Differences in Illness Severity among Circulating Norovirus Genotypes in a Large Pediatric Cohort with Acute Gastroenteritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Specimen Collection
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Enteropathogen Testing
2.5. P-C Genotyping with Sanger Sequencing
2.6. Clinical Characteristics and the Modified Vesikari Scale Score
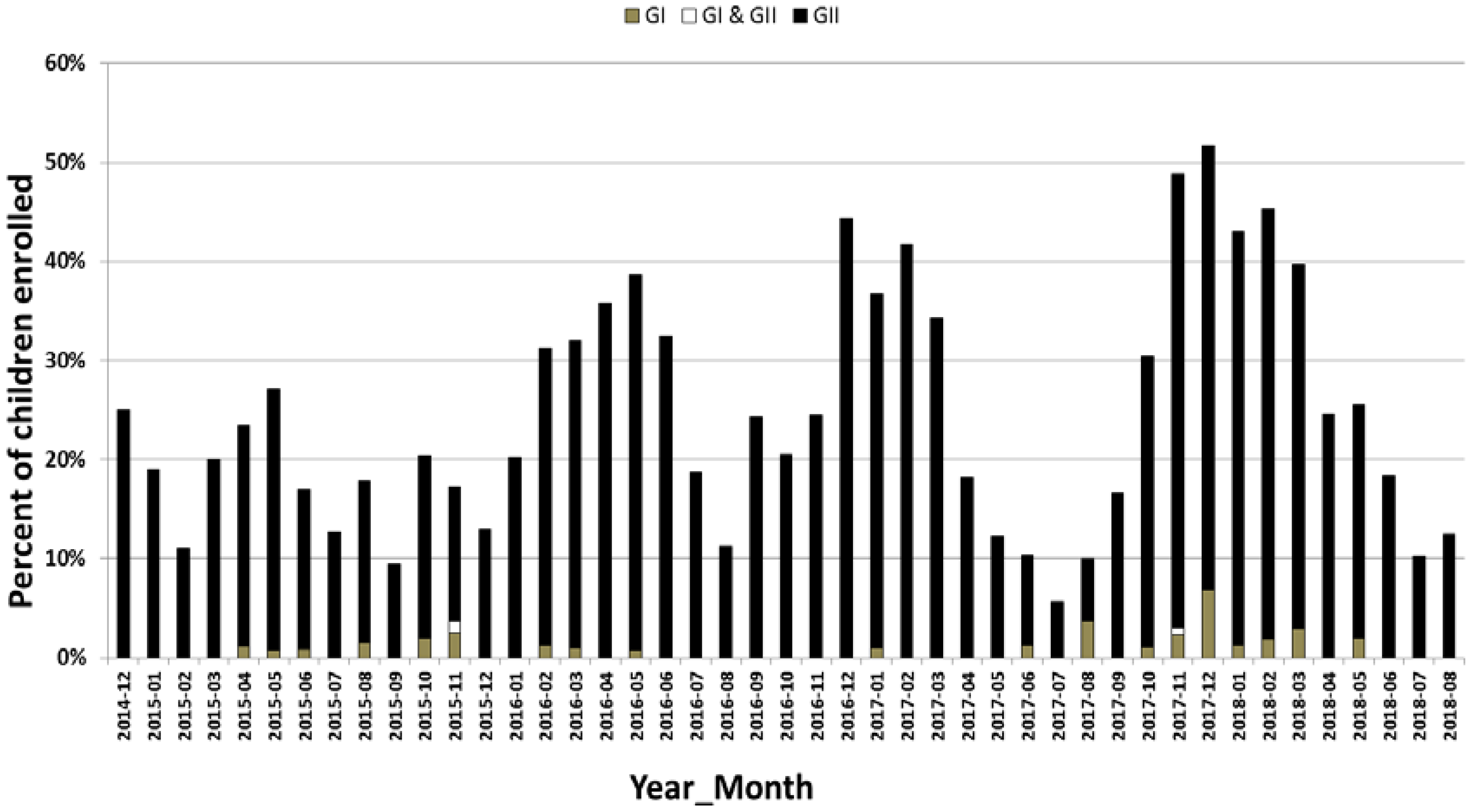
2.7. Annual Prevalence of Norovirus Strains
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Norovirus Genogroup and Genotype Distribution
Predominant Norovirus GII RdRp/Capsid Combination and Seasonal Distribution among AGE
3.3. Difference in Clinical Features between GI and GII, Predominant Genotypes, and Lower Infective Genotypes
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keddy, K.H. Old and new challenges related to global burden of diarrhoea. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1163–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.M.; Hall, A.J.; Robinson, A.E.; Verhoef, L.; Premkumar, P.; Parashar, U.D.; Koopmans, M.; Lopman, B.A. Global prevalence of norovirus in cases of gastroenteritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banyai, K.; Estes, M.K.; Martella, V.; Parashar, U.D. Viral gastroenteritis. Lancet 2018, 392, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.J.; Lopman, B.A.; Payne, D.C. Faculty Opinions recommendation of Norovirus disease in the United States. Fac. Opin. Post-Publ. Peer Rev. Biomed. Lit. 2017, 19, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, R.I.; Parashar, U.D.; Estes, M.K. Norovirus gastroenteritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1776–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shioda, K.; Kambhampati, A.; Hall, A.J.; Lopman, B.A. Global age distribution of pediatric norovirus cases. Vaccine 2015, 33, 4065–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebenga, J.; Vennema, H.; Zheng, D.; Vinjé, J.; Lee, B.E.; Pang, X.; Ho, E.C.M.; Lim, W.; Choudekar, A.; Broor, S.; et al. Norovirus Illness Is a Global Problem: Emergence and Spread of Norovirus GII.4 Variants, 2001–2007. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.-P.; Widdowson, M.-A.; Glass, R.I.; Vinjé, J. Molecular Epidemiology of Genogroup II-Genotype 4 Norovirsuses in the United States between 1994 and 2006. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wobus, C.E. Faculty Opinions recommendation of Genotypic and epidemiologic trends of norovirus outbreaks in the United States, 2009 to 2013. Fac. Opin. Post-Publ. Peer Rev. Biomed. Lit. 2017, 52, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, R.; Hembree, C.D.; Handel, A.; Matthews, J.E.; Dickey, B.W.; McDonald, S.; Hall, A.J.; Parashar, U.D.; Leon, J.S.; Lopman, B. Severe Outcomes Are Associated With Genogroup 2 Genotype 4 Norovirus Outbreaks: A Systematic Literature Review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroneman, A.; Vega, E.; Vennema, H.; Vinjé, J.; White, P.A.; Hansman, G.; Green, K.; Martella, V.; Katayama, K.; Koopmans, M. Proposal for a unified norovirus nomenclature and genotyping. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2059–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wobus, C.E. Faculty Opinions recommendation of Advances in laboratory methods for detection and typing of norovirus. Fac. Opin. Post-Publ. Peer Rev. Biomed. Lit. 2017, 53, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, P.; De Graaf, M.; Parra, G.I.; Chan, M.C.W.; Green, K.Y.; Martella, V.; Wang, Q.; White, P.A.; Katayama, K.; Vennema, H.; et al. Updated classification of norovirus genogroups and genotypes. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, T.-H.; Wang, J.; Dong, C.; Pan, J.; Moe, C.; Chen, W.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Tang, H.; et al. Symptomatic and asymptomatic infections of rotavirus, norovirus, and adenovirus among hospitalized children in Xi’an, China. J. Med. Virol. 2011, 83, 1476–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, T.G.; Kaneshi, K.; Ueda, Y.; Nakaya, S.; Nishimura, S.; Yamamoto, A.; Sugita, K.; Takanashi, S.; Okitsu, S.; Ushijima, H. Genetic heterogeneity, evolution, and recombination in noroviruses. J. Med. Virol. 2007, 79, 1388–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, N.M.; Kirby, A.; Abd-Eldayem, S.A.; Dove, W.; Nakagomi, T.; Nakagomi, O.; Cunliffe, N.A. Detection and molecular characterisation of rotavirus and norovirus infections in Jordanian children with acute gastroenteritis. Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 1477–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasing, M.E.; Lee, B.E.; Preiksaitis, J.K.; Tellier, R.; Honish, L.; Senthilselvan, A.; Pang, X.L. Emergence of a New Norovirus GII.4 Variant and Changes in the Historical Biennial Pattern of Norovirus Outbreak Activity in Alberta, Canada, from 2008 to 2013. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2204–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasing, M.E.; Lee, B.E.; Qiu, Y.; Xia, M.; Pabbaraju, K.; Wong, A.; Tipples, G.; Jiang, X.; Pang, X.L. Changes in norovirus genotype diversity in gastroenteritis outbreaks in Alberta, Canada: 2012–2018. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, S.B.; Lee, B.E.; Louie, M.; Pang, X.-L.; Ali, S.; Chuck, A.; Chui, L.; Currie, G.R.; Dickinson, J.; Drews, S.J.; et al. Alberta Provincial Pediatric EnTeric Infection TEam (APPETITE): Epidemiology, emerging organisms, and economics. BMC Pediatr. 2015, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.L.; Preiksaitis, J.K.; Lee, B.E. Enhanced enteric virus detection in sporadic gastroenteritis using a multi-target real-time PCR panel: A one-year study. J. Med Virol. 2013, 86, 1594–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilmanne, A.; Martiny, D.; Quach, C.; Wautier, M.; Vandenberg, O.; Lepage, P.; Hallin, M. Enteropathogens in paediatric gastroenteritis: Comparison of routine diagnostic and molecular methods. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, S.; Kageyama, T.; Fukushi, S.; Hoshino, F.B.; Shinohara, M.; Uchida, K.; Natori, K.; Takeda, N.; Katayama, K. Genogroup-specific PCR primers for detection of Norwalk-like viruses. J. Virol. Methods 2002, 100, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iritani, N.; Kaida, A.; Abe, N.; Sekiguchi, J.-I.; Kubo, H.; Takakura, K.-I.; Goto, K.; Ogura, H.; Seto, Y. Increase of GII.2 norovirus infections during the 2009–2010 season in Osaka City, Japan. J. Med Virol. 2012, 84, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnadower, D.; Tarr, P.I.; Gorelick, M.H.; O’Connell, K.; Roskind, C.G.; Powell, E.C.; Rao, J.; Bhatt, S.; Freedman, S.B. Validation of the Modified Vesikari Score in Children With Gastroenteritis in 5 US Emergency Departments. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 57, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, S.B.; Eltorky, M.; Gorelick, M. Pediatric Emergency Research Canada Gastroenteritis Study Group. Evaluation of a gastroenteritis severity score for use in outpatient settings. Pediatrics 2010, 125, e1278-85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera-Montes, M.; O’Ryan, M.; Verstraeten, T. Norovirus and Rotavirus Disease Severity in Children: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.N.; Goldman, R.D.; Srivastava, R.; Parkin, P.C. Development of a clinical dehydration scale for use in children between 1 and 36 months of age. J. Pediatr. 2004, 145, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.M.; Lopman, B.A.; Levy, K. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Global Seasonality of Norovirus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dove, W.; Cunliffe, N.A.; Gondwe, J.S.; Broadhead, R.L.; Molyneux, M.E.; Nakagomi, O.; Hart, C.A. Detection and characterization of human caliciviruses in hospitalized children with acute gastroenteritis in Blantyre, Malawi. J. Med. Virol. 2005, 77, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesema, I.; Vennema, H.; Heijne, J.; De Jager, C.; Teunis, P.F.M.; Van Der Linde, R.; Duizer, E.; Van Duynhoven, Y.T.H.P. Differences in clinical presentation between norovirus genotypes in nursing homes. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 46, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Tarr, G.A.M.; Ali, S.; Chui, L.; Pang, X.-L.; Lee, B.E.; Vanderkooi, O.G.; Tarr, P.I.; Zhuo, R.; Parsons, B.; et al. Pigment Visibility on Rectal Swabs Used To Detect Enteropathogens: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkwood, C.D.; Bishop, R.F. Molecular Detection of Human Calicivirus in Young Children Hospitalized with Acute Gastroenteritis in Melbourne, Australia, during 1999. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 2722–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lau, C.-S.; Wong, D.; Tong, L.K.; Lo, J.Y.; Ma, A.M.; Cheng, P.K.; Lim, W.W. High rate and changing molecular epidemiology pattern of norovirus infections in sporadic cases and outbreaks of gastroenteritis in Hong Kong. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 73, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fankhauser, R.L.; Monroe, S.S.; Noel, J.S.; Humphrey, C.D.; Bresee, J.S.; Parashar, U.D.; Ando, T.; Glass, R.I. Epidemiologic and Molecular Trends of “Norwalk-like Viruses & rdquo; Associated with Outbreaks of Gastroenteritis in the United States. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 186, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eden, J.-S.; Hewitt, J.; Lim, K.L.; Boni, M.F.; Merif, J.; Greening, G.; Ratcliff, R.M.; Holmes, E.C.; Tanaka, M.M.; Rawlinson, W.D.; et al. The emergence and evolution of the novel epidemic norovirus GII.4 variant Sydney 2012. Virology 2013, 450, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huhti, L.; Szakal, E.D.; Puustinen, L.; Salminen, M.; Huhtala, H.; Valve, O.; Blazevic, V.; Vesikari, T. Norovirus GII-4 Causes a More Severe Gastroenteritis Than Other Noroviruses in Young Children. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 1442–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.H.; Trainor, E.; Nakagomi, T.; Cunliffe, N.A.; Nakagomi, O. Molecular epidemiology of noroviruses associated with acute sporadic gastroenteritis in children: Global distribution of genogroups, genotypes and GII.4 variants. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 56, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abugalia, M.; Cuevas, L.E.; Kirby, A.; Dove, W.; Nakagomi, O.; Nakagomi, T.; Kara, M.; Gweder, R.; Smeo, M.; Cunliffe, N.A. Clinical features and molecular epidemiology of rotavirus and norovirus infections in Libyan children. J. Med. Virol. 2011, 83, 1849–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambhampati, A.; Koopmans, M.; Lopman, B.A. Burden of norovirus in healthcare facilities and strategies for outbreak control. J. Hosp. Infect. 2015, 89, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.G.; Nguyen, T.A.; Nishimura, S.; Nishimura, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Okitsu, S.; Ushijima, H. Etiologic agents of acute gastroenteritis among Japanese infants and children: Virus diversity and genetic analysis of sapovirus. Arch. Virol. 2005, 150, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreira, D.M.P.G.; Ferreira, M.S.R.; Fumian, T.M.; Checon, R.; De Sadovsky, A.D.I.; Leite, J.P.G.; Miagostovich, M.P.; Spano, L.C. Viral load and genotypes of noroviruses in symptomatic and asymptomatic children in Southeastern Brazil. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 47, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boon, D.; Mahar, J.E.; Abente, E.J.; Kirkwood, C.D.; Purcell, R.H.; Kapikian, A.Z.; Green, K.Y.; Bok, K. Comparative Evolution of GII.3 and GII.4 Norovirus over a 31-Year Period. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8656–8666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, S.K.; Phathammavong, O.; Okitsu, S.; Mizuguchi, M.; Ohta, Y.; Ushijima, H. Seasonal pattern and genotype distribution of norovirus infection in japan. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2010, 29, e32–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martella, V.; Medici, M.C.; De Grazia, S.; Tummolo, F.; Calderaro, A.; Bonura, F.; Saporito, L.; Terio, V.; Catella, C.; Lanave, G.; et al. Evidence for Recombination between Pandemic GII.4 Norovirus Strains New Orleans 2009 and Sydney 2012. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3855–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Emergence of new norovirus strain GII.4 Sydney—United States, 2012. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2013, 62, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, S.; MacLean, A.; Miller, R.S.; Aitken, C.; Gunson, R. Increased norovirus activity in Scotland in 2012 is associated with the emergence of a new norovirus GII.4 variant. Eurosurveillance 2013, 18, 20349. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsushima, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Ishikawa, M.; Komane, A.; Okabe, N.; Ryo, A.; Kimura, H.; Katayama, K.; Shimizu, H. Complete Genome Sequence of a Recombinant GII.P16-GII.4 Norovirus Detected in Kawasaki City, Japan, in 2016. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e01099-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidalot, M.; Théry, L.; Kaplon, J.; De Rougemont, A.; Ambert-Balay, K. Emergence of new recombinant noroviruses GII.p16-GII.4 and GII.p16-GII.2, France, winter 2016 to 2017. Eurosurveillance 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, Y.; Wang, J.; Ling, H. Norovirus GII.P16/GII.2-Associated Gastroenteritis, China, 2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1172–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wu, X.; Chen, L.; Fu, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhang, P.; Ji, L. Emergence of norovirus GII.P16-GII.2 strains in patients with acute gastroenteritis in Huzhou, China, 2016–2017. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, Y.; Cong, X.; Jin, M. Genetic Analysis of Reemerging GII.P16-GII.2 Noroviruses in 2016-2017 in China. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohma, K.; Lepore, C.J.; Ford-Siltz, L.A.; Parra, G.I. Phylogenetic Analyses Suggest that Factors Other Than the Capsid Protein Play a Role in the Epidemic Potential of GII.2 Norovirus. mSphere 2017, 2, e00187-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucardo, F.; Reyes, Y.; Becker-Dreps, S.; Bowman, N.; Gruber, J.F.; Vinjé, J.; Espinoza, F.; Paniagua, M.; Balmaseda, A.; Svensson, L.; et al. Pediatric norovirus GII.4 infections in Nicaragua, 1999–2015. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 55, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.C.; Sung, J.J.; Lam, R.K. Fecal viral load and norovirus-associated gastroenteritis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1278–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, D.; Kuribayashi, K.; Hosono, Y.; Tsuji, N.; Furuya, M.; Miyazaki, K.; Watanabe, N. Age, viral copy number, and immunosuppressive therapy affect the duration of norovirus RNA excretion in inpatients diagnosed with norovirus infection. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 64, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.; Chan, M.C.; Wong, B.; Choi, K.; Sin, W.; Lui, G.; Chan, P.K.; Lai, R.W.; Cockram, C.; Sung, J.J.; et al. Fecal Viral Concentration and Diarrhea in Norovirus Gastroenteritis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1399–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopman, B.; Vennema, H.; Kohli, E.; Pothier, P.; Sanchez, A.; Negredo, A.; Buesa, J.; Schreier, E.; Gray, J.; Gallimore, C.; et al. Increase in viral gastroenteritis outbreaks in Europe and epidemic spread of new norovirus variant. Lancet 2004, 363, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Donaldson, E.F.; LoBue, A.D.; Cannon, J.L.; Zheng, D.-P.; Vinje, J.; Baric, R.S. Mechanisms of GII.4 Norovirus Persistence in Human Populations. PloS Med. 2008, 5, e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, G.I.; Squires, R.B.; Karangwa, C.K.; Johnson, J.A.; Lepore, C.J.; Sosnovtsev, S.V.; Green, K.Y. Static and Evolving Norovirus Genotypes: Implications for Epidemiology and Immunity. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, R.A.; Eden, J.S.; Rawlinson, W.D.; White, P.A. Rapid evolution of pandemic noroviruses of the GII.4 lineage. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, V.K.; George, S.; Sarkar, R.; Giri, S.; Samuel, P.; Vivek, R.; Saravanabavan, A.; Liakath, F.B.; Ramani, S.; Iturriza-Gomara, M.; et al. Norovirus Gastroenteritis in a Birth Cohort in Southern India. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldak, E.; Sulik, A.; Rozkiewicz, D.; Liwoch-Nienartowicz, N. Norovirus infections in children under 5 years of age hospitalized due to the acute viral gastroenteritis in northeastern Poland. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 31, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hullegie, S.; Bruijning-Verhagen, P.; Uiterwaal, C.S.P.M.; Van Der Ent, C.K.; Smit, H.A.; De Hoog, M.L.A. First-year Daycare and Incidence of Acute Gastroenteritis. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20153356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamberti, L.M.; Walker, C.L.F.; Noiman, A.; Victora, C.G.; Black, R.E. Breastfeeding and the risk for diarrhea morbidity and mortality. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atmar, R.L.; Bernstein, D.I.; Harro, C.D.; Al-Ibrahim, M.S.; Chen, W.H.; Ferreira, J.; Estes, M.K.; Graham, D.Y.; Opekun, A.R.; Richardson, C.; et al. Norovirus Vaccine against Experimental Human Norwalk Virus Illness. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2178–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bok, K.; Parra, G.I.; Mitra, T.; Abente, E.; Shaver, C.K.; Boon, D.; Engle, R.; Yu, C.; Kapikian, A.Z.; Sosnovtsev, S.V.; et al. Chimpanzees as an animal model for human norovirus infection and vaccine development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 108, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Huang, P.; Xia, M.; Fang, P.-A.; Zhong, W.; McNeal, M.; Wei, C.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, X. Norovirus P Particle, a Novel Platform for Vaccine Development and Antibody Production. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Jiang, X. Norovirus P particle: A subviral nanoparticle for vaccine development against norovirus, rotavirus and influenza virus. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treanor, J.J.; Atmar, R.L.; Frey, S.E. A novel intramuscular bivalent norovirus virus-like particle vaccine candidate-reactogenicity, safety, and immunogenicity in a phase 1 trial in healthy adults. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| NoV-Positive Participants; N = 900 No. (%) | NoV-Negative Participants; N = 2447 No. (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Male; No. (%) | 422 (46.9) | 1328 (45.7) | 0.56 |
| Female; No. (%) | 478 (53.1) | 1119 (54.3) | |
| Age | |||
| <1.0 year; No. (%) | 272 (26.5) | 756 (73.5) | 0.03 |
| 1.0–3.0 years; No. (%) | 393 (29.2) | 954 (70.8) | |
| >3.0 years; No. (%) | 235 (24.2) | 737 (75.8) | |
| Year | |||
| December 2014–December 2015 | 142 (15.8) | 593 (24.2) | <0.001 |
| January 2016–December 2016 | 318 (35.3) | 775 (31.7) | |
| January 2017–December 2017 | 307 (34.1) | 765 (31.3) | |
| January 2018–August 2018 | 133 (14.8) | 314 (12.8) | |
| Number of Enteropathogens Detected | |||
| 0 | 661/899 (73.5) | 989/2421 (40.9) | Not applicable |
| 1 | 205/899 (22.8) | 1233/2421 (50.9) | |
| 2 | 31/899 (3.4) | 187/2421 (7.7) | |
| 3 | 1/899 (0.1) | 12/2421 (0.5) | |
| 4 | 1/899 (0.1) | 0/2421 (0) | |
| Enrollment Location | |||
| ED | 668 (74.2) | 2,028 (82.9) | <0.001 |
| Health-Link Alberta | 232 (25.8) | 419 (17.1) | |
| Norovirus Ct Value | |||
| GI (N = 31) Median (IQR) | 22.8 (16.75, 31.4) | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| GII (N = 872) Median (IQR) | 18.3 (15.7, 23.6) | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| GI Positive N = 31 | GII Positive N = 872 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, Months, Median (IQR) | 33.5 (17.3, 69.2) | 17.3 (10.6, 36.1) | 0.002 |
| Fever, Yes, N (%) | 11/30 (36.7) | 348/823 (42.3) | 0.58 |
| Max temperature (°C), Median (IQR) | 36.5 (36.5, 38.5) | 36.5 (36.5, 38.6) | 0.93 |
| Fever, No, N (%) | 19/30 (63.3) | 475/823 (57.7) | 0.58 |
| Vomiting, Yes, N (%) | 30/31 (96.8) | 846/868 (97.5) | >0.99 |
| Maximal Frequency (per 24 h), Median (IQR) | 7.0 (4.0, 12.0) | 7.0 (5.0, 11.0) | 0.75 |
| Frequency Past 24 h, Median (IQR) | 7.0 (4.0, 10.0) | 5.0 (3.0, 10.0) | 0.25 |
| Duration, hours, Median (IQR) | 53.0 (15.2, 77.8) | 64.3 (30.7, 114.4) | 0.20 |
| Diarrhea, Yes, N (%) | 27/30 (90.0) | 693/843 (82.2) | 0.33 |
| Maximal Frequency (per 24 h), Median (IQR) | 3.0 (2.0, 5.0) | 4.0 (2.0, 6.0) | 0.60 |
| Frequency Past 24 h, Median (IQR) | 0 (0, 3.0) | 1.0 (0, 4.0) | 0.35 |
| Duration, hours, Median (IQR) | 48.0 (24.0, 93.0) | 88.7 (24.0, 157.2) | 0.09 |
| Clinical Dehydration Scale score [27], Median (IQR) | 2.0 (0, 3.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 0.17 |
| No dehydration (score 0) | 9 (29.0) | 190 (21.8) | 0.62 |
| Mild (score 1–4) | 18 (58.1) | 531 (61.0) | |
| Moderate to Severe (score 5–8) | 4 (12.9) | 149 (17.1) | |
| MVS score at baseline | 8.0 (7.0, 12.0) | 9.0 (7.0, 11.0) | 0.36 |
| MVS score at follow-up phase | 6.0 (3.0, 8.5) | 6.0 (4.0, 9.0) | 0.50 |
| MVS score for total illness course | 11.0 (9.0, 14.0) | 12.0 (10.0, 14.0) | 0.51 |
| December 2014– June 2015 No. (%) | July 2015– June 2016 No. (%) | July 2016– June 2017 No. (%) | July 2017– June 2018 No. (%) | Total No. (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOTAL (N = 892) | |||||
| GI (N = 31; 3.5%) | 4 (12.9) | 8 (25.8) | 3 (9.6) | 16 (51.7) | |
| GI.1 | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0) | 2 (66.7) | 5 (31.3) | 7 (22.6) |
| G1.2 | 0(0.0) | 2 (25.0) | 0 (0) | 1 (6.3) | 3 (9.7) |
| GI.3 | 2 (50.0) | 3 (37.5) | 0 (0) | 3 (18.6) | 8 (25.8) |
| GI.5 | 0 (0) | 1 (12.5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (3.2) |
| GI.6 | 0 (0) | 1 (12.5) | 0 (0) | 4 (25.0) | 5 (16.1) |
| GI.7 | 1(25.0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 | 4 (12.9) |
| Genotype not determined | 1(25.0) | 1 (12.5) | 1(33.3) | 0 | 3 (9.7) |
| GII (N = 861; 96.5%) | 85 (9.9) | 250 (29.0) | 258 (30.0) | 268 (31.1) | |
| GII.2[P16] | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 60 (23.3) | 2 (0.7) | 62 (7.2) |
| GII 3 | |||||
| GII.3[P12] | 0(0) | 32 (12.8) | 97 * (37.6) | 30 (11.2) | 159 (18.5) |
| GII.3[P16] | 0(0) | 8 (3.2) | 8 (3.1) | 27 (10.1) | 43 (5.0) |
| GII.4 | |||||
| GII.4 Sydney[P12] | 2 (2.4) | 4 (1.6) | 4 (1.6) | 21 (7.8) | 31(3.6) |
| GII.4 Sydney[P16] | 0 (0) | 65 * (26) | 36 (14.0) | 105 * (39.2) | 206 (23.9) |
| GII.4 Sydney[P31] | 44 * (51.7) | 48 (19.2) | 9 (3.5) | 15 (5.6) | 116 (13.5) |
| GII.4 Sydney[P4New Orleans] | 1 (1.2) | 8 (3.2) | 12 (4.7) | 1 (0.4) | 22 (2.6) |
| GII.6[P7] | 10 (11.8) | 25 (10) | 1 (0.4) | 12 (4.5) | 48 (5.6) |
| Other GII Genotypes | 27 (31.7) | 53 (21.2) | 22 (8.5) | 43 (16) | 145 (16.80) |
| Genotype not determined | 1 (12) | 7 (2.8) | 9 (3.5) | 12 (4.5) | 29 (3.4) |
| Variable | GII.4 N = 416 | Non- GII.4 N = 425 | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, months, Median (IQR) | 16.9 (11.4, 28.9) | 17.7 (10.2, 46.8) | 0.28 |
| Diarrhea, yes, No. (%) | 353/406 (86.9) | 318 (77.8) | 0.001 |
| Diarrhea duration hours, Median (IQR) | 110.8 (48.0, 175.1) | 72.0 (9.3, 139.4) | <0.001 |
| Maximum number of times/24-h period, Median (IQR) | 4.0 (2.0, 7.0) | 3.0 (1.0, 5.0) | <0.001 |
| Vomiting, No. (%) | 407/415 (98.1) | 410/423 (96.9) | 0.38 |
| Vomiting duration hours, Median (IQR) | 74.7 (38.0, 125.4) | 53.8 (23.6, 103.0) | <0.001 |
| Maximum number of times/24-h period, Median (IQR) | 7 (4.0, 11.0) | 7 (5.0, 10.0) | 0.99 |
| MVS score at baseline | 9.0 (7.0, 11.0) | 9.0 (7.0, 10.0) | 0.005 |
| MVS score at follow-up phase | 7.0 (4.0, 10.0) | 6.0 (4.0, 9.0) | 0.002 |
| MVS score for total illness course | 12.0 (10.0, 14.0) | 11.0 (9.0, 13.0) | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhavanam, S.; Freedman, S.B.; Lee, B.E.; Zhuo, R.; Qiu, Y.; Chui, L.; Xie, J.; Ali, S.; Vanderkooi, O.G.; Pang, X.L.; et al. Differences in Illness Severity among Circulating Norovirus Genotypes in a Large Pediatric Cohort with Acute Gastroenteritis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121873
Bhavanam S, Freedman SB, Lee BE, Zhuo R, Qiu Y, Chui L, Xie J, Ali S, Vanderkooi OG, Pang XL, et al. Differences in Illness Severity among Circulating Norovirus Genotypes in a Large Pediatric Cohort with Acute Gastroenteritis. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(12):1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121873
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhavanam, Sudha, Stephen B. Freedman, Bonita E. Lee, Ran Zhuo, Yuanyuan Qiu, Linda Chui, Jianling Xie, Samina Ali, Otto G. Vanderkooi, Xiaoli L. Pang, and et al. 2020. "Differences in Illness Severity among Circulating Norovirus Genotypes in a Large Pediatric Cohort with Acute Gastroenteritis" Microorganisms 8, no. 12: 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121873
APA StyleBhavanam, S., Freedman, S. B., Lee, B. E., Zhuo, R., Qiu, Y., Chui, L., Xie, J., Ali, S., Vanderkooi, O. G., Pang, X. L., & on behalf of the Alberta Provincial Pediatric Enteric Infection Team (APPETITE). (2020). Differences in Illness Severity among Circulating Norovirus Genotypes in a Large Pediatric Cohort with Acute Gastroenteritis. Microorganisms, 8(12), 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121873





