Variations in Behavioral and Physiological Traits in Yearling Tibetan Sheep (Ovis aries)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Animal Breeding
2.3. Behavior Assay
2.4. Physiological Assay
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Mean-Level Difference and Prediction
3.2. Correlations between Traits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guenther, A.; Finkemeier, M.A.; Trillmich, F. The ontogeny of personality in the wild guinea pig. Anim. Behav. 2014, 90, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réale, D.; Martin, J.; Coltman, D.W.; Poissant, J.; Festa-Bianchet, M. Male personality, life-history strategies and reproductive success in a promiscuous mammal. J. Evol. Biol. 2009, 22, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibbald, A.M.; Erhard, H.W.; McLeod, J.E.; Hooper, R.J. Individual personality and the spatial distribution of groups of grazing animals: An example with sheep. Behav. Processes 2009, 82, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Launchbaugh, K.L.; Howery, L.D. Understanding landscape use patterns of livestock as a consequence of foraging behavior. Rangeland. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 58, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, I.; Dingemanse, N.J. Parasitism and the evolutionary ecology of animal personality. Philos. T. R. Soc. B 2010, 365, 4077–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamps, J.A.; Groothuis, T.G. Developmental perspectives on personality: Implications for ecological and evolutionary studies of individual differences. Philos. T. R. Soc. B 2010, 365, 4029–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réale, D.; Garant, D.; Humphries, M.M.; Bergeron, P.; Careau, V.; Montiglio, P.-O. Personality and the emergence of the pace-of-life syndrome concept at the population level. Philos. T. R. Soc. B 2010, 365, 4051–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, J.; Kirbach, A.; Reiter, L.; Lehmann, K.; Norton, P.; Storms, M.; Koblofsky, M.; Winter, S.; Georgieva, P.B.; Nguyen, H.; et al. Exploratory behaviour of honeybees during orientation flights. Anim. Behav. 2015, 102, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, S.R.; Silla, A.J.; Byrne, P.G. Animal personality and behavioral syndromes in amphibians: A review of the evidence, experimental approaches, and implications for conservation. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2018, 72, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favati, A.; Zidar, J.; Thorpe, H.; Jensen, P.; Løvlie, H. The ontogeny of personality traits in the red junglefowl, Gallus gallus. Behav. Ecol. 2016, 27, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gygax, L.; Vögeli, S. Reactions of sheep towards three sets of emotional stimuli: (In) Consistency in respect to stimulus valence and sheep identity. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2016, 174, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horback, K.M.; Parsons, T.D. Ontogeny of behavioral traits in commercial sows. Animals 2018, 12, 2365–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuerz, Y.; Krüger, O. Personality over ontogeny in zebra finches: Long-term repeatable traits but unstable behavioural syndromes. Front. Zool. 2015, 12, S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poissant, J.; Réale, D.; Martin, J.G.A.; Festa-Bianchet, M.; Coltman, D.W. A quantitative trait locus analysis of personality in wild bighorn sheep. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, S.H.; Kastner, N.; Loddenkemper, D.H.; Kaiser, S.; Sachser, N. A time to wean? Impact of weaning age on anxiety-like behaviour and stability of behavioural traits in full adulthood. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, H.; Inoue, M.; Makino, J. Ultrasonic isolation calls in genetically high-and low-emotional rat pups. Exp. Anim. Tokyo 2000, 49, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Robinson, J.E.; Evans, N.P.; Dumbell, R.; Solbakk, A.K.; Ropstad, E.; Haraldsen, I.R.H. Effects of inhibition of gonadotropin releasing hormone secretion on the response to novel objects in young male and female sheep. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2014, 40, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urszán, T.J.; Garamszegi, L.Z.; Nagy, G.; Hettyey, A.; Török, J.; Herczeg, G. Experience during development triggers between-individual variation in behavioural plasticity. J. Anim. Ecol. 2018, 87, 1264–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polverino, G.; Cigliano, C.; Nakayama, S.; Mehner, T. Emergence and development of personality over the ontogeny of fish in absence of environmental stress factors. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2016, 70, 2027–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, B.; Joshi, C.H.; Kalyadan, S.S.; Somanathan, H. Early ontogenic emergence of personality and its long-term persistence in a social spider. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2019, 73, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.R.; Blumstein, D.T. Fitness consequences of personality: A meta-analysis. Behav. Ecol. 2008, 19, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, A.F.K.; McClure, M.; Ethier, J.E. Exploration costs promote conservative collective foraging in the social caterpillar Malacosoma disstria. Anim. Behav. 2015, 105, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitten, P.L.; Stavisky, R.; Aureli, F.; Russell, E. Response of fecal cortisol to stress in captive chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes). Am. J. Primatol. 1998, 44, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubuc-Messier, G.; Réale, D.; Perret, P.; Charmantier, A. Environmental heterogeneity and population differences in blue tits personality traits. Behav. Ecol. 2017, 28, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, J.M.; Riechert, S.E.; O’Meara, B.C. The ontogeny of personality traits in the desert funnel-web spider, Agelenopsis lisa (Araneae: Agelenidae). Ethology 2017, 123, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathot, K.J.; Dingemanse, N.J.; Nakagawa, S. The covariance between metabolic rate and behaviour varies across behaviours and thermal types: Meta-analytic insights. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 1056–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.B. Rangeland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau: A review of the evidence of its magnitude and causes. J. Arid. Environ. 2010, 74, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolhaas, J.M.; Korte, S.M.; De Boer, S.F.; Van Der Vegt, B.; Van Reenen, C.; Hopster, H.; De Jong, I.; Ruis, M.; Blokhuis, H. Coping styles in animals: Current status in behavior and stress-physiology. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1999, 23, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Fletcher, Q.E.; Réale, D.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y. Independence between coping style and stress reactivity in plateau pika. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 197, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koolhaas, J.M.; De Boer, S.F.; Coppens, C.M.; Buwalda, B. Neuroendocrinology of coping styles: Towards understanding the biology of individual variation. Front. Neuroendocrin. 2010, 31, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Interpretation of Each Variable |
|---|---|
| Risk-taking | Emergence latency, the time from the single test area to the open field (s) |
| Vocalizations | Number of calls in the open field (number/3 min) |
| Exploration | Divided the surface of the open field into a grid with equal-sized squares (1 m × 1 m) and counted the number of gridlines passed by the Tibetan sheep as exploration. The Tibetan sheep with a body size covering more than half a square plus one or less than half a square did not count (number/3 min) |
| Novelty | Time before first touching a novel subject (s) |
| Heart rate | Heart rate under handling (bpm) |
| CORT | Cortisol concentration in feces (ng/mL) |
| Variable | Month | Mean ± SE | Comparison | Difference | Correlation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z/LSD | p | r/rho | p | ||||
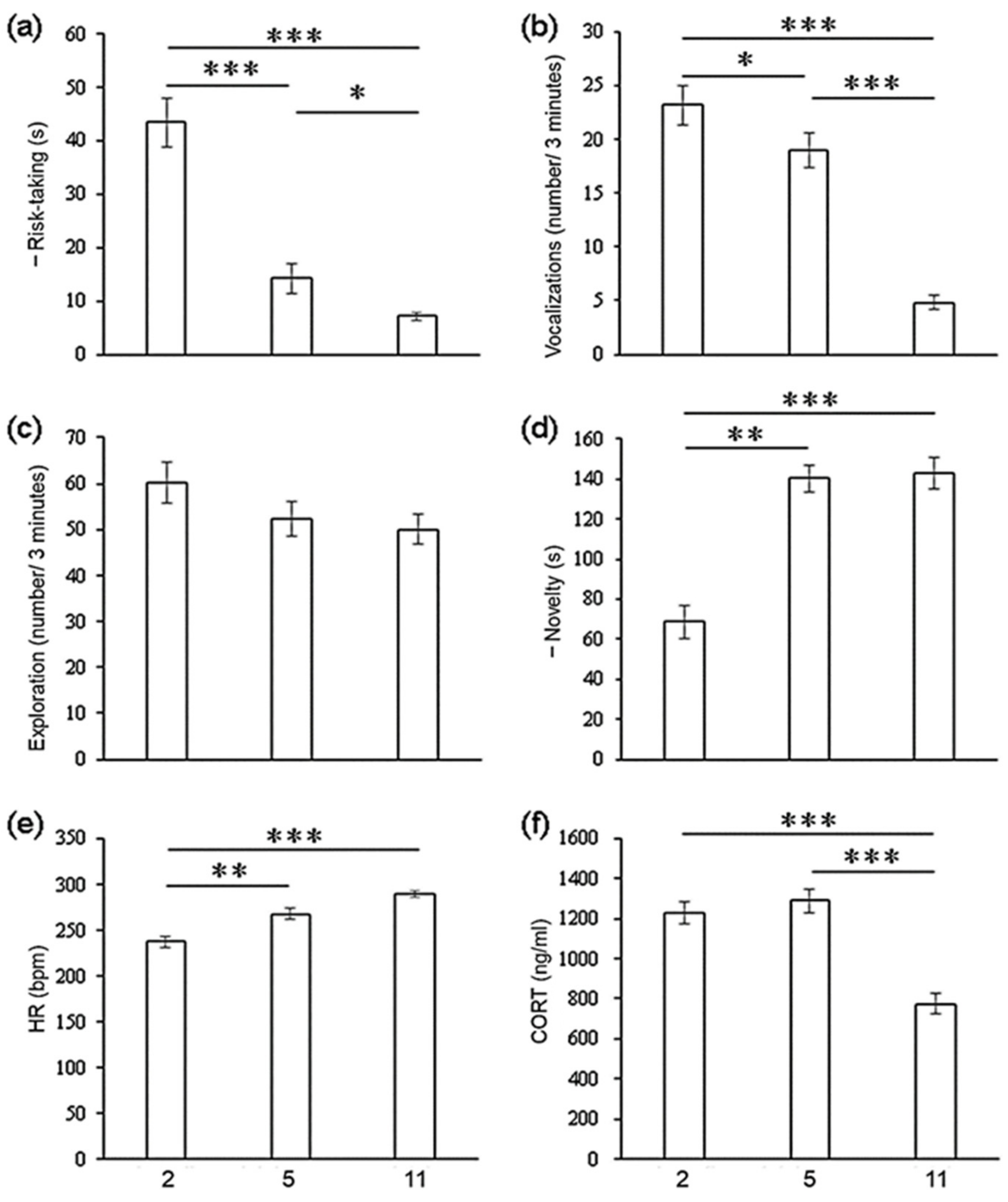
| Risk-taking | Mar. | 43.37 ± 4.46 | Mar.–Jun. | −5.228 | <0.001 ** | 0.183 | 0.218 |
| Jun. | 14.20 ± 2.73 | Jun.–Dec. | −2.500 | 0.012 * | 0.396 | 0.013 * | |
| Dec. | 7.12 ± 0.84 | Mar.–Dec. | −5.223 | <0.001 ** | −0.013 | 0.938 | |
| Vocalizations | Mar. | 23.20 ± 1.83 | Mar.–Jun. | −2.075 | 0.038 * | 0.379 | 0.019 * |
| Jun. | 19.02 ± 1.62 | Jun.–Dec. | −4.376 | <0.001 ** | 0.296 | 0.151 | |
| Dec. | 4.82 ± 0.67 | Mar.–Dec. | −4.445 | <0.001 ** | 0.161 | 0.422 | |
| Exploration | Mar. | 60.24 ± 4.56 | Mar.–Jun. | −0.414 | 0.679 | 0.020 | 0.898 |
| Jun. | 52.32 ± 3.67 | Jun.–Dec. | −1.275 | 0.202 | −0.050 | 0.764 | |
| Dec. | 49.95 ± 3.26 | Mar.–Dec. | −0.036 | 0.971 | 0.354 | 0.027 * | |
| Novelty | Mar. | 68.79 ± 8.15 | Mar.–Jun. | −3.404 | 0.001 ** | −0.022 | 0.903 |
| Jun. | 140.53 ± 6.69 | Jun.–Dec. | −0.747 | 0.455 | −0.011 | 0.959 | |
| Dec. | 142.86 ± 8.19 | Mar.–Dec. | −3.553 | <0.001 ** | 0.134 | 0.497 | |
| Heart rate | Mar. | 237.34 ± 6.12 | Mar.–Jun. | −3.045 | 0.002 ** | 0.066 | 0.678 |
| Jun. | 267.55 ± 5.88 | Jun.–Dec. | −1.733 | 0.083 | −0.055 | 0.742 | |
| Dec. | 289.71 ± 3.95 | Mar.–Dec. | −4.340 | <0.001 ** | −0.026 | 0.876 | |
| CORT | Mar. | 1227.35 ± 56.07 | Mar.–Jun. | 324.530 | 0.461 | −0.351 | 0.649 |
| Jun. | 1287.45 ± 60.25 | Jun.–Dec. | 316.550 | <0.001 ** | 0.710 | 0.048 * | |
| Dec. | 775.71 ± 51.90 | Mar.–Dec. | 311.762 | <0.001 ** | −0.426 | 0.400 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, L.; Zhu, H.; Qu, J. Variations in Behavioral and Physiological Traits in Yearling Tibetan Sheep (Ovis aries). Animals 2021, 11, 1676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061676
Yu Y, Wang Y, Zhong L, Zhu H, Qu J. Variations in Behavioral and Physiological Traits in Yearling Tibetan Sheep (Ovis aries). Animals. 2021; 11(6):1676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061676
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yibo, Yun Wang, Liang Zhong, Hongjuan Zhu, and Jiapeng Qu. 2021. "Variations in Behavioral and Physiological Traits in Yearling Tibetan Sheep (Ovis aries)" Animals 11, no. 6: 1676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061676
APA StyleYu, Y., Wang, Y., Zhong, L., Zhu, H., & Qu, J. (2021). Variations in Behavioral and Physiological Traits in Yearling Tibetan Sheep (Ovis aries). Animals, 11(6), 1676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061676







