Surface Layer Protein A Expressed in Clostridioides difficile DJNS06-36 Possesses an Encephalitogenic Mimotope of Myelin Basic Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Determination of Candidate Bacterial Mimicry Peptide Epitopes for Screening
2.2. Isolation and Characterization of Clostridioides difficile
2.3. Generation of Recombinant E. coli Expressing MBP, SLPA, or LacZ
2.4. Cell Culture, T Cell Proliferation and Flow Cytometry
2.5. Mice and EAE Induction of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE)
3. Results
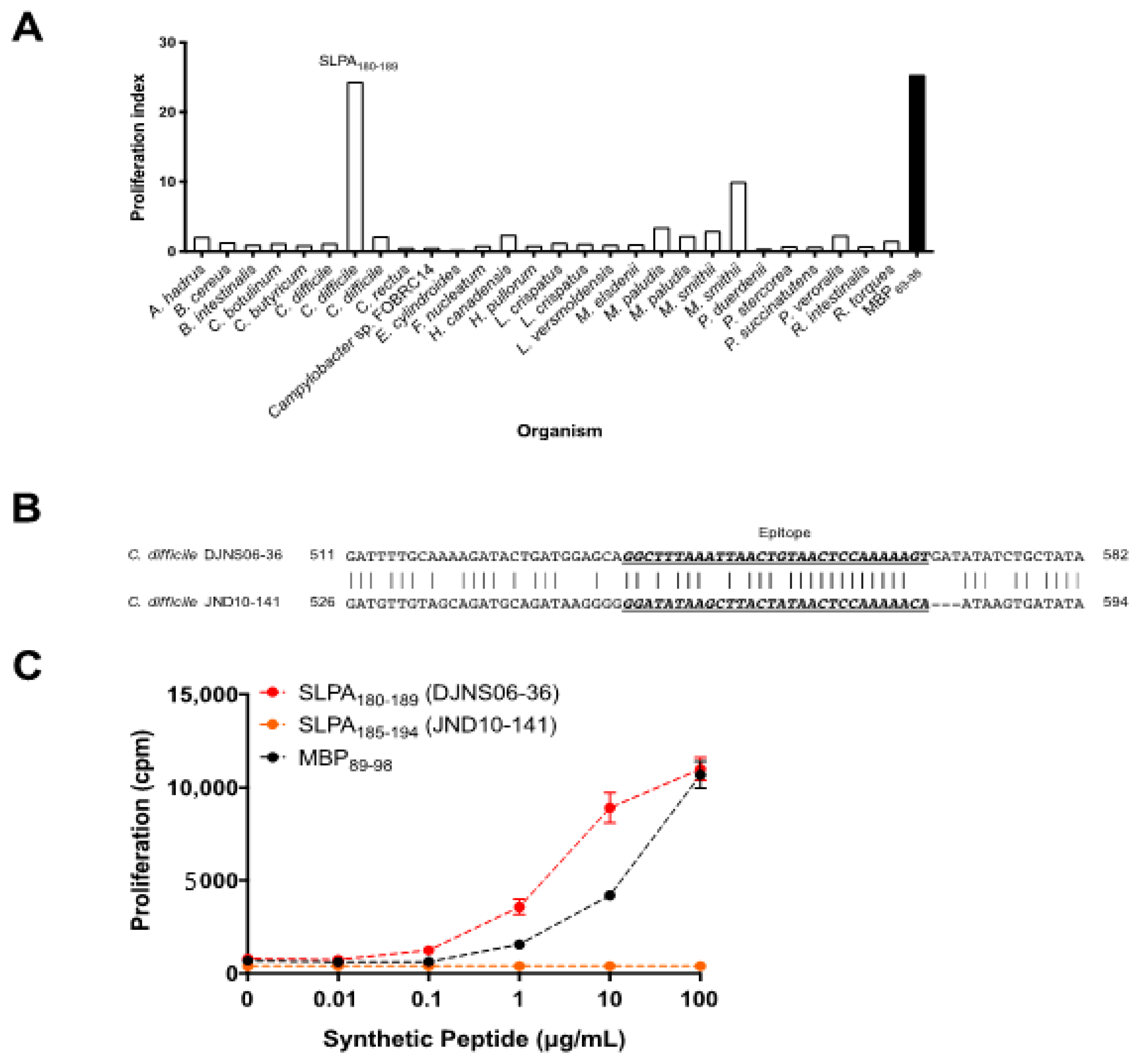
3.1. Screening of Gut Microbes for MBP89-98 Mimotope Peptides
3.2. Diversity amongst the SLPA Mimotopes in C. difficile Strains
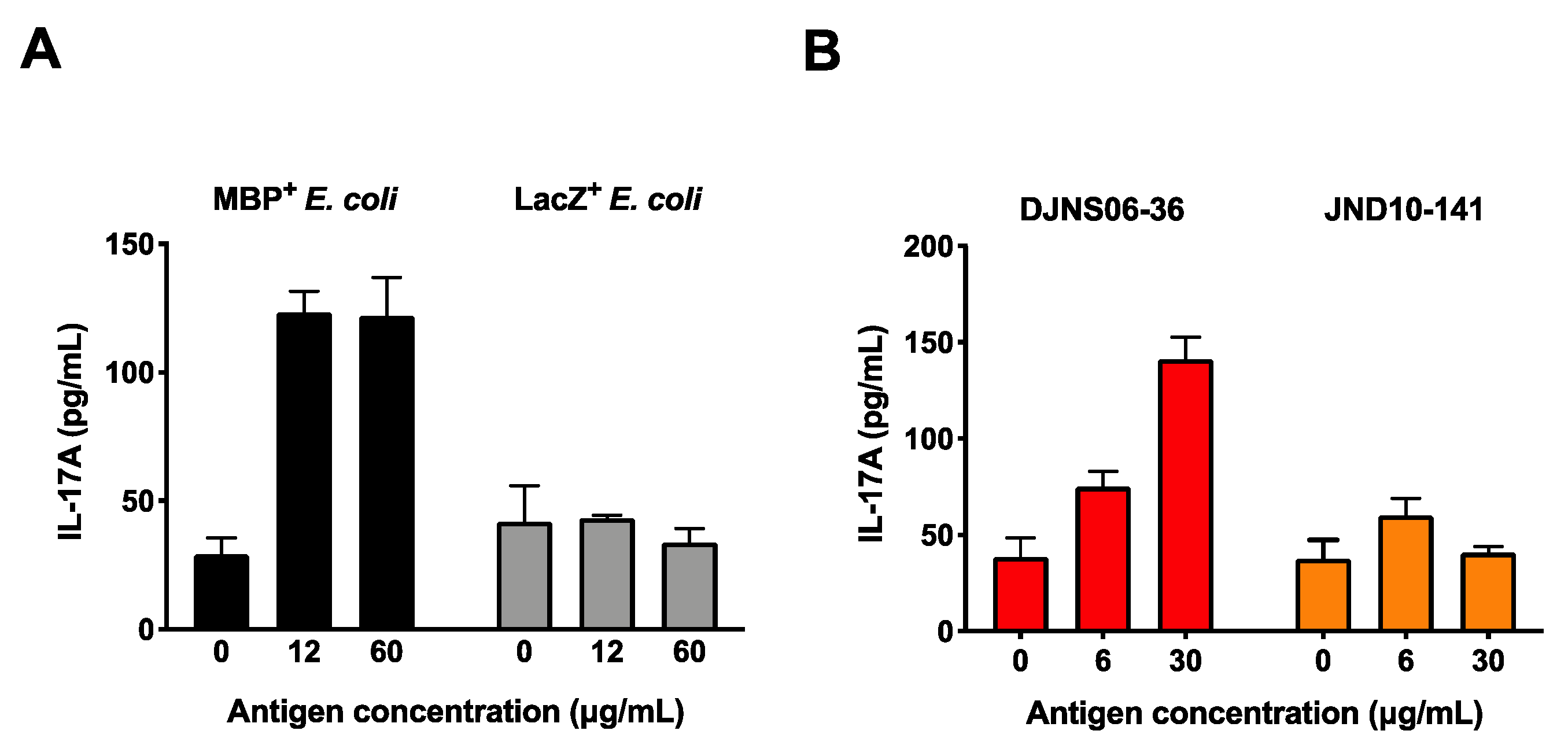
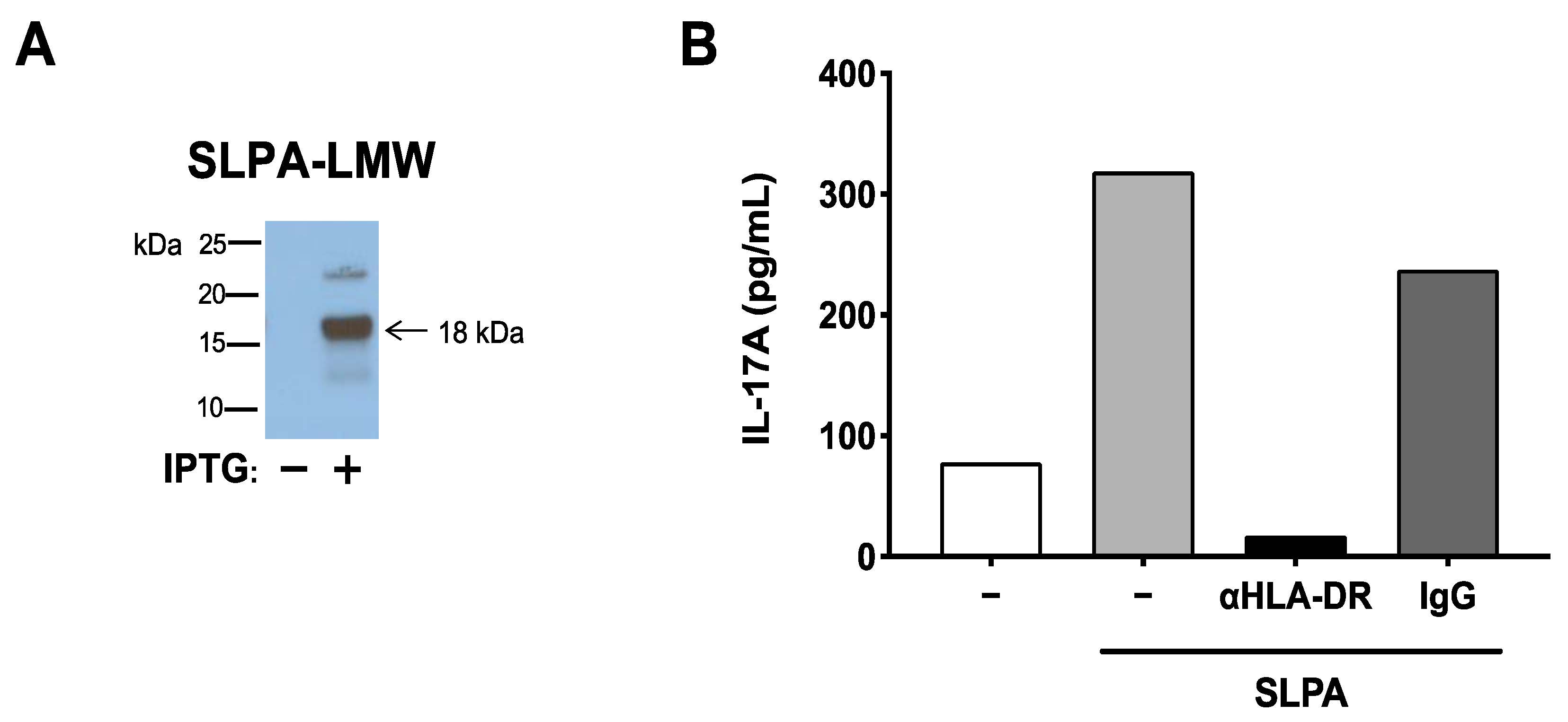
3.3. The SLPA Mimotope Can Be Processed and Presented to MBP89-98-Specific T Cells
3.4. Induction of EAE in MBP-TCR/DR2a Tg Mice upon Immunization with Purified SLPA
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yadav, S.K.; Mindur, J.E.; Ito, K.; Dhib-Jalbut, S. Advances in the immunopathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2015, 28, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujinami, R.S.; Oldstone, M.B. Amino acid homology between the encephalitogenic site of myelin basic protein and virus: Mechanism for autoimmunity. Science 1985, 230, 1043–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gran, B.; Hemmer, B.; Vergelli, M.; McFarland, H.F.; Martin, R. Molecular mimicry and multiple sclerosis: Degenerate T-cell recognition and the induction of autoimmunity. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 45, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.; Gran, B.; Zhao, Y.; Markovic-Plese, S.; Bielekova, B.; Marques, A.; Sung, M.H.; Hemmer, B.; Simon, R.; McFarland, H.F.; et al. Molecular mimicry and antigen-specific T cell responses in multiple sclerosis and chronic CNS Lyme disease. J. Autoimmun. 2001, 16, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venigalla, S.S.K.; Premakumar, S.; Janakiraman, V. A possible role for autoimmunity through molecular mimicry in alphavirus mediated arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Cruz, C.; Perez-Shibayama, C.; De Martin, A.; Ronchi, F.; van der Borght, K.; Niederer, R.; Onder, L.; Lutge, M.; Novkovic, M.; Nindl, V.; et al. Microbiota-derived peptide mimics drive lethal inflammatory cardiomyopathy. Science 2019, 366, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haines, J.L.; Terwedow, H.A.; Burgess, K.; Pericak-Vance, M.A.; Rimmler, J.B.; Martin, E.R.; Oksenberg, J.R.; Lincoln, R.; Zhang, D.Y.; Banatao, D.R.; et al. Linkage of the MHC to familial multiple sclerosis suggests genetic heterogeneity. The Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Group. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1998, 7, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, S.; Kim, S.; Suda, W.; Oshima, K.; Nakamura, M.; Matsuoka, T.; Chihara, N.; Tomita, A.; Sato, W.; Kim, S.W.; et al. Dysbiosis in the Gut Microbiota of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis, with a Striking Depletion of Species Belonging to Clostridia XIVa and IV Clusters. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangi, S.; Gandhi, R.; Cox, L.M.; Li, N.; von Glehn, F.; Yan, R.; Patel, B.; Mazzola, M.A.; Liu, S.; Glanz, B.L.; et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chia, N.; Kalari, K.R.; Yao, J.Z.; Novotna, M.; Soldan, M.M.; Luckey, D.H.; Marietta, E.V.; Jeraldo, P.R.; Chen, X.; et al. Multiple sclerosis patients have a distinct gut microbiota compared to healthy controls. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosorich, I.; Dalla-Costa, G.; Sorini, C.; Ferrarese, R.; Messina, M.J.; Dolpady, J.; Radice, E.; Mariani, A.; Testoni, P.A.; Canducci, F.; et al. High frequency of intestinal TH17 cells correlates with microbiota alterations and disease activity in multiple sclerosis. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atarashi, K.; Tanoue, T.; Shima, T.; Imaoka, A.; Kuwahara, T.; Momose, Y.; Cheng, G.; Yamasaki, S.; Saito, T.; Ohba, Y.; et al. Induction of colonic regulatory T cells by indigenous Clostridium species. Science 2011, 331, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangalam, A.; Shahi, S.K.; Luckey, D.; Karau, M.; Marietta, E.; Luo, N.; Choung, R.S.; Ju, J.; Sompallae, R.; Gibson-Corley, K.; et al. Human Gut-Derived Commensal Bacteria Suppress CNS Inflammatory and Demyelinating Disease. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buscarinu, M.C.; Fornasiero, A.; Romano, S.; Ferraldeschi, M.; Mechelli, R.; Renie, R.; Morena, E.; Romano, C.; Pellicciari, G.; Landi, A.C.; et al. The Contribution of Gut Barrier Changes to Multiple Sclerosis Pathophysiology. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.J.; Ivanov, I.I.; Darce, J.; Hattori, K.; Shima, T.; Umesaki, Y.; Littman, D.R.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D. Gut-residing segmented filamentous bacteria drive autoimmune arthritis via T helper 17 cells. Immunity 2010, 32, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, L.; Lisko, D.J.; Wong, M.Q.; Garcia, R.V.; Himmel, M.E.; Seidman, E.G.; Bressler, B.; Levings, M.K.; Steiner, T.S. Analysis of Flagellin-Specific Adaptive Immunity Reveals Links to Dysbiosis in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 9, 485–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, A.N.; West, N.R.; Stubbington, M.J.T.; Wendt, E.; Suijker, K.I.M.; Datsi, A.; This, S.; Danne, C.; Campion, S.; Duncan, S.H.; et al. Circulating and Tissue-Resident CD4(+) T Cells With Reactivity to Intestinal Microbiota Are Abundant in Healthy Individuals and Function Is Altered During Inflammation. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1320–1337.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wucherpfennig, K.W.; Zhang, J.; Witek, C.; Matsui, M.; Modabber, Y.; Ota, K.; Hafler, D.A. Clonal expansion and persistence of human T cells specific for an immunodominant myelin basic protein peptide. J. Immunol. 1994, 152, 5581–5592. [Google Scholar]
- Quandt, J.A.; Huh, J.; Baig, M.; Yao, K.; Ito, N.; Bryant, M.; Kawamura, K.; Pinilla, C.; McFarland, H.F.; Martin, R.; et al. Myelin basic protein-specific TCR/HLA-DRB5*01:01 transgenic mice support the etiologic role of DRB5*01:01 in multiple sclerosis. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 2897–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K.; Boppana, S.; Ito, N.; Mindur, J.E.; Mathay, M.T.; Patel, A.; Dhib-Jalbut, S.; Ito, K. Gut dysbiosis breaks immunological tolerance toward the central nervous system during young adulthood. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E9318–E9327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarner, F.; Malagelada, J.R. Gut flora in health and disease. Lancet 2003, 361, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, H.; Martin, R.; Mariuzza, R.A. Structural basis for the binding of an immunodominant peptide from myelin basic protein in different registers by two HLA-DR2 proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 304, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lue, J.; Quandt, J.A.; Martin, R.; Mariuzza, R.A. Structure of a human autoimmune TCR bound to a myelin basic protein self-peptide and a multiple sclerosis-associated MHC class II molecule. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 2968–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Sidney, J.; Dow, C.; Mothe, B.; Sette, A.; Peters, B. A systematic assessment of MHC class II peptide binding predictions and evaluation of a consensus approach. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2008, 4, e1000048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Sidney, J.; Kim, Y.; Sette, A.; Lund, O.; Nielsen, M.; Peters, B. Peptide binding predictions for HLA DR, DP and DQ molecules. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Kato, H.; Ito, Y.; Akahane, T.; Izumida, S.; Yokoyama, T.; Kaji, C.; Arakawa, Y. Typing of Clostridium difficile isolates endemic in Japan by sequencing of slpA and its application to direct typing. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Weiner, J.; Liu, Y.; Smith, A.J.; Huss, D.J.; Winger, R.; Peng, H.; Cravens, P.D.; Racke, M.K.; Lovett-Racke, A.E. T-bet is essential for encephalitogenicity of both Th1 and Th17 cells. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergelli, M.; Hemmer, B.; Utz, U.; Vogt, A.; Kalbus, M.; Tranquill, L.; Conlon, P.; Ling, N.; Steinman, L.; McFarland, H.F.; et al. Differential activation of human autoreactive T cell clones by altered peptide ligands derived from myelin basic protein peptide (87-99). Eur. J. Immunol. 1996, 26, 2624–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, A.B.; Kropshofer, H.; Kalbacher, H.; Kalbus, M.; Rammensee, H.G.; Coligan, J.E.; Martin, R. Ligand motifs of HLA-DRB5*0101 and DRB1*1501 molecules delineated from self-peptides. J. Immunol. 1994, 153, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar]
- Waligora, A.J.; Hennequin, C.; Mullany, P.; Bourlioux, P.; Collignon, A.; Karjalainen, T. Characterization of a cell surface protein of Clostridium difficile with adhesive properties. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 2144–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabi, E.; Calabi, F.; Phillips, A.D.; Fairweather, N.F. Binding of Clostridium difficile surface layer proteins to gastrointestinal tissues. Infect. Immun 2002, 70, 5770–5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrigan, M.M.; Venugopal, A.; Roxas, J.L.; Anwar, F.; Mallozzi, M.J.; Roxas, B.A.; Gerding, D.N.; Viswanathan, V.K.; Vedantam, G. Surface-layer protein A (SlpA) is a major contributor to host-cell adherence of Clostridium difficile. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drudy, D.; Calabi, E.; Kyne, L.; Sougioultzis, S.; Kelly, E.; Fairweather, N.; Kelly, C.P. Human antibody response to surface layer proteins in Clostridium difficile infection. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 41, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ausiello, C.M.; Cerquetti, M.; Fedele, G.; Spensieri, F.; Palazzo, R.; Nasso, M.; Frezza, S.; Mastrantonio, P. Surface layer proteins from Clostridium difficile induce inflammatory and regulatory cytokines in human monocytes and dendritic cells. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 2640–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, A.; Lynch, M.; Smith, S.M.; Amu, S.; Nel, H.J.; McCoy, C.E.; Dowling, J.K.; Draper, E.; O’Reilly, V.; McCarthy, C.; et al. A role for TLR4 in Clostridium difficile infection and the recognition of surface layer proteins. PLOS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruxelle, J.F.; Mizrahi, A.; Hoys, S.; Collignon, A.; Janoir, C.; Pechine, S. Immunogenic properties of the surface layer precursor of Clostridium difficile and vaccination assays in animal models. Anaerobe 2016, 37, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossu, D.; Yokoyama, K.; Hattori, N. Bacteria-Host Interactions in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldstone, M.B. Molecular mimicry, microbial infection, and autoimmune disease: Evolution of the concept. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 296, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Chastain, E.M.; Miller, S.D. Molecular mimicry as an inducing trigger for CNS autoimmune demyelinating disease. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 245, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goverman, J.M. Immune tolerance in multiple sclerosis. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 241, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wucherpfennig, K.W.; Strominger, J.L. Molecular mimicry in T cell-mediated autoimmunity: Viral peptides activate human T cell clones specific for myelin basic protein. Cell 1995, 80, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, H.L.; Jacobsen, H.; Ikemizu, S.; Andersson, C.; Harlos, K.; Madsen, L.; Hjorth, P.; Sondergaard, L.; Svejgaard, A.; Wucherpfennig, K.; et al. A functional and structural basis for TCR cross-reactivity in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomakin, Y.; Arapidi, G.P.; Chernov, A.; Ziganshin, R.; Tcyganov, E.; Lyadova, I.; Butenko, I.O.; Osetrova, M.; Ponomarenko, N.; Telegin, G.; et al. Exposure to the Epstein-Barr Viral Antigen Latent Membrane Protein 1 Induces Myelin-Reactive Antibodies In Vivo. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noto, D.; Miyake, S. Gut dysbiosis and multiple sclerosis. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 108380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farache, J.; Koren, I.; Milo, I.; Gurevich, I.; Kim, K.W.; Zigmond, E.; Furtado, G.C.; Lira, S.A.; Shakhar, G. Luminal bacteria recruit CD103+ dendritic cells into the intestinal epithelium to sample bacterial antigens for presentation. Immunity 2013, 38, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madan, R.; Petri, W.A., Jr. Immune responses to Clostridium difficile infection. Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Kita, H.; Karasawa, T.; Maegawa, T.; Koino, Y.; Takakuwa, H.; Saikai, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Yamagishi, T.; Nakamura, S. Colonisation and transmission of Clostridium difficile in healthy individuals examined by PCR ribotyping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 50, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyajima, F.; Roberts, P.; Swale, A.; Price, V.; Jones, M.; Horan, M.; Beeching, N.; Brazier, J.; Parry, C.; Pendleton, N.; et al. Characterisation and carriage ratio of Clostridium difficile strains isolated from a community-dwelling elderly population in the United Kingdom. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabi, E.; Fairweather, N. Patterns of sequence conservation in the S-Layer proteins and related sequences in Clostridium difficile. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 3886–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidhin, D.N.; Ryan, A.W.; Doyle, R.M.; Walsh, J.B.; Kelleher, D. Sequence and phylogenetic analysis of the gene for surface layer protein, slpA, from 14 PCR ribotypes of Clostridium difficile. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, W.J.; Roberts, A.K.; Shone, C.C.; Acharya, K.R. The structure of the S-layer of Clostridium difficile. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 12, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Katchar, K.; Goldsmith, J.D.; Nanthakumar, N.; Cheknis, A.; Gerding, D.N.; Kelly, C.P. A mouse model of Clostridium difficile-associated disease. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1984–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taverniti, V.; Stuknyte, M.; Minuzzo, M.; Arioli, S.; De Noni, I.; Scabiosi, C.; Cordova, Z.M.; Junttila, I.; Hamalainen, S.; Turpeinen, H.; et al. S-layer protein mediates the stimulatory effect of Lactobacillus helveticus MIMLh5 on innate immunity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mursalin, M.H.; Coburn, P.S.; Livingston, E.; Miller, F.C.; Astley, R.; Flores-Mireles, A.L.; Callegan, M.C. Bacillus S-Layer-Mediated Innate Interactions During Endophthalmitis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senoh, M.; Kato, H.; Fukuda, T.; Niikawa, A.; Hori, Y.; Hagiya, H.; Ito, Y.; Miki, H.; Abe, Y.; Furuta, K.; et al. Predominance of PCR-ribotypes, 018 (smz) and 369 (trf) of Clostridium difficile in Japan: A potential relationship with other global circulating strains? J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Senoh, M.; Honda, H.; Fukuda, T.; Tagashira, Y.; Horiuchi, H.; Chiba, H.; Suzuki, D.; Hosokawa, N.; Kitazono, H.; et al. Clostridioides (Clostridium) difficile infection burden in Japan: A multicenter prospective study. Anaerobe 2019, 60, 102011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebaihia, M.; Wren, B.W.; Mullany, P.; Fairweather, N.F.; Minton, N.; Stabler, R.; Thomson, N.R.; Roberts, A.P.; Cerdeno-Tarraga, A.M.; Wang, H.; et al. The multidrug-resistant human pathogen Clostridium difficile has a highly mobile, mosaic genome. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wust, J.; Sullivan, N.M.; Hardegger, U.; Wilkins, T.D. Investigation of an outbreak of antibiotic-associated colitis by various typing methods. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1982, 16, 1096–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Organism | Name of Gene Encoding Candidate Mimotope | Peptide Sequence | NCBI Protein Accession | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anaerostipes hadrus | Riboflavin biosynthesis protein RibF | D | F | K | L | I | V | I | P | K | L | ZP_19295054.1 |
| Bacillus cereus | Ger(X)C family germination protein | R | Y | K | L | T | I | T | P | K | E | ZP_17590229 |
| Bacteroides intestinalis | ATPase/histidine kinase/DNA gyrase B/HSP90 domain | A | K | K | L | M | L | S | K | R | K | EDV06450.1 |
| Clostridium botulinum | Putative histidine kinase | F | Y | K | L | V | L | S | K | R | N | YP_004385843.1 |
| Clostridium butyricum | Integral membrane protein domain protein | A | F | K | L | L | K | T | K | K | G | ZP_02949557 |
| Clostridium difficile | Biotin/lipoate A/B protein ligase family protein | L | F | K | L | I | K | T | K | T | P | ZP_17070733 |
| Clostridium difficile | Surface layer protein A | G | F | K | L | T | V | T | P | K | S | BAF02835 |
| Clostridium difficile | Cell wall-binding repeat 2 family protein | G | Y | K | L | T | I | T | P | K | T | WP_021360901 |
| Campylobacter rectus | Isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase | K | F | K | L | V | L | S | T | R | H | ZP_03610955.1 |
| Campylobacter sp. FOBRC14 | tRNA pseudouridine(38-40) synthase | F | G | K | L | V | L | S | S | R | T | ZP_10843097.1 |
| Eubacterium cylindroides | Glycosyltransferases involved in cell wall biogenesis | F | Y | K | L | I | K | T | K | K | A | CBK88797.1 |
| Fusobacterium nucleatum | Integrase/recombinase | F | F | K | L | I | Q | T | K | S | G | ZP_06750855.1 |
| Helicobacter canadensis | Glutathionylspermidine synthase | F | F | K | N | M | V | I | L | K | F | ZP_04870684.1 |
| Helicobacter pullorum | Glutathionylspermidine synthase | W | F | K | L | I | P | W | E | S | I | WP_065826614 |
| Lactobacillus crispatus | Transporter, major facilitator family | V | F | K | N | I | K | T | R | T | K | ZP_06627878.1 |
| Lactobacillus crispatus | Transporter, major facilitator family | Y | Y | K | P | V | T | P | K | K | T | ZP_06627878.1 |
| Lactobacillus versmoldensis | HNH endonuclease | D | Y | K | L | I | K | T | K | K | G | WP_040521112 |
| Megasphaera elsdenii | CRISPR-associated protein | A | F | K | L | M | K | T | K | K | P | CCC73991 |
| Methanobacterium paludis | MtaA/CmuA family methyltransferase | Q | F | K | S | I | V | K | P | R | L | WP_013825607 |
| Methanobacterium paludis | Thioesterase | M | F | K | T | V | V | T | P | R | F | WP_013825042 |
| Methanobrevibacter smithii | DEXX-box ATPase | M | F | K | R | V | V | T | P | L | N | WP_004032273 |
| Methanobrevibacter smithii | Thioesterase | M | F | R | T | I | V | T | P | K | F | WP_011953703 |
| Peptoniphilus duerdenii | Transcriptional regulator | N | F | K | L | V | K | T | K | K | A | WP_008901584 |
| Prevotella stercorea | Chain length determinant protein | V | F | K | L | L | K | T | K | K | K | CDE30894 |
| Phascolarctobacterium succinatutens | DNA topoisomerase I | A | K | K | T | I | V | T | K | K | T | ZP_08075451.1 |
| Prevotella veroralis | Glycine cleavage system T protein | G | Y | R | L | I | S | T | P | K | S | ZP_05856218 |
| Roseburia intestinalis | Lysine--tRNA ligase | F | K | K | N | I | V | T | K | T | Y | ZP_04745032.1 |
| Ruminococcus torques | Guanine deaminase | K | Y | K | N | T | L | P | I | L | T | CUN31532 |
| Homo sapiens | Myelin basic protein/Golli-Myelin basic protein | F | F | K | N | I | V | T | P | R | T | NP_001020272 |
| Mus musculus | Myelin basic protein/Golli-Myelin basic protein | F | F | K | N | I | V | T | P | R | T | NP_034907 |
| Organisms | Peptide | Peptide Sequence | NCBI Protein Accession | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. difficile DJNS 06-36 | SLPA180-189 | G | F | K | L | T | V | T | P | K | S | BAF02835.1 |
| C. difficile JND 10-141 | SLPA185-194 | G | Y | K | L | T | I | T | P | K | T | BAM66401.1 |
| Homo sapiens | MBP89-98 | F | F | K | N | I | V | T | P | R | T | CAG46717.1 |
| Mus musculus | MBP87-96 | F | F | K | N | I | V | T | P | R | T | NP_034907 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mindur, J.E.; Yadav, S.K.; Ito, N.; Senoh, M.; Kato, H.; Dhib-Jalbut, S.; Ito, K. Surface Layer Protein A Expressed in Clostridioides difficile DJNS06-36 Possesses an Encephalitogenic Mimotope of Myelin Basic Protein. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010034
Mindur JE, Yadav SK, Ito N, Senoh M, Kato H, Dhib-Jalbut S, Ito K. Surface Layer Protein A Expressed in Clostridioides difficile DJNS06-36 Possesses an Encephalitogenic Mimotope of Myelin Basic Protein. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleMindur, John E., Sudhir K. Yadav, Naoko Ito, Mitsutoshi Senoh, Haru Kato, Suhayl Dhib-Jalbut, and Kouichi Ito. 2021. "Surface Layer Protein A Expressed in Clostridioides difficile DJNS06-36 Possesses an Encephalitogenic Mimotope of Myelin Basic Protein" Microorganisms 9, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010034
APA StyleMindur, J. E., Yadav, S. K., Ito, N., Senoh, M., Kato, H., Dhib-Jalbut, S., & Ito, K. (2021). Surface Layer Protein A Expressed in Clostridioides difficile DJNS06-36 Possesses an Encephalitogenic Mimotope of Myelin Basic Protein. Microorganisms, 9(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010034




