Phenotypic and Genetic Characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates from Wild Animals in Central Italy
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The sample Collection
2.2. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
2.3. Real-Time PCR
2.4. MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry
2.5. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.6. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) and Data Analysis
2.7. Typing, AMR, and Virulence Gene Profiles
2.8. Clustering Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial Detection and Identification Results
3.2. Whole Genome Sequencing and Typing Results
3.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
3.4. AMR and Virulence Gene Profiles Results
3.5. cgMLST Analysis
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plaza-Rodríguez, C.; Alt, K.; Grobbel, M.; Hammerl, J.A.; Irrgang, A.; Szabo, I.; Stingl, K.; Schuh, E.; Wiehle, L.; Pfefferkorn, B.; et al. Wildlife as Sentinels of Antimicrobial Resistance in Germany? Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 627821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.E.V.; Boerlin, P. Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in animals and methodologies for their detection. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2020, 84, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Radhouani, H.; Poeta, P.; Gonçalves, A.; Pacheco, R.; Sargo, R.; Igrejas, G. Wild birds as biological indicators of environmental pollution: Antimicrobial resistance patterns of Escherichia coli and enterococci isolated from common buzzards (Buteo buteo). J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanardi, G.; Iemmi, T.; Spadini, C.; Taddei, S.; Cavirani, S.; Cabassi, C.S. Wild Micromammals as Bioindicators of Antibiotic Resistance in Ecopathology in Northern Italy. Animals 2020, 10, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittecoq, M.; Laurens, C.; Brazier, L.; Durand, P.; Elguero, E.; Arnal, A.; Thomas, F.; Aberkane, S.; Renaud, N.; Prugnolle, F.; et al. VIM-1 carbapenemase-producing Escherichia coli in gulls from southern France. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antilles, N.; García-Bocanegra, I.; Alba-Casals, A.; López-Soria, S.; Pérez-Méndez, N.; Saco, M.; González-Solís, J.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M. Occurrence and antimicrobial resistance of zoonotic enteropathogens in gulls from southern Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 143018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiful Islam, M.; Paul, A.; Talukder, M.; Roy, K.; Abdus Sobur, M.; Ievy, S.; Mehedi Hasan Nayeem, M.; Rahman, S.; Nazmul Hussain Nazir, K.H.M.; Tofazzal Hossain, M.; et al. Migratory birds travelling to Bangladesh are potential carriers of multi-drug resistant Enterococcus spp., Salmonella spp., and Vibrio spp. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 5963–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelloni, F.; Cilia, G.; Bogi, S.; Ebani, V.V.; Turini, L.; Nuvoloni, R.; Cerri, D.; Fratini, F.; Turchi, B. Pathotypes and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Escherichia coli Isolated from Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) in Tuscany. Animals 2020, 10, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambino, D.; Vicari, D.; Vitale, M.; Schirò, G.; Mira, F.; Giglia, M.; Riccardi, A.; Gentile, A.; Giardina, S.; Carrozzo, A.; et al. Study on Bacteria Isolates and Antimicrobial Resistance in Wildlife in Sicily, Southern Italy. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchi, B.; Dec, M.; Bertelloni, F.; Winiarczyk, S.; Gnat, S.; Bresciani, F.; Viviani, F.; Cerri, D.; Fratini, F. Antibiotic Susceptibility and Virulence Factors in Escherichia coli from Sympatric Wildlife of the Apuan Alps Regional Park (Tuscany, Italy). Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, T.P.; Pace, A.; Varriale, L.; Borrelli, L.; Gargiulo, A.; Pompameo, M.; Fioretti, A.; Dipineto, L. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Enteropathogenic Bacteria in Yellow-Legged Gulls (Larus michahellis) in Southern Italy. Animals Animals 2021, 11, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulani, M.S.; Kamble, E.E.; Kumkar, S.N.; Tawre, M.S.; Pardesi, K.R. Emerging Strategies to Combat ESKAPE Pathogens in the Era of Antimicrobial Resistance: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effah, C.Y.; Sun, T.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y. Klebsiella pneumoniae: An increasing threat to public health. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2020, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. Klebsiella pneumoniae as a key trafficker of drug resistance genes from environmental to clinically important bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 45, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wareth, G.; Neubauer, H. The Animal-foods-environment interface of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Germany: An observational study on pathogenicity, resistance development and the current situation. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.L.; Lam, M.M.C.; Holt, K.E. Population genomics of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.; Rodrigues, C.; Depret, G.; Passet, V.; Gal, L.; Piveteau, P.; Brisse, S. The ZKIR Assay, a Real-Time PCR Method for the Detection of. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02711–e02719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (EUCAST). EUCAST Guidelines, Version.11.0. 2021. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Breakpoint_tables/v_11.0_Breakpoint_Tables.pdf (accessed on 24 September 2021).
- Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 30th ed.; CLSI Supplement M100; Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI): Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Portmann, A.C.; Fournier, C.; Gimonet, J.; Ngom-Bru, C.; Barretto, C.; Baert, L. A Validation Approach of an End-to-End Whole Genome Sequencing Workflow for Source Tracking of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella enterica. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cito, F.; Di Pasquale, A.; Cammà, C.; Cito, P. The Italian information system for the collection and analysis of complete genome sequence of pathogens isolated from animal, food and environment. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 73, 296–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 17 June 2021).
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, M.M.C.; Wick, R.R.; Watts, S.C.; Cerdeira, L.T.; Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. A genomic surveillance framework and genotyping tool for Klebsiella pneumoniae and its related species complex. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyres, K.L.; Wick, R.R.; Gorrie, C.; Jenney, A.; Follador, R.; Thomson, N.R.; Holt, K.E. Identification of Klebsiella capsule synthesis loci from whole genome data. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, e000102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacterial Isolate Genome Sequence Database (BIGSdb). Available online: https://bigsdb.pasteur.fr/klebsiella/ (accessed on 17 June 2021).
- Brisse, S.; Fevre, C.; Passet, V.; Issenhuth-Jeanjean, S.; Tournebize, R.; Diancourt, L.; Grimont, P. Virulent clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae: Identification and evolutionary scenario based on genomic and phenotypic characterization. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Argimón, S.; Yeats, C.A.; Goater, R.J.; Abudahab, K.; Taylor, B.; Underwood, A.; Sánchez-Busó, L.; Wong, V.K.; Dyson, Z.A.; Nair, S.; et al. A global resource for genomic predictions of antimicrobial resistance and surveillance of Salmonella Typhi at pathogenwatch. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeman, T. ABRricate. Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/abricate (accessed on 17 June 2021).
- Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Yu, J.; Yao, Z.; Sun, L.; Shen, Y.; Jin, Q. VFDB: A reference database for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D325–D328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcock, B.P.; Raphenya, A.R.; Lau, T.T.Y.; Tsang, K.K.; Bouchard, M.; Edalatmand, A.; Huynh, W.; Nguyen, A.V.; Cheng, A.A.; Liu, S.; et al. CARD 2020: Antibiotic resistome surveillance with the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D517–D525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Padmanabhan, B.R.; Diene, S.M.; Lopez-Rojas, R.; Kempf, M.; Landraud, L.; Rolain, J.M. ARG-ANNOT, a new bioinformatic tool to discover antibiotic resistance genes in bacterial genomes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; García-Fernández, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Møller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morpheus Tool. Available online: https://software.broadinstitute.org/morpheus/ (accessed on 17 June 2021).
- Hennart, M.; Guglielmini, J.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Jolley, K.A.; Criscuolo, A.; Brisse, S. A dual barcoding approach to bacterial strain nomenclature: Genomic taxonomy of Klebsiella pneumoniae strains. bioRxiv 2021, 3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. Klebsiella pneumoniae Population Genomics and Antimicrobial-Resistant Clones. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 944–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santás-Miguel, V.; Rodríguez-González, L.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Álvarez-Rodríguez, E.; Díaz-Raviña, M.; Arias-Estévez, M.; Fernández-Calviño, D. Time-course evolution of bacterial community tolerance to tetracycline antibiotics in agricultural soils: A laboratory experiment. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, M.; Mascetti, A.; Fisichella, V.; Fulco, E.; Orlandella, B.M.; Lo Piccolo, F. Antibiotic resistance assessment in bacteria isolated in migratory Passeriformes transiting through the Metaponto territory (Basilicata, Italy). Avian Res. 2017, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giacopello, C.; Foti, M.; Mascetti, A.; Grosso, F.; Ricciardi, D.; Fisichella, V.; Lo Piccolo, F. Antimicrobial resistance patterns of Enterobacteriaceae in European wild bird species admitted in a wildlife rescue centre. Vet. Ital. 2016, 52, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachiri, T.; Bakour, S.; Ladjouzi, R.; Thongpan, L.; Rolain, J.M.; Touati, A. High rates of CTX-M-15-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in wild boars and Barbary macaques in Algeria. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2017, 8, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, C.; Wen, Q.; Duan, M.; Zhang, H.; He, H. Detection of drug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Chinese hares (Lepus sinensis). J. Wildl. Dis. 2014, 50, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcias, B.; Aguirre, L.; Seminati, C.; Reyes, N.; Allepuz, A.; Obón, E.; Molina-Lopez, R.A.; Darwich, L. Extended-Spectrum β-Lactam Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli in Wild European Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europeus) Living in Populated Areas. Animals 2021, 11, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncaric, I.; Beiglböck, C.; Feßler, A.T.; Posautz, A.; Rosengarten, R.; Walzer, C.; Ehricht, R.; Monecke, S.; Schwarz, S.; Spergser, J.; et al. Characterization of ESBL- and AmpC-Producing and Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Mouflons (Ovis orientalis musimon) in Austria and Germany. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.M.; Li, L.H.; Yan, J.J.; Tsao, N.; Liao, T.L.; Tsai, H.C.; Fung, C.P.; Chen, H.J.; Liu, Y.M.; Wang, J.T.; et al. Genome sequencing and comparative analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae NTUH-K2044, a strain causing liver abscess and meningitis. J Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 4492–4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Emergence of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae ST23 Carrying Carbapenemase Genes in EU/EEA Countries. 2021. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/risk-assessment-emergence-hypervirulent-klebsiella-pneumoniae-eu-eea (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Monecke, S.; Gavier-Widen, D.; Mattsson, R.; Rangstrup-Christensen, L.; Lazaris, A.; Coleman, D.C.; Shore, A.C.; Ehricht, R. Detection of mecC-positive Staphylococcus aureus (CC130-MRSA-XI) in diseased European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) in Sweden. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paterson, G.K.; Larsen, A.R.; Robb, A.; Edwards, G.E.; Pennycott, T.W.; Foster, G.; Mot, D.; Hermans, K.; Baert, K.; Peacock, S.J.; et al. The newly described mecA homologue, mecALGA251, is present in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from a diverse range of host species. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2809–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, R.T.; Carvalho, J.; Cunha, M.V.; Fonseca, C. Antimicrobial Resistance and Ecology: A Dialog Yet to Begin. EcoHealth 2019, 16, 402–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, G.S.; Price, L.B. Recent Research Examining Links Among Klebsiella pneumoniae from Food, Food Animals, and Human Extraintestinal Infections. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2016, 3, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.; Hauser, K.; Cahill, N.; Ligowska-Marzęta, M.; Centorotola, G.; Cornacchia, A.; Garcia Fierro, R.; Haenni, M.; Nielsen, E.M.; Piveteau, P.; et al. High Prevalence of Klebsiella pneumoniae in European Food Products: A Multicentric Study Comparing Culture and Molecular Detection Methods. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0237621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, G.S.; Waits, K.; Nordstrom, L.; Weaver, B.; Aziz, M.; Gauld, L.; Grande, H.; Bigler, R.; Horwinski, J.; Porter, S.; et al. Intermingled Klebsiella pneumoniae Populations between Retail Meats and Human Urinary Tract Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramey, A.M.; Ahlstrom, C.A. Antibiotic resistant bacteria in wildlife: Perspectives on trends, acquisition and dissemination, data gaps, and future directions. J. Wildl. Dis. 2020, 56, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoglica, C.; Di Francesco, C.E.; Angelucci, S.; Antonucci, A.; Innocenti, M.; Marsilio, F. Occurrence of the tetracycline resistance gene tetA(P) in Apennine wolves (Canis lupus italicus) from different human-wildlife interfaces. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 23, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
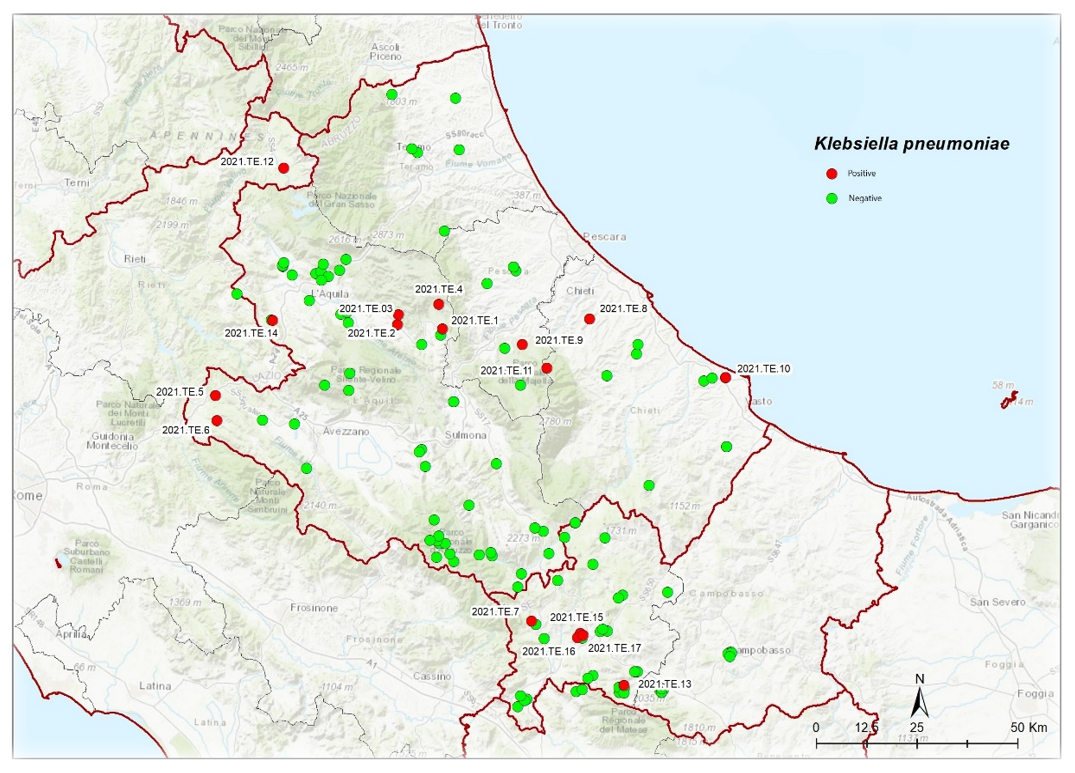
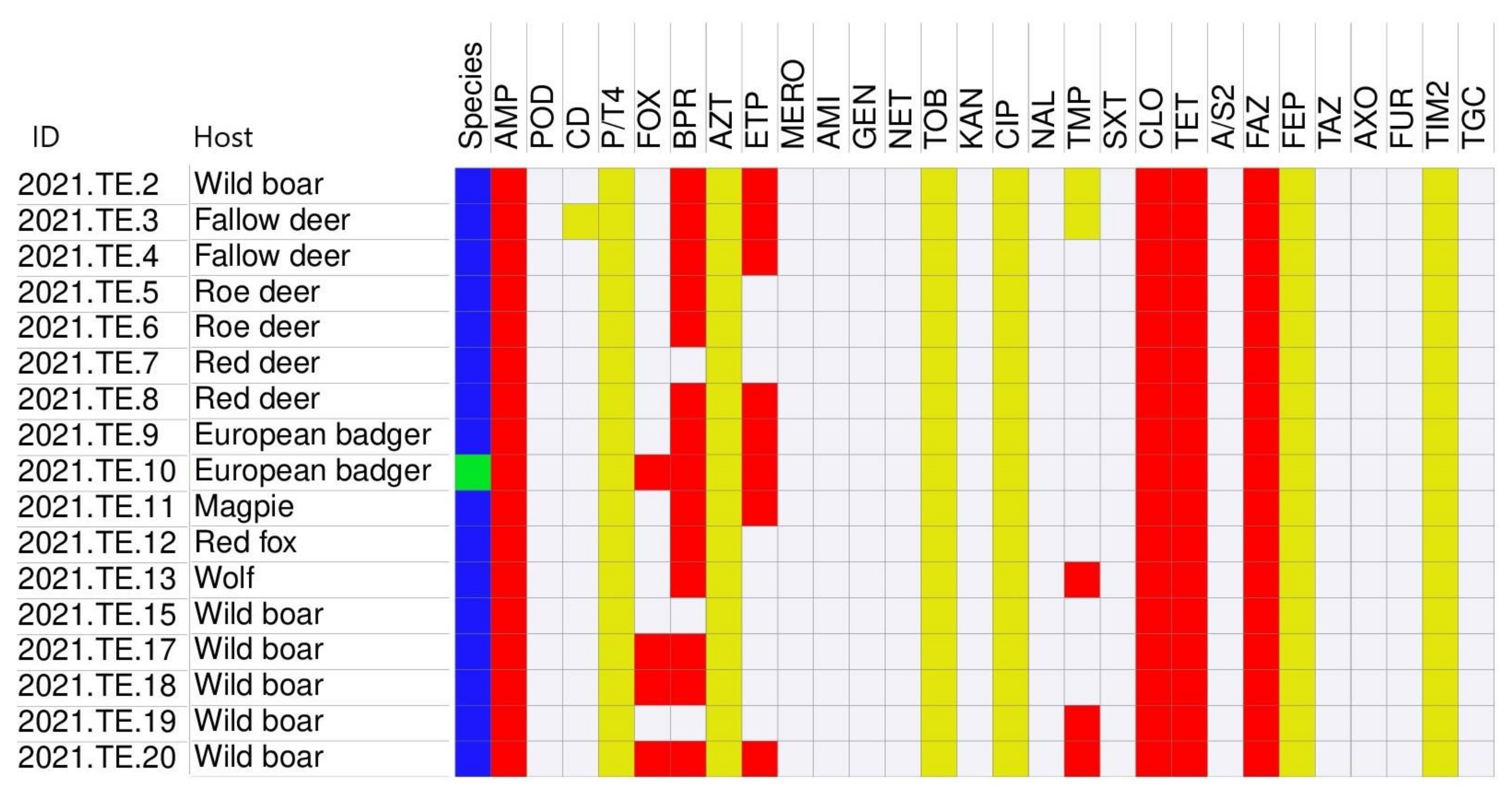
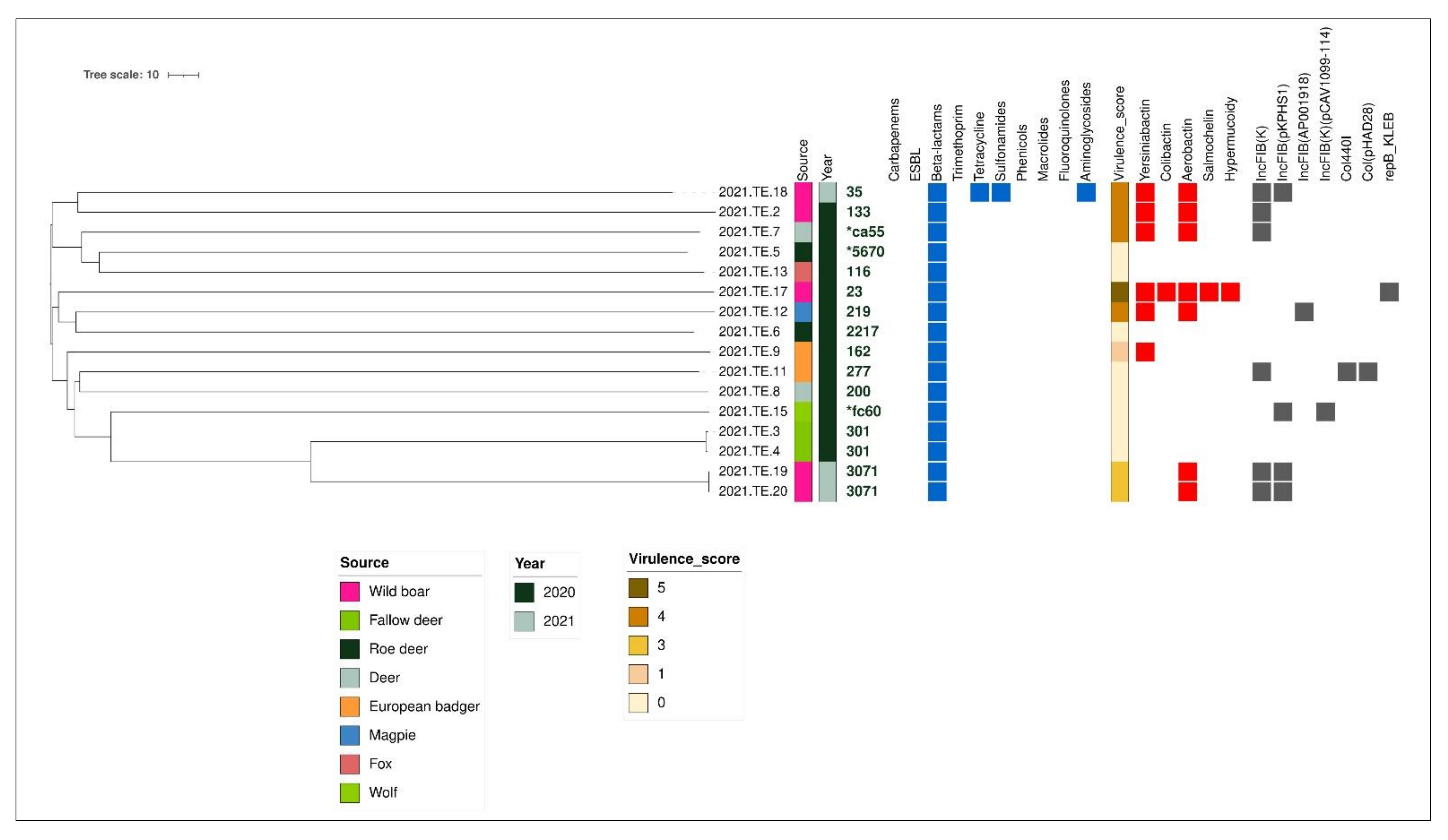

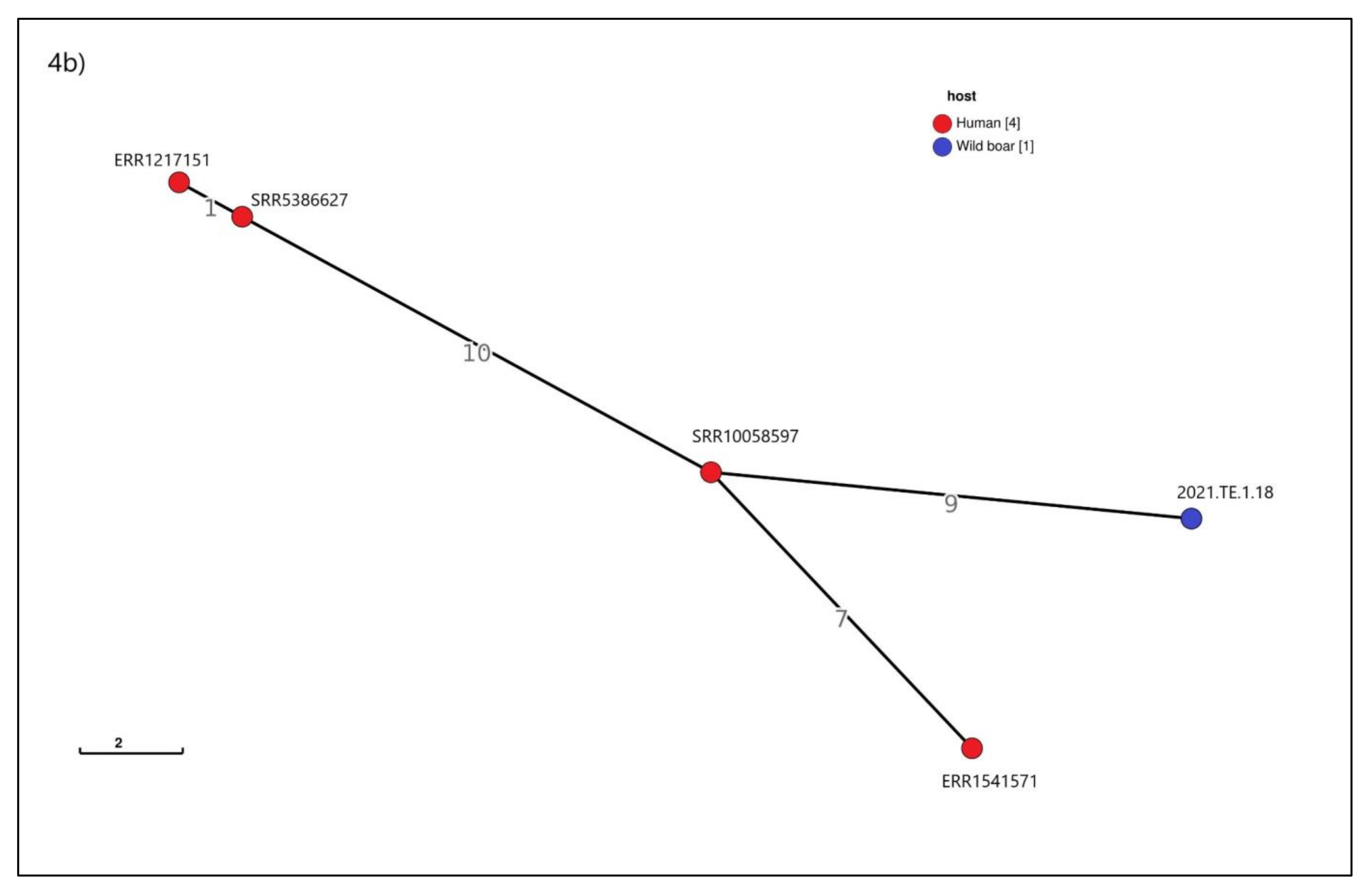
| ID | Year | Host | Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2021.TE.2 | 2020 | Wild boar | Feces |
| 2021.TE.3 | 2020 | Fallow deer | Feces |
| 2021.TE.4 | 2020 | Fallow deer | Feces |
| 2021.TE.5 | 2020 | Roe deer | Feces |
| 2021.TE.6 | 2020 | Roe deer | Feces |
| 2021.TE.7 | 2020 | Red deer | Feces |
| 2021.TE.8 | 2020 | Red deer | Feces |
| 2021.TE.9 | 2020 | European badger | Small intestine |
| 2021.TE.10 | 2020 | European badger | Feces |
| 2021.TE.11 | 2020 | Magpie | Small intestine |
| 2021.TE.12 | 2020 | Red fox | Small intestine |
| 2021.TE.13 | 2020 | Wolf | Feces |
| 2021.TE.15 | 2020 | Wild boar | Brain |
| 2021.TE.17 | 2020 | Wild boar | Small intestine |
| 2021.TE.18 | 2021 | Wild boar | Brain |
| 2021.TE.19 | 2021 | Wild boar | Brain |
| 2021.TE.20 | 2021 | Wild boar | Brain |
| ID | ST | KL | O | β-Lactams | Tet | Sul | Ami | Plasmid | Ybt | Clb | Iuc | Iro | rmpA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021.TE.2 | 133 | KL116 | O1v1 | SHV-75 | / | / | / | IncFIB(K) | ybt 9 ICEKp3 | / | unknown | / | / |
| 2021.TE.3 | 301 | KL116 | O2v1 | SHV-27 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 2021.TE.4 | 301 | KL116 | O2v1 | SHV-27 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 2021.TE.5 | *5670 | KL30 | O3/O3a | SHV-11 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 2021.TE.6 | 2217 | KL13 | O3b | SHV-1 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 2021.TE.7 | *ca55 | KL30 | O1v1 | SHV-65 | / | / | / | IncFIB(K) | ybt 9 ICEKp3 | / | iuc 3 | / | / |
| 2021.TE.8 | 200 | *KL13 | O3b | SHV-1 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 2021.TE.9 | 162 | KL13 | O3b | SHV-1 | / | / | / | / | ybt 16 ICEKp12 | / | / | / | / |
| 2021.TE.10 | 4895 | KL35 | O3/O3a | OKP-A-2 | / | / | / | IncFIB(K) | / | / | / | / | / |
| 2021.TE.11 | 277 | / | O3b | SHV-27 | / | / | / | IncFIB(K), Col(pHAD28) | / | / | / | / | / |
| 2021.TE.12 | 219 | KL121 | O1v1 | SHV-1 | / | / | / | IncFIB(AP001918) | ybt 16 ICEKp12 | / | iuc 3 | / | / |
| 2021.TE.13 | 116 | KL11 | O3/O3a | SHV-1 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 2021.TE.15 | *fc60 | KL117 | O2v2 | SHV-11 | / | / | / | IncFIB(pKPHS1) IncFIB(K)(pCAV1099-114) | / | / | / | / | / |
| 2021.TE.17 | 23 | KL1 | O1v2 | SHV-11 | / | / | / | repB (pK2044) | ybt 1 ICEKp1 | clb 2 | iuc 1 | iro1 | rmpA1 rmpA2 |
| 2021.TE.18 | 35 | KL22 | O1v1 | SHV-33 | tetA | sul2 | strA strB | IncFIB(pKPHS1) IncFIB(K) | ybt 5 ICEKp6 | / | iuc 3 | / | / |
| 2021.TE.19 | 3071 | KL31 | OL104 | SHV-27 | / | / | / | IncFIB(pKPHS1) IncFIB(K) | / | / | iuc 3 | / | / |
| 2021.TE.20 | 3071 | KL31 | O3b | SHV-27 | / | / | / | IncFIB(pKPHS1) IncFIB(K) | / | iuc 3 | / | / |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiaverini, A.; Cornacchia, A.; Centorotola, G.; Tieri, E.E.; Sulli, N.; Del Matto, I.; Iannitto, G.; Petrone, D.; Petrini, A.; Pomilio, F. Phenotypic and Genetic Characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates from Wild Animals in Central Italy. Animals 2022, 12, 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12111347
Chiaverini A, Cornacchia A, Centorotola G, Tieri EE, Sulli N, Del Matto I, Iannitto G, Petrone D, Petrini A, Pomilio F. Phenotypic and Genetic Characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates from Wild Animals in Central Italy. Animals. 2022; 12(11):1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12111347
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiaverini, Alexandra, Alessandra Cornacchia, Gabriella Centorotola, Elga Ersilia Tieri, Nadia Sulli, Ilaria Del Matto, Giorgio Iannitto, Domenico Petrone, Antonio Petrini, and Francesco Pomilio. 2022. "Phenotypic and Genetic Characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates from Wild Animals in Central Italy" Animals 12, no. 11: 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12111347
APA StyleChiaverini, A., Cornacchia, A., Centorotola, G., Tieri, E. E., Sulli, N., Del Matto, I., Iannitto, G., Petrone, D., Petrini, A., & Pomilio, F. (2022). Phenotypic and Genetic Characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates from Wild Animals in Central Italy. Animals, 12(11), 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12111347






