Riverbed Substrate Requirements for Natural Reproduction of Gymnocypris przewalskii
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Experimental Fish
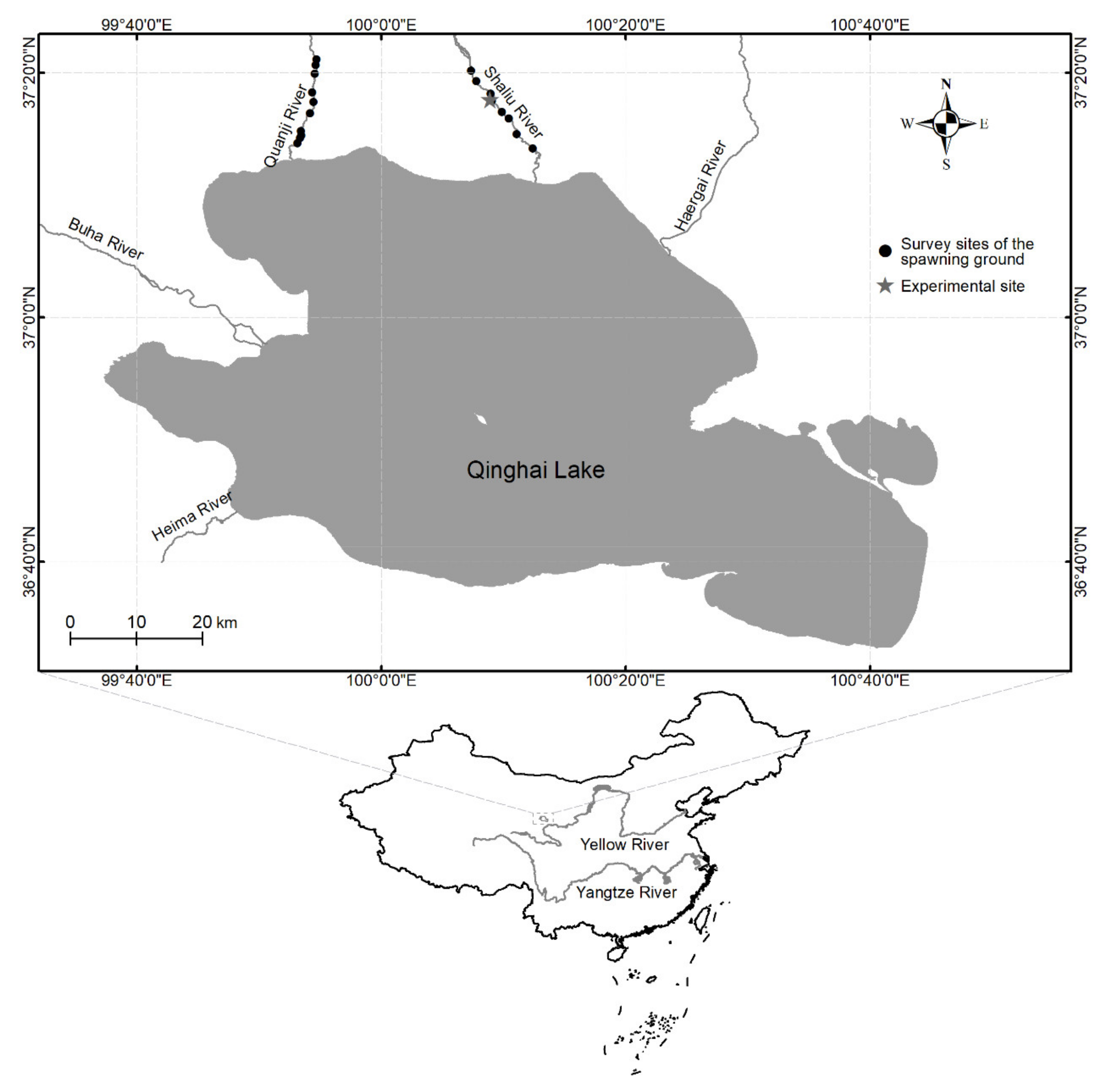
2.2. In Situ Observation of Natural Spawning Ground
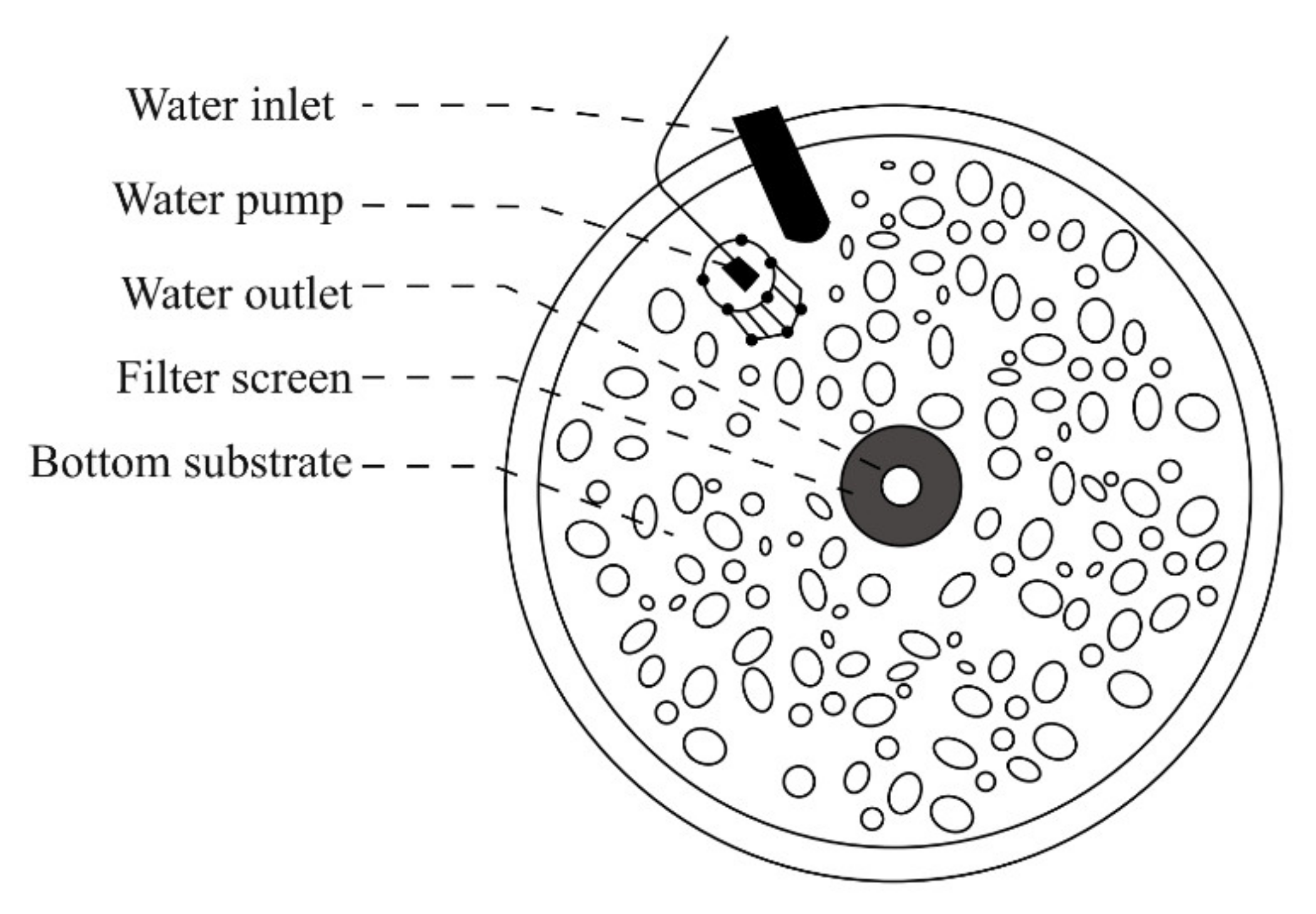
2.3. Riverbed Substrate Reference Experiment
2.4. Riverbed Substrate Inducement Experiment
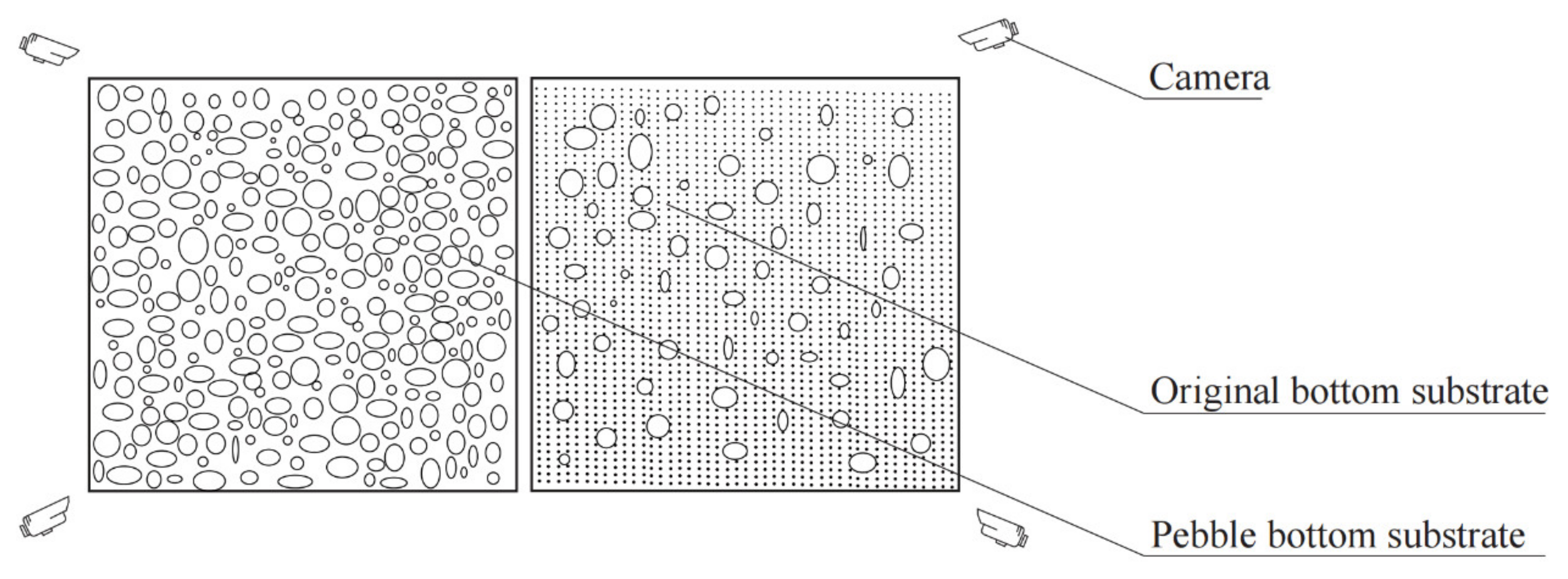
2.5. Field Riverbed Substrate Transformation Experiment
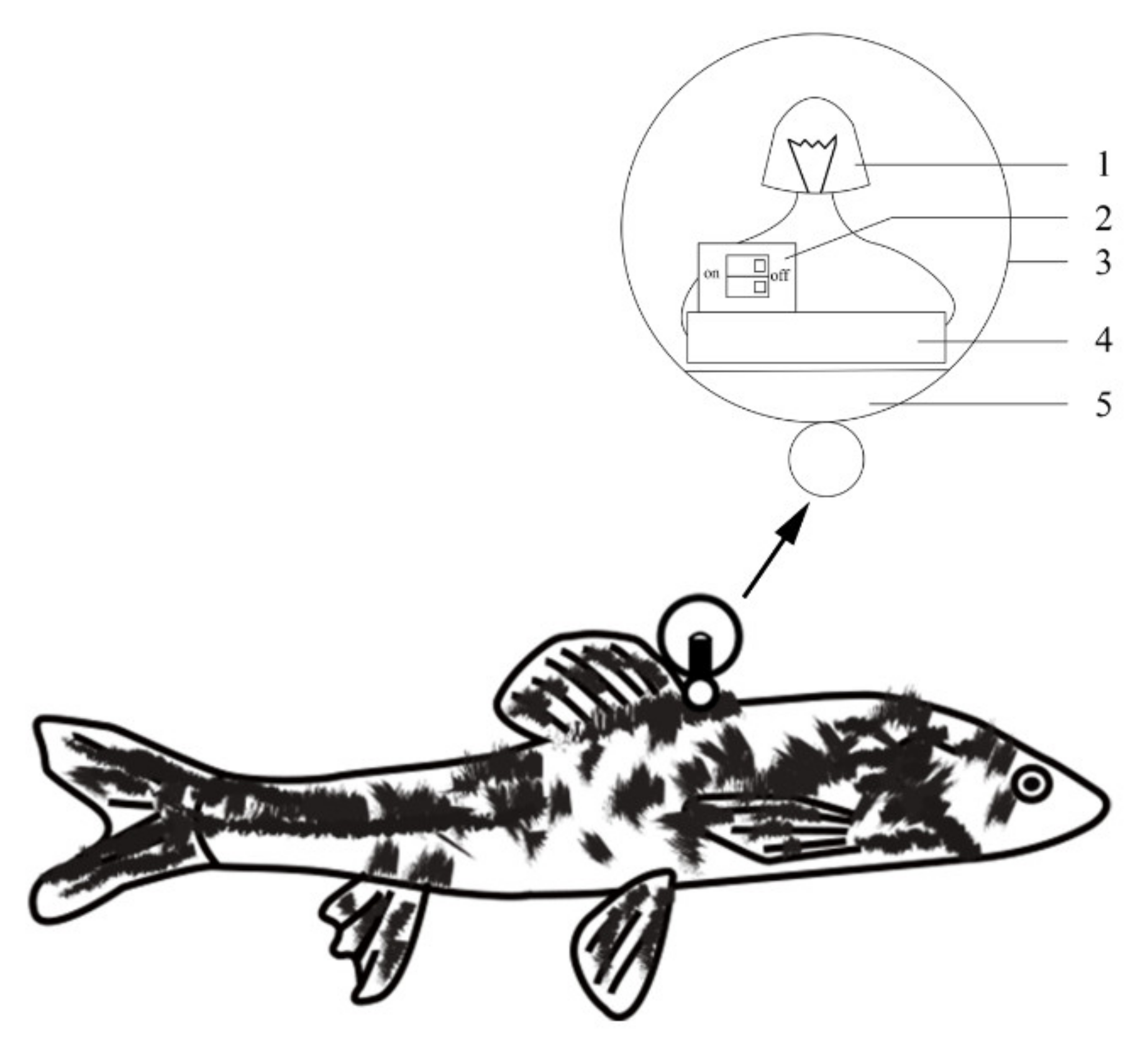
2.6. Parental Fish Marking and Videography
2.7. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
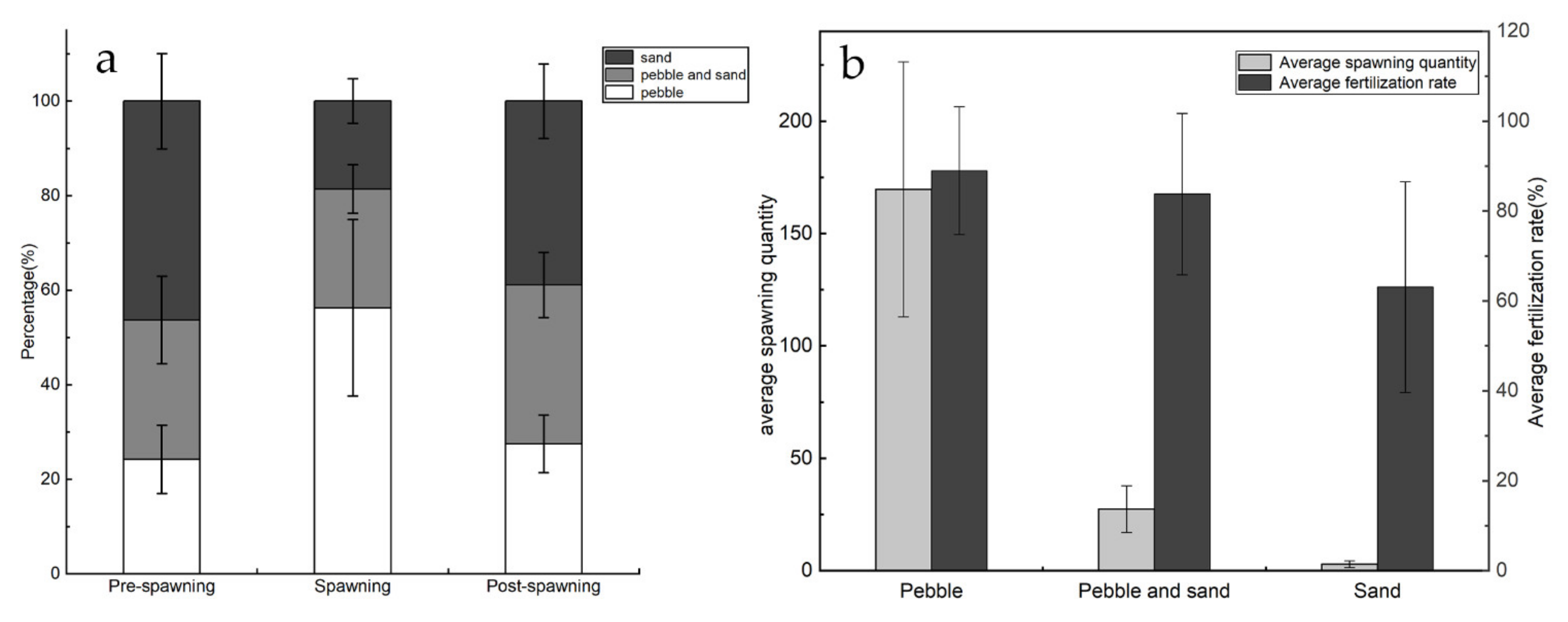
3.1. Habitat Preferences of Parent Fish Regarding Riverbed Substrate
3.2. Effectiveness of Reproduction Induced by Addition of Pebble
3.3. Effectiveness of Reproduction from Transformation of Natural Spawning Ground
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McDonald, R.; Nelson, J.; Asce, M.; Paragamian, V.; Barton, G. Modeling the Effect of Flow and Sediment Transport on White Sturgeon Spawning Habitat in the Kootenai River, Idaho. J. Hydraul. Eng.-ASCE 2010, 136, 1077–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galhardo, L.; Almeida, O.; Oliveira, R.F. Preference for the presence of substrate in male cichlid fish: Effects of social dominance and context. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2009, 120, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.D.; Harris, B.A.; Collums, J.R.; Bonett, R.M. Life between predators and a small space: Substrate selection of an interstitial space-dwelling stream salamander. J. Zool. 2012, 287, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Shibuno, T.; Lecchini, D.; Watanabe, Y. Habitat selection by emperor fish larvae. Aquat. Biol. 2009, 6, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snickars, M.; Sundblad, G.; Sandström, A.; Ljunggren, L.; Bergström, U.; Johansson, G.; Mattila, J. Habitat selectivity of substrate-spawning fish: Modeling requirements for the Eurasian perch Perca fluviatilis. Mar. Ecol.-Prog. Ser. 2010, 398, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kynard, B.; Horgan, M.; Kieffer, M.; Seibel, D. Habitats Used by Shortnose Sturgeon in Two Massachusetts Rivers, with Notes on Estuarine Atlantic Sturgeon: A Hierarchical Approach. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2000, 129, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulsby, C.; Youngson, A.F.; Moir, H.J.; Malcolm, I.A. Fine sediment influence on salmonid spawning habitat in a lowland agricultural stream: A preliminary assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 265, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennion, D.H.; Manny, B.A. A model to locate potential areas for lake sturgeon spawning habitat construction in the St. Clair–Detroit River System. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secor, D.H.; Arefjev, V.; Nikolaev, A.; Sharov, A. Restoration of sturgeons: Lessons from the Caspian Sea Sturgeon Ranching Programme. Fish Fish. 2000, 1, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, K.F.; Dunn, I.G.; Edwards, D.; Petr, T.; Yang, H.Z. A fishery in a changing lake environment: The naked carp Gymnocypris przewalskii (Kessler) (Cyprinidae: Schizothoracinae) in Qinghai Hu, China. Int. J. Salt Lake Res. 1995, 4, 169–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidlauskas, B.; Chakrabarty, P. The Diversity of Fishes: Biology, Evolution and Ecology. Copeia 2010, 2010, 527–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.B.; Chen, X.Q.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.C.; Wang, Y.X.; Chang, J.P.; Du, J.Z. Growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor of naked carp (Gymnocypris przewalskii) in Lake Qinghai: Expression in different water environments. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2009, 161, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Zhang, C.; Shi, J.; Qi, H.; Zhang, R.; Tang, Y.; Li, G.; Feng, C.; Zhao, K. Characterization of two paralogous myostatin genes and evidence for positive selection in Tibet fish: Gymnocypris przewalskii. Gene 2015, 565, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.Q.; Xiong, F.; Shi, J.Q.; Qi, H.F. The Protection Research of Gymnocypris Przewalskii; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2011; Volume 132. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Riley, S.C.; Marsden, J.E.; Ridgway, M.S.; Konrad, C.P.; Farha, S.A.; Binder, T.R.; Middel, T.A.; Esselman, P.C.; Krueger, C.C. A conceptual framework for the identification and characterization of lacustrine spawning habitats for native lake charr Salvelinus namaycush. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2019, 102, 1533–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibodeaux, L.J.; Boyle, J.D. Bedform-generated convective transport in bottom sediment. Nature 1987, 325, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, X.; Du, Y.; Liu, H.Z.; Ling, F. Applying instream flow incremental method for the spawning habitat protection of Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis). River Res. Appl. 2011, 27, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutant, C.C. A Riparian Habitat Hypothesis for Successful Reproduction of White Sturgeon. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2004, 12, 23–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, P.; D’Amours, J.; Thibodeau, S.; Dubuc, N.; Verdon, R.; Garceau, S.; Bilodeau, P.; Mailhot, Y.; Fortin, R. Effects of the development of a newly created spawning ground in the Des Prairies River (Quebec, Canada) on the reproductive success of lake sturgeon (Acipenser fulvescens). J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2011, 27, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.G.; Otake, S.; Lee, M.O. Estimating the effective wake region (current shadow) of artificial reefs. In Artificial Reefs in Fisheries Management; Bortone, S.A., Brandini, F.P., Fabi, G., Otake, S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 279–295. [Google Scholar]
- Buffington, J.M.; Tonina, D. Hyporheic Exchange in Mountain Rivers II: Effects of Channel Morphology on Mechanics, Scales, and Rates of Exchange. Geogr. Compass. 2009, 3, 1038–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, J.M.; Keller, W. Spawning Site Water Chemistry and Lake Trout (Salvelinus namaycush) Sac Fry Survival during Spring Snowmelt. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1984, 41, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sly, P.G. Interstitial Water Quality of Lake Trout Spawning Habitat. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 1988, 14, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, G.; Brown, R.S.; Imhof, J.G. Groundwater and fish—insights from northern North America. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, H.; Schmid, C. Is hatchery stocking a help or harm? Evidence, limitations and future directions in ecological and genetic surveys. Aquaculture. 2010, 308, S2–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsson, J.I.; Brockmark, S.; Näslund, J. Environmental effects on behavioural development consequences for fitness of captive-reared fishes in the wild. J. Fish. Biol. 2014, 85, 1946–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thériault, V.; Moyer, G.R.; Jackson, L.S.; Blouin, M.S.; Banks, M.A. Reduced reproductive success of hatchery coho salmon in the wild: Insights into most likely mechanisms. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 1860–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, H.; Ardren, W.R.; Olsen, E.; Cooper, B.; Blouin, M.S. Reproductive Success of Captive-Bred Steelhead Trout in the Wild: Evaluation of Three Hatchery Programs in the Hood River. Conserv. Biol. 2007, 21, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.; Day, R.L. The future of stock enhancements: Lessons for hatchery practice from conservation biology. Fish Fish. 2002, 3, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chebanov, M.S.; Galich, E.V.; Chmir, Y.N. Stock enhancement and conservation culture of sturgeons: Problems and prospects. J. Fish. Biol. 2004, 65, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milot, E.; Perrier, C.; Papillon, L.; Dodson, J.J.; Bernatchez, L. Reduced fitness of Atlantic salmon released in the wild after one generation of captive breeding. Evol. Appl. 2013, 6, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Näslund, J.; Johnsson, J.I. Environmental enrichment for fish in captive environments: Effects of physical structures and substrate. Fish Fish. 2016, 17, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Experiment | Number (Ind.) | Sex | Total Length (mm) | Body Length (mm) | Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Riverbed substrate preference experiments | 18 | F | 234.5 ± 57.5 | 203.5 ± 52.5 | 103.9 ± 65.1 |
| 18 | M | 220.5 ± 45.5 | 181.5 ± 30.5 | 68.6 ± 34.5 | |
| Riverbed substrate inducement experiments | 36 | F | 213.5 ± 53.5 | 198.5 ± 34.5 | 105.9 ± 63.2 |
| 36 | M | 195.5 ± 49.5 | 187.5 ± 36.5 | 68.4 ± 34.3 | |
| Total | 54 | F | 226.0 ± 66.0 | 210.0 ± 46.0 | 103.9 ± 65.1 |
| 54 | M | 205.5 ± 60.5 | 187.5 ± 36.5 | 68.4 ± 34.3 |
| Environmental Factor | Value |
|---|---|
| Velocity | 0.2 ± 0.08 m/s |
| Photoperiod | 14:10 (day and light in 24 h) |
| Water depth | 0.2 m |
| Water temperature | 10.3–13 ℃ |
| Ratio of pebble to sand | 7:3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Qi, H.; Yang, H.; Ban, X.; Yang, J.; Du, H. Riverbed Substrate Requirements for Natural Reproduction of Gymnocypris przewalskii. Animals 2021, 11, 3246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113246
Zhou Y, Li J, Qi H, Yang H, Ban X, Yang J, Du H. Riverbed Substrate Requirements for Natural Reproduction of Gymnocypris przewalskii. Animals. 2021; 11(11):3246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113246
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yanghao, Junyi Li, Hongfang Qi, Haile Yang, Xuan Ban, Jianxin Yang, and Hao Du. 2021. "Riverbed Substrate Requirements for Natural Reproduction of Gymnocypris przewalskii" Animals 11, no. 11: 3246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113246
APA StyleZhou, Y., Li, J., Qi, H., Yang, H., Ban, X., Yang, J., & Du, H. (2021). Riverbed Substrate Requirements for Natural Reproduction of Gymnocypris przewalskii. Animals, 11(11), 3246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113246







