Abstract
Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) depends on angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) for cellular entry, but it might also rely on attachment receptors such as heparan sulfates. Several groups have recently demonstrated an affinity of the SARS-CoV2 spike protein for heparan sulfates and a reduced binding to cells in the presence of heparin or heparinase treatment. Here, we investigated the inhibitory activity of several sulfated and sulfonated molecules, which prevent interaction with heparan sulfates, against vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV)-pseudotyped-SARS-CoV-2 and the authentic SARS-CoV-2. Sulfonated cyclodextrins and nanoparticles that have recently shown broad-spectrum non-toxic virucidal activity against many heparan sulfates binding viruses showed inhibitory activity in the micromolar and nanomolar ranges, respectively. In stark contrast with the mechanisms that these compounds present for these other viruses, the inhibition against SARS-CoV-2 was found to be simply reversible.
1. Introduction
Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is causing an unprecedented pandemic, and a better understanding of its biology and pathogenesis is required to identify effective antiviral strategies.
Presently, the only approved antiviral drug is remdesivir, a nucleoside analogue that inhibits viral RNA synthesis of several coronaviruses [1]. However, the results of randomized double-blind clinical trials showed only a reduction in hospitalization time (from 15 to 11 days), while mortality was not significantly reduced compared to placebo [2,3]. Hydroxychloroquine, despite being widely used, did not show any activity in human respiratory cell lines [4], animal models [5], and in vivo clinical trials [6,7]. Conversely, dexamethasone, a corticosteroid, significantly reduced mortality in patients with severe COVID-19 [8]; the efficacy of tocilizumab, a monoclonal antibody directed against interleukin-6 receptor, is being evaluated in clinical trials [9], and anticoagulant treatments have proven to be beneficial [10], demonstrating that targeting the excessive activation of the immune response is a promising strategy.
However, inhibiting viral replication during the initial stages of infection rather than treating the symptoms resulting from immune activation and inflammation will be largely more beneficial in preventing hospitalization and long-term sequelae of infection. For this reason, development of direct-acting antiviral compounds should be a research priority. One class of antiviral compounds in study are attachment inhibitors, with a strategy that is intrinsically broad-spectrum, since many different viruses use similar attachment receptors.
The two major classes of attachment receptors used by viruses are heparan sulfates (HS) [11] and sialic acid [12]. These receptors are widely expressed on eukaryotic cells and used by a wide range of viruses to adhere to the cell surface before interacting with a more specific entry receptor, which triggers uptake and entry [11]. This strategy is used as well by coronaviruses (CoVs). Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)—CoV uses sialic acid (with a preference for α2,3-linked SAs) [13], while NL63 [14] and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) CoV [15] were reported to use HS. In addition to adhesion receptors, NL63, SARS, and SARS-CoV-2 use angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as an entry receptor [16,17].
Sialic acid dependency of SARS-CoV-2 has so far only been investigated with computational methods [18,19], and no biological confirmation is available to date. In contrast, given the sequence similarity between SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV, the dependence on HS has already been investigated by many groups with different approaches. Several reports have shown that HS can act as a co-receptor for SARS-CoV2, inducing a conformational change on the spike that enhances the interaction with ACE2 [20,21,22].
In the work of Kim et al., the interaction of the receptor binding domain of the spike (S) protein of SARS-CoV-2 with heparin and HS was shown by surface plasmon resonance (SPR) [21]. Recombinant S protein was also used in glycan array studies to evaluate the interaction with different glycans, and highlighted a higher binding for highly sulfated glycans [23]. In two recent studies [20,22], the ability of heparin or heparinase treatment to inhibit the binding of SARS-CoV-2 was shown both with pseudotyped or wild-type viruses. In addition, docking studies [20] suggest that the interaction between S and HS is mediated by a site in proximity to but independent from the ACE2 binding domain. Interestingly, Clausen et al. [20] also pointed out that the virus is less dependent on HS on Vero E6, due to a high expression of ACE2.
The proposition of using heparin and heparin analogues to treat COVID-19 is extensively discussed by Tiwari et al. [24], and others are proposing to repurpose drugs mimicking or targeting HS, such as the anticancer pixatimod (PG454) [25], or mitoxantrone, a drug used for acute nonlymphocytic leukemia, prostate cancer, and multiple sclerosis [26].
Additionally, unfractionated heparin (UFH) and low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) are being tested in clinical trials. Heparin is known to have anti-clotting, anti-coagulant, anti-thrombotic, and anti-inflammatory properties and could therefore be effective in treating the coagulopathy and hyper inflammatory response characteristic of critically ill COVID-19 patients. However, this use is unrelated to the direct antiviral activity exerted on viral attachment [27].
Based on these published studies, we tested sulfonated compounds that were previously shown to be active against HS-dependent viruses. In the past, we synthetized gold nanoparticles [28], and β-cyclodextrins [29] coated with mercapto-undecan-sulfonates. In contrast to heparin and other molecules, in which a long alkyl moiety is not present, our compounds were endowed with an irreversible mechanism of action in the absence of toxicity. Upon interaction with HS-dependent viruses, the multivalent binding coupled to structural features of our compounds led to structural damage of the viruses, i.e., the compounds displayed a virucidal activity.
Here, we show that sulfonated materials with a hydrophobic component show inhibitory activity in the same concentration range reported for HS-dependent viruses, but unlike what was observed for a number of other viruses, the inhibition for SARS-CoV-2 is virustatic (reversible) and not virucidal (irreversible).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Compounds and Synthesis of Materials
Heparin sodium salt from porcine mucosa (H4784), Enoxaparin Sodium US Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard (1235820), European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference standard, ι-carrageenan and β-cyclodextrins sulfated sodium salt (CAS: 37191-69-8) were purchased from Sigma. K5N,OS(H) was obtained by Glycores SRL. Resonium A was purchased from Sanofi. Hydroxychloroquine and Heparin sodium salt (2812) were purchased from Tocris bioscience.
MUS:OT NP and MUS-CD were synthetized as previously described [28,29], and the characterization is shown in Figures S1 and S2.
2.2. Cells and Virus
Vero C1008 (clone E6) (ATCC CRL-1586) cells were a kind gift from Prof Gary Kobinger, and were propagated in DMEM High Glucose + Glutamax supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin/streptavidin (pen/strep).
SARS-CoV2/Switzerland/GE9586/2020 was isolated from a clinical specimen in the University Hospital in Geneva in Vero-E6 and passaged twice before the experiments. SARS-CoV-2/München-1.1/2020/929 (kindly provided by M. Müller and C. Drosten; Charité, Berlin, Germany) was propagated on Vero-E6 cells cultured in Dulbecco’s modified minimal essential medium supplemented with 10% heat inactivated fetal bovine serum, 1% non-essential amino acids, 100 µg/mL of streptomycin, 100 IU/mL of penicillin, and 15 mM of HEPES. Supernatant of infected cells was collected 3 days post infection, clarified, aliquoted, and frozen at −80 °C and subsequently titrated by plaque assay in Vero-E6.
2.3. VSV-CoV-2 Production
Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV)-based SARS-CoV-2 pseudotypes (VSV-CoV-2) generated according to [30] and [31] expressing a 19 amino acids C-terminal truncated spike protein (NCBI Reference sequence:NC_045512.2) were produced in HEK293F and titrated in Vero-E6.
2.4. VSV-CoV-2 Inhibition Assays
Vero-E6 cells (13,000 cells per well) were seeded in a 96-well plate. Compounds were serially diluted in DMEM and incubated with VSV-CoV-2 (MOI, 0.001 ffu/cell) for 1h at 37 °C. The mixture was added on cells for 1h at 37 °C. The monolayers were then washed and overlaid with medium containing 2% FBS for 18h. The following day cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde 4%, stained with DAPI, and visualized using an ImageXpress Micro XL (Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA, USA) microplate reader and a 10× S Fluor objective. The percentage of infected cells was estimated by counting the number of cells expressing GFP and the total number of cells (DAPI-positive cells) from four different fields per sample using MetaXpress software (Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA, USA).
2.5. Plaque Assay on VERO-E6 Cells
Vero-E6 cells (100,000 cells per well) were seeded in a 24-well plate. Compounds were serially diluted in DMEM and incubated with SARS-CoV-2 (MOI, 0.005 PFU/cell) for 1 h at 37 °C. The mixture was added on cells for 1h at 37 °C. The monolayers were then washed and overlaid with 0.8% avicel rc581 in DMEM supplemented with 5% FBS. For the experiments described in Figure S3, the protocol is the same as described with two modifications: the number of cells seeded is 83,000 cells per well and the overlay contained 1.2% avicel. Two days after infection, cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde 4% and stained with crystal violet solution containing ethanol. Plaques were counted, the percent inhibition of virus infectivity was determined by comparing the number of plaques in treated wells with the number in untreated control wells, and 50% effective concentration (EC50) was calculated with Prism 8 (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA). Serial dilutions of hydroxychloroquine were added on cells 1h before infection and readded during infection.
2.6. Virucidal Assay
Viruses (105 pfu of SARS-CoV-2) and or MUS:OT NPs or MUS CD (300 µg/mL) were incubated for 1 h at room temperature, and then the virucidal effect was investigated by adding serial dilutions of the mixtures on Vero-E6 for 1h, followed by addition of medium containing avicel as described above. Viral titers were determined at dilutions at which the material was not effective.
3. Results
In order to evaluate the ability of sulfonated compounds to inhibit the attachment of SARS-CoV-2, we pre-incubated VSV pseudo-viruses expressing the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 (VSV-CoV-2) or SARS-CoV-2 wild-type viruses and the compounds for 1 h at 37 °C, followed by addition on cells. After 1 h, cells were washed and the infection was quantified 48 hpi by plaque assay for the wild-type virus or 24 hpi through GFP-positive cells quantification for VSV-CoV-2. The results (Figure 1) show that our nanoparticles (MUS:OT NP) and cyclodextrins (MUS CD) showed inhibitory activity in both cases.
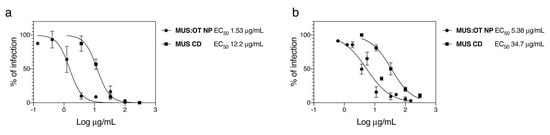
Figure 1.
Inhibitory activity of sulfonated nanomaterial against severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV2). (a) Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV)-CoV-2 or (b) SARS-CoV-2 were incubated for 1 h at 37 °C with different doses of MUS:OT NP or MUS CD and subsequently serially added on cells. In (a), the number of GFP positive cells was evaluated 24 hpi while in (b) the number of plaques was determined 48 hpi. Results are expressed as mean and SEM of three independent experiments.
Importantly, the results on SARS-CoV-2 with MUS:OT NP and MUS CD were confirmed in two independent labs with two different strains of SARS-CoV-2 (SARS-CoV-2/München-1.1/2020/929 and SARS-CoV2/Switzerland/GE9586/2020). In both cases, MUS:OT NP showed higher potency than MUS CD (Figure 1 and Figure S3).
The two compounds previously showed virucidal activity against different HS-dependent viruses, i.e., the ability to permanently impair viral infectivity. Therefore, we assessed whether they also displayed virucidal activity against SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 (105 pfu) was incubated for 1h with 300 µg/mL of the nanomaterials and the mixture was subsequently diluted on cells. The residual infectivity was evaluated at concentrations of molecules known to be non-inhibitory. The results (Figure 2) evidence a lack of virucidal activity of both materials.
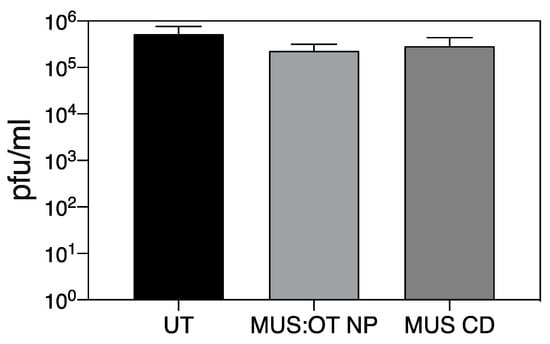
Figure 2.
Virucidal activity. 105 pfu of SARS-CoV-2 was incubated for 1 h at 37 °C with 300 µg/mL and subsequently serially diluted on cells. Infectious titers were evaluated for each treatment condition at dilutions at which the concentration of compound was not active. Results are expressed as mean and SEM of three independent experiments.
To address the HS-dependency of our SARS-CoV-2 strains, we tested, with the same protocol described for MUS:OT NP and MUS CD, the antiviral effect of heparins from different sources, of another sulfated polymer (K5N,OS(H)) and of commercially available sulfated beta-cyclodextrins against VSV-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-2. All of these molecules failed to show antiviral activity up to 1000 µg/mL, while a sulfated polymer, carrageenan, showed very weak antiviral activity but only against wild-type SARS-CoV-2 (Table 1).

Table 1.
Antiviral activity of heparan sulphates (HS) mimicking compounds against VSV-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-2.
4. Discussion
Here, we show the antiviral activity of sulfonated compounds against SARS-CoV-2. These compounds (MUS:OT NP and MUS CD) were previously reported to exert a virucidal (i.e., irreversible) activity against HS-dependent viruses such as Herpes Simplex Virus 2, respiratory syncytial virus, papillomavirus, and dengue virus [28,29], and virustatic (i.e., reversible) activity against vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), an HS-independent virus. The results displayed in Figure 1 and Figure 2 show reversible inhibition for both compounds against SARS-CoV-2, similarly to what we previously reported for VSV. In addition, we show that other HS-mimicking compounds are inactive against SARS-CoV2, as also reported for VSV.
Two different scenarios could account for the lack of virucidal activity of MUS:OT NP and MUS CD against SARS-CoV-2. The restricted virustatic effect may be explained by the peculiar shape of CoVs, whose receptor binding domain (RBD) is approximately ten nanometers away from the viral envelope. We suggested that the virucidal activity of our compound results from a pressure exerted on the RBD of the viral glycoprotein that is then transmitted to the whole virion [28]. This mechanism may then not be applicable to CoVs due to the distance between the RBD and the envelope. Alternatively, and as previously described for VSV [32], the absence of virucidal activity of MUS:OT NP and MUS CD could be due to the poor affinity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein for HS. This second scenario is supported by the absence of inhibitory activity of heparin and other sulfated compounds in our experimental settings. Of note, the observed virustatic effect of our compound compared to the absence of activity of various types of sulfated compounds could be explained by the presence of long hydrophobic linkers that may enhance binding to the basic amino-acid residues of the spike protein. We acknowledge that our results suggest that HS is not used by SARS-CoV2 for infection, and there is abundant literature showing the opposite [20,22,23,26,27,33]. However, also in the current literature, discrepancies in the antiviral potencies of the heparins and heparin analogues are present [33]. For instance, Tandon et al. report IC50 of 5.99 μg/L, 1.08 mg/L, for UFH and enoxaparin, respectively, while Tree et al. [27] report values of 41 μg/mL and 7800 μg/mL, respectively. In our experimental setting, both UFH and LMWH do not show efficacy up to 1000 μg/mL.
The discrepancy of our data with the existing literature could be explained by different hypotheses: (i) differences in the clinical isolate used: point mutations in the spike protein might result in different binding of the virus to HS, as reported for other viruses [34]; moreover, it is well known that multiple passaging in cell culture could lead to cell adaptation and the acquisition of the ability to bind heparan sulfates [11]. In order to prevent this from happening, our clinical isolates were passaged only twice in cells before the experiment, and there is no information about viral passage number in some of the published reports [20,22]. (ii) The secondary role of HS in SARS-CoV-2 entry and the presence of distinct putative domains of interaction on the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 for HS and ACE2. Indeed, Clausen et al. showed that SARS-CoV-2 exploits ACE2 as primary receptor for cell recognition, using heparan sulfate (HS) only as a binding enhancer. They also reported that in Vero-E6, the cell line used in our study, the abundance of ACE2 decreases the dependency of the virus on HS.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, we show that sulfonated cyclodextrin and nanoparticle show, respectively, micromolar and nanomolar inhibitory activity against SARS-CoV-2, further broadening the number of viruses inhibited by these compounds. However, the reversible nature of the inhibition points to less clinical relevance. The lack of irreversible activity could be due to the peculiar shape of coronaviruses or to the low dependency of SARS-CoV-2 on HS for viral attachment.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/8/12/1894/s1. Figure S1. Characterization of MUS: OT NPs. Figure S2. Characterization of MUS CD. Figure S3. Inhibitory activity of sulfonated nanomaterial against SARS-CoV2.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.G., C.T., F.S. and V.C.; methodology, P.V. and V.C.; investigation, M.G., P.V. and V.C.; resources, G.T.; data curation, M.G. and V.C.; writing—original draft preparation, V.C.; writing—review and editing, M.G., F.S. and C.T.; supervision, V.T., F.S. and C.T.; funding acquisition, F.S. and C.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
M.G. was supported by NCCR Bio-Inspired Materials. F.S. was supported by Werner Siemens Foundation. C.T. and F.S. were supported by Carigest Fundation and Swiss National Science Foundation grant 31CA30_196440, and C.T. was supported by the Fondation des HUG.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Isabelle Eckerle for the viral strain provided and Ronald Dijkman for useful discussions. M.G. and V.C. acknowledges Neeraj Dhar, Camille Freyssenet, and Eleonora Simeoni for the support in setting up the BSL3 activities.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pruijssers, A.J.; George, A.S.; Schafer, A.; Leist, S.R.; Gralinksi, L.E.; Dinnon, K.H., 3rd; Yount, B.L.; Agostini, M.L.; Stevens, L.J.; Chappell, J.D.; et al. Remdesivir Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in Human Lung Cells and Chimeric SARS-CoV Expressing the SARS-CoV-2 RNA Polymerase in Mice. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 107940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beigel, J.H.; Tomashek, K.M.; Dodd, L.E. Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19-Preliminary Report. Reply. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Peto, R.; Karim, Q.A.; Alejandria, M.; Henao-Restrepo, A.M.; García, C.H.; Kieny, M.-P.; Malekzadeh, R.; Murthy, S.; Preziosi, M.-P.; et al. Repurposed antiviral drugs for COVID-19 –interim WHO SOLIDARITY trial results. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Mosbauer, K.; Hofmann-Winkler, H.; Kaul, A.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Kruger, N.; Gassen, N.C.; Muller, M.A.; Drosten, C.; Pohlmann, S. Chloroquine does not inhibit infection of human lung cells with SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisonnasse, P.; Guedj, J.; Contreras, V.; Behillil, S.; Solas, C.; Marlin, R.; Naninck, T.; Pizzorno, A.; Lemaitre, J.; Goncalves, A.; et al. Hydroxychloroquine use against SARS-CoV-2 infection in non-human primates. Nature 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIH. NIH Halts Clinical Trial of Hydroxychloroquine. Available online: https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/nih-halts-clinical-trial-hydroxychloroquine (accessed on 10 August 2020).
- WHO. “Solidarity” Clinical Trial for COVID-19 Treatments. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/global-research-on-novel-coronavirus-2019-ncov/solidarity-clinical-trial-for-covid-19-treatments (accessed on 20 October 2020).
- Group, R.C.; Horby, P.; Lim, W.S.; Emberson, J.R.; Mafham, M.; Bell, J.L.; Linsell, L.; Staplin, N.; Brightling, C.; Ustianowski, A.; et al. Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19-Preliminary Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Han, M.; Li, T.; Sun, W.; Wang, D.; Fu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 10970–10975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Garg, I.; Bansal, A.; Kumar, B. COVID-19 infection and Thrombosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagno, V.; Tseligka, E.D.; Jones, S.T.; Tapparel, C. Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans and Viral Attachment: True Receptors or Adaptation Bias? Viruses 2019, 11, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stencel-Baerenwald, J.E.; Reiss, K.; Reiter, D.M.; Stehle, T.; Dermody, T.S. The sweet spot: Defining virus-sialic acid interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hulswit, R.J.G.; Widjaja, I.; Raj, V.S.; McBride, R.; Peng, W.; Widagdo, W.; Tortorici, M.A.; van Dieren, B.; Lang, Y.; et al. Identification of sialic acid-binding function for the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike glycoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8508–E8517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milewska, A.; Zarebski, M.; Nowak, P.; Stozek, K.; Potempa, J.; Pyrc, K. Human coronavirus NL63 utilizes heparan sulfate proteoglycans for attachment to target cells. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 13221–13230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.; Yang, N.; Deng, J.; Liu, K.; Yang, P.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, C. Inhibition of SARS pseudovirus cell entry by lactoferrin binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathewson, A.C.; Bishop, A.; Yao, Y.; Kemp, F.; Ren, J.; Chen, H.; Xu, X.; Berkhout, B.; van der Hoek, L.; Jones, I.M. Interaction of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus and NL63 coronavirus spike proteins with angiotensin converting enzyme-2. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 2741–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milanetti, E.; Miotto, M.; Rienzo, L.D.; Monti, M.; Gosti, G.; Ruocco, G. In-Silico evidence for two receptors based strategy of SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, B. Bioinformatics studies on a function of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein as the binding of host sialic acid glycans. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 122, 103849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, T.M.; Sandoval, D.R.; Spliid, C.B.; Pihl, J.; Perrett, H.R.; Painter, C.D.; Narayanan, A.; Majowicz, S.A.; Kwong, E.M.; McVicar, R.N.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Depends on Cellular Heparan Sulfate and ACE2. Cell 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Jin, W.; Sood, A.; Montgomery, D.W.; Grant, O.C.; Fuster, M.M.; Fu, L.; Dordick, J.S.; Woods, R.J.; Zhang, F.; et al. Characterization of heparin and severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike glycoprotein binding interactions. Antivir. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mycroft-West, C.J.; Su, D.; Pagani, I.; Rudd, T.R.; Elli, S.; Guimond, S.E.; Miller, G.; Meneghetti, M.C.Z.; Nader, H.B.; Li, Y.; et al. Heparin inhibits cellular invasion by SARS-CoV-2: Structural dependence of the interaction of the surface protein (spike) S1 receptor binding domain with heparin. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chopra, P.; Li, X.; Wolfert, M.A.; Tompkins, S.M.; Boons, G.-J. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein binds heparan sulfate in a length- and sequence-dependent manner. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, V.; Beer, J.C.; Sankaranarayanan, N.V.; Swanson-Mungerson, M.; Desai, U.R. Discovering small-molecule therapeutics against SARS-CoV-2. Drug. Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimond, S.E.; Mycroft-West, C.J.; Gandhi, N.S.; Tree, J.A.; Buttigieg, K.R.; Coombes, N.; Nystrom, K.; Said, J.; Setoh, Y.X.; Amarilla, A.; et al. Pixatimod (PG545), a clinical-stage heparan sulfate mimetic, is a potent inhibitor of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, C.Z.; Swaroop, M.; Xu, M.; Wang, L.; Lee, J.; Wang, A.Q.; Pradhan, M.; Hagen, N.; Chen, L. Heparan sulfate assists SARS-CoV-2 in cell entry and can be targeted by approved drugs in vitro. Cell Discov. 2020, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tree, J.A.; Turnbull, J.E.; Buttigieg, K.R.; Elmore, M.J.; Coombes, N.; Hogwood, J.; Mycroft-West, C.J.; Lima, M.A.; Skidmore, M.A.; Karlsson, R.; et al. Unfractionated heparin inhibits live wild-type SARS-CoV-2 cell infectivity at therapeutically relevant concentrations. Br. J. Pharm. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagno, V.; Andreozzi, P.; D’Alicarnasso, M.; Jacob Silva, P.; Mueller, M.; Galloux, M.; Le Goffic, R.; Jones, S.T.; Vallino, M.; Hodek, J.; et al. Broad-spectrum non-toxic antiviral nanoparticles with a virucidal inhibition mechanism. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.T.; Cagno, V.; Janecek, M.; Ortiz, D.; Gasilova, N.; Piret, J.; Gasbarri, M.; Constant, D.A.; Han, Y.; Vukovic, L.; et al. Modified cyclodextrins as broad-spectrum antivirals. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaax9318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger Rentsch, M.; Zimmer, G. A vesicular stomatitis virus replicon-based bioassay for the rapid and sensitive determination of multi-species type I interferon. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushi, S.; Mizutani, T.; Saijo, M.; Matsuyama, S.; Miyajima, N.; Taguchi, F.; Itamura, S.; Kurane, I.; Morikawa, S. Vesicular stomatitis virus pseudotyped with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2269–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagno, V.; Gasbarri, M.; Medaglia, C.; Gomes, D.; Clement, S.; Stellacci, F.; Tapparel, C. Sulfonated nanomaterials with broad-spectrum antiviral activity extending beyond heparan sulfate-dependent viruses. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, R.; Sharp, J.S.; Zhang, F.; Pomin, V.H.; Ashpole, N.M.; Mitra, D.; McCandless, M.G.; Jin, W.; Liu, H.; Sharma, P. Effective inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 entry by heparin and enoxaparin derivatives. J. Virol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseligka, E.D.; Sobo, K.; Stoppini, L.; Cagno, V.; Abdul, F.; Piuz, I.; Meylan, P.; Huang, S.; Constant, S.; Tapparel, C. A VP1 mutation acquired during an enterovirus 71 disseminated infection confers heparan sulfate binding ability and modulates ex vivo tropism. PLoS Pathog 2018, 14, e1007190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).