gga-miR-449b-5p Regulates Steroid Hormone Synthesis in Laying Hen Ovarian Granulosa Cells by Targeting the IGF2BP3 Gene
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.5. Plasmid Construction
2.6. Cell Transfection and Treatment
2.7. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.8. Flow Cytometric Analysis
2.9. ELISA for Steroid Hormones
2.10. Western Blotting Assay
2.11. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
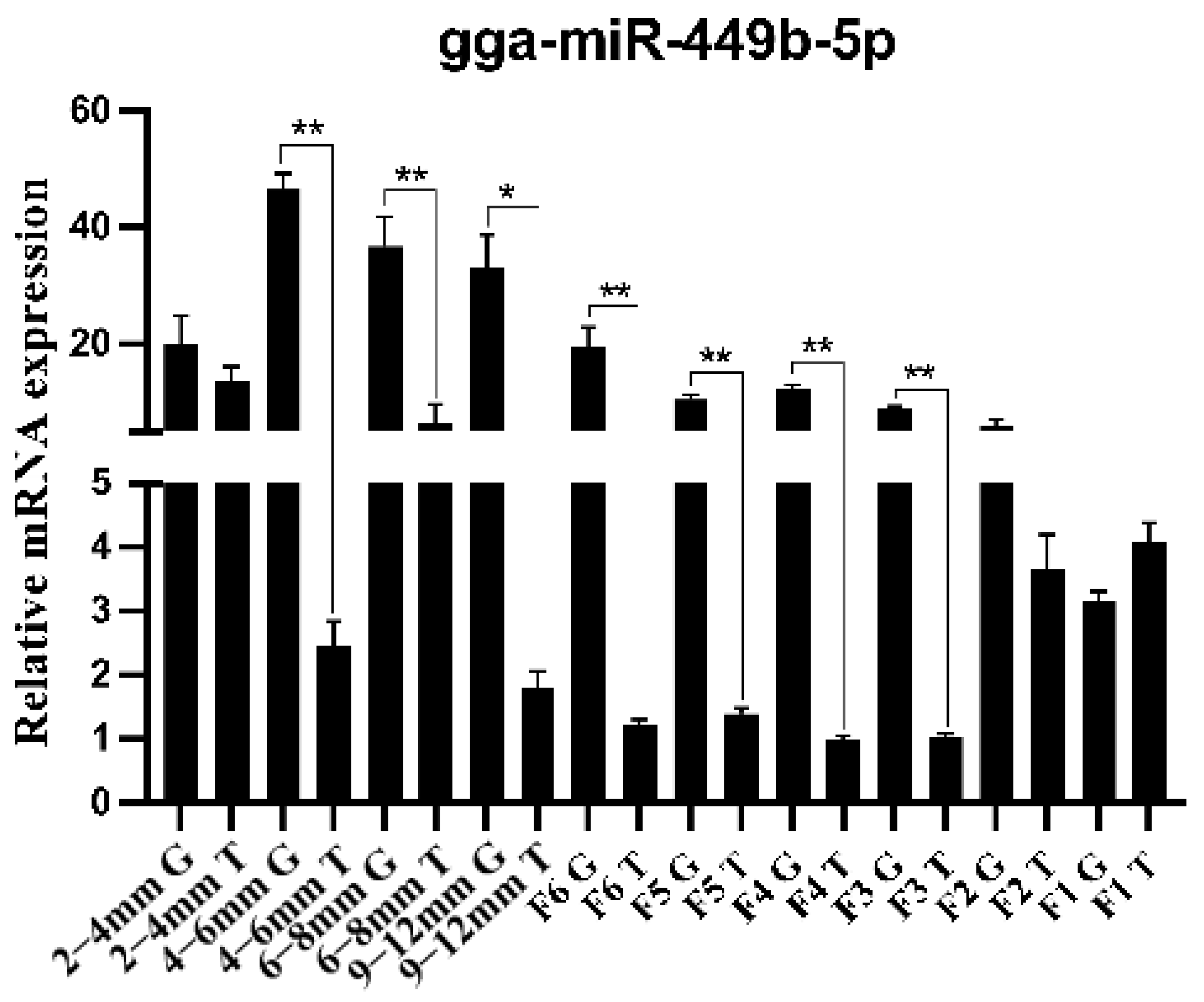
3.1. Differential Expression of gga-miR-449b-5p in TCs and GCs at All Levels
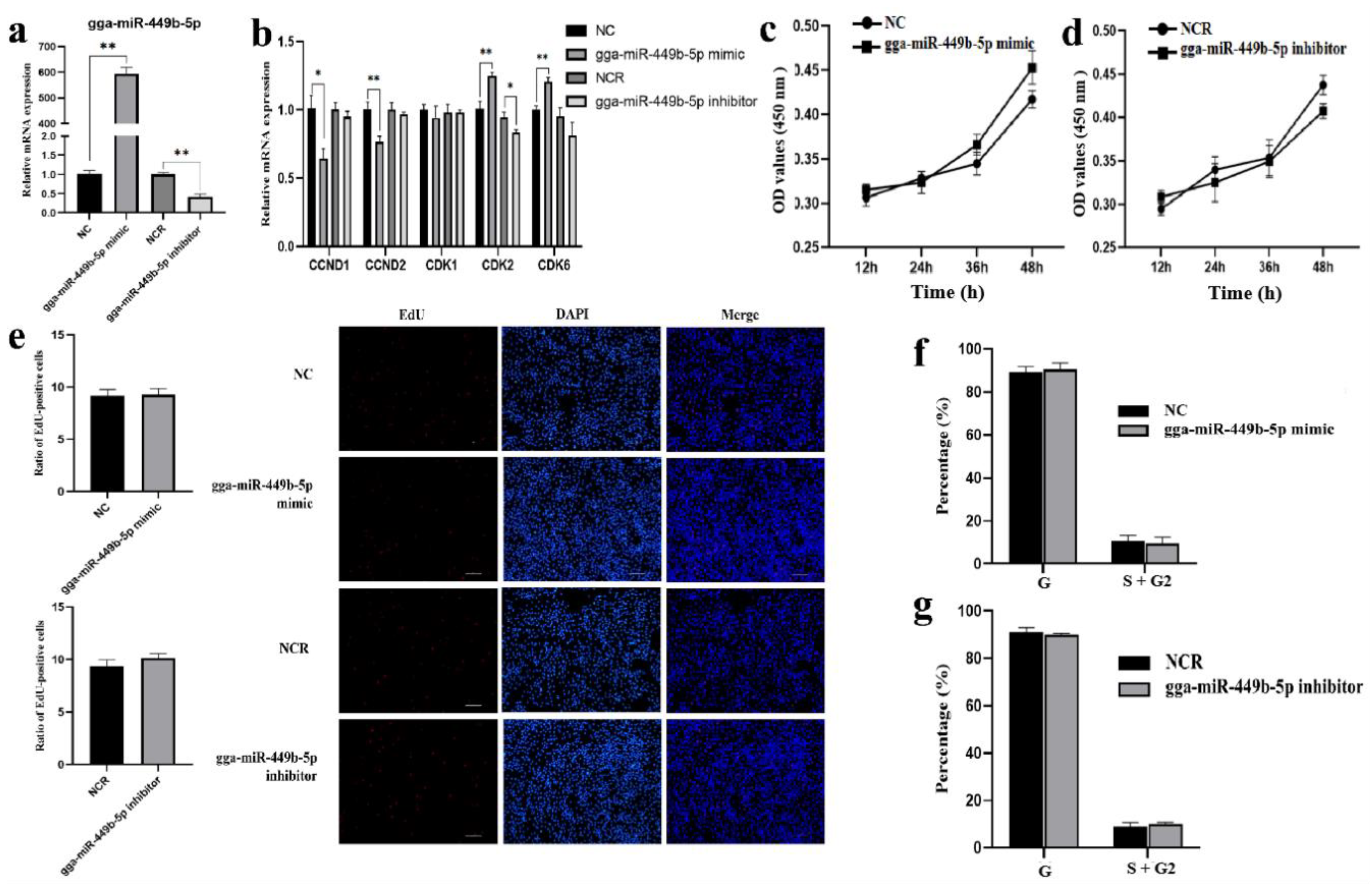
3.2. gga-miR-449b-5p Has No Effect on the Proliferation of GCs
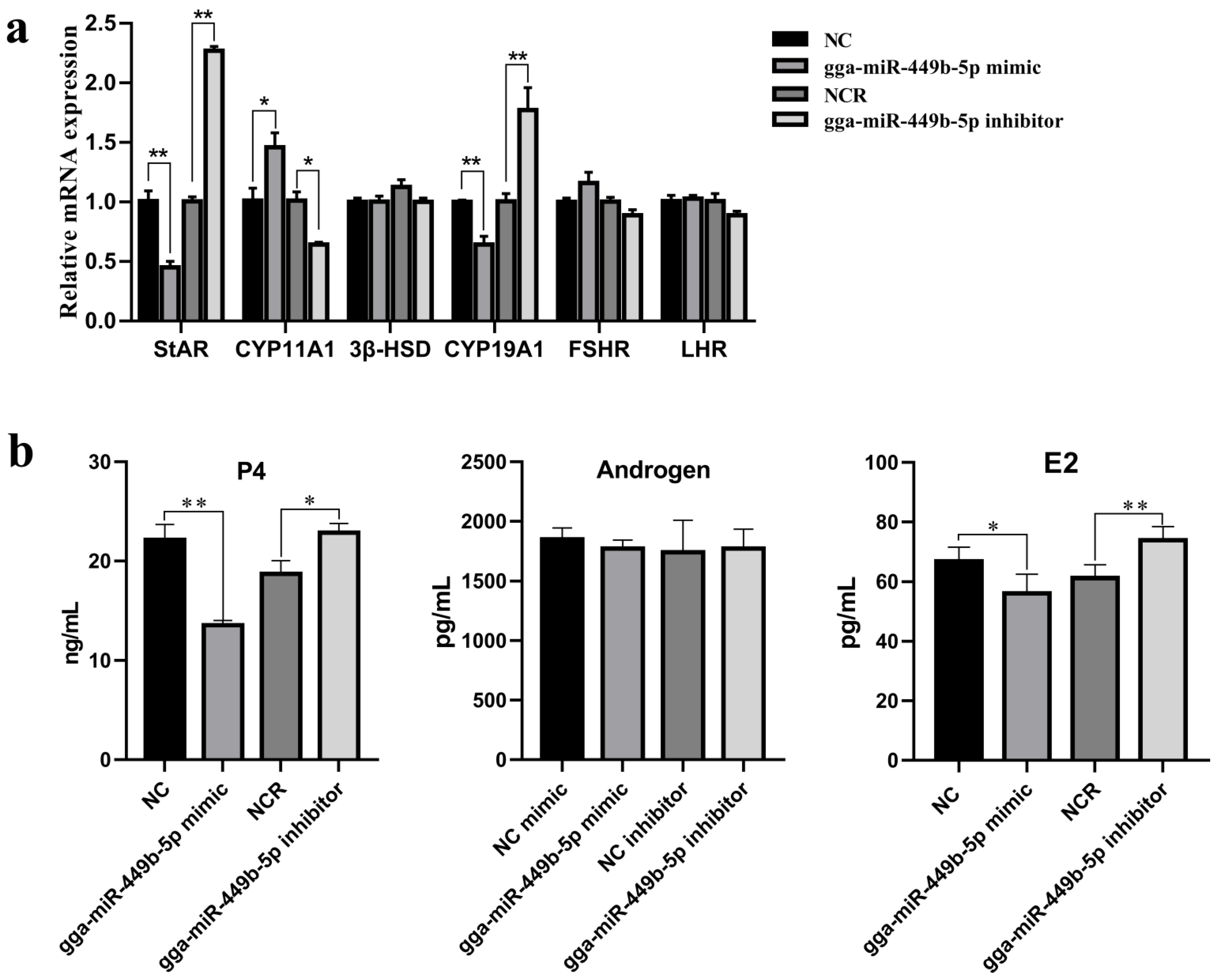
3.3. gga-miR-449b-5p Regulates Steroid Secretion by GCs
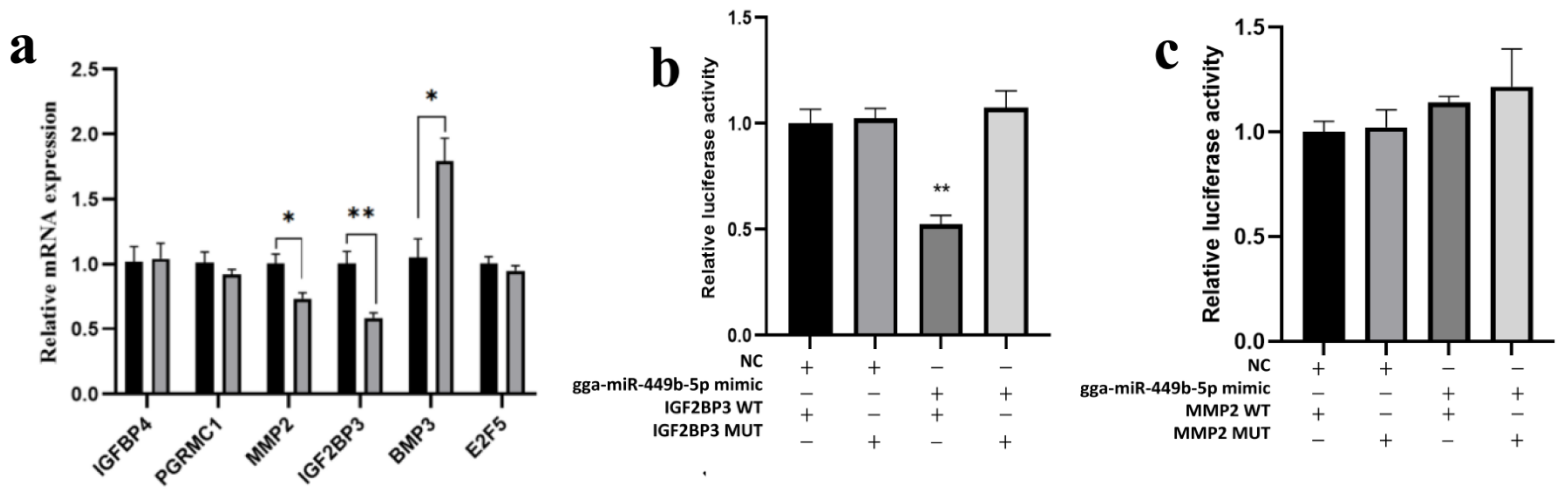
3.4. IGF2BP3 Is a gga-miR-449b-5p Target
3.5. Expression of IGF2BP3 Is Regulated by gga-miR-449b-5p
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Johnson, A.L. Reproduction in the Female. Sturkie’s Avian Physiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 635–665. [Google Scholar]
- Bahr, J.M. The chicken ovary as a model of follicular development. In Seminars in Reproductive Endocrinology; Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 352–359. [Google Scholar]
- Nitta, H.; Osawa, Y.; Bahr, J. Immunolocalization of steroidogenic cells in small follicles of the chicken ovary: Anatomical arrangement and location of steroidogenic cells change during follicular development. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 1991, 8, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechman, A.; Łakota, P.; Wojtysiak, D.; Hrabia, A.; Mika, M.; Lisowski, M.; Czekalski, P.; Rza˛sa, J.; Kapkowska, E.; Bednarczyk, M. Sex steroids level in blood plasma and ovarian follicles of the chimeric chicken. J. Vet. Med. Ser. A 2006, 53, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, Y.; Okamoto, T.; Tamura, T. Changes in localization of ovarian immunoreactive estrogen receptor during follicular development in hens. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1995, 100, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Shimada, K.; Saito, N.; Kansaku, N. Expression of messenger ribonucleic acids of luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone receptors in granulosa and theca layers of chicken preovulatory follicles. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1997, 105, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamura, N.; Takeishi, M.; Goto, N.; Tagami, M.; Mizutani, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Doi, O.; Kamiyoshi, M. Expression of messenger RNAs of luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone receptors in the granulosa layer during the ovulatory cycle of the hen. Br. Poult. Sci. 2000, 41 (Suppl. 1), 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Liu, L.; He, Y.; Dou, T.; Jia, J.; Ge, C.J.B.P.S. Endocrine and genetic factors affecting egg laying performance in chickens: A review. Br. Poult. Sci. 2020, 61, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gong, Y. Transcription of CYP19A1 is directly regulated by SF-1 in the theca cells of ovary follicles in chicken. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2017, 247, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, R.; Gu, L.; Li, J.; Gong, Y. A transcriptomic comparison of theca and granulosa cells in chicken and cattle follicles reveals ESR2 as a potential regulator of CYP19A1 expression in the theca cells of chicken follicles. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2018, 27, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.L. The avian ovary and follicle development: Some comparative and practical insights. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2014, 38, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, H.; Ian Mason, J.; Bahr, J.M. Localization of 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in the chicken ovarian follicle shifts from the theca layer to granulosa layer with follicular maturation. Biol. Reprod. 1993, 48, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Hidaka, K.; Sato, H.; Ito, K.; Ito, S.; Sasano, H. Immunolocalization of nuclear transcription factors, DAX-1 and COUP-TF II, in the normal human ovary: Correlation with adrenal 4 binding protein/steroidogenic factor-1 immunolocalization during the menstrual cycle. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 3415–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bennett, J.; Baumgarten, S.C.; Stocco, C. GATA4 and GATA6 silencing in ovarian granulosa cells affects levels of mRNAs involved in steroidogenesis, extracellular structure organization, IGF-I activity, and apoptosis. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 4845–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amsterdam, A.; Keren-Tal, I.; Aharoni, D.; Dantes, A.; Land-Bracha, A.; Rimon, E.; Sasson, R.; Hirsh, L. Steroidogenesis and apoptosis in the mammalian ovary. Steroids 2003, 68, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wu, K.; Jia, M.; Sun, S.; Kang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, H. Dynamic Changes in the Global MicroRNAome and Transcriptome Identify Key Nodes Associated with Ovarian Development in Chickens. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocłoń, E.; Hrabia, A. miRNA expression profile in chicken ovarian follicles throughout development and miRNA-mediated MMP expression. Theriogenology 2021, 160, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Cui, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.; Jiang, Y. Identification of miRNAs associated with sexual maturity in chicken ovary by Illumina small RNA deep sequencing. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Chang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Hu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Geng, L.; Liu, Z.; Gong, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Genome-wide differential expression of long noncoding RNAs and mRNAs in ovarian follicles of two different chicken breeds. Genomics 2019, 111, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Si, S.-J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Tao, Y.; Yang, P.; Li, D.; Li, G.; Liu, X.; et al. CircEML1 facilitates the steroid synthesis in follicular granulosa cells of chicken through sponging gga-miR-449a to release IGF2BP3 expression. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, A.; Brennecke, J.; Bushati, N.; Russell, R.B.; Cohen, S.M. Animal MicroRNAs confer robustness to gene expression and have a significant impact on 3′ UTR evolution. Cell 2005, 123, 1133–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehl, T.; Backes, C.; Kern, F.; Fehlmann, T.; Ludwig, N.; Meese, E.; Lenhof, H.; Keller, A. About miRNAs, miRNA seeds, target genes and target pathways. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 107167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushati, N.; Cohen, S.M. microRNA functions. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2007, 23, 175–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.B. MicroRNA (miRNA) in cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Yu, X.; Hu, S.; Yu, J. A brief review on the mechanisms of miRNA regulation. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2009, 7, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremedhn, S.; Salilew-Wondim, D.; Ahmad, I.; Sahadevan, S.; Hossain, M.M.; Hoelker, M.; Rings, F.; Neuhoff, C.; Tholen, E.; Looft, C.; et al. MicroRNA expression profile in bovine granulosa cells of preovulatory dominant and subordinate follicles during the late follicular phase of the estrous cycle. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maalouf, S.; Liu, W.; Pate, J.L. MicroRNA in ovarian function. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 363, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbar, T.; Eisenberg, I. Regulatory role of microRNAs in ovarian function. Fertil. Steril. 2014, 101, 1524–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, B.; Uddin, A.; Chakraborty, S. miRNAs and ovarian cancer: An overview. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 3846–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Lü, M.; Yao, G.; Tian, H.; Lian, J.; Liu, L.; Liang, M.; Wang, Y.; Sun, F. Transactivation of microRNA-383 by steroidogenic factor-1 promotes estradiol release from mouse ovarian granulosa cells by targeting RBMS1. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Lv, M.; Xing, Q.; Zhang, Z.; He, X.; Xu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Cao, Y. miR-323-3p regulates the steroidogenesis and cell apoptosis in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) by targeting IGF-1. Gene 2019, 683, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-L.; Wang, H.; Yan, C.-Y.; Gao, X.-F.; Ling, X.-J. Deregulation of RUNX2 by miR-320a deficiency impairs steroidogenesis in cumulus granulosa cells from polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) patients. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Jing, J.; Qin, S.; Zheng, Q.; Lu, J.; Zhu, C.; Liu, Y.; Fang, F.; Li, Y.; Ling, Y. miR-130a-3p regulates steroid hormone synthesis in goat ovarian granulosa cells by targeting the PMEPA1 gene. Theriogenology 2021, 165, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, J.; Lu, W.; Wang, J. Kisspeptin-10 Promotes Progesterone Synthesis in Bovine Ovarian Granulosa Cells via Downregulation of microRNA-1246. Genes 2022, 13, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Q.; Guo, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, C.; Schinckel, A.P.; Zhou, B. MiR-31 targets HSD17B14 and FSHR, and miR-20b targets HSD17B14 to affect apoptosis and steroid hormone metabolism of porcine ovarian granulosa cells. Theriogenology 2022, 180, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Chu, G. MiR-214-3p promotes proliferation and inhibits estradiol synthesis in porcine granulosa cells. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Z.; He, X.; Tao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Lan, R.; Hong, Q.; Chu, M. chi-miR-324-3p Regulates Goat Granulosa Cell Proliferation by Targeting DENND1A. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 732440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Li, M.; Hu, J.; Wang, W.; Gao, M. MiRNA-335-5p negatively regulates granulosa cell proliferation via SGK3 in PCOS. Reproduction 2018, 156, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, L.; Yang, C.; Wu, H.; Chen, Q.; Huang, L.; Li, X.; Tang, H.; Jiang, Y. miR-26a-5p regulates TNRC6A expression and facilitates theca cell proliferation in chicken ovarian follicles. DNA Cell Biol. 2017, 36, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hou, L.; Sun, Y.; Xing, J.; Jiang, Y.; Kang, L. Single nucleotide polymorphism rs737028527 (G > A) affect miR-1b-3p biogenesis and effects on chicken egg-laying traits. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2020, 218, 106476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Li, J.; He, H.; Cao, Y.; Li, D.; Amevor, F.K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, C.; Yang, C.; et al. miR-23b-3p inhibits chicken granulosa cell proliferation and steroid hormone synthesis via targeting GDF9. Theriogenology 2022, 177, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, C.; Li, Q.; Li, W.-T.; Li, H.; Li, G.-X.; Kang, X.; Liu, X.; Tian, Y. Identification of the Key microRNAs and miRNA-mRNA Interaction Networks during the Ovarian Development of Hens. Animals 2020, 10, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, J.L.; Wächter, K.; Mühleck, B.; Pazaitis, N.; Köhn, M.; Lederer, M.; Hüttelmaier, S. Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding proteins (IGF2BPs): Post-transcriptional drivers of cancer progression? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. Cmls 2013, 70, 2657–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, F.C.; Nielsen, J.; Christiansen, J. A family of IGF-II mRNA binding proteins (IMP) involved in RNA trafficking. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2001, 61, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniuchi, K.; Furihata, M.; Hanazaki, K.; Saito, M.; Saibara, T. IGF2BP3-mediated translation in cell protrusions promotes cell invasiveness and metastasis of pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 6832–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancarella, C.; Scotlandi, K. IGF2BP3 From Physiology to Cancer: Novel Discoveries, Unsolved Issues, and Future Perspectives. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Sheng, Y.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wen, D.; Liu, C.; Cui, L.; Yang, Y.; Du, P. Increased IGF2BP3 expression promotes the aggressive phenotypes of colorectal cancer cells in vitro and vivo. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 18466–18479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell, T.; Gladwell, R.; Groome, N.; Knight, P. Ovarian follicle development in the laying hen is accompanied by divergent changes in inhibin, A.; inhibin, B.; activin A and follistatin production in granulosa and theca layers. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 177, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, X.-J.; Wu, X.; Si, S.-J.; Li, C.; Yang, P.-K.; Li, G.; Liu, X.; Tian, Y.; Kang, X. Adiponectin modulates steroid hormone secretion, granulosa cell proliferation and apoptosis via binding its receptors during hens’ high laying period. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himly, M.; Foster, D.N.; Bottoli, I.; Iacovoni, J.S.; Vogt, P.K. The DF-1 chicken fibroblast cell line: Transformation induced by diverse oncogenes and cell death resulting from infection by avian leukosis viruses. Virology 1998, 248, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, L.; Feng, G.; Xiang, W.; Zhang, K.; Chu, M.; Wang, P. MicroRNA mediating networks in granulosa cells associated with ovarian follicular development. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 4585213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Yang, X.; He, X.; Ma, W.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Li, M.; Yu, S. MicroRNA-449b-5p suppresses the growth and invasion of breast cancer cells via inhibiting CREPT-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2019, 302, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, X.; Tao, S.J.; Liu, X.L.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.M.; Chen, Y. MDM4 is targeted by miR-449b-5p to promote the proliferation of endometrial carcinoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 11528–11535. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Shi, X.; Huo, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H. MiR-449b-5p regulates cell proliferation, migration and radioresistance in cervical cancer by interacting with the transcription suppressor FOXP1. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 856, 172399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haneke, K.; Schott, J.; Lindner, D.; Hollensen, A.K.; Damgaard, C.K.; Mongis, C.; Knop, M.; Palm, W.; Ruggieri, A.; Stoecklin, G. CDK1 couples proliferation with protein synthesis. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 219, e201906147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, I.; Dynlacht, B.D. New insights into cyclins, CDKs, and cell cycle control. In Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 311–321. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.; Li, D.; Tozer, A.J.; Docherty, S.M.; Iles, R.K. Estradiol, progesterone, testosterone profiles in human follicular fluid and cultured granulosa cells from luteinized pre-ovulatory follicles. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2010, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillier, S.G.; Whitelaw, P.F.; Smyth, C.D. Follicular oestrogen synthesis: The ‘two-cell, two-gonadotrophin’model revisited. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1994, 100, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.C.; Hsu, H.J.; Guo, I.C.; Chung, B.C. Function of Cyp11a1 in animal models. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2004, 215, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sechman, A.; Pawlowska, K.; Hrabia, A. Effect of 3, 3′, 5-triiodothyronine and 3, 5-diiodothyronine on progesterone production, cAMP synthesis, and mRNA expression of STAR, CYP11A1, and HSD3B genes in granulosa layer of chicken preovulatory follicles. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2011, 41, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, E.S.-R.; Nalbandov, A. Steroidogenesis of chicken granulosa and theca cells: In vitro incubation system. Biol. Reprod. 1979, 20, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A. Steroidogenesis and actions of steroids in the hen ovary. Crit. Rev. Poult. Biol. 1990, 2, 319–346. [Google Scholar]
- Marrone, B.L.; Hertelendy, F. Steroid metabolism by avian ovarian cells during follicular maturation. Biol. Reprod. 1983, 29, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treinen, K.A.; Dodson, W.C.; Heindel, J.J. Inhibition of FSH-stimulated cAMP accumulation and progesterone production by mono (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in rat granulosa cell cultures. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1990, 106, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.T.; Bahr, J.M. Inhibition of the activities of P450 cholesterol side-chain cleavage and 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and the amount of P450 cholesterol side-chain cleavage by testosterone and estradiol-17β in hen granulosa cells. Endocrinology 1990, 126, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.; Christiansen, J.; Lykke-Andersen, J.; Johnsen, A.H.; Wewer, U.M.; Nielsen, F.C. A family of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding proteins represses translation in late development. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudice, L.C. Insulin-like growth factor family in Graafian follicle development and function. J. Soc. Gynecol. Investig. 2001, 8, S26–S29. [Google Scholar]
- Spicer, L.; Aad, P. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) 2 stimulates steroidogenesis and mitosis of bovine granulosa cells through the IGF1 receptor: Role of follicle-stimulating hormone and IGF2 receptor. Biol. Reprod. 2007, 77, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.; Shen, M.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Lin, S.; Chow, N.; Cheng, S.; Chou, C.; Ho, C. Overexpression of the RNA-binding proteins Lin28B and IGF2BP3 (IMP3) is associated with chemoresistance and poor disease outcome in ovarian cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Lin, Q.; Gong, G.; Du, X.; Dan, H.; Qin, W.; Cheng, S.-W.; Chou, C.-Y.; Ho, C.-L. Igf2bp3 maintains maternal RNA stability and ensures early embryo development in zebrafish. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Chang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Guo, A.; Kang, Y.; Guo, H.; Xu, H.; Chen, L.; et al. Loss of Gsdf leads to a dysregulation of Igf2bp3-mediated oocyte development in medaka. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 277, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer Name | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Product Length (bp) | Genbank Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCND1 | F: ATAGTCGCCACTTGGATGCT | 122 | NM_205381 |
| R: AACCGGCTTTTCTTGAGGGG | |||
| CCND2 | F: TCCGGAAACATGCACAAACG | 257 | XM_015292118.2 |
| R: CCGGACTTGCCTAAGGTTGC | |||
| CDK1 | F: TGGCCTTGAACCACCCATAC | 147 | NM_205314.1 |
| R: AGGCAGGCAGGCAAAGATAA | |||
| CDK2 | F: ACGTGATCCACACGGAGAAC | 132 | NM_001199857 |
| R: GCAGCTGGAACAGGTAGCTC | |||
| CDK6 | F: AGCAGCCCAGAAGAGATGATT | 132 | NM_001007892.2 |
| R: GAGAAATACGCACAAACCCTGT | |||
| StAR | F: GTCCCTCGCAGACCAAGT | 196 | NM_204686 |
| R: TCCCTACTGTTAGCCCTGA | |||
| CYP11A1 | F: GTGGACACGACTTCCATGACT | 174 | NM_001001756 |
| R: GAGAGTCTCCTTGATGGCGG | |||
| 3β-HSD | F: TGGAAGAAGATGAGGCGCTG | 185 | NM_205118 |
| R: GGAAGCTGTGTGGATGACGA | |||
| CYP19A1 | F: GGCCTCCAGCAGGTTGAAAG | 214 | NM_001001761.3 |
| R: ATAGGCACTGTGGCAACTGG | |||
| FSHR | F: GAGCGAGGTCTACATACA | 281 | NM_205079 |
| R: GCACAAGCCATAGTCA | |||
| LHR | F: GGGCTTTCCCAAGCCTACAT | 133 | NM_204936.2 |
| R: TGGTGTCTTTATTGGCGGCT | |||
| IGFBP4 | F: AACTTCCACCCCAAGCAGT | 123 | NM_204353.1 |
| R: GCAATCCAAGTCCCCCTTCA | |||
| PGRMC1 | F: AGATCGTGGGCTCACCTCTA | 157 | NM_001271939.1 |
| R: AGCTGCTCCAGTGTGAAGTC | |||
| MMP2 | F: CGATGCTGTCTACGAGTCCC | 96 | NM_204420.2 |
| R: TAGCCCCTATCCAGGTTGCT | |||
| IGF2BP3 | F: TCCTGGTGAAGACGGGCTAC | 133 | XM_015281444.4 |
| R: CTTTTAGGGACCGAATGCTC | |||
| BMP3 | F: ACAGGGCAAAGAGTAAGAAAAAG | 136 | NM_001034819.2 |
| R: AGATAGCGTCGGGCACAATA | |||
| E2F5 | F: GCCTTCCAGACTCAGTGTTG | 148 | NM_001030942.1 |
| R: GGCTCCTCCATCTTTGCTAT | |||
| β-actin | F: CAGCCAGCCATGGATGATGA | 147 | NM_205518.2 |
| R: ACCAACCATCACACCCTGAT | |||
| IGF2BP3 WT | F: ccgctcgagTTACATAACACTGCCATGAATA | 244 | - |
| R: ataagaatgcggccgcAGTCCGTAGTACTCCTGGCTGG | |||
| IGF2BP3 MUT | F: ccgctcgagTTACATAATGACATAGTGAATAACCTAAGGGA | 244 | - |
| R: ataagaatgcggccgcAGTCCGTAGTACTCCTGGCTGG | |||
| MMP2 WT | F: ccgctcgagCGAGTTTGATCATTACTGCCA | 337 | - |
| R: ataagaatgcggccgcGAAAGCCTAACCAAACAAAAC | |||
| MMP2 MUT | F: ccgctcgagCGAGTTTGATCATTGACATTGTTTATTTACATAAT | 337 | - |
| R: ataagaatgcggccgcGAAAGCCTAACCAAACAAAAC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Jiang, R.; Li, H.; et al. gga-miR-449b-5p Regulates Steroid Hormone Synthesis in Laying Hen Ovarian Granulosa Cells by Targeting the IGF2BP3 Gene. Animals 2022, 12, 2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192710
Wu X, Zhang N, Li J, Zhang Z, Guo Y, Li D, Zhang Y, Gong Y, Jiang R, Li H, et al. gga-miR-449b-5p Regulates Steroid Hormone Synthesis in Laying Hen Ovarian Granulosa Cells by Targeting the IGF2BP3 Gene. Animals. 2022; 12(19):2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192710
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xing, Na Zhang, Jing Li, Zihao Zhang, Yulong Guo, Donghua Li, Yanhua Zhang, Yujie Gong, Ruirui Jiang, Hong Li, and et al. 2022. "gga-miR-449b-5p Regulates Steroid Hormone Synthesis in Laying Hen Ovarian Granulosa Cells by Targeting the IGF2BP3 Gene" Animals 12, no. 19: 2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192710
APA StyleWu, X., Zhang, N., Li, J., Zhang, Z., Guo, Y., Li, D., Zhang, Y., Gong, Y., Jiang, R., Li, H., Li, G., Liu, X., Kang, X., & Tian, Y. (2022). gga-miR-449b-5p Regulates Steroid Hormone Synthesis in Laying Hen Ovarian Granulosa Cells by Targeting the IGF2BP3 Gene. Animals, 12(19), 2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192710





