Simple Summary
Fascioliasis is an economically important parasitic snail-borne disease of ruminant animals including cattle, sheep and goats that has public health significance due to risk of infection transmission to humans. The disease causes growth retardation, decreased milk and meat production, and liver damage in infected animals. The current cross-sectional study was conducted at the Lira Municipal abattoir in Northern Uganda to estimate the prevalence of fascioliasis and evaluate the risk factors (region, breed, sex, and age of animals) associated with infection in slaughter cattle. Each selected carcass was examined for fascioliasis by dissecting the liver. Infested sections of the livers were trimmed off, condemned and incinerated. Out of the 216 liver samples examined, the majority (65.7%; n = 142) were infested with Fasciola spp. This study revealed that cattle aged 4 years or older were at a higher risk of fascioliasis in comparison to young cattle (0–3.5 years). The estimated monetary loss due to liver damage was 9900 UGX (2.67 USD)/infected animal. The outcome of this study underscores the need for increased awareness of the disease burden, and implementation of appropriate control measures.
Abstract
Fascioliasis (liver fluke infestation) is one of the most important parasitic diseases affecting cattle, other ruminant animals and humans. Fascioliasis causes large, but usually neglected, economic losses to cattle farmers and traders. The objectives of this study were to assess the prevalence and associated risks for fascioliasis in slaughter cattle and estimate the financial losses due to liver condemnation at the Lira Municipal abattoir in Uganda. A total of 216 cattle were sampled during the study period. Animal breed and sex were determined by observing the phenotypic characteristics of the animals. Age was determined by assessing the eruption and wearing of permanent teeth. After slaughter, the liver was examined for presence of Fasciola spp. (liver flukes) by visual inspection, palpation, and incisions. The bile ducts and gall bladder were similarly examined for presence of mature Fasciola spp. The gross weight and amount of liver trimmed-off due to fluke infestation were determined. Of the 216 liver examined, 65.7% (n = 142) were infested with Fasciola spp. Cattle that were aged 4–5 years old at the time of slaughter had significantly greater odds (OR = 5.84; CI [2.79–12.22]) of being infested with Fasciola spp. compared to those that were younger than 3.5 years old. In contrast, cattle that had a body condition score of 3.5 or 4 had lower odds (OR= 0.42; CI [0.21–0.88] and OR = 0.22; CI [0.04–1.10]) of fascioliasis than those with a BCS of 3. Other tested variables including animal origin, breed, sex, and gross weight of the liver had no significant effect on the prevalence of fascioliasis. This study also revealed that the abattoir loses an estimated 38 million UGX annually due to condemnation of Fasciola-infested liver (one UGX= 0.00027 USD; July 2016). Our study showed that the prevalence of fascioliasis was high in Lira District, Uganda, which results in a large amount of liver being condemned and destroyed, leading to financial losses for affected farmers in the area. Therefore, there is a need to take the necessary preventive measures to control the disease and increase awareness among farmers and medical personnel in the area due to the zoonotic nature of fascioliasis.
1. Introduction
Fascioliasis, also known as liver rot, is an important parasitic infection disease of cattle caused by two main species of trematodes: Fasciola gigantica, and Fasciola hepatica [1]. In Europe, the Americas, and Oceania, only Fasciola hepatica is a concern, but the distributions of both Fasciola spp. overlap in many areas of Africa and Asia [2]. The Lymnaea snails living along the riverbanks are suitable intermediate hosts for Fasciola spp. [3]. The prevalence of fascioliasis varies between herds and regions. In 2015, a study conducted on farms from the Nile Delta region in Egypt reported a herd prevalence of 9.77% [4]. In Denmark, an increase in annual herd prevalence was reported between the years 2011 (25.6%) to 2013 (29.3%) [5]. At the animal level, several studies have reported fascioliasis prevalence ranging from 10% to 50.5% in slaughter animals from different abattoirs in South Africa [6], Ethiopia [7] and Nigeria [8,9].
Fascioliasis causes acute and chronic infections [10], and it occurs chiefly in cattle, sheep, goats, and buffalos but may affect humans and other species [1]. As meat consumption increases worldwide, there are growing concerns about meat hygiene and safety, especially given that the worldwide distribution of fascioliasis is estimated at 90% in ruminants [11]. According to Mas-Coma et al. [2,12], and Esteban et al. [13], fascioliasis has recently been shown to be a re-emerging and widespread zoonosis affecting multiple human populations, hence gaining attention as a public health issue. In addition, fascioliasis is now recognized as an emerging human disease. The World Health Organization has estimated that 2.4 million people are infected with Fasciola spp. and a further 180 million are at risk of infection [14].
Economically, worldwide losses in animal productivity due to fascioliasis were conservatively estimated at over $3.2 billion USD per annum according to 1999 publication [15]. The economic losses are categorized as direct losses, which consist of drug costs, drenches, labor, and liver condemnation at abattoirs; and indirect losses associated with decreased productivity such as reduced production, poor growth rate, increased costs for replacement stock, reduced production and quality of milk, and lower feed conversion rates in cattle [16]. Therefore, the aim of this study was to estimate the point prevalence of fascioliasis and evaluate risk factors and the direct financial loss caused by Fasciola spp. in slaughtered cattle in Northern Uganda.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
This was a cross-sectional study conducted in July 2016 at Lira Municipal abattoir, Lira District, Northern Uganda (Figure 1). Lira Municipality is located at latitude 20′ 17′ north of the equator and longitude 32′ 56′ east of the principal meridian. The municipality consists of four sub-counties including Central division, Railways division, Ojwina division and Adyel division. Over the course of this study, the temperature ranged from 28.88 to 27.77 °C and relative humidity ranged from 8% to 12%. The wetter season lasts 7.4 months, from 1 April to 14 November, with a greater than 34% chance of a given day being a wet day. The slaughtered animals were sourced from within Lira district and nearby surrounding districts (Table 1).
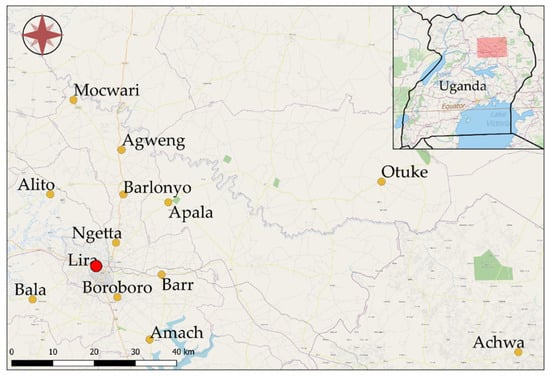
Figure 1.
Sources of animals slaughtered at Lira Municipal abattoir in Uganda, Africa. The abattoir location is marked by the red dot. Sampling locations were reclassified into three regions: Southern (Achwa, Amach, Bala, Boroboro), Eastern (Apala, Barr, Otuke), and Northern regions (Agweng, Alito, Barlonyo, Mocwari, Ngetta).

Table 1.
Summary of distribution and characteristics of slaughter cattle (n = 214) at Lira Municipal abattoir examined for Fasciola spp. infestation. Physical characteristics were determined during antemortem examination, while liver samples were examined post-slaughter.
2.2. Sample Collection and Gross Examination
At the abattoir, information on individual animal source was recorded. Physical examination (antemortem) was performed shortly prior to slaughter in order to determine animal breed, sex, age, and body condition score. Animal breed and sex were determined by observation of phenotypic characteristics of each animal. Age of cattle was determined using a guide [17], which gauges age based on the eruptions, and wear of permanent teeth. Body condition for each cattle was estimated based on a 5-point scoring system according to Wildman et al. [18], ranging from score 1 (emaciated) to score 5 (obese). The classes of scoring used were emaciated (score 1), lean (score 2), medium (score 3 and 4) and obese (score 5). After slaughter of animals, the liver and associated bile duct was carefully examined at post-mortem (PM) for presence of liver flukes and associated pathology by visualization inspection and palpation. Further examination of the liver for liver flukes was conducted by making incisions into the bile ducts and gall bladder. The condemnation of the liver was based on the guidelines on meat inspection for developing countries [19]. According to these guidelines, liver that is infested with Fasciola at slaughter is only partially condemned; only the liver sections containing the Fasciola parasites and/with gross sclerosis condemned and trimmed off. Livers classified as totally condemned because of gross and generalized morphological abnormalities were rejected and destroyed to avoid human consumption. In cases of partial condemnation, the liver was trimmed, and the weight (in metric units) of the trimmed part was taken. All livers were weighed before and after trimming. The monetary loss was calculated based on current market price (in UGX) per kilogram as of July 2016 (one UGX = 0.00027 USD).
2.3. Liver Condemnation and Associated Financial Loss
The financial loss due to liver condemnation was assessed by calculating the price value of the portion of liver trimmed due to fascioliasis infestation. One kilogram of liver on the local market cost 10,000 UGX on average. The unit monetary loss was calculated by multiplying the amount in kilograms trimmed off by the market value of liver. The total loss was calculated by multiplying the unit monetary loss by frequency. This was used to compute the estimated financial loss for the entire study period.
2.4. Sample Size Calculation
The sample size was determined using the Cochran formula [20]. With the assumption of 84% expected prevalence of fasciolosis, at 95% CI and 5% level of precision, the total sample size computed was 206 cows.
2.5. Data Management and Analysis
The data collected were entered into Microsoft Excel 2010 spreadsheet and exported to Stata software for analysis. Frequencies and proportions, and their standard error (SE), were computed for categorical and ordinal variables. The continuous data were checked for normality using normal quantile, and normal probability plots in Stata. Mean and SE were computed for continuous variables. Confidence intervals for proportions were calculated using the normal distribution approximation method. Data on the location of cows were reclassified into three regions: Northern regions (Agweng, Alito, Barlonyo, Mocwari, Ngetta), Southern (Achwa, Amach, Bala, Boroboro), and Eastern (Apala, Barr, Otuke). The age of cows was classified into three groups: young (0–3.5 years), middle (4–5 years), and adult cows (6–10 years). The gross liver weight data were categorized into 3 levels: (1) from 0 to 2 kg, (2) from 2.1 to 4 kg, and (3) from 4.1 to 6 kg. Logistic regression models using logit function were used to study the association between dichotomous outcome variable (Fasciola spp. infestation) and explanatory variables (region, breed, sex, BCS, liver gross weight, and age of animal at slaughter). Two-way interactions for potential effect modifiers were tested using significance testing (p < 0.05). Information theory’s Akaike’s Information Criterion (AIC) was used to build and compare competing models and the model with the lowest value was deemed as the best fit. Odds ratio (OR) and associated SE were represented in final tables. All statistics were performed using Stata 15 software (Stata Corp, College Station, TX, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Socio-Demographic Characteristics of Cattle Assessed in This Study
Characteristics of animals included this study are summarized in Table 1. Most of the animals assessed were of the small East African Zebu breed, accounting for 89.8% (n = 194) of the sample population, with a few animals of the Ankole breed, accounting for 10.2% (n = 22) of the total animals assessed (n = 216). The majority of the cattle slaughtered were males (74.1%, n = 160) while females comprised 25.9% (n = 56). The age distribution of the slaughtered animals was as follows: 18.5% (n = 40) of cattle were 3.5 years old, 37.5% (n = 81) were 4 years old, 20.4% (n = 44) were 5 years old, and 6.9% (n = 15) were 6 years old.
3.2. Prevalence of Fascioliasis in Slaughtered Cattle
Out of the 216 liver examined, 65.7% (n = 142) were infested with Fasciola spp. (Table 2). The Small East African Zebu breed had a higher prevalence of infestation (67.5%, n = 131) when compared to the Ankole breed (50%, n = 11). Between sexes, males had a higher prevalence of fasciolosis 68.8% (n = 110) than females 57.1% (n = 32). Among the various age groups, cattle aged 4–5 years old had higher fasciolosis prevalence (75.3%) compared to cows younger than 4 years (43.24%) or cows older than 6 year olds (70.58%). Additionally, cows with a BCS of 3 had higher fascioliasis prevalence (69.33%) compared to cows with a BCS of 3.5 (64.34%) or BCS of 4 (58.33%) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Prevalence of fascioliasis in examined cattle (n = 142) assessed by region, breed and sex, age, and source of animals.
3.3. Risk Factors for Fasciola Infestation
Logistic regression models were used to estimate the association between Fasciola spp. infestation and various animal and environmental factors as predictors for Fasciola infestation at the time of slaughter (Table 3). Our results showed that cattle age at slaughter, and body condition score were the main factors predicting Fasciola spp. infestation. Cattle that were aged 4–5 years old at the time of slaughter had significant greater odds (OR = 5.84) of being infested with fascioliasis compared to those that were younger than 3.5 years old (Table 3). Furthermore, our results indicated that cattle with body condition scores of 3.5 or 4 had lower odds (OR = 0.42 and 0.22) of being infested with fascioliasis than those with a BCS of 3. Other tested variables including animal origin, breed, sex, and gross weight of the liver had no significant effect on the prevalence of fascioliasis (Table 3).

Table 3.
Estimated odds ratio (OR) from logistic regression model for the association between fascioliasis infestation (Yes, No) and explanatory variables (region, breed, sex, body condition score, and liver gross weight).
3.4. Financial Losses Associated with Liver Condemnation
Financial losses due to fasciolosis were assessed by calculating the value of the liver sections trimmed due to Fasciola infestation. During the 2 week study period, a total of 145.7 kg of livers was trimmed from 141 slaughtered cattle that had with Fasciola-infested liver, which averaged to 0.99 kg/infected animal. At the time of this study (July 2016), one kilogram of liver on the local market cost 10,000 UGX or 2.7 USD on average at the time of this study; hence, the estimated monetary loss was 9900 UGX (2.67 USD)/infected animal (one UGX = 0.00027 USD; July 2016). The total estimated financial loss within the two weeks of the study period was 1.457 million UGX, equivalent to 396.41 USD, and the annual projected loss was 37.88 million UGX (10,306.66 USD). The minimum unit monetary loss per animal was 3000 UGX, while the maximum was 50,000 UGX per animal (Table S1).
4. Discussion
Fascioliasis is a serious infectious parasitic disease in domestic ruminant animals [3]. The prevalence and financial losses associated with liver condemnation due to fascioliasis was assessed at Lira Municipal abattoir in this study. The prevalence of fascioliasis was generally high; 65.7% of the total cattle carcasses examined were infested. This prevalence approximately agrees with findings from similar studies by Howell et al., [21], which reported a prevalence of 64.5% in a study performed on the slopes of Mount Elgon, Uganda; and with Jean-Richard et al. [22], which reported a prevalence of 68% in South Eastern Lake Chad. However, a much higher prevalence of 75% was reported by Ssimbwa et al., [23] in a study to determine the prevalence and financial losses associated with fascioliasis at Lyantonde town abattoir. A more recent study by Joan et al. [24] at Kampala City Abattoir, Central Uganda reported a prevalence of 84%. Despite several studies reporting high rates of prevalence, low prevalence was reported in several other studies as well. For example, [25] reported a low prevalence of 13.4% of Fasciola gigantica in Onitsha Nigeria.
The difference in these prevalence reports could be attributed to several factors, one of which could be the season of the study. Studies performed in rainy seasons generally reported high prevalence compared to those performed in dry seasons. This could be attributed to the fact that the snail, which serves as the intermediate host, abounds in rainy season [25,26]. Another factor could be type of sample examined, whether liver or feces. A study conducted by [11] reported that detection of fascioliasis through liver examination at PM is more sensitive than coprological assay. The sensitivity of the test used could also account for this difference—for example, Nguyen et al. [27] reported a higher prevalence with ELISA test compared to fecal and liver examination. In addition, there are management systems that expose cattle to eggs. For example, animals managed under intensive management system are less likely to be infected compared to those that are managed under an extensive system. On the other hand, higher prevalence is likely to be encountered in herds receiving poor veterinary services and/or irregular deworming practices.
This study also revealed that there was a significant association between body condition score and fascioliasis infestation. Animals with a BCS of 3 at time of slaughter were most affected by Fasciola spp. (69.33%). This result agrees with results obtained by Nyirenda et al. [28] that showed that the most prevalent liver fluke identified was Fasciola gigantica (56.1%) and it mostly affected animals with a poor body condition (71.4%). Many studies showed a positive association between fasciolosis and BCS [29,30,31,32].
Our results also showed that young cattle of 4–5 years old were highly infested with Fasciola spp. in comparison to cows ≥6 years. This in agreement with the previous study conducted in South Africa [33], with risk factors such as age (young: 18.2% and old: 14.1%) and sex (male: 29.1% and female: 3.2%). The results of the current study revealed that the infection rate was significantly higher in 4–5-year-old animals than in young animals. Cattle at this age frequently graze pastures and have longer exposure time, which may increase the likelihood of infection with Fasciola metacercariae [34]. Additionally, the low prevalence in older cattle (6–10 years) can be attributed to the high immunogenicity of the parasite, which aids in the stimulation of acquired immunity in older animals [35].
The sex of animals was not associated with the infestation rate. Similar to our results, Khan et al. (2009) found no sex-related differences in prevalence of fasciolosis [36]. However, the prevalence of fasciolosis in our study was higher in males than females. A study in Nigeria showed higher infection rates in males than females [37]. The higher prevalence in males could be attributed to several factors, including grazing disparity between both sexes, especially if the cow is pregnant, and the fact that females are mainly used for milk production and seldom raised for beef production [31,35,38]. This finding agrees with Magaji et al. [3], who reported that the disparity in susceptibility between sexes could be attributed to intrinsic factors such as genetics, physiology and immunology and extrinsic factors such as environment and management practices.
Furthermore, there was no significant association between cattle breed and infestation. However, the Small East African Zebu breed had a higher prevalence compared to the Ankole breed. This could be due to better management and husbandry practices such as zero grazing and more intensive veterinary care for the Ankole breed compared to the Zebu breed. In most cases, the Zebu is managed under extensive grazing systems which predispose them to water from swampy areas despite being presumed to be highly resistant to parasites and diseases.
Our study also revealed abattoir losses of 1,457,000 UGX within the study period of two weeks because of liver condemnation due to Fasciola spp. infestation, which is equivalent to 37,882,000 UGX after a year. This financial loss is less than the financial loss reported by Joan et al. [24], 231,186,550,000 UGX, in their study at Kampala City Abattoir, Central Uganda. This could be attributed to the fact that many more cattle are slaughtered per day in the Kampala abattoir compared to the Lira municipality abattoir, probably due to a lower population of meat consumers in Lira. This financial loss is also less than the economic loss of 1.5 million USD reported in Kenya [26]. This could be attributed to the fact that many abattoirs were sampled in Kenya while only one abattoir was sampled in this study.
These results highlight significant decreases in the household incomes of small-scale farmers, as reported elsewhere [39,40]. Therefore, effective control measures should be taken to minimize these losses through the control of the intermediate hosts. It is also important to educate the public about the significance of this zoonotic disease. Furthermore, meat inspection should be intensified in all abattoirs to monitor the prevalence of the disease and avoid humans ingesting the liver flukes in infected cattle livers.
One drawback of this study was the cross-sectional design, implemented at a single time point. Any projections of prevalence estimate for Fasciola infestation and associated financial losses could be affected by seasonal variations in infection rates. In addition, animal trade and movements are common within the study area, but we only recorded the last reported area of origin of the slaughter animals prior to transportation to the abattoir. The sample size calculated in this study was based on a prevalence of 84%, but our study estimated a prevalence of 65.7%.
5. Conclusions
Our study revealed that the prevalence of Fasciola spp. was generally high in Lira Municipal abattoir, Uganda. Fasciola spp. infestation was associated with significant financial losses for farmers in that area. Our study also revealed that there was a significant association between age of animal and body condition score and Fasciola spp. infestation in cattle. Continuous meat inspection should be performed since the prevalence was significantly high in the area to avoid human infection by liver flukes. Additional studies should be carried out in this area to assess the zoonotic risk and human infestation with fasciolosis.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2615/11/3/681/s1, Table S1: The financial losses associated with liver condemnation from 142 cows due to fascioliasis in cattle slaughtered at Lira municipality abattoir in Northern Uganda over 14 days.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.O. and L.G.O.; methodology, L.G.O.; data analysis, E.M.A. and L.G.O.; data interpretation, E.M.A., E.O., L.G.O. and S.O.; original draft preparation, L.G.O. and J.T.; review and editing, S.O., E.M.A., J.T. and E.O.; supervision, E.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Special Research Project Grant for undergraduate students at Makerere University, Uganda. The APC was funded by UC Davis Open Access Fund and Specialist Support Fund.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, due to study focus on post-slaughter samples. Animal contact during antemortem examination was minimal, consistent with routine physical examination procedure, and conducted under supervision of licensed veterinarian.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Lira District Veterinary Officers and the Lira Municipal abattoir staff for assistance during sample collection.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rana, M.A.A.; Roohi, N.; Khan, M.A. Fascioliasis in cattle—A review. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2014, 24, 668–675. [Google Scholar]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Bargues, M.D.; Valero, M.A. Fascioliasis and other plant-borne trematode zoonoses. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 1255–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaji, A.A.; Ibrahim, K.; Salihu, M.D.; Saulawa, M.A.; Mohammed, A.A.; Musawa, A.I. Prevalence of Fascioliasis in Cattle Slaughtered in Sokoto Metropolitan Abattoir, Sokoto, Nigeria. Adv. Epidemiol. 2014, 2014, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Tahawy, A.S.; Bazh, E.K.; Khalafalla, R.E. Epidemiology of bovine fascioliasis in the Nile Delta region of Egypt: Its prevalence, evaluation of risk factors, and its economic significance. Vet. World 2017, 10, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, A.; Frankena, K.; Bødker, R.; Toft, N.; Thamsborg, S.M.; Enemark, H.L.; Halasa, T. Prevalence, risk factors and spatial analysis of liver fluke infections in Danish cattle herds. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaja, I.F.; Mushonga, B.; Green, E.; Muchenje, V. Seasonal prevalence, body condition score and risk factors of bovine fasciolosis in South Africa. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2017, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getahun, A.; Aynalem, Y.; Haile, A. Prevalence of Bovine fasciolosis infectionin Hossana municipal abattoir, Southern Ethiopia. J. Nat. Sci. Res. 2017. Available online: www.iiste.org (accessed on 22 February 2021).
- Onyeabor, A.; Wosu, M. Prevalence of Bovine Fasciolosis Observed in Three Major Abattoirs in Abia State Nigeria. J. Vet. Adv. 2014, 4, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardo, M.; Aliyara, Y.; Lawal, H. Prevalence of Bovine Fasciolosis in major Abattiors of Adamawa State, Nigeria. Bayero J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2013, 6, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio Silva, M.L.; Correia Da Costa, J.M.; Viana Da Costa, A.M.; Pires, M.A.; Lopes, S.A.; Castro, A.M.; Monjour, L. Antigenic components of excretory-secretory products of adult Fasciola hepatica recognized in human infections. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1996, 54, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odigie, B.E.; Odigie, J.O. Fascioliasis in Cattle: A Survey of Abattoirs in Egor, Ikpoba- Okha and Oredo Local Government Areas of Edo State, Using Histochemical Techniques. Int. J. Basic Appl. Innov. Res. 2013, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Bargues, M.D. Human Liver Flukes: A Review. Res. Rev. Parasitol. 1997, 57, 145–218. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, J.G.; Gonzalez, C.; Curtale, F.; Muñoz-Antoli, C.; Valero, M.A.; Bargues, M.D.; El Sayed, M.; El Wakeel, A.A.E.W.; Abdel-Wahab, Y.; Montresor, A.; et al. Hyperendemic fascioliasis associated with schistosomiasis in villages in the Nile Delta of Egypt. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003, 69, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawa, M. Control of Foodborne Trematode Infections. WHO Technical Report Series 849. 157 Seiten, 4 Tabellen. World Health Organization, Geneva 1995. Preis: 26—Sw.fr. Food/Nahrung 1996, 40, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spithill, T.W.; Smooker, P.M.; Copeman, D.B. Fasciola Gigantica: Epidemiology, Control, Immunology, and Molecular Biology; Dalton, F.J.P., Ed.; Commonwealth Agriculture Bureau International Publishing: New York, UK; Wallingford, UK, 1999; pp. 465–525. [Google Scholar]
- Chick, B.F.; Blumer, C.; Veterinary, D.; Mailbag, P. Economic significance of Fasciola hepatica infestation of beef cattle—A definition study based on field trial and grazier questionnaire. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Veterinary Epidemiology and Economics, Canberra, Australia, 7–11 May 1979; pp. 377–382. [Google Scholar]
- Food Safety Inspection Service. Using Dentition to Age Cattle; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. Available online: https://www.fsis.usda.gov/OFO/TSC/bse_information.htm (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Wildman, E.E.; Jones, G.M.; Wagner, P.E.; Boman, R.L.; Troutt, H.F.; Lesch, T.N. A Dairy Cow Body Condition Scoring System and Its Relationship to Selected Production Characteristics. J. Dairy Sci. 1982, 65, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herenda, D.; Chambers, P.G.; Ettriqui, A.; Seneviratnap, P.; DaSilvat, T.J.P. Manual on Meat Inspection for Developing Countries; FAO Animal Production and Health Paper 119; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Cochran, W.G. Sampling Techniques, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, A.; Mugisha, L.; Davies, J.; Lacourse, E.J.; Claridge, J.; Williams, D.J.; Kelly-Hope, L.; Betson, M.; Kabatereine, N.B.; Stothard, J.R. Bovine fasciolosis at increasing altitudes: Parasitological and malacological sampling on the slopes of Mount Elgon, Uganda. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean-Richard, V.; Crump, L.; Abicho, A.A.; Naré, N.B.; Greter, H.; Hattendorf, J.; Schelling, E.; Zinsstag, J. Prevalence of Fasciola gigantica infection in slaughtered animals in south-eastern Lake Chad area in relation to husbandry practices and seasonal water levels. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ssimbwa, G.; Baluka, S.A.; Ocaido, M. Prevalence and financial losses associated with bovine fasciolosis at Lyantonde Town. Livest. Res. Rural Dev. 2014, 26, 165. Available online: http://www.lrrd.org/lrrd26/9/ssim26165.html (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Joan, N.; Stephen, M.; Bashir, M.; Kiguli, J.; Orikiriza, P.; Bazira, J.; Itabangi, H.; Stanley, I. Prevalence and Economic Impact of Bovine Fasciolosis at Kampala City Abattoir, Central Uganda. Br. Microbiol. Res. J. 2015, 7, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekwunife, C.A.; Eneanya, C.I. Fasciola gigantica in Onitsha and environs. Anim. Res. Int. 2008, 3, 448–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kithuka, J.M.; Maingi, N.; Njeruh1, F.M.; Ombui1, J.N. The Prevalence and Economic Importance of Bovine Fasciolosis in Kenya—An Analysis of Abattoir Data. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2002, 69, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, S.T.; Nguyen, D.T.; van Nguyen, T.; Huynh, V.V.; Le, D.Q.; Fukuda, Y.; Nakai, Y. Prevalence of Fasciola in cattle and of its intermediate host Lymnaea snails in central Vietnam. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2012, 44, 1847–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyirenda, S.S.; Sakala, M.; Moonde, L.; Kayesa, E.; Fandamu, P.; Banda, F.; Sinkala, Y. Prevalence of bovine fascioliasis and economic impact associated with liver condemnation in abattoirs in Mongu district of Zambia. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abunna, F.; Asfaw, L.; Megersa, B.; Regassa, A. Bovine fasciolosis: Coprological, abattoir survey and its economic impact due to liver condemnation at Soddo municipal abattoir, Southern Ethiopia. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2010, 42, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragaw, K.; Negus, Y.; Denbarga, Y.; Sheferaw, D. Fasciolosis in slaughtered cattle in Addis Ababa abattoir, Ethiopia. Glob. Vet. 2012, 8, 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Dawa, D.; Abattoir, M.; Mebrahtu, G.; Beka, K. Prevalence and economic significance of fasciolosis in cattle slaughtered at Dire Dawa Municipal Abattoir, Ethiopia. J. Vet. Adv. 2013, 3, 319–324. [Google Scholar]
- Demssie, A.; Birku, F.; Biadglign, A. An Abattoir survey on the prevalence and monetary loss of fasciolosis in cattle in Jimma Town, Ethiopia. Glob. Vet. 2012, 8, 381–385. [Google Scholar]
- Jaja, I.F.; Mushonga, B.; Green, E.; Muchenje, V. A quantitative assessment of causes of bovine liver condemnation and its implication for food security in the Eastern Cape province South Africa. Sustainability 2017, 9, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Andrade, R.; Paz-Silva, A.; Suárez, J.L.; Panadero, R.; Pedreira, J.; López, C. Influence of age and breed on natural bovine fasciolosis in an endemic area (Galicia, NW Spain). Vet. Res. Commun. 2002, 26, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.N.; Sajid, M.S.; Khan, M.K.; Iqbal, Z.; Hussain, A. Gastrointestinal helminthiasis: Prevalence and associated determinants in domestic ruminants of district Toba Tek Singh, Punjab, Pakistan. Parasitol. Res. 2010, 107, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.K.; Sajid, M.S.; Khan, M.N.; Iqbal, Z.; Iqbal, M.U. Bovine fasciolosis: Prevalence, effects of treatment on productivity and cost benefit analysis in five districts of Punjab, Pakistan. Res. Vet. Sci. 2009, 87, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyaji, F.O.; Yaro, C.A.; Peter, M.F.; Abutu, A.E.O. Fasciola hepatica and Associated Parasite, Dicrocoelium dendriticum in Slaughterhouses in Anyigba, Kogi State, Nigeria. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zeleke, G.; Menkir, S.; Desta, M. Original article Prevalence of ovine fasciolosis and its economic significance in Basona worana district, central Ethiopia. Sci. J. Zool. 2013, 2, 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Simwanza, C.; Mumba, C.; Pandey, G.S.; Samui, K.L. Financial Losses Arising from Condemnation of Liver Due to Financial Losses Arising from Condemnation of Liver Due to Fasciolosis in Cattle from the Western Province of Zambia. Int. J. Livest. Res. 2012, 2, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmood, K.; Zhang, H.; Sabir, A.J.; Abbas, R.Z.; Ijaz, M.; Durrani, A.Z.; Saleem, M.H.; Ur Rehman, M.; Iqbal, M.K.; Wang, Y.; et al. A review on epidemiology, global prevalence, and economical losses of fasciolosis in ruminants. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 109, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).