A Possible Role of Insertion Sequence IS1216V in Dissemination of Multidrug-Resistant Elements MESPM1 and MES6272-2 between Enterococcus and ST59 Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolates
2.2. PCR Mapping of MES Structures
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST)
2.5. Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis (PFGE)
2.6. S1 Nuclease-Digested PFGE
2.7. Southern Blot
2.8. Sequencing and Analysis of the MES Structures and Their Adjacent Environments
2.9. Filter Mating
2.10. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
3. Results
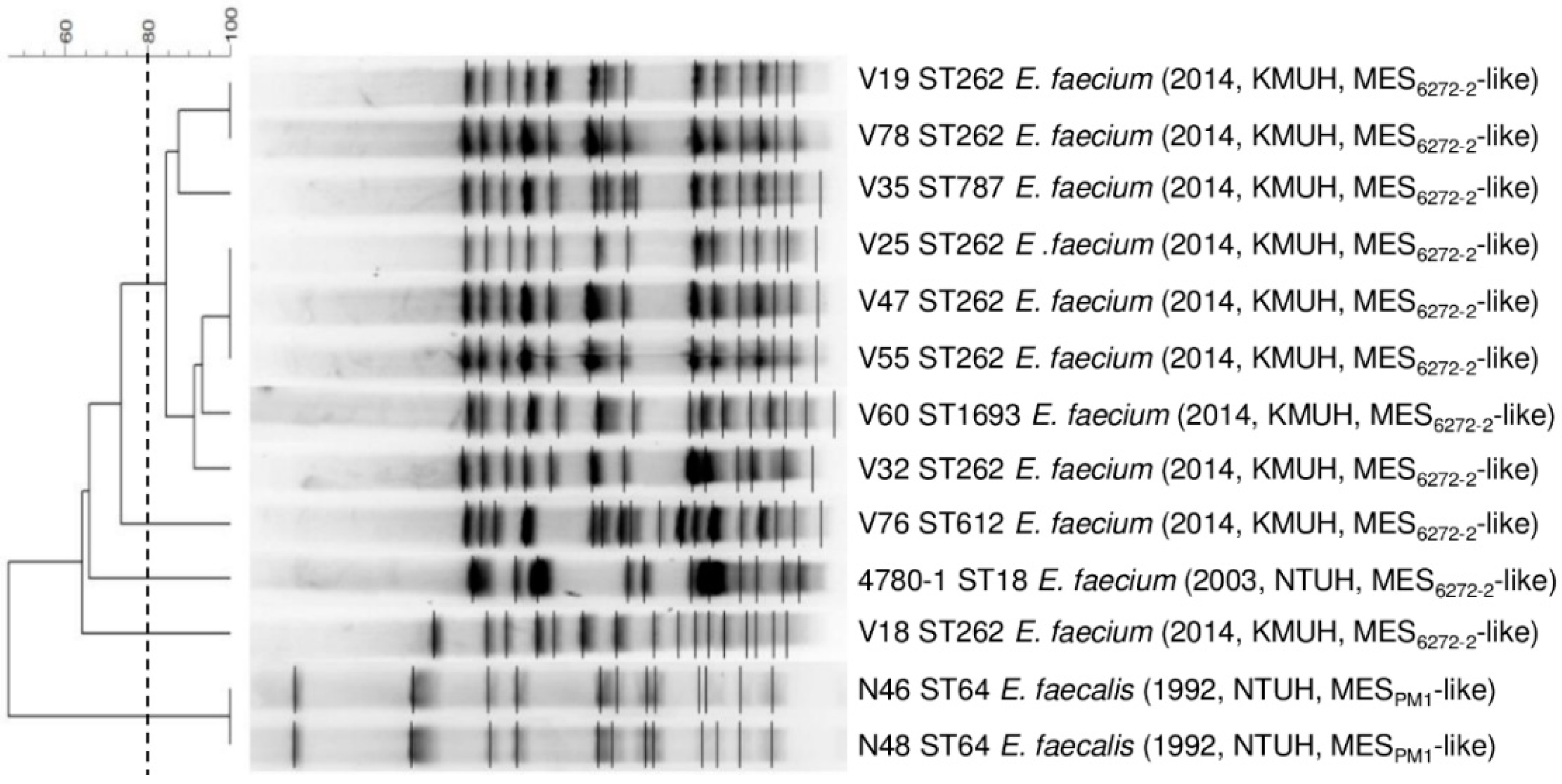
3.1. Molecular Characteristics of MESPM1- or MES6272-2-Carrying Enterococcal Strains
3.2. Localization of the MESPM1- or MES6272-2-Like Elements in Enterococcal Strains
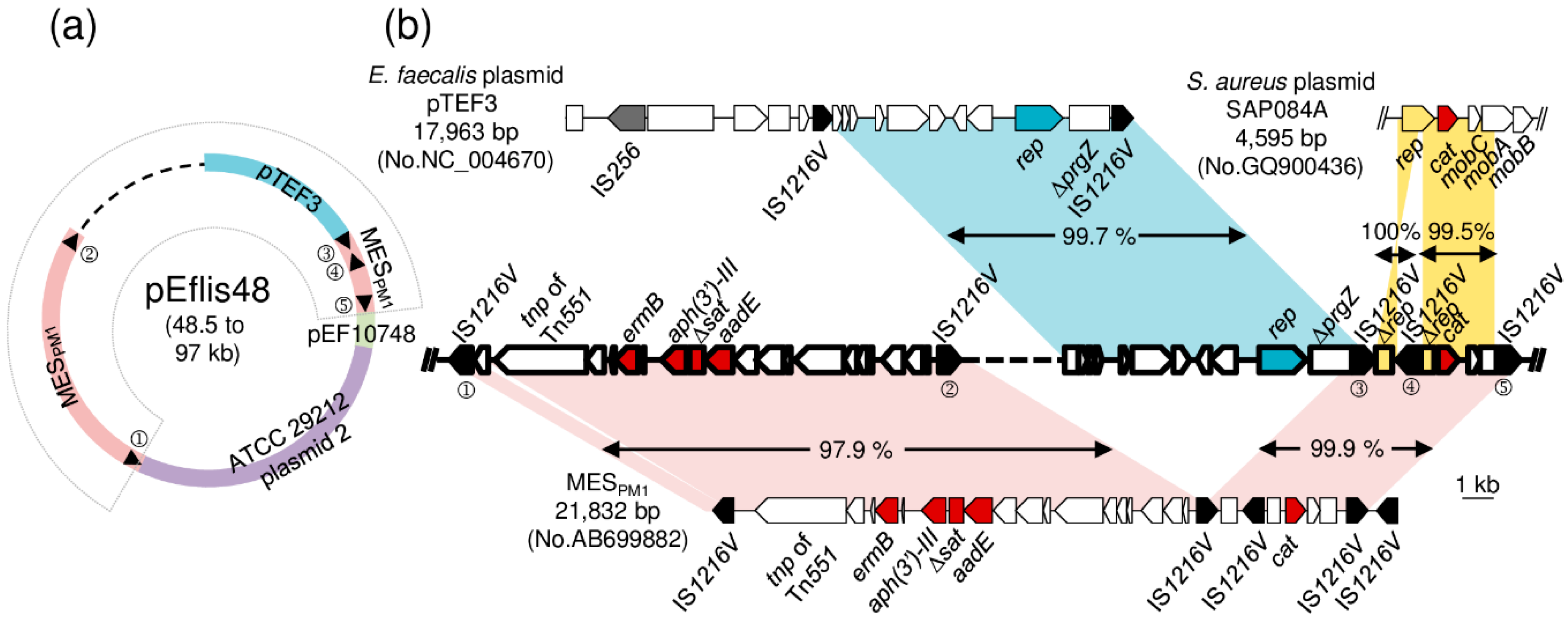
3.3. Sequencing of the MESPM1-Like Elements and the Adjacent Genetic Environments in Enterococcal Strains
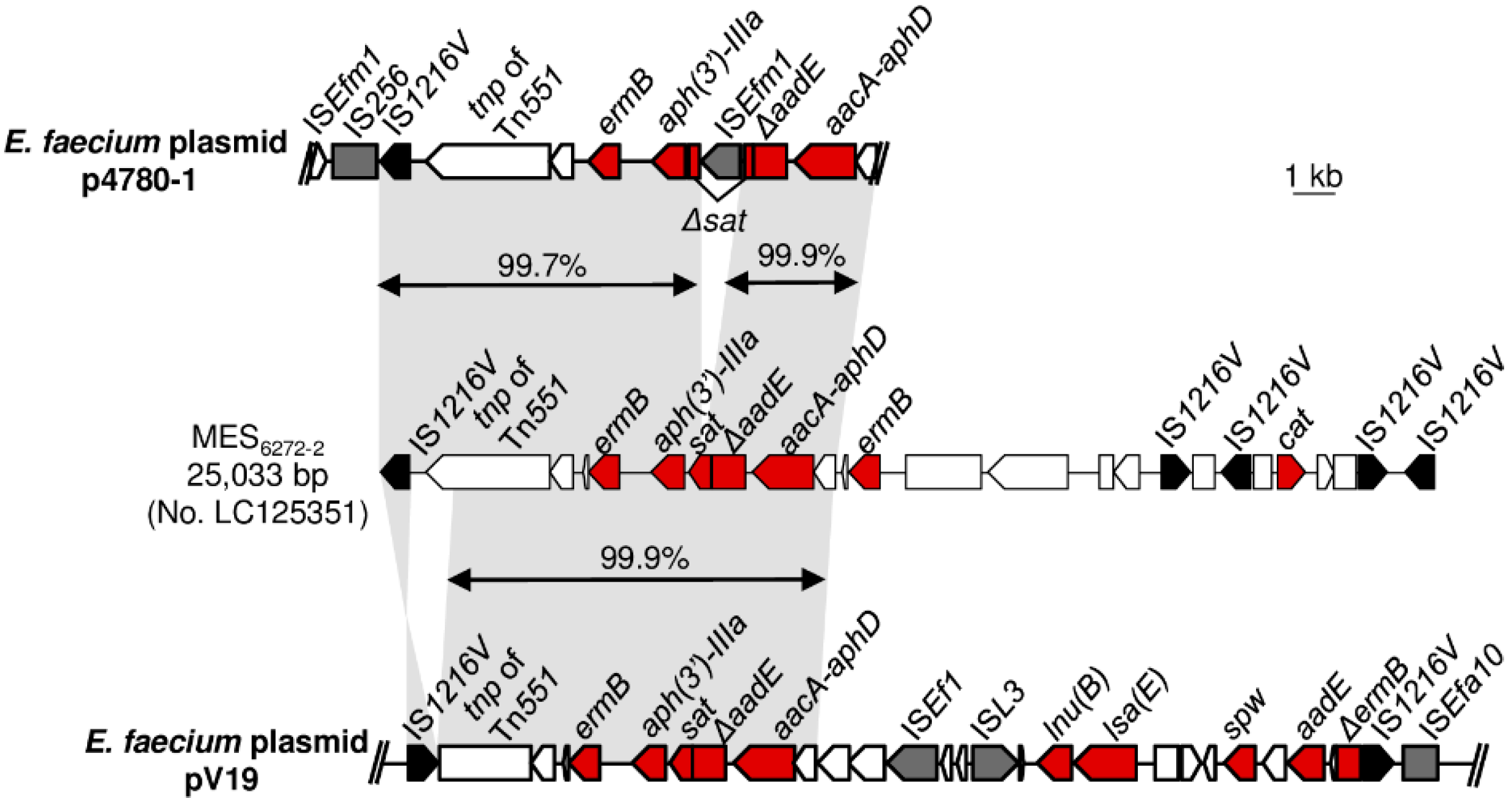
3.4. Sequencing of the MES6272-2-Like Elements and the Adjacent Genetic Environments in Enterococcal Strains
3.5. Horizontal Transfer of MESPM1 or MES6272-2 Encoding Drug Resistance
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, C.J.; Huang, Y.C. New epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus infection in Asia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 605–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.C.; Chen, C.J. Community-associated meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in children in Taiwan, 2000s. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 38, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.C.; Hung, W.W.; Lin, J.M.; Chang, C.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Lai, Y.L.; Tseng, S.P.; Lu, P.L.; Yamamoto, T.; Teng, L.J.; et al. Tracking the evolution of the two successful CC59 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones in Taiwan: The divergence time of the two clades is estimated to be the 1980s. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 106047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.C.; Wan, T.W.; Kuo, Y.C.; Yamamoto, T.; Tsai, J.C.; Lin, Y.T.; Hsueh, P.R.; Teng, L.J. Molecular Evolutionary Pathways toward Two Successful Community-Associated but Multidrug-Resistant ST59 Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Lineages in Taiwan: Dynamic Modes of Mobile Genetic Element Salvages. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, W.C.; Takano, T.; Higuchi, W.; Iwao, Y.; Khokhlova, O.; Teng, L.J.; Yamamoto, T. Comparative genomics of community-acquired ST59 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Taiwan: Novel mobile resistance structures with IS1216V. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahillon, J.; Chandler, M. Insertion sequences. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 725–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmer, C.J.; Hall, R.M. An analysis of the IS6/IS26 family of insertion sequences: Is it a single family? Microb. Genom. 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, C.A.; Murray, B.E. The rise of the Enterococcus: Beyond vancomycin resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Solache, M.; Rice, L.B. The Enterococcus: A model of adaptability to its environment. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00058-00018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, S.; Silva, V.; Dapkevicius, M.L.E.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Enterococci, from harmless bacteria to a pathogen. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenbeck, B.L.; Rice, L.B. Intrinsic and acquired resistance mechanisms in Enterococcus. Virulence 2012, 3, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, S.R.; Kwong, S.M.; Firth, N.; Jensen, S.O. Mobile genetic elements associated with antimicrobial resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegstad, K.; Mikalsen, T.; Coque, T.M.; Werner, G.; Sundsfjord, A. Mobile genetic elements and their contribution to the emergence of antimicrobial resistant Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haaber, J.; Penades, J.R.; Ingmer, H. Transfer of antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, N.C.; Weigel, L.M.; Patel, J.B.; Tenover, F.C. Comparison of Tn1546-like elements in vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from Michigan and Pennsylvania. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 470–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sletvold, H.; Johnsen, P.J.; Wikmark, O.G.; Simonsen, G.S.; Sundsfjord, A.; Nielsen, K.M. Tn1546 is part of a larger plasmid-encoded genetic unit horizontally disseminated among clonal Enterococcus faecium lineages. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 1894–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.W.; Chen, Y.H.; Tseng, S.P.; Jao, Y.T.; Teng, L.J.; Hung, W.C. Using groEL as the target for identification of Enterococcus faecium clades and 7 clinically relevant Enterococcus species. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2019, 52, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. In Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 30th ed.; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Homan, W.L.; Tribe, D.; Poznanski, S.; Li, M.; Hogg, G.; Spalburg, E.; Van Embden, J.D.; Willems, R.J. Multilocus sequence typing scheme for Enterococcus faecium. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Garbajosa, P.; Bonten, M.J.; Robinson, D.A.; Top, J.; Nallapareddy, S.R.; Torres, C.; Coque, T.M.; Canton, R.; Baquero, F.; Murray, B.E.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing scheme for Enterococcus faecalis reveals hospital-adapted genetic complexes in a background of high rates of recombination. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2220–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, A.P.; Bugalho, M.; Ramirez, M.; Carrico, J.A. Global optimal eBURST analysis of multilocus typing data using a graphic matroid approach. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.C.; Chen, H.J.; Lin, Y.T.; Tsai, J.C.; Chen, C.W.; Lu, H.H.; Tseng, S.P.; Jheng, Y.Y.; Leong, K.H.; Teng, L.J. Skin commensal staphylococci may act as reservoir for fusidic acid resistance genes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, B.M.; Harding, G.P.; Zuccarelli, A.J. A general method for detecting and sizing large plasmids. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 226, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurk, S.; Bankevich, A.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.; Korobeynikov, A.; Lapidus, A.; Prjibelsky, A.; Pyshkin, A.; Sirotkin, A.; Sirotkin, Y. Assembling genomes and mini-metagenomes from highly chimeric reads. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference on Research in Computational Molecular Biology, Beijing, China, 7–10 April 2013; pp. 158–170. [Google Scholar]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; Garcia-Fernandez, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Moller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle-Vavra, S.; Ereshefsky, B.; Wang, C.C.; Daum, R.S. Successful multiresistant community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus lineage from Taipei, Taiwan, that carries either the novel Staphylococcal chromosome cassette mec (SCCmec) type VT or SCCmec type IV. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4719–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, L.B.; Carias, L.L. Transfer of Tn5385, a composite, multiresistance chromosomal element from Enterococcus faecalis. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handwerger, S.; Skoble, J. Identification of chromosomal mobile element conferring high-level vancomycin resistance in Enterococcus faecium. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 2446–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaton, M.P.; Discotto, L.F.; Pucci, M.J.; Handwerger, S. Mobilization of vancomycin resistance by transposon-mediated fusion of a VanA plasmid with an Enterococcus faecium sex pheromone-response plasmid. Gene 1996, 171, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morroni, G.; Brenciani, A.; Litta-Mulondo, A.; Vignaroli, C.; Mangiaterra, G.; Fioriti, S.; Citterio, B.; Cirioni, O.; Giovanetti, E.; Biavasco, F. Characterization of a new transferable MDR plasmid carrying the pbp5 gene from a clade B commensal Enterococcus faecium. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S. Tetracycline and chloramphenicol resistance mechanisms. In Antimicrobial Drug Resistance; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 231–243. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, S.; Kehrenberg, C.; Doublet, B.; Cloeckaert, A. Molecular basis of bacterial resistance to chloramphenicol and florfenicol. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 28, 519–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, V.; Vaishampayan, A.; Grohmann, E. Broad-host-range Inc18 plasmids: Occurrence, spread and transfer mechanisms. Plasmid 2018, 99, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Murray, P.R.; Huskins, W.C.; Jernigan, J.A.; McDonald, L.C.; Clark, N.C.; Anderson, K.F.; McDougal, L.K.; Hageman, J.C.; Olsen-Rasmussen, M.; et al. Dissemination of an Enterococcus Inc18-like vanA plasmid associated with vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4314–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Clark, N.; Patel, J.B. pSK41-like plasmid is necessary for Inc18-like vanA plasmid transfer from Enterococcus faecalis to Staphylococcus aureus in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinones, D.; Kobayashi, N.; Nagashima, S. Molecular epidemiologic analysis of Enterococcus faecalis isolates in Cuba by multilocus sequence typing. Microb. Drug Resist. 2009, 15, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Nomura, T.; Yomoda, S.; Tanimoto, K.; Tomita, H. Nosocomial infection caused by vancomycin-susceptible multidrug-resistant Enterococcus faecalis over a long period in a university hospital in Japan. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 58, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Pang, S.; Abraham, S.; Coombs, G.W. Antimicrobial-resistant CC17 Enterococcus faecium: The past, the present and the future. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 16, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, R. Epidemiological and resistance issues in multidrug-resistant staphylococci and enterococci. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer Set | Primer Name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) | PCR Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | IS1216VF | AGTTTACGCACTGCCTCT | 2170 |
| tnpF | CGGTATCCTGGGTGT | ||
| II | IS1216V-fo | CTTCGGTTCATCAAACTGC | 1384 |
| tnp-rev | TCAAATCACCTTCCTACTACCC | ||
| III | tnp-fo | GCGTGTATCTTCGGAGGTA | 2727 |
| ermB-rev | TTGGAACAGGTAAAGGGC | ||
| IV | ermB-fo | ATCTGTGGTATGGCGGGTA | 1432 |
| aphIIIa-rev | ATGACATTGCCTTCTGCG | ||
| V | aphIIIa-fo | TGTCATACCACTTGTCCGC | 1345 (2331 if ISEfm1 insertion) |
| aadE-rev | GCTGCCTGGATAGCACATA | ||
| VI | aadE-R | GTTCCCGCCTCTCTTCTA | 2254 |
| aacA-aphD-F | ATACAGAGCCTTGGGAAG | ||
| A | 1F | AGTAGCCTTTCCCTCACTT | 1301 |
| 35R | GCTTTGACGCTATGACGA | ||
| B | 35F | CCTTACCAGTTGTTCCGAA | 1619 |
| LA-R2 | CCCATGCAGGTTTCAAAATGTGTAAGTCA |
| No. of Isolates | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolation Year | Total | |||
| 1991–1993 | 2002–2003 | 2013–2014 | ||
| Enterococcus species | 95 | 26 | 149 | 270 |
| E. faecalis | 82 | 14 | 30 | 126 |
| E. faecium | 10 | 12 | 117 | 139 |
| Others | 3 (E. hirae) | 0 | 2 (E. raffinosus) | 5 |
| Positive for ermB+, aph3′-IIIa+, aadE+ | 54 | 11 | 63 | 128 |
| MES structures | ||||
| MESPM1-like | 2 (E. faecalis) | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| MES6272-2-like | 0 | 1 (E. faecium) | 10 (E. faecium) | 11 |
| Transfer Frequency | MIC (mg/L) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | KM | SM | GM | C | ||
| Recipient: E. faecalis JH2-2 | 0.25 | 64 | 128 | 16 | 8 | |
| Donor: E. faecalis N48 | 3.7 × 10−2 | >256 | >1024 | >1024 | >1024 | 64 |
| Transconjugants (E. faecalis N48) | >256 | >1024 | >1024 | - | 64 | |
| Donor: E. faecium V19 | 2.5 × 10−7 | >256 | >1024 | 32 | >1024 | 8 |
| Transconjugants (E. faecium V19) | >256 | >1024 | - | 512 | - | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.-T.; Tseng, S.-P.; Hung, W.-W.; Chang, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Jao, Y.-T.; Chen, Y.-H.; Teng, L.-J.; Hung, W.-C. A Possible Role of Insertion Sequence IS1216V in Dissemination of Multidrug-Resistant Elements MESPM1 and MES6272-2 between Enterococcus and ST59 Staphylococcus aureus. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1905. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121905
Lin Y-T, Tseng S-P, Hung W-W, Chang C-C, Chen Y-H, Jao Y-T, Chen Y-H, Teng L-J, Hung W-C. A Possible Role of Insertion Sequence IS1216V in Dissemination of Multidrug-Resistant Elements MESPM1 and MES6272-2 between Enterococcus and ST59 Staphylococcus aureus. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(12):1905. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121905
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yu-Tzu, Sung-Pin Tseng, Wei-Wen Hung, Chen-Chia Chang, You-Han Chen, Ya-Ting Jao, Yen-Hsu Chen, Lee-Jene Teng, and Wei-Chun Hung. 2020. "A Possible Role of Insertion Sequence IS1216V in Dissemination of Multidrug-Resistant Elements MESPM1 and MES6272-2 between Enterococcus and ST59 Staphylococcus aureus" Microorganisms 8, no. 12: 1905. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121905
APA StyleLin, Y.-T., Tseng, S.-P., Hung, W.-W., Chang, C.-C., Chen, Y.-H., Jao, Y.-T., Chen, Y.-H., Teng, L.-J., & Hung, W.-C. (2020). A Possible Role of Insertion Sequence IS1216V in Dissemination of Multidrug-Resistant Elements MESPM1 and MES6272-2 between Enterococcus and ST59 Staphylococcus aureus. Microorganisms, 8(12), 1905. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121905






