The Impact of the Inoculation of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Pantoea agglomerans on Phosphorus Availability and Bacterial Community Dynamics of a Semi-Arid Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phosphate-Solubilizing Strain Origin and Phylogenetic Identification
2.2. Characterization of the In Vitro Mineral Phosphate Solubilization (MPS) Activity in P. agglomerans V8R67
2.3. Detection of Genes Involved in the Expression of the MPS Phenotype in P. agglomerans V8R67
2.4. Collection of Soil for Microcosm Test
2.5. Soil Microcosm Setup
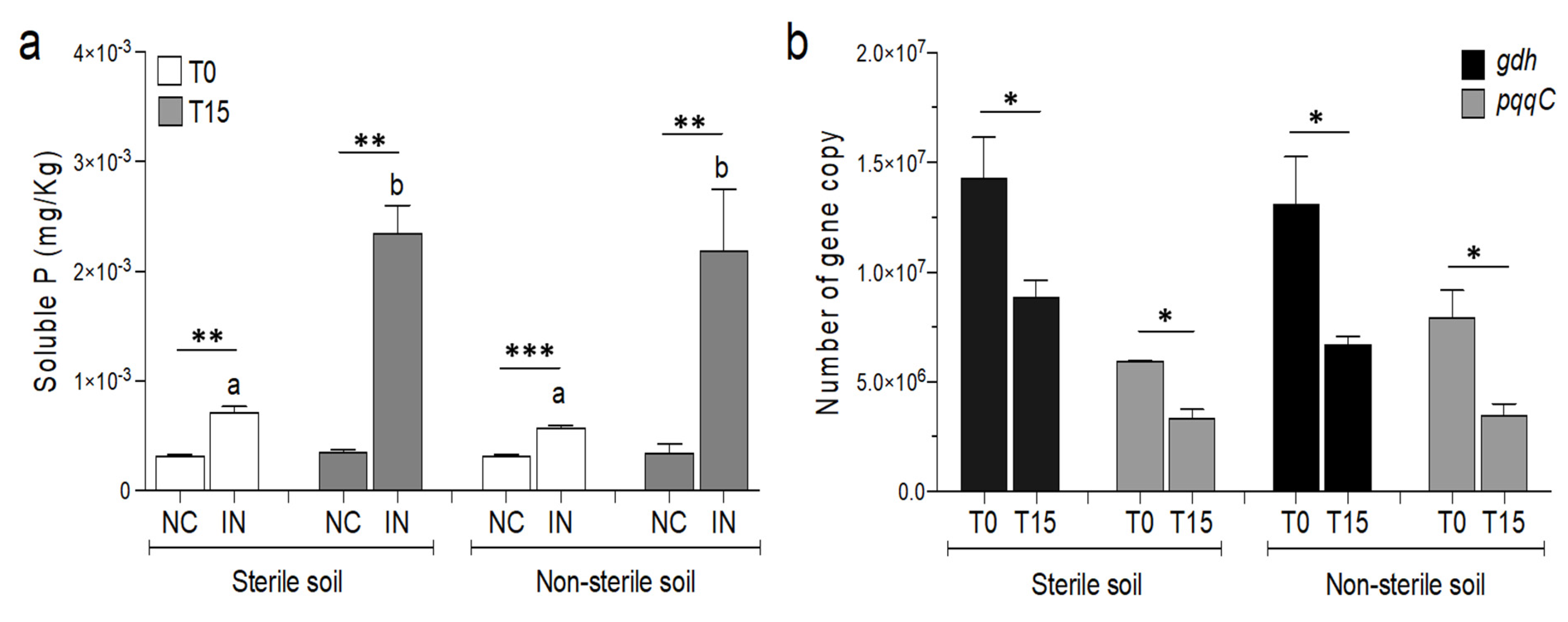
2.6. Quantification of Genes Involved in the Expression of the MPS Phenotype in P. agglomerans V8R67 in Soil Microcosms
2.7. Total Bacterial DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and Purification
2.8. Indexing PCR and Purification
2.9. Illumina Sequencing and Data Analysis
3. Results
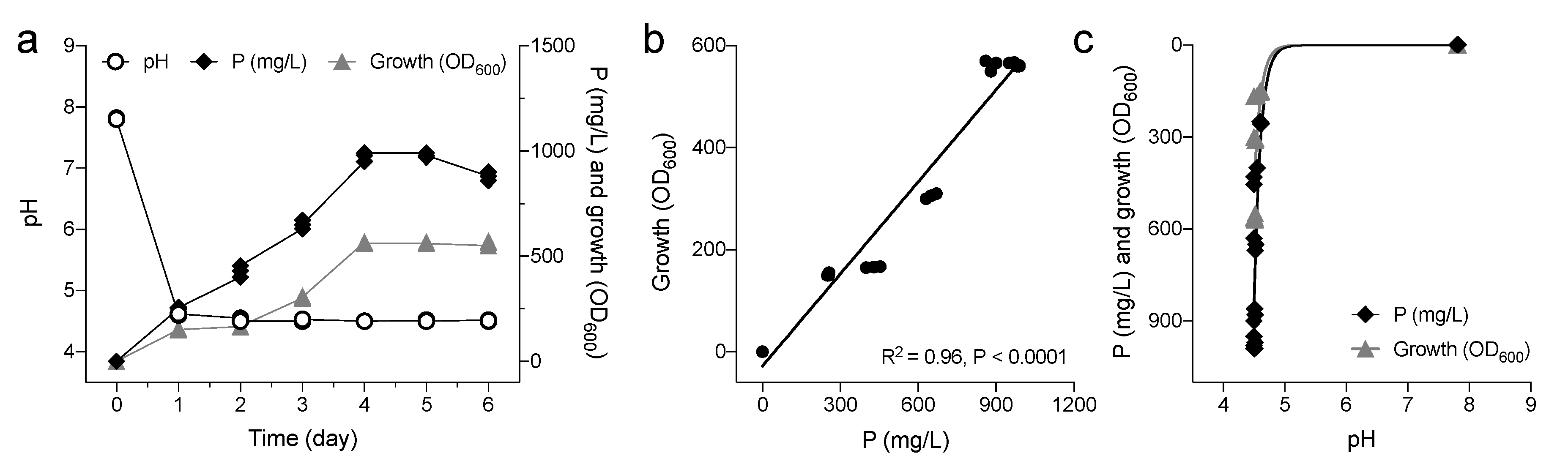
3.1. Identification of PSB Pantoea Agglomerans V8R67 and Characterization of Its MPS Ability
3.2. Effects of P. agglomerans V8R67 Inoculum Application on the Availability of P and Diversity of Edaphic Bacterial Community
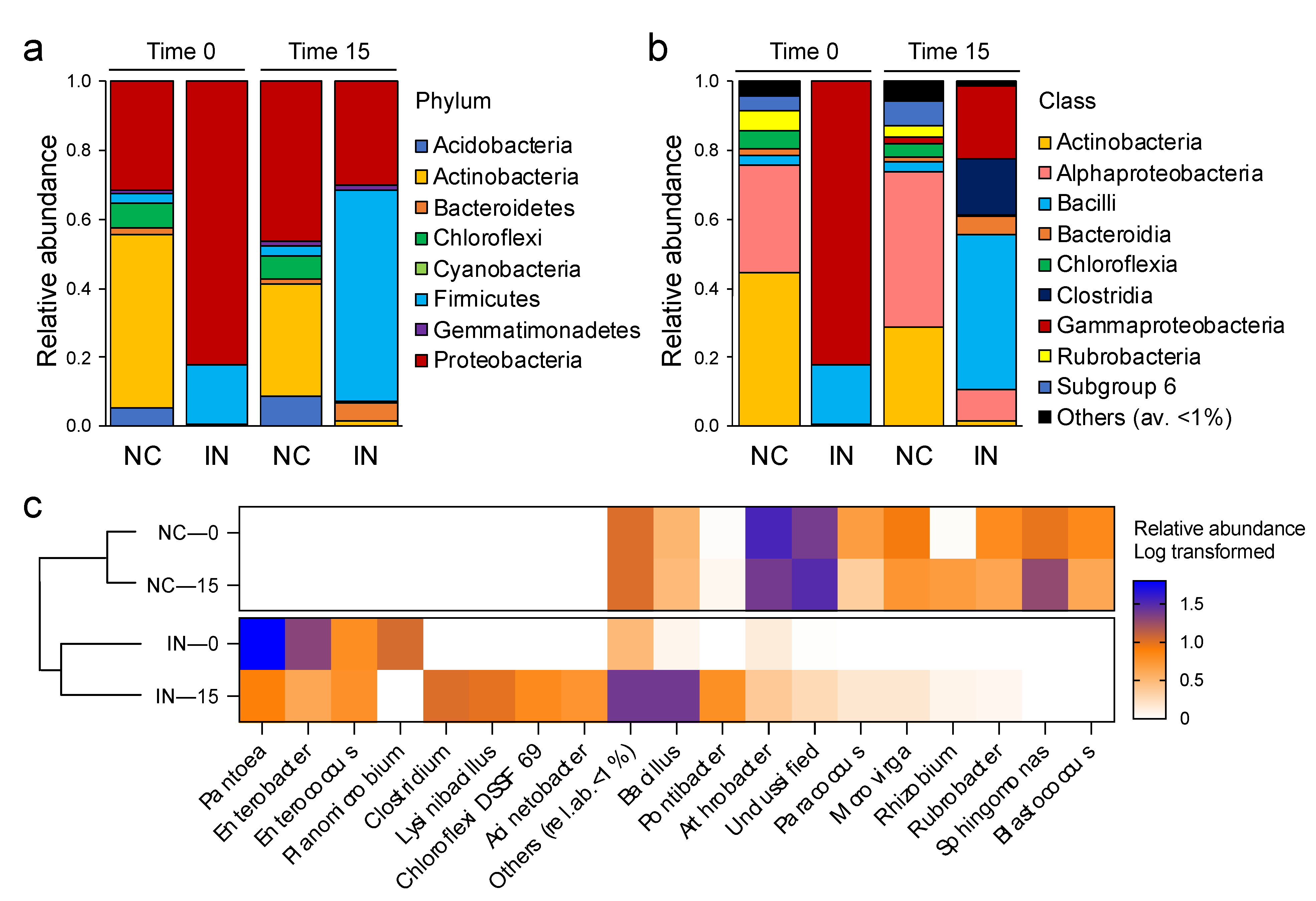
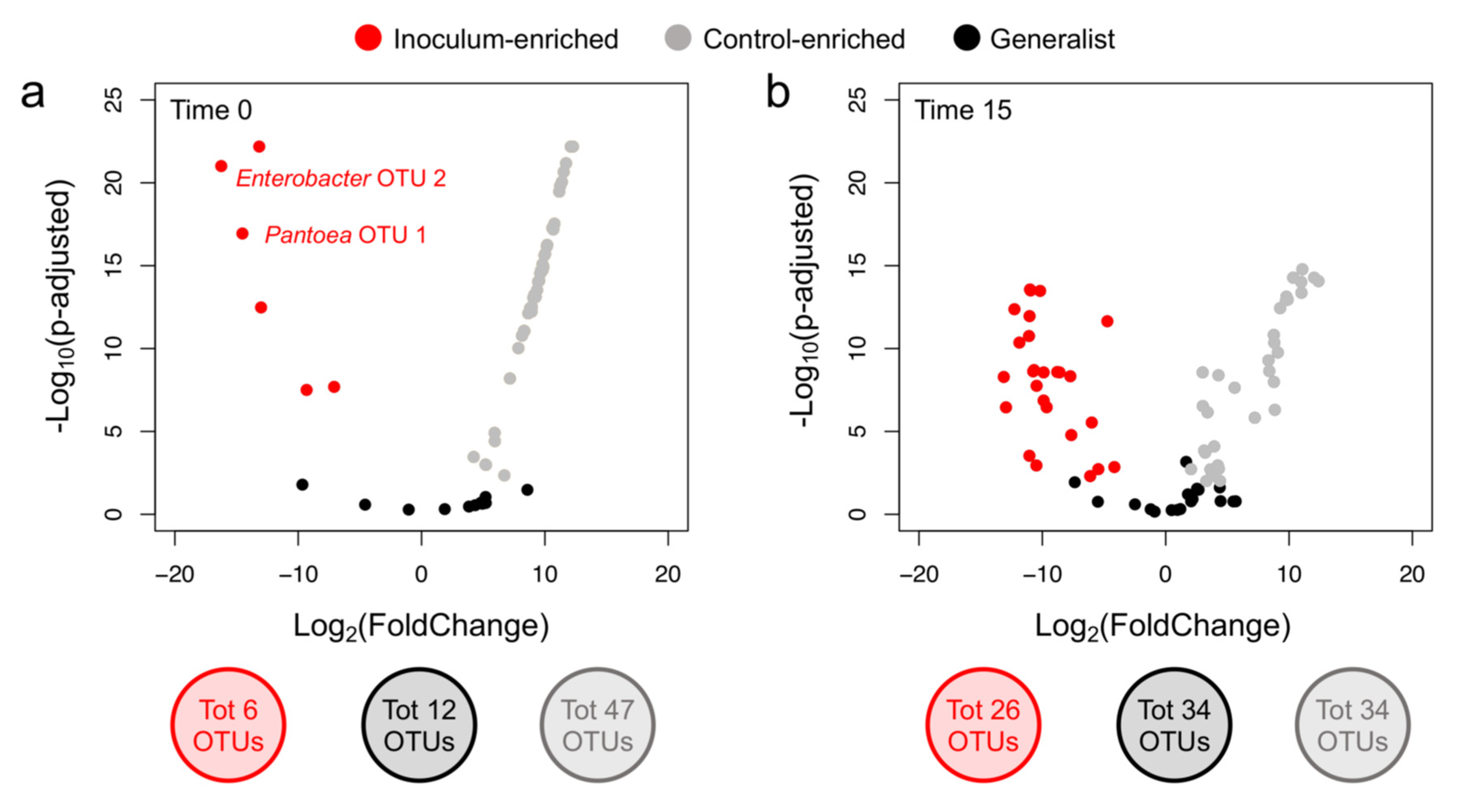
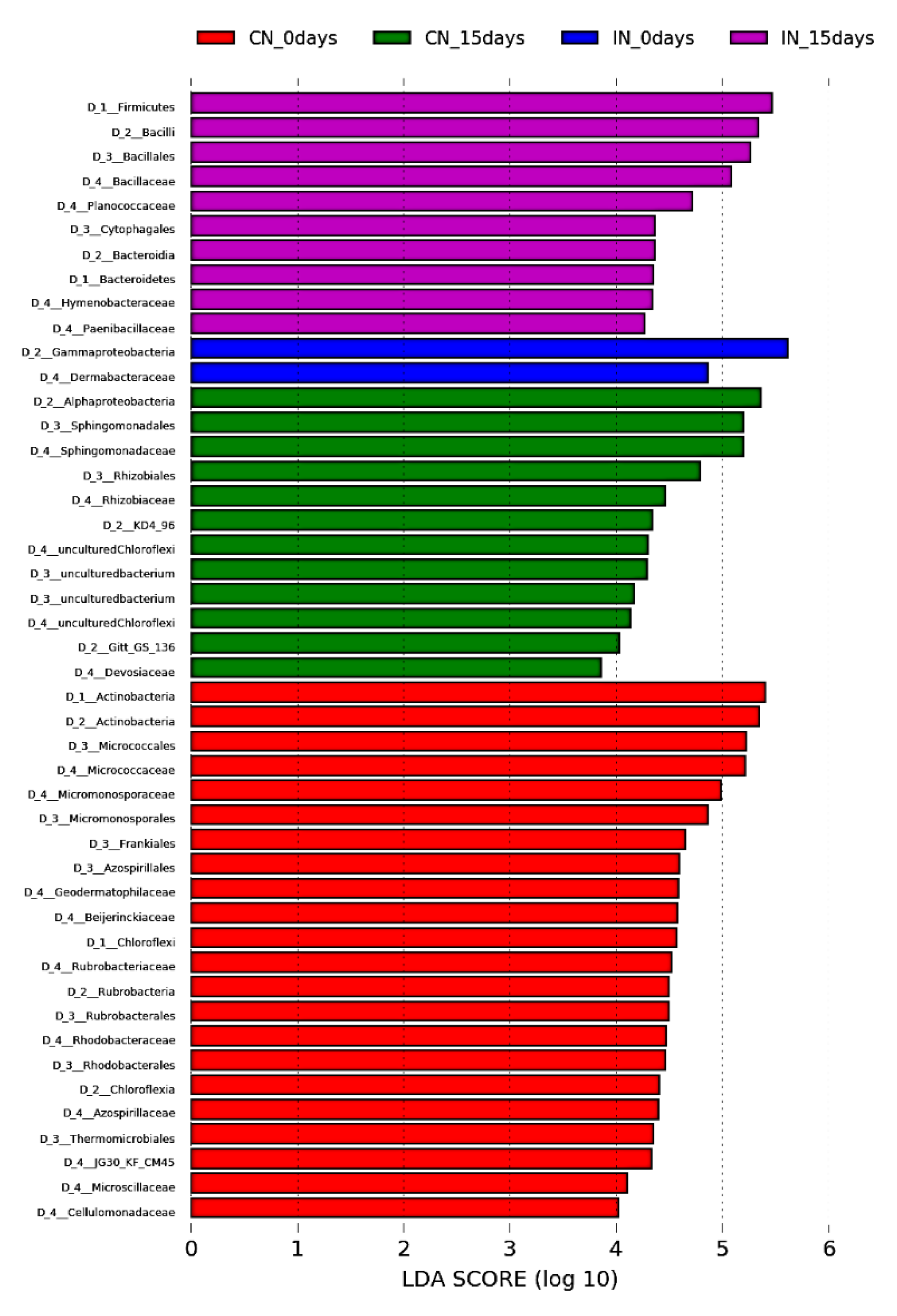
3.3. P. agglomerans Treatment Influences the Relative Abundance of Specific Taxa
3.4. Relationships between the Soil Bacterial Community and the Critical Soil Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwedt, G. The Essential Guide to Environmental Chemistry; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.B.; Sayyed, R.; Trivedi, M.H.; Gobi, T. Phosphate solubilizing microbes: Sustainable approach for managing phosphorus deficiency in agricultural soils. SpringerPlus 2013, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Binkley, D.; Doxtader, K.G. A new method for estimating gross phosphorus mineralization and immobilization rates in soils. Plant Soil 1992, 147, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauwenbergh, S.J.V.; Stewart, M.; Mikkelsen, R. World Reserves of Phos-phate Rock… A Dynamic and Unfolding Story. Better Crops 2013, 97, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Cordell, D.; White, S. Peak Phosphorus: Clarifying the Key Issues of a Vigorous Debate about Long-Term Phosphorus Security. Sustainability 2011, 3, 2027–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyaneshwar, P.; Kumar, G.N.; Parekh, L.J.; Poole, P.S. Role of soil microorganisms in improving P nutrition of plants. Plant Soil 2002, 245, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, J.; Koerselman, W.; Meuleman, A. Nitrogen- or phosphorus-limited growth in herbaceous, wet vegetation: Relations with atmospheric inputs and management regimes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1996, 11, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, A.; Khan, M.S.; Ahemad, M.; Oves, M.; Wani, P.A. Recent Advances in Plant Growth Promotion by Phosphate-Solubilizing Microbes. In Microbial Strategies for Crop Improvement; Khan, M.S., Zaidi, A., Musarrat, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 23–50. [Google Scholar]
- Anthony, C. The quinoprotein dehydrogenases for methanol and glucose. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2004, 428, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biville, F.; Turlin, E.; Gasser, F. Cloning and Genetic Analysis of Six Pyrroloquinoline Quinone Biosynthesis Genes in Methylobacterium organophilum DSM 760. Microbiology 1989, 135, 2917–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, C.H.; Han, S.H.; Kim, K.Y.; Cho, B.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Koo, B.S.; Kim, Y.C. Cloning and Expression of Pyrroloquinoline Quinone (PQQ) Genes from a Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacterium Enterobacter intermedium. Curr. Microbiol. 2003, 47, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.-P.; Zhong, G.-F.; Lin, J.-P.; Mao, D.-B.; Wei, D.-Z. Pyrroloquinoline quinone biosynthesis in Escherichia coli through expression of the Gluconobacter oxydans pqqABCDE gene cluster. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 37, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.H.; Wertz, D.L.; Klinman, J.P. Implication for Functions of the Ectopic Adipocyte Copper Amine Oxidase (AOC3) from Purified Enzyme and Cell-Based Kinetic Studies. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, O.T.; Toyama, H.; Saeki, M.; Rojas, A.; Reed, J.C.; Liddington, R.C.; Klinman, J.P.; Schwarzenbacher, R. Quinone biogenesis: Structure and mechanism of PqqC, the final catalyst in the production of pyrroloquinoline quinone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7913–7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.; Park, M.; Madhaiyan, M.; Seshadri, S.; Song, J.; Cho, H.; Sa, T. Isolation and characterization of phosphate solubilizing bacteria from the rhizosphere of crop plants of Korea. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 1970–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; McDonald, G.A.; Jordan, D. Solubilization of hydroxyapatite by Enterobacter agglomerans and cloned Escherichia coli in culture medium. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1997, 24, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, I.; Park, D.-H.; Park, K. A study of the growth condition and solubilization of phosphate from hydroxyapatite byPantoea agglomerans. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2002, 7, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.; Sharma, D. Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene, its alkylated derivatives and crude oil by a newly isolated strain Pantoea agglomerans D23W3. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 50, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walterson, A.M.; Stavrinides, J. Pantoea:insights into a highly versatile and diverse genus within the Enterobacteriaceae. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 968–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.-J.; Park, G.-T.; Cha, M.-S.; Heo, M.-S. Solubilization of insoluble inorganic phosphates by a novel salt- and pH-tolerant Pantoea agglomerans R-42 isolated from soybean rhizosphere. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.S.; Pujol, C.; Kado, C. Identification and characterization of a Pantoea citrea gene encoding glucose dehydrogenase that is essential for causing pink disease of pineapple. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreeva, I.G.; Golubeva, L.I.; Kuvaeva, T.M.; Gak, E.R.; Katashkina, J.I.; Mashko, S.V. Identification of Pantoea ananatis gene encoding membrane pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ)-dependent glucose dehydrogenase and pqqABCDEF operon essential for PQQ biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 318, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferjani, R.; Marasco, R.; Rolli, E.; Cherif, H.; Cherif, A.; Gtari, M.; Boudabous, A.; Daffonchio, D.; Ouzari, H.-I. The Date Palm Tree Rhizosphere Is a Niche for Plant Growth Promoting Bacteria in the Oasis Ecosystem. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.J. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics; Stackebrandt, E., Goodfellow, M., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1991; pp. 115–148. [Google Scholar]
- Hartley, J.L.; Bowen, H. PEG precipitation for selective removal of small DNA fragments. Focus 2003, 25, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nautiyal, C.S. An efficient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 170, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA; AWWA; WPCF; WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1915; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, E.; Sulbarán, M.; Ball, M.M.; Yarzábal, L.A. Isolation and characterization of mineral phosphate-solubilizing bacteria naturally colonizing a limonitic crust in the south-eastern Venezuelan region. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2905–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Using Maximum Likelihood, Evolutionary Distance, and Maximum Parsimony Methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arraouadi, S.; Nasraoui, R.; Gharbi, W.; Sellami, M.H. Genetic Variation of Response to irrigation system of three durum wheat varieties (Triticum durum Desf.) cultivated in Sidi Bouzid (Tunisia). New Sci. 2015, 20, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Cherni, M.; Ferjani, R.; Mapelli, F.; Boudabous, A.; Borin, S.; Ouzari, H.-I. Soil parameters drive the diversity of Citrus sinensis rhizosphere microbiota which exhibits a potential in plant drought stress alleviation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 135, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najib, S. Fertility of agricultural soils in the area of Jorf Lasfar (El Jadida-Morocco). Int. J. Environ. Agric. Biotechnol. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.N.; Zhang, F.S.; Marschner, P.; Fan, F.L.; Gao, H.M.; Bao, X.G.; Sun, J.H.; Li, L. Effect of intercropping on crop yield and chemical and microbiological properties in rhizosphere of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), maize (Zea mays L.), and faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Biol. Fertil. Soils 2007, 43, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntougias, S.; Polkowska, Z.; Nikolaki, S.; Dionyssopoulou, E.; Stathopoulou, P.; Doudoumis, V.; Ruman, M.; Kozak, K.; Namiesnik, J.; Tsiamis, G. Bacterial Community Structures in Freshwater Polar Environments of Svalbard. Microbes Environ. 2016, 31, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. SEARCH_16S: A new algorithm for identifying 16S ribosomal RNA genes in contigs and chromosomes. BioRxiv 2017, 124131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UNOISE2: Improved error-correction for Illumina 16S and ITS amplicon sequencing. BioRxiv 2016, 081257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A. Non-parametric estimation of the classes in a population. Scand. J. Stat. 1984, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, A.; Lee, S.-M. Estimating the Number of Classes via Sample Coverage. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1992, 87, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An Ordination of the Upland Forest Communities of Southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, J.C. Principal Coordinates Analysis. In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; American Cancer Society: Chichester, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- VennDiagram: Generate High-Resolution Venn and Euler Plots. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=VennDiagram (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.J. DISTLM v. 5: A FORTRAN Computer Program to Calculate a Distance-Based Multivariate Analysis for a Linear Model; Department of Statistics, University of Auckland: Auckland, New Zealand, 2004; Volume 10, p. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gorley, A.M.; Clarke, K.R. PERMANOVA+ for PRIMER: Guide to Software and Statistical Methods; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sulbarán, M.; Pérez, E.; Ball, M.M.; Bahsas, A.; Yarzábal, L.A. Characterization of the Mineral Phosphate-Solubilizing Activity of Pantoea aglomerans MMB051 Isolated from an Iron-Rich Soil in Southeastern Venezuela (Bolívar State). Curr. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amann, R.I.; Ludwig, W.; Schleifer, K.H. Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1995, 59, 143–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strigul, N.S.; Kravchenko, L.V. Mathematical modeling of PGPR inoculation into the rhizosphere. Environ. Model. Softw. 2006, 21, 1158–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selbitschka, W.; Keller, M.; Miethling-Graff, R.; Dresing, U.; Schwieger, F.; Krahn, I.; Homann, I.; Dammann-Kalinowski, T.; Pühler, A.; Tebbe, C.C. Long-Term Field Release of Bioluminescent Sinorhizobium meliloti Strains to Assess the Influence of a recA Mutation on the Strains’ Survival. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 52, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billah, M.; Khan, M.; Bano, A.; Hassan, T.U.; Munir, A.; Gurmani, A.R. Phosphorus and phosphate solubilizing bacteria: Keys for sustainable agriculture. Geomicrobiol. J. 2019, 36, 904–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, A.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L. Application of 31P NMR spectroscopy in determining phosphatase activities and P composition in soil aggregates influenced by tillage and residue management practices. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 138, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbeva, P.; Postma, J.; Van Veen, J.A.; Van Elsas, J.D. Effect of above-ground plant species on soil microbial community structure and its impact on suppression of Rhizoctonia solani AG3. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaer, G.; Fernandes, M.; Myrold, D.; Bottomley, P. Comparative Resistance and Resilience of Soil Microbial Communities and Enzyme Activities in Adjacent Native Forest and Agricultural Soils. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 58, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantigoso, H.A.; Manter, D.K.; Vivanco, J.M. Phosphorus addition shifts the microbial community in the rhizosphere of blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.). Rhizosphere 2018, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindasamy, V.; Senthilkumar, M.; Magheshwaran, V.; Kumar, U.; Bose, P.; Sharma, V.; Annapurna, K. Bacillus and Paenibacillus spp.: Potential PGPR for Sustainable Agriculture. In Beneficial Microorganisms in Food and Nutraceuticals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 18, pp. 333–364. [Google Scholar]
- Ueki, A.; Kaku, N.; Ueki, K. Role of anaerobic bacteria in biological soil disinfestation for elimination of soil-borne plant pathogens in agriculture. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 6309–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowlick, S.; Inoue, T.; Takehara, T.; Tonouchi, A.; Kaku, N.; Ueki, K.; Ueki, A. Usefulness of Japanese-radish residue in biological soil disinfestation to suppress spinach wilt disease accompanying with proliferation of soil bacteria in the Firmicutes. Crop. Prot. 2014, 61, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Nagao, N.; Toda, T.; Kurosawa, N. The dominant bacteria shifted from the order “Lactobacillales” to Bacillales and Actinomycetales during a start-up period of large-scale, completely-mixed composting reactor using plastic bottle flakes as bulking agent. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.-E.; Yao, H.; Huang, Y.; Wei, W.; Zhu, Y.-G. Phosphate levels influence the utilisation of rice rhizodeposition carbon and the phosphate-solubilising microbial community in a paddy soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 118, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naureen, Z.; Rehman, N.U.; Hussain, H.; Hussain, J.; Gilani, S.A.; Al Housni, S.K.; Mabood, F.; Khan, A.L.; Farooq, S.; Abbas, G.; et al. Exploring the Potentials of Lysinibacillus sphaericus ZA9 for Plant Growth Promotion and Biocontrol Activities against Phytopathogenic Fungi. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzuay, M.S.; Ludueña, L.M.; Angelini, J.G.; Fabra, A.; Taurian, T. Beneficial effects of native phosphate solubilizing bacteria on peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) growth and phosphorus acquisition. Symbiosis 2015, 66, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbeva, P.; Van Veen, J.; Van Elsas, J. Predominant Bacillus spp. in Agricultural Soil under Different Management Regimes Detected via PCR-DGGE. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 45, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabanamol, S.; Varghese, E.M.; Meenu, T.; Karthika, S.; Sreekumar, J.; Jisha, M.S. Enhancement of Growth and Yield of Rice (Oryza sativa) by Plant Probiotic Endophyte, Lysinibacillus sphaericus under Greenhouse Conditions. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2020, 51, 1268–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Shirkot, C.; Balgir, P.P. Characterization ofAneurinibacillus aneurinilyticusStrain CKMV1 as a Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria. Int. J. Agric. Environ. Biotechnol. 2014, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Cai, Z. The families Ruminococcaceae, Lachnospiraceae, and Clostridiaceae are the dominant bacterial groups during reductive soil disinfestation with incorporated plant residues. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 135, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastager, S.G.; Deepa, C.; Pandey, A. Plant growth promoting potential of Pontibacter niistensis in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.). Appl. Soil Ecol. 2011, 49, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, C.; Hanson, K.; Selles, F.; Cruz, A.F.; Lemke, R.; McConkey, B.; Zentner, R. Seasonal and long-term resource-related variations in soil microbial communities in wheat-based rotations of the Canadian prairie. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 2104–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousk, J.; Bååth, E.; Brookes, P.C.; Lauber, C.L.; Lozupone, C.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, S.; Palmer, A.S.; Winsley, T.; Lamb, E.; Bissett, A.; Brown, M.V.; van Dorst, J.; Ji, M.; Ferrari, B.; Grogan, P.; et al. Soil fertility is associated with fungal and bacterial richness, whereas pH is associated with community composition in polar soil microbial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.-P.; Zhang, L.; Guo, J.-F.; Ray, J.L.; He, J.-Z. Impact of long-term fertilization practices on the abundance and composition of soil bacterial communities in Northeast China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 46, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ni, T.; Li, Y.; Xiong, W.; Ran, W.; Shen, B.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, R. Responses of Bacterial Communities in Arable Soils in a Rice-Wheat Cropping System to Different Fertilizer Regimes and Sampling Times. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, R.; Xue, C.; Xun, W.; Sun, L.; Xu, Y.; Shen, Q. Pyrosequencing Reveals Contrasting Soil Bacterial Diversity and Community Structure of Two Main Winter Wheat Cropping Systems in China. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 67, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhalnina, K.; Dias, R.; de Quadros, P.D.; Davis-Richardson, A.; Camargo, F.A.; Clark, I.M.; McGrath, S.P.; Hirsch, P.R.; Triplett, E.W. Soil pH determines microbial diversity and composition in the park grass experiment. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, W.; Di, H.J.; Ma, L.; Liu, W.; Li, B. Effects of microbial inoculants on phosphorus and potassium availability, bacterial community composition, and chili pepper growth in a calcareous soil: A greenhouse study. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 3597–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Liu, J.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. Changes of bacterial community compositions after three years of biochar application in a black soil of northeast China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 113, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeola, O. Nutrient management procedures to enhance environmental conditions: An introduction. J. Anim. Sci. 1999, 77, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, C.; Wu, M.; Li, Z. Shifts in bacterial and fungal diversity in a paddy soil faced with phosphorus surplus. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 54, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Ye, B.-C. Bacterial community and phosphorus species changes in pepper rhizosphere soils after Pseudomonas putida Rs-198 inoculation. Rhizosphere 2019, 11, 100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroumand, N.; Behbahani, M.; Dini, G. Combined Effects of Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria and Nanosilica on the Growth of Land Cress Plant. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 20, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safirzadeh, S.; Chorom, M.; Enayatizamir, N. Speciation and Fractionation of Phosphorus Affected by Enterobacter cloacae in the Rhizosphere of Sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.). J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Han, L.; Jiang, B.; Long, C. Identification of a phosphorus-solubilizing Tsukamurella tyrosinosolvens strain and its effect on the bacterial diversity of the rhizosphere soil of peanuts growth-promoting. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradáčová, K.; Sittinger, M.; Tietz, K.; Neuhäuser, B.; Kandeler, E.; Berger, N.; Ludewig, U.; Neumann, G. Maize Inoculation with Microbial Consortia: Contrasting Effects on Rhizosphere Activities, Nutrient Acquisition and Early Growth in Different Soils. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Time | Treatment | Chao1 | ACE | Simpson | Shannon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 day | NC | 53 ± 0.57 ac | 53 ± 0.57 ac | 0.87± 0.00 ac | 4.32 ± 0.07 ac |
| IN | 9.66 ± 0.66 ab | 9.66 ± 0.66 ab | 0.55 ± 0.02 ab | 1.59 ± 0.06 ab | |
| 15 days | NC | 55 ± 1 b | 55 ± 1 b | 0.90 ± 0.02 b | 4.41 ± 0.24 b |
| IN | 56.66 ± 1.20 c | 56.66 ± 1.20 c | 0.89 ± 0.02 c | 4.14 ± 0.16 c |
| Marginal Tests | |||||||
| Variable | SS (trace) | F | P | Prop. | |||
| AP | 10037 | 4.6681 | 0.011 | 0.31825 | |||
| pH | 10137 | 4.7367 | 0.008 | 0.32142 | |||
| Sequential Tests | |||||||
| Variable | R2 | SS (trace) | F | P | Prop. | Cumul | Res.df |
| AP | 0.31825 | 10037 | 4.6681 | 0.012 | 0.31825 | 0.31825 | 10 |
| pH | 0.36913 | 1604.8 | 0.72588 | 0.435 | 0.32142 | 0.36913 | 9 |
| Phylum | pH | AP |
|---|---|---|
| Acidobacteria | 0.545 | −0.606 * |
| Actinobacteria | 0.574 | −0.594 * |
| Bacteroidetes | −0.653 * | 0.799 ** |
| Chloroflexi | 0.552 | −0.599 * |
| Firmicutes | −0.910 * | 0.906 ** |
| Gemmatimonadetes | −0.279 | 0.103 |
| Proteobacteria | 0.385 | −0.356 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saadouli, I.; Mosbah, A.; Ferjani, R.; Stathopoulou, P.; Galiatsatos, I.; Asimakis, E.; Marasco, R.; Daffonchio, D.; Tsiamis, G.; Ouzari, H.-I. The Impact of the Inoculation of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Pantoea agglomerans on Phosphorus Availability and Bacterial Community Dynamics of a Semi-Arid Soil. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081661
Saadouli I, Mosbah A, Ferjani R, Stathopoulou P, Galiatsatos I, Asimakis E, Marasco R, Daffonchio D, Tsiamis G, Ouzari H-I. The Impact of the Inoculation of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Pantoea agglomerans on Phosphorus Availability and Bacterial Community Dynamics of a Semi-Arid Soil. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(8):1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081661
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaadouli, Ilhem, Amor Mosbah, Raoudha Ferjani, Panagiota Stathopoulou, Ioannis Galiatsatos, Elias Asimakis, Ramona Marasco, Daniele Daffonchio, George Tsiamis, and Hadda-Imene Ouzari. 2021. "The Impact of the Inoculation of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Pantoea agglomerans on Phosphorus Availability and Bacterial Community Dynamics of a Semi-Arid Soil" Microorganisms 9, no. 8: 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081661
APA StyleSaadouli, I., Mosbah, A., Ferjani, R., Stathopoulou, P., Galiatsatos, I., Asimakis, E., Marasco, R., Daffonchio, D., Tsiamis, G., & Ouzari, H.-I. (2021). The Impact of the Inoculation of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Pantoea agglomerans on Phosphorus Availability and Bacterial Community Dynamics of a Semi-Arid Soil. Microorganisms, 9(8), 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081661










