Common and Differential Dynamics of the Function of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells between Holstein and Jersey Cows in Heat-Stress Environment
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Measurement of THI, Respiration, and Rectal Temperature
2.3. Blood Collection and PBMC Isolation
2.4. Total RNA Isolation and Sequencing
2.5. Data Handling Procedures
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
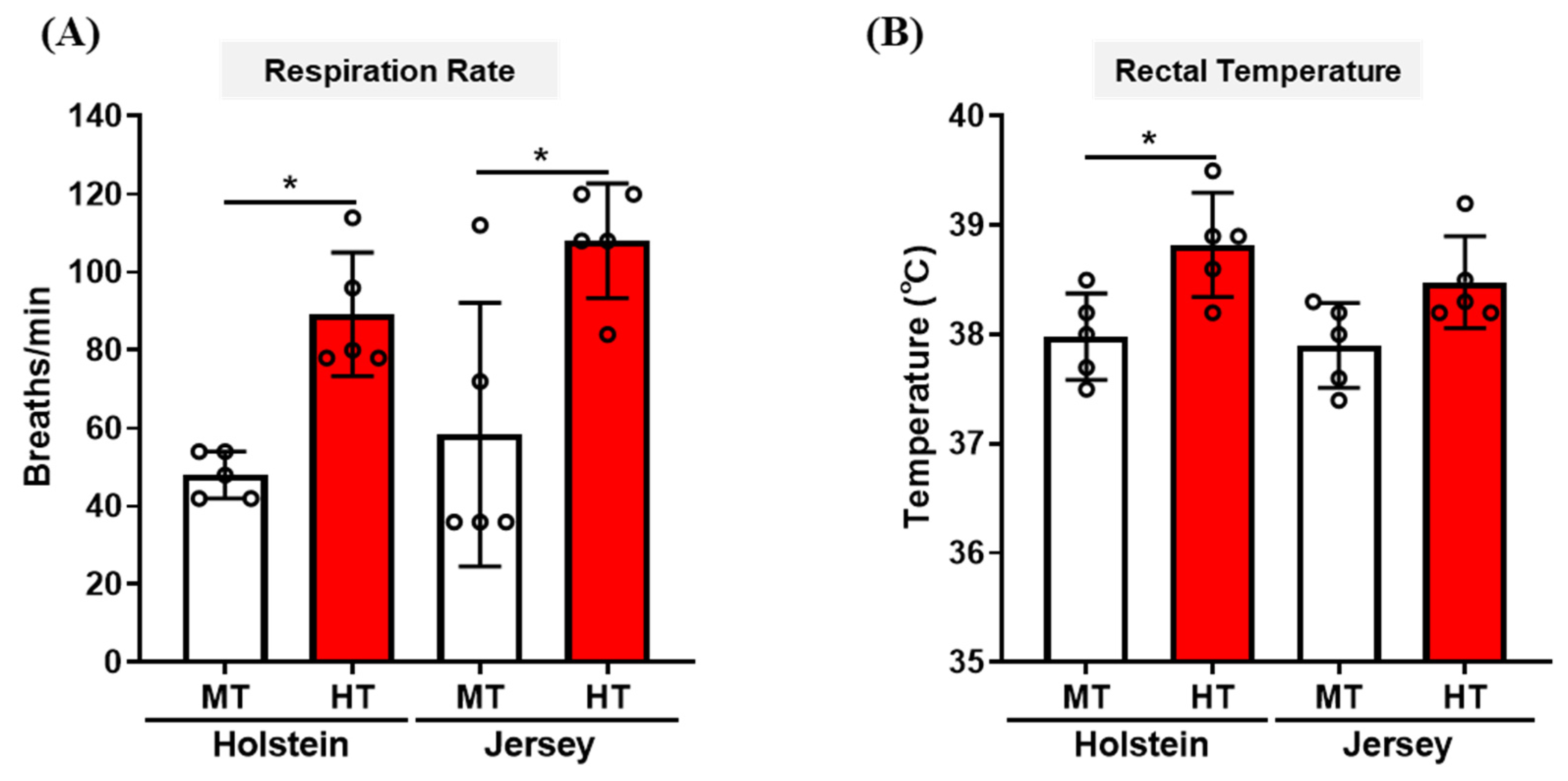
3.1. Changes in Respiration Rate and Rectal Temperature of Two Breeds of Dairy Cow by THI Condition
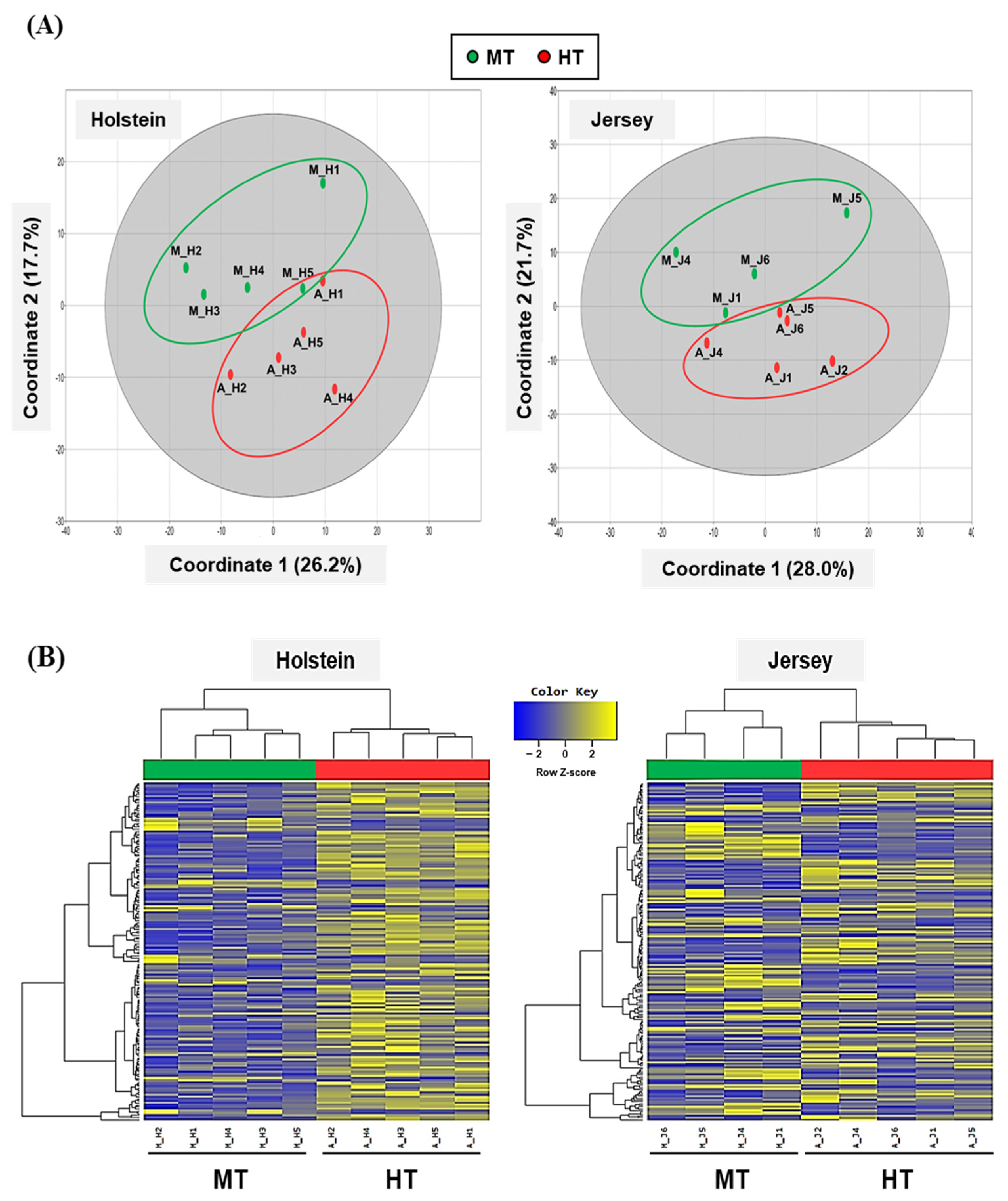
3.2. Preliminary Analysis and Summary Statistics for RNA Sequencing Data
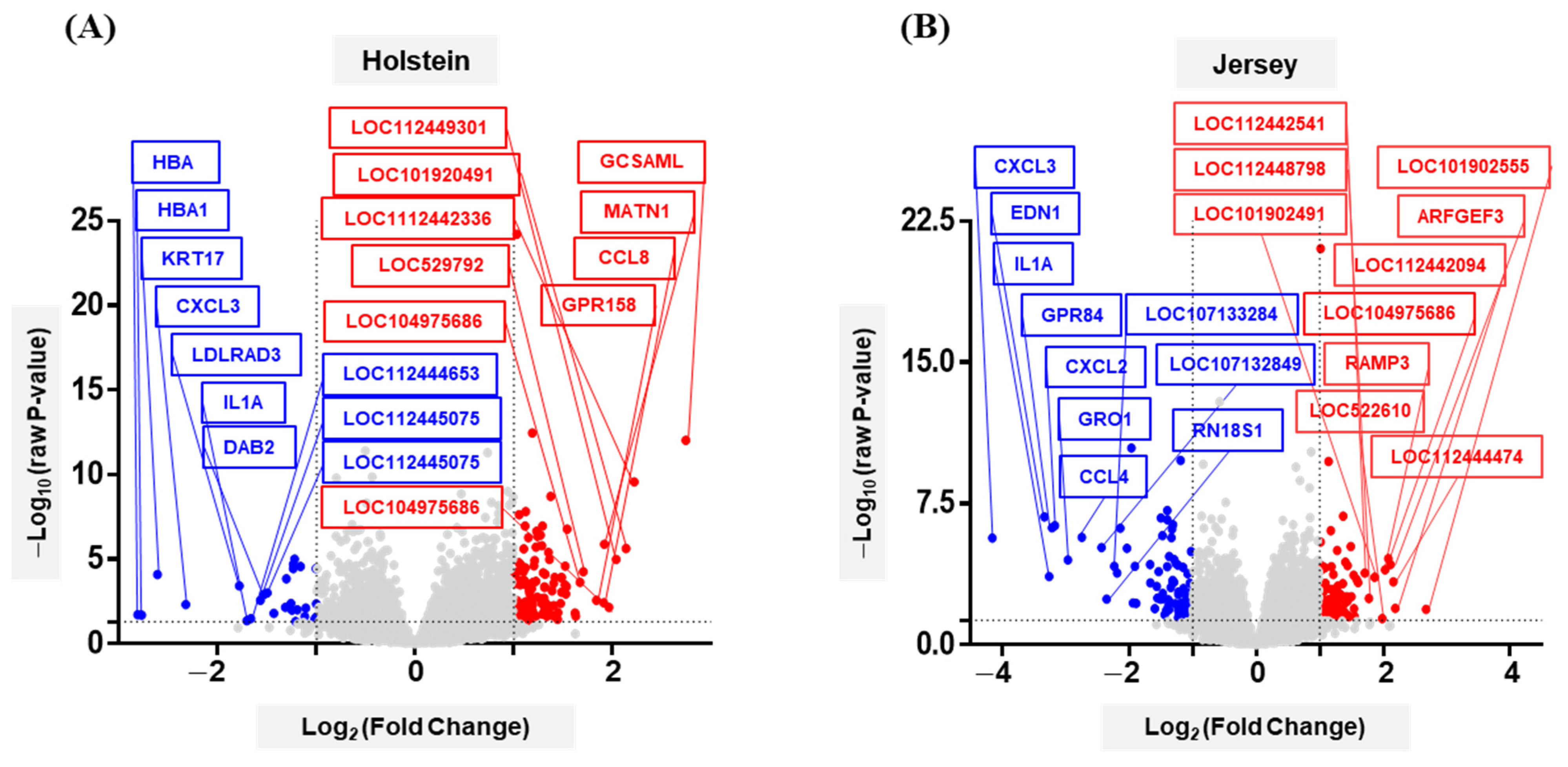
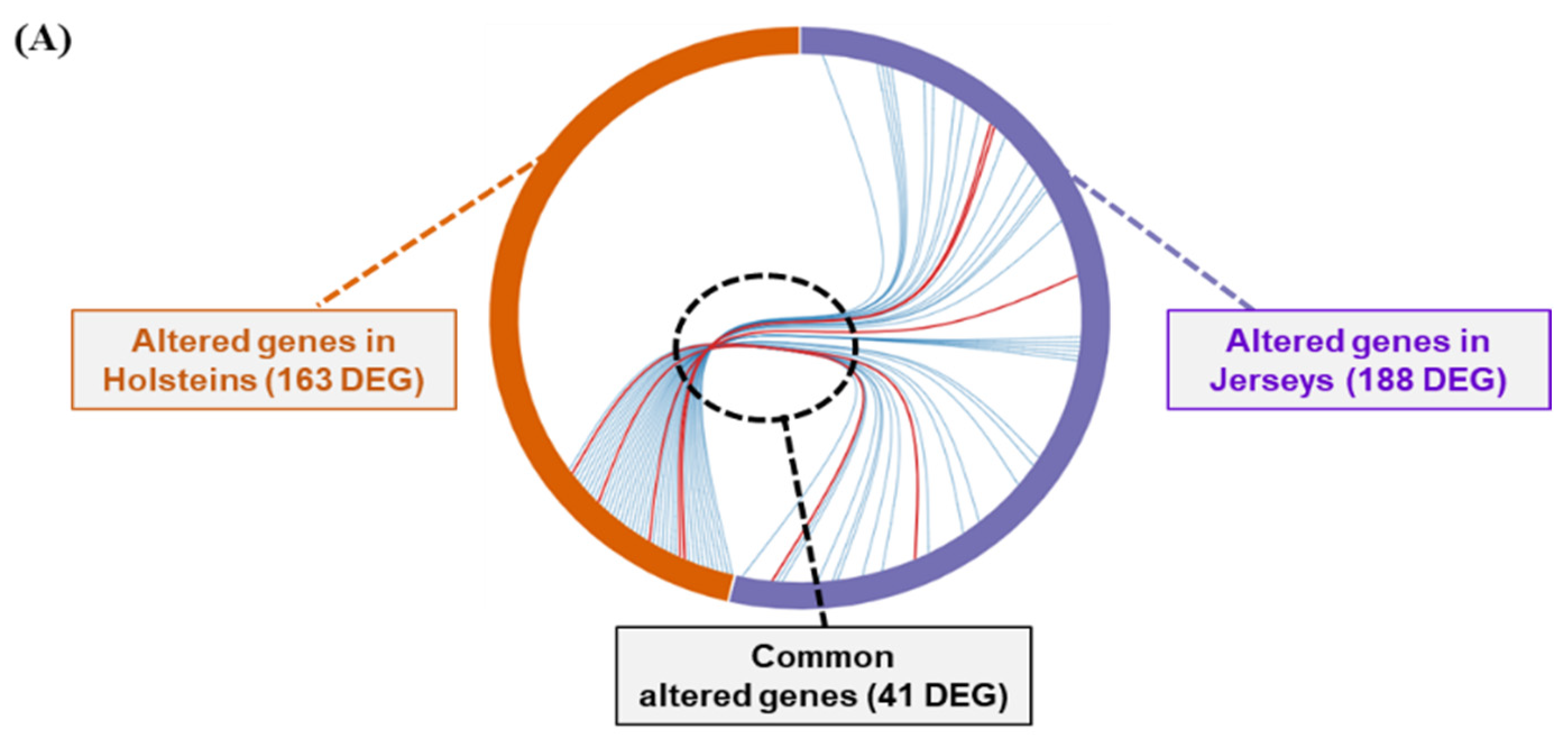
3.3. Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes of Two Breeds of Dairy Cow by THI Condition
3.4. Functional Annotation of Differentially Expressed Genes of Dairy Cows
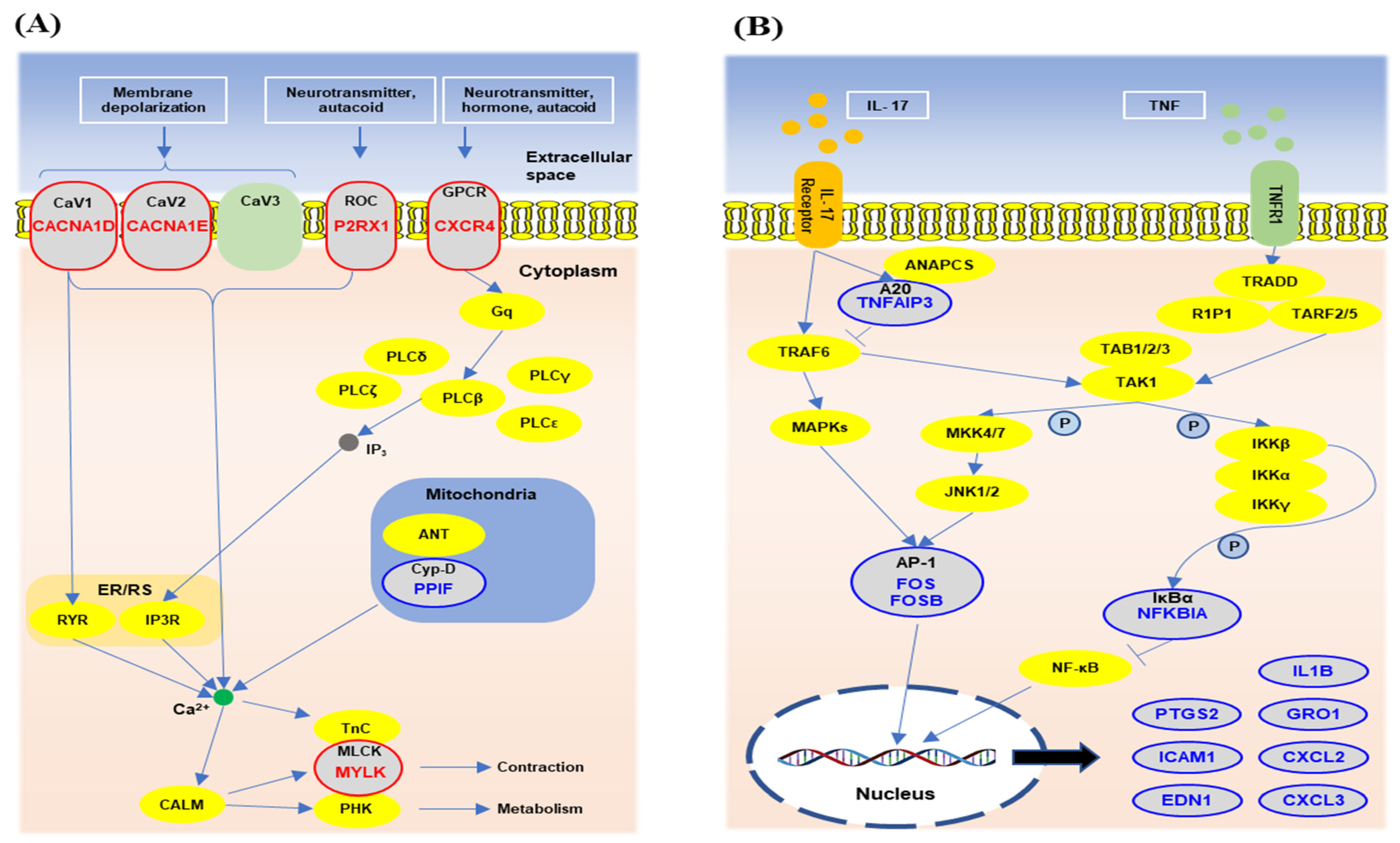
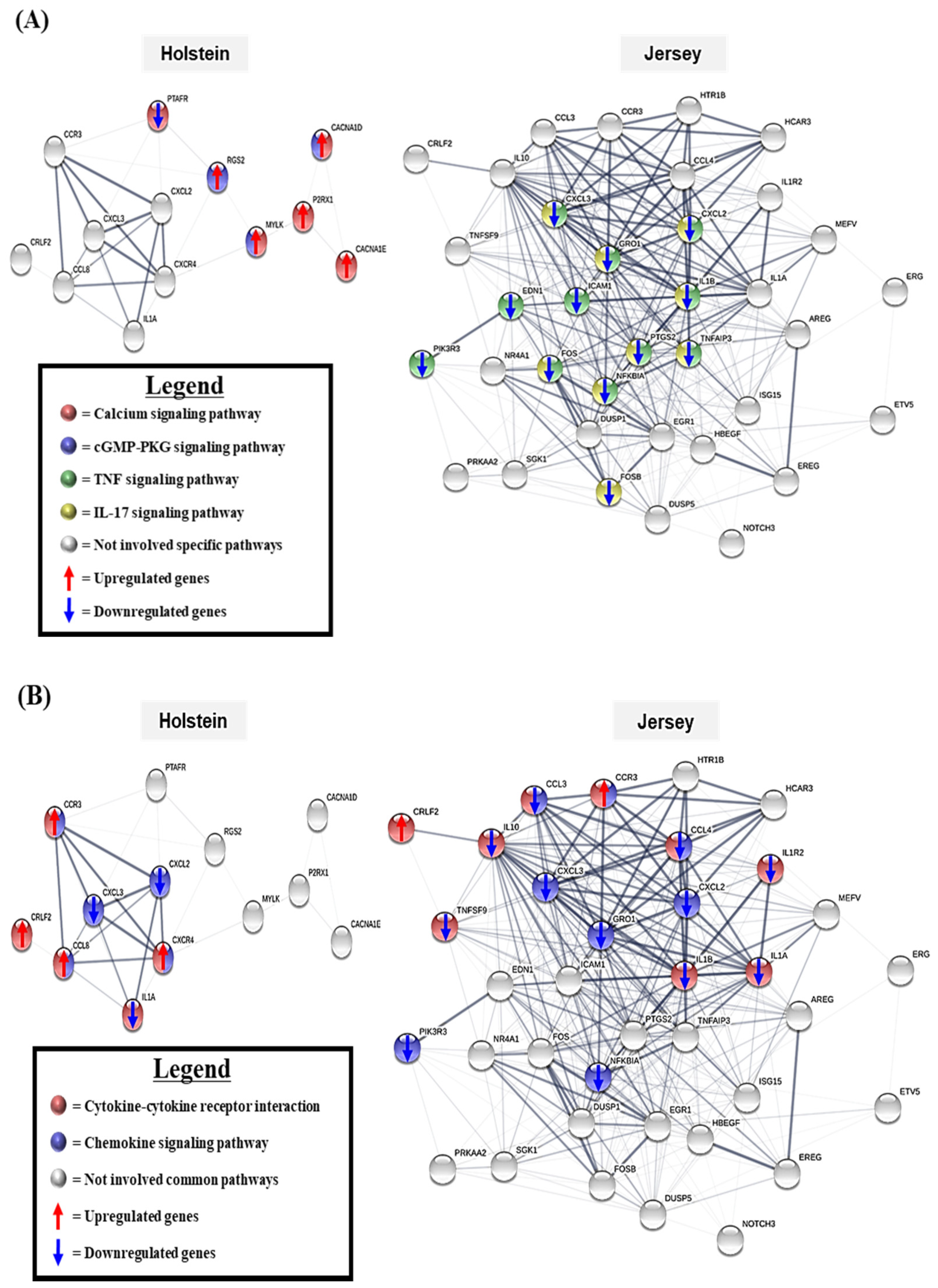
3.5. The Gene Network Analysis of the Unique Differentially Expressed Genes
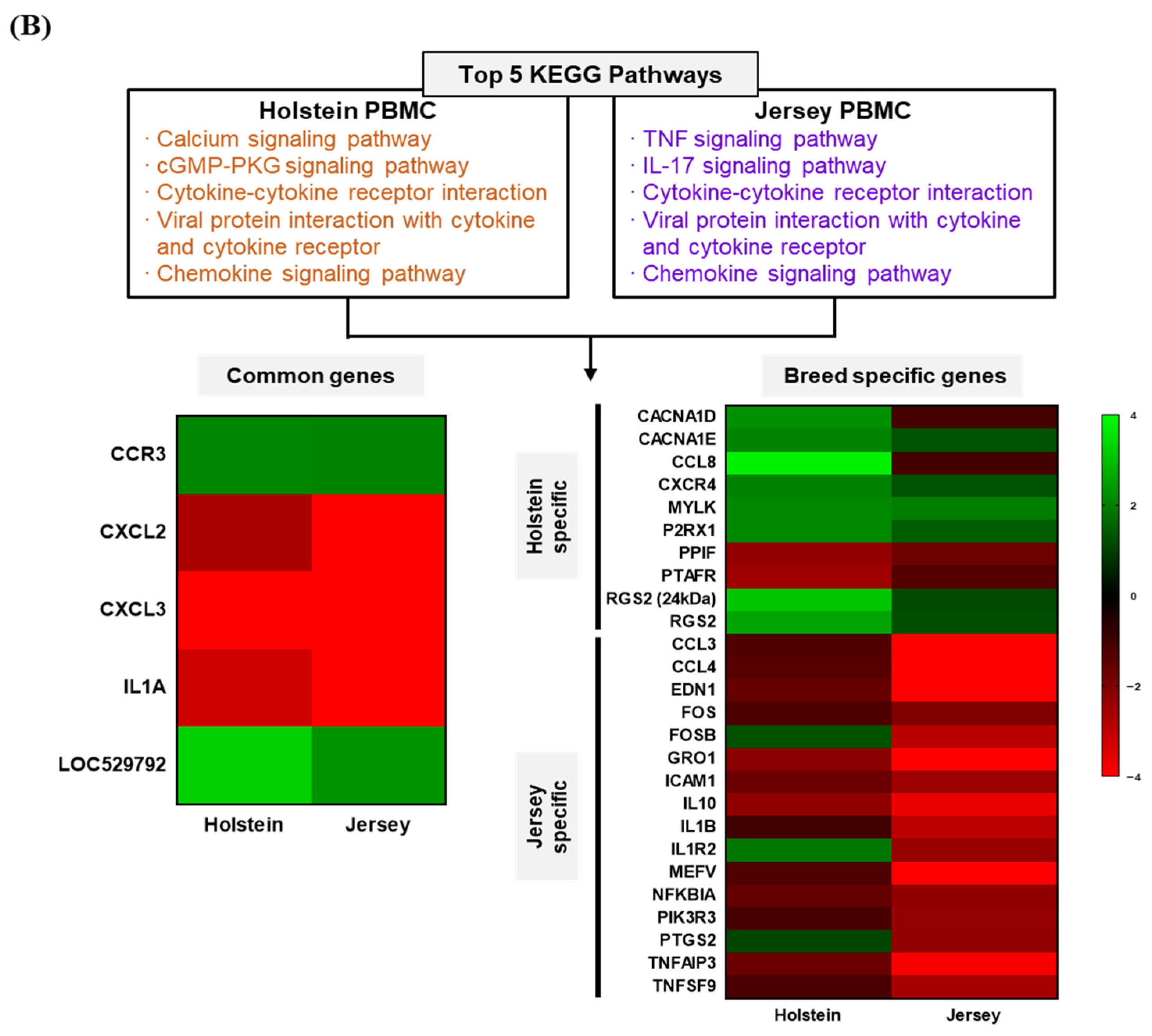
3.6. Summary of Differentially Expressed Genes and KEGG Pathways in Holstein and Jersey Cows in Response to THI Environmental Condition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Belhadj Slimen, I.; Najar, T.; Ghram, A.; Abdrrabba, M. Heat stress effects on livestock: Molecular, cellular and metabolic aspects, a review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 100, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Sailo, L.; Verma, N.; Bharti, P.; Saikia, J.; Imtiwati, K.R. Impact of heat stress on health and performance of dairy animals: A review. Vet. World 2016, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagath, M.; Krishnan, G.; Devaraj, C.; Rashamol, V.P.; Pragna, P.; Lees, A.M.; Sejian, V. The impact of heat stress on the immune system in dairy cattle: A review. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 126, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gernand, E.; König, S.; Kipp, C. Influence of on-farm measurements for heat stress indicators on dairy cow productivity, female fertility, and health. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 6660–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louie, A.P.; Rowe, J.D.; Love, W.J.; Lehenbauer, T.W.; Aly, S.S. Effect of the environment on the risk of respiratory disease in preweaning dairy calves during summer months. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 10230–10247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jingar, S.; Mehla, R.; Singh, M. Climatic effects on occurrence of clinical mastitis in different breeds of cows and buffaloes. Arch. Zootec. 2014, 63, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Webster, A.J. Environmental stress and the physiology, performance and health of ruminants. J. Anim. Sci. 1983, 57, 1584–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, G.E.; Tao, S.; Laporta, J. Heat stress impacts immune status in cows across the life cycle. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elenkov, I.J. Glucocorticoids and the Th1/Th2 balance. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1024, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.H.; Grandison, A.S.; Fagan, C.C. Effect of blending Jersey and Holstein-Friesian milk on Cheddar cheese processing, composition, and quality. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.L.; Smith, T.; Rude, B.J.; Ward, S.H. Comparison of the effects of heat stress on milk and component yields and somatic cell score in Holstein and Jersey cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 3028–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utech, K.; Wharton, R.; Kerr, J.D. Resistance to Boophilus microplus (Canestrini) in different breeds of cattle. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1978, 29, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, E.L.; Horan, B.; Evans, R.D.; Berry, D.P. Milk production and fertility performance of Holstein, Friesian, and Jersey purebred cows and their respective crosses in seasonal-calving commercial farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 5681–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seath, D.M.; Miller, G.D. Heat tolerance comparisons between Jersey and Holstein cows. J. Anim. Sci. 1947, 6, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.K.; Rodriguez, L.A.; Mekonnen, G.; Wilcox, C.J.; Bachman, K.C.; Collier, R.J. Climatological and genetic effects on milk composition and yield. J. Dairy Sci. 1983, 66, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Cardoso, F.; Pineda, A.; Trevisi, E.; Shen, X.; Rosa, F.; Osorio, J.; Loor, J.J. Grain challenge affects systemic and hepatic molecular biomarkers of inflammation, stress, and metabolic responses to a greater extent in Holstein than Jersey cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 9153–9162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, D.; Earley, B.; Cormican, P.; Kenny, D.A.; McCabe, M.; Kelly, A.K.; McGee, M.; Waters, S.M. Characterisation of the whole blood mRNA transcriptome in Holstein-Friesian and Jersey calves in response to gradual weaning. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council, N.R. A Guide to Environmental Research on Animals; National Academies: Washington, DC, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, S.; Joung, J.G.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Y.R.; Liu, B.; Shao, Y.; Xiang, J.Z.; Fei, Z.; Giovannoni, J.J. High-throughput illumina strand-specific RNA sequencing library preparation. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2011, 2011, pdb. prot 5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Kim, D.; Pertea, G.M.; Leek, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. g: Profiler: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouellet, V.; Cabrera, V.E.; Fadul-Pacheco, L.; Charbonneau, É. The relationship between the number of consecutive days with heat stress and milk production of Holstein dairy cows raised in a humid continental climate. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 8537–8545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, G.E.; Tao, S.; Monteiro, A.P.A. Effects of late-gestation heat stress on immunity and performance of calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 3193–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Peng, D.; Li, G.; Chen, J.; Gu, X. Exposure to heat-stress environment affects the physiology, circulation levels of cytokines, and microbiome in dairy cows. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polsky, L.; von Keyserlingk, M.A.G. Invited review: Effects of heat stress on dairy cattle welfare. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 8645–8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radostits, O.M.; Gay, C.C.; Hinchcliff, K.W.; Constable, P.D. Veterinary Medicine E-Book: A Textbook of the Diseases of Cattle, Horses, Sheep, Pigs and Goats; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wenz, J.R.; Moore, D.A.; Kasimanickam, R. Factors associated with the rectal temperature of Holstein dairy cows during the first 10 days in milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 1864–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igono, M.O.; Steevens, B.J.; Shanklin, M.D.; Johnson, H.D. Spray cooling effects on milk production, milk, and rectal temperatures of cows during a moderate temperate summer season. J. Dairy Sci. 1985, 68, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabuga, J.D. The influence of thermal conditions on rectal temperature, respiration rate and pulse rate of lactating Holstein-Friesian cows in the humid tropics. Int. J. Biometeorol. 1992, 36, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, T.; Bera, S.; Deb, S.; Pal, P.; Debbarma, N.; Haldar, A. Application of radio frequency based digital thermometer for real-time monitoring of dairy cattle rectal temperature. Vet. World 2017, 10, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- West, J.W.; Mullinix, B.G.; Bernard, J.K. Effects of hot, humid weather on milk temperature, dry matter intake, and milk yield of lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianca, W. Section A. Physiology. Cattle in a hot environment. J. Dairy Res. 1965, 32, 291–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekblom, R.; Galindo, J. Applications of next generation sequencing in molecular ecology of non-model organisms. Hereditary (Edinb) 2011, 107, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Nadeem, A.; Zhang, B.; Babar, M.; Soller, M.; Khatib, H. Characterization and comparison of the leukocyte transcriptomes of three cattle breeds. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikanth, K.; Kwon, A.; Lee, E.; Chung, H. Chaperones. Characterization of genes and pathways that respond to heat stress in Holstein calves through transcriptome analysis. Cell Stress Chaperones 2017, 22, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yue, T.; Ahmad, M.J.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Deng, T.; Hu, Y.; He, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, L. Transcriptome analysis reveals potential regulatory genes related to heat tolerance in holstein dairy cattle. Genes 2020, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talker, S.C.; Baumann, A.; Barut, G.T.; Keller, I.; Bruggmann, R.; Summerfield, A. Precise delineation and transcriptional characterization of bovine blood dendritic-cell and monocyte subsets. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Simonavicius, N.; Tian, H.; Ling, L. Medium-chain fatty acids as ligands for orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR84. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 34457–34464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Takaishi, S.; Nagasaki, M.; Onozawa, Y.; Iino, I.; Maeda, H.; Komai, T.; Oda, T. Medium-chain fatty acid-sensing receptor, GPR84, is a proinflammatory receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 10684–10691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recio, C.; Lucy, D.; Purvis, G.S.D.; Iveson, P.; Zeboudj, L.; Iqbal, A.J.; Lin, D.; O’Callaghan, C.; Davison, L.; Griesbach, E.; et al. Activation of the immune-metabolic receptor GPR84 enhances inflammation and phagocytosis in macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucy, D.; Purvis, G.S.D.; Zeboudj, L.; Chatzopoulou, M.; Recio, C.; Bataille, C.J.R.; Wynne, G.M.; Greaves, D.R.; Russel, A.J. A biased agonist at Immunometabolic receptor GPR84 causes distinct functional effects in macrophages. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 2055–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, B.D.; Machado, F.S.; Tanowitz, H.B.; Desruisseaux, M.S. Endothelin-1 and its role in the pathogenesis of infectious diseases. Life Sci. 2014, 118, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Chen, Y.; Ding, C.; Qiu, J.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Su, L.; Jiang, D. Heat stress combined with lipopolysaccharide alter the activity and superficial molecules of peripheral monocytes. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2019, 33, 2058738419828891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecchi, C.; Rota, N.; Vitali, A.; Ceciliani, F.; Lacetera, N. In vitro assessment of the effects of temperature on phagocytosis, reactive oxygen species production and apoptosis in bovine polymorphonuclear cells. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2016, 182, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.M.; An, J. Cytokines, inflammation and pain. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2007, 45, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.D.; Nedjai, B.; Hurst, T.; Pennington, D.J. Cytokines and chemokines: At the crossroads of cell signalling and inflammatory disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 2563–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotnik, A.; Yoshie, O.; Nomiyama, H. The chemokine and chemokine receptor superfamilies and their molecular evolution. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.C.; Liu, Y.N.; Hu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z. Macrophage inflammatory protein-2 as mediator of inflammation in acute liver injury. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paolo, N.C.; Shayakhmetov, D.M. Interleukin 1α and the inflammatory process. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Amaral, B.; Connor, E.; Tao, S.; Hayen, M.; Bubolz, J.; Dahl, G.J. Heat stress abatement during the dry period influences metabolic gene expression and improves immune status in the transition period of dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, F.B.; Cunha, P.; Jensen, K.; Glass, E.J.; Foucras, G.; Robert-Granié, C.; Rupp, R.; Rainard, P. Differential response of bovine mammary epithelial cells to Staphylococcus aureus or Escherichia coli agonists of the innate immune system. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Deng, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, M.-Q. RNA-seq analysis of different inflammatory reactions induced by lipopolysaccharide and lipoteichoic acid in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 130, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, I.; Tao, S.; Monteiro, A.; Jeong, K.; Dahl, G.J. Effect of cooling during the dry period on immune response after Streptococcus uberis intramammary infection challenge of dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 7426–7436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Chen, Q.; Hoover, D.M.; Staley, P.; Tucker, K.D.; Lubkowski, J.; Oppenheim, J.J. Many chemokines including CCL20/MIP-3α display antimicrobial activity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2003, 74, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdivia-Silva, J.; Medina-Tamayo, J.; Garcia-Zepeda, E.A. Chemokine-derived peptides: Novel antimicrobial and antineoplasic agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 12958–12985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paolo, N.C.; Shafiani, S.; Day, T.; Papayannopoulou, T.; Russell, D.W.; Iwakura, Y.; Sherman, D.; Urdahl, K.; Shayakhmetov, D.M. Interdependence between interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor regulates TNF-dependent control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Immunity 2015, 43, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehla, K.; Magotra, A.; Choudhary, J.; Singh, A.K.; Mohanty, A.K.; Upadhyay, R.C.; Srinivasan, S.; Gupta, P.; Choudhary, N.; Antony, B.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of the heat stress response in Zebu (Sahiwal) cattle. Gene 2014, 533, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, P.; Sada-Ovalle, I.; Nishimura, T.; Anderson, A.C.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Remold, H.G.; Behar, S.M. IL-1β promotes antimicrobial immunity in macrophages by regulating TNFR signaling and caspase-3 activation. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 4196–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M.; Delhase, M. The IκB kinase (IKK) and NF-κB: Key elements of proinflammatory signalling. Semin. Immunol. 2000, 12, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, P.; Karin, M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1072, 129–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Kang, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, X. IL-17 signaling in host defense and inflammatory diseases. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 7, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGill, J.L.; Rusk, R.A.; Guerra-Maupome, M.; Briggs, R.E.; Sacco, R.E. Bovine gamma delta T cells contribute to exacerbated IL-17 production in response to co-infection with bovine RSV and Mannheimia haemolytica. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Mao, L.; Shu, X.; Liu, R.; Hao, F.; Li, J.; Liu, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, W.; Sun, M.; et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals differential immune related genes expression in bovine viral diarrhea virus-2 infected goat peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiser, A.; McCarthy, A.; Wedlock, N.; Meier, S.; Kay, J.; Walker, C.; Crookenden, M.A.; Mitchell, M.D.; Morgan, S.; Watkins, K.; et al. Grazing dairy cows had decreased interferon-γ, tumor necrosis factor, and interleukin-17, and increased expression of interleukin-10 during the first week after calving. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feske, S.; Wulff, H.; Skolnik, E.Y. Ion channels in innate and adaptive immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 291–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feske, S.; Skolnik, E.Y.; Prakriya, M. Ion channels and transporters in lymphocyte function and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 532–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldon, J.; Thorsteinsson, T.; Olafsson, T. The concentration of blood glucose, urea, calcium and magnesium in milking dairy cows. J. Vet. Med. 1988, 35, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riekerink, R.O.; Barkema, H.; Stryhn, H. The effect of season on somatic cell count and the incidence of clinical mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 1704–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, C.; Wei, T.; Zou, Q.; Wang, M. Chronic heat stress inhibits immune responses to H5N1 vaccination through regulating CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ tregs. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, P.; Curtis, N. Factors that influence the immune response to vaccination. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00084-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corman, L.C. The relationship between nutrition, infection, and immunity. Med. Clin. North. Am. 1985, 69, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, C.E.; Calder, P.C.; Miles, E.A. Diet and immune function. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-H.; Kim, M.-H.; Kim, S.-B.; Son, J.-K.; Lee, J.-H.; Joo, S.-S.; Gu, B.-H.; Park, T.; Park, B.-Y.; Kim, E.-T. Differential dynamics of the ruminal microbiome of Jersey Cows in a heat stress environment. Animals 2020, 10, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, G.; Irons, P.C.; Webb, E.C.; Chapwanya, A. Interactions between negative energy balance, metabolic diseases, uterine health and immune response in transition dairy cows. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2014, 144, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qaisi, M.; Mayorga, E.J.; Horst, E.A.; Kvidera, S.K.; McCarthy, C.S.; Abeyta, M.A.; Goetz, B.M.; Ramirez-Ramirez, H.A.; Timms, L.L.; Baumgard, L.H. Validating a heat stress model: The effects of an electric heat blanket and nutritional plane on lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 5550–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, E.T.; Joo, S.S.; Kim, D.H.; Gu, B.-H.; Park, D.S.; Rahman, M.A.; Son, J.K.; Park, B.Y.; Kim, S.B.; Hur, T.-Y.; et al. Common and Differential Dynamics of the Function of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells between Holstein and Jersey Cows in Heat-Stress Environment. Animals 2021, 11, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010019
Kim ET, Joo SS, Kim DH, Gu B-H, Park DS, Rahman MA, Son JK, Park BY, Kim SB, Hur T-Y, et al. Common and Differential Dynamics of the Function of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells between Holstein and Jersey Cows in Heat-Stress Environment. Animals. 2021; 11(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Eun Tae, Sang Seok Joo, Dong Hyeon Kim, Bon-Hee Gu, Da Som Park, Md Atikur Rahman, Jun Kyu Son, Beom Young Park, Sang Bum Kim, Tai-Young Hur, and et al. 2021. "Common and Differential Dynamics of the Function of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells between Holstein and Jersey Cows in Heat-Stress Environment" Animals 11, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010019
APA StyleKim, E. T., Joo, S. S., Kim, D. H., Gu, B.-H., Park, D. S., Rahman, M. A., Son, J. K., Park, B. Y., Kim, S. B., Hur, T.-Y., & Kim, M. (2021). Common and Differential Dynamics of the Function of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells between Holstein and Jersey Cows in Heat-Stress Environment. Animals, 11(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010019





