Effects of Fermented Bamboo Powder Supplementation on Serum Biochemical Parameters, Immune Indices, and Fecal Microbial Composition in Growing–Finishing Pigs
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, Diets, and Experimental Design
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Chemical Analyses
2.4. DNA Extraction and 16S rDNA Gene Sequencing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance
3.2. Serum Biochemical Parameters, Immunoglobulins, and Inflammatory Cytokines
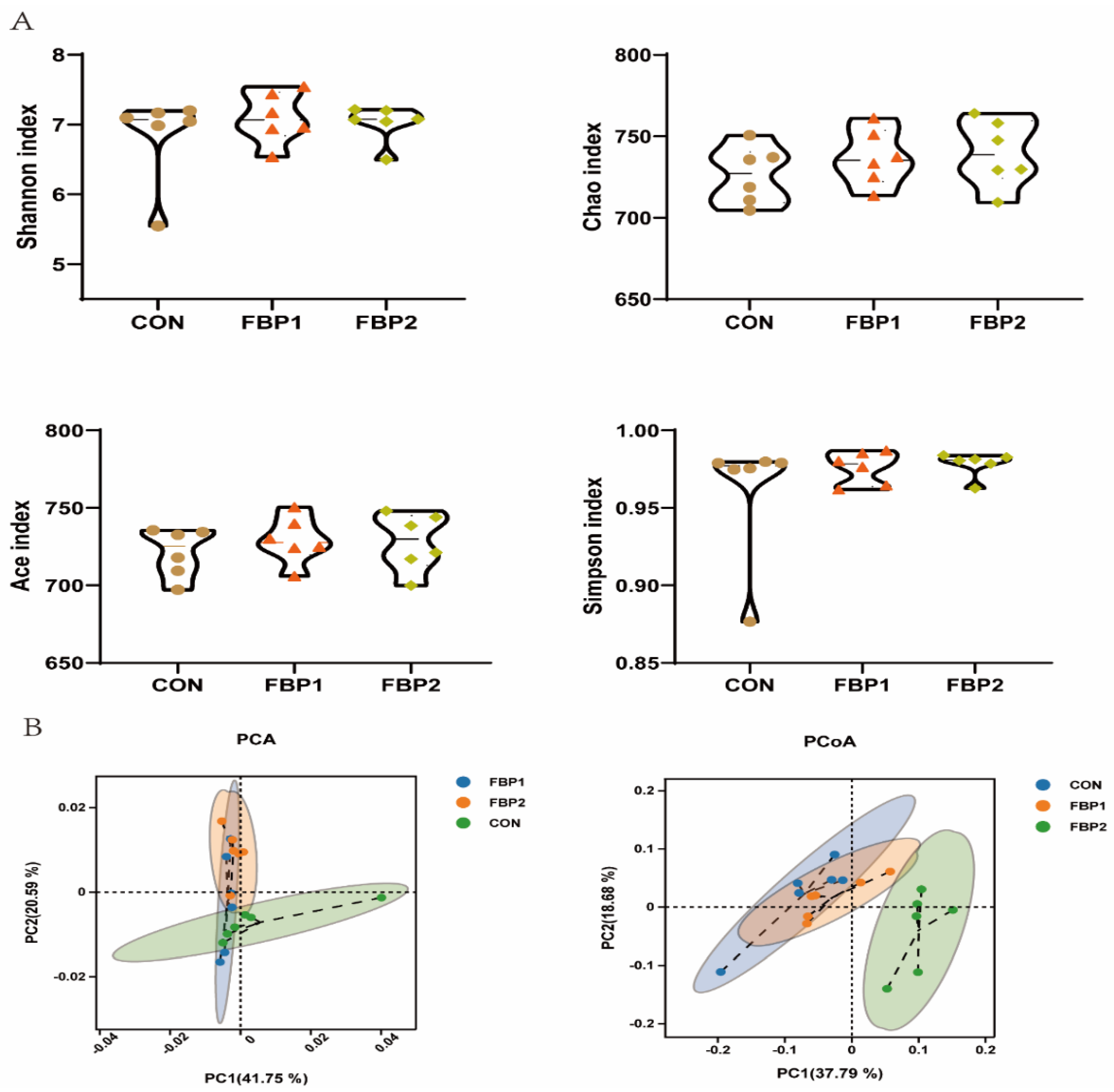
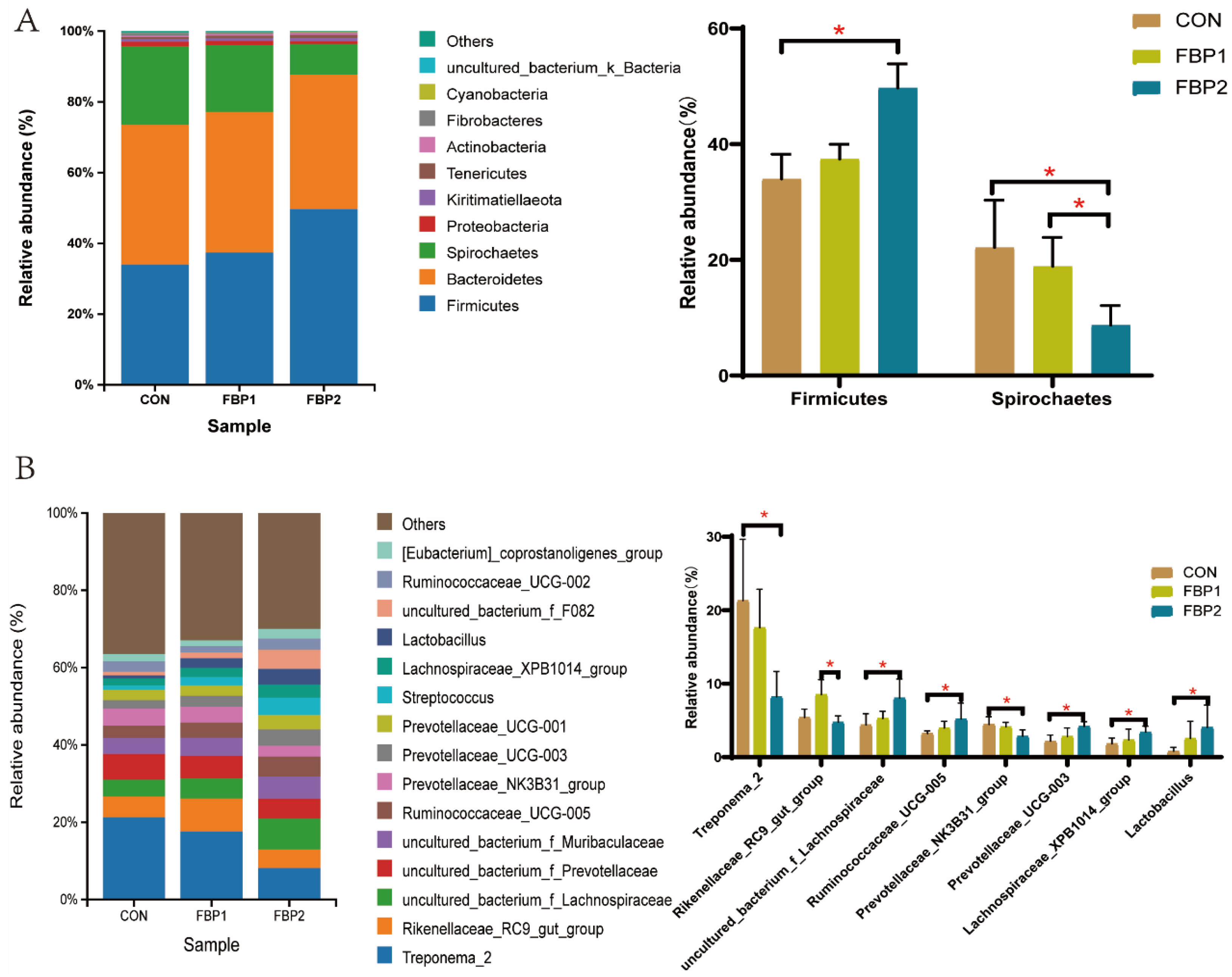
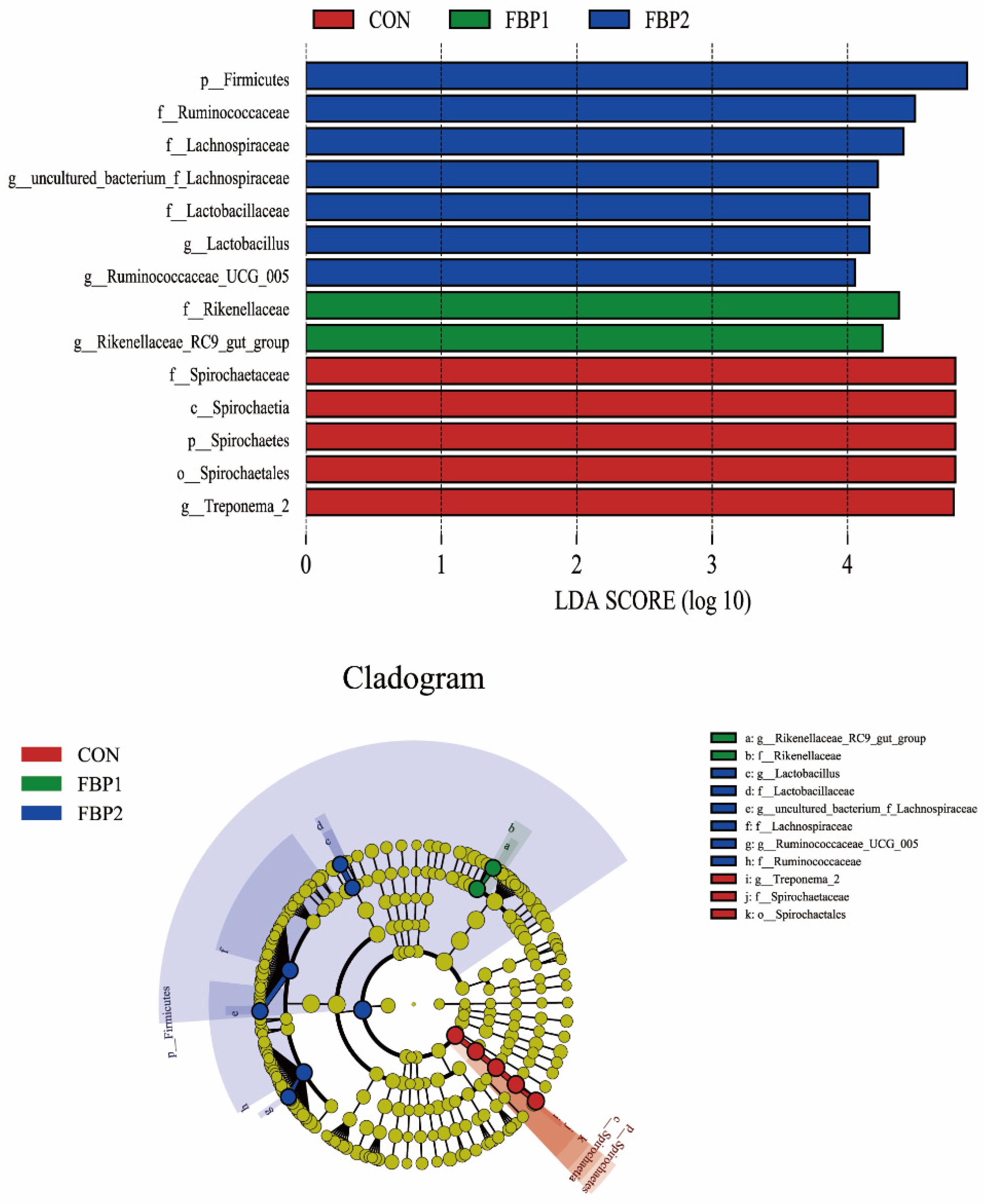
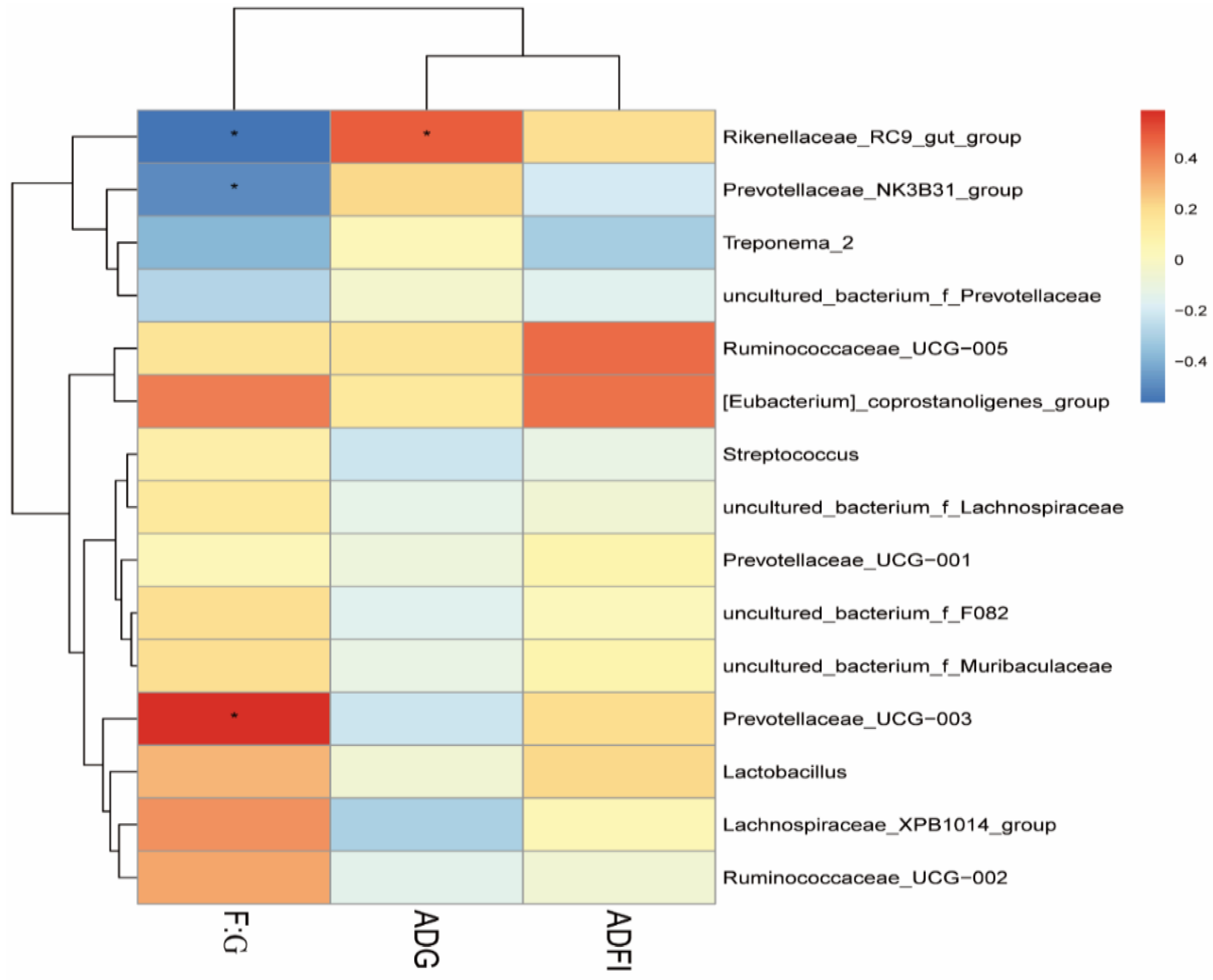
3.3. Fecal Bacterial Community
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food Security: The Challenge of Feeding 9 Billion People. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMichael, A.J.; Powles, J.W.; Butler, C.D.; Uauy, R. Food, livestock production, energy, climate change, and health. Lancet 2007, 370, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lee, D.J. Lignocellulosic biomass pretreatment by deep eutectic solvents on lignin extraction and saccharification enhancement: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 339, 125587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woyengo, T.; Beltranena, E.; Zijlstra, R. Nonruminant nutrition symposium: Controlling feed cost by including alternative ingredients into pig diets: A review. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 1293–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Y.; Lam, S.S.; Wu, Y.; Ge, S.; Wu, J.; Cai, L.; Huang, Z.; Le, Q.V.; Sonne, C.; Xia, C. Enzymatic conversion of pretreated lignocellulosic biomass: A review on influence of structural changes of lignin. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 324, 124631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D. Biomass recalcitrance. Part II: Fundamentals of different pre-treatments to increase the enzymatic digestibility of lignocellulose. Biofuels Bioprod. Bioref. 2012, 6, 561–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, R.; Binod, P.; Pandey, A. Biological pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass—An overview. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 199, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Chen, Y.; Luo, L.; Heidari, F.; Tiffany, D.G.; Urriola, P.E.; Shurson, G.G.; Hu, B. Feeding value improvement by co-fermentation of corn-ethanol co-product and agro-industrial residues with Rhizopus oryzae. Process Biochem. 2021, 111, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, R.; Chakraborty, R.; Dutta, A. Role of Fermentation in Improving Nutritional Quality of Soybean Meal—A Review. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 29, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, F.; Zhong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; Gai, X. Bamboo—An untapped plant resource for the phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, M.; Yrjälä, K.; Vinod, K.K.; Sharma, A.; Cho, J.; Satheesh, V.; Zhou, M. Genetics and genomics of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis): Current status, future challenges, and biotechnological opportunities toward a sustainable bamboo industry. Food Energy Secur. 2020, 9, e229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, K.; Ohkoshi, N.; Nishiyama, A.; Usagawa, T.; Kitagawa, M. Improving the nutritive value of madake bamboo, Phyllostachys bambusoides, for ruminants by culturing with the white-rot fungus Ceriporiopsis subvermispora. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2009, 152, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayota, M.; Karashima, J.; Kouketsu, T.; Nakano, M.; Ohtani, S. Seasonal changes in the digestion and passage rates of fresh dwarf bamboo (Pleioblastus argenteostriatus f. glaber) in sheep. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2009, 149, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kuijk, S.J.A.; Sonnenberg, A.S.M.; Baars, J.J.P.; Hendriks, W.H.; Cone, J.W. Fungal treated lignocellulosic biomass as ruminant feed ingredient: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, G.M.; Jung, C.K.; Kim, H.Y.; Ha, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Jung, M.S.; Lee, S.J.; Song, Y.; Ibrahim, R.I.H.; Cho, J.H.; et al. Effects of bamboo charcoal and bamboo vinegar as antibiotic alternatives on growth performance, immune responses and fecal microflora population in fattening pigs. Anim. Sci. J. 2013, 84, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Lin, T.; Cheng, L.; Wang, J.; Zuo, J.; Feng, D. Effects of micronized bamboo powder on growth performance, serum biochemical indexes, cecal chyme microflora and metabolism of broilers aged 1–22 days. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2022, 54, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.F.; Wang, J.L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.M.; Liu, J.X.; Dai, B. Effect of bamboo vinegar as an antibiotic alternative on growth performance and fecal bacterial communities of weaned piglets. Livest. Sci. 2012, 144, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRC. Nutrient Requirements of Swine, 11th ed.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Gaithersburgs, MD, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhao, J. Variations on gut health and energy metabolism in pigs and humans by intake of different dietary fibers. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 4639–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Lin, T.; Su, B.; Yao, H.; Gu, D.; Yang, Y. Effects of feeding bamboo powder on growth performance, serum biochemical indexes and fecal microorganism of weaned piglets. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 33, 6709–6720. [Google Scholar]
- Balan, P.; Sik-Han, K.; Moughan, P.J. Impact of oral immunoglobulins on animal health—A review. Anim. Sci. J. 2019, 90, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtaugh, M.P.; Baarsch, M.J.; Zhou, Y.; Scamurra, R.W.; Lin, G. Inflammatory cytokines in animal health and disease. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1996, 54, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbuewu, I.P.; Emenalom, O.O.; Okoli, I.C. Alternative feedstuffs and their effects on blood chemistry and haematology of rabbits and chickens: A review. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 26, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayanagi, K. Prevention of Adiposity by the Oral Administration of β-Cryptoxanthin. Front. Neurol. 2011, 2, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa-Pereira, P.; Woof, J.M. IgA: Structure, Function, and Developability. Antibodies 2019, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Q.; Li, H.; Wu, P.; Sha, R.; Xiao, Z.; Dai, J.; Mao, J. Investigation of physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of ultrafine bamboo leaf powder prepared by ball milling. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanawut, J.; Pimpa, O.; Venkatachalam, K.; Yamauchi, K.-E. Effects of bamboo charcoal powder, bamboo vinegar, and their combination in laying hens on performance, egg quality, relative organ weights, and intestinal bacterial populations. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Song, D.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Y. Microbiota in fermented feed and swine gut. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 2941–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xiao, H.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, Q.; Wen, X.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, L. Effects of Fermented Feed on the Growth Performance, Intestinal Function, and Microbiota of Piglets Weaned at Different Age. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 841762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, D.; Di Cagno, R.; Fåk, F.; Flint, H.J.; Nyman, M.; Saarela, M.; Watzl, B. Contribution of diet to the composition of the human gut microbiota. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 26164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, W.-M.; Chang, C.-R.; Chang, T.-J.; Li, S.-Y.; Chen, W.-J.; Chau, C.-F. Inclusion of Fructooligosaccharide and Resistant Maltodextrin in High Fat Diets Promotes Simultaneous Improvements on Body Fat Reduction and Fecal Parameters. Molecules 2018, 23, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, Y.; Hu, J.; Shi, B.; Dingkao, R.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Luo, Y.; Liu, X. Characteristics and Functions of the Rumen Microbial Community of Cattle-Yak at Different Ages. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 3482692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ouyang, Y.; Li, H.; Shen, L.; Ni, Y.; Fang, Q.; Wu, G.; Qian, L.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Metabolic phenotypes and the gut microbiota in response to dietary resistant starch type 2 in normal-weight subjects: A randomized crossover trial. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, G.; Cox, F.; Ganesh, S.; Jonker, A.; Young, W.; Global Rumen Census, C.; Janssen, P.H. Rumen microbial community composition varies with diet and host, but a core microbiome is found across a wide geographical range. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Item | Fermented Bamboo Powder |
|---|---|
| Dry matter | 89.80 |
| Crude protein | 2.28 |
| Ether extract | 0.18 |
| Neutral detergent fiber | 60.80 |
| Acid detergent fiber | 47.36 |
| Calcium | 0.12 |
| Total phosphorus | 0.02 |
| Gross energy, MJ/kg | 16.85 |
| Item 1 | CON | FBP1 | FBP2 | SEM | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANOVA | Linear | Quadratic | |||||
| Initial body weight, kg | 56.28 | 56.47 | 56.28 | 0.15 | 0.864 | 0.649 | 0.782 |
| Final body weight, kg | 131.80 | 132.81 | 131.66 | 0.21 | 0.052 | 0.047 | 0.131 |
| Average daily gain, kg | 1.03 | 1.05 | 1.03 | 0.00 | 0.265 | 0.197 | 0.315 |
| Average daily feed intake, kg | 2.91 | 2.93 | 2.94 | 0.01 | 0.438 | 0.316 | 0.426 |
| Feed:gain | 2.81 a,b | 2.80 b | 2.84 a | 0.01 | 0.016 | 0.479 | 0.005 |
| Item 1 | CON | FBP1 | FBP2 | SEM | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANOVA | Linear | Quadratic | |||||
| IgG, g/L | 8.71 | 8.78 | 8.62 | 0.15 | 0.925 | 0.875 | 0.722 |
| IgA, g/L | 0.97 b | 1.27 a | 1.04 a,b | 0.05 | 0.046 | 0.019 | 0.401 |
| IgM, g/L | 0.78 | 0.75 | 0.76 | 0.01 | 0.586 | 0.369 | 0.625 |
| IL-4, pg/mL | 23.66 | 30.19 | 21.41 | 2.88 | 0.482 | 0.390 | 0.401 |
| IL-10, pg/mL | 17.80 | 28.71 | 8.85 | 5.19 | 0.334 | 0.412 | 0.218 |
| TNF-α, pg/mL | 36.38 | 35.45 | 19.19 | 6.28 | 0.502 | 0.955 | 0.249 |
| IFN-γ, pg/mL | 47.73 | 42.89 | 34.09 | 2.91 | 0.172 | 0.496 | 0.082 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Li, N.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, C.; Liang, S.; Li, Y.; Yan, J.; Li, Q.; Mu, S. Effects of Fermented Bamboo Powder Supplementation on Serum Biochemical Parameters, Immune Indices, and Fecal Microbial Composition in Growing–Finishing Pigs. Animals 2022, 12, 3127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223127
Liu Z, Li N, Zhou X, Zheng Z, Zhang C, Liang S, Li Y, Yan J, Li Q, Mu S. Effects of Fermented Bamboo Powder Supplementation on Serum Biochemical Parameters, Immune Indices, and Fecal Microbial Composition in Growing–Finishing Pigs. Animals. 2022; 12(22):3127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223127
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhengqun, Ning Li, Xiaoqiao Zhou, Zi Zheng, Chunhua Zhang, Shiyue Liang, Yuanming Li, Jun Yan, Qianjun Li, and Shuqin Mu. 2022. "Effects of Fermented Bamboo Powder Supplementation on Serum Biochemical Parameters, Immune Indices, and Fecal Microbial Composition in Growing–Finishing Pigs" Animals 12, no. 22: 3127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223127
APA StyleLiu, Z., Li, N., Zhou, X., Zheng, Z., Zhang, C., Liang, S., Li, Y., Yan, J., Li, Q., & Mu, S. (2022). Effects of Fermented Bamboo Powder Supplementation on Serum Biochemical Parameters, Immune Indices, and Fecal Microbial Composition in Growing–Finishing Pigs. Animals, 12(22), 3127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223127





