Comparison of Microbial Populations in Saliva and Feces from Healthy and Celiac Adolescents with Conventional and Molecular Approaches after Cultivation on Gluten-Containing Media: An Exploratory Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Isolation of GDMs
2.3. Bacterial 16S RNA Metagenome Sequencing of Fecal Samples and Cultivated Fractions
2.4. Quantification of Fecal SCFAs
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial Community Structure of Fecal Samples from CD Patients and HVs
3.2. GDMs Isolated from Feces and Saliva
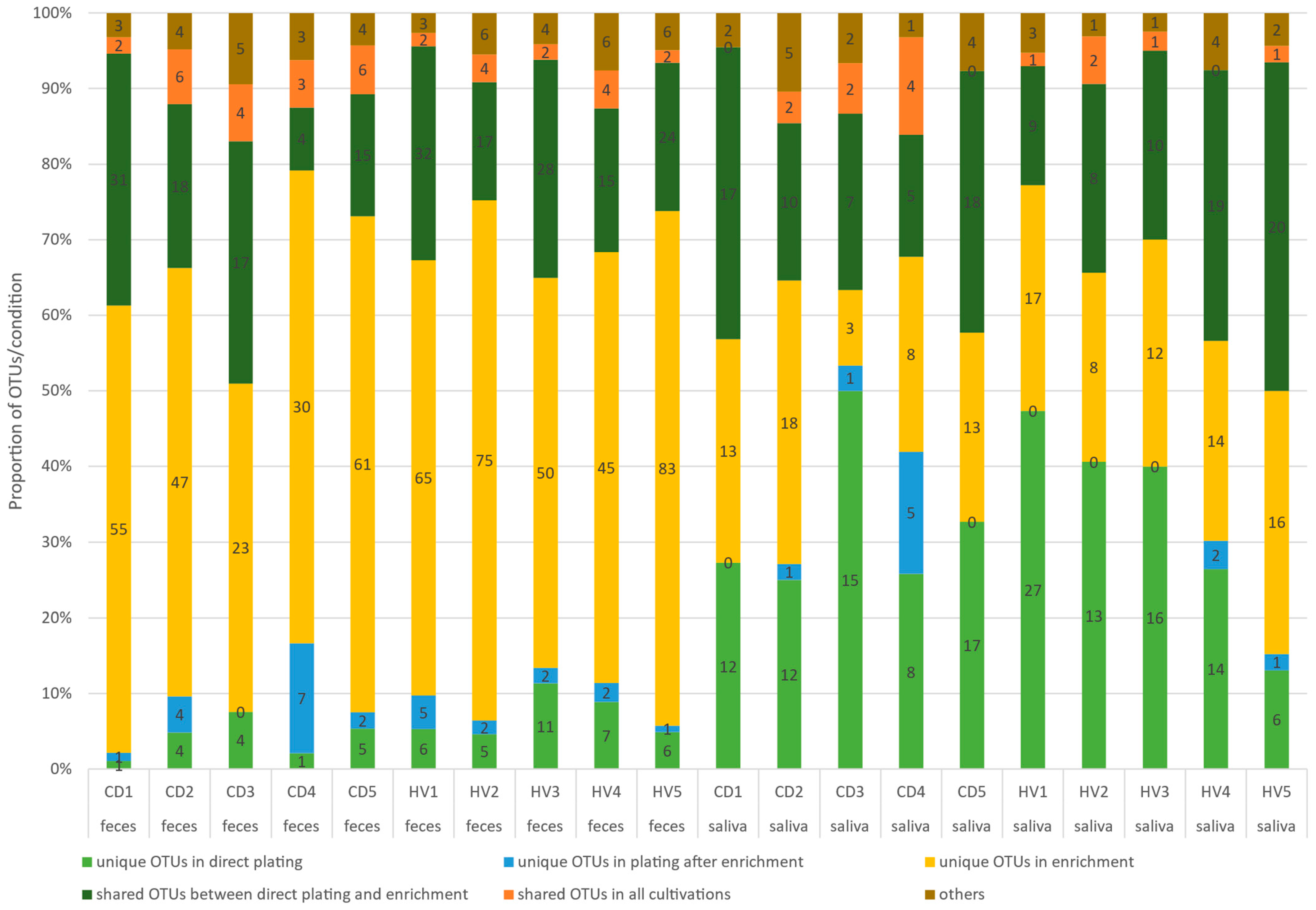
3.3. The Detection of Operational Taxonomic Units (OTUs) after Different Cultivation Approaches of Feces and Saliva Samples from CD Patients and HVs
3.4. SCFA Profiles of Fecal Samples from CD Patients and HVs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caio, G.; Volta, U.; Sapone, A.; Leffler, D.A.; de Giorgio, R.; Catassi, C.; Fasano, A. Celiac disease: A comprehensive current review. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verdu, E.F.; Galipeau, H.; Jabri, B. Novel players in coeliac disease pathogenesis: Role of the gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poddighe, D.; Kushugulova, A. Salivary Microbiome in Pediatric and Adult Celiac Disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panelli, S.; Capelli, E.; Lupo, G.F.D.; Schiepatti, A.; Betti, E.; Sauta, E.; Marini, S.; Bellazzi, R.; Vanoli, A.; Pasi, A.; et al. Comparative Study of Salivary, Duodenal, and Fecal Microbiota Composition Across Adult Celiac Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Solares, J.; Sanchez, L.; Pablo-Torres, C.; Diaz-Fernandez, C.; Sørensen, P.; Barber, D.; Gomez-Casado, C. Celiac Disease Causes Epithelial Disruption and Regulatory T Cell Recruitment in the Oral Mucosa. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akobeng, A.K.; Singh, P.; Kumar, M.; Al Khodor, S. Role of the gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of coeliac disease and potential therapeutic implications. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 3369–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafeiropoulou, K.; Nichols, B.; Mackinder, M.; Biskou, O.; Rizou, E.; Karanikolou, A.; Clark, C.; Buchanan, E.; Cardigan, T.; Duncan, H.; et al. Alterations in Intestinal Microbiota of Children with Celiac Disease at the Time of Diagnosis and on a Gluten-free Diet. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 2039–2051.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofori, F.; Indrio, F.; Miniello, V.L.; De Angelis, M.; Francavilla, R. Probiotics in Celiac Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kõiv, V.; Tenson, T. Gluten-degrading bacteria: Availability and applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 3045–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminero, A.; Galipeau, H.J.; McCarville, J.L.; Johnston, C.W.; Bernier, S.P.; Russell, A.K.; Jury, J.; Herran, A.R.; Casqueiro, J.; Tye-Din, J.A.; et al. Duodenal Bacteria from Patients with Celiac Disease and Healthy Subjects Distinctly Affect Gluten Breakdown and Immunogenicity. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 670–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berger, M.; Sarantopoulos, C.; Ongchangco, D.; Sry, J.; Cesario, T. Rapid isolation of gluten-digesting bacteria from human stool and saliva by using gliadin-containing plates. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 240, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zamakhchari, M.; Wei, G.; Dewhirst, F.; Lee, J.; Schuppan, D.; Oppenheim, F.G.; Helmerhorst, E.J. Identification of Rothia Bacteria as Gluten-Degrading Natural Colonizers of the Upper Gastro-Intestinal Tract. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-Feo, M.; Wei, G.; Blumenkranz, G.; Dewhirst, F.; Schuppan, D.; Oppenheim, F.G.; Helmerhorst, E.J. The cultivable human oral gluten-degrading microbiome and its potential implications in coeliac disease and gluten sensitivity. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, e386–e394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, N.; Faller, L.; Leffler, D.A.; Kelly, C.P.; Hansen, J.; Bosch, J.A.; Wei, G.; Paster, B.J.; Schuppan, D.; Helmerhorst, E.J. Salivary Gluten Degradation and Oral Microbial Profiles in Healthy Individuals and Celiac Disease Patients. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e03330-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Helmerhorst, E.J.; Wei, G. Experimental strategy to discover microbes with gluten-degrading enzyme activities. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2014, 9112, 91120D. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caminero, A.; Verdu, E.F. Metabolism of wheat proteins by intestinal microbes: Implications for wheat related disorders. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019, 42, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aas, J.A.; Paster, B.J.; Stokes, L.N.; Olsen, I.; Dewhirst, F.E. Defining the Normal Bacterial Flora of the Oral Cavity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5721–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caminero, A.; Herrán, A.R.; Nistal, E.; Pérez-Andrés, J.; Vaquero, L.; Vivas, S.; De Morales, J.M.G.R.; Albillos, S.M.; Casqueiro, J. Diversity of the cultivable human gut microbiome involved in gluten metabolism: Isolation of microorganisms with potential interest for coeliac disease. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 88, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahnic, A.; Rupnik, M. Different host factors are associated with patterns in bacterial and fungal gut microbiota in Slovenian healthy cohort. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harnett, J.; Myers, S.P.; Rolfe, M. Significantly higher faecal counts of the yeasts candida and saccharomyces identified in people with coeliac disease. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Renga, G.; Bellet, M.M.; Stincardini, C.; Pariano, M.; Oikonomou, V.; Villella, V.R.; Brancorsini, S.; Clerici, C.; Romani, L.; Costantini, C. To Be or Not to Be a Pathogen: Candida albicans and Celiac Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Guryn, K.; Leone, V.; Chang, E.B. Regional Diversity of the Gastrointestinal Microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atarashi, K.; Suda, W.; Luo, C.; Kawaguchi, T.; Motoo, I.; Narushima, S.; Kiguchi, Y.; Yasuma, K.; Watanabe, E.; Tanoue, T.; et al. Ectopic colonization of oral bacteria in the intestine drives T H 1 cell induction and inflammation. Science 2017, 358, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, F.J.; Waddell, B.; Syed, S.A.; Shekarriz, S.; Rabin, H.R.; Parkins, M.D.; Surette, M.G. Culture-enriched metagenomic sequencing enables in-depth profiling of the cystic fibrosis lung microbiota. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjellström, B.; Högberg, L.; Stenhammar, L.; Fälth-Magnusson, K.; Magnusson, K.-E.; Norin, E.; Sundqvist, T.; Midtvedt, T. Faecal short-chain fatty acid pattern in childhood coeliac disease is normalised after more than one year’s gluten-free diet. Microb. Ecol. Heal. Dis. 2013, 24, 20905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Feces | Saliva | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy Volunteers (HVs) | Celiac Disease (CD) Patients | Healthy Volunteers (HVs) | Celiac Disease (CD) Patients | |
| No. of GDM-positive samples | 3/5 | 2/5 | 3/5 | 3/5 |
| No. of strains | 9 | 3 | 21 | 12 |
| Aerobic conditions | Bacillus pumilus (HV2, D) Escherichia coli (HV3, D) Enterobacter cloacae (HV2, D) Klebsiella aerogenes (HV3, D, 3 strains), Lactobacillus paracasei (HV4, E) Lactobacillus plantarum (HV4, E) Paenibacillus pasadenensis (HV3, E) | Candida albicans (CD3, E) | Candida albicans (HV4, D, 3 strains) Rothia mucilaginosa (HV1, D, 3 strains; HV4, D, 3 strains) Streptococcus salivarius (HV4, D) Klebsiella aerogenes (HV3, D) Micrococcus luteus (HV3, D, 2 strains) Staphylococcus epidermidis (HV1, D; HV4, D) | Candida albicans (CD3, E, 5 strains) Rothia mucilaginosa (CD1, D) Streptococcus salivarius (CD2, D) 5 unidentified strains (CD2, D) * |
| Anaerobic conditions | Veillonella atypica (CD1, E, 2 strains) | Veillonella atypica (HV4, D) Veillonella parvula (HV4, D) Prevotella histicola (HV4, D, 4 strains) | ||
| Acetic Acid (Acetate) | Propionic Acid (Propionate) | Isobutyric Acid | Butyric Acid (Butyrate) | Isovaleric Acid | Valeric Acid (Valerate) | Caproic Acid | Total SCFA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | 0.040 | 0.222 | 0.150 | 0.169 | 0.469 | 0.393 | 0.089 | 0.047 |
| HV Average (SD) | 124.987 (25.988) | 19.838 (6.856) | 3.099 (0.708) | 13.740 (3.857) | 4.042 (1.169) | 2.304 (0.407) | 0.143 (0.026) | 168.154 (34.1) |
| CD Average (SD) | 92.377 (14.348) | 14.798 (5.056) | 2.297 (0.877) | 9.412 (5.084) | 3.388 (1.528) | 1.798 (1.185) | 0.747 (0.698) | 124.817 (20.125) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Senicar, T.; Kukovicic, A.; Tkalec, V.; Mahnic, A.; Dolinsek, J.; Rupnik, M. Comparison of Microbial Populations in Saliva and Feces from Healthy and Celiac Adolescents with Conventional and Molecular Approaches after Cultivation on Gluten-Containing Media: An Exploratory Study. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9112375
Senicar T, Kukovicic A, Tkalec V, Mahnic A, Dolinsek J, Rupnik M. Comparison of Microbial Populations in Saliva and Feces from Healthy and Celiac Adolescents with Conventional and Molecular Approaches after Cultivation on Gluten-Containing Media: An Exploratory Study. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(11):2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9112375
Chicago/Turabian StyleSenicar, Tilen, Andraz Kukovicic, Valerija Tkalec, Aleksander Mahnic, Jernej Dolinsek, and Maja Rupnik. 2021. "Comparison of Microbial Populations in Saliva and Feces from Healthy and Celiac Adolescents with Conventional and Molecular Approaches after Cultivation on Gluten-Containing Media: An Exploratory Study" Microorganisms 9, no. 11: 2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9112375
APA StyleSenicar, T., Kukovicic, A., Tkalec, V., Mahnic, A., Dolinsek, J., & Rupnik, M. (2021). Comparison of Microbial Populations in Saliva and Feces from Healthy and Celiac Adolescents with Conventional and Molecular Approaches after Cultivation on Gluten-Containing Media: An Exploratory Study. Microorganisms, 9(11), 2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9112375






