Equine Milk Production and Valorization of Marginal Areas—A Review
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Equine Milk: Properties, Potentials, and Benefits
2.1. Equine Milk Compositional and Nutritional Features
2.2. Functional and Bioactive Compounds
3. Dairy Equine Management and Nutrition
3.1. Equine Milk Yield and Management of the Dairy Equine Enterprise
3.2. Equine Milk: Hygiene and Health Issues
3.3. Feeding the Dairy Equine and Pasture Management
3.3.1. Feeding the Dairy Horse
3.3.2. Feeding the Dairy Donkey
3.4. Pasture in the Dairy Equine Enterprise
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin-Rosset, W. Research, development and transfer in Equine Science. In EAAP Leroy Fellowship Award, Barcelona, Spain, 24–27 August 2009; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Miraglia, N. Sustainable development and equids in rural areas: An open challenge for the territory cohesion. In EAAP Scientific Series; Vial, C., Evans, R., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 136, pp. 167–176. ISBN 978-90-8686-279-5. [Google Scholar]
- Rzekec, A.; Vial, C.; Bigot, G. Green assets of equines in the european context of the ecological transition of agriculture. Animals 2020, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salimei, E.; Fantuz, F.; Coppola, R.; Chiofalo, B.; Polidori, P.; Varisco, G. Composition and characteristics of ass’s milk. Anim. Res. 2004, 53, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraglia, N.; Saastamoinen, M.; Martin-Rosset, W. Role of pastures in mares and foals management in Europe. In Nutrition and Feeding of the Broodmare; Miraglia, N., Martin-Rosset, W., Eds.; Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 120, pp. 279–297. [Google Scholar]
- Fleurance, G.; Duncan, P.; Mallevaud, B. Daily intake and the selection of feeding sites by horses in heterogeneous wet grasslands. Anim. Res. 2001, 50, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edouard, N.; Fleurance, G.; Martin-Rosset, W.; Duncan, P.; Dulphy, J.P.; Dubroeucq, H.; Grange, E.; Baumont, R.; Perez-Barberia, F.J.; Gordon, I.J. Voluntary intake and digestibility in horses: effect of forage quality with emphasis for individual variability. Animal 2008, 2, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Zijpp, A.; Boyazoglu, J.; Renaud, J.; Hoste, C. Research Strategy for Animal Production in Europe in the 21st Century; Wageningen Press: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1993; Volume 64, p. 163. [Google Scholar]
- Yachi, S.; Loreau, M. Biodiversity and ecosystem productivity in a fluctuating environment: The insurance hypothesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1463–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doreau, M.; Martin-Rosset, W. Animals that produce dairy foods – horse. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences, 2nd ed.; Fuquay, J.W., Fox, P.F., McSweeney, P.L.H., Eds.; Elsevier Academy Press: London, UK, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 358–364. [Google Scholar]
- Salimei, E.; Fantuz, F. Horse and donkey milk. In Milk and Dairy Products in Human Nutrition: Production, Composition and Health; Park, Y.W., Haenlein, G.F.W., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 594–613. [Google Scholar]
- McLean, A.K.; Navas Gonzalez, F.J. Can scientists influence donkey welfare? Historical perspective and a contemporary view. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2018, 65, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, F. The Genuine Works of Hippocrates; The Sydenham Society: London, UK, 1849; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Mustoxidi, A. Le Nove Muse di Erodoto Alicarnasseo, 2nd ed.; Sonzogno Publisher: Milan, Italy, 1822. [Google Scholar]
- Salimei, E.; Park, Y.W. Mare milk. In Handbook of Milk of Non-Bovine Mammals, 2nd ed.; Park, Y.W., Haenlein, G.F.W., Wendorff, W.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 369–408. [Google Scholar]
- Langlois, B. The history, ethnology and social importance of mare’s milk consumption in Central Asia. J. Life Sci. 2011, 5, 863–872. [Google Scholar]
- Bimbetov, B.; Zhangabylov, A.; Aitbaeva, S.; Benberin, V.; Zollmann, H.; Musaev, A.; Rakhimzhanova, M.; Esnazarova, G.; Bakytzhanuly, A.; Malaeva, N. Mare’s milk: Therapeutic and dietary properties. Bull. Natl. Acad. Sci. Rep. Kazakhstan 2019, 3, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romaniuk, K.; Majszyk-Świątek, M.; Kryszak, K.; Danielewicz, A.; Andraszek, K. Alternative use of mare milk. Folia Pomer. Univ. Technol. Stetin. 2019, 348, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, X.; Guo, H. The nutritional ingredients and antioxidant activity of donkey milk and donkey milk powder. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimei, E. Animals that Produce Dairy Foods: Donkey. In Reference Module in Food Sciences, 1st ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: London, UK, 2016; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Drogoul, C.; Prevost, H.; Maubois, J.L. Le lait de juments un produit. Une filiere a developer? In Quoi de Neuf en Matiere d’Etudes de Recherches sur le Cheval, 18eme Journee d’Etude, 4 Mars; CEREOPA: Paris, France, 1992; pp. 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Giacometti, F.; Bardasi, L.; Merialdi, G.; Morbarigazzi, M.; Federici, S.; Piva, S.; Serraino, A. Shelf life of donkey milk subjected to different treatment and storage conditions. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4291–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordonaro, S.; Dimauro, C.; Criscione, A.; Marletta, D.; Macciotta, N.P.P. The mathematical modeling of the lactation curve for dairy traits of the donkey (Equus asinus). J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 4005–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camillo, F.; Rota, A.; Biagini, L.; Tesi, M.; Fanelli, D.; Panzani, D. The current situation and trend of donkey industry in Europe. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2018, 65, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, C.; Paolino, R.; Musto, M.; Freschi, P. Innovative use of jenny milk from sustainable rearing. In The Sustainability of Agro-Food and Natural Resource Systems in the Mediterranean Basin; Vastola, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 113–132. [Google Scholar]
- Uniacke-Lowe, T.; Fox, P.F. Milk, Equid milk. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences, 2nd ed.; Fuquay, J.W., Fox, P.F., McSweeney, P.L.H., Eds.; Elsevier Academy Press: London, UK, 2011; Volume 3, pp. 518–529. [Google Scholar]
- Mansueto, P.; Iacono, G.; Seidita, A.; D’Alcamo, A.; Iacono, S.; Carroccio, A. Ass’s milk in allergy to cow’s milk protein: A review. J. Food Allergy 2012, 1, 181–191. [Google Scholar]
- Fantuz, F.; Salimei, E.; Papademas, P. Macro- and micronutrients in non-cow milk and products and their impact on human health. In Non-Bovine Milk and Milk Products, 1st ed.; Tsakalidou, E., Papadimitriou, K., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: London, UK, 2016; pp. 209–261. [Google Scholar]
- Kaić, A.; Luštrek, B.; Simčič, M.; Potočnik, K. Milk quantity, composition and hygiene traits of routinely machine milked Lipizzan mares. Slov. Vet. Res. 2019, 56, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Aroua, M.; Jemmali, B.; Said, S.B.; Kbaier, H.B.H.; Mahouachi, M. Physicochemical properties of north African donkey milk. Agric. Res. Tech. Open Access J. 2019, 21, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Malacarne, M.; Criscione, A.; Franceschi, P.; Bordonaro, S.; Formaggioni, P.; Marletta, D.; Summer, A. New insights into chemical and mineral composition of donkey milk throughout nine months of lactation. Animals 2019, 9, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantuz, F.; Maglieri, C.; Lebboroni, G.; Salimei, E. Ca, Mg, Zn, Fe, Cu and Mn content of ass’s milk. It. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 8, 703–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantuz, F.; Ferraro, S.; Todini, L.; Piloni, R.; Mariani, P.; Salimei, E. Donkey milk concentration of Calcium, Phosphorus, Potassium, Sodium and Magnesium. Int. Dairy J. 2012, 24, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantuz, F.; Ferraro, S.; Todini, L.; Mariani, P.; Piloni, R.; Salimei, E. Essential trace elements in milk and blood serum of lactating donkeys as affected by lactation stage and dietary supplementation with trace elements. Animal 2013, 7, 1893–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantuz, F.; Ferraro, S.; Todini, L.; Piloni, R.; Mariani, P.; Malissiova, E.; Salimei, E. Minor and potentially toxic trace elements in milk and blood serum of dairy donkeys. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 5125–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieszka, M.; Luszczyński, J.; Zamachowska, M.; Augustyn, R.; Dlugosz, B.; Hędrzak, M. Is mare milk an appropriate food for people?—A review. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2016, 16, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, M.; Altomonte, I.; Licitra, R.; Salari, F. Short communication: Technological and seasonal variations of vitamin D and other nutritional components in donkey milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacono, G.; Carroccio, A.; Cavataio, F.; Montaldo, G.; Soresi, M.; Balsamo, V. Use of ass’s milk in multiple food allergy. J. Ped. Gastroent. Nutr. 1992, 14, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Businco, L.; Giampietro, P.G.; Lucenti, P.; Lucaroni, F.; Pini, C.; Di Felice, G.; Iacovacci, P.; Curadi, C.; Orlandi, M. Allergenicity of mare’s milk in children with cow’s milk allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 105, 1031–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarti, L.; Martini, M.; Brajon, G.; Barni, S.; Salari, F.; Altomonte, I.; Ragona, G.; Mori, F.; Pucci, N.; Muscas, G.; et al. Donkey’s milk in the management of children with cow’s milk protein allergy: nutritional and hygienic aspects. It. J. Ped. 2019, 45, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restani, P.; Ballabio, C.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Tripodi, S.; Fiocchi, A. Molecular aspects of milk allergens and their role in clinical events. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, M.; D’Auria, E.; Caffarelli, C.; Verduci, E.; Barberi, S.; Indinnimeo, L.; Dello Iacono, I.; Martelli, A.; Riva, E.; Bernardini, R. Nutritional management and follow up of infants and children with food allergy: Italian Society of Pediatric Nutrition/Italian Society of Pediatric Allergy and Immunology Task Force Position Statement. It. J. Ped. 2014, 40, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uniacke-Lowe, T.; Huppertz, T.; Fox, P.F. Equine milk proteins: chemistry, structure and nutritional significance. Int. Dairy J. 2010, 20, 609–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunsolo, V.; Saletti, R.; Muccilli, V.; Gallina, S.; Di Francesco, A.; Foti, S. Proteins and bioactive peptides from donkey milk: the molecular basis for its reduced allergenic properties. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieslak, J.; Wodas, L.; Borowska, A.; Sadoch, J.; Pawlak, P.; Puppel, K.; Kuczynska, B.; Mackowski, M. Variability of lysozyme and lactoferrin bioactive protein concentrations in equine milk in relation to LYZ and LTF gene polymorphisms and expression. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2174–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wodas, Ł.; Maćkowski, M.; Borowska, A.; Pawlak, P.; Puppel, K.; Kuczyńska, B.; Czyżak-Runowska, G.; Wójtowski, J.; Cieślak, J. 5’-flanking variants of the equine α-lactalbumin (LALBA) gene–relationship with gene expression and mare’s milk composition. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2018, 27, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieslak, J.; Wodas, L.; Borowska, A.; Pawlak, P.; Czyzak-Runowska, G.; Wojtowski, J.; Puppel, K.; Kuczynska, B.; Mackowski, M. 5’-flanking variants of equine casein genes (CSN1S1, CSN1S2, CSN2,CSN3) and their relationship with gene expression and milk composition. J. Appl. Genet. 2019, 60, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard, O.; Morrow, A.L. Human milk composition: nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 60, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, M.; Delavaud, C.; Laud, K.; Gourdou, I.; Leroux, C.; Djiane, J.; Chilliard, Y. Mammary leptin synthesis, milk leptin and their putative physiological roles. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2002, 42, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglingstad, R.A.; Devold, T.G.; Eriksen, E.K.; Holm, H.; Jacobsen, M.; Liland, K.H.; Rukke, E.O.; Vegarud, G.E. Comparison of the digestion of caseins and whey proteins in equine, bovine, caprine and human milk by human gastrointestinal enzymes. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2010, 90, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidona, F.; Criscione, A.; Devold, T.G.; Bordonaro, S.; Marletta, D.; Vegarud, G.E. Protein composition and micelle size of donkey milk with different protein patterns: Effects on digestibility. Int. Dairy J. 2014, 35, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, M.; Salari, F.; Licitra, R.; La Motta, C.; Altomonte, I. Lysozyme activity in donkey milk. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 96, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yvon, S.; Schwebel, L.; Belahcen, L.; Tormo, H.; Peter, M.; Haimoud-Lekhal, D.A.; Eutamene, H.; Jard, G. Effects of thermized donkey milk with lysozyme activity on altered gut barrier in mice exposed to water-avoidance stress. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 7697–7706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claeys, W.L.; Verraes, C.; Cardoen, S.; De Block, J.; Huyghebaert, A.; Raes, K.; Dewettinck, K.; Herman, L. Consumption of raw or heated milk from different species: an evaluation of the nutritional and potential health benefits. Food Control 2014, 42, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todini, L.; Salimei, E.; Malfatti, A.; Ferraro, S.; Fantuz, F. Thyroid hormones in milk and blood of lactating donkeys as affected by stage of lactation and dietary supplementation with trace elements. J. Dairy Res. 2012, 79, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brumini, D.; Criscione, A.; Bordonaro, S.; Vegarud, G.E.; Marletta, D. Whey proteins and their antimicrobial properties in donkey milk: A brief review. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2016, 96, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotschki, J.; Szyc, A.M.; Laparra, J.M.; Markiewicz, L.H.; Wróblewska, B. Immune-modulating properties of horse milk administered to mice sensitized to cow milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 9395–9404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushugulova, A.; Kozhakhmetov, S.; Sattybayeva, R.; Nurgozhina, A.; Ziyat, A.; Yadav, H.; Marotta, F. Mare’s milk as a prospective functional product. Funct. Food Health Dis. 2018, 8, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspri, M.; Leni, G.; Galaverna, G.; Papademas, P. Bioactive properties of fermented donkey milk, before and after in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth-Walter, F.; Berin, M.C.; Arnaboldi, P.; Escalante, C.R.; Dahan, S.; Rauch, J.; Jensen-Jarolim, E.; Mayer, L. Pasteurization of milk proteins promotes allergic sensitization by enhancing uptake through Peyer’s patches. Allergy 2008, 63, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newburg, D.S.; Walker, W.A. Protection of the neonate by the innate immune system of developing gut and of human milk. Pediatr. Res. 2007, 61, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimei, E.; Fantuz, F. Equid milk for human consumption. Int. Dairy J. 2012, 24, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, M.; Altomonte, I.; Manica, E.; Salari, F. Changes in donkey milk lipids in relation to season and lactation. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 41, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirillo, F.; Magrone, T. Anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic properties of donkey’s and goat’s milk. Endocr. Metab. Immune 2014, 14, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillo, A.; Figliola, L.; Ciliberti, M.G.; Caroprese, M.; Marino, R.; Albenzio, M. Focusing on fatty acid profile in milk from different species after in vitro digestion. J. Dairy Res. 2018, 85, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laiho, K.; Ouwehand, A.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E. Inventing probiotic functional foods for patients with allergic disease. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002, 89, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, E.; Salimei, E.; Succi, M.; Gammariello, D.; Di Criscio, T.; Panfili, G.; Coppola, R. Heat treatment of ass’s milk, a hypoallergenic food for infancy. In Technological Innovation and Enhancement of Marginal Products; Severini, C., DePilli, T., Giuliani, R., Eds.; Claudio Grezi Editore: Foggia, Italy, 2005; pp. 569–574. [Google Scholar]
- Salimei, E. Animals that produce dairy foods – donkey. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences, 2nd ed.; Fuquay, J.W., Fox, P.F., McSweeney, P.L.H., Eds.; Elsevier Academy Press: London, UK, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 365–373. [Google Scholar]
- Dzidic, A.; Knopf, L.; Bruckmaier, R.M. Oxytocin release and milk removal in machine-milked mares. Milchwiss. Milk Sci. Int. 2002, 57, 423–424. [Google Scholar]
- Bat-Oyun, T.; Ito, T.Y.; Purevdorj, Y.; Shinoda, M.; Ishii, S.; Buho, H.; Morinaga, Y. Movements of dams milked for fermented horse milk production in Mongolia. Anim. Sci. J. 2018, 89, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naert, L.; Vandevyvere, B.; Verhoeven, G.; Duchateau, L.; De Smet, S.; Coopman, F. Assessing heterogeneity of the composition of mare’s milk in Flanders. Vlaams Diergenskund. Tijds. 2013, 82, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, F.; Segati, G.; Dalla Costa, E.; Burden, F.; Judge, A.; Minero, M. Management practices and milk production in dairy donkey farms distributed over the italian territory. Mac. Vet. Rev. 2017, 40, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, J.; Jagannathan, V.; Drogenmuller, C.; Rieder, S.; Leeb, T.; Thaller, G.; Tetens, J. Genetic variability of the equine casein genes. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 5486–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayle-Labouré, J. Approche Technico-économique de l’opportunité de Développement d’une Filière “Lait de Jument Comtoise”. Thesis Ingénieure Spécialité Agriculture, Éstablissement National d’Enseignement Supérieur Agronomique de Dijon (ENESAD), Dijon, France, 2007; p. 154. [Google Scholar]
- Mazhitova, A.T.; Kulmyrzaev, A.A.; Ozbekova, Z.E.; Bodoshev, A. Amino acid and fatty acid profile of the mare’s milk produced on Suusamyr pastures of the Kyrgyz Republic during lactation period. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 195, 2683–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Palo, P.; Maggiolino, A.; Albenzio, M.; Caroprese, M.; Centoducati, P.; Tateo, A. Evaluation of different habituation protocols for training dairy jennies to the milking parlor: effect on milk yield, behavior, heart rate and salivary cortisol. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2018, 204, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, F.; Ciampolini, R.; Mariti, C.; Millanta, F.; Altomonte, I.; Licitra, R.; Auzino, B.; D’ Ascenzi, C.; Bibbiani, C.; Giuliotti, L.; et al. A multi-approach study of the performance of dairy donkey during lactation: Preliminary results. It. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 18, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centoducati, P.; Maggiolino, A.; De Palo, P.; Tateo, A. Application of Wood’s model to lactation curve of Italian Heavy Draft horse mares. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 5770–5775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raspa, F.; Cavallarin, L.; McLean, A.K.; Bergero, D.; Valle, E. A review of the appropriate nutrition welfare criteria of dairy donkeys: nutritional requirements, farm management requirements and animal-based indicators. Animals 2019, 9, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Palo, P.; Maggiolino, A.; Centoducati, P.; Calzaretti, G.; Milella, P.; Tateo, A. Equid milk production: evaluation of Martina Franca jennies and IDH mares by Wood’s model application. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2017, 57, 2110–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todini, L.; Salimei, E.; Malfatti, A.; Brunetti, V.L.; Fantuz, F. Thyroid hormones in donkey blood and milk: correlations with milk yield and environmental temperatures. It. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 14, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimbekov, A.R.; Baymukanov, D.A.; Yuldashbaev, Y.A.; Iskhan, K.Z. Productive qualities of the Seleti factory-type Kazakh horse of the toad. Bull. Natl. Acad. Sci. Rep. Kazakhstan 2017, 3, 100–110. [Google Scholar]
- Iskhan, K.Z.; Akimbekov, A.R.; Baimukanov, A.D.; Aubakirov, K.A.; Karynbayev, A.K.; Rzabayev, T.S.; Mukhatai, G.; Dzhunusova, R.Z.; Apeev, K.B. Dairy productivity of the kazakh horse mares and their cross breeds with roadsters. Bull. Natl. Acad. Sci. Rep. Kazakhstan 2019, 3, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhatai, G.G.; Chen, L.; Rugoho, I.; Xiao, G.; Chen, G.; Hodge, S.; Zhou, S. Effect of parity, milking time and stage of lactation on milk yield of Jiangyue donkey (Equus asinus) in North West China. J. Dairy Res. 2017, 84, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minjidgorj, N.; Baldorj, O.; Austbø, D. Chemical composition of Mongolian mare milk. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. A-Anim. Sci. 2012, 62, 66–72. [Google Scholar]
- Proops, L.; Osthaus, B.; Bell, N.; Long, S.; Hayday, K.; Burden, F. Shelter-seeking behavior of donkeys and horses in a temperate climate. J. Vet. Behav. 2019, 32, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colavita, G.; Amadoro, C.; Rossi, F.; Fantuz, F.; Salimei, E. Hygienic characteristics and microbiological hazard identification in horse and donkey raw milk. Vet. It. 2016, 52, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, F.; Dalla Costa, E.; Burden, F.; Judge, A.; Minero, M. The development of guidelines to improve dairy donkey management and welfare. It. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 18, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieslak, J.; Mackowski, M.; Czyzak-Runowska, G.; Wojtowski, J.; Puppel, K.; Kuczynska, B.; Pawlak, P. Screening for the most suitable reference genes for gene expression studies in equine milk somatic cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139688. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J. Nutritional Ecology of the Ruminant, 2nd ed.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA; London, UK, 1994; p. 476. [Google Scholar]
- Cavallarin, L.; Giribaldi, M.; Soto-Del Rio, M.D.; Valle, E.; Barbarino, G.; Gennero, M.S.; Civera, T. A survey on the milk chemical and microbiological quality in dairy donkey farms located in NorthWestern Italy. Food Control 2015, 50, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimei, E.; Malissiova, E.; Papademas, P.; Colavita, G.; Galaverna, G.; Fletouris, D.; Manouras, A.; Habib, I.; Šarić, L.; Budak, S.O.; et al. Donkey milk and dairy donkey farming in Mediterranean Countries: current situation, challenges and prospects. In Proceedings of the 7th IDF International Symposium on Sheep, Goat and Other Non-Cow Milk, Limassol, Cyprus, 23–25 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- INRA. Equine Nutrition. INRA Nutrient Requirements, Recommended Allowances and Feed Tables; Martin-Rosset, W., Ed.; Wageningen Academic Press: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2015; p. 691. [Google Scholar]
- Miraglia, N.; Burger, D.; Kapron, M.; Flanagan, J.; Langlois, B.; Martin-Rosset, W. Local animal resources and products in sustainable development: Role and potential of equids. In Product Quality Based on Local Resources Leading to Improve Sustainability; Rubino, R., Sepe, L., Dimitriadou, A., Gibon, A., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 217–233. [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Rosset, W.; Trillaud-Geyl, C.; Jussiaux, M.; Agabriel, J.; Loiseau, P.; Beranger, C. Exploitation du pâturage par le cheval en croissance ou à l’engrais. In Le Cheval. Reproduction, sélection, Alimentation, Exploitation; Jarrige, R., Martin-Rosset, W., Eds.; INRA: Paris, France, 1984; pp. 583–599. [Google Scholar]
- Moulin, C. Le pâturage du cheval: questions posées par les pratiques d’éleveurs. (Grazing by horses: From farm practices to technical questions). Fourrages 1997, 149, 37–54. [Google Scholar]
- Burden, F.; Thiemann, A. Donkeys Are Different. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2015, 35, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Rosset, W. Donkey nutrition and feeding: Nutrient requirements and recommended allowances—A review and prospect. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2018, 65, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burden, F.A.; Bell, N. Donkey nutrition and malnutrition. Vet. Clin. Equine 2019, 35, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRC. Donkeys and other equids. In Nutrient Requirements of Horses, 6th ed.; National Research Council, Ed.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; pp. 268–279. [Google Scholar]
- Couto, M.; Santos, A.S.; Laborda, J.; Nóvoa, M.; Ferreira, L.M.; Madeira de Carvalho, L.M. Grazing behavior of Miranda donkeys in a natural mountain pasture and parasitic level changes. Livest. Sci. 2016, 186, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.J.; Smith, D.G.; Morriss, C.J.; Oliver, J.; Cuddeford, D. The effect of pasture restriction on dry matter intake of foraging donkeys in the United Kingdom. In Forages and Grazing in Horse Nutrition; Saastamoinen, M., Fradinho, M.J., Santos, A.S., Miraglia, N., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 163–176. [Google Scholar]
- Kouba, J.M.; Burns, T.A.; Webel, S.K. Effect of dietary supplementation with long-chain n-3 fatty acids during late gestation and early lactation on mare and foal plasma fatty acid composition, milk fatty acid composition, and mare reproductive variables. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2019, 203, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Palo, P.; Maggiolino, A.; Milella, P.; Centoducati, N.; Papaleo, A.; Tateo, A. Artificial suckling in Martina Franca donkey foals: effect on in vivo performances and carcass composition. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2016, 48, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awin Welfare Assessment Protocol for Donkeys, University of Milan (Italy) and Donkey Sanctuary (UK). Available online: https://air.unimi.it/retrieve/handle/2434/269100/384805/AWINProtocolDonkeys.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2019).
- Micol, D.; Martin-Rosset, W. Feeding systems for horses on high forage diets in the temperate zone. In Recent Developments in the Nutrition of Herbivores; Journet, M., Grenet, E., Farce, M.-H., Thériez, M., Demarquilly, C., Eds.; INRA Editions: Paris, France, 1995; pp. 569–584. [Google Scholar]
- Fatica, A.; Circelli, L.; DiIorio, E.; Colombo, C.; Crawford, T.W.; Salimei, E. Stresses in pasture areas in South-Central Apennines, Italy, and evolution at landscape level. In Handbook of Plant & Crop Stress, 4th ed.; Pessarakli, M., Ed.; CRC Press Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 271–291. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, L.M.M.; Celaya, R.; Benavides, R.; Jáuregui, B.M.; García, U.; Santos, A.S.; García, R.R.; Rodrigues, M.A.M.; Osoro, K. Foraging behavior of domestic herbivore species grazing on heathlands associated with improved pasture areas. Livest. Sci. 2013, 155, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doreau, M.; Moretti, C.; Martin-Rosset, W. Effect of quality of hay given to mares around foaling on their voluntary intake and foal growth. Ann. Zootech. 1990, 39, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, P. Horses and Grasses: The Nutritional Ecology of Equids and Their Impact on the Camargue; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992; p. 287. [Google Scholar]
- Parrini, S. Caratterizzazione nutrizionale delle erbe dei pascoli naturali e impiego di metodi di valutazione innovativi. Ph.D. Thesis (28th cycle), Università degli Studi di Firenze, Florence, Italy, December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hristov, A.N.; Degaetano, A.T.; Rotz, C.A.; Hoberg, E.; Skinner, R.H.; Felix, T.; Li, H.; Patterson, P.H.; Roth, G.; Hall, M.; et al. Climate change effects on livestock in the Northeast US and strategies for adaptation. Clim. Chang. 2018, 146, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulina, G.; Salimei, E.; Masala, G.; Sikosana, J. A computerised spreadsheet model for the assessment of sustainable stocking rate in semiarid and subhumid regions. Livest. Prod. Sci. 1999, 61, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraglia, N.; Polidori, M.; Salimei, E. A review on feeding strategies, feeds and management of equines in Central-Southern Italy. In Working Animals in Agriculture and Transport; Pearson, R.A., Lhoste, P., Saastamoinen, M., Martin-Rosset, W., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Dumont, B.; Rook, A.J.; Coran, C.; Rover, K.U. Effects of livestock breed and grazing intensity on biodiversity and production in grazing systems. 2. Diet selection. Grass and Forage Sci. 2007, 62, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, B.; Garel, J.P.; Ginane, C.; Decuq, F.; Farruggia, A.; Pradel, P.; Rigolot, C.; Petit, M. Effect of cattle grazing a species-rich mountain pasture under different stocking rates on the dynamics of diet selection and sward structure. Animal 2007, 1, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bele, B.; Norderhaug, A.; Sickel, H. Localized agri-food systems and biodiversity. Agriculture 2018, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
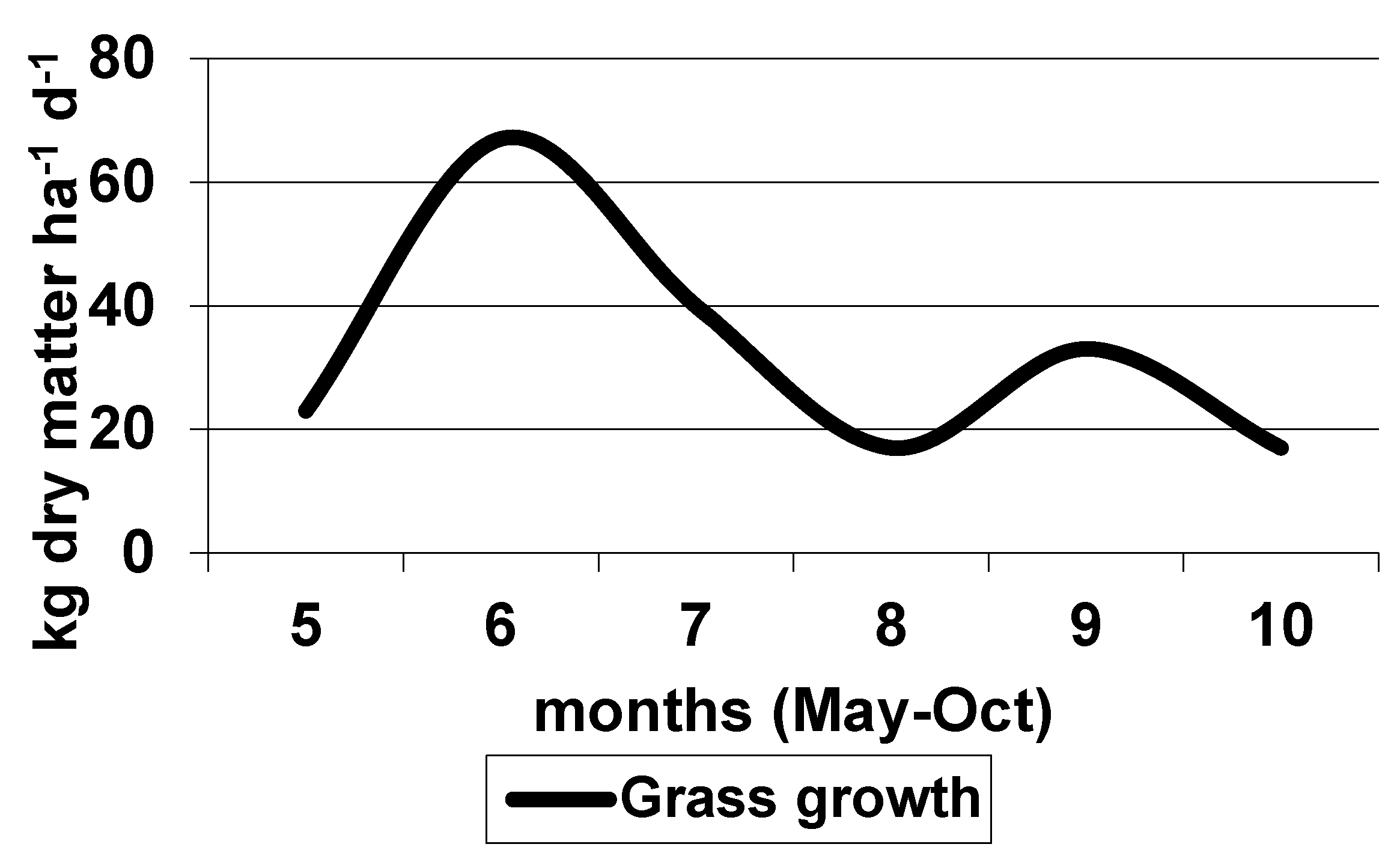
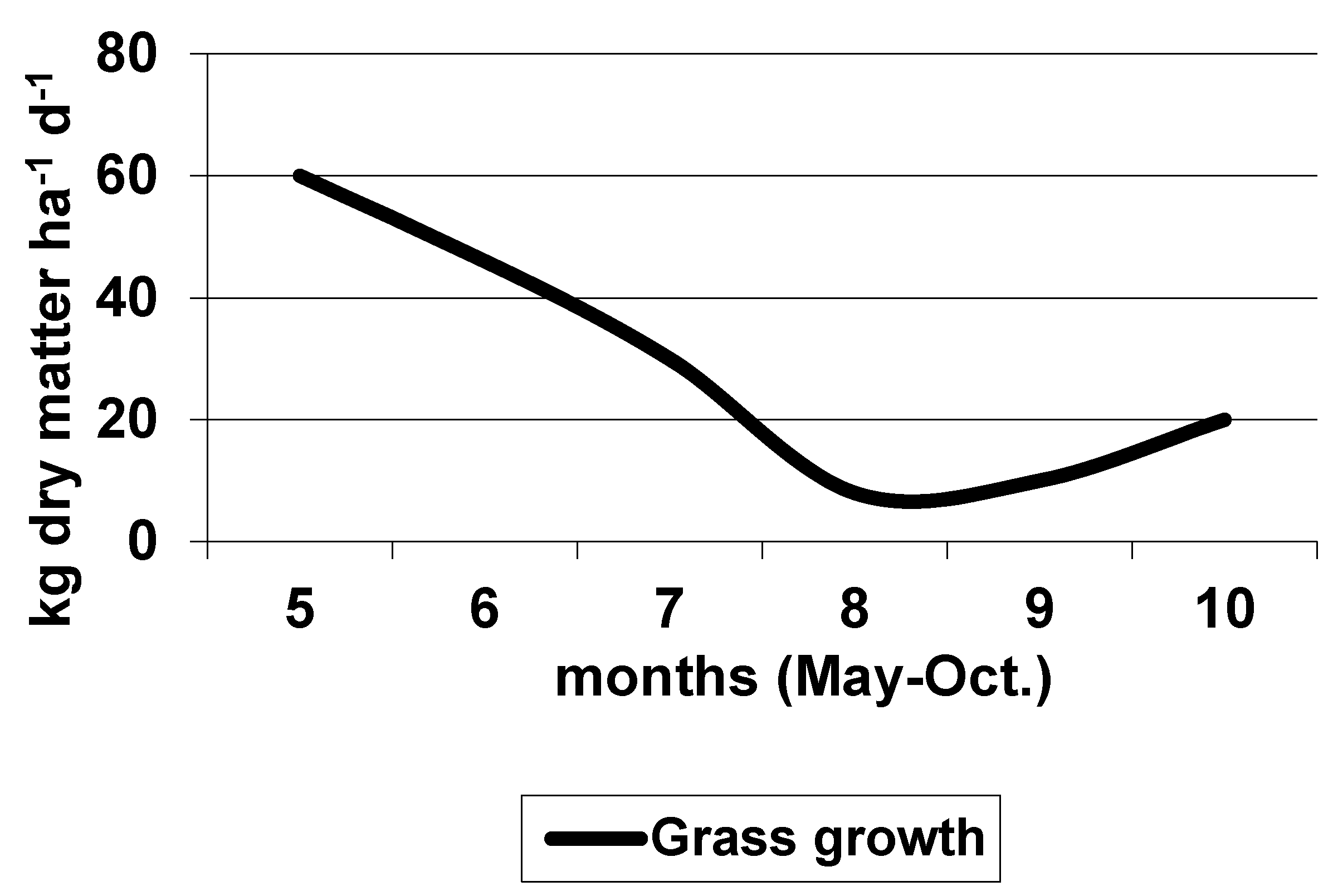
| Item | Horse | Donkey | Human | Cow |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total solids, g kg−1 | 103.1 | 95.3 | 125 | 127 |
| Fat, g kg−1 | 10.3 | 7 | 35 | 41 |
| Protein, g kg−1 | 16.8 | 16 | 12 | 34 |
| Lactose, g kg−1 | 63 | 66 | 64 | 48 |
| Ash, g kg−1 | 4.2 | 4.1 | 1.9 | 7 |
| Gross energy, MJ kg−1 | 1.98 | 1.75 | 2.69 | 3.19 |
| Item | Horse | Donkey |
|---|---|---|
| Mean value | 11.66 | 2.68 |
| s.d.2 | 5.3 | 1.96 |
| Min | 3.9 | 0.72 |
| Max | 17.2 | 6 |
| Lactation, Month | Milk Yield, kg d−1 | Horse Feed Units *, n d−1 | Horse Digestible Crude Protein **, g d−1 | Dry Matter Intake, kg d−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 18 | 10.1 | 1131 | 13.5–18.0 |
| 2nd | 19.8 | 10.3 | 1091 | 15.0–19.0 |
| 3rd | 19.2 | 9.6 | 1030 | 15.0–19.0 |
| 4th | 17.4 | 9.1 | 844 | 13.5–18.0 |
| 5th | 13.2 | 7.9 | 629 | 12.5–15.0 |
| 6th | 12 | 7.6 | 603 | 10.5–13.0 |
| Body Weight, kg | Gain, g d−1 | Horse Feed Units *, n d−1 | Horse Digestible Crude Protein **, g d−1 | Dry Matter Intake, kg d−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 249 | 1000–1200 | 6 | 647 | 6.0–8.0 |
| 207 | 800–900 | 4.8 | 497 | 5.5–7.5 |
| Country | Crude Protein, g kg−1 | Crude Fiber, g kg−1 | Horse Feed Units *, n kg−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Finland | 200–230 | 180–200 | 0.69–0.73 |
| France, lowlands | 131–168 | 244–276 | 0.76–0.82 |
| France, uplands | 111–166 | 223–304 | 0.66–0.92 |
| Italy, lowlands | 85–159 | 242–325 | 0.67–0.90 |
| Italy, uplands | 117–155 | 285–345 | 0.63–0.85 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miraglia, N.; Salimei, E.; Fantuz, F. Equine Milk Production and Valorization of Marginal Areas—A Review. Animals 2020, 10, 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10020353
Miraglia N, Salimei E, Fantuz F. Equine Milk Production and Valorization of Marginal Areas—A Review. Animals. 2020; 10(2):353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10020353
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiraglia, Nicoletta, Elisabetta Salimei, and Francesco Fantuz. 2020. "Equine Milk Production and Valorization of Marginal Areas—A Review" Animals 10, no. 2: 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10020353
APA StyleMiraglia, N., Salimei, E., & Fantuz, F. (2020). Equine Milk Production and Valorization of Marginal Areas—A Review. Animals, 10(2), 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10020353





