Diversity of Gut Microbiota and Bifidobacterial Community of Chinese Subjects of Different Ages and from Different Regions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
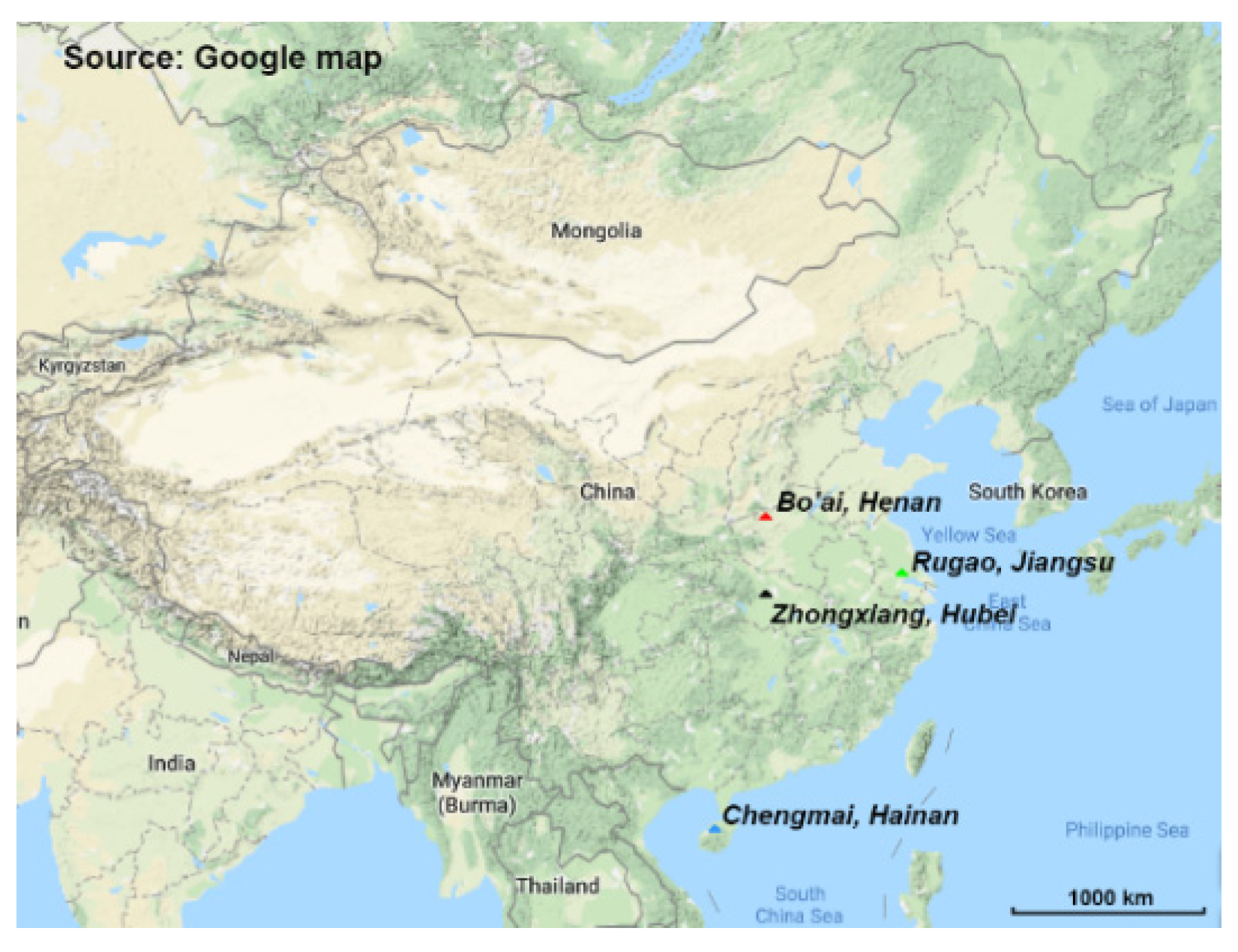
2.1. Subject Recruitment and Fecal Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Alpha-Diversity of Gut Microbiota of Subjects from Different Regions and across Age Groups
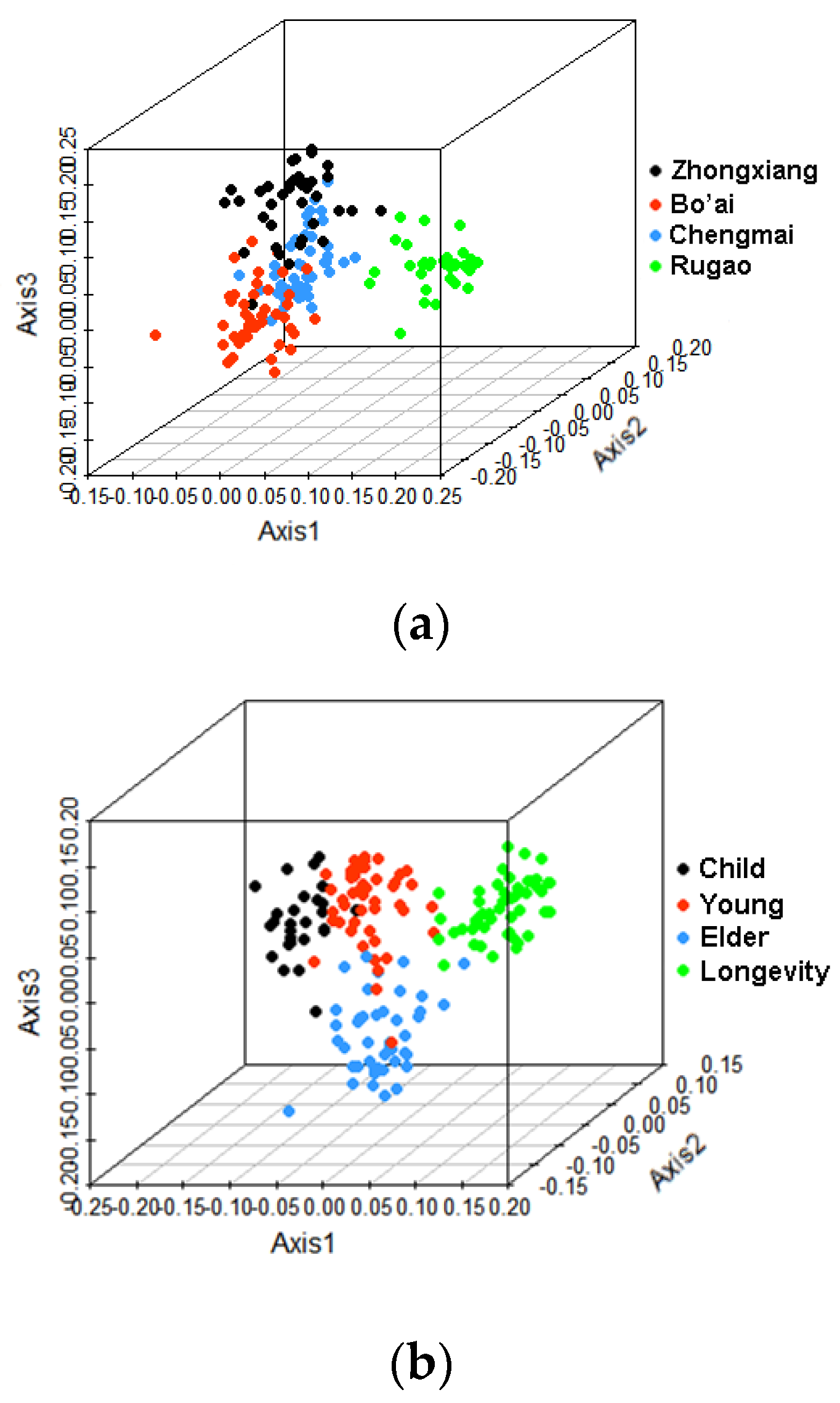
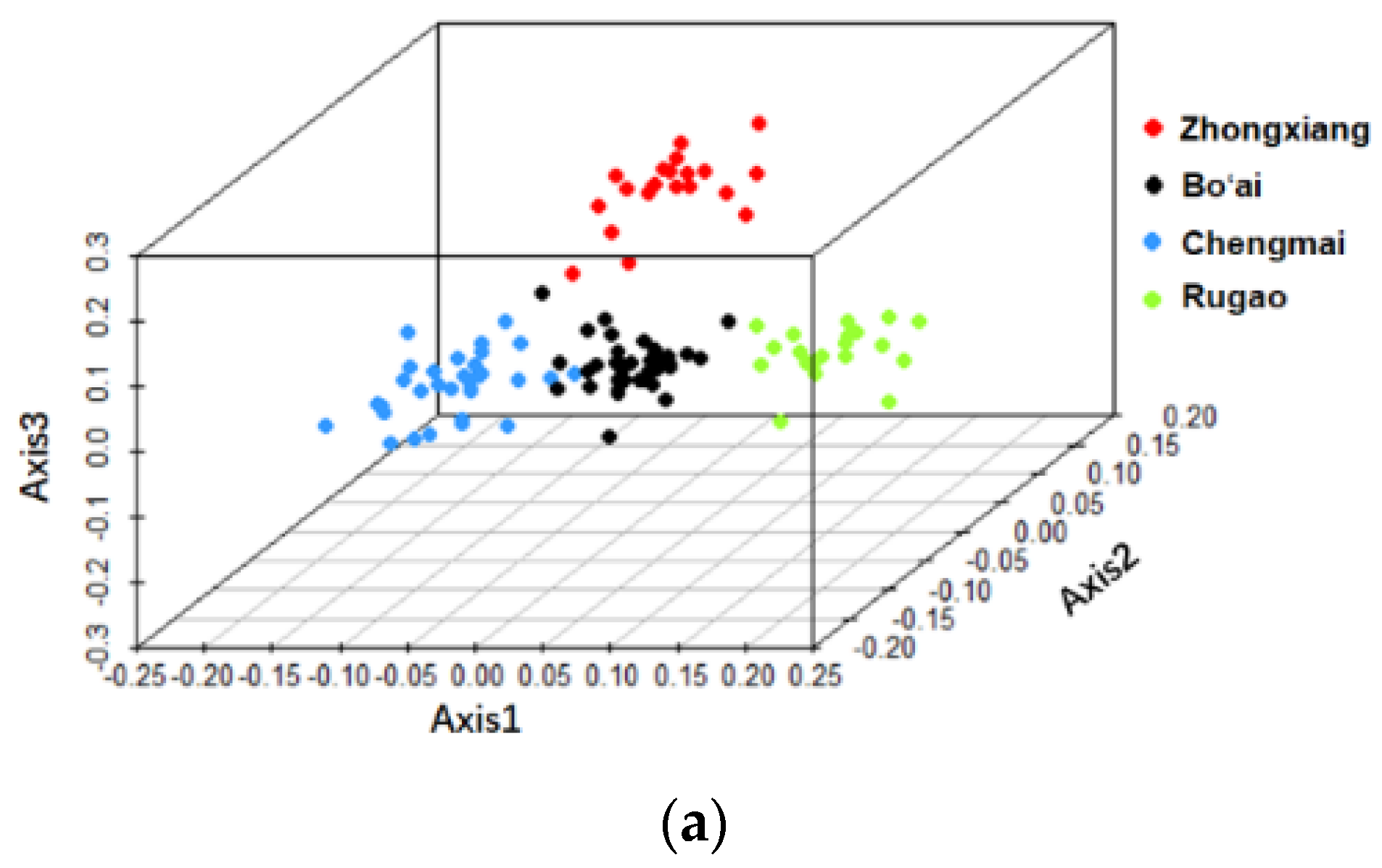
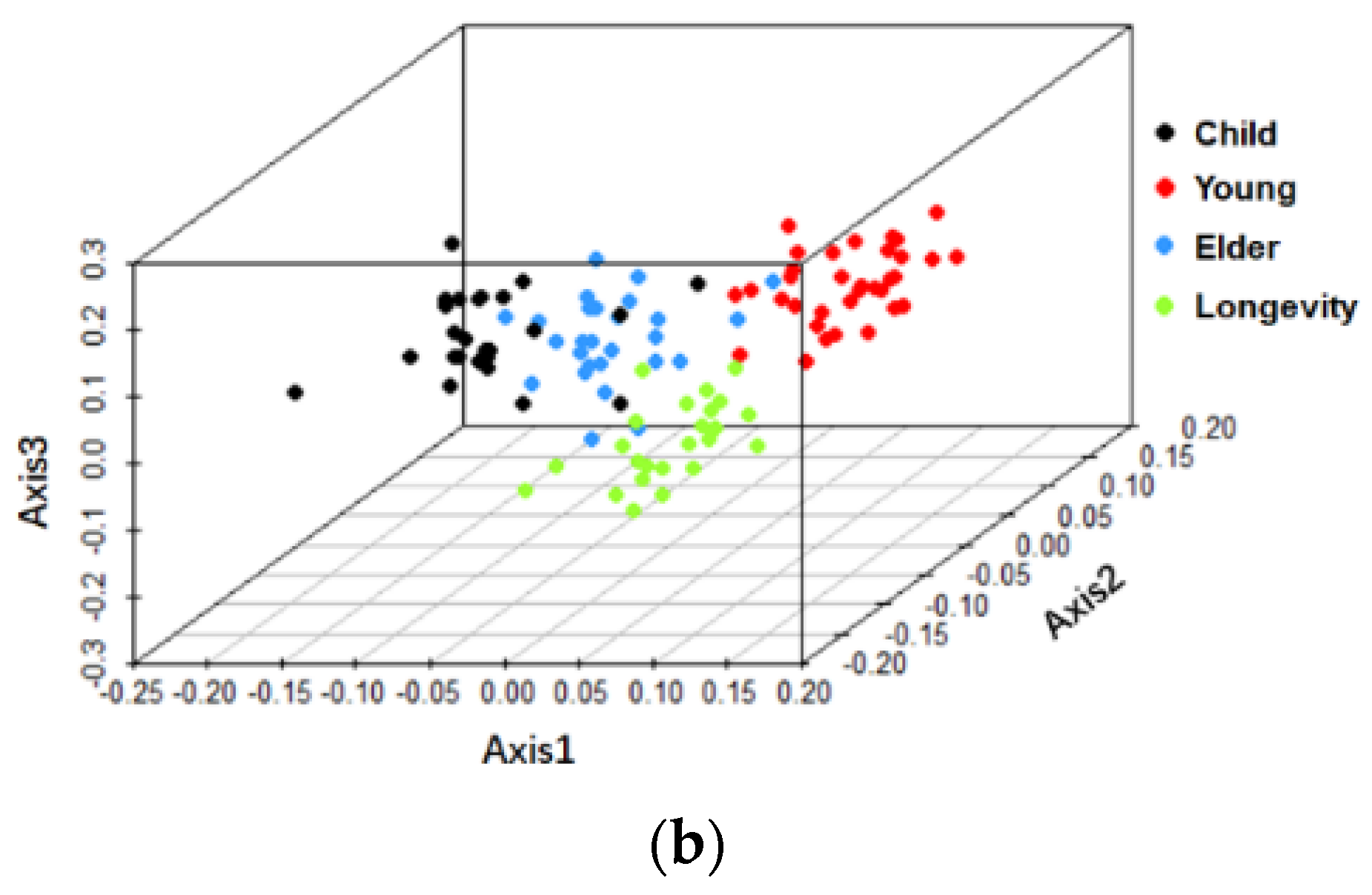
3.2. Beta-Diversity of Gut Microbiota of Subjects from Different Regions and across Age Groups
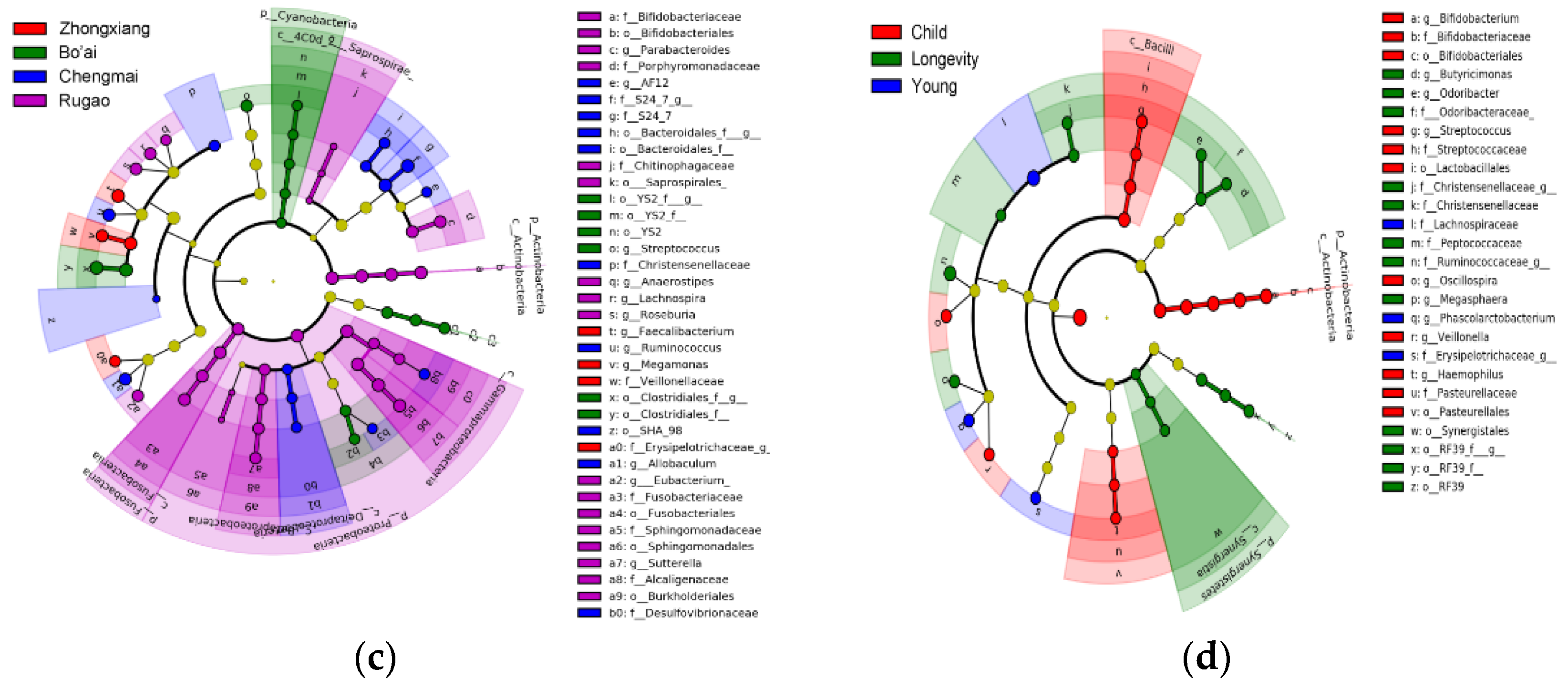
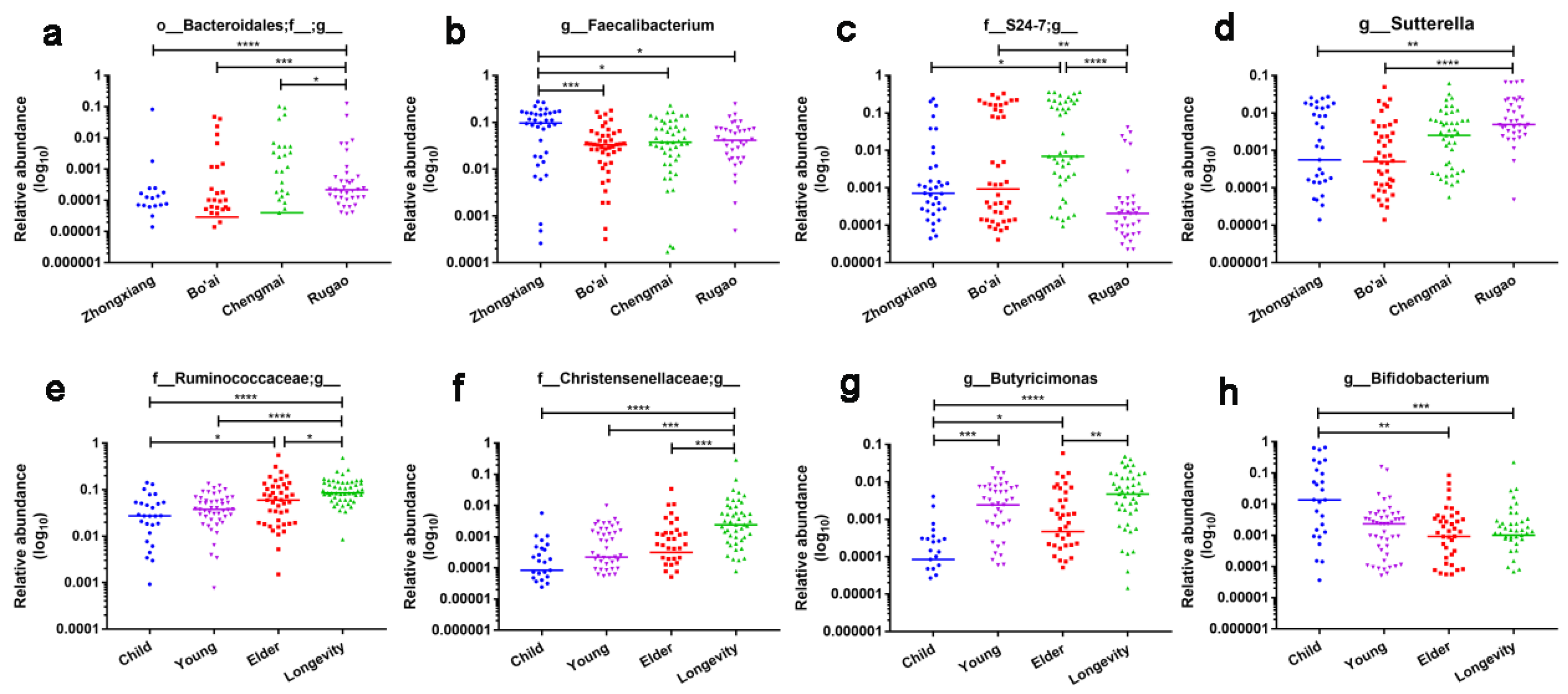
3.3. Composition of Gut Microbes of Subjects from Different Regions and Age Profiles
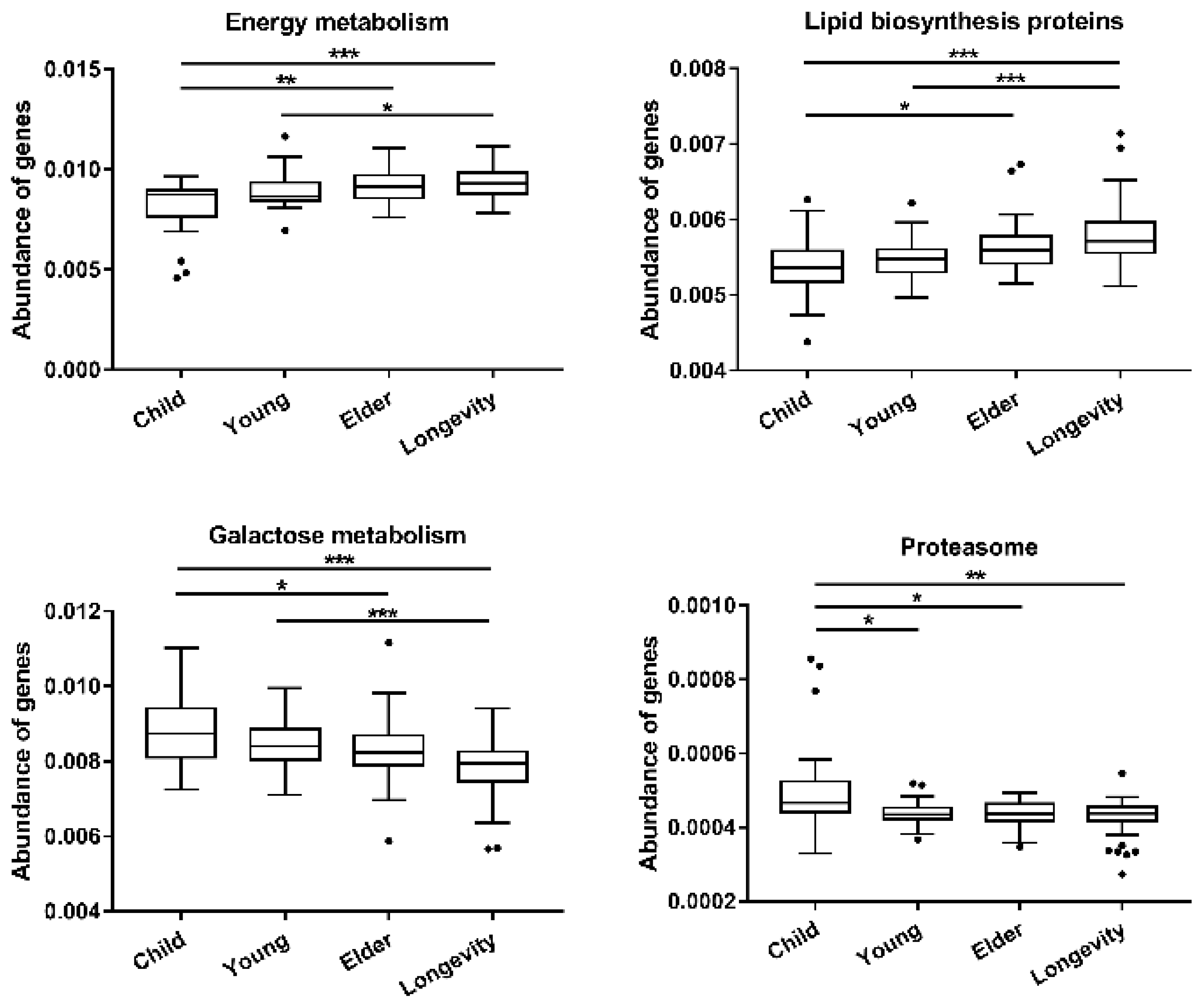
3.4. Functional Gene Composition of Gut Microbiota Predicted by PICRUSt
3.5. Alpha- and Beta-Diversity Analysis of Bifidobacterium Composition within Gut Microbiota of Subjects from Different Regions and across Age Groups
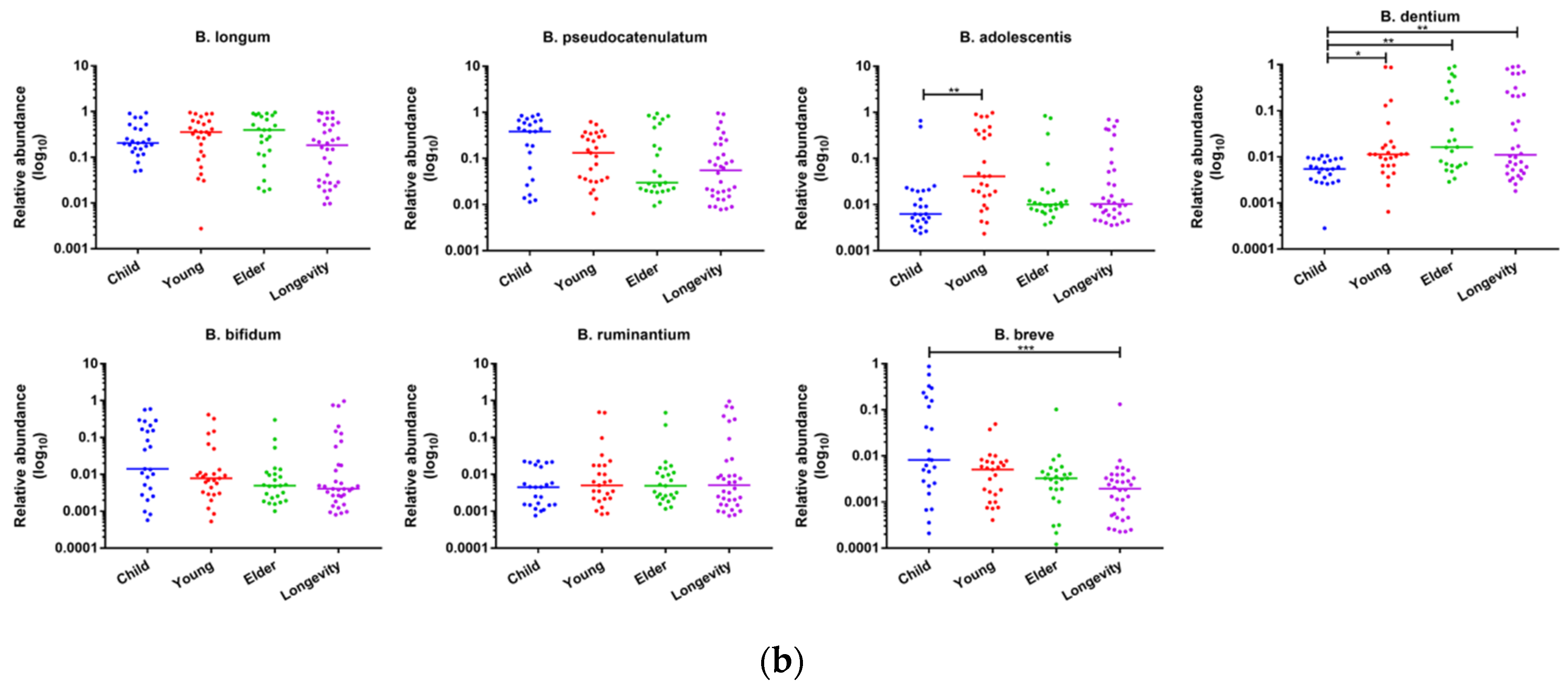
3.6. Composition of Bifidobacterium in Subjects from Different Regions and Age Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sender, R.; Fuchs, S.; Milo, R. Revised Estimates for the Number of Human and Bacteria Cells in the Body. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costea, P.I.; Hildebrand, F.; Arumugam, M.; Backhed, F.; Blaser, M.J.; Bushman, F.D.; de Vos, W.M.; Ehrlich, S.D.; Fraser, C.M.; Hattori, M.; et al. Enterotypes in the landscape of gut microbial community composition. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ventura, M.; Turroni, F.; Motherway, M.O.; MacSharry, J.; van Sinderen, D. Host-microbe interactions that facilitate gut colonization by commensal bifidobacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, N.; Yang, F.; Li, A.; Prifti, E.; Chen, Y.; Shao, L.; Guo, J.; Le Chatelier, E.; Yao, J.; Wu, L.; et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis. Nature 2014, 513, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, S.L.; Gold, M.J.; Hartmann, M.; Willing, B.P.; Thorson, L.; Wlodarska, M.; Gill, N.; Blanchet, M.R.; Mohn, W.W.; McNagny, K.M.; et al. Early life antibiotic-driven changes in microbiota enhance susceptibility to allergic asthma. Embo. Rep. 2012, 13, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, M.P.; Schippa, S.; Zamboni, I.; Penta, M.; Chiarini, F.; Seganti, L.; Osborn, J.; Falconieri, P.; Borrelli, O.; Cucchiara, S. Gut-associated bacterial microbiota in paediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2006, 55, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Ang, K.Y.; Huang, S.; Hou, Q.; Su, X.; Qiao, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Intestinal Microbiota Distinguish Gout Patients from Healthy Humans. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumas, M.E.; Barton, R.H.; Toye, A.; Cloarec, O.; Blancher, C.; Rothwell, A.; Fearnside, J.; Tatoud, R.; Blanc, V.; Lindon, J.C.; et al. Metabolic profiling reveals a contribution of gut microbiota to fatty liver phenotype in insulin-resistant mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12511–12516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schirmer, M.; Garner, A.; Vlamakis, H.; Xavier, R.J. Microbial genes and pathways in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuade, J.L.; Daniel, C.R.; Helmink, B.A.; Wargo, J.A. Modulating the microbiome to improve therapeutic response in cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, e77–e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelzang, A.; Guerrini, M.M.; Minato, N.; Fagarasan, S. Microbiota-an amplifier of autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 55, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.I.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Man and the Microbiome: A New Theory of Everything? Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2019, 15, 371–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; Knight, R.; Abubucker, S.; Badger, J.H.; Chinwalla, A.T.; Creasy, H.H.; Earl, A.M.; FitzGerald, M.G.; Fulton, R.S.; et al. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Chatelier, E.; Nielsen, T.; Qin, J.; Prifti, E.; Hildebrand, F.; Falony, G.; Almeida, M.; Arumugam, M.; Batto, J.M.; Kennedy, S.; et al. Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature 2013, 500, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.J.; Li, R.Q.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, R.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falony, G.; Joossens, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Wang, J.; Darzi, Y.; Faust, K.; Kurilshikov, A.; Bonder, M.J.; Valles-Colomer, M.; Vandeputte, D.; et al. Population-level analysis of gut microbiome variation. Science 2016, 352, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, J.E.; Spor, A.; Scalfone, N.; Fricker, A.D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R.; Angenent, L.T.; Ley, R.E. Succession of microbial consortia in the developing infant gut microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4578–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeffery, I.B.; Claesson, M.J.; O’Toole, P.W.; Shanahan, F. Categorization of the gut microbiota: Enterotypes or gradients? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueimonde, M.; Laitinen, K.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E. Breast milk: A source of bifidobacteria for infant gut development and maturation? Neonatology 2007, 92, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, S.; Toh, H.; Hase, K.; Oshima, K.; Nakanishi, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Tobe, T.; Clarke, J.M.; Topping, D.L.; Suzuki, T.; et al. Bifidobacteria can protect from enteropathogenic infection through production of acetate. Nature 2011, 469, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Rivenson, A.; Tomita, M.; Shimamura, S.; Ishibashi, N.; Reddy, B.S. Bifidobacterium longum, a lactic acid-producing intestinal bacterium inhibits colon cancer and modulates the intermediate biomarkers of colon carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 1997, 18, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, H.; Akedo, I.; Umesaki, Y.; Tanaka, R.; Imaoka, A.; Otani, T. Randomized controlled trial of the effect of bifidobacteria-fermented milk on ulcerative colitis. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2003, 22, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, P.V.P.; Lima, L.N.; Souza, T.C.; Mazochi, V.; Penna, F.J.; Silva, A.M.; Nicoli, J.R.; Guimaraes, E.V. Pediatric functional constipation treatment with Bifidobacterium-containing yogurt: A crossover, double-blind, controlled trial. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 3916–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loman, N.J.; Misra, R.V.; Dallman, T.J.; Constantinidou, C.; Gharbia, S.E.; Wain, J.; Pallen, M.J. Performance comparison of benchtop high-throughput sequencing platforms. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milani, C.; Hevia, A.; Foroni, E.; Duranti, S.; Turroni, F.; Lugli, G.A.; Sanchez, B.; Martin, R.; Gueimonde, M.; van Sinderen, D.; et al. Assessing the fecal microbiota: An optimized ion torrent 16S rRNA gene-based analysis protocol. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turroni, F.; Marchesi, J.R.; Foroni, E.; Gueimonde, M.; Shanahan, F.; Margolles, A.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. Microbiomic analysis of the bifidobacterial population in the human distal gut. ISME J. 2009, 3, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, L.; Lu, W.; Wang, L.; Pan, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W. Assessment of Bifidobacterium Species Using groEL Gene on the Basis of Illumina MiSeq High-Throughput Sequencing. Genes 2017, 8, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, G.; Siegel, P.; He, C.; Wang, H.; Zhao, W.; Zhai, Z.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Quantitative genetic background of the host influences gut microbiomes in chickens. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R. PyNAST: A flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stoddard, S.F.; Smith, B.J.; Hein, R.; Roller, B.R.K.; Schmidt, T.M. rrnDB: Improved tools for interpreting rRNA gene abundance in bacteria and archaea and a new foundation for future development. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D593–D598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anderson, M.J.; Willis, T.J. Canonical Analysis of Principal Coordinates: A Useful Method of Constrained Ordination for Ecology. Ecology 2003, 84, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langille, M.G.I.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, V.; Petr, J. A new selective medium for the isolation of glucose non-fermenting bifidobacteria from hen caeca. J. Microbiol. Methods 2000, 43, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Nomoto, K. Development of multi-color FISH method for analysis of seven Bifidobacterium species in human feces. J. Microbiol. Methods 2004, 58, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, E.; Matsuki, T.; Kubota, H.; Makino, H.; Sakai, T.; Oishi, K.; Kushiro, A.; Fujimoto, J.; Watanabe, K.; Watanuki, M.; et al. Ethnic diversity of gut microbiota: Species characterization of Bacteroides fragilis group and genus Bifidobacterium in healthy Belgian adults, and comparison with data from Japanese subjects. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 116, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, S.J.; Chen, H.C.; Lin, C.K.; Lin, W.H.; Chiang, Y.C.; Hwang, W.Z.; Tsen, H.Y. Development and application of tuf gene-based PCR and PCR-DGGE methods for the detection of 16 Bifidobacterium species. J. Food Drug Anal. 2013, 21, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, F.L.; Yuan, J.H.; Li, J.; Jiang, D.D.; Zhang, J.J.; Li, H.; Wang, R.Y.; Tang, J.; Huang, T.; et al. Effects of dietary fat on gut microbiota and faecal metabolites, and their relationship with cardiometabolic risk factors: A 6-month randomised controlled-feeding trial. Gut 2019, 68, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlsson, C.; Ahrne, S.; Molin, G.; Berggren, A.; Palmquist, I.; Fredrikson, G.N.; Jeppsson, B. Probiotic therapy to men with incipient arteriosclerosis initiates increased bacterial diversity in colon: A randomized controlled trial. Atherosclerosis 2010, 208, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eckburg, P.B.; Bik, E.M.; Bernstein, C.N.; Purdom, E.; Dethlefsen, L.; Sargent, M.; Gill, S.R.; Nelson, K.E.; Relman, D.A. Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 2005, 308, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hollister, E.B.; Riehle, K.; Luna, R.A.; Weidler, E.M.; Rubio-Gonzales, M.; Mistretta, T.A.; Raza, S.; Doddapaneni, H.V.; Metcalf, G.A.; Muzny, D.M.; et al. Structure and function of the healthy pre-adolescent pediatric gut microbiome. Microbiome 2015, 3, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fouhy, F.; Watkins, C.; Hill, C.J.; O’Shea, C.-A.; Nagle, B.; Dempsey, E.M.; O’Toole, P.W.; Ross, R.P.; Ryan, C.A.; Stanton, C. Perinatal factors affect the gut microbiota up to four years after birth. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonnenburg, E.D.; Smits, S.A.; Tikhonov, M.; Higginbottom, S.K.; Wingreen, N.S.; Sonnenburg, J.L. Diet-induced extinctions in the gut microbiota compound over generations. Nature 2016, 529, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dethlefsen, L.; Huse, S.; Sogin, M.L.; Relman, D.A. The pervasive effects of an antibiotic on the human gut microbiota, as revealed by deep 16S rRNA sequencing. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlan, P.D.; Shanahan, F.; O’Mahony, C.; Marchesi, J.R. Culture-independent analyses of temporal variation of the dominant fecal microbiota and targeted bacterial subgroups in Crohn’s disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 3980–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.; Xue, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, G.; Wang, F.; Xu, J.; Cao, H.; et al. A phylo-functional core of gut microbiota in healthy young Chinese cohorts across lifestyles, geography and ethnicities. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1979–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, M.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Le Paslier, D.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, T.; Batto, J.M.; et al. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.D.; Jung, M.J.; Roh, S.W.; Kim, M.S.; Bae, J.W. Comparative analysis of Korean human gut microbiota by barcoded pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking Long-Term Dietary Patterns with Gut Microbial Enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duncan, S.H.; Hold, G.L.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Stewart, C.S.; Flint, H.J. Growth requirements and fermentation products of Fusobacterium prausnitzii, and a proposal to reclassify it as Faecalibacterium prausnitzii gen. nov., comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 2141–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inan, M.S.; Rasoulpour, R.J.; Yin, L.; Hubbard, A.K.; Rosenberg, D.W.; Giardina, C. The luminal short-chain fatty acid butyrate modulates NF-kappaB activity in a human colonic epithelial cell line. Gastroenterology 2000, 118, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, M.; Reynders, V.; Loitsch, S.; Steinhilber, D.; Stein, J.; Schroder, O. Involvement of different nuclear hormone receptors in butyrate-mediated inhibition of inducible NFKB signalling. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 3625–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klampfer, L.; Huang, J.; Sasazuki, T.; Shirasawa, S.; Augenlicht, L. Inhibition of interferon gamma signaling by the short chain fatty acid butyrate. Mol. Cancer Res. 2003, 1, 855–862. [Google Scholar]
- Panasevich, M.R.; Kerr, K.R.; Dilger, R.N.; Fahey, G.C.; Guerin-Deremaux, L.; Lynch, G.L.; Wils, D.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M.; Dowd, S.E.; et al. Modulation of the faecal microbiome of healthy adult dogs by inclusion of potato fibre in the diet. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biagi, E.; Nylund, L.; Candela, M.; Ostan, R.; Bucci, L.; Pini, E.; Nikkila, J.; Monti, D.; Satokari, R.; Franceschi, C.; et al. Through ageing, and beyond: Gut microbiota and inflammatory status in seniors and centenarians. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Hua, Y.; Zeng, B.; Ning, R.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J. Gut microbiota signatures of longevity. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R832–R833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salonen, A.; Lahti, L.; Salojarvi, J.; Holtrop, G.; Korpela, K.; Duncan, S.H.; Date, P.; Farquharson, F.; Johnstone, A.M.; Lobley, G.E.; et al. Impact of diet and individual variation on intestinal microbiota composition and fermentation products in obese men. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2218–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, K.P.; Martin, J.C.; Duncan, S.H.; Flint, H.J. Prebiotic stimulation of human colonic butyrate-producing bacteria and bifidobacteria, in vitro. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 87, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ley, R.E.; Goodrich, J.; Waters, J. Modulation of Fat Storage in a Subject by Altering Population Levels of Christensenellaceae in the GI Tract. US Patent US2017042948(A1), 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont, M. Genetic and Environmental Factors Affecting the Human Gut Microbiom in Obesity. Ph.D. Thesis, King’s College London, London, UK, April 2016. Available online: https://kclpure.kcl.ac.uk/portal/en/theses/genetic-and-environmental-factors-affecting-the-human-gut-microbiom-in-obesity(35617f62-1441-4df1-92db-c3940f530f24).html (accessed on 21 June 2020).
- Samaras, T.T.; Storms, L.H.; Elrick, H. Longevity, mortality and body weight. Ageing Res. Rev. 2002, 1, 673–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.; An, J.; Lee, S.; Kong, H.; Song, Y.; Lee, C.K.; Kim, K. Modulation of the gut microbiota by metformin improves metabolic profiles in aged obese mice. Gut Microbes 2018, 9, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Starr, M.E.; Saito, M.; Evers, B.M.; Saito, H. Age-Associated Increase in Cytokine Production During Systemic Inflammation-II: The Role of IL-1 beta in Age-Dependent IL-6 Upregulation in Adipose Tissue. J. Gerontol. A Biol. 2015, 70, 1508–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weigert, C.; Hennige, A.M.; Brodbeck, K.; Haring, H.U.; Schleicher, E.D. Interleukin-6 acts as insulin sensitizer on glycogen synthesis in human skeletal muscle cells by phosphorylation of Ser(473) of Akt. Am. J. Physiol Endoc. Metab. 2005, 289, E251–E257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rotter, V.; Nagaev, I.; Smith, U. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) induces insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and is, like IL-8 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, overexpressed in human fat cells from insulin-resistant subjects. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 45777–45784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Candore, G.; Caruso, C.; Colonna-Romano, G. Inflammation, genetic background and longevity. Biogerontology 2010, 11, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minciullo, P.L.; Catalano, A.; Mandraffino, G.; Casciaro, M.; Crucitti, A.; Maltese, G.; Morabito, N.; Lasco, A.; Gangemi, S.; Basile, G. Inflammaging and Anti-Inflammaging: The Role of Cytokines in Extreme Longevity. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2016, 64, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Indias, I.; Sanchez-Alcoholado, L.; Garcia-Fuentes, E.; Cardona, F.; Queipo-Ortuno, M.I.; Tinahones, F.J. Insulin resistance is associated with specific gut microbiota in appendix samples from morbidly obese patients. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 5672–5684. [Google Scholar]
- Louca, S.; Polz, M.F.; Mazel, F.; Albright, M.B.N.; Huber, J.A.; O’Connor, M.I.; Ackermann, M.; Hahn, A.S.; Srivastava, D.S.; Crowe, S.A.; et al. Function and functional redundancy in microbial systems. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favier, C.F.; Vaughan, E.E.; De Vos, W.M.; Akkermans, A.D.L. Molecular monitoring of succession of bacterial communities in human neonates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuki, T.; Yahagi, K.; Mori, H.; Matsumoto, H.; Hara, T.; Tajima, S.; Ogawa, E.; Kodama, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Yamada, T.; et al. A key genetic factor for fucosyllactose utilization affects infant gut microbiota development. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, A.; van Sinderen, D. Bifidobacteria and Their Role as Members of the Human Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turroni, F.; Peano, C.; Pass, D.A.; Foroni, E.; Severgnini, M.; Claesson, M.J.; Kerr, C.; Hourihane, J.; Murray, D.; Fuligni, F.; et al. Diversity of bifidobacteria within the infant gut microbiota. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odamaki, T.; Kato, K.; Sugahara, H.; Hashikura, N.; Takahashi, S.; Xiao, J.Z.; Abe, F.; Osawa, R. Age-related changes in gut microbiota composition from newborn to centenarian: A cross-sectional study. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajilic-Stojanovic, M.; Heilig, H.G.H.J.; Molenaar, D.; Kajander, K.; Surakka, A.; Smidt, H.; de Vos, W.M. Development and application of the human intestinal tract chip, a phylogenetic microarray: Analysis of universally conserved phylotypes in the abundant microbiota of young and elderly adults. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1736–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodmansey, E.J.; McMurdo, M.E.; Macfarlane, G.T.; Macfarlane, S. Comparison of compositions and metabolic activities of fecal microbiotas in young adults and in antibiotic-treated and non-antibiotic-treated elderly subjects. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 6113–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, F.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Isolauri, E.; Hosoda, M.; Benno, Y.; Salminen, S. Differences in composition and mucosal adhesion of bifidobacteria isolated from healthy adults and healthy seniors. Curr. Microbiol. 2001, 43, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, M.J.; MacFarlane, G.T. Changes in predominant bacterial populations in human faeces with age and with Clostridium difficile infection. J. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 51, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Zhang, C.; Wu, H.; Wang, R.; Shen, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Pang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; et al. Genomic Microdiversity of Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum Underlying Differential Strain-Level Responses to Dietary Carbohydrate Intervention. MBio 2017, 8, e02348-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodfellow, M.; Kämpfer, P.; Busse, H.-J.; Trujillo, M.; Suzuki, K.-i; Ludwig, W.; Whitman, W. Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology: Volume 5: The Actinobacteria; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaassens, E.S.; Boesten, R.J.; Haarman, M.; Knol, J.; Schuren, F.H.; Vaughan, E.E.; de Vos, W.M. Mixed-Species Genomic Microarray Analysis of Fecal Samples Reveals Differential Transcriptional Responses of Bifidobacteria in Breast- and Formula-Fed Infants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 2668–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duranti, S.; Turroni, F.; Lugli, G.A.; Milani, C.; Viappiani, A.; Mangifesta, M.; Gioiosa, L.; Palanza, P.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. Genomic Characterization and Transcriptional Studies of the Starch-Utilizing Strain Bifidobacterium adolescentis 22L. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 6080–6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, B.; Yan, S.; Chen, Y.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Diversity of Gut Microbiota and Bifidobacterial Community of Chinese Subjects of Different Ages and from Different Regions. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081108
Yang B, Yan S, Chen Y, Ross RP, Stanton C, Zhao J, Zhang H, Chen W. Diversity of Gut Microbiota and Bifidobacterial Community of Chinese Subjects of Different Ages and from Different Regions. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(8):1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081108
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Bo, Shuang Yan, Yang Chen, R. Paul Ross, Catherine Stanton, Jianxin Zhao, Hao Zhang, and Wei Chen. 2020. "Diversity of Gut Microbiota and Bifidobacterial Community of Chinese Subjects of Different Ages and from Different Regions" Microorganisms 8, no. 8: 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081108
APA StyleYang, B., Yan, S., Chen, Y., Ross, R. P., Stanton, C., Zhao, J., Zhang, H., & Chen, W. (2020). Diversity of Gut Microbiota and Bifidobacterial Community of Chinese Subjects of Different Ages and from Different Regions. Microorganisms, 8(8), 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081108




