The Intestinal Bacterial Community and Functional Potential of Litopenaeus vannamei in the Coastal Areas of China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. L. vannamei Procurement and Intestinal Sample Collection
2.2. L. vannamei Intestinal DNA Extraction
2.3. 16S rRNA Gene Amplification, Illumina Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
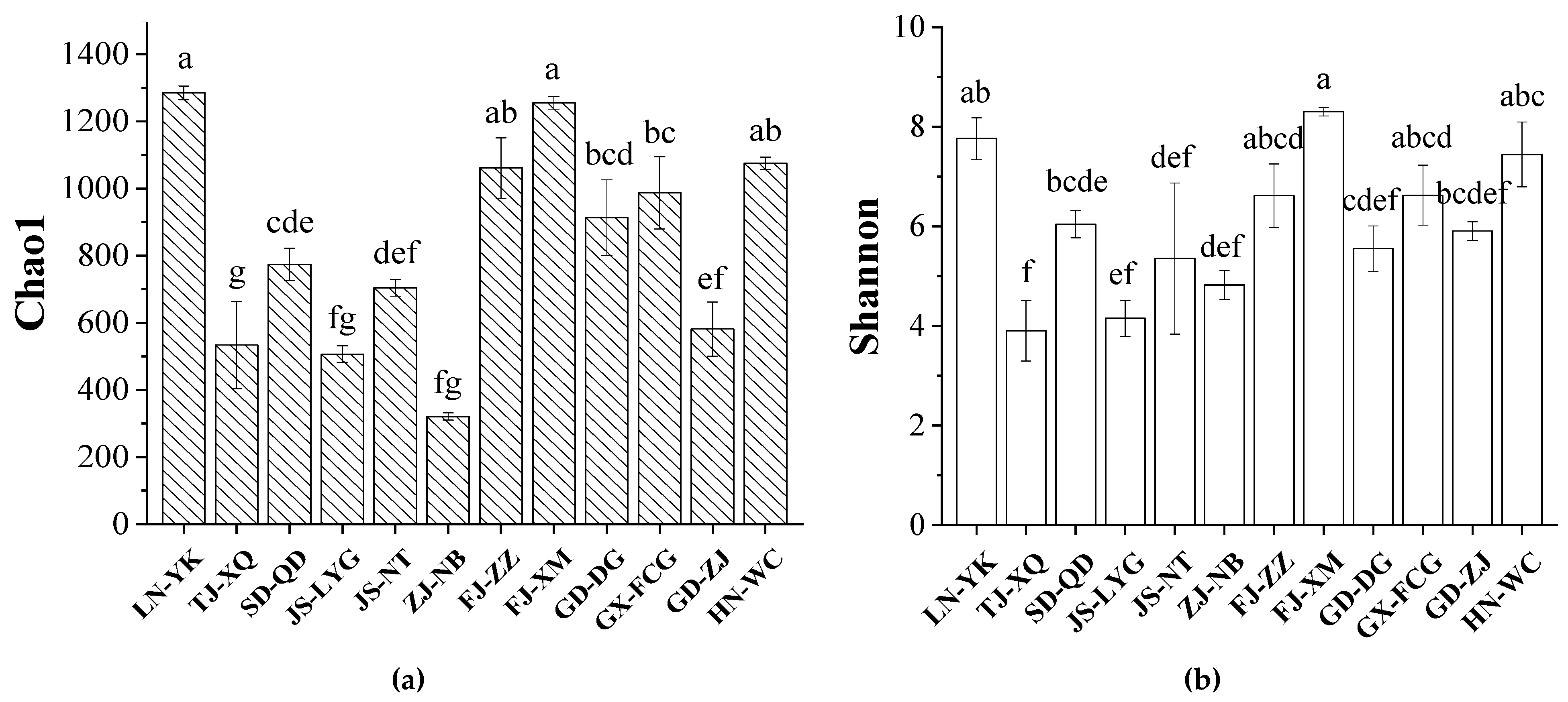
3.1. Diversity of the Intestinal Bacterial Community of L. vannamei from Different Regions
3.2. Composition of the Intestinal Bacterial Community of L. vannamei from Different Regions
3.2.1. Composition of the Gut Microbiota
3.2.2. Potential Pathogen and Spoilage Organisms in the Intestine of L. vannamei
3.3. Prediction of Gut Microbial Functions
3.4. Correlation of Intestinal Bacteria and the Predicted Functional Profile
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shiekh, K.A.; Benjakul, S. Melanosis and quality changes during refrigerated storage of Pacific white shrimp treated with Chamuang (Garcinia cowa Roxb.) leaf extract with the aid of pulsed electric field. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightner, D.; Redman, R.; Pantoja, C.; Tang, K.; Noble, B.; Schofield, P.; Mohney, L.; Nunan, L.; Navarro, S. Historic emergence, impact and current status of shrimp pathogens in the Americas. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 110, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapsell, L.C.; Neale, E.P.; Satija, A.; Hu, F.B. Foods, Nutrients, and Dietary Patterns: Interconnections and Implications for Dietary Guidelines. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhu, T.; Jin, M.; Jiao, L.; Sun, P.; Ward, T.L.; Ji, F.; Xu, G.; Zhou, Q. Alteration of growth performance, meat quality, antioxidant and immune capacity of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei in response to different dietary dosage forms of zinc: Comparative advantages of zinc amino acid complex. Aquaculture 2020, 522, 735120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Fu, Z.; Huang, M.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Qin, J.G.; Chen, L.; Han, F.; Li, E. Growth, physiological, biochemical, and molecular responses of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei fed different levels of dietary selenium. Aquaculture 2021, 535, 736393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.J.; Lotz, J.M. Comparing salinities of 10, 20, and 30‰ in intensive, commercial-scale biofloc shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) production systems. Aquaculture 2017, 476, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Li, N.; Dong, T.; Fu, Q.; Cui, Y.; Li, Y. Analysis of differential gene expression in Litopenaeus vannamei under High salinity stress. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 18, 100423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuy, H.T.T.; Nga, L.P.; Loan, T.T.C. Antibiotic contaminants in coastal wetlands from Vietnamese shrimp farming. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, D.G.; Weston, D.P.; Miller, V.; Shoemaker, C. Antibacterial residues in marine sediments and invertebrates following chemotherapy in aquaculture. Aquaculture 1996, 145, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.-R.; Liu, S.-S.; Zhou, G.; Sun, K.-F.; Zhao, J.-L.; Ying, G.-G. Antibiotics in typical marine aquaculture farms surrounding Hailing Island, South China: Occurrence, bioaccumulation and human dietary exposure. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 90, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleder, D.D.; Peruch, L.G.B.; Poli, M.A.; Ferreira, T.H.; Silva, C.; Andreatta, E.R.; Hayashi, L.; Vieira, F.D.N. Effect of brown seaweeds on Pacific white shrimp growth performance, gut morphology, digestive enzymes activity and resistance to white spot virus. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, G.S.; Priyadharshini, S.; Sajayyan, A.; Ravindran, A.; Priyadharshini, G.B.; Ramesh, U.; Suarez, L.E.C.; Selvin, J. Dietary administration of gelatinised polyhydroxybutyrate to Penaeus vannamei improved growth performance and enhanced immune response against Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Aquaculture 2020, 517, 734773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Protective effectiveness of feeding phage cocktails in controlling Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.-F.; Guo, H.; Li, G.-L.; Zhu, C.-H. Effects of dietary hydrolyzable tannins on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, intestinal microflora and resistance against Vibrio parahaemolyticus of juvenile Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931). Aquac. Rep. 2021, 19, 100601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.-L.; Ruan, Y.-H.; Li, Y.-C.; Hsieh, P.-S.; Hu, C.-H.; Kuo, C.-M. Immune and physiological responses in Pacific white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) to Vibrio alginolyticus. Aquaculture 2008, 275, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungrassamee, W.; Kingcha, Y.; Srimarut, Y.; Maibunkaew, S.; Karoonuthaisiri, N.; Visessanguan, W. Mannooligosaccharides from copra meal improves survival of the Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) after exposure to Vibrio harveyi. Aquaculture 2014, 434, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndraha, N.; Sung, W.-C.; Hsiao, H.-I. Evaluation of the cold chain management options to preserve the shelf life of frozen shrimps: A case study in the home delivery services in Taiwan. J. Food Eng. 2019, 242, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeshina, I.; Adetunji Adewale, Y.; Oloyede Tiamiyu, L.; Modupeola Ajibola, M.; Babatunde Dauda, A. Gut Microbiota and Innate Immune Response of Macrobrachium vollenhovenii Infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Aeromonas hydrophila Fed Diets Supplemented with Lactobacillus acidophilus. In Aquaculture—Plants and Invertebrates; InechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Liu, G.; Li, F. Characterization of two pathogenic Photobacterium strains isolated from Exopalaemon carinicauda causing mortality of shrimp. Aquaculture 2016, 464, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thitamadee, S.; Prachumwat, A.; Srisala, J.; Jaroenlak, P.; Salachan, P.V.; Sritunyalucksana, K.; Flegel, T.W.; Itsathitphaisarn, O. Review of current disease threats for cultivated penaeid shrimp in Asia. Aquaculture 2016, 452, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Pena, L.D.; Lavilla-Pitogo, C.R.; Villar, C.B.R.; Paner, M.G.; Capulos, G.C. Prevalence of monodon baculovirus (MBV) in wild shrimp Penaeus monodon in the Philippines. Aquaculture 2008, 285, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangnonngiw, W.; Laisutisan, K.; Sriurairatana, S.; Senapin, S.; Chuchird, N.; Limsuwan, C.; Chaivisuthangkura, P.; Flegel, T.W. Monodon baculovirus (MBV) infects the freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii cultivated in Thailand. Virus Res. 2010, 148, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senapin, S.; Phiwsaiya, K.; Anantasomboon, G.; Sriphaijit, T.; Browdy, C.L.; Flegel, T.W. Knocking down a Taura syndrome virus (TSV) binding protein Lamr is lethal for the whiteleg shrimp Penaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2010, 29, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madan, N.; Raj, N.S.; Farook, M.; Vimal, S.; Venkatesan, C.; Majeed, S.A.; Nambi, K.; Hameed, A.S. Partial cloning and production of polyclonal antiserum against recombinant capsid protein of Hepatopancreatic Parvovirus (HPV) and its application for diagnostics in penaeid shrimp. Process. Biochem. 2013, 48, 1893–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, H.; Gao, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, N.; Miao, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. The pathogenicity characterization of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae and its activation on immune system in freshwater shrimp Macrobrachium nipponense. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 87, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, Y.; Yokoyama, M.; Satomi, M.; Oikawa, H.; Chen, S.-S. Occurrence of Vibrio vulnificus in Fish and Shellfish Available from Markets in China. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, S.; Otta, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Karunasagar, I.; Nishibuchi, M.; Karunasagar, I. The occurrence of Vibrio species in tropical shrimp culture environments; implications for food safety. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 102, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, M.A.; Thompson, C.C.; Freitas, F.S.; Fonseca, E.L.; Aboderin, A.; Zailani, S.B.; Quartey, N.K.E.; Okeke, I.; Vicente, A.C.P. Cholera Outbreaks in Nigeria Are Associated with Multidrug Resistant Atypical El Tor and Non-O1/Non-O139 Vibrio cholerae. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Ghosh, K.; Raychoudhuri, A.; Chowdhury, G.; Bhattacharya, M.K.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Ramamurthy, T.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Klose, K.E.; Nandy, R.K. Incidence, Virulence Factors, and Clonality among Clinical Strains of Non-O1, Non-O139 Vibrio cholerae Isolates from Hospitalized Diarrheal Patients in Kolkata, India. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dutta, D.; Chowdhury, G.; Pazhani, G.P.; Guin, S.; Dutta, S.; Ghosh, S.; Rajendran, K.; Nandy, R.K.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Bhattacharya, M.K.; et al. Vibrio cholerae Non-O1, Non-O139 Serogroups and Cholera-like Diarrhea, Kolkata, India. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zeng, S.; Hou, D.; Liu, J.; Weng, S.; He, J.; Huang, Z. Occurrence of human pathogenic bacteria carrying antibiotic resistance genes revealed by metagenomic approach: A case study from an aquatic environment. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 80, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letchumanan, V.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.-H. Vibrio parahaemolyticus: A review on the pathogenesis, prevalence, and advance molecular identification techniques. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Stombaugh, J.; Gordon, J.I.; Jansson, J.; Knight, R. Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 489, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, D.; An, X.-L.; Chen, Q.-L.; Yang, X.-R.; Christie, P.; Ke, X.; Wu, L.-H.; Zhu, Y.-G. Antibiotics Disturb the Microbiome and Increase the Incidence of Resistance Genes in the Gut of a Common Soil Collembolan. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3081–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorokhova, E.; Rivetti, C.; Furuhagen, S.; Edlund, A.; Ek, K.; Breitholtz, M. Bacteria-Mediated Effects of Antibiotics on Daphnia Nutrition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5779–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yao, H.; Chapman, S.J.; Su, J.; Wang, C. Changes in gut bacterial communities and the incidence of antibiotic resistance genes during degradation of antibiotics by black soldier fly larvae. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, M.; Bruno, D.; Caccia, S.; Sgambetterra, G.; Cappellozza, S.; Jucker, C.; Tettamanti, G.; Casartelli, M. Structural and Functional Characterization of Hermetia illucens Larval Midgut. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynants, E.; Frooninckx, L.; Van Miert, S.; Geeraerd, A.; Claes, J.; Van Campenhout, L. Risks related to the presence of Salmonella sp. during rearing of mealworms (Tenebrio molitor) for food or feed: Survival in the substrate and transmission to the larvae. Food Control. 2019, 100, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Yao, H.; Chapman, S.J. Pretreatment is an important method for increasing the conversion efficiency of rice straw by black soldier fly larvae based on the function of gut microorganisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 144118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, C.L.; Elson, C.O.; Hatton, R.; Weaver, C.T. Reciprocal interactions of the intestinal microbiota and immune system. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 489, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drew, G.C.; Stevens, E.J.; King, K.C. Microbial evolution and transitions along the parasite–mutualist continuum. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yao, H.; Wang, C. Black Soldier Fly Larvae Can Effectively Degrade Oxytetracycline Bacterial Residue by Means of the Gut Bacterial Community. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.O.; Mahboob, S.; Viayaraghavan, P.; Biji, D.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Al-Misned, F.; Ahmed, Z.; Kwon, J.-T.; Na, S.W.; Kim, H.-J. Growth promoting activity of Penaeus indicus by secondary metabolite producing probiotic bacterium Bacillus subtilis isolated from the shrimp gut. J. King Saud Univ.Sci. 2020, 32, 1641–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, C.J. The Rasputin Effect: When Commensals and Symbionts Become Parasitic. In Advances in Environmental Microbiology; Springer: Berelin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Zheng, C.; Zheng, Z.; Wei, Y.; Lu, K.; Zhu, J. Nutrient enrichment during shrimp cultivation alters bacterioplankton assemblies and destroys community stability. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 156, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sun, Y.; Chen, K.; Yu, N.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, L.; Du, Z.; Li, E. Characterization of the intestinal microbiota in Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, fed diets with different lipid sources. Aquaculture 2014, 434, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, A.; Stephens, W.Z.; Stagaman, K.; Wong, S.; Rawls, J.; Guillemin, K.; Bohannan, B.J. Contribution of neutral processes to the assembly of gut microbial communities in the zebrafish over host development. ISME J. 2016, 10, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Q.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; He, Z.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Kempher, M.L.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Liao, L.; et al. Environmental filtering decreases with fish development for the assembly of gut microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 4739–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Li, M.; Leng, X.; Wen, H.; Wu, F.; Yu, L.; Jiang, M.; Lu, X.; Gao, W.; Zhang, W.; et al. Creatine improves the flesh quality of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) reared in freshwater. Food Chem. 2021, 354, 129498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilotto, M.R.; Goncalves, A.N.A.; Vieira, F.N.; Seifert, W.Q.; Bachère, E.; Rosa, R.D.; Perazzolo, L.M. Exploring the Impact of the Biofloc Rearing System and an Oral WSSV Challenge on the Intestinal Bacteriome of Litopenaeus vannamei. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akbary, P.; Adeshina, I.; Jahanbakhshi, A. Growth performance, digestive enzymes, antioxidant activity and immune responses of Litopenaeus vannamei fed with Jania adhaerens J.V. Supplemented diet against Photobacterium damselae infection. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2020, 270, 114696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo-Granados, F.; Lopez-Zavala, A.A.; Gallardo-Becerra, L.; Mendoza-Vargas, A.; Sánchez, F.; Vichido, R.; Brieba, L.G.; Viana, M.T.; Sotelo-Mundo, R.R.; Ochoa-Leyva, A. Microbiome of Pacific Whiteleg shrimp reveals differential bacterial community composition between Wild, Aquacultured and AHPND/EMS outbreak conditions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Pan, L.; Song, M.; Tian, C.; Gao, S. Microbiota assemblages of water, sediment, and intestine and their associations with environmental factors and shrimp physiological health. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 8585–8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widder, S.; Klapper Isaac Newton Institute Fellows; Allen, R.; Pfeiffer, T.; Curtis, T.P.; Wiuf, C.; Sloan, W.T.; Cordero, O.X.; Brown, S.P.; Momeni, B.; et al. Challenges in microbial ecology: Building predictive understanding of community function and dynamics. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2557–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abid, A.; Davies, S.; Waines, P.; Emery, M.; Castex, M.; Gioacchini, G.; Carnevali, O.; Bickerdike, R.; Romero, J.; Merrifield, D. Dietary synbiotic application modulates Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) intestinal microbial communities and intestinal immunity. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2013, 35, 1948–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahenzli, J.; Köller, Y.; Wyss, M.; Geuking, M.B.; McCoy, K.D. Intestinal Microbial Diversity during Early-Life Colonization Shapes Long-Term IgE Levels. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Q.; Tan, B.; Dong, X.; Chi, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S. Effects of replacing soybean meal with cottonseed meal on growth, feed utilization and non-specific immune enzyme activities for juvenile white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 16, 100255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneguz, M.; Gasco, L.; Tomberlin, J.K. Impact of pH and feeding system on black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens, L; Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larval development. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, M.A.; Weber, B.; Gonçalves, J.; Santos, G.; Rema, P.; Ozorio, R. Dietary probiotic supplementation modulated gut microbiota and improved growth of juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2013, 166, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenburg, J.L.; Bäckhed, F. Diet–microbiota interactions as moderators of human metabolism. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 535, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, A.K.; Kelly, S.A.; Legge, R.; Ma, F.; Low, S.J.; Kim, J.; Zhang, M.; Oh, P.L.; Nehrenberg, D.; Hua, K.; et al. Individuality in gut microbiota composition is a complex polygenic trait shaped by multiple environmental and host genetic factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18933–18938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clarke, G.; Stilling, R.M.; Kennedy, P.J.; Stanton, C.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Minireview: Gut microbiota: the neglected endocrine organ. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 28, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rungrassamee, W.; Klanchui, A.; Maibunkaew, S.; Chaiyapechara, S.; Jiravanichpaisal, P.; Karoonuthaisiri, N. Characterization of intestinal bacteria in wild and domesticated adult black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). PloS ONE 2014, 9, e91853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oxley, A.; Shipton, W.; Owens, L.; McKay, D. Bacterial flora from the gut of the wild and cultured banana prawn, Penaeus merguiensis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 93, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, C.; Chen, C.; Jia, L.; He, X.; Zhang, B. Comparison of the intestinal microbiota composition and function in healthy and diseased Yunlong Grouper. AMB Express 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, K.; Wu, J.; Qiuqian, L.; Yang, K.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, D. Changes in intestinal bacterial communities are closely associated with shrimp disease severity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 6911–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Zhu, J.; Dai, W.; Dong, C.; Qiu, Q.; Li, C. Integrating gut microbiota immaturity and disease-discriminatory taxa to diagnose the initiation and severity of shrimp disease. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1490–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Rodriguez, S.A.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Lozano-Olvera, R.; Betancourt-Lozano, M.; Morales-Covarrubias, M.S. Field and experimental evidence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus as the causative agent of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease of cultured shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) in Northwestern Mexico. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, J.; Liu, L.; Ke, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y. Shrimp AHPND-causing plasmids encoding the PirAB toxins as mediated by pirAB-Tn903 are prevalent in various Vibrio species. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep42177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froelich, B.; Ayrapetyan, M.; Oliver, J.D. Integration of Vibrio vulnificus into Marine Aggregates and Its Subsequent Uptake by Crassostrea virginica Oysters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 1454–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lyons, M.M.; Ward, J.E.; Uhlinger, K.R.; Gast, R.J.; Smolowitz, R. Lethal marine snow: Pathogen of bivalve mollusc concealed in marine aggregates. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1983–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Z.; Qin, Y.; Ye, Q. Effect of nano-TiO2-LDPE packaging on microbiological and physicochemical quality of Pacific white shrimp during chilled storage. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 1567–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Ma, J. Enhancing microbial management and shelf life of shrimp Penaeus vannamei by using nanoparticles of metallic oxides as an alternate active packaging tool to synthetic chemicals. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2021, 28, 100652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Huang, Z.; Zeng, S.; Liu, J.; Weng, S.; He, J. Comparative analysis of the bacterial community compositions of the shrimp intestine, surrounding water and sediment. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 125, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, E.; Gueguen, Y.; Magré, K.; Lorgeoux, B.; Piquemal, D.; Pierrat, F.; Noguier, F.; Saulnier, D. Bacterial community characterization of water and intestine of the shrimp Litopenaeus stylirostris in a biofloc system. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiyapechara, S.; Rungrassamee, W.; Suriyachay, I.; Kuncharin, Y.; Klanchui, A.; Karoonuthaisiri, N.; Jiravanichpaisal, P. Bacterial Community Associated with the Intestinal Tract of P. monodon in Commercial Farms. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 63, 938–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hempel, S.; Newberry, S.J.; Maher, A.R.; Wang, Z.; Miles, J.N.V.; Shanman, R.; Johnsen, B.; Shekelle, P.G. Probiotics for the prevention and treatment of antibiotic-associated diarrhea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2012, 307, 1959–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desriac, F.; Defer, D.; Bourgougnon, N.; Brillet, B.; Le Chevalier, P.; Fleury, Y. Bacteriocin as weapons in the marine animal-associated bacteria warfare: inventory and potential applications as an aquaculture probiotic. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1153–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dopson, M.; Ossandon, F.J.; Lövgren, L.; Holmes, D.S. Metal resistance or tolerance? Acidophiles confront high metal loads via both abiotic and biotic mechanisms. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lukhele, T.; Selvarajan, R.; Nyoni, H.; Mamba, B.; Msagati, T.A.M. Diversity and functional profile of bacterial communities at Lancaster acid mine drainage dam, South Africa as revealed by 16S rRNA gene high-throughput sequencing analysis. Extremophiles 2019, 23, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Y.; Ge, C.; Li, W.; Yao, H. The Intestinal Bacterial Community and Functional Potential of Litopenaeus vannamei in the Coastal Areas of China. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091793
Cheng Y, Ge C, Li W, Yao H. The Intestinal Bacterial Community and Functional Potential of Litopenaeus vannamei in the Coastal Areas of China. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(9):1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091793
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Yimeng, Chaorong Ge, Wei Li, and Huaiying Yao. 2021. "The Intestinal Bacterial Community and Functional Potential of Litopenaeus vannamei in the Coastal Areas of China" Microorganisms 9, no. 9: 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091793
APA StyleCheng, Y., Ge, C., Li, W., & Yao, H. (2021). The Intestinal Bacterial Community and Functional Potential of Litopenaeus vannamei in the Coastal Areas of China. Microorganisms, 9(9), 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091793




