Keystone Taxa Lactiplantibacillus and Lacticaseibacillus Directly Improve the Ensiling Performance and Microflora Profile in Co-Ensiling Cabbage Byproduct and Rice Straw
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Materials and Additives
2.2. Silage Set-Up and Sampling
2.3. Analytical Sample Preparation
2.4. Analyses of the Physicochemical Properties
2.5. DNA Extraction and MiSeq Sequencing
2.6. Bioinformatics Analyses
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Physicochemical Properties of Silage
3.2. Silage Bacterial and Fungal Composition
3.3. Functional Diversity of Bacterial and Fungal Community
3.4. Co-Occurrence Network Analysis for Correlations in Microbial Community
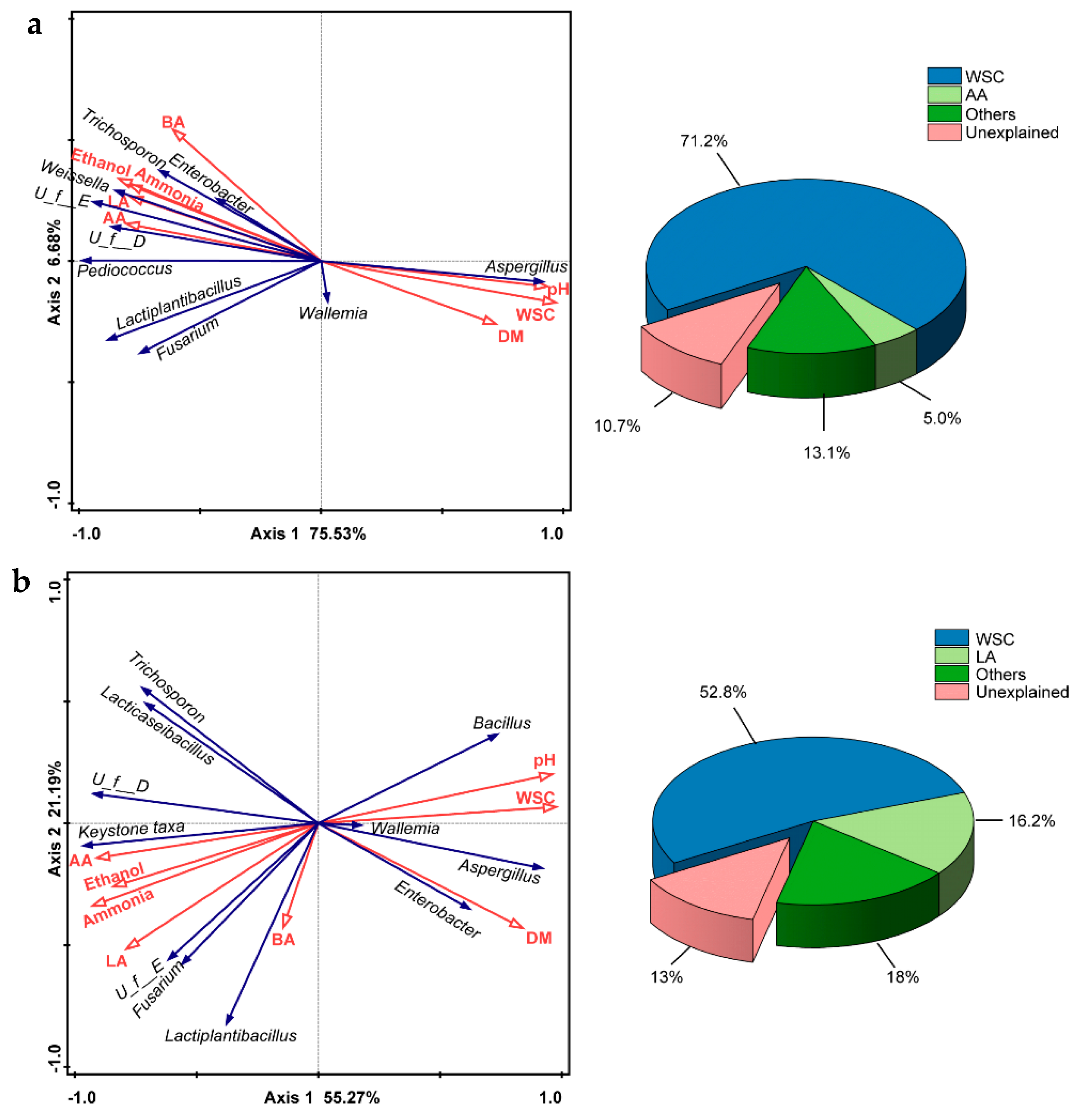
3.5. Redundancy Analysis for Correlations of Dominant Microbes and Physicochemical Properties of Silage
3.6. PLS-PM Analysis to the Effect of Investigated LP Inoculation
4. Discussion
4.1. The Effects of LP Inoculation on Physicochemical Properties of Silage
4.2. Dynamic Variations of Microbial Composition and Functional Diversity
4.3. Correlations of Dominant Microbes and Physicochemical Properties of Silage
4.4. Intricate Relationships of LP Inoculation Augmentation Effects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Halmemies-Beauchet-Filleau, A.; Rinne, M.; Lamminen, M.; Mapato, C.; Ampapon, T.; Wanapat, M.; Vanhatalo, A. Review: Alternative and novel feeds for ruminants: Nutritive value, product quality and environmental aspects. Animal 2018, 12, S295–S309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, H.; Feng, Y.; Pei, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Fu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Peng, Z. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum additive and temperature on the ensiling quality and microbial community dynamics of cauliflower leaf silages. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 307, 123238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of People’s Republic of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Ren, H.; Feng, Y.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Fu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Peng, Z. Effects of different simulated seasonal temperatures on the fermentation characteristics and microbial community diversities of the maize straw and cabbage waste co-ensiling system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zealand, A.M.; Mei, R.; Roskilly, A.P.; Liu, W.; Graham, D.W. Molecular microbial ecology of stable versus failing rice straw anaerobic digesters. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Avila, C.L.S.; Carvalho, B.F. Silage fermentation-updates focusing on the performance of micro-organisms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 966–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dzuman, Z.; Zachariasova, M.; Lacina, O.; Veprikova, Z.; Slavikova, P.; Hajslova, J. A rugged high-throughput analytical approach for the determination and quantification of multiple mycotoxins in complex feed. Talanta 2014, 121, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puntillo, M.; Gaggiotti, M.; Oteiza, J.M.; Binetti, A.; Massera, A.; Vinderola, G. Potential of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated From Different Forages as Silage Inoculants for Improving Fermentation Quality and Aerobic Stability. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 586716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Xie, Z.; Hu, L.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Z. Cellulase interacts with Lactobacillus plantarum to affect chemical composition, bacterial communities, and aerobic stability in mixed silage of high-moisture amaranth and rice straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; He, L.; Xing, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yang, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Effects of mixing Neolamarckia cadamba leaves on fermentation quality, microbial community of high moisture alfalfa and stylo silage. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keshri, J.; Chen, Y.; Pinto, R.; Kroupitski, Y.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Sela Saldinger, S. Microbiome dynamics during ensiling of corn with and without Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 4025–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, N.; Rinne, M.; Ke, W.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Da, M.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Guo, X. The bacterial community and metabolome dynamics and their interactions modulate fermentation process of whole crop corn silage prepared with or without inoculants. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, H.; Shuai, Y.; Yan, Y.; Ran, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, X. Microbial Community and Fermentation Dynamics of Corn Silage Prepared with Heat-Resistant Lactic Acid Bacteria in a Hot Environment. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Kirkby, C.A.; Schmutter, D.; Bissett, A.; Kirkegaard, J.A.; Richardson, A.E. Network analysis reveals functional redundancy and keystone taxa amongst bacterial and fungal communities during organic matter decomposition in an arable soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 97, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Nuccio, E.E.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, N.; Xue, K.; Cohan, F.M.; Zhou, J.; Sun, B. Differentiation strategies of soil rare and abundant microbial taxa in response to changing climatic regimes. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 1327–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Shi, J.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Z.; Liu, X.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Harrison, M.D. Exogenous Probiotics Improve Fermentation Quality, Microflora Phenotypes, and Trophic Modes of Fermented Vegetable Waste for Animal Feed. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Nazar, M.; Shao, T. Microbial diversity and fermentation profile of red clover silage inoculated with reconstituted indigenous and exogenous epiphytic microbiota. Bioresour. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, S.; Hu, Q.; Yi, L.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; Cai, M.; Yu, C. Characteristics and nutrient function of intestinal bacterial communities in black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.) larvae in livestock manure conversion. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva, A.; Quintana, A.; Sanchez, M.; Rodriguez, E.N.; Cremata, J.; Sanchez, J.C. Rapid and sensitive anthrone-sulfuric acid assay in microplate format to quantify carbohydrate in biopharmaceutical products: Method development and validation. Biologicals 2008, 36, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Feng, W.; Cai, H.; Ma, Z.; Liu, X.; Yuan, C.; Shi, J.; Zhang, B. Exogenous enzyme amendment accelerates maturity and changes microflora succession in horse and wildlife animal manure co-composting. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.J.; Krieg, N.R.; Staley, J.R. Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, L.C.; Vetcininova, A.; Carbasse, J.S.; Sohngen, C.; Gleim, D.; Ebeling, C.; Overmann, J. BacDive in 2019: Bacterial phenotypic data for High-throughput biodiversity analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D631–D636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Song, Z.W.; Bates, S.T.; Branco, S.; Tedersoo, L.; Menke, J.; Schilling, J.S.; Kennedy, P.G. FUNGuild: An open annotation tool for parsing fungal community datasets by ecological guild. Fungal Ecol. 2016, 20, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Lu, X.; Rensing, C.; Friman, V.P.; Geisen, S.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Z.; Wei, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, Y. Hyperthermophilic Composting Accelerates the Removal of Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Mobile Genetic Elements in Sewage Sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keshri, J.; Chen, Y.; Pinto, R.; Kroupitski, Y.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Sela Saldinger, S. Bacterial Dynamics of Wheat Silage. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babini, E.; Taneyo-Saa, D.L.; Tassoni, A.; Ferri, M.; Kraft, A.; Gran-Heedfeld, J.; Bretz, K.; Roda, A.; Michelini, E.; Calabretta, M.M.; et al. Microbial Fermentation of Industrial Rice-Starch Byproduct as Valuable Source of Peptide Fractions with Health-Related Activity. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Tao, X.; Li, J.; Jia, Y.; Shao, T. Enhancement of biomass conservation and enzymatic hydrolysis of rice straw by dilute acid-assisted ensiling pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agneessens, L.; Viaene, J.; Nest, T.V.; Vandecasteele, B.; De Neve, S. Effect of ensilaged vegetable crop residue amendments on soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 192, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, F.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, W.H.; Oh, Y.K.; Park, K.; Kwak, W.S. Long-term anaerobic conservation of fruit and vegetable discards without or with moisture adjustment after aerobic preservation with sodium metabisulfite. Waste Manag. 2019, 87, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Lv, H.; Xing, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Intrinsic tannins affect ensiling characteristics and proteolysis of Neolamarckia cadamba leaf silage by largely altering bacterial community. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 311, 123496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.D.; Phillips, B.A.; Zanoni, P. Deoxyribonucleic Acid Homology Studies of Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus paracasei sp. nov., subsp. paracasei and subsp. tolerans, and Lactobacillus rhamnosus sp. nov., comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1989, 39, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duarte-Oliveira, C.; Rodrigues, F.; Goncalves, S.M.; Goldman, G.H.; Carvalho, A.; Cunha, C. The Cell Biology of the Trichosporon-Host Interaction. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diepeningen, A.D.; Hoog, G.S. Challenges in Fusarium, a Trans-Kingdom Pathogen. Mycopathologia 2016, 181, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McAllister, T.A.; Duniere, L.; Drouin, P.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Munns, K.; Zaheer, R. Silage review: Using molecular approaches to define the microbial ecology of silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4060–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tedersoo, L.; Bahram, M.; Polme, S.; Koljalg, U.; Yorou, N.S.; Wijesundera, R.; Villarreal Ruiz, L.; Vasco-Palacios, A.M.; Thu, P.Q.; Suija, A.; et al. Fungal biogeography. Global diversity and geography of soil fungi. Science 2014, 346, 1256688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paradhipta, D.H.V.; Lee, S.S.; Kang, B.; Joo, Y.H.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.C. Dual-Purpose Inoculants and Their Effects on Corn Silage. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Material | Rice Straw | Cabbage Leaf | Corn Flour |
|---|---|---|---|
| DM (Dry matter, g·kg−1) | 864.7 ± 1.3 | 59.4 ± 0.7 | 877.3 ± 1.9 |
| WSC (Water-soluble carbohydrates, g·kg−1 DM) | 29.5 ± 1.7 | 439.4 ± 36.4 | 71.8 ± 2.9 |
| CF (Crude fat, g·kg−1 DM) | 98.9 ± 6.1 | 425.0 ± 2.6 | 52.9 ± 3.5 |
| CP (Crude Protein, g·kg−1 DM) | 76.3 ± 1.9 | 220.0 ± 5.7 | 90.5 ± 6.1 |
| ADF (Acid detergent fiber, g·kg−1 DM) | 428.9 ± 16.1 | 176.9 ± 7.8 | 11.8 ± 1.3 |
| NDF (Neutral detergent fiber, g·kg−1 DM) | 676.6 ± 13.0 | 233.6 ± 4.8 | 24.7 ± 2.0 |
| Item | Time (Days) | SEM | Significance | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3 | 7 | 15 | 30 | TR | TI | TR × TI | ||
| DM (Dry matter, g·kg−1) | |||||||||
| CKGP | 309.5 ± 6.1 Aa | 295.9 ± 3.4 Ab | 285.3 ± 0.7 Bb | 287.0 ± 5.7 Ab | 270.9 ± 5.5 Bc | 2.255 | *** | *** | 0.268 |
| LPGP | 310.3 ± 4.5 Aa | 299.7 ± 9.2 Aab | 292.1 ± 4.1 Abc | 291.8 ± 4.1 Abc | 283.4 ± 2.5 Ac | ||||
| pH | |||||||||
| CKGP | 5.93 ± 0.03 Aa | 4.48 ± 0.09 Ab | 4.24 ± 0.08 Ac | 3.79 ± 0.06 Ae | 3.99 ± 0.07 Ad | 0.157 | *** | *** | *** |
| LPGP | 5.87 ± 0.06 Aa | 3.78 ± 0.04 Bb | 3.55 ± 0.06Bc | 3.55 ± 0.09 Bc | 3.80 ± 0.11 Ab | ||||
| WSC (g·kg−1 DM) | |||||||||
| CKGP | 68.8 ± 5.1 Aa | 13.9 ± 1.3 Bb | 20.2 ± 7.8 Ab | 13.8 ± 5.3 Ab | 12.5 ± 5.7 Ab | 4.214 | 0.306 | *** | * |
| LPGP | 68.7 ± 5.9 Aa | 23.3 ± 0.2 Ab | 7.4 ± 0.9 Ac | 9.8 ± 1.7 Ac | 10.8 ± 0.1 Ac | ||||
| Lactic acid (g·kg−1 DM) | |||||||||
| CKGP | 0.0 ± 0.0 Ac | 21.3 ± 3.4 Bb | 23.7 ± 1.3 Ba | 35.8 ± 4.5 Bb | 22.4 ± 1.4 Ab | 3.279 | *** | *** | *** |
| LPGP | 0.0 ± 0.0 Ad | 38.3 ± 1.2 Ab | 46.6 ± 3 Aab | 52.1 ± 7 Aa | 25.3 ± 0.8 Ac | ||||
| Acetic acid (g·kg−1 DM) | |||||||||
| CKGP | 0.0 ± 0.0 Ad | 12.8 ± 0.8 Aa | 7.7 ± 0.6 Ab | 8.3 ± 1.7 Abc | 5.4 ± 0.4 Ac | 0.720 | *** | *** | *** |
| LPGP | 0.0 ± 0.0 Ad | 4.6 ± 0.4 Bb | 5.0 ± 0.1 Bb | 6.0 ± 0.3 Aa | 3.7 ± 0.2 Ac | ||||
| Butyric acid (g·kg−1 DM) | |||||||||
| CKGP | 0.0 ± 0.0 Ab | 5.0 ± 1.6 Aa | 2.5 ± 0.1 Aa | 2.5 ± 0.9 Aab | 2.4 ± 0.5 Aab | 0.329 | *** | *** | *** |
| LPGP | 0.0 ± 0.0 Ab | 0.3 ± 0.0 Ba | 0.3 ± 0.0 Bab | 0.1 ± 0.2 Bab | 0.0 ± 0.0 Bb | ||||
| Ethanol (g·kg−1 DM) | |||||||||
| CKGP | 0.0 ± 0.0 Ab | 9.9 ± 0.7 Aa | 6.7 ± 1.1 Ba | 7.1 ± 1.8 Aa | 6.6 ± 0.8 Aa | 0.828 | 0.274 | *** | 0.051 |
| LPGP | 0.0 ± 0.0 Ab | 7.3 ± 0.1 Ba | 12.5 ± 2 Aa | 11.5 ± 4.1 Aa | 7.9 ± 1.7 Aa | ||||
| Ammonia/total N (%) | |||||||||
| CKGP | 1.1 ± 0.1 Ac | 11.9 ± 0.3 Aa | 8.6 ± 0. 1Aa | 8.6 ± 1.2 Aab | 6.4 ± 0.6 Ab | 0.644 | *** | *** | *** |
| LPGP | 0.9 ± 0.1 Bc | 4.5 ± 0.4 Bab | 5.1 ± 0.3 Ba | 5.7 ± 0.5 Ba | 4.1 ± 0.2 Bb | ||||
| Item | Time (Days) | SEM | Significance | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3 | 7 | 15 | 30 | TR | TI | TR × TI | ||
| CF (Crude fat, g × kg−1 DM) | |||||||||
| CKGP | 145.9 ± 8.6 Aa | 112.7 ± 5.1 Ab | 142.9 ± 4.6 Aa | 150.1 ± 3.0 Aa | 121.1 ± 3.2 Ab | 2.916 | 0.458 | *** | 0.372 |
| LPGP | 142.4 ± 8.8 Aa | 125.9 ± 16.3 Aab | 129.7 ± 1.7 Bab | 151 ± 8.5 Aa | 111.6 ± 8.4 Ab | ||||
| CP (Crude Protein, g × kg−1 DM) | |||||||||
| CKGP | 99.7 ± 1.2 Aa | 101 ± 3.5 Aa | 102.4 ± 1.7 Aa | 102.1 ± 3.3 Aa | 102.3 ± 2.2 Aa | 0.476 | 0.379 | 0.133 | 0.275 |
| LPGP | 98.8 ± 0.7 Aa | 102.5 ± 1.6 Aa | 99.1 ± 2.3 Aa | 104.4 ± 2.1 Aa | 101.6 ± 3.4 Aa | ||||
| Acid detergent fiber (ADF, g × kg−1 DM) | |||||||||
| CKGP | 202.4 ± 2.3 Ac | 233.0 ± 1.2 Ab | 230.6 ± 3.1 Ab | 248.7 ± 7.3 Aa | 238.4 ± 3.8 Aab | 2.870 | *** | ** | *** |
| LPGP | 215.6 ± 6.4 Aab | 211.8 ± 3.5 Bbc | 224.8 ± 4.6 Aab | 199.4 ± 1.7 Bc | 227.8 ± 1.5 Ba | ||||
| Neutral detergent fiber (NDF, g × kg−1 DM) | |||||||||
| CKGP | 301.5 ± 3.2 Ac | 343.6 ± 8.8 Aa | 322.3 ± 5.7 Ab | 324.2 ± 1.5 Ab | 316.9 ± 5.0 Aab | 2.996 | * | *** | *** |
| LPGP | 302.6 ± 4.3 Ac | 304.6 ± 6.8 Bbc | 325.4 ± 5.7 Aab | 306.4 ± 0.3 Bbc | 335.9 ± 13.4 Aa | ||||
| Item | Time (Days) | SEM | Significance | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3 | 7 | 15 | 30 | TR | TI | TR × TI | ||||
| Formic acid (g·kg−1 DM) | |||||||||||
| CKGP | 0.0 ± 0.0 Ab | 5.61 ± 0.76 Ba | 8.24 ± 1.13 Ba | 8.76 ± 0.54 Aa | 6.82 ± 2.58 Aa | 0.296 | *** | *** | *** | ||
| LPGP | 0.0 ± 0.0 Ad | 12.21 ± 0.92 Ab | 13.19±0.33 Ab | 16.66 ± 1.90 Aa | 4.44 ± 0.89 Ac | - | |||||
| Propionic acid (g·kg−1 DM) | |||||||||||
| CKGP | 0.0 ± 0.0 Ad | 0.64 ± 0.02 Bc | 1.03 ± 0.08 Bb | 1.27 ± 0.0 Ba | 1.28 ± 0.0 Ba | 0.059 | *** | *** | *** | ||
| LPGP | 0.0 ± 0.0 Ad | 0.90 ± 0.06 Ac | 1.87 ± 0.03 Ab | 3.09 ± 0.51 Ba | 2.56 ± 0.10 Aab | - | |||||
| Lactic acid/TOA (%) | |||||||||||
| CKGP | NA | 52.06 | 63.27 | 72.47 | 69.15 | - | - | ||||
| LPGP | NA | 81.31 | 83.36 | 81.41 | 80.76 | - | |||||
| Acetic acid/TOA (%) | |||||||||||
| CKGP | NA | 31.32 | 23.10 | 16.72 | 16.77 | - | - | ||||
| LPGP | NA | 9.42 | 8.61 | 9.43 | 12.47 | - | |||||
| Butyric acid/TOA (%) | |||||||||||
| CKGP | NA | 12.12 | 6.55 | 4.99 | 7.31 | - | - | ||||
| LPGP | NA | 0.92 | 0.51 | 0.16 | 0.00 | - | |||||
| Flieg’s evalution (score) | |||||||||||
| CKGP | NA | Bad (31) | Medium (45) | Good (61) | Medium (53) | - | - | ||||
| LPGP | NA | Very good (100) | Very good (100) | Very good (100) | Very good (100) | - | |||||
| Community | Treatment | Time (Days) | Coverage | Chao1 | Shannon | Simpson | Ace |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial community | LPGP | 0 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 222.3 ± 0.93 | 3.79 ± 0.07 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 222.37 ± 1.87 |
| 3 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 106.1 ± 32.3 | 0.74 ± 0.14 | 0.73 ± 0.06 | 129.15 ± 43.81 | ||
| 7 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 147.4 ± 10.0 | 0.90 ± 0.17 | 0.68 ± 0.07 | 168.09 ± 20.69 | ||
| 15 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 190.4 ± 12.4 | 1.93 ± 0.30 | 0.27 ± 0.08 | 187.06 ± 14.56 | ||
| 30 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 158.0 ± 10.7 | 0.56 ± 0.18 | 0.84 ± 0.05 | 154.51 ± 20.81 | ||
| CKGP | 0 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 218.4 ± 6.37 | 3.66 ± 0.06 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 217.31 ± 6.69 | |
| 3 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 117.8 ± 26.8 | 1.82 ± 0.16 | 0.28 ± 0.05 | 130.21 ± 41.01 | ||
| 7 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 119.8 ± 45.5 | 1.76 ± 0.14 | 0.28 ± 0.05 | 142.55 ± 58.92 | ||
| 15 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 176.2 ± 51.6 | 1.89 ± 0.15 | 0.26 ± 0.06 | 191.51 ± 50.8 | ||
| 30 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 174.0 ± 10.9 | 2.24 ± 0.08 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 172.22 ± 6.22 | ||
| Fungal community | LPGP | 0 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 34.4 ± 2.51 | 1.99 ± 0.0 | 0.19 ± 0.02 | 222.37 ± 1.87 |
| 3 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 36.7 ± 1.04 | 1.92 ± 0.31 | 0.23 ± 0.08 | 129.15 ± 43.81 | ||
| 7 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 30.1 ± 2.71 | 1.52 ± 0.05 | 0.30 ± 0.02 | 168.09 ± 20.69 | ||
| 15 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 33.4 ± 7.06 | 2.18 ± 0.29 | 0.17 ± 0.05 | 187.06 ± 14.56 | ||
| 30 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 31.0 ± 5.51 | 1.90 ± 0.14 | 0.20 ± 0.04 | 154.51 ± 20.81 | ||
| CKGP | 0 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 29.6 ± 4.03 | 1.83 ± 0.07 | 0.23 ± 0.03 | 217.31 ± 6.69 | |
| 3 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 37.8 ± 14.8 | 2.00 ± 0.04 | 0.18 ± 0.02 | 130.21 ± 41.01 | ||
| 7 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 35.6 ± 4.80 | 1.75 ± 0.21 | 0.27 ± 0.08 | 142.55 ± 58.92 | ||
| 15 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 33.6 ± 7.88 | 2.02 ± 0.31 | 0.21 ± 0.10 | 191.51 ± 50.8 | ||
| 30 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 32.6 ± 7.94 | 1.66 ± 0.57 | 0.33 ± 0.24 | 172.22 ± 6.22 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, G.; Zhang, G.; Shi, J.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Z.; Liu, X.; Yuan, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, B. Keystone Taxa Lactiplantibacillus and Lacticaseibacillus Directly Improve the Ensiling Performance and Microflora Profile in Co-Ensiling Cabbage Byproduct and Rice Straw. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9051099
Du G, Zhang G, Shi J, Zhang J, Ma Z, Liu X, Yuan C, Li X, Zhang B. Keystone Taxa Lactiplantibacillus and Lacticaseibacillus Directly Improve the Ensiling Performance and Microflora Profile in Co-Ensiling Cabbage Byproduct and Rice Straw. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(5):1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9051099
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Guilin, Guilong Zhang, Jiping Shi, Jingxian Zhang, Zhiguo Ma, Xiangcen Liu, Chenyang Yuan, Xiang Li, and Baoguo Zhang. 2021. "Keystone Taxa Lactiplantibacillus and Lacticaseibacillus Directly Improve the Ensiling Performance and Microflora Profile in Co-Ensiling Cabbage Byproduct and Rice Straw" Microorganisms 9, no. 5: 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9051099
APA StyleDu, G., Zhang, G., Shi, J., Zhang, J., Ma, Z., Liu, X., Yuan, C., Li, X., & Zhang, B. (2021). Keystone Taxa Lactiplantibacillus and Lacticaseibacillus Directly Improve the Ensiling Performance and Microflora Profile in Co-Ensiling Cabbage Byproduct and Rice Straw. Microorganisms, 9(5), 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9051099








