Evaluation of a Novel Precision Biotic on Enterohepatic Health Markers and Growth Performance of Broiler Chickens under Enteric Challenge
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Ethics
2.2. Trial 1
2.2.1. Animals and Intestinal Inflammation Model
2.2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.3. Sample Collection and Analyses
2.2.4. Immunoglobulin A and Alpha 1-Acid Gycoprotein
2.2.5. Isolation and Phenotyping of Intestinal T Cells
2.2.6. Gene Expression
2.2.7. Liver and Ileal Histology
2.2.8. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Trial 2
2.3.1. Animals, Diets, and Experimental Design
2.3.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
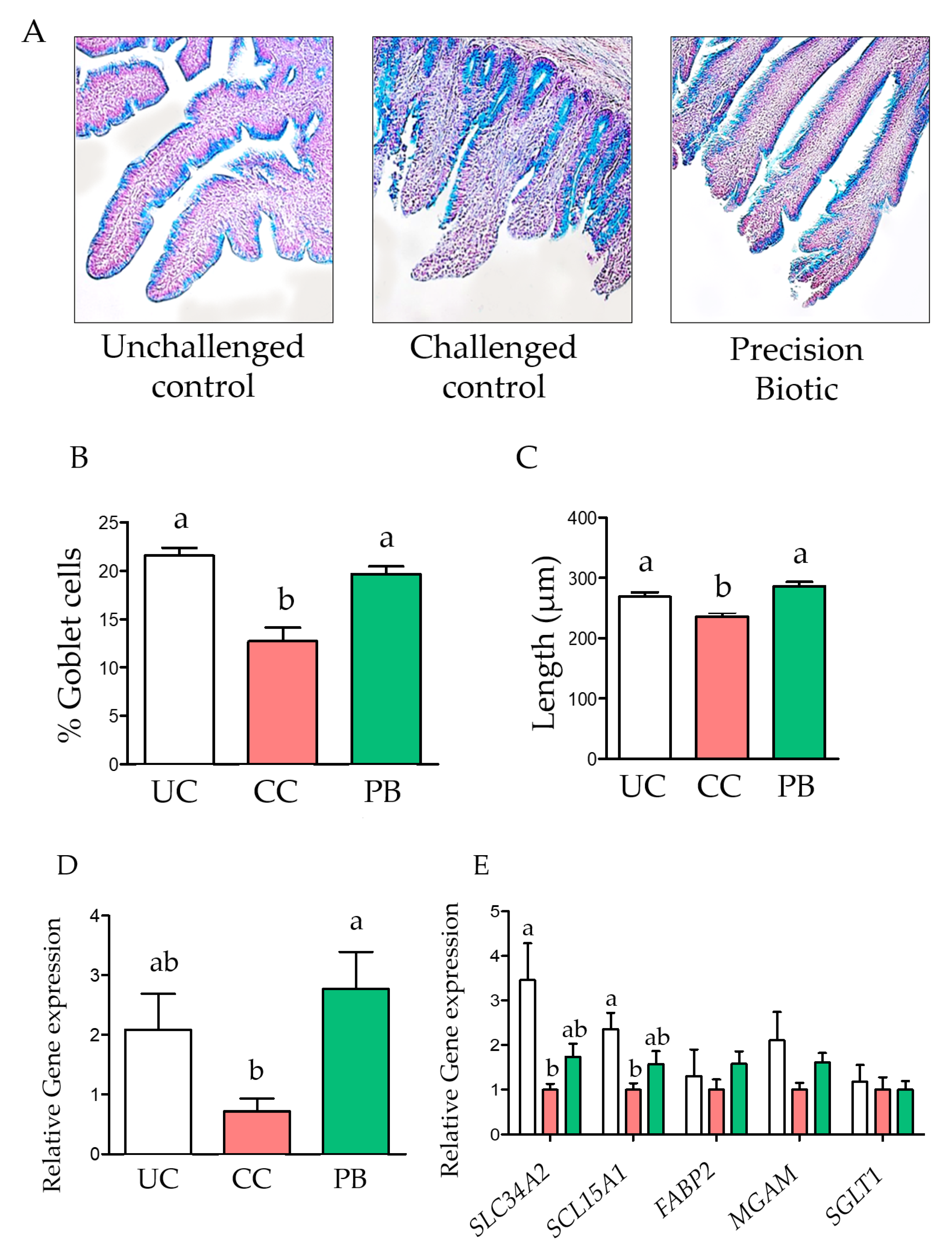
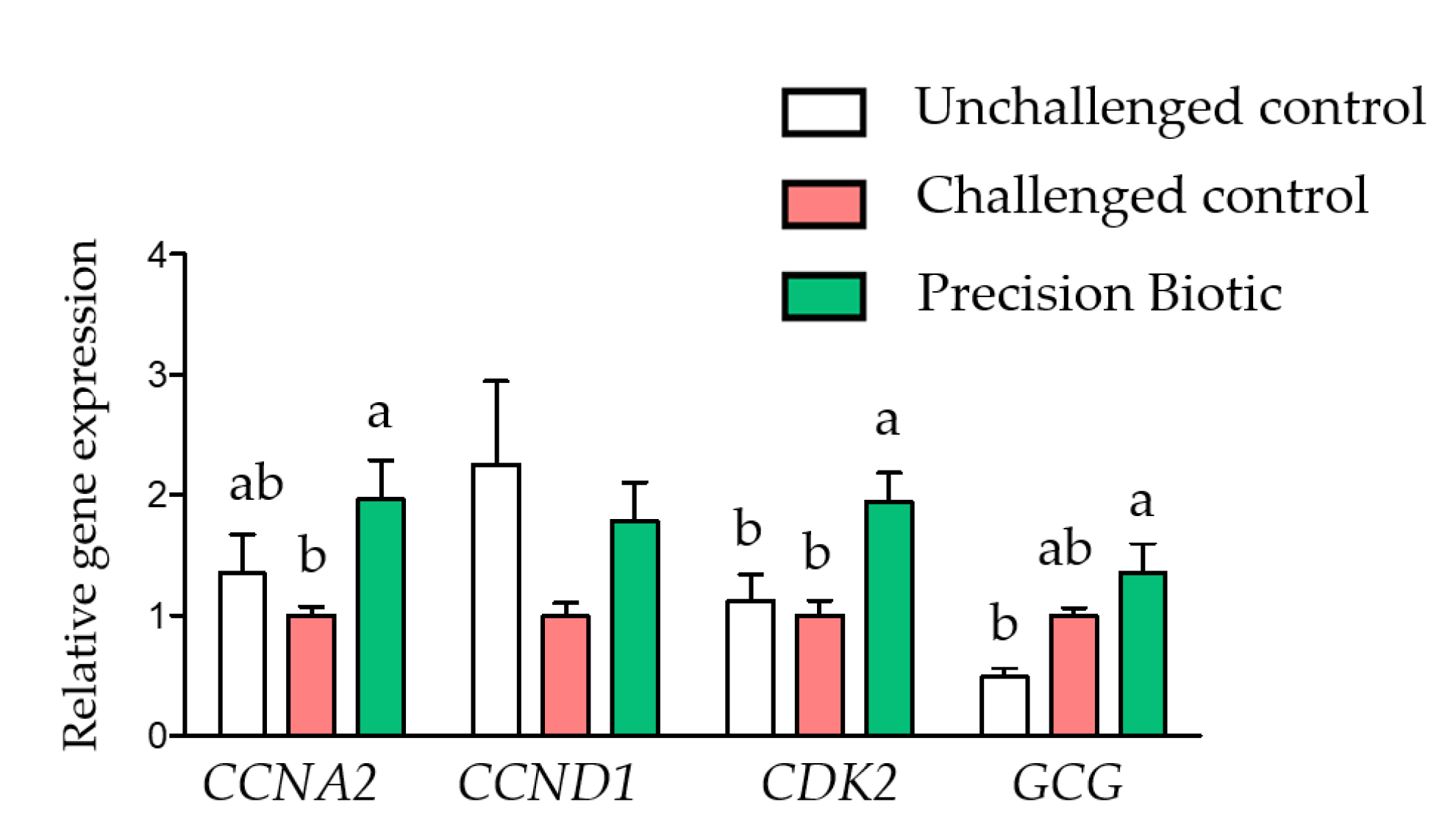
3.1. Trial 1
3.2. Trial 2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; Mende, R.D.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergeant, M.J.; Constantinidou, C.; Cogan, T.A.; Bedford, M.R.; Penn, C.W.; Pallen, M.J. Extensive microbial and functional diversity within the chicken cecal microbiome. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glendinning, L.; Stewart, R.D.; Pallen, M.J.; Watson, K.A.; Watson, M. Assembly of hundreds of novel bacterial genomes from the chicken caecum. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, M.C.; Jacquier, V.; Schyns, G.; Claypool, J.; Tamburini, I.; Blokker, B.; Geremia, J.M. A novel microbiome metabolic modulator improves the growth performance of broiler chickens in multiple trials and modulates targeted energy and amino acid metabolic pathways in the caecal metagenome. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 100800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquier, V.; Walsh, M.C.; Schyns, G.; Claypool, J.; Blokker, B.; Bortoluzzi, C.; Geremia, J. Evaluation of a Precision Biotic on the Growth Performance, Welfare Indicators, Ammonia Output, and Litter Quality of Broiler Chickens. Animals 2022, 12, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Danska, J.; Parkinson, J. Metatranscriptomic analysis of diverse microbial communities reveals core metabolic pathways and microbiome-specific functionality. Microbiome 2016, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kers, J.G.; Velkers, F.C.; Fischer, E.A.J.; Hermes, G.D.A.; Stegeman, J.A.; Smidt, H. Host and environmental factors affecting the intestinal microbiota in chickens. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geremia, J.M.; Murphy, A.V.; Han, S.; Seigal, B.A.; Landry, A.; Sherry, K.; Panos, S.; Churchman, D.; O’Connor, A. Oligosaccharide Compositions and Methods for Producing Thereof. Patent No. WO2016007778A1, 14 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Geremia, J.M.; Hoeller, U.; Tamburini, I.; Baur, M.; Liobomirov, A.V.; Canet-Martinez, E.; Matthew Liu, C.; Laprade, L.A.; Schyns, G.; Hecht, M.B.; et al. Oligosaccharide Preparations and Compositions. Patent No. WO2020097458, 14 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Flint, H.J.; Bayer, E.A.; Rincon, M.T.; Lamed, R.; White, B.A. Polysaccharide utilization by gut bacteria: Potential for new insights from genomic analysis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koropatkin, N.M.; Cameron, E.A.; Martens, E.C. How glycan metabolism shapes the human gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourabedin, M.; Zhao, X. Prebiotics and gut microbiota in chickens. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, fnv122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postler, T.S.; Ghosh, S. Understanding the holobiont: How microbial metabolites affect human health and shape the immune system. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 110–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordenstein, S.R.; Theis, K.R. Host biology in light of the microbiome: Ten principles of holobionts and hologenomes. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palliyeguru, M.; Rose, S.; Mackenzie, A. Effect of dietary protein concentrates on the incidence of subclinical necrotic enteritis and growth performance of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueden, C.T.; Schindelin, J.; Hiner, M.C.; DeZonia, B.E.; Walter, A.E.; Arena, E.T.; Eliceiri, K.W. ImageJ2: ImageJ for the next generation of scientific image data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Fukusato, T. Histopathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 15539–15548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tellez, G.; Richards, J.D.; Escobar, J. Identification of potential biomarkers for gut barrier failure in broiler chickens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2015, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Applegate, T.J.; Liu, S.; Guo, Y.; Eicher, S.D. Supplemental dietary L-arginine attenuates intestinal mucosal disruption during a coccidial vaccine challenge in broiler chickens. Br. J. Nut. 2014, 112, 1098–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, C.; Hofacre, C.; Payne, A.; Anderson, D.; Kaiser, P.; Mackie, R.I.; Gaskins, H.R. Coccidia-induced mucogenesis promotes the onset of necrotic enteritis by supporting Clostridium perfringens growth. Vet. Immunol Immunop. 2008, 122, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, H.M.; Jonkers, D.; Venema, K.; Vanhoutvin, S.; Troost, F.; Brummer, R.J. The role of butyrate on colonic function. Aliment. Pharm. Ther. 2008, 27, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-Oliveira, R.; Fachi, J.L.; Vieira, A.; Sato, F.T.; Vinolo, M.A. Regulation of immune cell function by short-chain fatty acids. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2016, 5, e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortoluzzi, C.; Castro, F.L.S.; Kogut, M.H. Butyrate and intestinal homeostasis: Effects on the intestinal microbiota and epithelial hypoxia. In Gut Microbiota, Immunity, and Health in Production Animals; Kogut, M.H., Zhang, G., Eds.; The Microbiomes of Humans, Animals, Plants, and the Environments; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; Volume 4, pp. 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- Miska, K.B.; Fetterer, R.H. The mRNA expression of amino acid and sugar transporters, aminopeptidase, as well as the di- and tri-peptide transporter PepT1 in the intestines of Eimeria infected broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedokun, S.; Ajuwon, K.; Romero, L.; Adeola, O. Ileal endogenous amino acid losses: Response of broiler chickens to fiber and mild coccidial vaccine challenge. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, T.; Medjoubi, N.N.; Porquet, D. Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1482, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Miyake, N.; Ohta, T.; Akiba, Y.; Tamura, K. Changes in plasma alpha 1-acid glycoprotein concentration and selected immune response in broiler chickens injected with Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Br. Poult. Sci. 1998, 39, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-W.; Lillehoj, H.S.; Jang, S.-I.; Lee, S.-H. Effects of Various Field Coccidiosis Control Programs on Host Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Commercial Broiler Chickens. Korean J. Poult. Sci. 2012, 39, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.H.; Chaudhari, A.A.; Lillehoj, H.S. Involvement of T Cell Immunity in Avian Coccidiosis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, M.S.; Kaiser, P.; Fife, M. The chicken IL-1 family: Evolution in the context of the studied vertebrate lineage. Immunogenetics 2014, 66, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.W.; Li, C. Butyrate induces profound changes in gene expression related to multiple signal pathways in bovine kidney epithelial cells. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gilbert, E.R.; Zhang, Y.; Crasta, O.; Emmerson, D.; Webb, K., Jr.; Wong, E.A. Expression profiling of the solute carrier gene family in chicken intestine from the late embryonic to early post-hatch stages. Anim. Genet. 2008, 39, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Lei, F.; Zhu, L.; Li, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Gao, G.F.; Wang, X. Exposure of different bacterial inocula to newborn chicken affects gut microbiota development and ileum gene expression. ISME J. 2010, 4, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, M.P.; McMurty, J.P. Expression of proglucagon and proglucagon-derived peptide hormone receptor genes in the chicken. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2008, 156, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, M.P.; McMurtry, J.P. The avian proglucagon system. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2009, 163, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Ingredient, % | Basal Diet | Challenge Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Corn | 55.40 | 65.80 |
| Soybean meal | 38.75 | - |
| Rapeseed meal | - | 13.00 |
| Potato protein | - | 16.00 |
| Soya oil | 2.00 | 1.50 |
| Calcium carbonate | 0.40 | 0.15 |
| Dicalcium phosphate | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| NaCl | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| DL-Methionine | 0.20 | 0.10 |
| L-Lysine | 0.09 | 0.20 |
| Vitamin-mineral premix 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Coccidiostat 2 | 0.06 | - |
| Calculated Nutrient Composition | ||
| AME (kcal/kg) | 2990 | 3083 |
| Crude protein (%) | 22.0 | 21.9 |
| Lysine (%) | 1.27 | 1.25 |
| Cysteine + Methionine (%) | 0.87 | 0.90 |
| Threonine (%) | 0.84 | 1.07 |
| Total P (%) | 0.74 | 0.73 |
| Total Ca (%) | 0.96 | 0.92 |
| Analyzed Protein Composition | ||
| Crude protein (%) | 23.3 | 20.9 |
| Sample | Age | Analyses |
|---|---|---|
| Blood (plasma, serum) | day 21 and 28 | ELISA: IgA, and AGP |
| Ileum tissue | day 21 and 28 | Gene expression Morphology, crypt villus length |
| Liver | day 21 and 28 | Morphology Pathology |
| Ileum Tissue | day 21 and 28 | T Cell phenotyping |
| Cell-Surface Marker | Target | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| CD45 | Leukocytes | MCA2413PE Biorad |
| CD3 | T cells | MA5-28694 Invitrogen |
| CD4 | T-helper cells | MCA2164F Biorad |
| CD8a | Cytotoxic T cells | MA5-28725 Invitrogen |
| CD8b | Cytotoxic T cells | C2259-99N US Biologica |
| Gene | Function | Primer Sequences (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | Pro-inflammatory | Primer sequences provided by Qiagen, Courtaboeuf, France |
| IFN-γ | Pro-inflammatory | |
| SLC5A10 | Glucose transporter (SGLT1) | |
| SCL15A1 | Peptide transporter | |
| SLC34A2 | Phosphorus transporter | |
| SLC5A8 | Sodium coupled monocarboxylate transporter 1 | F: GGT-GGG-ACC-TTC-ACA-TGG-AC R: AGA-GGG-ACA-TTT-TTG-CGT-GG |
| SGLT1 | Na+-D-glucose cotransporter | F: TGG-TTG-TTC-TAG-GAT-GGG-TG R: CAG-TGA-CAG-CAT-CTC-GGA-AG |
| CCNA2 | Cyclin A1 | F: TTG-CCT-CAT-GGA-CCT-TCA-CA R: GCA-TGG-TAC-TTT-GTG-CTC-TTG-T |
| CCND1 | Cyclin D1 | F: CAC-TTG-GAT-GCT-GGA-GGT-CTG R: CGA-ACG-ACA-AAA-ACC-TGT-CCA |
| CDK2 | Cyclin dependent kinase 2 | F: ATT-TTT-GCT-GAG-ATG-GTG-ACG-C R: ACG-TGC-GGA-AGA-TAC-GGA-AG |
| GCG | Pro-glucagon | F: TCC-AGA-ACA-TGG-GAA-CAG-AGA R: CTG-TAT-GCC-AGA-CTT-CCA-TTG-T |
| Ingredient, % | Starter 1–10 Days | Grower 10–24 Days | Finisher 24–48 Days |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat 1 | 55.88 | 55.63 | 58.22 |
| Soybean meal | 28.12 | 22.56 | 17.24 |
| Canola meal | 4.25 | 6.00 | 7.00 |
| Meat meal | 4.00 | 3.20 | 2.52 |
| canola oil | 2.60 | 3.55 | 4.08 |
| Barley | 2.00 | 4.00 | 5.00 |
| Canola seed | 1.00 | 3.00 | 4.00 |
| Limestone fine | 0.733 | 0.753 | 0.770 |
| Salt | 0.316 | 0.283 | 0.203 |
| DL-Methionine | 0.293 | 0.247 | 0.213 |
| HCL-Lysine | 0.261 | 0.239 | 0.236 |
| Vitamin-Mineral Premix 2 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 |
| L-Thr | 0.143 | 0.111 | 0.088 |
| Na Bicarbonate | 0.103 | 0.120 | 0.135 |
| Choline Chloride (70%) | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.050 |
| Protease | 0.020 | 0.020 | 0.020 |
| Phytase | 0.020 | 0.020 | 0.020 |
| Carbohydrase | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.010 |
| Calculated nutrient composition | |||
| AME (Kcal/kg) | 2990 | 3100 | 3180 |
| Crude Protein (%) | 23.1 | 21.3 | 19.4 |
| Dry Matter (%) | 90.80 | 90.84 | 90.83 |
| Dig Lys (%) | 1.274 | 1.153 | 1.027 |
| Dig Met (%) | 0.603 | 0.543 | 0.492 |
| Dig M + C (%) | 0.945 | 0.873 | 0.805 |
| Dig Thr (%) | 0.856 | 0.773 | 0.685 |
| Calcium (%) | 0.900 | 0.850 | 0.800 |
| Av P (%) | 0.450 | 0.425 | 0.400 |
| Na (%) | 0.220 | 0.210 | 0.180 |
| Cl (%) | 0.330 | 0.302 | 0.249 |
| K (%) | 0.833 | 0.775 | 0.711 |
| Treatment | BWG, g | cFCR | ROI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1372 | 2.236 a | - |
| Avilamycin | 1451 | 1.917 b | - |
| Precision biotic | 1431 | 1.929 b | 22.5 |
| SEM | 28.8 | 0.11 | |
| p Value | 0.15 | 0.04 |
| Lesion Scores 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Duodenum | Ileum | Caeca | Whole Intestine |
| Control | 3.56 a | 1.50 a | 0.25 | 5.31 a |
| Avilamycin | 1.00 b | 0.31 b | 0.63 | 1.94 b |
| Precision biotic | 0.81 b | 0.62 ab | 0.69 | 2.13 b |
| SEM | 0.42 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.66 |
| p Value | 0.007 | 0.005 | 0.16 | 0.005 |
| Ileal Morphology | ||||
| Treatment | Mucosa Thickness (µm) | Villus Length (µm) | Crypt Depth (µm) | Villus/Crypt |
| Control | 584.7 b | 323.5 b | 246.5 | 1.380 b |
| Avilamycin | 774.4 a | 517.7 a | 242.2 | 2.349 a |
| Precision biotic | 782.4 a | 461.1 a | 306.4 | 1.633 b |
| SEM | 48.4 | 45.8 | 17.6 | 0.22 |
| p Value | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blokker, B.; Bortoluzzi, C.; Iaconis, C.; Perez-Calvo, E.; Walsh, M.C.; Schyns, G.; Tamburini, I.; Geremia, J.M. Evaluation of a Novel Precision Biotic on Enterohepatic Health Markers and Growth Performance of Broiler Chickens under Enteric Challenge. Animals 2022, 12, 2502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192502
Blokker B, Bortoluzzi C, Iaconis C, Perez-Calvo E, Walsh MC, Schyns G, Tamburini I, Geremia JM. Evaluation of a Novel Precision Biotic on Enterohepatic Health Markers and Growth Performance of Broiler Chickens under Enteric Challenge. Animals. 2022; 12(19):2502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192502
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlokker, Britt, Cristiano Bortoluzzi, Christelle Iaconis, Estefania Perez-Calvo, Maria C. Walsh, Ghislain Schyns, Ian Tamburini, and Jack M. Geremia. 2022. "Evaluation of a Novel Precision Biotic on Enterohepatic Health Markers and Growth Performance of Broiler Chickens under Enteric Challenge" Animals 12, no. 19: 2502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192502
APA StyleBlokker, B., Bortoluzzi, C., Iaconis, C., Perez-Calvo, E., Walsh, M. C., Schyns, G., Tamburini, I., & Geremia, J. M. (2022). Evaluation of a Novel Precision Biotic on Enterohepatic Health Markers and Growth Performance of Broiler Chickens under Enteric Challenge. Animals, 12(19), 2502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192502








