Tetra-Primer Amplification-Refractory Mutation System (ARMS)—PCR for Genotyping Mouse Leptin Gene Mutation
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. DNA Extraction from Tail Tissue
2.3. Primer Design and ARMS-PCR Parameters
2.4. Sequencing of Tetra-Primer ARMS-PCR Amplicons
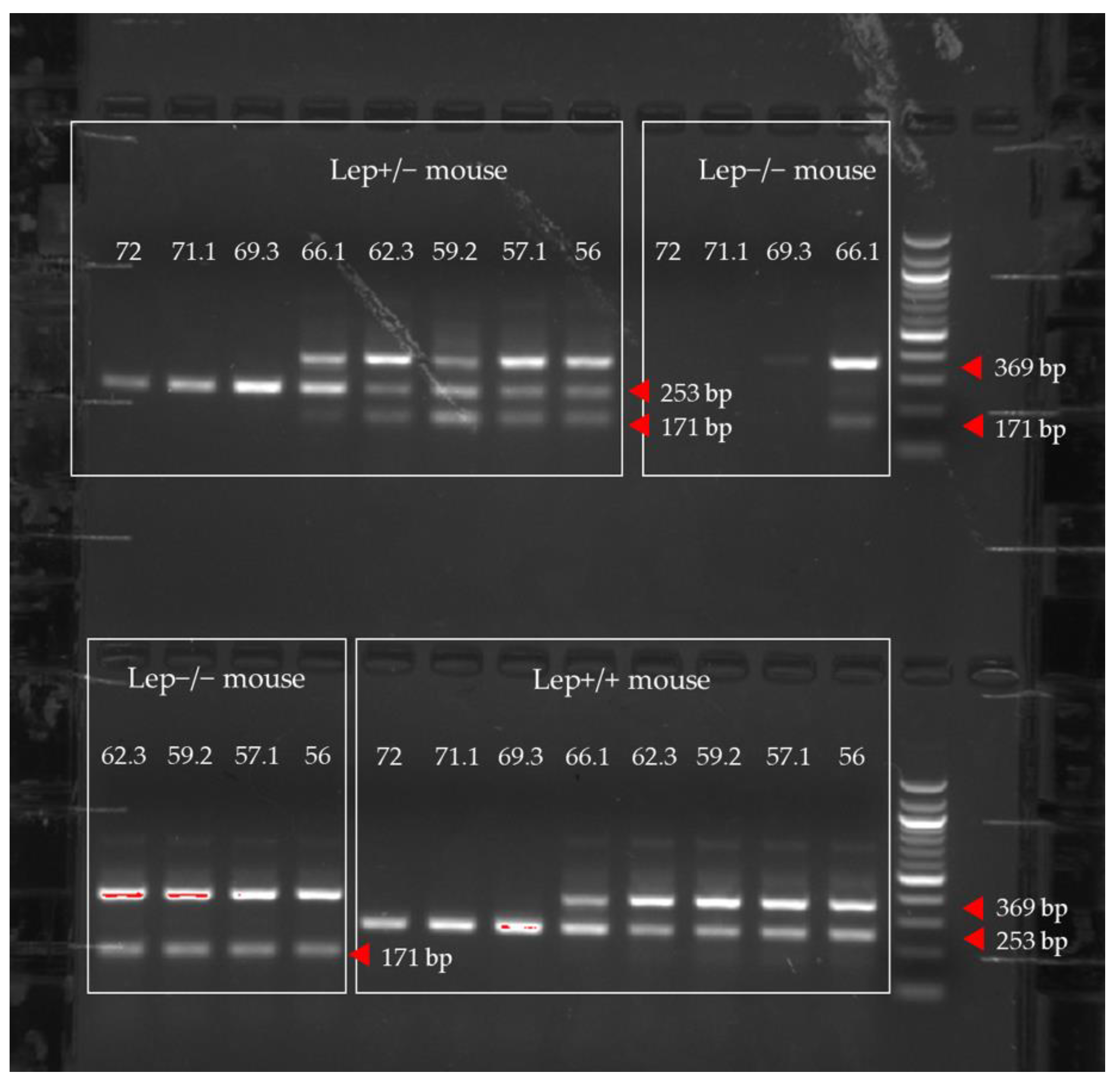
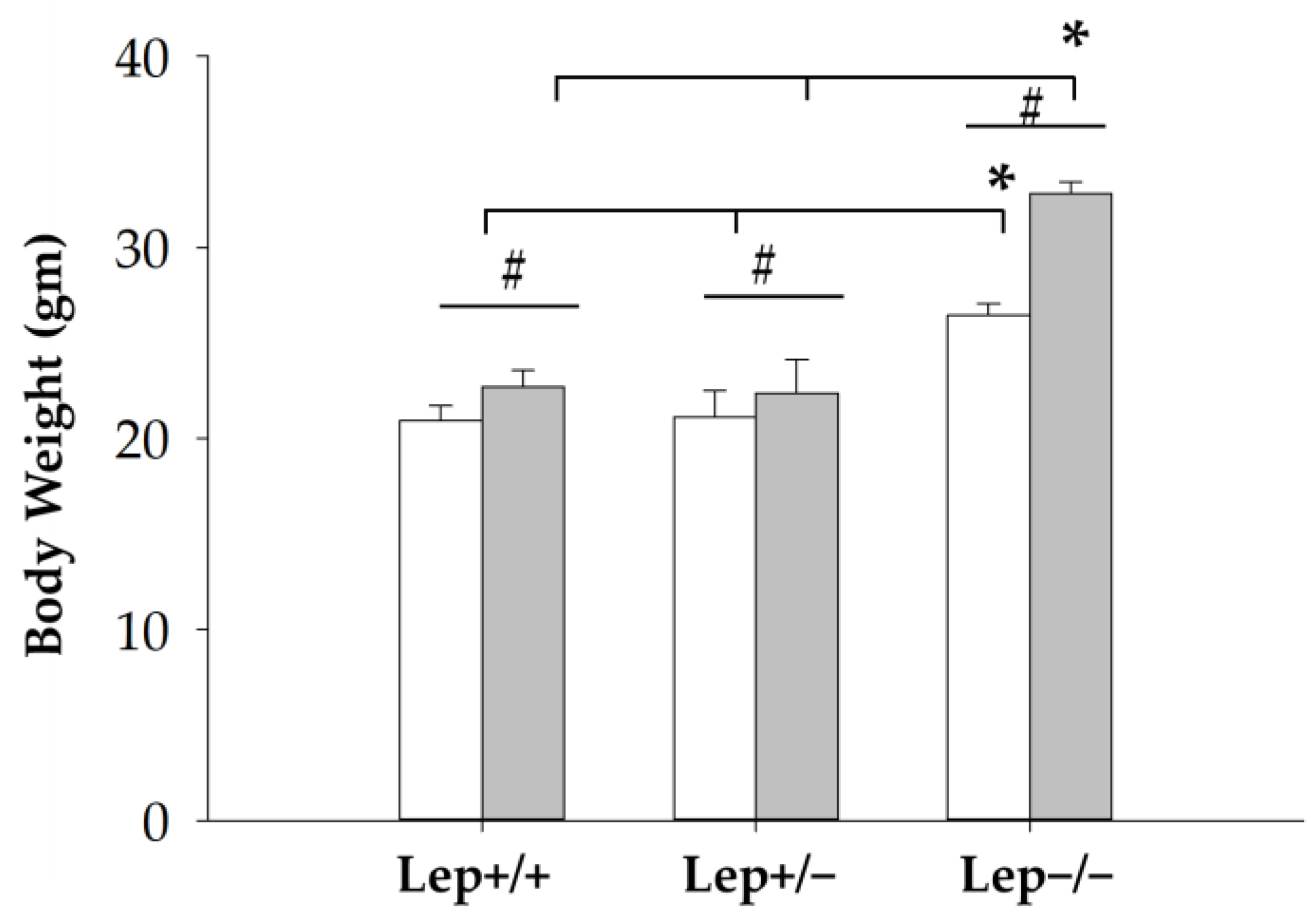
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lindstrom, P. The physiology of obese-hyperglycemic mice [ob/ob mice]. ScientificWorldJournal 2007, 7, 666–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Sanchez, N. There and Back Again: Leptin Actions in White Adipose Tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steppan, C.M.; Crawford, D.T.; Chidsey-Frink, K.L.; Ke, H.; Swick, A.G. Leptin is a potent stimulator of bone growth in ob/ob mice. Regul. Pept. 2000, 92, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chandrasekera, P.C.; Pippin, J.J. Leptin- and leptin receptor-deficient rodent models: Relevance for human type 2 diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2014, 10, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munzberg, H.; Morrison, C.D. Structure, production and signaling of leptin. Metabolism 2015, 64, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.C.; Lord, R.A.; Anderson, G.M. Multiple Leptin Signalling Pathways in the Control of Metabolism and Fertility: A Means to Different Ends? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.K.; Ahima, R.S. Leptin signaling. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Filho, G.; Mastronardi, C.; Delibasi, T.; Wong, M.L.; Licinio, J. Congenital leptin deficiency: Diagnosis and effects of leptin replacement therapy. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2010, 54, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Proenca, R.; Maffei, M.; Barone, M.; Leopold, L.; Friedman, J.M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994, 372, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehab, F.F.; Lim, M.E.; Lu, R. Correction of the sterility defect in homozygous obese female mice by treatment with the human recombinant leptin. Nat. Genet. 1996, 12, 318–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquot, S.; Chartoire, N.; Piguet, F.; Herault, Y.; Pavlovic, G. Optimizing PCR for Mouse Genotyping: Recommendations for Reliable, Rapid, Cost Effective, Robust and Adaptable to High-Throughput Genotyping Protocol for Any Type of Mutation. Curr. Protoc. Mouse Biol. 2019, 9, e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.Y.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Y.H.; He, J.F.; Tan, T.; Zhu, H. A novel and quick PCR-based method to genotype mice with a leptin receptor mutation (db/db mice). Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehnert, S.; Linnemann, C.; Braun, B.; Botsch, J.; Leibiger, K.; Hemmann, P.; Nussler, A.A.K. One-Step ARMS-PCR for the Detection of SNPs-Using the Example of the PADI4 Gene. Methods Protoc. 2019, 2, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Alam, A.R.U.; Sakib, N.; Hasan, M.S.; Chakrovarty, T.; Tawyabur, M.; Islam, O.K.; Al-Emran, H.M.; Jahid, M.I.K.; Anwar Hossain, M. A rapid and cost-effective multiplex ARMS-PCR method for the simultaneous genotyping of the circulating SARS-CoV-2 phylogenetic clades. J Med Virol. 2021, 93, 2962–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, S. Amplification-refractory mutation system (ARMS) analysis of point mutations. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2001, 9, 9-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komijani, M.; Shahin, K.; Azhar, E.I.; Bahram, M. Designing PCR Primers for the Amplification-Refractory Mutation System. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2392, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Dhillon, S.; Ke, X.; Collins, A.R.; Day, I.N. An efficient procedure for genotyping single nucleotide polymorphisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, E88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamvakopoulos, J.E. Multiplex universal genotyping using a modified ARMS-PCR protocol. Biotechniques 2002, 33, 1110–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.M.; Arnheim, N.; Goodman, M.F. Extension of base mispairs by Taq DNA polymerase: Implications for single nucleotide discrimination in PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 4567–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrano, R.F.; de Oliveira, C.A. Guidelines for the tetra-primer ARMS-PCR technique development. Mol. Biotechnol. 2014, 56, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, C.R.; Graham, A.; Heptinstall, L.E.; Powell, S.J.; Summers, C.; Kalsheker, N.; Smith, J.C.; Markham, A.F. Analysis of any point mutation in DNA. The amplification refractory mutation system (ARMS). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989, 17, 2503–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, S.; Sun, M.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Hua, W. An improved allele-specific PCR primer design method for SNP marker analysis and its application. Plant Methods 2012, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laboratory, T.J. B6.Cg-Lepob/J. Available online: https://www.jax.org/strain/000632 (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Suriano, F.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Roumain, M.; Paquot, A.; Pelicaen, R.; Regnier, M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Raes, J.; Muccioli, G.G.; et al. Novel insights into the genetically obese (ob/ob) and diabetic (db/db) mice: Two sides of the same coin. Microbiome 2021, 9, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laboratory, T.J. B6.BKS(D)-Leprdb/J. Available online: https://www.jax.org/strain/000697 (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- Chung, W.K.; Chua, S.C.; Lee, G.H.; Leibel, R.L. Polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphisms (PCR-RFLP) and electrophoretic assays for the mouse obese (Lepob) mutation. Obes. Res. 1997, 5, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellett, J.D.; Evans, Z.P.; Zhang, G.; Chavin, K.D.; Spyropoulos, D.D. A rapid PCR-based method for the identification of ob mutant mice. Obesity 2009, 17, 402–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oler, A.T.; Attie, A.D. A rapid, microplate SNP genotype assay for the leptinob allele. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1126–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mein, C.A.; Barratt, B.J.; Dunn, M.G.; Siegmund, T.; Smith, A.N.; Esposito, L.; Nutland, S.; Stevens, H.E.; Wilson, A.J.; Phillips, M.S.; et al. Evaluation of single nucleotide polymorphism typing with invader on PCR amplicons and its automation. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayabe, H.; Ikeda, S.; Maruyama, S.; Shioyama, S.; Kikuchi, M.; Kawaguchi, A.; Yamada, T.; Ikeda, T. Development of an efficient genotyping method to detect obese mutation in the mouse leptin gene for use in SPF barrier facilities. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 : Refractory to the mutation, therefore the PCR reaction cannot proceed.
: Refractory to the mutation, therefore the PCR reaction cannot proceed.
 : Refractory to the mutation, therefore the PCR reaction cannot proceed.
: Refractory to the mutation, therefore the PCR reaction cannot proceed.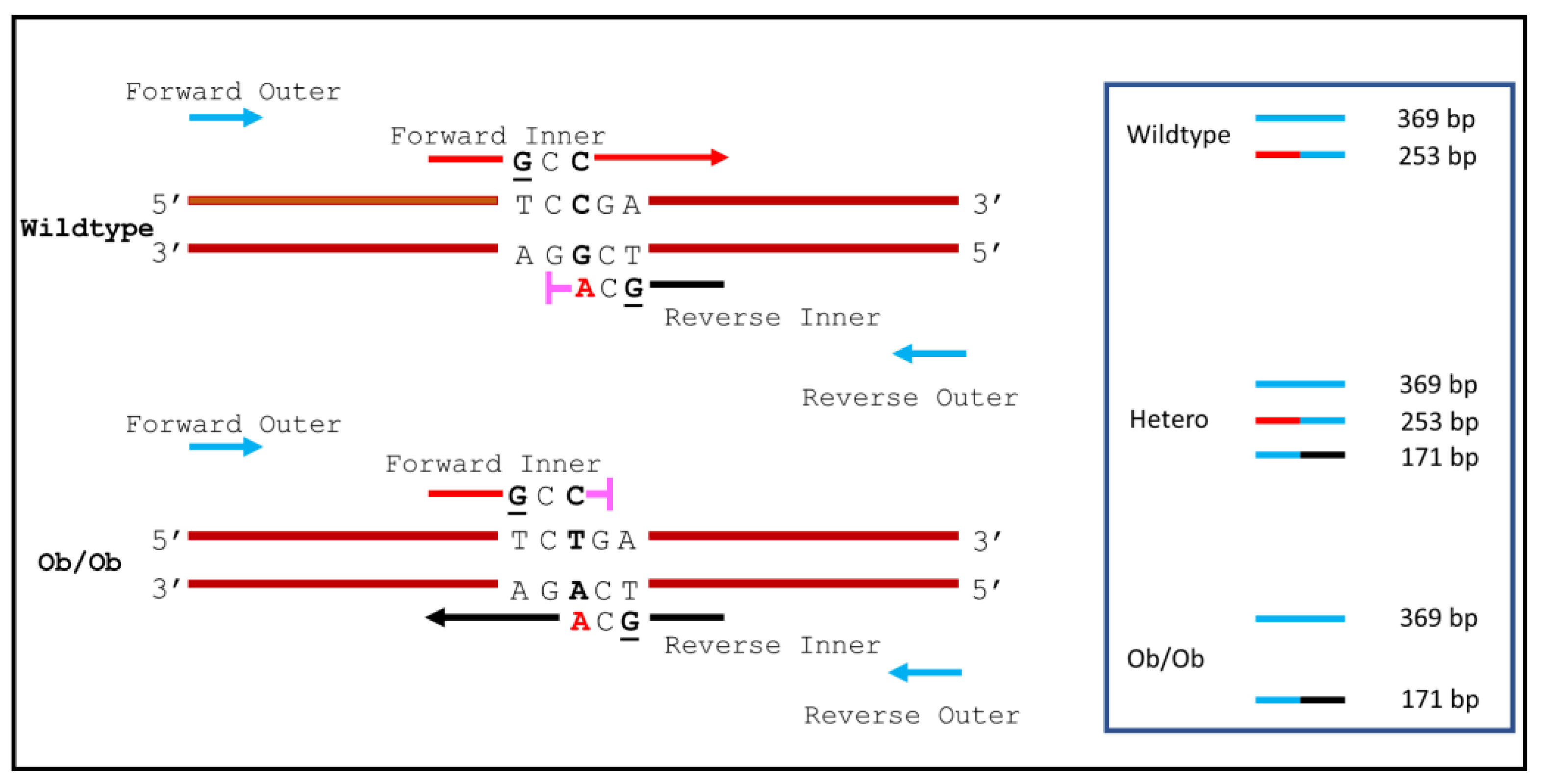
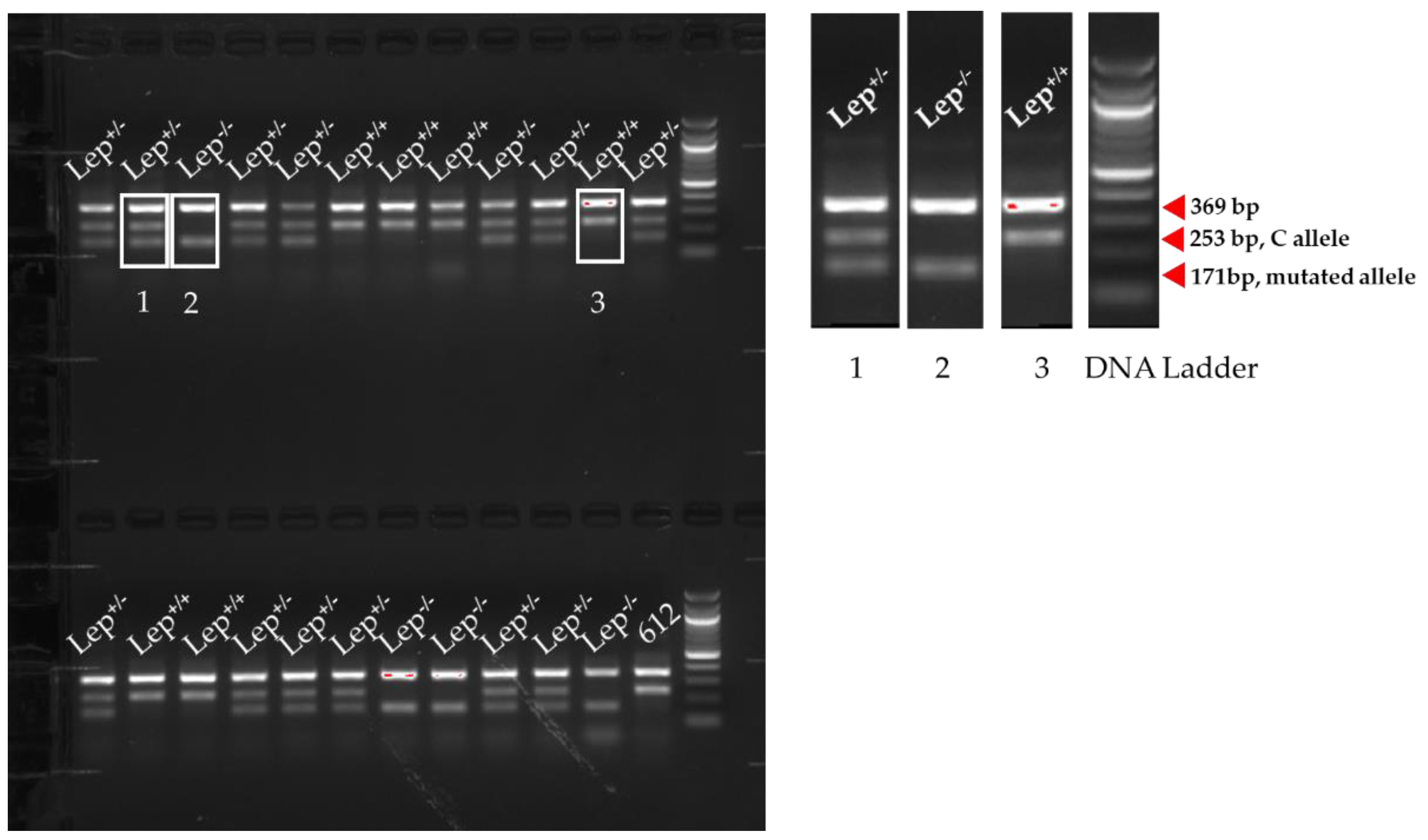

| Name | Sequences | Length of Expected PCR Amplicons |
|---|---|---|
| Forward Outer (FO) | 5′-GGTCACTGGCTTGGACTTCA-3′ | Between FO and RO pair: 369 bp |
| Reverse Outer (RO) | 5′-TGATTCTTGGGAGCCTGGTGGCCTTTGA-3′ | Between FI and RO pair: 253 bp (C allele, wildtype) |
| Forward Inner (FI) | 5′-TGCAGATAGCCAATGACCTGGAGAATCGCC-3′ | Between FO and RI pair: 171 bp (T allele, mutant) |
| Reverse Inner (RI) | 5′-AAGGCCAGCAGATGGAGGAGGTCGCA-3′ |
| Animal ID | Sequencing Results | Allele | Genotype |
|---|---|---|---|
| 129 | CTGGAGAATCTCTGCGACCTC | T allele | Lep+/−, heterozygous |
| 129 | CTGGAGAATCGCCGAGACCTC | C allele | |
| 136 | CTGGAGAATCTCTGCGACCTC | T allele | Lep+/−, heterozygous |
| 136 | CTGGAGAATCGCCGAGACCTC | C allele | |
| 137 | CTGGAGAATCTCTGCGACCTC | T allele | Lep+/−, heterozygous |
| 137 | CTGGAGAATCGCCGAGACCTC | C allele | |
| 128 | CTGGAGAATCGCCGAGACCTC | C allele | Lep+/+, wildtype |
| 130 | CTGGAGAATCGCCGAGACCTC | C allele | Lep+/+, wildtype |
| 131 | CTGGAGAATCGCCGAGACCTC | C allele | Lep+/+, wildtype |
| 138 | CTGGAGAATCTCTGCGACCTC | T allele | Lep−/−, ob/ob |
| 139 | CTGGAGAATCTCTGCGACCTC | T allele | Lep−/−, ob/ob |
| 135 | CTGGAGAATCTCTGCGACCTC | T allele | Lep−/−, ob/ob |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Dalhaimer, P.; Zhao, L. Tetra-Primer Amplification-Refractory Mutation System (ARMS)—PCR for Genotyping Mouse Leptin Gene Mutation. Animals 2022, 12, 2680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192680
Chen J, Xu X, Dalhaimer P, Zhao L. Tetra-Primer Amplification-Refractory Mutation System (ARMS)—PCR for Genotyping Mouse Leptin Gene Mutation. Animals. 2022; 12(19):2680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192680
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jiangang, Xinyun Xu, Paul Dalhaimer, and Ling Zhao. 2022. "Tetra-Primer Amplification-Refractory Mutation System (ARMS)—PCR for Genotyping Mouse Leptin Gene Mutation" Animals 12, no. 19: 2680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192680
APA StyleChen, J., Xu, X., Dalhaimer, P., & Zhao, L. (2022). Tetra-Primer Amplification-Refractory Mutation System (ARMS)—PCR for Genotyping Mouse Leptin Gene Mutation. Animals, 12(19), 2680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192680









