Using Time Lapse Monitoring for Determination of Morphological Defect Frequency in Feline Embryos after in Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Collection of Ovaries
2.2. Collection and Classification of Oocytes
2.3. In Vitro Maturation of Oocytes (IVM)
2.4. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
2.5. In Vitro Culture (IVC) of Embryos in the Time-Lapse System
2.6. Analysis of Frequency of Embryo Characteristics
- Presence of a blastocyst cavity.
- Hatching rate (%).
- Normal morphology (regular blastomeres and absence of morphological defects).
- Presence of two or more morphological defects.
- Presence of one morphological defect.
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IVF | in vitro fertilization |
| TLM | time lapse monitoring |
| COC’s | cumulus-oocyte complexes |
| IVM | in vitro maturation |
| IVC | in vitro culture |
| ART | assisted reproductive techniques |
References
- Hardy, K. Cell death in the mammalian blastocyst. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 1997, 3, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fragouli, E.; Alfarawati, S.; Spath, K.; Wells, D. Morphological and cytogenetics assessment of cleavage and blastocyst stage embryos. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2014, 20, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magata, F.; Ideta, A.; Okubo, H.; Matsuda, F.; Urakawa, M.; Oono, Y. Growth potential of bovine embryos presenting abnormal cleavage observed through time lapse cinematography. Theriogenology 2019, 133, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziebe, S.; Petersen, K.; Lindenberg, S.; Andersen, A.G.; Gabrielsen, A.; Andersen, A.N.; Petersen, K.; Lindenberg, S. Embryo morphology or cleavage stage: How to select the best embryos for transfer after in-vitro fertilization. Hum. Reprod. 1997, 12, 1545–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.C.; Loewke, K.E.; Bossert, N.L.; Behr, B.; De Jonge, C.J.; Baer, T.M.; Reijro Pera, R.A. Non-invasive imaging of human embryos before embryonic genome activation predicts development of the blastocyst stage. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, T.; Moser, M.; Tews, G. Is oocyte morphology prognostic of embryo developmental potential after ICSI? Reprod. Biomed. Online 2006, 12, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meseguer, M.; Herrero, J.; Tejera, A.; Hilligsoe, K.M.; Ramsing, N.B.; Remohi, J. The use of morphokinetics as a predictor of embryo implantation. Hum. Reprod. 2011, 26, 2658–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, T.; Yaman, C.; Moser, M.; Sommergruber, M.; Polz, W.; Tews, G. Embryo fragmentation in vitro and its impact on treatment and pregnancy outcome. Fertil. Steril. 2001, 76, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kola, I.; Trounson, A.; Dawson, G.; Rogers, P. Tripronuclear human oocytes: Altered cleavage patterns and subsequent karyotypic analysis of embryos. Biol. Reprod. 1987, 37, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmen, J.G.; Agerholm, I.; Ziebe, S. Kinetic markers of human embryo quality using time-lapse system recordings of IVF/ICSI-fertilized oocytes. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2008, 17, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, I.; Kuhlmann, R.; Agerholm, I.; Kirk, J.; Herrero, J.; Escriba, M.J.; Bellver, J.; Meseguer, M. Limited implantation success of direct-cleaved human zygotes: A time-lapse study. Fertil. Steril. 2012, 98, 1458–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fancsovits, P.; Tóthne, G.Z.; Murber, A.; Takacs, F.Z.; Papp, Z.; Urbansek, J. Correlation between first polar body morphology and further embryo development. Acta Biol. Hung. 2006, 57, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rienzi, L.; Ubaldi, F.M.; Lacobelli, M.; Minasi, M.G.; Romano, S.; Ferrero, S.; Sapienza, F.; Baroni, E.; Litwicka, K.; Greco, E. Significance of metaphase II human oocyte morphology on ICSI outcome. Fertil. Steril. 2008, 90, 1692–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochota, M.; Niżański, W. Time of early cleavage affects the developmental potential of feline preimplantation embryos in vitro. Theriogenology 2017, 89, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwa, K.; Ohara, K.; Hosoi, Y.; Iritani, A. Early events of in-vitro fertilization of cat eggs by epididymal spermatozoa. Reproduction 1985, 74, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameel, T. Sperm swim-up: A simple and effective technique of semen processing for intrauterine insemination. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2018, 58, 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Klinkumhom, N.; Techakumphu, M.; Chatdarong, K. Time of first embryonic cleavage indicates cat blastocyst quality. Thai J. Vet. Med. 2012, 42, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Somfai, T.; Inaba, Y.; Aikawa, Y.; Ohtake, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Konishi, K.; Imai, K. Relationship between the length of cell cycles, cleavage pattern and developmental competence in bovine embryos generated by in vitro fertilization or parthenogenesis. J. Reprod. Dev. 2010, 56, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathananthan, A.H. Paternal centrosomal dynamics in early human development and infertility. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 1998, 15, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikani, M.; Cohen, J.; Tomkin, G.; Garrisi, J.; Mack, C.; Scott, R.T. Human embryo fragmentation and its implications for pregnancy and implantation. Fetil. Steril. 1999, 71, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halvaei, I.; Ali Khalili, M.; Esfandiari, N.; Safari, S.; Talebi, A.R.; Miglietta, S.; Nottola, S.A. Ultrastructure of cytoplasmic fragments in human cleavage stage embryos. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2016, 33, 1677–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munne, S.; Cohen, J. Chromosome abnormalities in human embryos. Hum. Reprod. Update 1998, 4, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandalinas, M.; Sadowy, S.; Alikani, M.; Calderon, G.; Cohen, J.; Munne, S. Developmental ability of chromosomally abnormal human embryos to develop to the blastocyst stage. Hum. Reprod. 2001, 16, 1954–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, C.M.; Cao, W.; Exley, G.E.; McElhinny, A.S.; Alikani, M.; Cohen, J.; Scot, R.T.; Brenner, C.A. Genetic regulation of egg and embryo survival. Hum. Reprod. 1998, 13, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathananthan, A.H.; Wood, C.; Leeton, J. Ultrastructural evaluation of 8-16 cell human embryos developed in vitro. Micron 1982, 13, 193–203. [Google Scholar]
- Van Blerkom, J. Occurrence and developmental consequences of aberrant cellular organization in meiotically mature human oocytes after exogenous ovarian hyperstimulation. J. Electron Microsc. Tech. 1990, 16, 324–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, T.; Moser, M.; Sommergruber, M.; Gaiswinkler, U.; Shebl, O.; Jesacher, K.; Tews, G. Occurrence and developmental consequences of vacuoles throughout preimplantation development. Fertil. Steril. 2005, 83, 1635–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Stadium of Development | Embryo Development | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Direct Cleavage | Fragmentation of Cytoplasm | Cytoplasmic Vacuoles | |
| Zygote |  | 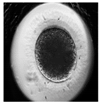 | 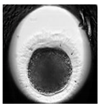 | 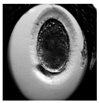 |
| First cleavage | 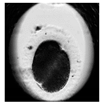 | 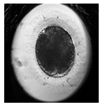 | 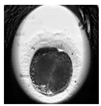 | 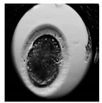 |
| Morula | 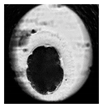 | 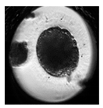 | 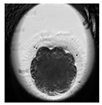 | 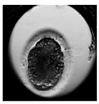 |
| Blastocyst |  | 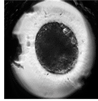 | 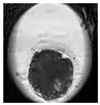 |  |
| Expanded blastocyst | 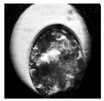 | 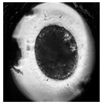 |  | 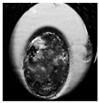 |
| Normal | Multi | Single | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of cleavage embryos | 41 | 25 | 10 |
| Number of blastocysts | 15 | 11 | 6 |
| Hatching rate (%) | 62.0 | 13.2 | 24.8 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kij, B.; Kochan, J.; Nowak, A.; Niżański, W.; Prochowska, S.; Fryc, K.; Bugno-Poniewierska, M. Using Time Lapse Monitoring for Determination of Morphological Defect Frequency in Feline Embryos after in Vitro Fertilization (IVF). Animals 2020, 10, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10010003
Kij B, Kochan J, Nowak A, Niżański W, Prochowska S, Fryc K, Bugno-Poniewierska M. Using Time Lapse Monitoring for Determination of Morphological Defect Frequency in Feline Embryos after in Vitro Fertilization (IVF). Animals. 2020; 10(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleKij, Barbara, Joanna Kochan, Agnieszka Nowak, Wojciech Niżański, Sylwia Prochowska, Karolina Fryc, and Monika Bugno-Poniewierska. 2020. "Using Time Lapse Monitoring for Determination of Morphological Defect Frequency in Feline Embryos after in Vitro Fertilization (IVF)" Animals 10, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10010003
APA StyleKij, B., Kochan, J., Nowak, A., Niżański, W., Prochowska, S., Fryc, K., & Bugno-Poniewierska, M. (2020). Using Time Lapse Monitoring for Determination of Morphological Defect Frequency in Feline Embryos after in Vitro Fertilization (IVF). Animals, 10(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10010003







