Whole Genome Sequencing Reveals the Effects of Recent Artificial Selection on Litter Size of Bamei Mutton Sheep
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and DNA Preparation
2.2. Genome Sequencing
2.3. Read Processing and Variant Calling
2.4. Population Genetics Analysis
2.5. Selective Sweep Analysis
2.6. Sanger Sequencing Validation
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing and Mapping of the Sheep
3.2. Identification of the Variation of the Sheep
3.3. Population Structure Analysis
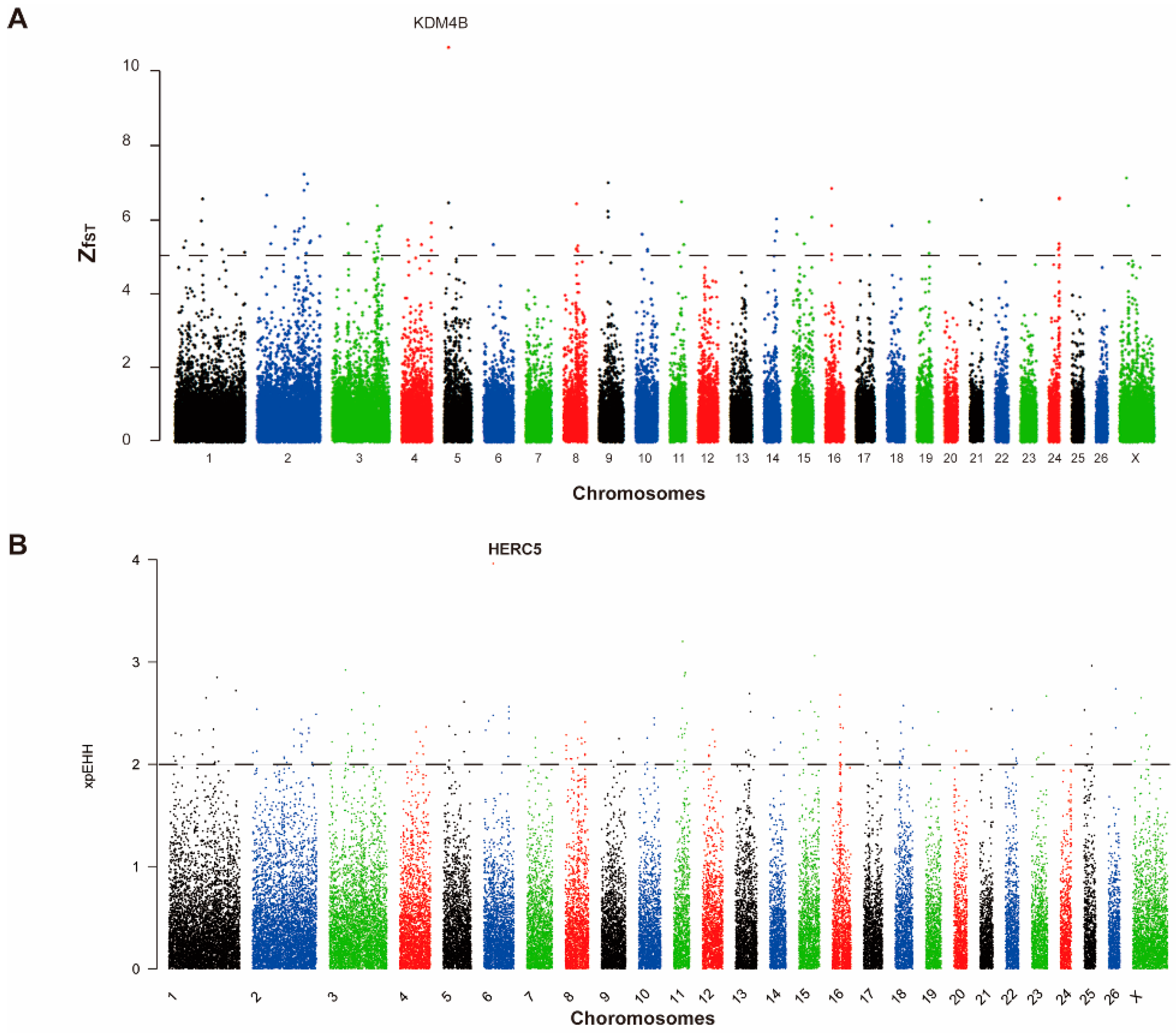
3.4. Analysis of the Selected Loci and Candidate Genes
3.5. Mutations in the KDM4B Gene
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kijas, J.W.; Lenstra, J.A.; Hayes, B.; Boitard, S.; Porto Neto, L.R.; San Cristobal, M.; Servin, B.; McCulloch, R.; Whan, V.; Gietzen, K.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of the World’s Sheep Breeds Reveals High Levels of Historic Mixture and Strong Recent Selection. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.-X.; Yang, J.; Lv, F.-H.; Hu, X.-J.; Xie, X.-L.; Zhang, M.; Li, W.-R.; Liu, M.-J.; Wang, Y.-T.; Li, J.-Q.; et al. Genomic Reconstruction of the History of Native Sheep Reveals the Peopling Patterns of Nomads and the Expansion of Early Pastoralism in East Asia. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2380–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Wu, M.; Cao, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, R.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, L.; Lu, J.; et al. Genome-wide analysis reveals population structure and selection in Chinese indigenous sheep breeds. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Li, W.-R.; Lv, F.-H.; He, S.-G.; Tian, S.-L.; Peng, W.-F.; Sun, Y.-W.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Tu, X.-L.; Zhang, M.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Native Sheep Provides Insights into Rapid Adaptations to Extreme Environments. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 2576–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Su, R.; Zhang, W.; Li, J. The identification and assessment on genetic characteristics in grading breeding sheep populations with microsatellite markers. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2008, 9, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Jiang, H.; Ma, Y.; Luo, H. Comparison of meat-productivities between Bamei Sheep and Small-tall Han Sheep under intensive feeding pattern. J. China Agric. Univ. 2014, 19, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; Jin, Y.; Jin, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Jia, X. Study on growth and meat output in different carcass levels of Bamei mutton sheep and their hybrid progeny. Meat Ind. 2013, 2013, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.; Li, B.; Zhao, Y. Current Status and Developing Prospect of Sheep and Goat Breeding in China. Chin. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 51, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Notter, D.R. Genetic aspects of reproduction in sheep. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2008, 43 (Suppl. 2), 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Pan, Z.; Wang, X.; Hu, W.; Di, R.; Yao, Y.; Chu, M. Progress on major genes for high fecundity in ewes. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2014, 1, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juengel, J.L. How the quest to improve sheep reproduction provided insight into oocyte control of follicular development. J. R. Soc. N. Z. 2018, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xie, M.; Chen, W.; Talbot, R.; Maddox, J.F.; Faraut, T.; Wu, C.; Muzny, D.M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. The sheep genome illuminates biology of the rumen and lipid metabolism. Science 2014, 344, 1168–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Di, R.; Miao, B.; Hu, W.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; et al. Whole-genome sequences of 89 Chinese sheep suggest role of RXFP2 in the development of unique horn phenotype as response to semi-feralization. GigaScience 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fariello, M.I.; Servin, B.; Tosser-Klopp, G.; Rupp, R.; Moreno, C.; San Cristobal, M.; Boitard, S. Selection signatures in worldwide sheep populations. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moioli, B.; Pilla, F.; Ciani, E. Signatures of selection identify loci associated with fat tail in sheep. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 4660–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Di, R.; An, X.; Miao, B.; Wang, X.; Hu, W.; et al. Rapid evolution of a retro-transposable hotspot of ovine genome underlies the alteration of BMP2 expression and development of fat tails. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Ni, W.; Xu, Y.; Yao, R.; Wei, B.; Zhang, M.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Whole-Genome Resequencing Reveals Loci Associated With Thoracic Vertebrae Number in Sheep. Front. Genet. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ye, J.; Han, X.; Qiao, R.; Li, X.; Lv, G.; Wang, K. Whole-genome sequencing identifies potential candidate genes for reproductive traits in pigs. Genomics 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-T.; Zhang, M.-M.; Li, Q.-G.; Tang, H.; Zhang, L.-F.; Wang, K.-J.; Zhu, M.-Z.; Lu, Y.-F.; Bao, H.-G.; Zhang, Y.-M.; et al. Whole-genome resequencing reveals candidate mutations for pig prolificacy. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 284, 20172437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Luo, N.; Tan, X.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Na, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y. Scanning of selection signature provides a glimpse into important economic traits in goats (Capra hircus). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.-N.; Zhai, H.-L.; Cheng, M.; Ma, J.-Y.; Cheng, S.-F.; Ge, W.; Zhang, G.-L.; Wang, J.-J.; Zhang, R.-Q.; Wang, X.; et al. Whole-genome scanning for the litter size trait associated genes and SNPs under selection in dairy goat (Capra hircus). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolebo, A.T.; Khayatzadeh, N.; Melesse, A.; Wragg, D.; Rekik, M.; Haile, A.; Rischkowsky, B.; Rothschild, M.F.; Mwacharo, J.M. Genome-wide scans identify known and novel regions associated with prolificacy and reproduction traits in a sub-Saharan African indigenous sheep (Ovis aries). Mamm. Genome 2019, 30, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Larrañaga, O.; Langa, J.; Rendo, F.; Manzano, C.; Iriondo, M.; Estonba, A. Genomic selection signatures in sheep from the Western Pyrenees. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2018, 50, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.K.; Jain, M. NGS QC Toolkit: A Toolkit for Quality Control of Next Generation Sequencing Data. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; Proc, G.P.D. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.Y.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.Y.; Kim, C.; Paterson, A.H. SNPhylo: A pipeline to construct a phylogenetic tree from huge SNP data. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.C.; Fry, B.; Maller, J.; Daly, M.J. Haploview: Analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, C.-J.; Zody, M.C.; Eriksson, J.; Meadows, J.R.S.; Sherwood, E.; Webster, M.T.; Jiang, L.; Ingman, M.; Sharpe, T.; Ka, S.; et al. Whole-genome resequencing reveals loci under selection during chicken domestication. Nature 2010, 464, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, B.S.; Cockerham, C.C. Estimating F-Statistics for the analysis of population structure. Evolution 1984, 38, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stajich, J.E.; Block, D.; Boulez, K.; Brenner, S.E.; Chervitz, S.A.; Dagdigian, C.; Fuellen, G.; Gilbert, J.G.R.; Korf, I.; Lapp, H.; et al. The bioperl toolkit: Perl modules for the life sciences. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelsson, E.; Ratnakumar, A.; Arendt, M.-L.; Maqbool, K.; Webster, M.T.; Perloski, M.; Liberg, O.; Arnemo, J.M.; Hedhammar, Å.; Lindblad-Toh, K. The genomic signature of dog domestication reveals adaptation to a starch-rich diet. Nature 2013, 495, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheet, P.; Stephens, M. A fast and flexible statistical model for large-scale population genotype data: Applications to inferring missing genotypes and haplotypic phase. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 78, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickrell, J.K.; Coop, G.; Novembre, J.; Kudaravalli, S.; Li, J.Z.; Absher, D.; Srinivasan, B.S.; Barsh, G.S.; Myers, R.M.; Feldman, M.W.; et al. Signals of recent positive selection in a worldwide sample of human populations. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.H. Gap: Genetic Analysis Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2020, 23, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Tian, D.; Li, C.; Tang, B.; Dong, L.; Xiao, J.; Bao, Y.; Zhao, W.; He, H.; Zhang, Z. Genome Variation Map: A data repository of genome variations in BIG Data Center. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 46, D944–D949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partners, N.G.D.C.M.A. Database Resources of the National Genomics Data Center in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D24–D33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, R. Molecular Signatures of Natural Selection. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2005, 39, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jiang, R. Prediction of Deleterious Nonsynonymous Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism for Human Diseases. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, A.K.; Judge, R.A.; Li, L.; Pithawalla, R.; Simanis, J.; Bodelle, P.M.; Marin, V.L.; Henry, R.F.; Petros, A.M.; Sun, C. Targeting lysine specific demethylase 4A (KDM4A) tandem TUDOR domain—A fragment based approach. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 1708–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke Molly, K. How does adaptation sweep through the genome? Insights from long-term selection experiments. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 5029–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, A.M.; Pettersson, M.E.; Siegel, P.B.; Carlborg, Ö. Genome-Wide Effects of Long-Term Divergent Selection. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabeti, P.C.; Varilly, P.; Fry, B.; Lohmueller, J.; Hostetter, E.; Cotsapas, C.; Xie, X.; Byrne, E.H.; McCarroll, S.A.; Gaudet, R.; et al. Genome-wide detection and characterization of positive selection in human populations. Nature 2007, 449, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosrati, M.; Asadollahpour Nanaei, H.; Amiri Ghanatsaman, Z.; Esmailizadeh, A. Whole genome sequence analysis to detect signatures of positive selection for high fecundity in sheep. Reprod. Domest. Anim. Zuchthyg. 2019, 54, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ji, Z.; Wang, G.; Chao, T.; Hou, L.; Wang, J. Genome-wide analysis reveals signatures of selection for important traits in domestic sheep from different ecoregions. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, I.J.; Arbabi, L. New concepts of the central control of reproduction, integrating influence of stress, metabolic state, and season. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2016, 56, S165–S179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filis, P.; Lannagan, T.; Thomson, A.; Murray, A.A.; Kind, P.C.; Spears, N. Phospholipase C-β1 Signaling Affects Reproductive Behavior, Ovulation, and Implantation. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 3259–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cao, Z.; Fan, R.; Meng, B.; Xing, Z.; Liu, M.; Gao, M.; Luan, X. Comparative proteomic analysis of hypothalamus tissue from Huoyan geese between pre-laying period and laying period using an iTRAQ-based approach. Anim. Sci. J. 2018, 89, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatiades, G.A.; Carroll, R.S.; Kaiser, U.B. GnRH—A Key Regulator of FSH. Endocrinology 2018, 160, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonak, C.R.; Lainez, N.M.; Boehm, U.; Coss, D. GnRH Receptor Expression and Reproductive Function Depend on JUN in GnRH Receptor‒Expressing Cells. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 1496–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.; Krieg, A.J. KDM4B: A Nail for Every Hammer? Genes 2019, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaughan, L.; Stockley, J.; Coffey, K.; O’Neill, D.; Jones, D.L.; Wade, M.; Wright, J.; Moore, M.; Tse, S.; Rogerson, L.; et al. KDM4B is a Master Regulator of the Estrogen Receptor Signalling Cascade. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 6892–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieg, A.J.; Mullinax, S.R.; Grimstad, F.; Marquis, K.; Constance, E.; Hong, Y.; Krieg, S.A.; Roby, K.F. Histone demethylase KDM4A and KDM4B expression in granulosa cells from women undergoing in vitro fertilization. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2018, 35, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieg, S.A.; Fan, X.; Hong, Y.; Sang, Q.-X.; Giaccia, A.; Westphal, L.M.; Lathi, R.B.; Krieg, A.J.; Nayak, N.R. Global alteration in gene expression profiles of deciduas from women with idiopathic recurrent pregnancy loss. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 18, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Annotation Cluster 1 | Enrichment Score: 1.95 | |||
| Category | Term | Count | Genes | p-Value |
| KEGG_PATHWAY | oas04660:T cell receptor signaling pathway | 8 | CD3D CD3E CD3G JUN MALT1 CARD11 MAP3K14 PAK6 | 1.35 × 10−5 |
| KEGG_PATHWAY | oas05142:Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis) | 5 | CD3D CD3E CD3G JUN PLCB2 | 0.013 |
| KEGG_PATHWAY | oas05166:HTLV-I infection | 6 | ATM CD3D CD3E CD3G JUN MAP3K14 | 0.072 |
| KEGG_PATHWAY | oas05162:Measles | 4 | CD3D CD3E CD3G ADAR | 0.094 |
| KEGG_PATHWAY | oas04640:Hematopoietic cell lineage | 3 | CD3D CD3E CD3G | 0.157 |
| Annotation Cluster 2 | Enrichment Score: 0.67 | |||
| Category | Term | Count | Genes | p-Value |
| KEGG_PATHWAY | oas04912:GnRH signaling pathway | 3 | JUN ITPR3 PLCB2 | 0.151 |
| KEGG_PATHWAY | oas04915:Estrogen signaling pathway | 3 | JUN ITPR3 PLCB2 | 0.188 |
| KEGG_PATHWAY | oas04921:Oxytocin signaling pathway | 3 | JUN ITPR3 PLCB2 | 0.340 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, Y.; Pan, Z.; Di, R.; Liu, Q.; Hu, W.; Guo, X.; He, X.; Gan, S.; Wang, X.; Chu, M. Whole Genome Sequencing Reveals the Effects of Recent Artificial Selection on Litter Size of Bamei Mutton Sheep. Animals 2021, 11, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010157
Yao Y, Pan Z, Di R, Liu Q, Hu W, Guo X, He X, Gan S, Wang X, Chu M. Whole Genome Sequencing Reveals the Effects of Recent Artificial Selection on Litter Size of Bamei Mutton Sheep. Animals. 2021; 11(1):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010157
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Yaxin, Zhangyuan Pan, Ran Di, Qiuyue Liu, Wenping Hu, Xiaofei Guo, Xiaoyun He, Shangquan Gan, Xiangyu Wang, and Mingxing Chu. 2021. "Whole Genome Sequencing Reveals the Effects of Recent Artificial Selection on Litter Size of Bamei Mutton Sheep" Animals 11, no. 1: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010157
APA StyleYao, Y., Pan, Z., Di, R., Liu, Q., Hu, W., Guo, X., He, X., Gan, S., Wang, X., & Chu, M. (2021). Whole Genome Sequencing Reveals the Effects of Recent Artificial Selection on Litter Size of Bamei Mutton Sheep. Animals, 11(1), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010157






