Sex Differences in Mouse Exploratory Behaviour to Fel d 1, a Cat ABP-Like Protein
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
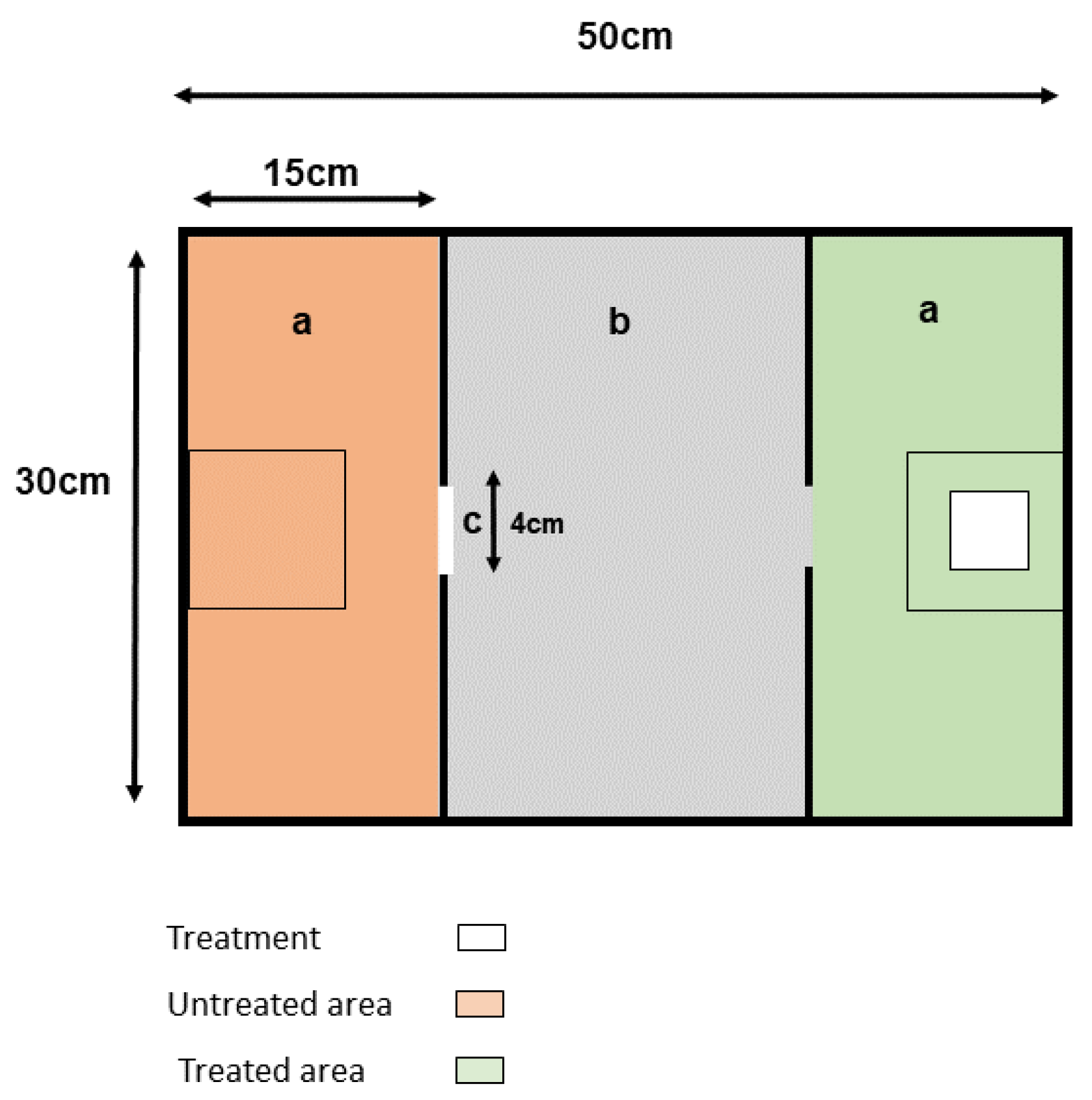
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Treatments and Treatment Application
2.3.1. Blank
2.3.2. Fel d 1 Protein
2.3.3. 2,5-Dihydro-2,4,5-Trimethylthiazoline (TMT)
2.4. Behavioural Test
2.5. Measurements and Video Analysis
2.6. Statistical Tests
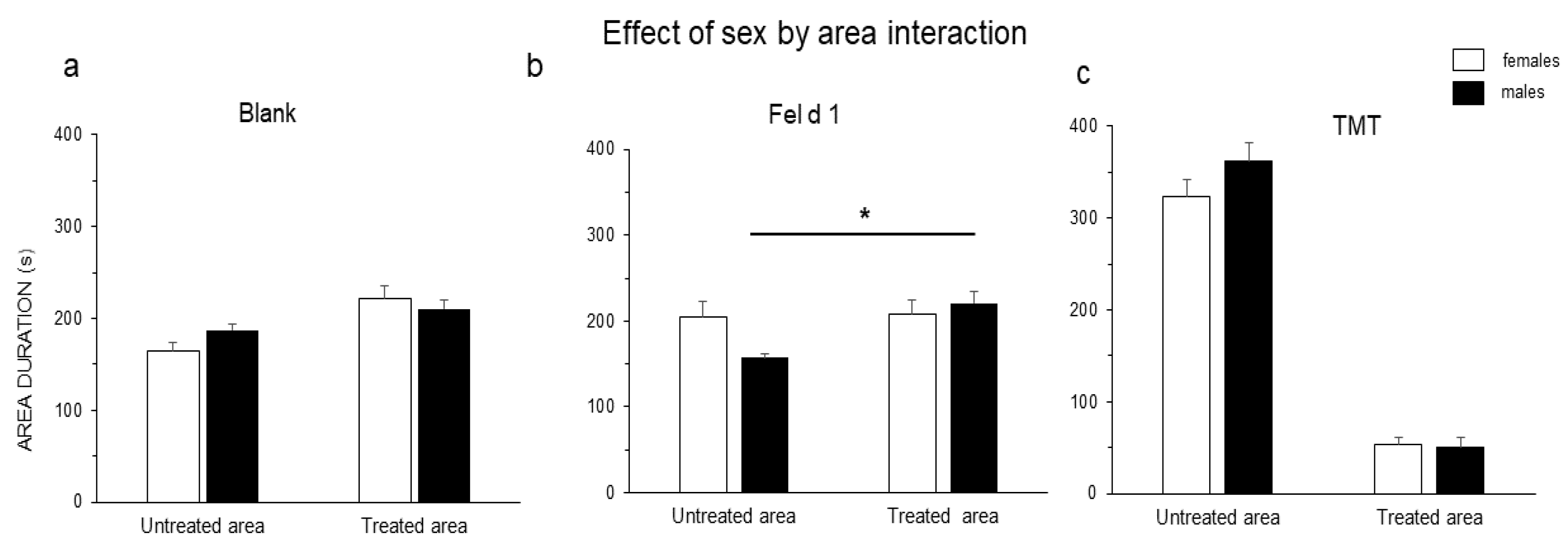
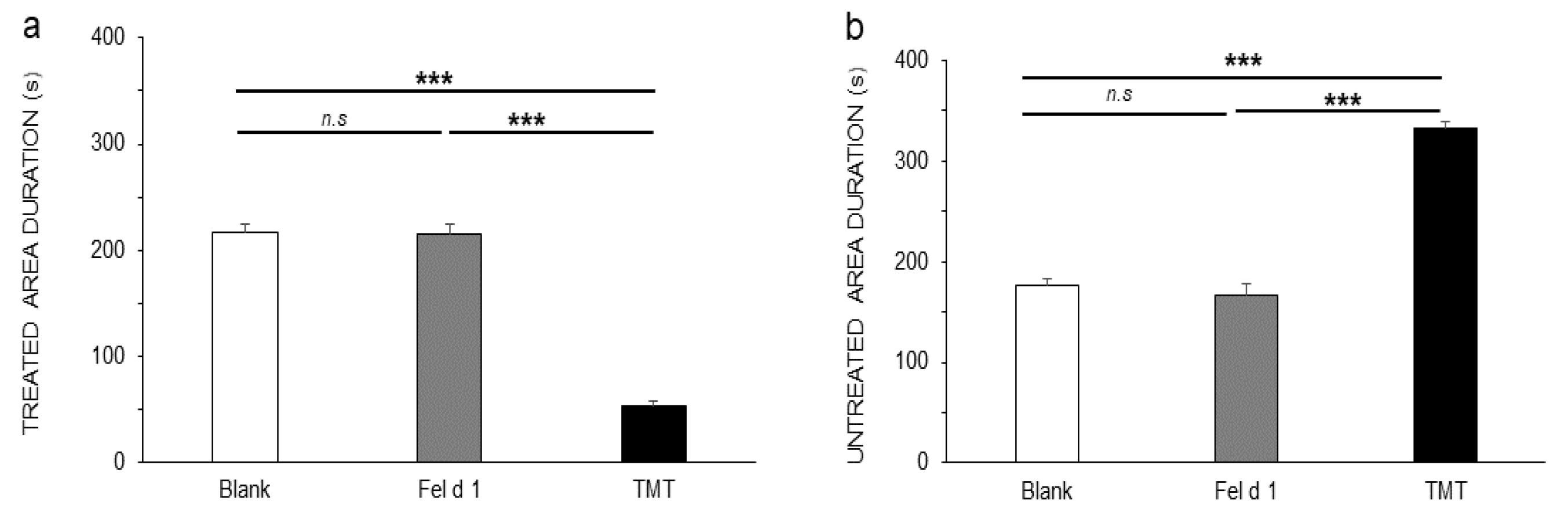
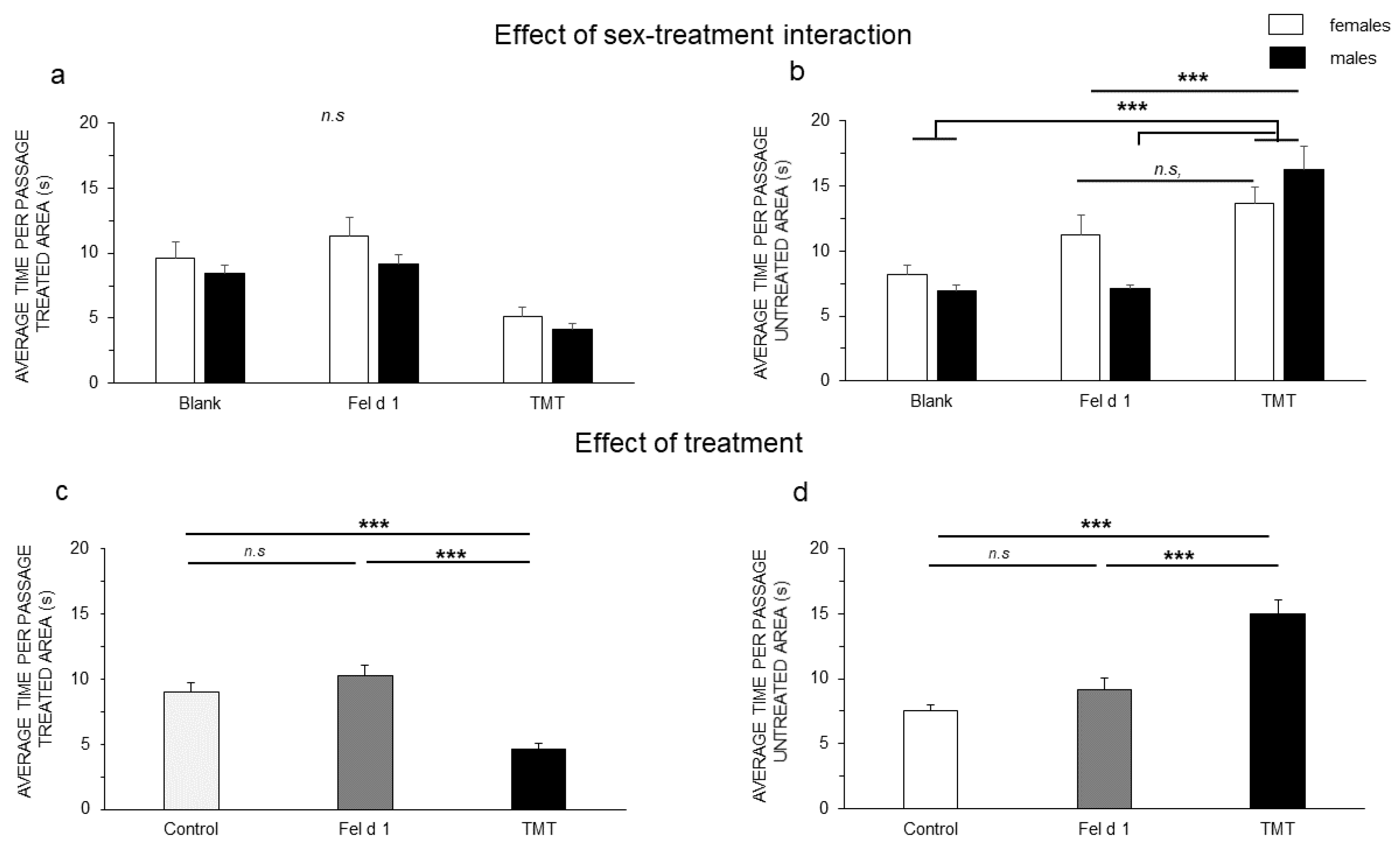
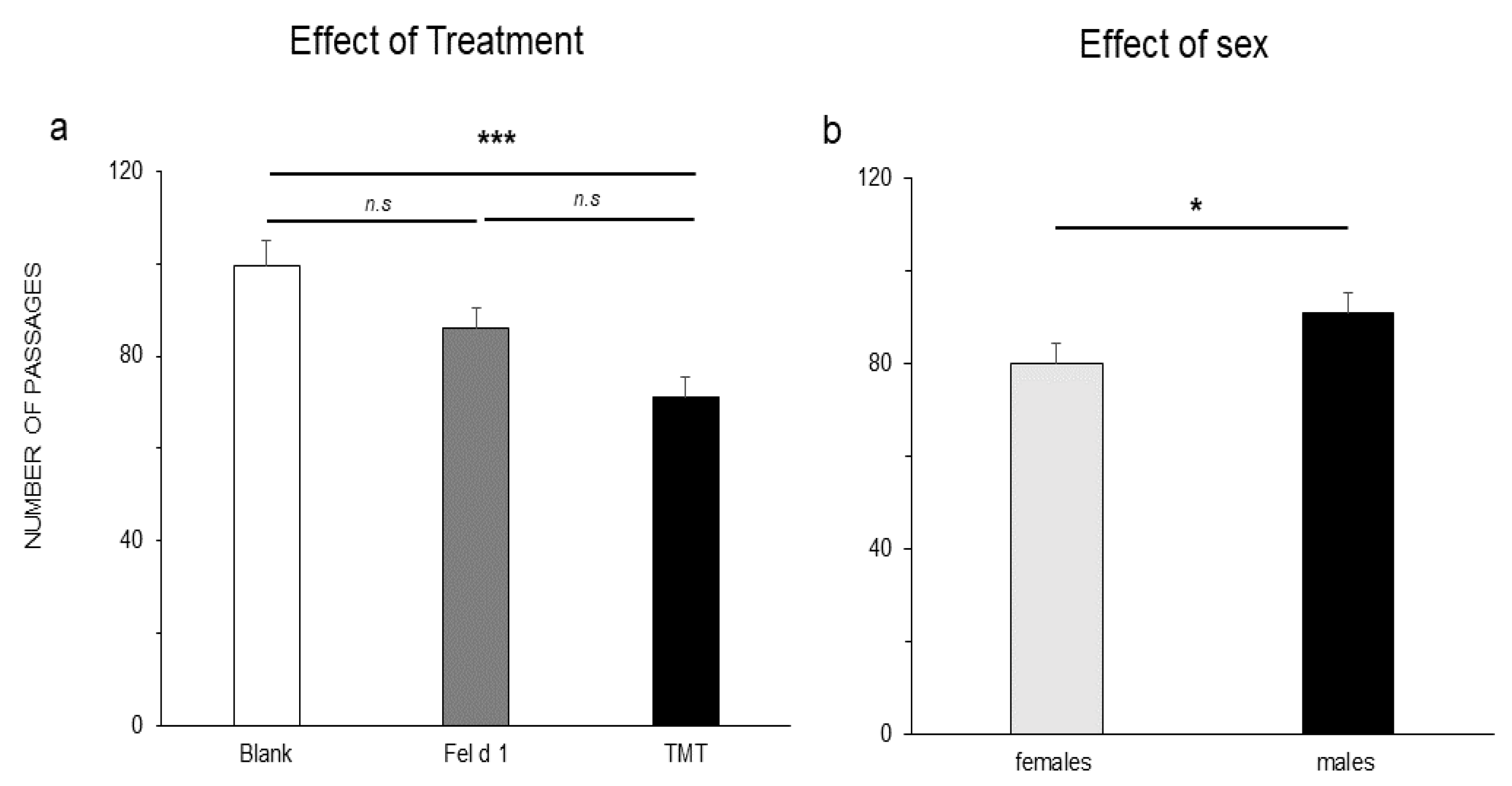
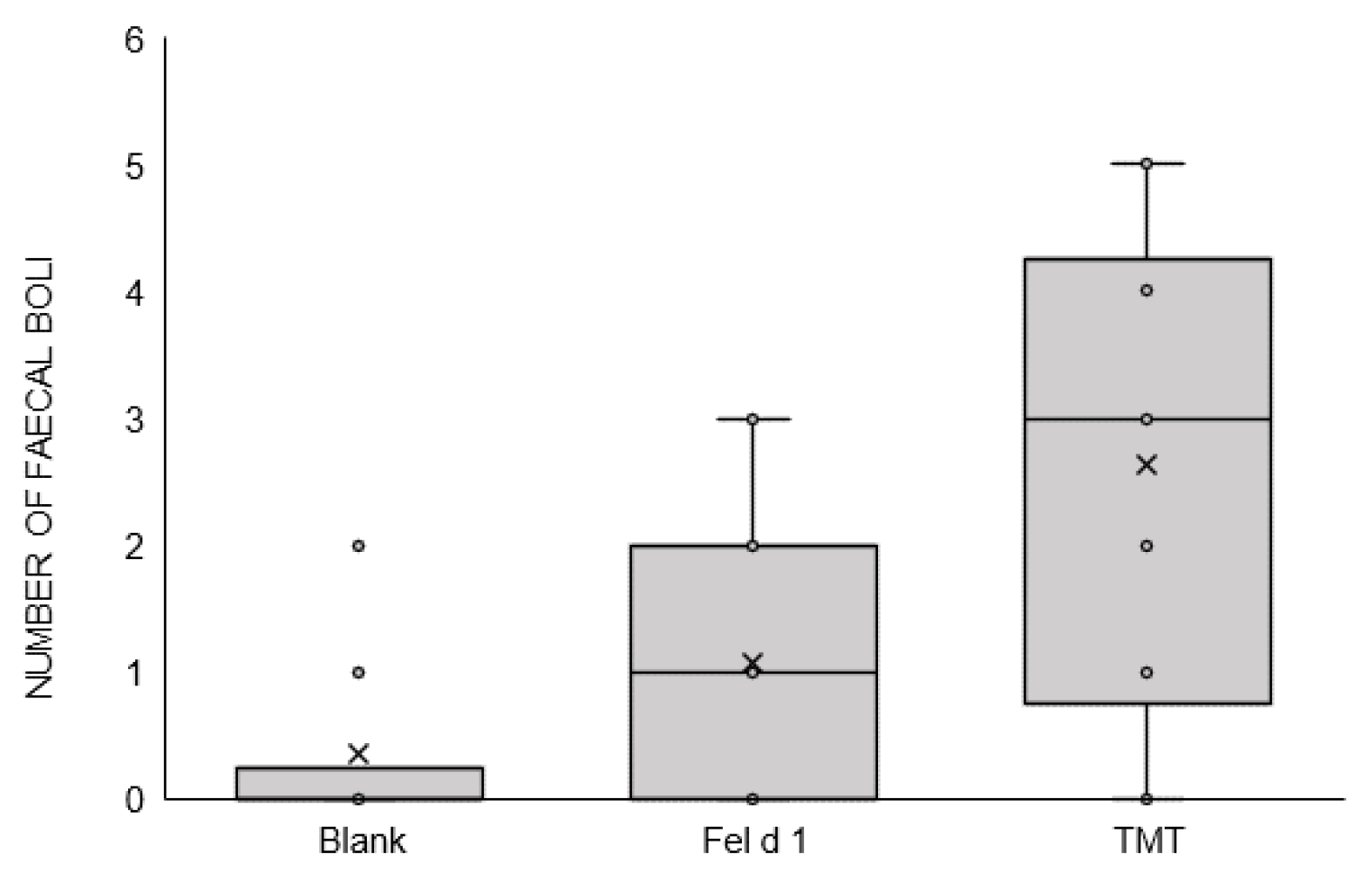
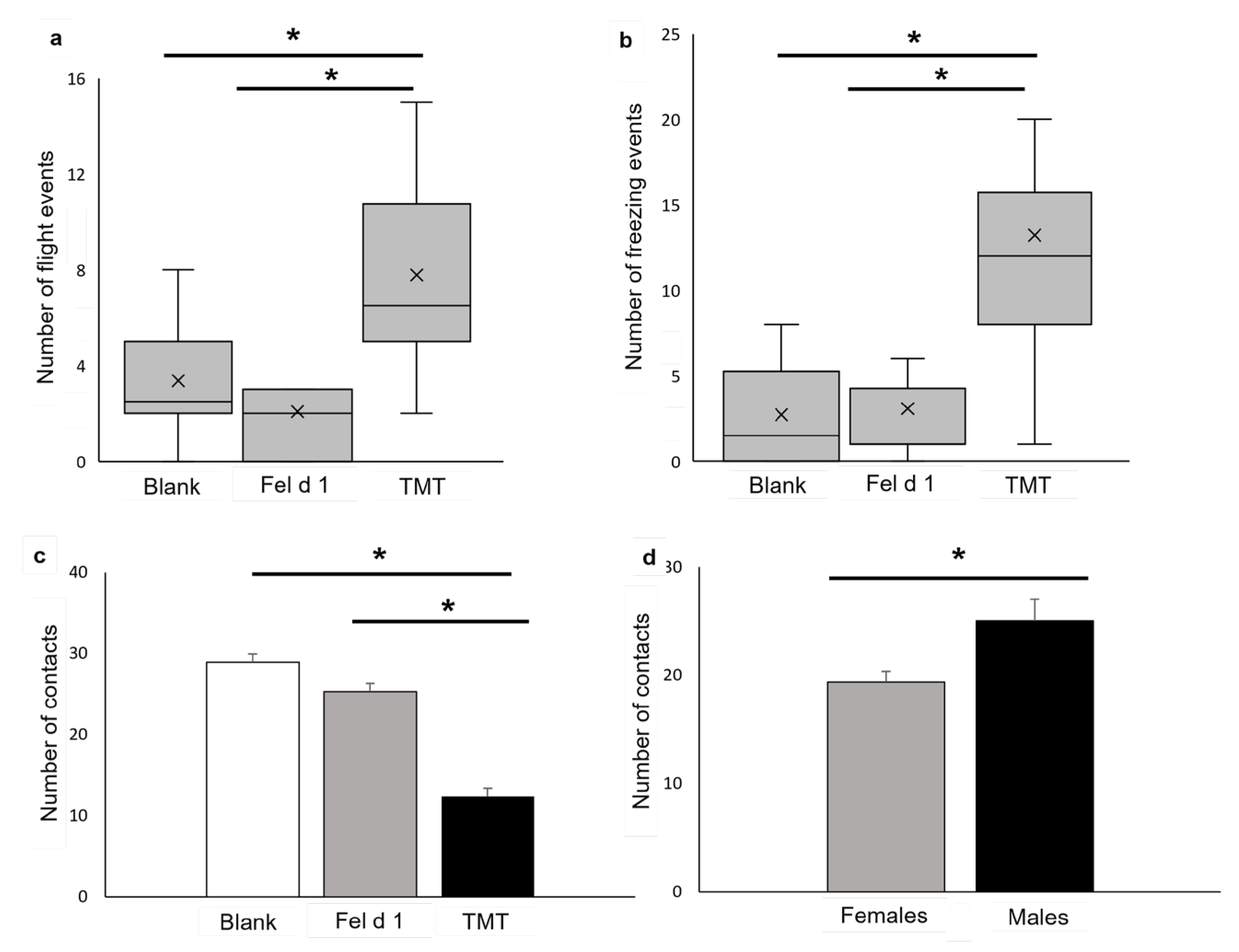
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dietl, G.; Kelley, P. The fossil record of predator-prey arms races: Coevolution and escalation hypotheses. Paleontol. Soc. Pap. 2002, 8, 353–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alberti, M.; Correa, C.; Marzluff, J.M.; Hendry, A.P.; Palkovacs, E.P.; Gotanda, K.M. Global urban signatures of phenotypic change in animal and plant populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 8951–8956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bull, J.W.; Maron, M. How humans drive speciation as well as extinction. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20160600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, M.T.J.; Munshi-South, J. Evolution of life in urban environments. Science 2017, 358, eaam8327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, H.; Lill, A.; Wong, B.B.M. Behavioural responses of wildlife to urban environments. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2013, 88, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loss, S.R.; Will, T.; Marra, P.P. The impact of free-ranging domestic cats on wildlife of the United States. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wyatt, T.D. Pheromones and Animal Behavior: Chemical Signals and Signatures, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; ISBN 0521112907. [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt, T.D. Proteins and peptides as pheromone signals and chemical signatures. Anim. Behav. 2014, 97, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, B.; Messaoudi, K.; Jacomet, F.; Michaud, E.; Fauquert, J.L.; Caillaud, D.; Evrard, B. An update on molecular cat allergens: Fel d 1 and what else? Chapter 1: Fel d 1, the major cat allergen. Allergy, Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klug, J.; Beier, H.M.; Bernard, A.; Chilton, B.S.; Fleming, T.P.; Leherer, R.I.; Miele, L.; Pattabiraman, N.; Singh, G. Uteroglobin/Clara Cell 10-kDa Family of Proteins: Nomenclature Committee Report. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 923, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabrowski, A.J.; van der Brempt, X.; Soler, M.; Seguret, N.; Lucciani, P.; Charpin, D. Cat skin as an important source of Fel d I allergen. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1990, 86, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carayol, N.; Birnbaum, J.; Magnan, A.; Ramadour, M.; Lanteaume, A.; Vervloet, D.; Tessier, Y.; Pageat, P. Fel d 1 production in the cat skin varies according to anatomical sites. Allergy 2000, 55, 570–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apfelbach, R.; Blanchard, D.C.; Blanchard, R.J.; Hayes, R.A.; McGregor, I.S. The effects of predator odors in mammalian prey species: A review of field and laboratory studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2005, 29, 1123–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, D.C.; Griebel, G.; Blanchard, R.J. Mouse defensive behaviors: Pharmacological and behavioral assays for anxiety and panic. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2001, 25, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papes, F.; Logan, D.W.; Stowers, L. The Vomeronasal Organ Mediates Interspecies Defensive Behaviors through Detection of Protein Pheromone Homologs. Cell 2010, 141, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, A.G.; Belone, P.M.; Bímová, B.V.; Karn, R.C.; Laukaitis, C.M. Studies of an androgen-binding protein knockout corroborate a role for salivary ABP in mouse communication. Genetics 2017, 205, 1517–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durairaj, R.; Pageat, P.; Bienboire-Frosini, C. Another cat and mouse game: Deciphering the evolution of the SCGB superfamily and exploring the molecular similarity of major cat allergen Fel d 1 and mouse ABP using computational approaches. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karn, R.C.; Laukaitis, C.M. Characterization of two forms of mouse salivary androgen-binding protein (ABP): Implications for evolutionary relationships and ligand-binding function. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 7162–7170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.D.; Bowen, M.T.; McGregor, I.S.; Timberlake, W. Rubbings deposited by cats elicit defensive behavior in rats. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 107, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, H.N. Methods of scent marking in the domestic cat. Can. J. Zool. 1994, 72, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chew, G.L.; Higgins, K.M.; Gold, D.R.; Muilenberg, M.L.; Burge, H.A. Monthly measurements of indoor allergens and the influence of housing type in a northeastern US city. Allergy 1999, 54, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cain, G.; Elderfield, A.J.; Green, R.; Smillie, F.I.; Chapman, M.D.; Custovic, A.; Woodcock, A. The effect of dry heat on mite, cat, and dog allergens. Allergy 1998, 53, 1213–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grönlund, H.; Saarne, T.; Gafvelin, G.; Van Hage, M. The major cat allergen, Fel d 1, in diagnosis and therapy. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 151, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konradsen, J.R.; Fujisawa, T.; van Hage, M.; Hedlin, G.; Hilger, C.; Kleine-Tebbe, J.; Matsui, E.C.; Roberts, G.; Rönmark, E.; Platts-Mills, T.a.E. Allergy to furry animals: New insights, diagnostic approaches, and challenges. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bienboire-Frosini, C.; Lebrun, R.; Vervloet, D.; Pageat, P.; Ronin, C. Distribution of core fragments from the major cat allergen Fel d 1 is maintained among the main anatomical sites of production. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 152, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, I.S.; Taylor-Jeffs, J. The use of sodium lamps to brightly illuminate mouse houses during their dark phases. Lab. Anim. 2004, 38, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, S.E.; Rohr, S.; Dufour, B.D.; Gaskill, B.N.; Pajor, E.A.; Garner, J.P. Home improvement: C57BL/6J mice given more naturalistic nesting materials build better nests. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2008, 47, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Grau, C.; Teruel, E.; Leclercq, J.; Pageat, P. House Mouse (Mus musculus) Avoidance of Olfactory Cues from Ferrets and Other Mammalian and Reptilian Predators: Preliminary Results. In Chemical Signals in Vertebrates 14; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Grau, C.; Leclercq, J.; Descout, E.; Teruel, E.; Bienboire-Frosini, C.; Pageat, P. Ethanol and a chemical from fox faeces modulate exploratory behaviour in laboratory mice. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2019, 213, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau Paricio, C. Influence of Predator and Food Chemical Cues in the Behaviour of the House Mouse (Mus Musculus). Ph.D. Thesis, Université Politechnique de Toulouse, Toulouse, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas, C.; Wegienka, G.; Havstad, S.; Ownby, D.; Johnson, C.C. Influence of cat characteristics on Fel d 1 levels in the home. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008, 101, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernet-Maury, E. Trimethyl-thiazoline in fox feces: A natural alarming substance for the rat. In Olfaction and Taste VII; IRL Press: London, UK, 1980; p. 407. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, K.J.; Rosen, J.B. Predator odor as an unconditioned fear stimulus in rats: Elicitation of freezing by trimethylthiazoline, a component of fox feces. Behav. Neurosci. 2000, 114, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes-Marco, L.; Lanuza, E.; Martínez-García, F.; Agustín-Pavón, C. Avoidance and contextual learning induced by a kairomone, a pheromone and a common odorant in female CD1 mice. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurst, J.L.; West, R.S. Taming anxiety in laboratory mice. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 825–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mönnikes, H.; Schmidt, B.G.; Taché, Y. Psychological stress-induced accelerated colonic transit in rats involves hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor. Gastroenterology 1993, 104, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienboire-Frosini, C.; Durairaj, R.; Pelosi, P.; Pageat, P. The major cat allergen fel d 1 binds steroid and fatty acid semiochemicals: A combined in silico and in vitro study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bienboire-frosini, C.; Durairaj, R.; Vick, G.; Pelosi, P.; Cozzi, A.; Pageat, P.; Asproni, P. Secretoglobins as a novel class of Pheromone-Binding Proteins: The case of cat Fel d 1. Chem. Senses 2019, 44, 45–46. [Google Scholar]
- Sbarbati, A.; Osculati, F. Allelochemical communication in vertebrates: Kairomones, allomones and synomones. Cells. Tissues. Organs 2006, 183, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karn, R.C. Steroid binding by mouse salivary proteins. Biochem. Genet. 1998, 36, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varner, E.; Jackson, H.; Mahal, M.; Takács, S.; Gries, R.; Gries, G. Brown rats and house mice eavesdrop on each other’s volatile sex pheromone components. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienboire-Frosini, C.; Cozzi, A.; Lafont-Lecuelle, C.; Vervloet, D.; Ronin, C.; Pageat, P. Immunological differences in the global release of the major cat allergen Fel d 1 are influenced by sex and behaviour. Vet. J. 2012, 193, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laska, M.; Fendt, M.; Wieser, A.; Endres, T.; Hernandez Salazar, L.T.; Apfelbach, R. Detecting danger—Or just another odorant? Olfactory sensitivity for the fox odor component 2,4,5-trimethylthiazoline in four species of mammals. Physiol. Behav. 2005, 84, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endres, T.; Fendt, M. Aversion-vs. fear-inducing properties of 2,4,5-trimethyl-3-thiazoline, a component of fox odor, in comparison with those of butyric acid. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 2324–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, S.M.; Karsh, J.; Marcelo, J.; Boeckh, D.; Stepner, N.; Santone, B.; Yang, J.; Yang, W.H. Fel d 1 and Fel d 4 levels in cat fur, saliva, and urine. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 1990–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michaux, J.R.; Chevret, P.; Filippucci, M.G.; Macholan, M. Phylogeny of the genus Apodemus with a special emphasis on the subgenus Sylvaemus using the nuclear IRBP gene and two mitochondrial markers: Cytochrome b and 12S rRNA. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2002, 23, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, K.F.; Gemeno, C.; Yeargan, K.V.; Millar, J.G.; Johnson, K.M. Aggressive chemical mimicry of moth pheromones by a bolas spider: How does this specialist predator attract more than one species of prey? Chemoecology 2002, 12, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takacs, S.; Gries, R.; Gries, G.J.; Takács, S.; Gries, R.; Gries, G. Sex hormones function as sex attractant pheromones in house mice and brown rats. Chembiochem 2017, 18, 1391–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beery, A.K.; Zucker, I. Sex bias in neuroscience and biomedical research. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 35, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prendergast, B.J.; Onishi, K.G.; Zucker, I. Female mice liberated for inclusion in neuroscience and biomedical research. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 40, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grau, C.; Bienboire-Frosini, C.; Arroub, S.; Lafont-Lecuelle, C.; Leclercq, J.; Pageat, P. Sex Differences in Mouse Exploratory Behaviour to Fel d 1, a Cat ABP-Like Protein. Animals 2021, 11, 3149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113149
Grau C, Bienboire-Frosini C, Arroub S, Lafont-Lecuelle C, Leclercq J, Pageat P. Sex Differences in Mouse Exploratory Behaviour to Fel d 1, a Cat ABP-Like Protein. Animals. 2021; 11(11):3149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113149
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrau, Carlos, Cécile Bienboire-Frosini, Sana Arroub, Céline Lafont-Lecuelle, Julien Leclercq, and Patrick Pageat. 2021. "Sex Differences in Mouse Exploratory Behaviour to Fel d 1, a Cat ABP-Like Protein" Animals 11, no. 11: 3149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113149
APA StyleGrau, C., Bienboire-Frosini, C., Arroub, S., Lafont-Lecuelle, C., Leclercq, J., & Pageat, P. (2021). Sex Differences in Mouse Exploratory Behaviour to Fel d 1, a Cat ABP-Like Protein. Animals, 11(11), 3149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113149






