In Silico Analysis of a Novel Plasmid from the Coral Pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus Reveals Two Potential “Ecological Islands”
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Studies
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
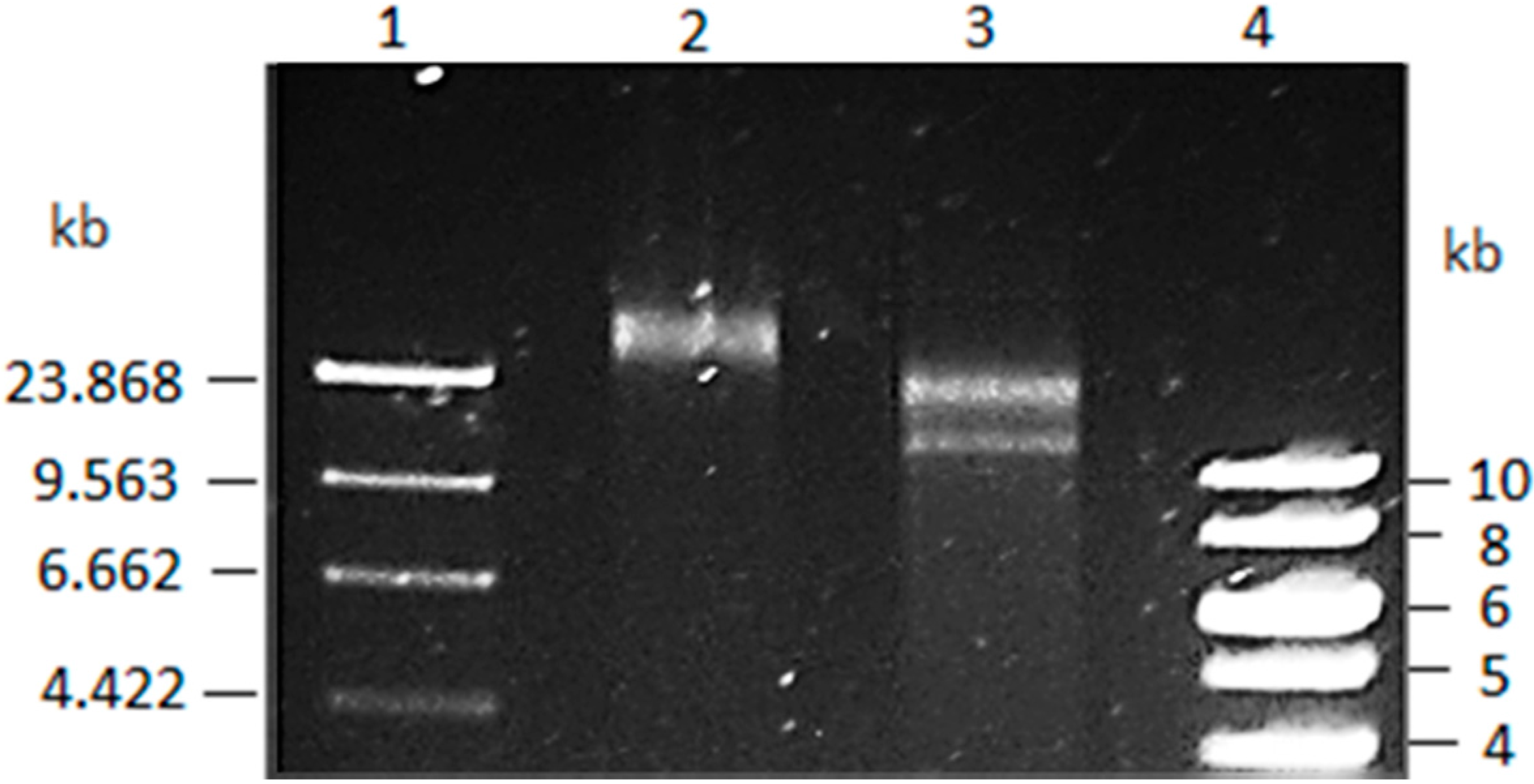
2.2. Vibrio Coralliilyticus Plasmid Isolation
2.3. Molecular Biology Protocols
2.4. Vibrio coralliilyticus BAA-450 Plasmid Sequencing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Vibrio Coralliilyticus BAA-450 Plasmid
3.2. Annotation and Identification of Plasmid-Encoded Orfs

3.3. Identification of Potential “Ecological” Islands within the Plasmid Replicon
| Name | Starting and Ending Base | Length (bp) | Reading Frame | Putative Protein | e-Value | % AT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| orf236 | 1–711 | 711 | +1 | ABC transporter, ATP-binding protein LivF-like | 3 × 10-17 | 57 |
| orf387 | 742–1905 | 1164 | +1 | transposase, IS4 | 6 × 10-123 | 43 |
| orf163 | 2058–2549 | 492 | +3 | Na+/H+ antiporter | 2 × 10-65 | 59 |
| orf294 | 3053–3937 | 885 | +2 | Biotin-protein ligase | 2 × 10-46 | 59 |
| orf164 | 4967–4473 | 495 | −2 | branched-chain amino acid ABC transporter permease protein, LivM-like | 2 × 10-24 | 62 |
| orf220 | 5694–6356 | 663 | +3 | oligoendopeptidase F | 8 × 10−80 | 62 |
| orf354 | 6380–7444 | 1065 | +2 | Trk transporter membrane-spanning protein-K+ transport | 9 × 10−103 | 62 |
| orf241 | 9244–8519 | 726 | −3 | methylglyoxyl synthase | 9 × 10−68 | 58 |
| orf251 | 10,005–9250 | 756 | −1 | purine nucleoside phophorylase | 7 × 10−73 | 64 |
| orf115 | 10,790–10,443 | 348 | −2 | oxaloacetate decarboxylase α-chain | 3 × 10−34 | 61 |
| orf176 | 11,426–10,896 | 531 | −2 | phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase | 4 × 10−44 | 65 |
| orf142 | 11,793–12,218 | 426 | +3 | maltose/maltodextrin ABC transporter, permease protein | 4 × 10−19 | 57 |
| orf234 | 12,438–13,142 | 705 | +3 | ykvW heavy metal-(Cd/Co/Hg/Pb/Zn)-translocating P-type ATPase | 1 × 10−39 | 62 |
| orf187 | 13,290–13,853 | 564 | +3 | mobilization protein | 3 × 10−18 | 59 |
| orf80 * | 14,423–14,662 | 240 | +2 | RepE replication protein | 2 × 10−15 | 73 |
| orf213 | 15,225–14,587 | 639 | −1 | transposase | 1 × 10−35 | 65 |
| orf389 | 17,190–16,021 | 1170 | −1 | glutathione reductase | 6 × 10−104 | 58 |
| orf200 | 17,234–17,836 | 603 | +2 | replication protein | 6 × 10−29 | 67 |
| orf297 | 17,904–18,797 | 894 | +3 | DNA replication protein, putative | 1 × 10−36 | 62 |
| Clp protease protein | 5 × 10−32 | |||||
| orf332 | 19,200–20,198 | 999 | +3 | maltodextrin-binding protein MdxE | 3 × 10−129 | 58 |
| orf167 | 20,696–21,199 | 504 | +2 | branched-chain amino acid ABC transporter, permease protein, LivH-like | 4 × 10−57 | 56 |
| orf136 | 21,865–21,455 | 411 | −3 | rlx domain protein | 9 × 10−56 | 57 |
| orf223 | 22,518–21,847 | 672 | −1 | mobilization protein | 1 × 10−108 | 54 |
| orf237 | 23,324–22,611 | 714 | −2 | ABC superfamily ATP binding cassette transporter, permease protein | 1 × 10−34 | 61 |
| orf276 | 24,222–23,392 | 831 | −1 | YKVW heavy metal-(Cd/Co/Hg/Pb/Zn)-translocating P-type ATPase | 7 × 10−51 | 63 |
| orf238 | 24,465–25,181 | 717 | +3 | hypothetical protein CAT7 09585 | 4 × 10−91 | 60 |
| orf148 | 25,392–25,838 | 447 | +3 | PTS system, IIC component | 5 × 10−22 | 61 |
| orf134 | 25,636–25,232 | 405 | −3 | glycosyltransferase | 6 × 10−21 | 62 |
| orf291 | 26,533–25,658 | 876 | −3 | ABC exporter, membrane-spanning/permease subunit | 2 × 10−143 | 62 |
| Name | Starting and Ending Base | Length | Amino Acid | Codon |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| trnDGUC | 1807–1879 | 73 | Aspartic acid | GAC |
| trnFGAA | 1896–1968 | 73 | Phenylalanine | TTC |
| trnGUCC | 1979–2049 | 71 | Glycine | GGA |
| trnNGUU | 8159–8230 | 72 | Asparagine | AAC |
| trnPUGG | 15,608–1,5681 | 74 | Proline | CCA |
| trnSACU | 8557–8484 | 74 | Serine | AGT |
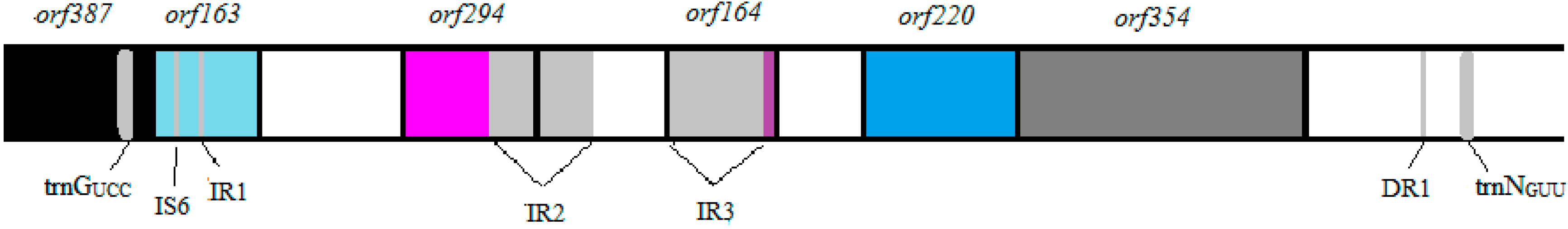

| Vibrio coralliilyticus | Length (bp) | % GC Content |
|---|---|---|
| Entire Plasmid | 26,631 | 40 |
| Plasmid without tRNA segments | 13,472 | 42 |
| Segment between trnGUCC and trnNGUU | 6111 | 41 |
| Segment between trnPUGG and trnSACU | 7052 | 37 |
| Genome | 5,680,628 | 45 |
3.4. Identification of Putative Pathogenicity Proteins on the BAA-450 Plasmid
3.5. Functional Cooperativity between Putative Plasmid- and Chromosomally-Encoded Proteins

4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bally, M.; Garrabou, J. Thermodependent bacterial pathogens and mass mortalities in temperate benthic communities: A new case of emerging disease linded to climate change. Glob. Change Biol. 2007, 13, 2078–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizcaino, M.I.; Johnson, W.R.; Kimes, N.E.; Williams, K.; Torralba, M.; Nelson, K.E.; Smith, G.W.; Weil, E.; Moeller, P.D.; Morris, P.J. Antimicrobial Resistance of the Coral Pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus and Carribbean Sister Phylotypes Isolated from a Diseased Octocoral. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 59, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meron, D.; Efrony, R.; Johnson, W.R.; Schaefer, A.L.; Morris, P.J.; Rosenberg, E.; Greenberg, E.P.; Banin, E. Role of Flagella in Virulence of the Coral Pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5704–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, E.; Falkovitz, L. The Vibrio shiloi/Oculina patagonica Model System of Coral Bleaching. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 58, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Haim, Y.; Thompson, F.L.; Thompson, C.C.; Cnockaert, M.C.; Hoste, B.; Swings, J.; Rosenberg, E. Vibrio coralliilyticus sp. nov., a temperature dependent pathogen of the coral Pocillopora damicornis. Int. J. Sys. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sussman, M.; Willis, B.; Victor, S.; Bourne, D. Coral Pathogens Identified for White Syndrome (WS) Epizootics in the Indo-Pacific. PLoS ONE 2008, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, L.S.; Oliver, J.D. Plasmid Carriage in Vibrio vulnificus and other Lactose-Fermenting Marine Vibrios. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1986, 51, 211–213. [Google Scholar]
- Reynaud, Y.; Saulnier, D.; Mazel, D.; Goarant, C.; Le Roux, F. Correlation between Detection of a Plasmid and High-Level Virulence of Vibrio nigripulchritudo, a Pathogen of the Shrimp Litopenaeus stylirostris. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 3038–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivian, A.; Murrillo, J.; Jackson, R.W. The roles of plasmids in phytopathogenic bacteria: Mobile arsenals? Microbiology 2001, 147, 763–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, B.A.; Ye, C.; Griffiths, R.P.; Moyer, C.L.; Morita, R.Y. Plasmid Expression and Maintenance during Long-Term Starvation-Survival of Bacteria in Well Water. App. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 1860–1864. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, G.P.; Bono, J.L.; Watson, M.A.; Needleman, D.S. Complete genome sequence for the shellfish pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus RE98 isolated from a shellfish hatchery. Genome Announc. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santos, E.; Alves, N.; Dias, G.M.; Mazotto, A.M.; Vermelho, A.; Vora, G.J.; Wilson, B.; Beltran, V.H.; Bourne, D.G.; Le Roux, F.; et al. Genomic and proteomic analysis of the coral pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus reveal a diverse viruence repertoire. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1471–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temperton, B.; Thomas, S.; Tait, K.; Parry, H.; Emery, M.; Allen, M.; Quinn, J.; Macgrath, J.; Gilbert, J. Permanent draft genome sequence of Vibrio tubiashii strain NCIMB 1337 (ATCC19106). Stand. Genomic. Sci. 2011, 4, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushijima, B.; Videau, P.; Aeby, G.S.; Callahan, S.M. Draft genome sequence of Vibrio coralliilyticus strain OCN008, isolated from Kane’ohe Bay, Hawaii. Genome. Announc. 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushijima, B.; Videau, P.; Poscablo, D.; Vine, V.; Salcedo, M.; Aeby, G.S.; Callahan, S.M. Complete genome sequence of Vibrio coralliilyticus strain OCN014, isolated from a diseased coral at Palmyra Atoll. Genome. Announc. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnboim, H.C.; Dohly, J. Plasmid Alkaline Plasmid Preparation. Nucl. Acids Res. 1979, 7, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, T.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic. Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, D.L.; Church, D.M.; Federhen, S.; Lash, A.E.; Madden, T.L.; Pontius, J.U.; Schuler, G.D.; Schriml, L.M.; Sequeira, E.; Tatusova, T.A.; et al. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2003, 31, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stothard, P. The Sequence Manipulation Suite. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.org/sms2/ (accessed on 14 December 2015).
- Vincze, T.; Posfai, J.; Roberts, R.J. NEB cutter: A program to cleave DNA with restriction enzymes. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3688–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solovyev, V.; Salamov, A. Automatic Annotation of Microbial Genomes and Metagenomics Sequences. In Metagenomics and its Applications in Agriculture, Biomedicine, and Environmental Studies; Li, R.W., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA; pp. 61–78.
- Schattner, P.; Brooks, A.N.; Lowe, T.M. The tRNA scan-SE, snoscan and snoGPS web servers for the detection of tRNAs and snoRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, w686–w689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, P.; Longden, I.; Bleasby, A. EMBOSS: The European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siguier, P.; Perochon, J.; Lestrade, L.; Mahillon, J.; Chandler, M. ISfinder: The reference center for bacterial insertion sequences. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2006, 34, D32–D36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Soding, J.; Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conant, G.C.; Wolfe, K.H. GenomeVx: Simple web-based creation of editable circular chromosome maps. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 861–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanc-Potard, A.B.; Groisman, E.A. The Salmonella selC locus contains a pathogenicity island mediating intramacrophage survival. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 5376–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacker, J.; Blum-Oehler, G.; Muhldorfer, I.; Tschape, H. Pathogenicity islands of virulent bacteria: Structure, function and impact on microbial evolution. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 23, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, A.; Perham, R.N.; Scrutton, N.S.; Berry, A. Altering kinetic mechanism and enzyme stability by mutagenesis of the dimer interface of glutathione reductase. Biochem. J. 1995, 312, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, H.; Jonson, G.; Holmgren, J.; Palva, E.T. The maltose regulon of Vibrio cholera affects production and secretion of virulence factors. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 4781–4788. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wachter, J.; Hill, S.A. In Silico Analysis of a Novel Plasmid from the Coral Pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus Reveals Two Potential “Ecological Islands”. Microorganisms 2016, 4, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms4010003
Wachter J, Hill SA. In Silico Analysis of a Novel Plasmid from the Coral Pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus Reveals Two Potential “Ecological Islands”. Microorganisms. 2016; 4(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms4010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleWachter, Jenny, and Stuart A. Hill. 2016. "In Silico Analysis of a Novel Plasmid from the Coral Pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus Reveals Two Potential “Ecological Islands”" Microorganisms 4, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms4010003
APA StyleWachter, J., & Hill, S. A. (2016). In Silico Analysis of a Novel Plasmid from the Coral Pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus Reveals Two Potential “Ecological Islands”. Microorganisms, 4(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms4010003





