Effects of Inoculants Producing Antifungal and Carboxylesterase Activities on Corn Silage and Its Shelf Life against Mold Contamination at Feed-Out Phase
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inoculant Preparation
2.2. Silage Production
2.3. Chemical Compositions
2.4. Fermentation Characteristics
2.5. Microbial Counts
2.6. Rumen Degradation Kinetics and Fermentation Indices
2.7. Microbial Changes and Aerobic Stability at Feed-Out Phase
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Compositions
3.2. Fermentation Characteristics and Microbial Counts
3.3. Rumen Degradation Kinetics
3.4. Rumen Fermentation Indices
3.5. Microbial Changes at Feed-Out Phase
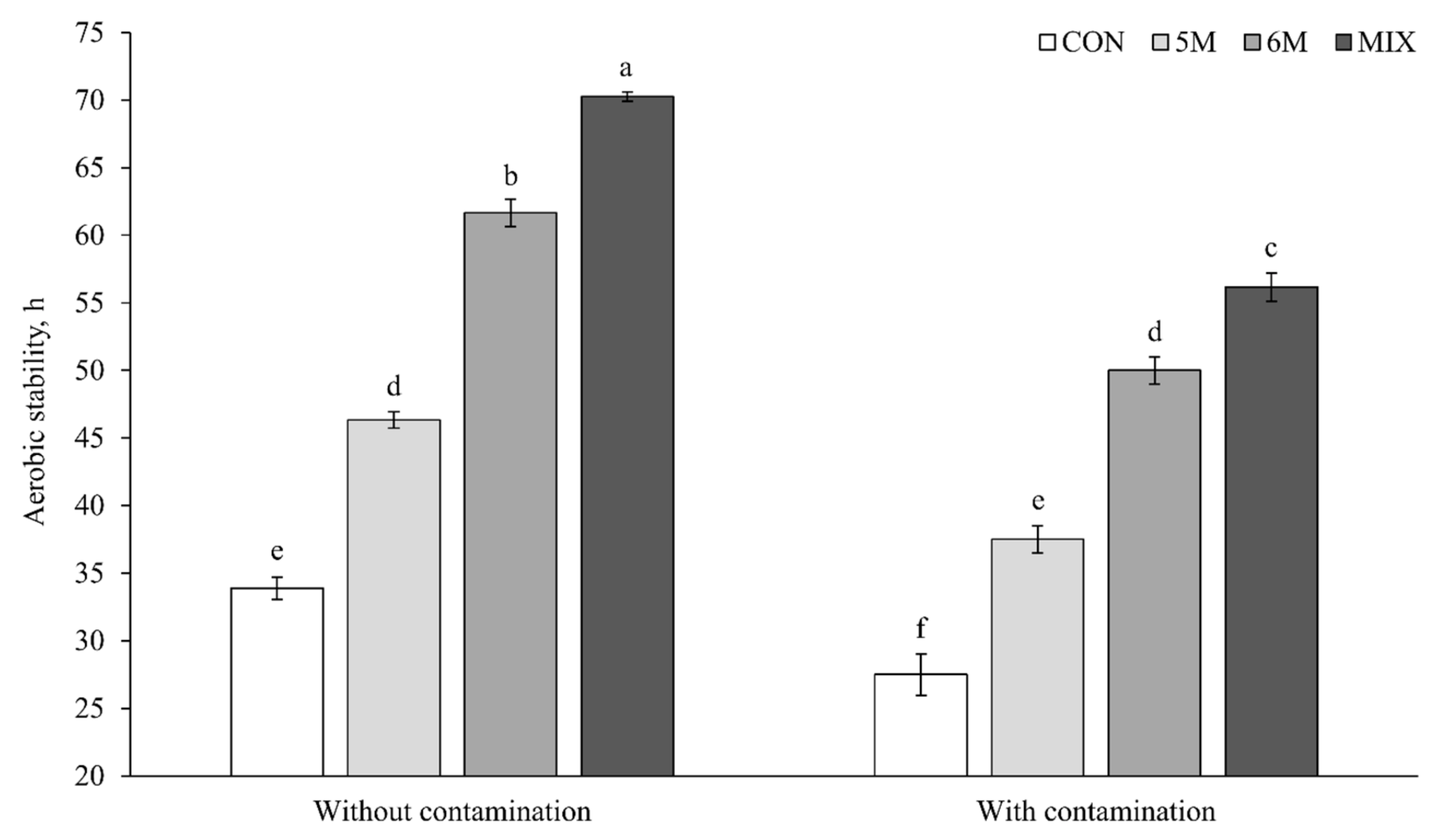
3.6. Aerobic Stability
4. Discussion
4.1. Chemical Compositions and Fermentation Characteristics
4.2. Rumen Degradation
4.3. Aerobic Deterioration
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allen, M.S.; Coors, J.G.; Roth, G.W. Corn silage. In Silage Science and Technology; Buxton, D.R., Muck, R.E., Harrison, J.H., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 2003; pp. 547–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L., Jr.; Shaver, R.D.; Grant, R.J.; Schmidt, R.J. Silage review: Interpretation of chemical, microbial, and organoleptic components of silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muck, R.E.; Nadeau, E.M.G.; McAllister, T.A.; Contreras-Govea, F.E.; Santos, M.C.; Kung, L., Jr. Silage review: Recent advances and future uses of silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3980–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnürer, J.; Magnusson, J. Antifungal lactic acid bacteria as biopreservatives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesogan, A.T.; Ma, Z.X.; Romero, J.J.; Arriola, K.G. Ruminant Nutrition Symposium: Improving cell wall digestion and animal performance with fibrolytic enzymes. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinschmit, D.H.; Schmidt, R.J.; Kung, L., Jr. The effects of various antifungal additives on the fermentation and aerobic stability of corn silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 2130–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Lindow, S.E.; Zhang, J. Lactobacillus parafarraginis ZH1 producing anti-yeast substance to improve the aerobic stability of silage. Anim. Sci. J. 2018, 89, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nsereko, V.L.; Smiley, B.K.; Rutherford, W.M.; Spielbauer, A.; Forrester, K.J.; Hettinger, G.H.; Harman, E.K.; Harman, B.R. Influence of inoculating forage with lactic acid bacterial strains that produce ferulate esterase on ensilage and ruminal degradation of fiber. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2008, 145, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Duniere, L.; Lynch, J.P.; McAllister, T.A.; Baah, J.; Wang, Y. Impact of ferulic acid esterase producing lactobacilli and fibrinolytic enzymes on conservation characteristics, aerobic stability, and fiber degradability of barley silage. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2015, 207, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunade, I.M.; Matinex-Tuppia, C.; Queiroz, O.C.M.; Jiang, Y.; Drouin, P.; Wu, F. Silage review: Mycotoxins in silage: Occurrence, effects, prevention, and mitigation. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4034–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, O.C.M.; Kim, S.C.; Adesogan, A.T. Effect of treatment with a mixture of bacteria and fibrolytic enzymes on the quality and safety of corn silage infested with different levels of rust. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 5285–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, L.A.M.; Pereyra, M.L.G.; Keller, K.M.; Alonso, V.A.; Oliveira, A.A.; Almeida, T.X.; Barbosa, T.S.; Nunes, L.M.T.; Cavaglieri, L.R.; Rosa, C.A.R. Fungal and mycotoxins contamination in corn silage: Monitoring risk before and after fermentation. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2013, 52, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, O.C.M.; Ogunade, I.M.; Weinberg, Z.; Adesogan, A.T. Silage review: Foodborne pathogens in silage and their mitigation by silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4132–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C.; Adesogan, A.T. Influence of ensiling temperature, simulated rainfall, and delayed sealing on fermentation characteristics and aerobic stability of corn silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 3122–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudamore, K.A.; Livesey, C.T. Occurrence and significance of mycotoxins in forage crops and silage: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1998, 77, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradhipta, D.H.V.; Lee, S.S.; Kang, B.; Joo, Y.H.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.C. Dual-purpose inoculants and their effects on corn silage. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Jeon, J.J.; Kim, H.S.; Zeller, K.A.; Carter, L.L.A.; Leslie, J.F.; Lee, Y.W. Population structure of and mycotoxin production by Fusarium graminearum from maize in South Korea. J. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 2161–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, T.W.; Adesogan, A.T.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, S.S. Effects of an esterase-producing inoculant on fermentation, aerobic stability, and neutral detergent fiber digestibility of corn silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.P.; Lin, L.; Lara, E.C.; Baah, J.; Beauchemin, K.A. The effect of exogenous fibrinolytic enzymes and a ferulic acid esterase-producing inoculant on the fiber degradability, chemical composition and conservation characteristics of alfalfa silage. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 193, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriola, K.G.; Kim, S.C.; Huisden, C.M.; Adesogan, A.T. Stay-green ranking and maturity of corn hybrids: 1. Effects on dry matter yield, nutritional value, fermentation characteristics, and aerobic stability of silage hybrids in Florida. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed.; AOAC International: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tilley, J.M.A.; Terry, R.A. A two-stage technique for the in vitro digestion of forage crops. J. Br. Grassl. Soc. 1963, 18, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaney, A.L.; Marbach, E.P. Modified reagents for determination of urea and ammonia. Clin. Chem. 1962, 8, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Lee, H.J.; Paradhipta, D.H.V.; Joo, Y.H.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.C. Temperature and microbial changes of corn silage during aerobic exposure. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R.E.; Dickerson, J.T. Storage temperature effects on proteolysis in alfalfa silage. Trans. ASASE 1988, 31, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesogan, A.T.; Krueger, N.K.; Kim, S.C. A novel, wireless, automated system for measuring fermentation gas production kinetics of feeds and its application to feed characterization. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2005, 123–124, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS Institute Inc. SAS/STAT User’s Guide, Version 9; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, I. A revised model for the estimation of protein degradability in the rumen. J. Agric. Sci. 1981, 96, 251–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, G.O.; Gruninger, R.J.; Badhan, A.; McAllister, T.A. Mining the rumen for fibrolytic feed enzymes. Anim. Front. 2016, 6, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, P.; Henderson, A.R.; Heron, S.J.E. The Biochemistry of Silage, 2nd ed.; Chalcombe Publ.: Marlow, UK, 1991; pp. 48–291. [Google Scholar]
- Danner, H.; Holzer, M.; Mayrhuber, E.; Braun, R. Acetic acid increases stability of silage under aerobic conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.S.; Nogueira, M.A.; Hungria, M. Microbial inoculants: Reviewing the past, discussing the present and previewing an outstanding future for the use of beneficial bacteria in agriculture. AMB Express 2019, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinderola, C.G.; Mocchiutti, P.; Reinheimer, J.A. Interactions among lactic acid starter and probiotic bacteria used for fermented dairy products. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradhipta, D.H.V.; Joo, Y.H.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, J.D.; Kim, S.C. Effects of inoculant application on fermentation quality and rumen digestibility of high moisture sorghum-sudangrass silage. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2019, 47, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesson, A.; Forsberg, C.W. Polysaccharide degradation by rumen microorganisms. In The Rumen Microbial Ecosystem, 2nd ed.; Hobson, P.N., Stewart, C.S., Eds.; Blackie Academic and Professional: London, UK, 1997; pp. 329–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradhipta, D.H.V.; Joo, Y.H.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, S.S.; Kwak, Y.S.; Han, O.K.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.C. Effects of wild or mutated inoculant on rye silage and its rumen fermentation indices. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 33, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, J.D.; Dhanoa, M.S.; Morant, S.V.; France, J.; Napper, D.J.; Schuller, E. Rates of production of acetate, propionate, and butyrate in the rumen of lactating dairy cows given normal and low-roughage diets. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 3620–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, C.; Chaves-López, C.; Serio, A.; Casaccia, M.; Maggio, F.; Paparella, A. Effectiveness and mechanisms of essential oils for biofilm control on food-contact surfaces: An update review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donadu, M.G.; Le, N.T.; Ho, D.V.; Doan, T.Q.; Le, A.T.; Raal, A.; Usai, M.; Marchetti, M.; Sanna, G.; Madeddu, S.; et al. Phytochemical compositions and biological activities of essential oil from the leaves, rhizomes, and whole plant of Hornstedtia bella Škorničk. Antibiotics 2020, 8, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindgren, S.; Pettersson, K.; Kaspersson, A.; Jonsson, A.; Lingvall, P. Microbial dynamic during aerobic deterioration of silage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1985, 36, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Item 1 | Forage | SE |
|---|---|---|
| Dry matter | 287 | 0.431 |
| Crude protein | 89.8 | 0.100 |
| Ether extract | 35.1 | 0.208 |
| Crude ash | 49.8 | 0.192 |
| Neutral detergent fiber | 404 | 1.070 |
| Acid detergent fiber | 219 | 0.902 |
| Hemicellulose | 186 | 1.884 |
| IVDMD | 661 | 2.058 |
| IVNDFD | 334 | 2.251 |
| Item 1 | Treatment 2 | SEM | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 5M | 6M | MIX | |||
| Dry matter | 263 | 268 | 267 | 266 | 2.115 | 0.088 |
| Crude protein | 87.9 | 88.5 | 88.5 | 88.2 | 1.451 | 0.948 |
| Ether extract | 30.3 | 33.2 | 35.6 | 32.2 | 3.839 | 0.421 |
| Crude ash | 51.8 | 49.8 | 50.5 | 52.7 | 4.410 | 0.812 |
| Neutral detergent fiber | 415 | 416 | 406 | 418 | 13.57 | 0.881 |
| Acid detergent fiber | 230 | 227 | 228 | 223 | 6.443 | 0.673 |
| Hemicellulose | 185 | 189 | 180 | 185 | 13.32 | 0.840 |
| IVDMD | 659 b | 695 a | 676 a b | 693 a | 6.620 | 0.004 |
| IVNDFD | 347 b | 403 a | 375 a b | 393 a | 14.05 | 0.006 |
| Item | Treatment 1 | SEM | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 5M | 6M | MIX | |||
| Fermentation characteristics | ||||||
| pH | 3.73 a | 3.68 b | 3.68 b | 3.67 b | 0.018 | 0.008 |
| Ammonia-N, g/kg DM | 0.88 | 0.81 | 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.040 | 0.061 |
| Lactate, g/kg DM | 78.3 c | 86.2 b c | 100.1 a | 97.5 a b | 4.798 | 0.001 |
| Acetate, g/kg DM | 49.7 c | 77.3 b | 87.3 b | 119.8 a | 12.15 | <0.001 |
| Propionate, g/kg DM | ND 2 | ND | ND | ND | N/A | N/A |
| Butyrate, g/kg DM | ND | ND | ND | ND | N/A | N/A |
| Lactate: acetate | 1.58 a | 1.12 b | 1.15 b | 0.81 c | 0.065 | <0.001 |
| Microbial count, log10 cfu/g | ||||||
| Lactic acid bacteria | 7.81 b | 8.78 a | 8.83 a | 8.77 a | 0.109 | <0.001 |
| Yeast | 5.57 a | 5.15 b | 5.18 b | 5.13 b | 0.164 | 0.012 |
| Mold | 3.68 a | 3.32 b | 3.23 b | 3.21 b | 0.097 | <0.001 |
| Item 1 | Treatment 2 | SEM | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 5M | 6M | MIX | |||
| A, mL/g DM | 0.79 a | 0.77 a | 0.78 a | 0.69 b | 0.012 | <0.001 |
| B, mL/g DM | 3.77 b | 3.92 b | 4.05 a b | 4.33 a | 0.099 | 0.007 |
| A + B, mL/g DM | 4.56 b | 4.69 a b | 4.83 a b | 5.02 a | 0.211 | 0.032 |
| C, %/h | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.007 | 0.206 |
| L, h | 3.58 a b | 3.39 b | 3.17 b | 4.11 a | 0.230 | 0.016 |
| Item 1 | Treatment 2 | SEM | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 5M | 6M | MIX | |||
| pH | 6.32 a | 6.28 b | 6.26 b | 6.25 b | 0.014 | 0.004 |
| Ammonia-N, mg/dL | 35.0 | 35.2 | 34.3 | 33.4 | 1.310 | 0.318 |
| Total VFA, mM/L | 138.6 b | 143.0 b | 147.2 b | 161.0 a | 4.668 | 0.001 |
| Acetate, % molar | 57.8 | 57.7 | 58.6 | 58.4 | 0.552 | 0.089 |
| Propionate, % molar | 22.0 a | 21.3 a,b | 20.2 b | 20.1 b | 0.654 | 0.004 |
| Iso-butyrate, % molar | 1.25 | 1.35 | 1.34 | 1.29 | 0.130 | 0.688 |
| Butyrate, % molar | 14.6 b | 14.8 b | 15.3 a,b | 15.7 a | 0.337 | 0.004 |
| Iso-valerate, % molar | 2.74 b | 3.20 a | 3.08 a,b | 3.03 a | 0.181 | 0.022 |
| Valerate, % molar | 1.56 | 1.63 | 1.49 | 1.44 | 0.221 | 0.629 |
| Acetate: propionate | 2.63 b | 2.70 a,b | 2.90 a | 2.91 a | 0.116 | 0.009 |
| Item | Without Contamination 1 | With Contamination | SEM | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 5M | 6M | MIX | CON | 5M | 6M | MIX | |||
| Lactic acid bacteria | ||||||||||
| 24 h | 7.19 c | 8.04 b | 8.51 a | 8.21 b | 7.11 c | 7.83 b | 7.93 b | 7.97 b | 0.103 | |
| 48 h | 6.23 c | 7.81 a | 7.38 b | 8.02 a | 5.23 d | 6.12 c | 6.28 c | 6.28 c | 0.137 | |
| 72 h | 5.42 b | 8.17 a | 8.50 a | 8.35 a | 4.74 c | 5.41 b | 5.52 b | 5.28 b | 0.168 | |
| 96 h | 4.16 c | 5.11 b | 5.80 a | 5.86 a | 4.06 c | 5.05 b | 5.52 a b | 5.28 b | 0.137 | |
| 120 h | 3.88 c | 4.19 b c | 4.29 b | 4.68 a | 4.04 b c | 4.21 b c | 4.13 b c | 4.36 a b | 0.143 | |
| Yeast | ||||||||||
| 24 h | 5.55 c | 5.19 d | 5.19 d | 5.10 d | 6.25 a | 5.81 b | 5.75 b c | 5.58 b c | 0.094 | |
| 48 h | 6.91 b | 6.35 d | 5.94 e | 5.89 e | 7.43 a | 7.37 a | 6.77 b c | 6.67 c | 0.073 | |
| 72 h | 7.98 b c | 7.52 d | 6.93 e | 6.96 e | 8.29 a | 8.00 b | 7.80 c | 7.85 b c | 0.083 | |
| 96 h | 9.12 a | 8.81 b c | 8.46 c d | 8.36 d | 9.17 a | 8.90 b | 8.70 b c | 8.61 c | 0.087 | |
| 120 h | 9.27 a | 9.09 a | 9.13 a | 8.76 b | 9.17 a | 9.13 a | 9.19 a | 9.14 a | 0.058 | |
| Mold | ||||||||||
| 24 h | 3.74 a | 3.27 c | 3.30 b c | 3.25 c | 3.83 a | 3.39 b c | 3.49 b | 3.51 b | 0.093 | |
| 48 h | 4.92 b | 4.33 c | 4.38 c | 4.43 c | 5.52 a | 5.02 b | 4.92 b | 5.03 b | 0.103 | |
| 72 h | 6.92 b | 6.04 c | 5.64 d | 5.67 d | 7.29 a | 7.04 a b | 6.75 b | 6.76 b | 0.124 | |
| 96 h | 9.14 a | 8.97 a b | 8.50 c | 7.94 d | 9.08 a b | 9.04 a b | 8.92 b | 8.52 c | 0.089 | |
| 120 h | 9.43 a | 9.15 a | 9.23 a | 8.85 b | 9.43 a | 9.23 a | 9.30 a | 9.36 a | 0.120 | |
| Contrast 2 | Lactic acid bacteria | Yeast | Mold | |||||||
| INO | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||
| FUS | <0.001 | 0.007 | <0.001 | |||||||
| HOUR | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | |||||||
| INO*FUS | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | |||||||
| INO*HOUR | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | |||||||
| FUS*HOUR | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||
| INO*FUS*HOUR | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||
| HOUR linear | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||
| HOUR quadratic | 0.679 | 0.617 | 0.412 | |||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paradhipta, D.H.V.; Joo, Y.H.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, S.S.; Noh, H.T.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, J.; Min, H.G.; Kim, S.C. Effects of Inoculants Producing Antifungal and Carboxylesterase Activities on Corn Silage and Its Shelf Life against Mold Contamination at Feed-Out Phase. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9030558
Paradhipta DHV, Joo YH, Lee HJ, Lee SS, Noh HT, Choi JS, Kim J, Min HG, Kim SC. Effects of Inoculants Producing Antifungal and Carboxylesterase Activities on Corn Silage and Its Shelf Life against Mold Contamination at Feed-Out Phase. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(3):558. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9030558
Chicago/Turabian StyleParadhipta, Dimas Hand Vidya, Young Ho Joo, Hyuk Jun Lee, Seong Shin Lee, Hyeon Tak Noh, Jeong Seok Choi, Jinwoo Kim, Hyeong Gyu Min, and Sam Churl Kim. 2021. "Effects of Inoculants Producing Antifungal and Carboxylesterase Activities on Corn Silage and Its Shelf Life against Mold Contamination at Feed-Out Phase" Microorganisms 9, no. 3: 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9030558
APA StyleParadhipta, D. H. V., Joo, Y. H., Lee, H. J., Lee, S. S., Noh, H. T., Choi, J. S., Kim, J., Min, H. G., & Kim, S. C. (2021). Effects of Inoculants Producing Antifungal and Carboxylesterase Activities on Corn Silage and Its Shelf Life against Mold Contamination at Feed-Out Phase. Microorganisms, 9(3), 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9030558






