Assessment of Adaptation Status of Reintroduced Equus Przewalskii Based on Comparative Analysis of Fecal Bacteria with Those of Captive E. Przewalskii, Domestic Horse and Mongolian Wild Ass
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
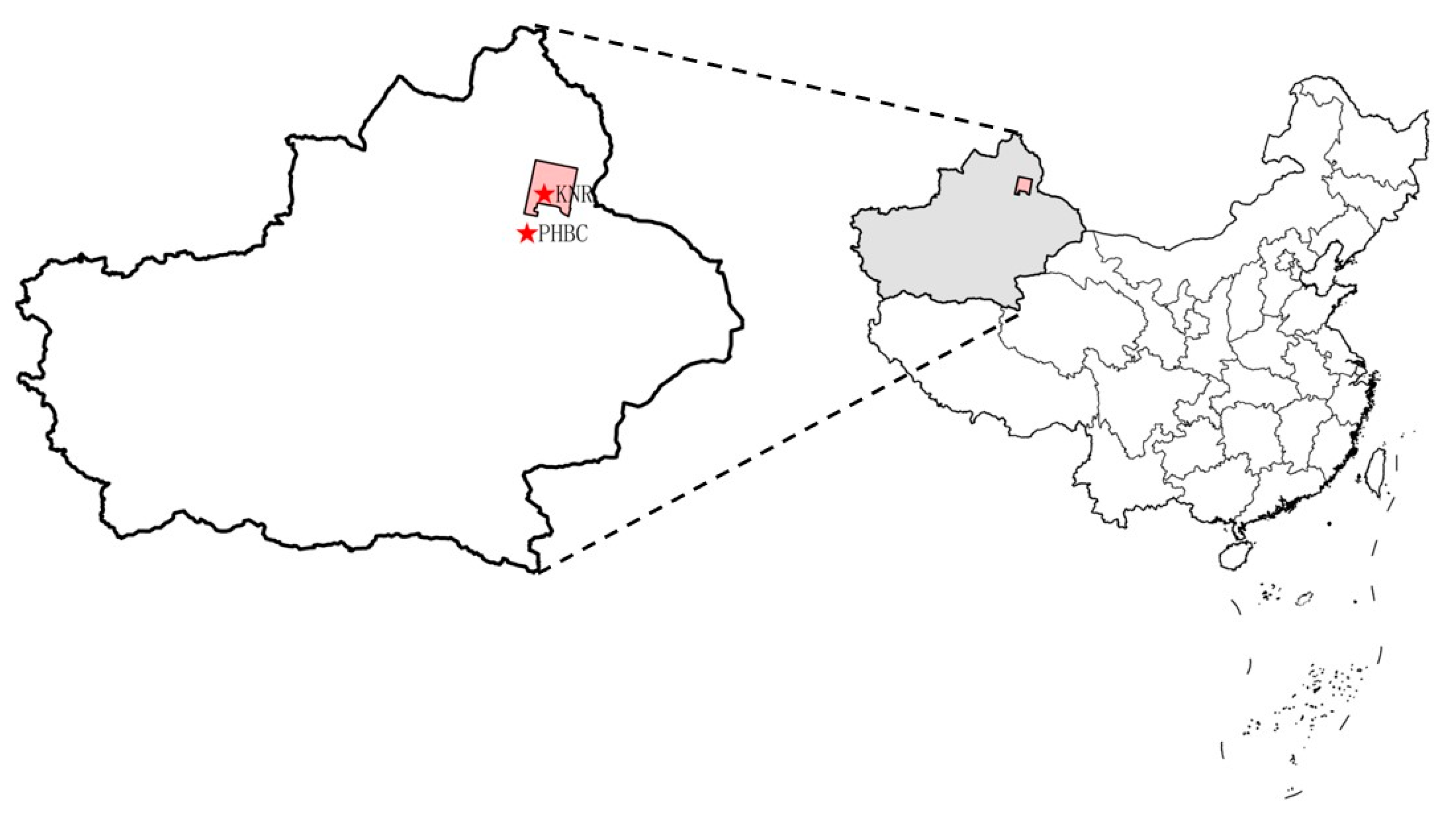
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Sequencing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Sequence Statistics
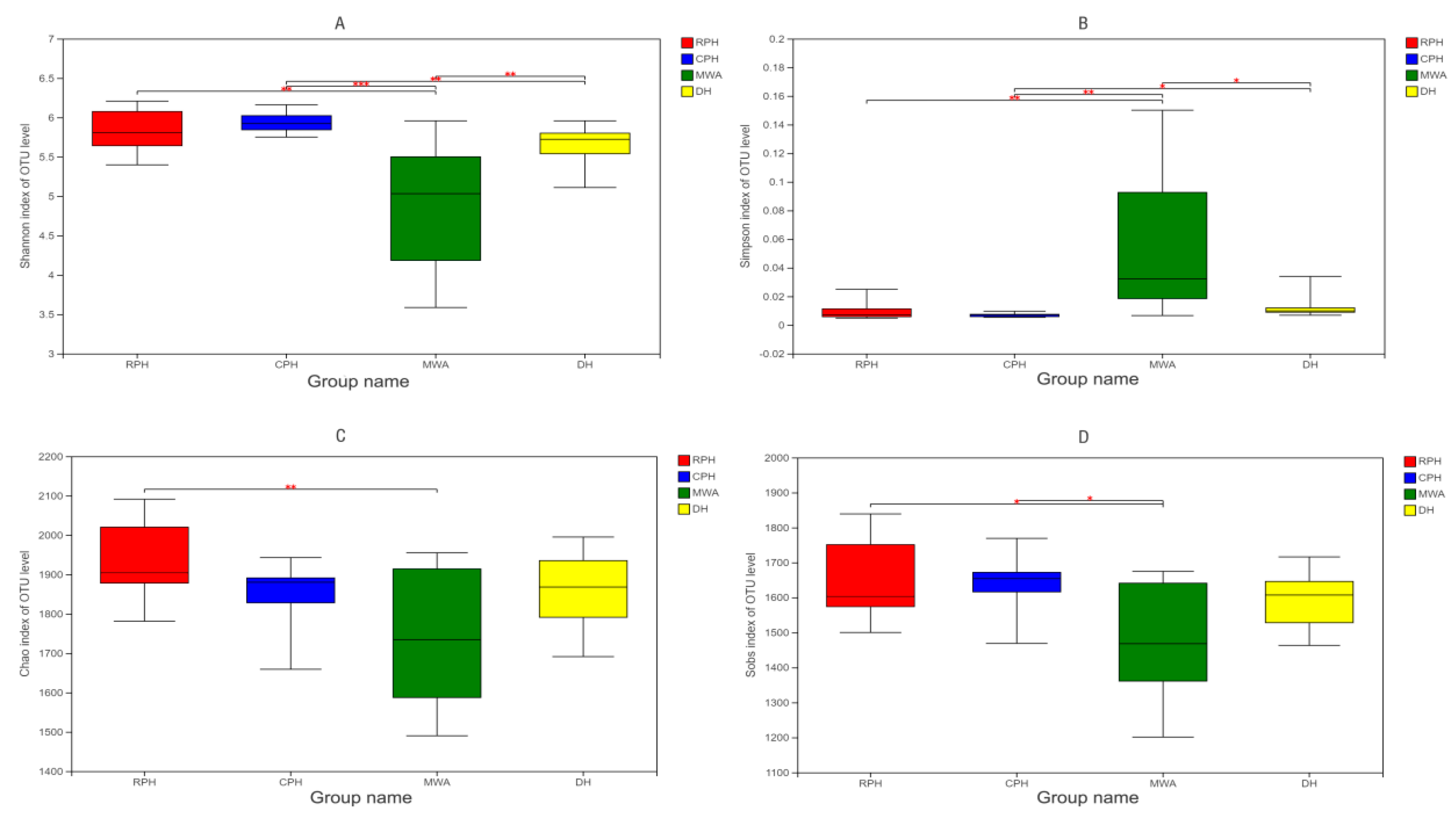
3.2. The Differences in the Microbiota Diversity among Different Groups
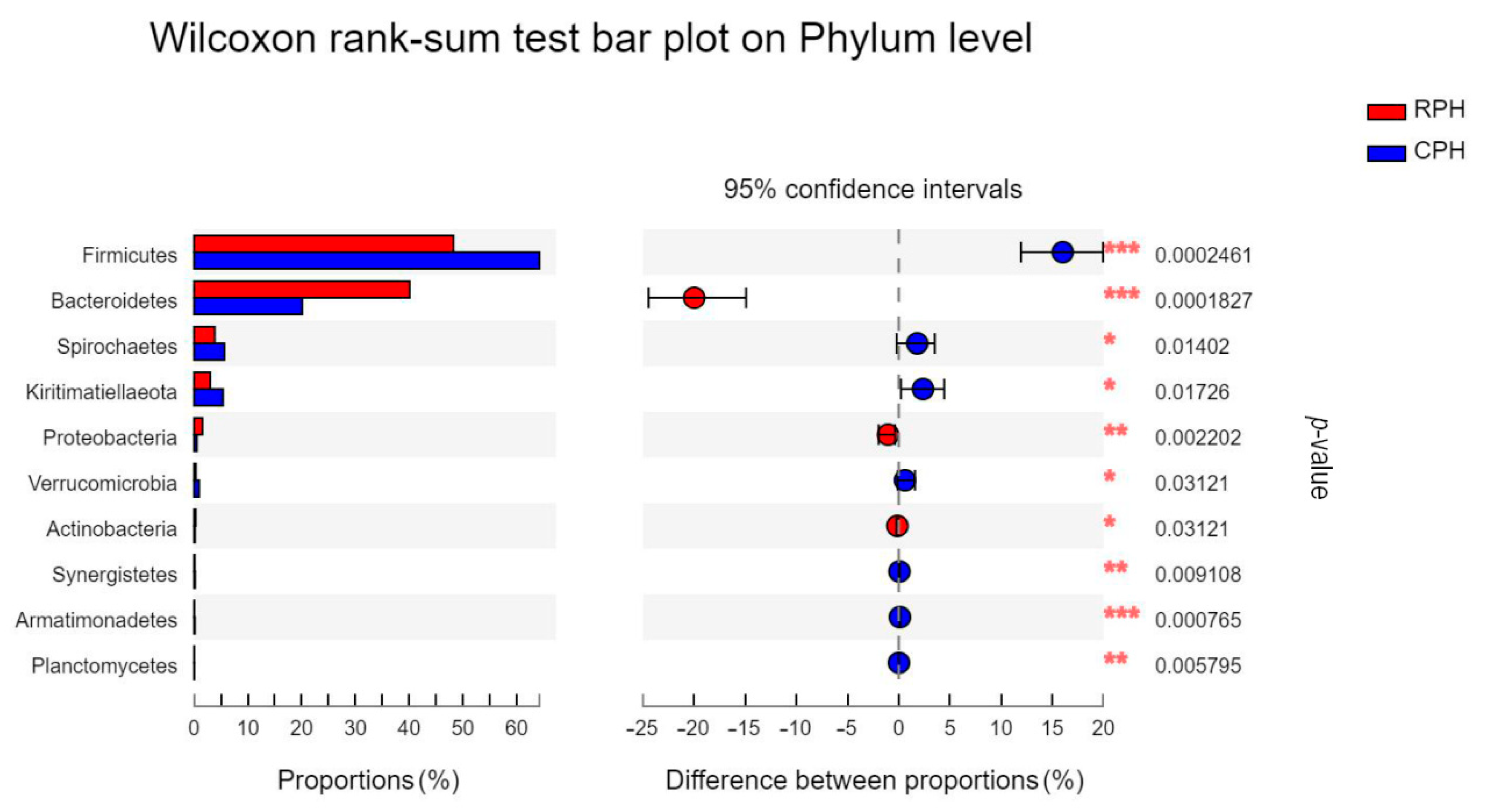
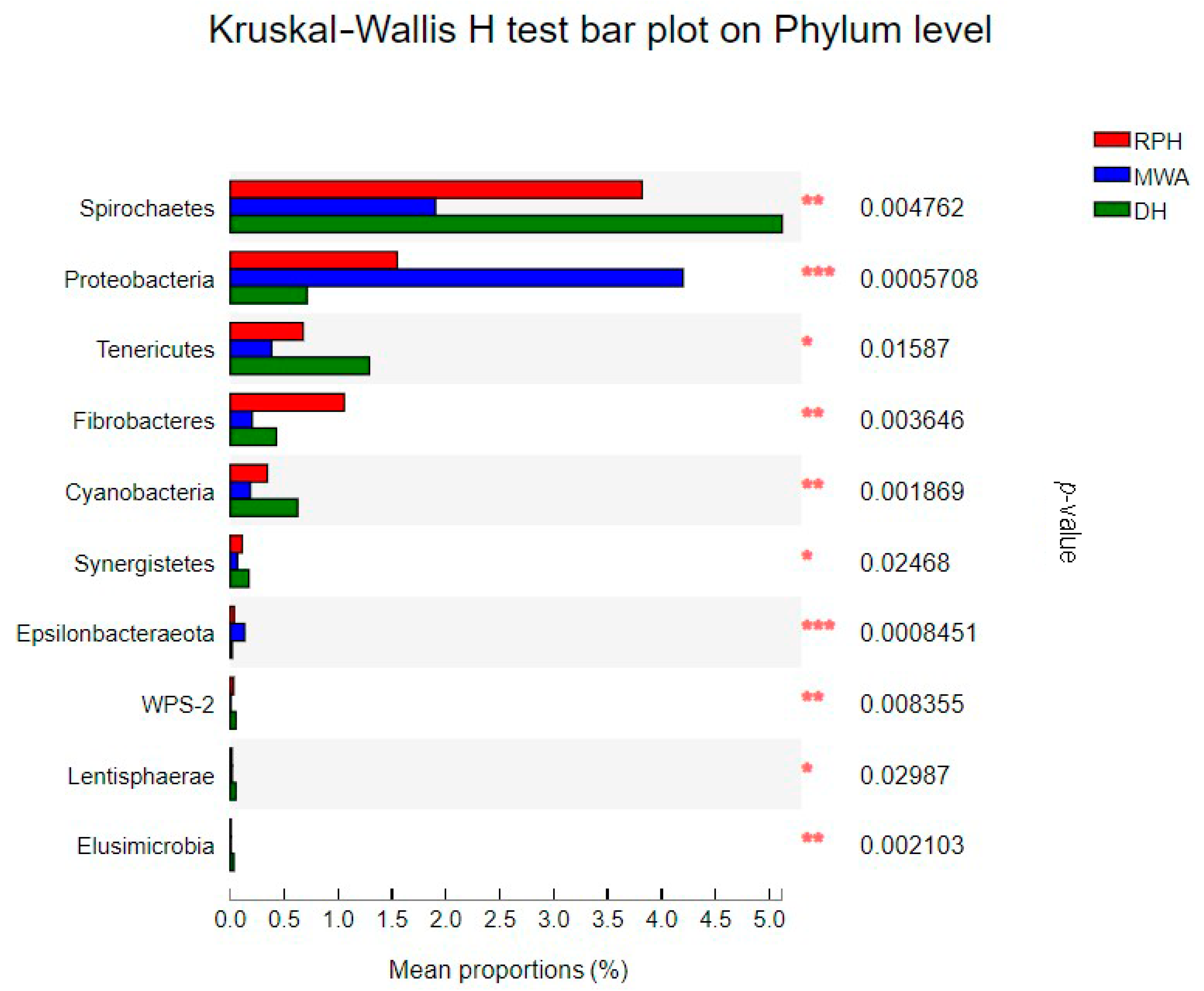
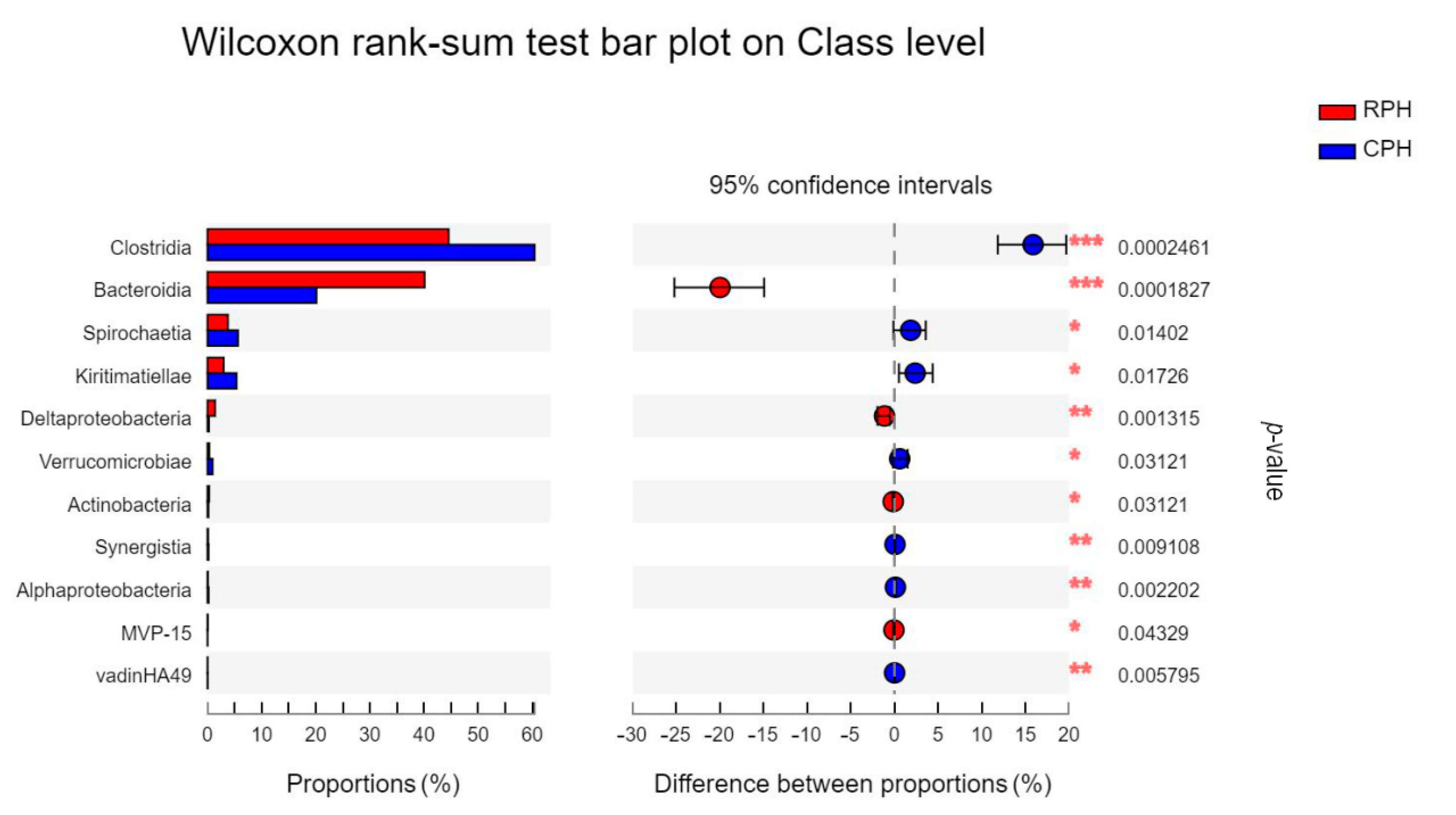
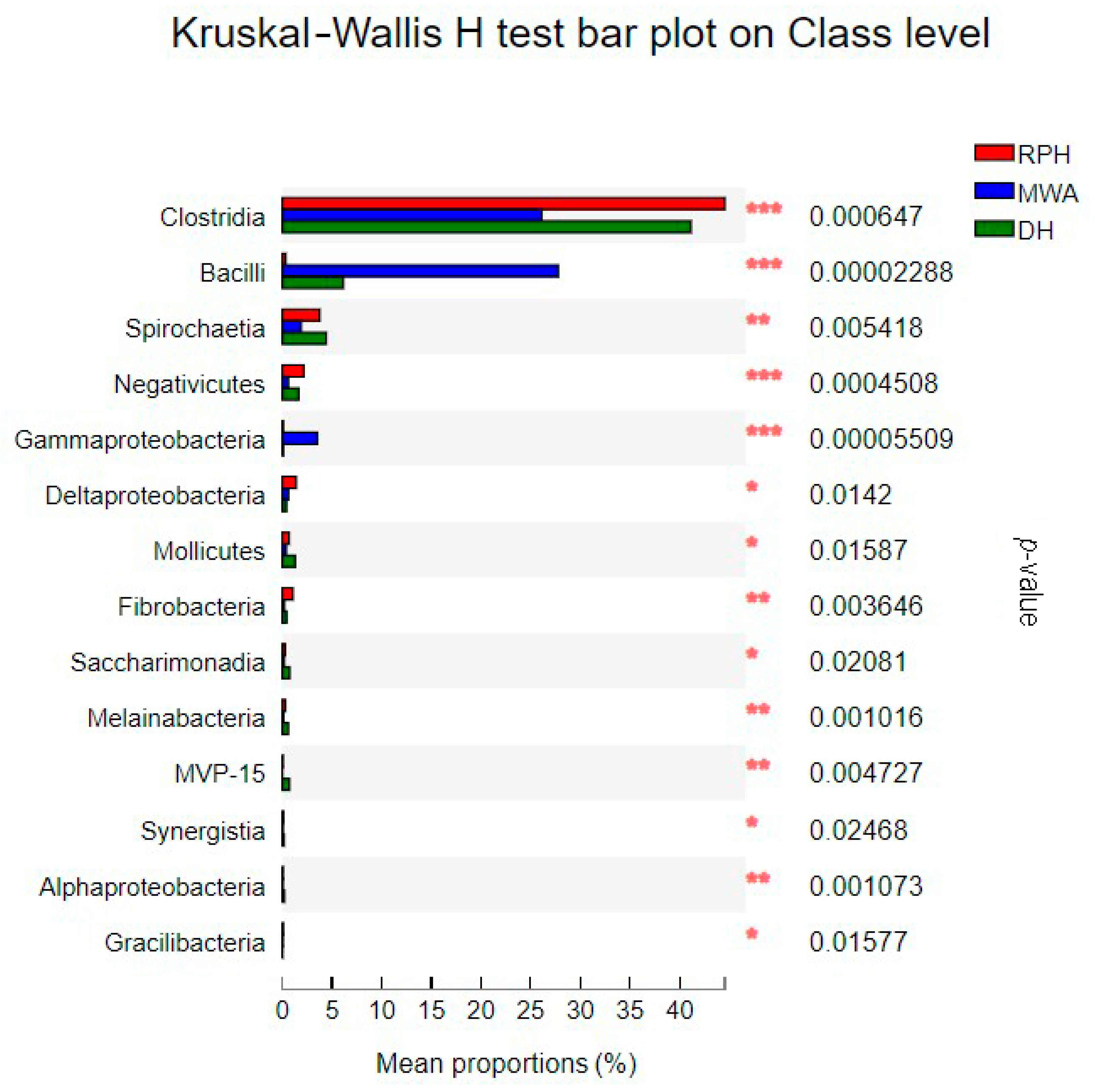
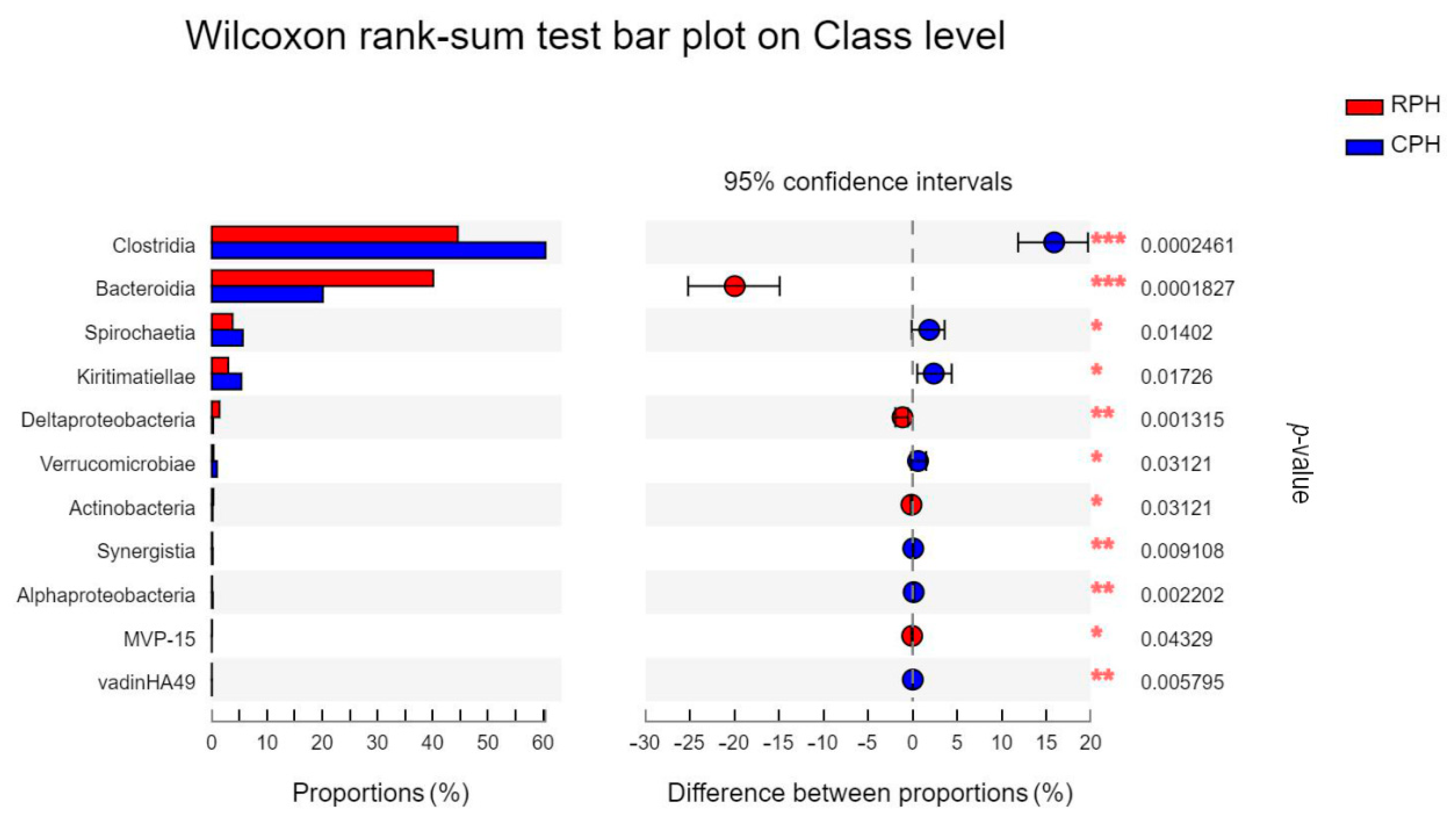
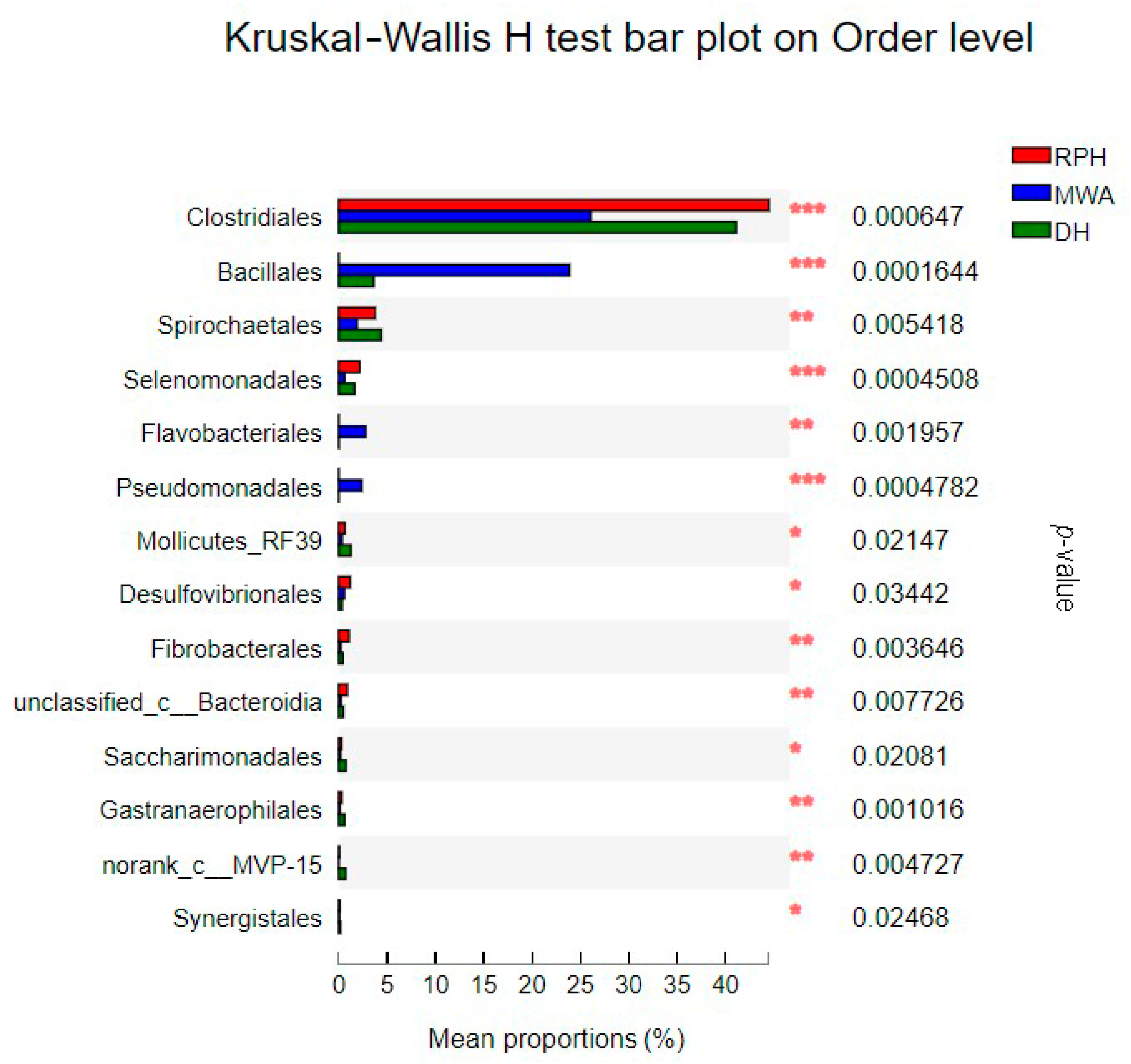
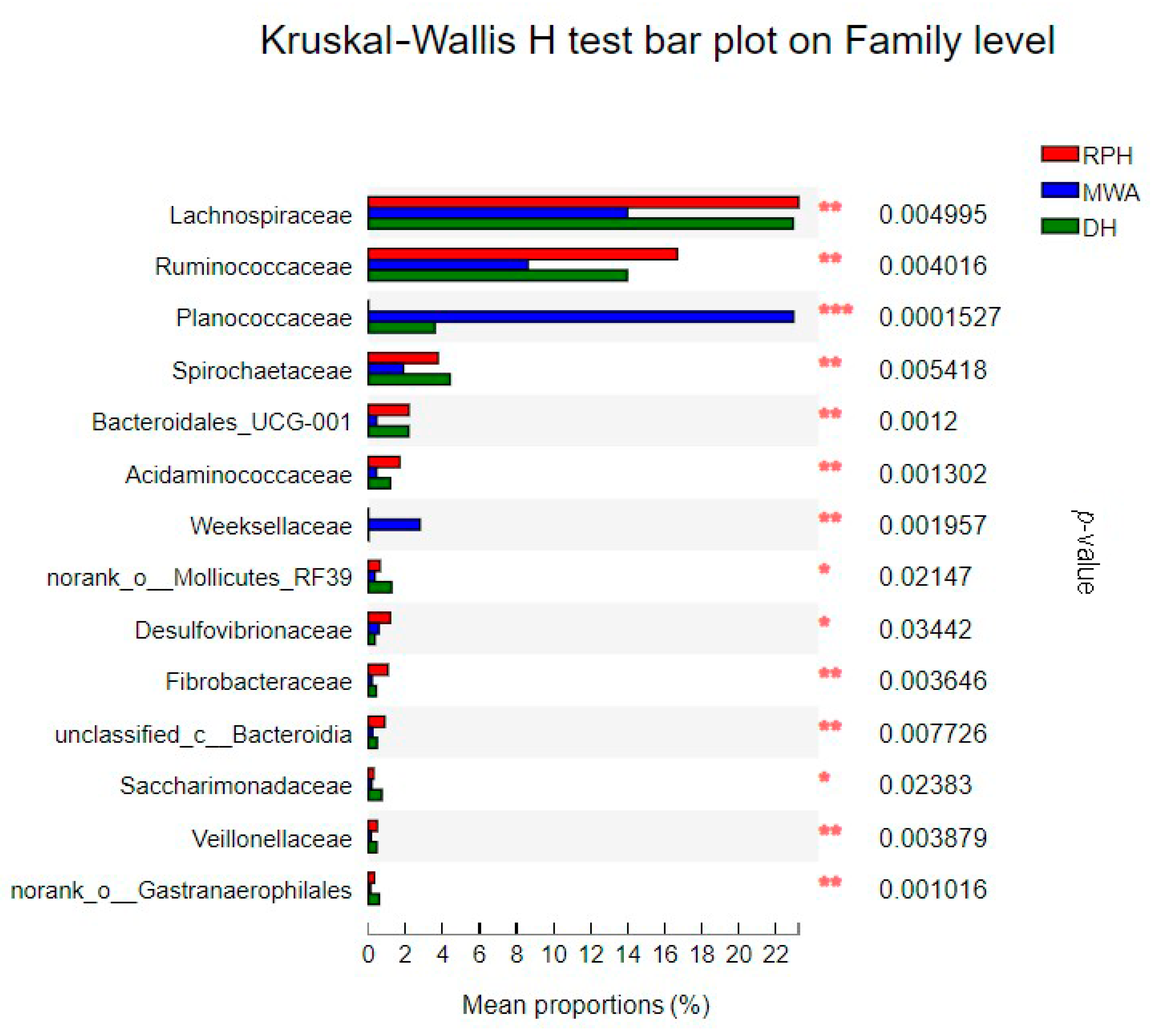
3.3. The Comparison of Microbial Community Composition and Structure
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- King, S.R.B.; Boyd, L.; Zimmermann, W.; Kendall, B. Equus ferus ssp. Przewalskii. In IUCN 2016; IUCN Red List of Threatened Species: Cambridg, UK, 2015; Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/ (accessed on 16 October 2022).
- Mohr, E. The Asiatic Wild Horse; J. A. Ellen & Co. Ltd.: London, UK, 1972; pp. 1–124. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, L.; Cao, J. The Breeding Status of Captive Przewalskii horse in Xinjiang. Chin. J. Zool. 2002, 70–72. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chu, H.; Jiang, Z.G.; Lan, W.; Wang, C.; Tao, Y.S.; Jiang, F. Dietary overlap among Kulan Equus hemionus, Goitered gazelle Gazella subgutturosa and livestock. Acta. Zool. Sin. 2008, 54, 941–954. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Hu, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H. A preliminary observation on the behavioral changes of released Prezwalski’s horses in rewilding process. J. Xinjiang Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2007, 4, 69–73. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J. Utilization of Food, Water and Space by Released Przewalski horse (Equus przewalski) with Reference to Survival Strategies Analysis. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2008. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Hu, D.; Li, K.; Chen, J. Study on the behavior and activity budgets of reintroduced female Przewalski horse in lactation period. J. Xinjiang Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2009, 28, 13–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Hu, D.; Li, K.; Cao, J.; Chen, J.; Waltrau, Z. The agonistic behavior and hierarchical formation of the Equus przewalskii herd in the individual coalition and initial releasing period. Chin. J. Zool. 2009, 44, 58–63. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Hu, D.; Tang, Y.; Ji, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G. Physiological response of behavior and stress in breeding group of Przewalskii horse during releasing process. China Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2011, 38, 561–580. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Ji, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Chu, H.; Li, K.; Hu, D. Change of released Equus przewalskii family and the implication to their management in initial period. Sichuan J. Zool. 2012, 31, 488–491+496. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Hu, D.; He, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, F. The breeding status of the released Przewalski horses in Xinjiang, China. Bull. Biol. 2009, 44, 5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Chu, H.; Cao, J.; Bu, L.; Hu, D.; Zhang, D.; Li, K. Distribution of Gasterophilus (Diptera, Gasterophilidae) myiasis foci in arid desert steppe: A case study of Kalamaili Mountain Ungulate Nature Reserve. Scien. Silva. Sin. 2017, 53, 142–149. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Shafer, A.B.; Zimmermann, W.; Hu, D.; Wang, W.T.; Chu, H.J.; Cao, J.; Zhao, C.X. Evaluating the reintroduction project of Przewalski’s horse in China using genetic and pedigree data. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 171, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Chao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, C.; Qi, Y.; Ente, M.; Zhang, D.; Li, K.; Mok, K.M. Effects of Gasterophilus pecorum infestation on the intestinal microbiota of the rewilded Przewalski’s horses in China. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e025151. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, D.; Kuzyk, O.; Rauch, I.; Heider, S.; Schwab, C.; Hainzl, E.; Decker, T.; Müller, M.; Strobl, B.; Schleper, C.; et al. Intestinal microbiota signatures associated with inflammation history in mice experiencing recurring colitis. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, K.; Wu, J.; Qiuqian, L.; Yang, K.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, D. Changes in intestinal bacterial communities are closely associated with shrimp disease severity. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2015, 99, 6911–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadet-Bourgeteau, S.; Julliand, V. The diversity of the microbial ecosystem in the equine digestive tract. INRA. Prod. Anim. 2012, 25, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadet-Bourgeteau, S.; Julliand, V. Equine microbial gastro-intestinal health. EAAP Sci. Ser. 2010, 128, 161–182. [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen, P.; Mykytczuk, N.; Mastromonaco, G.F.; Schulte-Hostedde, A. Effects of captivity, diet, and relocation on the gut bacterial communities of white-footed mice. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 94, 4677–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjögren, Y.M.; Tomicic, S.; Lundberg, A.; Böttcher, M.F.; Björkstén, B.; Sverremark-Ekström, E.; Jenmalm, M.C. Influence of early gut microbiota on the maturation of childhood mucosal and systemic immune responses: Gut microbiota and immune responses. Clini. Exp. Allergy. 2009, 39, 1842–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Aidy, S.; Van Den Bogert, B.; Kleerebezem, M. The small intestine microbiota, nutritional modulation and relevance for health. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 2015, 32, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michail, S.; Lin, M.; Frey, M.R.; Fanter, R.; Wai, D.; Cleary, J.G.; Hilbush, B. Altered gut microbial energy and metabolism in children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Fems. Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.A.; Velazquez, K.T.; Herbert, K.M. Influence of high-fat-diet on gut microbiota: A driving force for chronic disease risk. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care. 2015, 18, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulangé, C.L.; Neves, A.L.; Chilloux, J.; Nicholson, J.K.; Dumass, M.E. Impact of the gut microbiota on inflammation, obesity, and metabolic disease. Genome. Med. 2016, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Watanabe, K.; Kimura, I. Gut microbiota dysbiosis drives and implies novel therapeutic strategies for diabetes mellitus and related metabolic diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.F.; Shen, Y.Q. Dysbiosis of gut microbiota and microbial metabolites in Parkinson’s Disease. Ageing. Res. Rev. 2018, 45, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga-González, C.; Cardenas, L.A.C.; Ramírez, M.; Reyes, A.; González, C.; Stevenson, P.R. Monitoring the variation in the gut microbiota of captive woolly monkeys related to changes in diet during a reintroduction process. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, W.M.S.; Burch, R. The Principles of Humane Experimental Technique; Methuen: London, UK, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Chu, H.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Ge, Y. Monitoring activity rhythms of Equus hemionus at watering holes by camera traps in Mount Kalamaili Ungulate Nature Reserve, Xinjiang. Biodivers. Sci. 2014, 22, 752–757. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, Z.; Qing, C.; Keremu, A.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, D. Food patch particularity and forging strategy of reintroduced Przewalski’s horse in North Xinjiang, China. Turk. J. Zool. 2017, 41, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Hu, D.; Chen, J. Study on feeding source plants and strategy of wild Przewalskii horse. In Proceedings of the Fourth National Symposium on Wildlife Ecology and Resource Conservation 2007, Xining, China, 2–5 December 2007. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y.; Liu, C.; Chu, H.; Tao, Y. Present situation of the Equus hemionus resources in the Karamori Mountain Nature Reserve, Xinjiang. Arid Zone Res. 2003, 20, 32–34, 66. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, S. Non-Invasive Study of the Behavioral and Physiological Ecology Adaptation in Captive Przewalski’s horse (Equus ferus przewalskii). Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Hu, D.; Li, K.; Cao, J.; Meng, Y.; Cui, Y.Y. The diurnal feeding behavior comparison between the realeased and captive adult female Przewalski’s horse (Equus przewalskii) in summer. Acta. Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 1104–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Riquelme, J.; Cazanga, V.; Jeldres, J.; Pérez, R. Pharmacokinetics of ivermectin in sheep following pretreatment with Escherichia coli endotoxin. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 41, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Jia, H.; Zhou, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, M.; Zou, Z. Variations in gut microbiota and fecal metabolic phenotype associated with depression by 16S rRNA gene sequencing and LC/MS-based metabolomics. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2017, 138, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2012, 41, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, S.E.; Maddox, T.W.; Berg, A.; Antczak, P.; Ketley, J.M.; Williams, N.J.; Archer, D.C. Variation in faecal microbiota in a group of horses managed at pasture over a 12-month period. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Peddada, S.D. Analysis of microbial compositions: A review of normalization and differential abundance analysis. NPJ. Biofilms. Microbi. 2020, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods. 2010, 7, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihaka, R.; Gentleman, R. R: A language for data analysis and graphics. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1996, 5, 299–314. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, G.; Zha, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Peng, X.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Y. Comparison of human and animal fecal microbiota with Illumina sequencing of 16S rRNA tags. Ecologic. Sci. 2014, 33, 851–857. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, K.; Hu, D.; Wronski, T. Community composition and diversity of intestinal microbiota in captive and reintroduced Przewalski’s horse (Equus ferus przewalskii). Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Li, Y.; Srivathsan, A.; Guo, Y.; Li, K.; Hu, D.; Zhang, D. Gut microbiomes of endangered Przewalski’s horse populations in short-and long-term captivity: Implication for species reintroduction based on the soft-release strategy. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hu, D.; Cao, J.; Lv, Q.; Men, Y. A preliminary report on the summer water resources used by Equus przewalskii. J. Xinjiang Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2008, 27, 76–79. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Shi, J.; Shultz, S.; Guo, D.; Liu, D. Fecal bacterial community of allopatric Przewalski’s gazelles and their sympatric relatives. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 737042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Bai, D.; Huang, J.; Shiraigo, W.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Ren, X.; Wu, J.; Bao, W.; et al. Comparison of fecal microbiota of Mongolian and thoroughbred horses by high-throughput sequencing of the V4 Region of the 16S rRNA gene. Asian–Austral. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 29, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Yang, H.; Han, S.; Feng, L.; Wang, T.; Ge, J. Comparison of the gut microbiota composition between wild and captive sika deer (Cervus nippon hortulorum) from feces by high-throughput sequencing. AMB Express 2017, 7, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Shi, M.; Fan, M.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Cha, M.; Liu, Y.; Guo, X.; Chen, Q.; et al. Comparative analysis of gut microbiota changes in Père David’s deer populations in Beijing Milu Park and Shishou, Hubei province in China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Bjursell, M.K.; Himrod, J.; Deng, S.; Carmichael, L.K.; Chiang, H.C.; Hooper, L.V.; Gordon, J.I. A genomic view of the human-Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron symbiosis. Science 2003, 299, 2074–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ley, R.E.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Peterson, D.A.; Gordon, J.I. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 2005, 307, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cheng, H.; Wyckoff, K.N.; He, Q. Linkages of Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes populations to methanogenic process performance. J Ind. Microbiol. Biot. 2016, 43, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddle, A.; Tomb, J.F.; Fan, Z. Microbiome and blood analyte differences point to community and metabolic signatures in lean and obese horses. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, C.; Cristescu, B.; Northrup, J.M.; Stenhouse, G.B.; Ganzle, M. Diet and environment shape fecal bacterial microbiota composition and enteric pathogen load of grizzly bears. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, P.; Magne, F.; Araneda, C.; Fuentes, P.; Barros, L.; Opazo, R.; Espejo, R.; Romero, J. PCR-TTGE analysis of 16S rRNA from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) gut microbiota reveals host-specific communities of active bacteria. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, B.; Chu, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, K. Gasterophilus (Diptera, Gasterophilidae) infestation of equids in the Kalamaili nature Reserve, China. Parasite 2016, 23, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Xu, W.; Yang, W.; Qiao, J. Food habits of Kulan (Equus hemionus) in Kalamaili Mountain Nature Reserve, Xinjiang, China. Acta Theriologica Sin. 2009, 29, 427–431. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]



| Sex | CPH | RPH | MWA | DH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | CPH1, CPH4, CPH5, CPH8, CPH10 | RPH1, RPH2, RPH5, RPH7, RPH10 | MWA1, MWA3, MWA4, MWA7, MWA10 | DH2, DH4, DH5, DH6, DH9 |
| Male | CPH2, CPH3, CPH6, CPH7, CPH9 | RPH3, RPH4, RPH6, RPH8, RPH9 | MWA2, MWA5, MWA6, MWA8, MWA9 | DH1, DH3, DH7, DH8, DH10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, D.; Wang, C.; Ente, M.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Li, K.; Chu, H. Assessment of Adaptation Status of Reintroduced Equus Przewalskii Based on Comparative Analysis of Fecal Bacteria with Those of Captive E. Przewalskii, Domestic Horse and Mongolian Wild Ass. Animals 2022, 12, 2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202874
Hu D, Wang C, Ente M, Zhang K, Zhang D, Li X, Li K, Chu H. Assessment of Adaptation Status of Reintroduced Equus Przewalskii Based on Comparative Analysis of Fecal Bacteria with Those of Captive E. Przewalskii, Domestic Horse and Mongolian Wild Ass. Animals. 2022; 12(20):2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202874
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Dini, Chen Wang, Make Ente, Ke Zhang, Dong Zhang, Xuefeng Li, Kai Li, and Hongjun Chu. 2022. "Assessment of Adaptation Status of Reintroduced Equus Przewalskii Based on Comparative Analysis of Fecal Bacteria with Those of Captive E. Przewalskii, Domestic Horse and Mongolian Wild Ass" Animals 12, no. 20: 2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202874
APA StyleHu, D., Wang, C., Ente, M., Zhang, K., Zhang, D., Li, X., Li, K., & Chu, H. (2022). Assessment of Adaptation Status of Reintroduced Equus Przewalskii Based on Comparative Analysis of Fecal Bacteria with Those of Captive E. Przewalskii, Domestic Horse and Mongolian Wild Ass. Animals, 12(20), 2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202874





