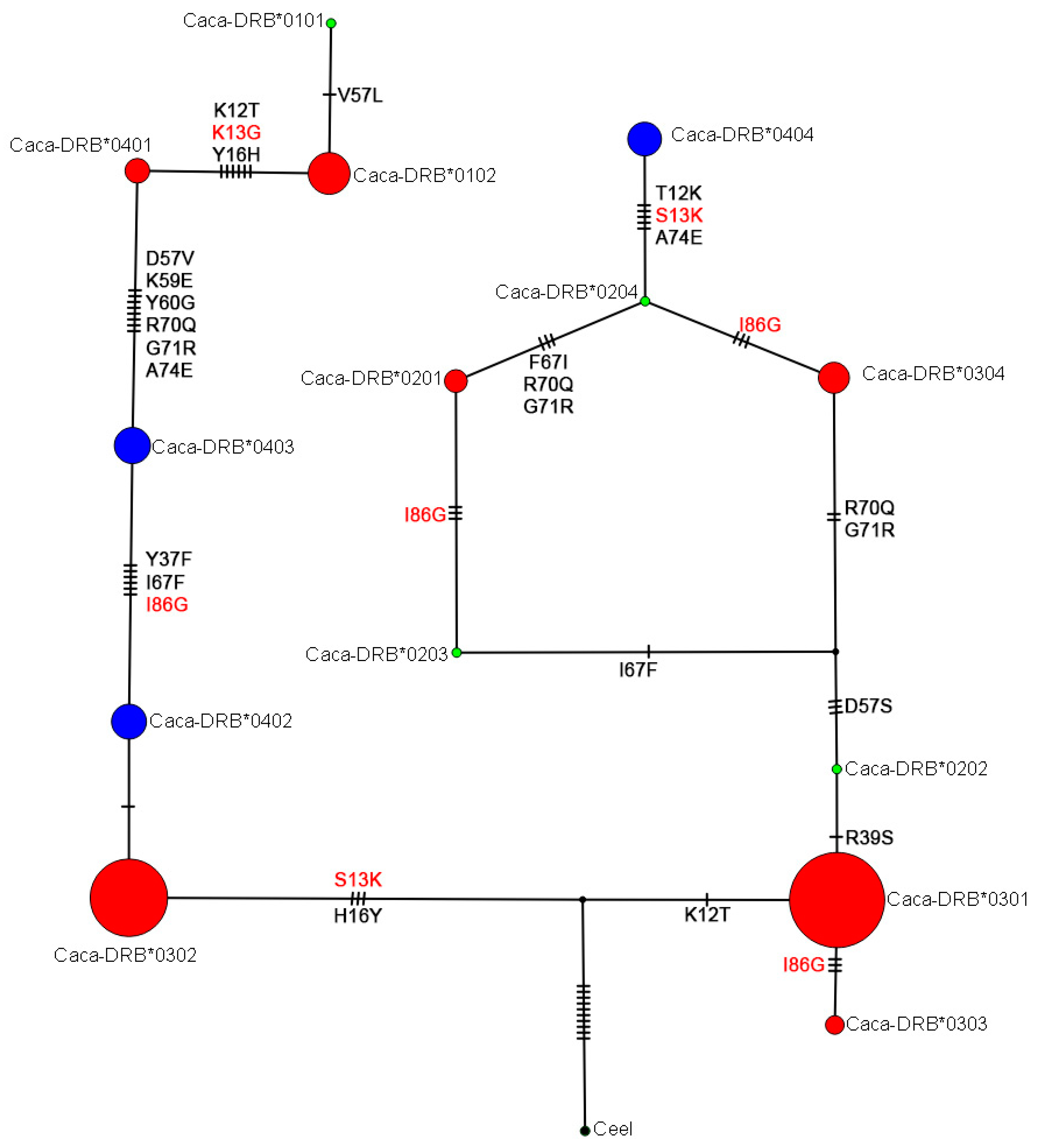
3.4. Evolutionary Relationships among DRB Exon 2 Alleles in Roe Deer
3.5. Genetic Diversity and Genetic Structure Based on Neutral Loci
4. Discussion
4.1. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure
4.2. Selection and Recombination
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Constent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hansen, J.; Sato, M.; Ruedy, R. Perception of climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2415–E2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pauls, S.U.; Nowak, C.; Bálint, M.; Pfenninger, M. The impact of global climate change on genetic diversity within populations and species. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 925–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allendorf, F.; Luikart, G. Conservation and the Genetics of Populations; Blackwell Publishing: Malden, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hoelzel, A.R.; Bruford, M.W.; Fleischer, R.C. Conservation of adaptive potential and functional diversity. Conserv. Genet. 2019, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bekessy, S.A.; Ennos, R.A.; Burgman, M.A.; Newton, A.C.; Ades, P.K. Neutral DNA markers fail to detect genetic divergence in an ecologically important trait. Biol. Conserv. 2003, 110, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, F.G.; Owen, J.G.; Baker, R.J. mtDNA perspective of chromosomal diversification and hybridization in Peters’ tent-making bat (Uroderma bilobatum: Phyllostomidae). Mol. Ecol. 2003, 12, 2981–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedrick, P.W. Conservation genetics: Where are we now? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2001, 16, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, T.L.; Wells, K.; Pfeiffer, M.; Sommer, S. Diverse MHC IIB allele repertoire increases parasite resistance and body condition in the long-tailed giant rat (Leopoldamys sabanus). BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliver, M.K.; Telfer, S.; Piertney, S.B. Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) heterozygote superiority to natural multi-parasite infections in the water vole (Arvicola terrestris). Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 276, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kloch, A.; Babik, W.; Bajer, A.; Siński, E.; Radwan, J. Effects of an MHC-DRB genotype and allele number on the load of gut parasites in the bank vole Myodes glareolus. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winternitz, J.C.; Minchey, S.G.; Garamszegi, L.Z.; Huang, S.; Stephens, P.R.; Altizer, S. Sexual selection explains more functional variation in the mammalian major histocompatibility complex than parasitism. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20131605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sin, Y.W.; Annavi, G.; Newman, C.; Buesching, C.; Burke, T.; Macdonald, D.W.; Dugdale, H.L. MHC class II-assortative mate choice in European badgers (Meles meles). Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 3138–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, P.S.C.; Michler, F.U.; Sommer, S. Can MHC-assortative partner choice promote offspring diversity? A new combination of MHC-dependent behaviours among sexes in a highly successful invasive mammal. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 2392–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, S.; Wilson, K.; Pemberton, J.M. Major histocompatibility complex variation associated with juvenile survival and parasite resistance in a large unmanaged ungulate population (Ovis aries L.). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3714–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carrington, M.; O’Brien, S.J. The Influence of HLA Genotype on AIDS. Annu. Rev. Med. 2003, 54, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pitcher, T.E.; Neff, B.D. MHC class IIB alleles contribute to both additive and nonadditive genetic effects on survival in Chinook salmon. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 2357–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, L.; Barr, I.; Van De Pol, M.; Burke, T.; Komdeur, J.; Richardson, D.S. MHC-dependent survival in a wild population: Evidence for hidden genetic benefits gained through extra-pair fertilizations. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 3444–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eizaguirre, C.; Lenz, T.L.; Kalbe, M.; Milinski, M. Rapid and adaptive evolution of MHC genes under parasite selection in experimental vertebrate populations. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hill, A.V.S.; Allsopp, C.E.M.; Kwiatkowski, D.; Anstey, N.M.; Twumasi, P.; Rowe, P.A.; Bennett, S.; Brewster, D.; McMichael, A.J.; Greenwood, B.M. Common West African HLA antigens are associated with protection from severe malaria. Nature 1991, 352, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafer, A.B.A.; Fan, C.W.; Côté, S.D.; Coltman, D.W. (Lack of) genetic diversity in immune genes predates glacial isolation in the North American mountain goat (Oreamnos americanus). J. Hered. 2012, 103, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Potts, W.K.; Manning, C.J.; Wakeland, E.K. The role of infectious disease, inbreeding and mating preferences in maintaining MHC genetic diversity: An experimental test. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1994, 346, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyce, W.M.; Hedrick, P.W.; Muggli-Cockett, N.E.; Kalinowski, S.; Penedo, M.C.T.; Ramey, R.R. Genetic variation of major histocompatibility complex and microsatellite loci: A comparison in bighorn sheep. Genetics 1997, 145, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, A.; Roemer, G.; Debenham, S.; Binns, M.; Garcelon, D.; Wayne, R.K. High MHC diversity maintained by balancing selection in an otherwise genetically monomorphic mammal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3490–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campos, J.L.; Posada, D.; Morán, P. Genetic variation at MHC, mitochondrial and microsatellite loci in isolated populations of Brown trout (Salmo trutta). Conserv. Genet. 2006, 7, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quéméré, E.; Galan, M.; Cosson, J.F.; Klein, F.; Aulagnier, S.; Gilot-Fromont, E.; Merlet, J.; Bonhomme, M.; Hewison, A.J.M.; Charbonnel, N. Immunogenetic heterogeneity in a widespread ungulate: The European roe deer (Capreolus capreolus). Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 3873–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Espona, S.; Goodall-Copestake, W.P.; Savirina, A.; Bobovikova, J.; Molina-Rubio, C.; Pérez-Barbería, F.J. First assessment of MHC diversity in wild Scottish red deer populations. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2019, 65, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, W.C.; Mckay, J.K.; Hohenlohe, P.A.; Allendorf, F.W. Harnessing genomics for delineating conservation units. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fennessy, J.; Bidon, T.; Reuss, F.; Kumar, V.; Elkan, P.; Nilsson, M.A.; Vamberger, M.; Fritz, U.; Janke, A. Multi-locus analyses reveal four giraffe species instead of one. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 2543–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acevedo-Whitehouse, K.; Cunningham, A.A. Is MHC enough for understanding wildlife immunogenetics? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.A.; Klaper, R. Genomics for the ecological toolbox. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, M.J.; Ben-Shahar, Y.; Smid, H.M.; Vet, L.E.; Robinson, G.E.; Sokolowski, M.B. Candidate genes for behavioural ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colegrove, K.M.; Lowenstine, L.J.; Gulland, F. Leptospirosis in northern elephant seals (Mirounga angustirostris) stranded along the California coast. J. Wildl. Dis. 2005, 41, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visscher, P.M.; Smith, D.; Hall, S.; Williams, J.L. A viable herd of genetically uniform cattle. Nature 2001, 409, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikko, S.; Røed, K.; Schmutz, S.; Andersson, L. Monomorphism and polymorphism at MHC DRB loci in domestic and wild ruminants. Immunol. Rev. 1999, 167, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikko, S.; Spencer, M.; Morris, B.; Stabile, S.; Basu, T.; Stormont, C.; Andersson, L. A comparative analysis of MHC DRB3 polymorphism in the American bison (Bison bison). J. Hered. 1997, 88, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Linnell, J.D.C.; Duncan, P.; Andersen, R. The European roe deer: A portrait of a successful species. In The European Roe Deer: The Biology of Success; Andersen, R., Duncan, P., Linnell, J.D.C., Eds.; Scandinavian University Press: Oslo, Norway, 1998; pp. 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kurt, F. Das Reh in der Kulturlandschaft: Sozialverhalten und Oëkologie eines Anpassers; Parey: Hamburg, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Hewison, A.J.M.; Vincent, J.P.; Reby, D. Social organisation of European roe deer. In The European Roe Deer: The Biology of Success; Andersen, R., Duncan, P., Linnell, J.D., Eds.; Scandinavian University Press: Oslo, Norway, 1998; pp. 189–219. [Google Scholar]
- Strandgaard, H. The Roe Deer (Capreolus capreolus) Population at Kalø and the Factors Regulating Its Size; Danish Review of Game Biology; Vildtbiologisk Station: Rønde, Denmark, 1972; Volume 7, 205p. [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberg, H. The population ecology of roe deer, Capreolus capreolus (Cervidae) in Central Europe. Spixiana 1978, 2, 5–211. [Google Scholar]
- Stubbe, C. Rehwild, 3rd ed.; Deutscher Landwirtschaftsverlag: Berlin, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Danilkin, A.; Hewison, A.J.M. Behavioural Ecology of Siberian and European Roe Deer; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, R.; Duncan, P.; Linnell, J.D.C. (Eds.) The European Roe Deer: The Biology of Success; Scandinavian University Press: Oslo, Norway, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Buzan, E.; Gerič, U.; Potušek, S.; Flajšman, K.; Pokorny, B. First insights into the population genetic structure and heterozygosity–fitness relationship in roe deer inhabiting the area between the Alps and Dinaric Mountains. Animals 2020, 10, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurdardóttir, S.; Borsch, C.; Gustafsson, K.; Andersson, L. Cloning and sequence analysis of 14 DRB alleles of the bovine major histocompatibility complex by using the polymerase chain reaction. Anim. Genet. 1991, 22, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, A.; Herdegen, M.; Migalska, M.; Radwan, J. Amplisas: A web server for multilocus genotyping using next-generation amplicon sequencing data. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Den Bussche, R.A.; Hoofer, S.R.; Lochmiller, R.L. Characterization of Mhc-DRB allelic diversity in white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) provides insight into Mhc-DRB allelic evolution within Cervidae. Immunogenetics 1999, 49, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sanchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sanchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.H.; Jardetzky, T.S.; Gorga, J.C.; Stern, L.J.; Urban, R.G.; Strominger, J.L.; Wiley, D.C. Three-dimensional structure of the human class II histocompatibility antigen HLA-DR1. Nature 1993, 364, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellicour, S.; Mardulyn, P. spads 1.0: A toolbox to perform spatial analyses on DNA sequence data sets. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 14, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, E.J.; Dempster, E.R. An exact test for Hardy-Weinberg and multiple alleles. Biometrics 1987, 43, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond, M.; Rousset, F. An exact test for population differentiation. Evolution 1995, 49, 1280–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Excoffier, L.; Smouse, P.E.; Quattro, J.M. Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: Application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 1992, 131, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nei, M.; Gojobori, T. Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1986, 3, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jukes, T.; Cantor, C. Evolution of protein molecules. In Mammalian Protein Metabolism; Munro, H., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1969; pp. 21–132. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Chen, C.; Arab, D.A.; Du, Z.; He, Y.; Ho, S.Y.W. EasyCodeML: A visual tool for analysis of selection using CodeML. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weaver, S.; Shank, S.D.; Spielman, S.J.; Li, M.; Muse, S.V.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L. Datamonkey 2.0: A modern web application for characterizing selective and other evolutionary processes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Posada, D.; Gravenor, M.B.; Woelk, C.H.; Frost, S.D.W. GARD: A genetic algorithm for recombination detection. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 3096–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, D.; Rybicki, E. RDP: Detection of recombination amongst aligned sequences. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 562–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.P.; Williamson, C.; Posada, D. RDP2: Recombination detection and analysis from sequence alignments. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, M.O.; Carr, J.K.; Burke, D.S.; Mccutchan, F.E. Identification of breakpoints in intergenotypic recombinants of HIV Type 1 by bootscanning. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 1995, 11, 1423–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padidam, M.; Sawyer, S.; Fauquet, C.M. Possible emergence of new geminiviruses by frequent recombination. Virology 1999, 265, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. Evaluation of methods for detecting recombination from DNA sequences: Computer simulations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13757–13762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, J.M. Analyzing the mosaic structure of genes. J. Mol. Evol. 1992, 34, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, M.J.; Armstrong, J.S.; Gibbs, A.J. Sister-Scanning: A Monte Carlo procedure for assessing signals in recombinant sequences. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boni, M.F.; Posada, D.; Feldman, M.W. An exact nonparametric method for inferring mosaic structure in sequence triplets. Genetics 2007, 176, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falush, D.; Stephens, M.; Pritchard, J.K. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: Linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics 2003, 164, 1567–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stergar, M.; Borkovič, D.; Hiršelj, J.; Kavčič, I.; Krofel, M.; Mrakič, M.; Troha, R.; Videmšek, U.; Vrčon, B.; Jerina, K. Ugotavljanje Gostot Prostoživečih Parkljarjev s Kombinirano Metodo Štetja Kupčkov Iztrebkov in Podatkov o Odvzemu; Biotehniška Fakulteta, Oddelek za Gozdarstvo in Obnovljive Gozdne Vire: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kryštufek, B. Sesalci Slovenije; Prirodoslovni Muzej Slovenije: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- De Jong, J.F.; van Hooft, P.; Megens, H.J.; Crooijmans, R.P.M.A.; de Groot, G.A.; Pemberton, J.M.; Huisman, J.; Bartoš, L.; Iacolina, L.; van Wieren, S.E.; et al. Fragmentation and translocation distort the genetic landscape of ungulates: Red deer in the Netherlands. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quéméré, E.; Hessenauer, P.; Galan, M.; Fernandez, M.; Merlet, J.; Chaval, Y.; Morellet, N.; Verheyden, H.; Gilot-Fromont, E.; Charbonnel, N. Pathogen-mediated selection favours the maintenance of innate immunity gene polymorphism in a widespread wild ungulate. J. Evol. Biol. 2021, 34, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartl, G.B.; Reimoser, F.; Willing, R.; Koller, J. Genetic variability and differentiation in roe deer (Capreolus capreolus L.) of Central Europe. Genet. Sel. Evol. 1991, 23, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaschl, H.; Goodman, S.J.; Suchentrunk, F. Sequence analysis of the MHC class II DRB alleles in Alpine chamois (Rupicapra r. rupicapra). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2004, 28, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallero, S.; Marco, I.; Lavín, S.; D’Amelio, S.; López-Olvera, J.R. Polymorphisms at MHC class II DRB1 exon 2 locus in Pyrenean chamois (Rupicapra pyrenaica pyrenaica). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buczek, M.; Okarma, H.; Demiaszkiewicz, A.W.; Radwan, J. MHC, parasites and antler development in red deer: No support for the Hamilton & Zuk hypothesis. J. Evol. Biol. 2016, 29, 617–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arbanasić, H.; Konjević, D.; Vranković, L.; Bujanić, M.; Stipoljev, S.; Balažin, M.; Šprem, N.; Škorić, D.; Galov, A. Evolution of MHC class II SLA-DRB1 locus in the Croatian wild boar (Sus scrofa) implies duplication and weak signals of positive selection. Anim. Genet. 2019, 50, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loehr, J.; Worley, K.; Grapputo, A.; Carey, J.; Veitch, A.; Coltman, D.W. Evidence for cryptic glacial refugia from North American mountain sheep mitochondrial DNA. J. Evol. Biol. 2006, 19, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainguy, J.; Worley, K.; Côté, S.D.; Coltman, D.W. Low MHC DRB class II diversity in the mountain goat: Past bottlenecks and possible role of pathogens and parasites. Conserv. Genet. 2007, 8, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, L.; Sigurdardóttir, S.; Borsch, C.; Gustafsson, K. Evolution of MHC polymorphism: Extensive sharing of polymorphic sequence motifs between human and bovine DRB alleles. Immunogenetics 1991, 33, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.H.; Jardetzky, T.; Saper, M.A.; Samraoui, B.; Bjorkman, P.J.; Wiley, D.C. A hypothetical model of the foreign antigen binding site of Class II histocompatibility molecules. Nature 1988, 332, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, E.Y.; Fugger, L.; Strominger, J.L.; Siebold, C. MHC class II proteins and disease: A structural perspective. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langefors, A.; Lohm, J.; Grahn, M.; Andersen, O.; von Schantz, T. Association between major histocompatibility complex class IIB alleles and resistance to Aeromonas salmonicida in Atlantic salmon. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2001, 1268, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernatchez, L.; Landry, C. MHC studies in nonmodel vertebrates: What have we learned about natural selection in 15 years? J. Evol. Biol. 2003, 16, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Charbonnel, N.; Cosson, J.F. Molecular epidemiology of disease resistance genes with perspectives for researches on biological invasions and hybrid zones. In New Frontiers of Molecular Epidemiology of Infectious Diseases; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 255–290. ISBN 9789400721142. [Google Scholar]
- White, T.A.; Perkins, S.E. The ecoimmunology of invasive species. Funct. Ecol. 2012, 26, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.A.; Klasing, K.C. A role for immunology in invasion biology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flajšman, K. Effects of Individual, Population and Environmental Factors on Parameters of Reproductive Success of Female Roe Deer (Capreolus capreolus L.). Ph.D. Thesis, Biotehniška Fakulteta, Oddelek za Gozdarstvo in Obnovljive Gozdne Vire, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, R. Molecular signatures of natural selection. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2005, 39, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Nielsen, R. Codon-substitution models for detecting molecular adaptation at individual sites along specific lineages. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alcaide, M. On the relative roles of selection and genetic drift in shaping MHC variation. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 3842–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, J.T.; Nakagawa, S.; Robertson, B.C.; Jamieson, I.G. Disentangling the roles of natural selection and genetic drift in shaping variation at MHC immunity genes. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 4408–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oomen, R.A.; Gillett, R.M.; Kyle, C.J. Comparison of 454 pyrosequencing methods for characterizing the major histocompatibility complex of nonmodel species and the advantages of ultra deep coverage. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, M.K.; Piertney, S.B. Isolation and characterization of a MHC class II DRB locus in the European water vole (Arvicola terrestris). Immunogenetics 2006, 58, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrigan, D.; Hedrick, P.W. Perspective: Detecting adaptive molecular polymorphism: Lessons from the MHC. Evolution 2003, 57, 1707–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellis, D.; Callahan, B.J.; Petrov, D.A.; Messer, P.W. Heterozygote advantage as a natural consequence of adaptation in diploids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20666–20671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haldane, J.B.S. Suggestions as to quantitative measurement of rates of evolution. Evolution 1949, 3, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charbonnel, N.; Pemberton, J. A long-term genetic survey of an ungulate population reveals balancing selection acting on MHC through spatial and temporal fluctuations in selection. Heredity 2005, 95, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hedrick, P.W. Genetics of Populations, 4th ed.; Jones and Bartlett Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 2011; ISBN 9780763757373. [Google Scholar]
- Earl, D.A.; vonHoldt, B.M. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters Related to Nucleotide Differences | Overall Nucleotide Evolutionary Distance | Amino Acid Evolutionary Distance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | S | All Sites | ABS | Non-ABS | All Sites | ABS | Non-ABS |
| 9.833 | 22 + 1 indel (13 + 1 indel) * | 0.05 (0.01) | 0.17 (0.06) | 0.02 (0.01) | 0.09 (0.03) | 0.43 (0.22) | 0.03 (0.02) |
| Geographical Group | Abbr. | n | A | AR | Ho | He | π (SD) | θ | Tajima’s D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 156 | 10 | 10.000 | 0.529 | 0.739 | 0.045 (0.004) | 0.015 | 2.263 | |
| Southwestern | SW | 29 | 8 | 8.000 | 0.414 | 0.713 | 0.028 (0.004) | 0.022 | 0.579 |
| Central | C | 68 | 10 | 8.357 | 0.524 | 0.724 | 0.029 (0.002) | 0.017 | 1.610 |
| Northeastern | NE | 59 | 9 | 8.602 | 0.593 | 0.759 | 0.027 (0.002) | 0.017 | 1.428 |
| Main Parameters | Overall | ABS | Non-ABS |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 83 | 16 | 67 |
| dS (SE) | 0.02 (0.01) | 0.02 (0.02) | 0.03 (0.01) |
| dN (SE) | 0.05 (0.02) | 0.20 (0.08) | 0.02 (0.01) |
| ω dN/dS) | 1.40 | 2.60 | −0.40 |
| p-value | 0.08 | 0.01 | 1.00 |
| Codon Sites under Positive Selection | Selection Model |
|---|---|
| 12, 13, 16, 57, 67, 70, 71, 86 | M2a |
| 12, 13, 16, 57, 67, 70, 71, 86 | M8 |
| Event | Recombinant Sequence | Major/Minor Parent | Consensus Score | Beginning/Ending Breakpoint | Probability (MC Corrected) * | Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Caca-DRB*0403 | Unknown/ Caca-DRB*0401 | 0.534 | 170/242 | 0.0235 | MaxChi, SiScan, 3Seq |
| 2 | Caca-DRB*0401 | Caca-DRB*0404/Unknown | 0.481 | 84/266 | 0.0177 | MaxChi |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buzan, E.; Potušek, S.; Duniš, L.; Pokorny, B. Neutral and Selective Processes Shape MHC Diversity in Roe Deer in Slovenia. Animals 2022, 12, 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12060723
Buzan E, Potušek S, Duniš L, Pokorny B. Neutral and Selective Processes Shape MHC Diversity in Roe Deer in Slovenia. Animals. 2022; 12(6):723. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12060723
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuzan, Elena, Sandra Potušek, Luka Duniš, and Boštjan Pokorny. 2022. "Neutral and Selective Processes Shape MHC Diversity in Roe Deer in Slovenia" Animals 12, no. 6: 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12060723
APA StyleBuzan, E., Potušek, S., Duniš, L., & Pokorny, B. (2022). Neutral and Selective Processes Shape MHC Diversity in Roe Deer in Slovenia. Animals, 12(6), 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12060723







