Revealing Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Endangered Altay White-Headed Cattle Population Using 100 k SNP Markers
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Main Test Reagents
2.2. Test Animals
2.3. Test Method
2.3.1. DNA Extraction
2.3.2. DNA Quality Detection
2.3.3. SNP Typing of Genomic DNA
2.3.4. Genetic Diversity Analysis
2.3.5. Inbreeding Coefficient Analysis Based on Long Homozygous Fragments
2.3.6. Genetic Relationship Analysis of Population Genome
2.3.7. Cluster Analysis to Construct Altay White-Headed Cattle Family
3. Results
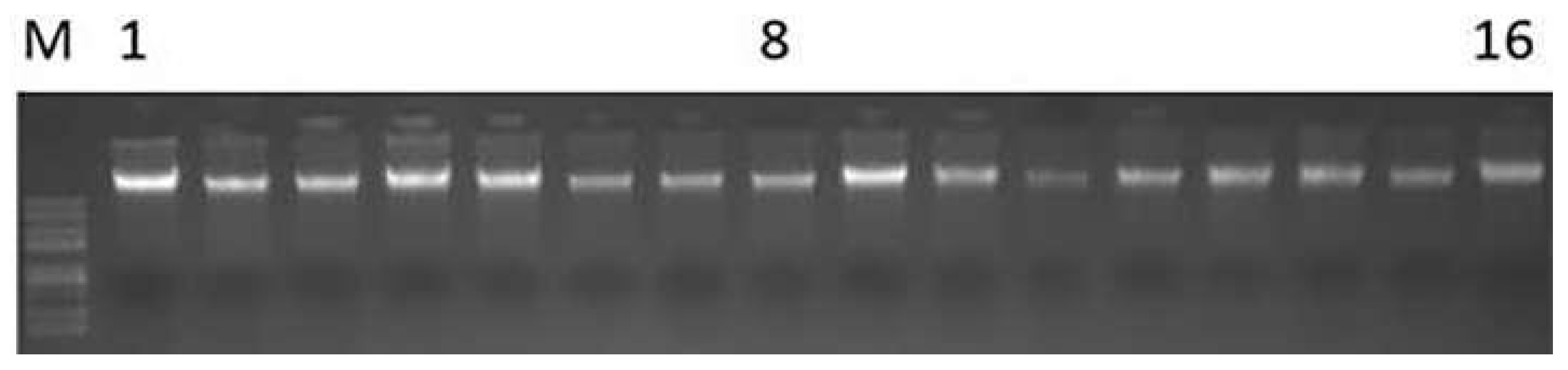
3.1. Genomic DNA Detection
3.2. SNP Quality Control and Typing
3.2.1. Sample Quality Control
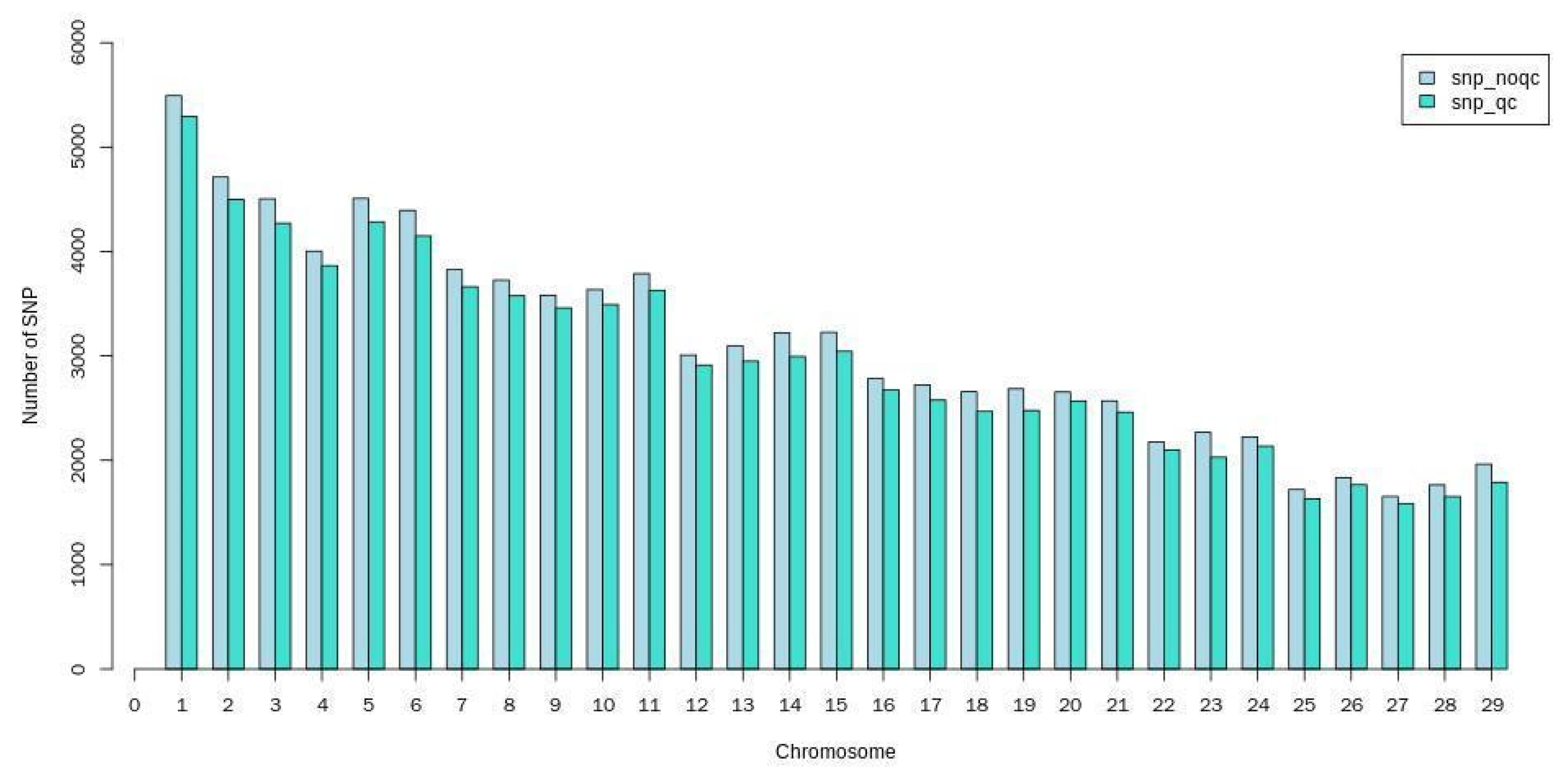
3.2.2. SNP Locus Quality Control
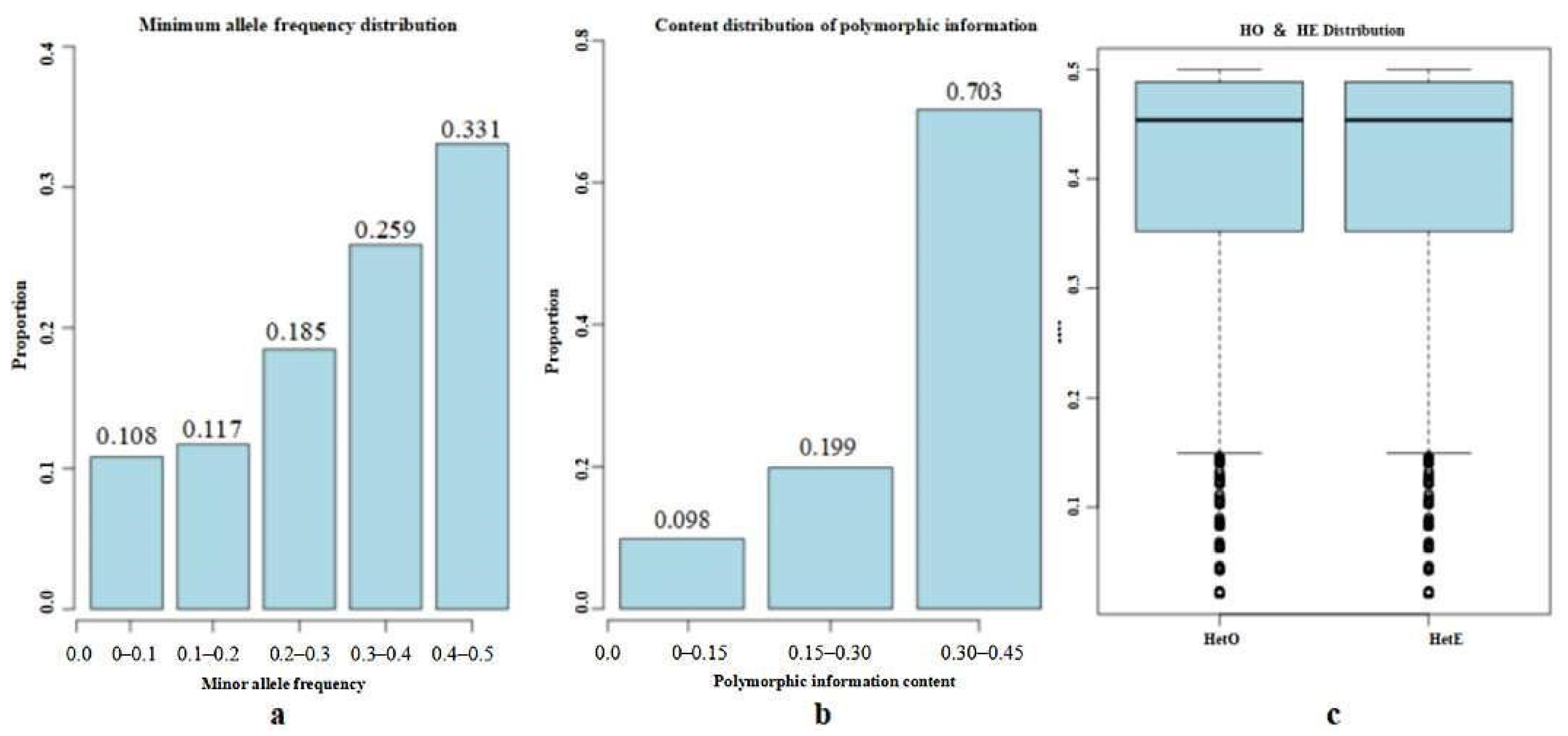
3.3. Genetic Diversity Analysis
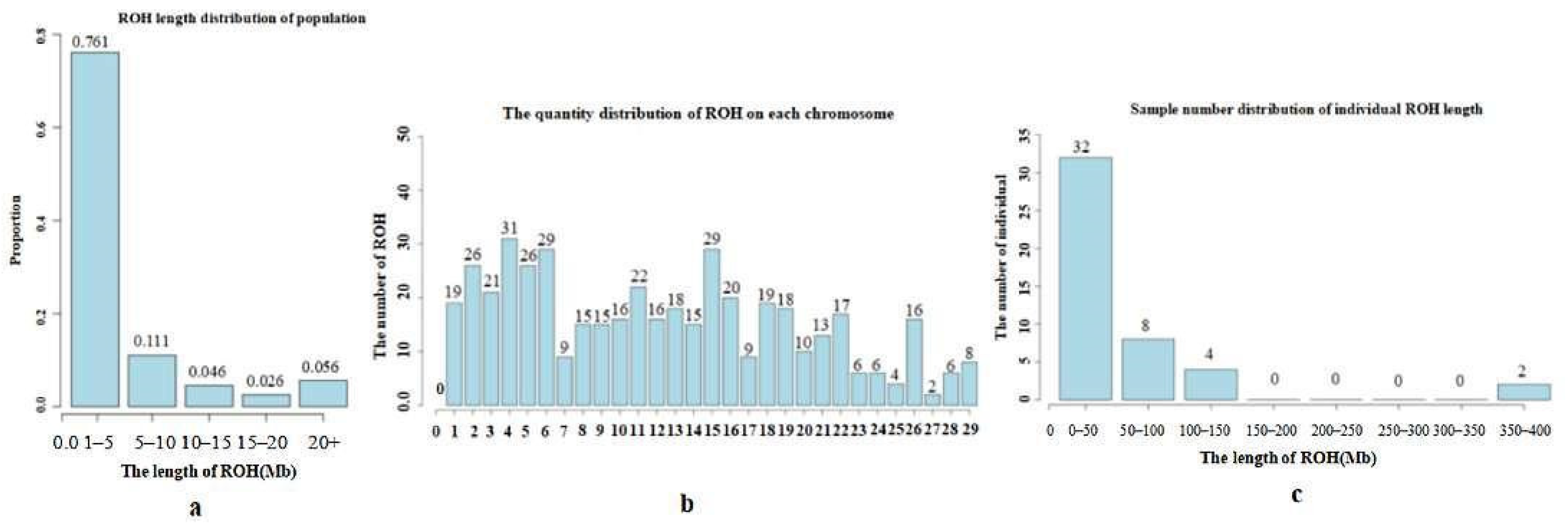
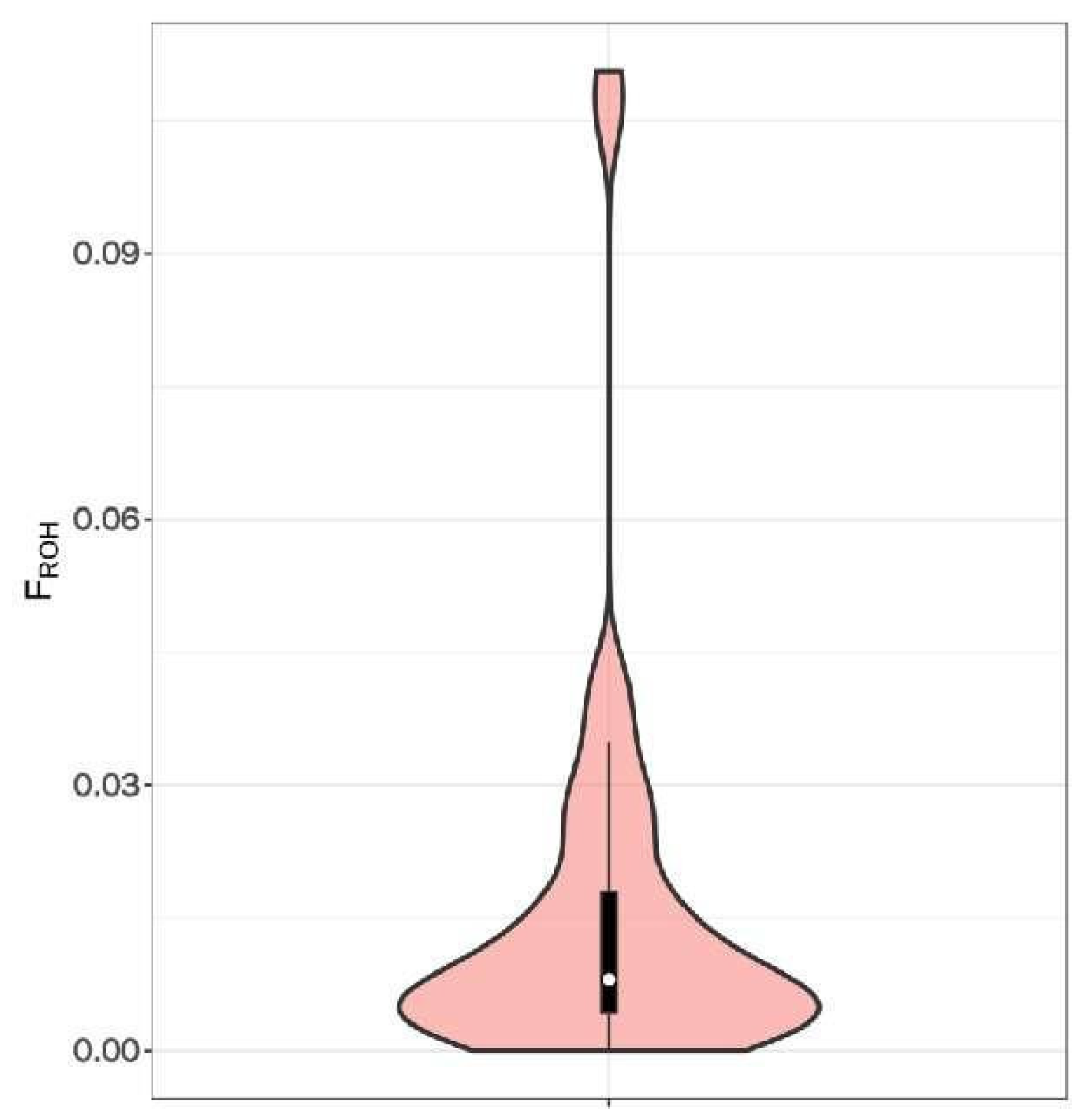
3.4. Inbreeding Coefficient Analysis Based on Long Homozygous Segments
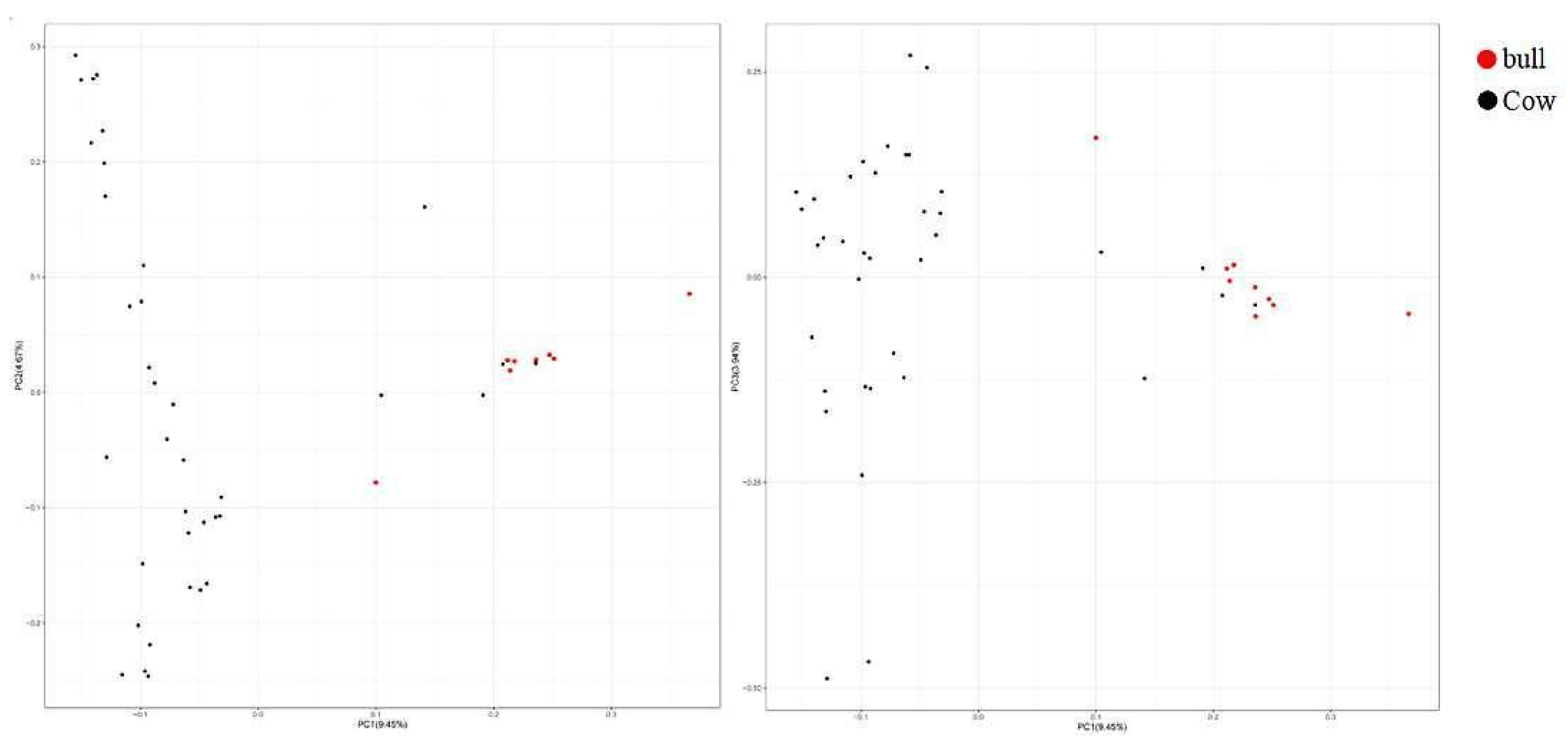
3.5. Genetic Relationship Analysis of Population Genome
3.5.1. Kinship Analysis Based on G Matrix
3.5.2. Genetic Distance Analysis of IBS
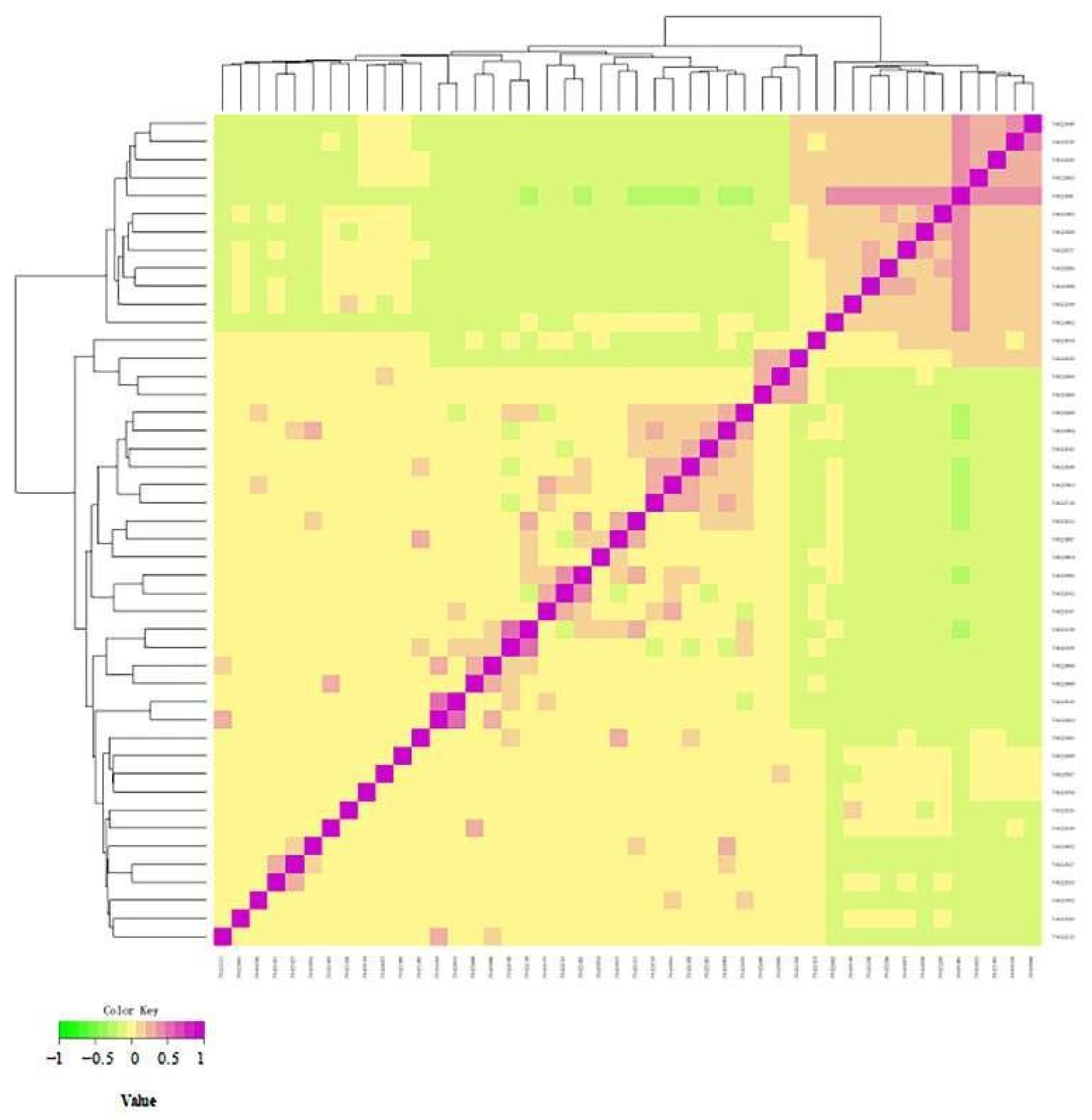
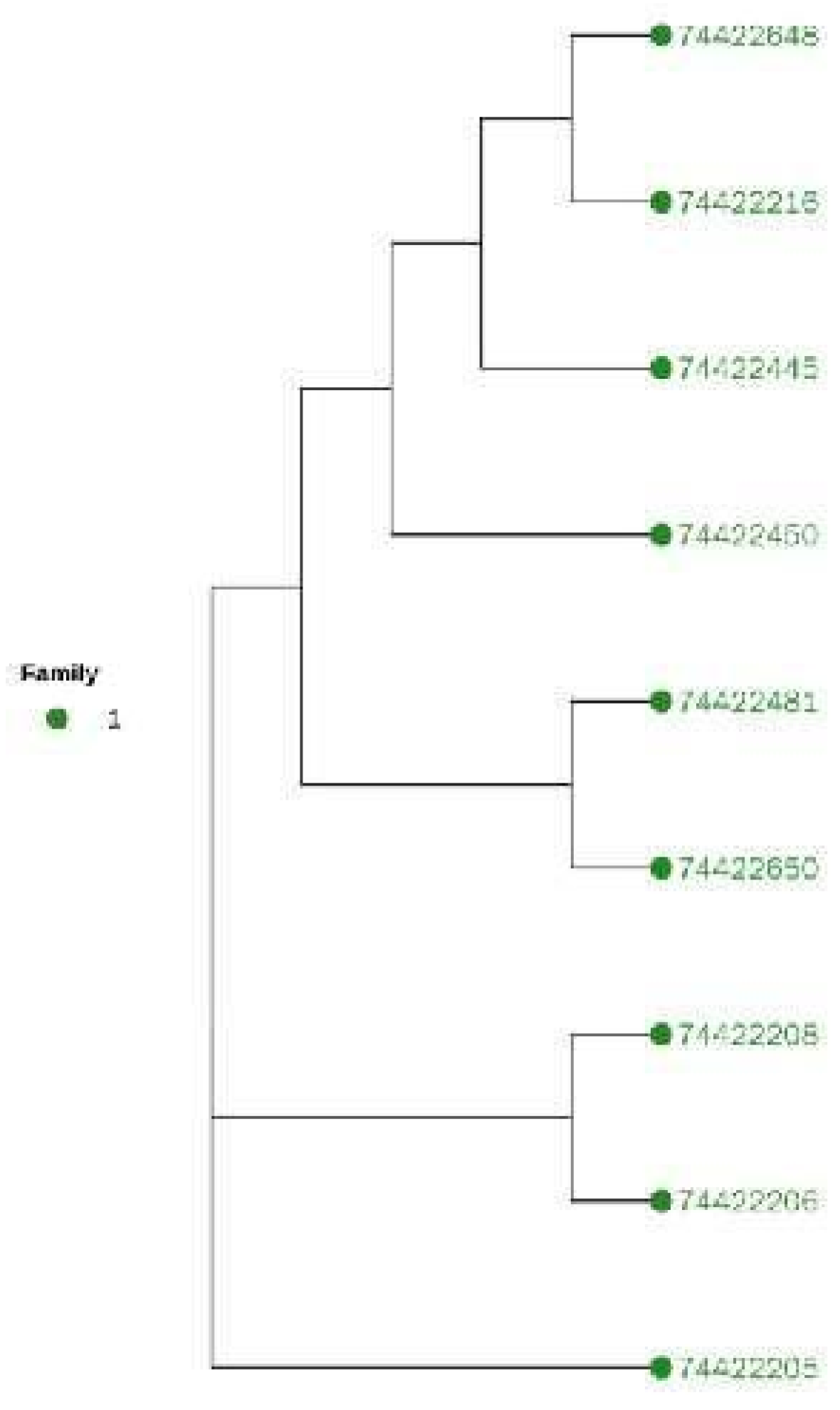
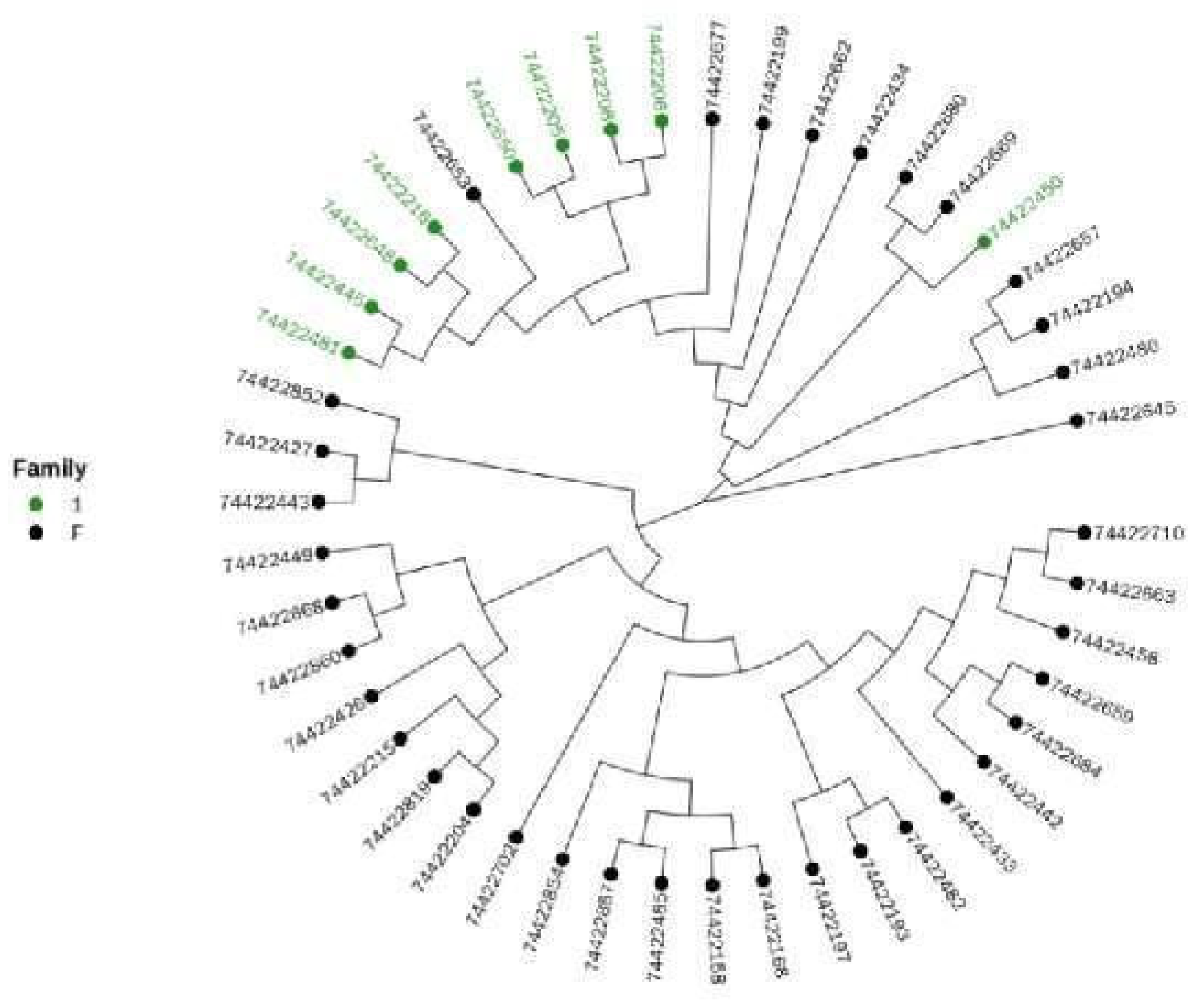
3.6. Cluster Analysis to Construct Altay White-Headeded Cattle Family
Cluster Analysis
3.7. Family Structure Analysis of Altay White-Headed Cattle Conservation Population
4. Discussion
4.1. Genetic Diversity Analysis
4.2. Inbreeding Degree Analysis
4.3. Analysis of Genetic Relationship and Genetic Structure
4.4. Develop Ment of Appropriate Breeding Programmes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daka, P. Introduction to Altay white-headeded Cattle. China’s Livest. Poult. Seed Ind. 2010, 6, 64–65. [Google Scholar]
- Yugang, W.; Xia, L. Discussion on the Improvement of Livestock Varieties in Altay. Heilongjiang Anim. Breed. 2015, 23, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Hazi, W.T.; Muhan, B.; Bahati; Adali; Shaken; Hatipa. Introduction to Altay white-headeded Cattle. Heilongjiang Anim. Husb. Vet. 2004, 5, 20–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hazi, W.T.; Sweat, B.W. Altay white-headeded cattle, a local fine breed. Rural. Pract. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2006, 11, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhongrong. Breeding conservation of Altay white-headeded cattle. Xinjiang Anim. Husb. 2015, 4, 41–43. [Google Scholar]
- Laikre, L.; Hoban, S.; Bruford, M.W.; Segelbacher, G.; Allendorf, F.W.; Gajardo, G.; Rodriguez, A.G.; Hedrick, P.W.; Heuertz, M.; Hohenlohe, P.A.; et al. Post-2020 goals overlook genetic diversity. Science 2020, 367, 1083–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignal, A.; Milan, D.; SanCristobal, M.; Eggen, A. A review on SNP and other types of molecular markers and their use in animal genetics. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2002, 34, 275–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.Z.; Sasazaki, S.; Mannen, H. Genetic diversity and structure in Bos taurus and Bos indicus populations analyzed by SNP markers. Anim. Sci. J. 2010, 81, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notter, D.R. The importance of genetic diversity in livestock populations of the future. J. Anim. Sci. 1999, 77, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, S.; Zhen, W.; Zhe, Z.; Qian, X.; Zhong, X.; Xiangzhe, Z.; Hongjie, Y.; Manxing, Z.; Ming, X.; Xiaohui, L.; et al. Analysis of Meishan Pig Conservation Status Based on Genome Sequencing Data. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Agric. Sci. Ed.) 2017, 35, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Barbato, M.; Orozco-terWengel, P.; Tapio, M.; Bruford, M.W. SNeP: A tool to estimate trends in recent effective population size trajectories using genome-wide SNP data. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botstein, D.; White, R.L.; Skolnick, M.; Davis, R.W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1980, 32, 314–331. [Google Scholar]
- Silio, L.; Rodriguez, M.C.; Fernandez, A.; Barragan, C.; Benitez, R.; Ovilo, C.; Fernandez, A.I. Measuring inbreeding and inbreeding depression on pig growth from pedigree or SNP-derived metrics. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2013, 130, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanRaden, P.M. Efficient methods to compute genomic predictions. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 4414–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, M.; Eriksson, S.; Mikko, S.; Strandberg, E.; Stalhammar, H.; Groenen, M.; Crooijmans, R.; Andersson, G.; Johansson, A.M. Genomic relatedness and diversity of Swedish native cattle breeds. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2019, 51, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautier, M.; Laloe, D.; Moazami-Goudarzi, K. Insights into the genetic history of French cattle from dense SNP data on 47 worldwide breeds. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beynon, S.E.; Slavov, G.T.; Farre, M.; Sunduimijid, B.; Waddams, K.; Davies, B.; Haresign, W.; Kijas, J.; MacLeod, I.M.; Newbold, C.J.; et al. Population structure and history of the Welsh sheep breeds determined by whole genome genotyping. BMC Genet. 2015, 16, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukuckova, V.; Moravcikova, N.; Curik, I.; Simcic, M.; Meszaros, G.; Kasarda, R. Genetic diversity of local cattle. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2018, 65, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yao, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Yang, P.; Chen, N.; Xia, X.; Lyu, S.; Shi, Q.; et al. Assessing genomic diversity and signatures of selection in Pinan cattle using whole-genome sequencing data. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agung, P.P.; Saputra, F.; Zein, M.; Wulandari, A.S.; Putra, W.; Said, S.; Jakaria, J. Genetic diversity of Indonesian cattle breeds based on microsatellite markers. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meszaros, G.; Boison, S.A.; Perez, O.A.; Ferencakovic, M.; Curik, I.; Da, S.M.; Utsunomiya, Y.T.; Garcia, J.F.; Solkner, J. Genomic analysis for managing small and endangered populations: A case study in Tyrol Grey cattle. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 173. [Google Scholar]
- Makina, S.O.; Muchadeyi, F.C.; van Marle-Koster, E.; MacNeil, M.D.; Maiwashe, A. Genetic diversity and population structure among six cattle breeds in South Africa using a whole genome SNP panel. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmanova, A.S.; Kharzinova, V.R.; Volkova, V.V.; Mishina, A.I.; Dotsev, A.V.; Sermyagin, A.A.; Boronetskaya, O.I.; Petrikeeva, L.V.; Chinarov, R.Y.; Brem, G.; et al. Genetic Diversity of Historical and Modern Populations of Russian Cattle Breeds Revealed by Microsatellite Analysis. Genes 2020, 11, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, H.; Yang, B.; Li, J.; Xie, X.; Chen, H.; Ren, J. Population history and genomic signatures for high-altitude adaptation in Tibetan pigs. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuiyan, M.; Lee, S.H.; Hossain, S.; Deb, G.K.; Afroz, M.F.; Lee, S.H.; Bhuiyan, A. Unraveling the Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Bangladeshi Indigenous Cattle Populations Using 50 k SNP Markers. Animals 2021, 11, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jia, Y.; Zhu, B.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Gao, H.; et al. Genome-wide assessment of genetic diversity and population structure insights into admixture and introgression in Chinese indigenous cattle. BMC Genet. 2018, 19, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, L.; Baird, M.; Hilborn, R.; Seeb, L.W.; Seeb, J.E. An empirical comparison of SNPs and microsatellites for parentage and kinship assignment in a wild sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) population. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2011, 11 (Suppl. 1), 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, G.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Ma, P.P.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, X.D. Chinese Holstein Cattle effective population size estimated from whole genome linkage disequilibrium. Yi Chuan 2012, 34, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, W.G. Linkage disequilibrium among multiple neutral alleles produced by mutation in finite population. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1975, 8, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qanbari, S.; Pimentel, E.C.; Tetens, J.; Thaller, G.; Lichtner, P.; Sharifi, A.R.; Simianer, H. A genome-wide scan for signatures of recent selection in Holstein cattle. Anim. Genet. 2010, 41, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhihua, C.; Fenggui, T.; Jincheng, Z. Study on Genetic Diversity and Systemic Differentiation of Cattle Breeds. In Proceedings of the 7th National Congress and Academic Seminar of Animal Ecology Branch of Chinese Society of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, Yangling, China, 26–29 July 2008; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Ceballos, F.C.; Joshi, P.K.; Clark, D.W.; Ramsay, M.; Wilson, J.F. Runs of homozygosity: Windows into population history and trait architecture. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolini, F.; Cardoso, T.F.; Marras, G.; Nicolazzi, E.L.; Rothschild, M.F.; Amills, M. Genome-wide patterns of homozygosity provide clues about the population history and adaptation of goats. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2018, 50, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhancheng, Y.; Sky, Y.R.; Qingxia, Y.; Yachun, W.; Ying, Y.; Shaohu, C.; Dongxiao, S.; Shengli, Z.; Yi, Z. Genomic Inbreeding Analysis of Chinese Holstein Cattle Using High Density SNP Markers. Inheritance 2017, 39, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, E.S.; Cole, J.B.; Huson, H.; Wiggans, G.R.; Van Tassell, C.P.; Crooker, B.A.; Liu, G.; Da, Y.; Sonstegard, T.S. Effect of artificial selection on runs of homozygosity in u.s. Holstein cattle. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honghao, W.; Xiaokang, R.; Yi, Z.; Huijiang, G.; Leijie, C.; Xi, W. Application of Gene Chip Technology in Jinnan Bull Breeding. J. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2021, 52, 2803–2813. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, S.; Yi, Z.; Yachun, W.; Tao, H.; Guochang, L.; Tao, Y.; Zhenxi, L.; Xixia, H.; Xinpu, W.; Shutang, F.; et al. Evaluation of Genomic Homozygosity of Xinjiang Inbred Cattle Using SNP Chip Information. Inheritance 2020, 42, 493–506. [Google Scholar]
- Wiggans, G.R.; Su, G.; Cooper, T.A.; Nielsen, U.S.; Aamand, G.P.; Guldbrandtsen, B.; Lund, M.S.; VanRaden, P.M. Short communication: Improving accuracy of Jersey genomic evaluations in the United States and Denmark by sharing reference population bulls. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 3508–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Calus, M.P.; Guldbrandtsen, B.; Lund, M.S.; Sahana, G. Estimation of inbreeding using pedigree, 50 k SNP chip genotypes and full sequence data in three cattle breeds. BMC Genet. 2015, 16, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, W.; Yuanqing, Z.; Dongchang, H.; Xizhong, Z.; Bo, L.; Dongcai, W.; Guang, J.; Fuxing, L.; Xiaomin, Y.; Fang, X. Analysis of Genetic Diversity between Jinnan Cattle and Some Local Yellow Cattle. J. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2015, 46, 911–923. [Google Scholar]
- Ocampo, R.J.; Martinez, J.F.; Martinez, R. Assessment of genetic diversity and population structure of Colombian Creole cattle using microsatellites. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utsunomiya, Y.T.; Bomba, L.; Lucente, G.; Colli, L.; Negrini, R.; Lenstra, J.A.; Erhardt, G.; Garcia, J.F.; Ajmone-Marsan, P. Revisiting AFLP fingerprinting for an unbiased assessment of genetic structure and differentiation of taurine and zebu cattle. BMC Genet. 2014, 15, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, A.C.; Uffo, O.; Sanz, A.; Ronda, R.; Osta, R.; Rodellar, C.; Martin-Burriel, I.; Zaragoza, P. Genetic diversity and differentiation of five Cuban cattle breeds using 30 microsatellite loci. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2013, 130, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michailidou, S.; Tsangaris, G.T.; Tzora, A.; Skoufos, I.; Banos, G.; Argiriou, A.; Arsenos, G. Analysis of genome-wide DNA arrays reveals the genomic population structure and diversity in autochthonous Greek goat breeds. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e226179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuditschko, M.; Raadsma, H.W.; Khatkar, M.S.; Jonas, E.; Steinig, E.J.; Flury, C.; Signer-Hasler, H.; Frischknecht, M.; von Niederhausern, R.; Leeb, T.; et al. Identification of key contributors in complex population structures. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e177638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Quality Control Standard | Number of SNPs |
|---|---|
| Total number of SNPs | 101,220 |
| SNP with MAF < 0.01 | 3157 |
| SNP not in Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium p < 10−6 | 66 |
| SNP with callrate < 0.90 | 1010 |
| SNPs on chromosome X | 3785 |
| SNPs on chromosome Y | 330 |
| SNPs on chromosome 0 | 6267 |
| insertion/deletion | 174 |
| SNPs used after quality control | 85,993 |
| Effective Population Content (Ne) | 2.4 |
| Proportion of Polymorphic Markers (PN) | 0.935 |
| Expected Heterozygosity (HE) | 0.403 |
| Heterozygosity Observed (HO) | 0.413 |
| Polymorphism Information Content (PIC) | 0.304 |
| Effective Numbers of Alleles | 1.704 |
| Minor Allele Frequency (MAF) | 0.309 |
| Family 1 Male Altay White-Headed Cattle | Family 1 Female Altay White-Headed Cattle | Miscellaneous | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 74422650 | 74422199 | 74422645 | 74422702 |
| 74422481 | 74422677 | 74422657 | 74422668 |
| 74422205 | 74422653 | 74422480 | 74422854 |
| 74422648 | 74422662 | 74422194 | 74422819 |
| 74422206 | 74422434 | 74422426 | 74422204 |
| 74422216 | 74422669 | 74422449 | 74422857 |
| 74422208 | 74422680 | 74422443 | 74422442 |
| 74422445 | 74422485 | 74422482 | |
| 74422450 | 74422852 | 74422458 | |
| 74422197 | 74422158 | ||
| 74422168 | 74422684 | ||
| 74422193 | 74422433 | ||
| 74422427 | 74422659 | ||
| 74422860 | 74422663 | ||
| 74422215 | 74422710 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.; Tao, W.; Feng, D.; Wang, Y.; Heizatuola, N.; Ahemetbai, T.; Wu, W. Revealing Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Endangered Altay White-Headed Cattle Population Using 100 k SNP Markers. Animals 2022, 12, 3214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223214
Liu B, Tao W, Feng D, Wang Y, Heizatuola N, Ahemetbai T, Wu W. Revealing Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Endangered Altay White-Headed Cattle Population Using 100 k SNP Markers. Animals. 2022; 12(22):3214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223214
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Bo, Weikun Tao, Donghe Feng, Yue Wang, Nazigul Heizatuola, Tenes Ahemetbai, and Weiwei Wu. 2022. "Revealing Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Endangered Altay White-Headed Cattle Population Using 100 k SNP Markers" Animals 12, no. 22: 3214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223214
APA StyleLiu, B., Tao, W., Feng, D., Wang, Y., Heizatuola, N., Ahemetbai, T., & Wu, W. (2022). Revealing Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Endangered Altay White-Headed Cattle Population Using 100 k SNP Markers. Animals, 12(22), 3214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223214






