Impact of Drought on Soil Microbial Communities
Abstract
1. Drought Stress and Climate Change
Materials and Methods
2. Effect of Drought on Soil Habitat
2.1. Soil Moisture
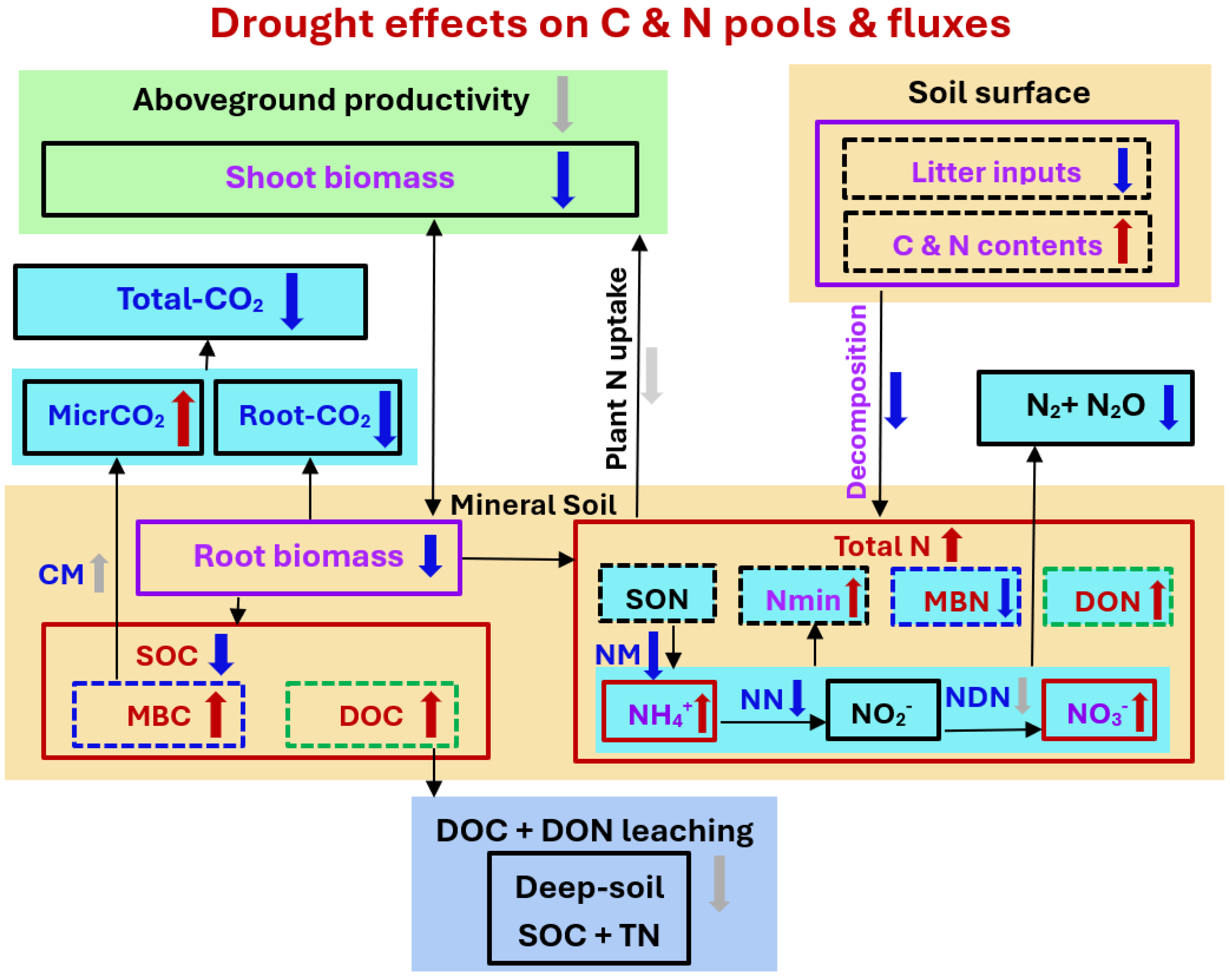
2.2. Soil Carbon Availability
2.3. Soil Nitrogen Storage
2.4. Soil pH
3. Effect of Drought on Soil Microbial Structure
3.1. Drought as an Ecological Disturbance
3.2. Impact of Soil Moisture on Microbial Activity
3.3. Variability of Drought Effects on Soil Microbial Communities
3.4. Impact of Drought on Microbial Biomass and Recovery
3.5. Drought Effects on Fungal and Bacterial Communities
3.6. Microbial Effects on Plants Under Drought Conditions
4. Effect of Drought on Microbiome Functions
4.1. Enzymatic Activity in Soil
4.2. Nutrient Availability and Potential Nutrient Cycling
4.3. Microbial Metabolite Production and Gene Expression Shifts
4.4. Impact of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi (AMF) and Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) on Drought-Tolerant Crops
4.5. Role of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) in Mitigating Drought Stress
5. Future Needs and Approaches
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; MassonDelmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, A.; Sheffield, J. Climate change and drought: The soil moisture perspective. Curr. Clim. Change Rep. 2018, 4, 180–191. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40641-018-0095-0 (accessed on 28 August 2024). [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Mishra, A.; Trenberth, K.E. Climate change and drought: A perspective on drought indices. Curr. Clim. Change Rep. 2018, 4, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariyawasam Hetti Gamage, L.R.; Gnanavelrajah, N.; Ketheesan, B.; Kajeevan, K. Chlorella sp. Cultivation Using Parboiled Rice Effluent and Utilization of the Microalgae as Co-organic Fertilizer for Brinjal (Solanum melongina). Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2023, 14, 4243–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Hueso, R.; Collins, S.L.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Hamonts, K.; Pockman, W.T.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Smith, M.D.; Knapp, A.K.; Power, S.A. Drought consistently alters the composition of soil fungal and bacterial communities in grasslands from two continents. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 2818–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, J.P. Life in dry soils: Effects of drought on soil microbial communities and Processes. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2018, 49, 409–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogati, K.; Walczak, M. The impact of drought stress on soil microbial community, enzyme activities and plants. Agronomy 2022, 12, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.; Zhang, J.; Luo, T.; Liu, J.; Ni, F.; Rizwan, M.; Hu, L. Morpho-physiological and biochemical responses of tolerant and sensitive rapeseed cultivars to drought stress during early seedling growth stage. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2019, 41, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaka, A.; Ozimek, E.; Reszczy’nska, E.; Jaroszuk-’Sciseł, J.; Stolarz, M. Plant tolerance to drought stress in the presence of supporting bacteria and fungi: An efficient strategy in horticulture. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaurin, A.; Kihelic, R.; Kastelec, D.; Greman, H.; Bru, D.; Philippot, L.; Suhadolc, M. Resilience of bacteria, archaea, fungi, and N-cycling microbial guilds under plough and conservation tillage, to agricultural drought. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristy, B.; Carrell, A.A.; Johnston, E.; Cumming, J.R.; Klingeman, D.M.; Gwinn, K.; Syring, K.C.; Skalla, C.; Emrich, S.; Cregger, M.A. Chronic drought differentially alters the belowground microbiome of drought-tolerant and drought-susceptible genotypes of Populus trichocarpa. Phytobiomes J. 2022, 6, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preece, C.; Verbruggen, E.; Liu, L.; Weedon, J.T.; Peñuelas, J. Effects of past and current drought on the composition and diversity of soil microbial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 131, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.K.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Egidi, E.; Guirado, E.; Leach, J.E.; Liu, H.; Trivedi, P. Climate change impacts on plant pathogens, food security and paths forward. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 640–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, R.; Ruan, H.; Yang, J. Drought stress induced increase of fungi: Bacteria ratio in a poplar plantation. Catena 2020, 193, 104607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liao, J.; Zou, X.; Xu, X.; Yang, J.; Chen, H.Y.; Ruan, H. Coherent responses of terrestrial C: N stoichiometry to drought across plants, soil, and microorganisms in forests and grasslands. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 292, 108104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, S.; Yapa, P.I.; Mahatantila, K.; Das, S.; Maharjan, B. Creeper legume, in conjunction with biochar, is a potential tool to minimize soil erosion. Agrosyst. Geosci. Environ. 2023, 6, e20394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.; Li, J.; Yahya, M.; Sher, A.; Ma, C.; Wang, X.; Qiu, L. Research progress and perspective on drought stress in legumes: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, J.; Zohaib, M.; Kim, U.; Aadil, M.; Choi, M. Agricultural drought assessment based on multiple soil moisture products. J. Arid Environ. 2019, 167, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.F.; Bourrie, G.; Trolard, F. Soil compaction impact and modelling: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markewitz, D.; Devine, S.; Davidson, E.A.; Brando, P.; Nepstad, D.C. Soil moisture depletion under simulated drought in the Amazon: Impacts on deep root uptake. New Phytol. 2010, 187, 592–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indoria, A.K.; Sharma, K.L.; Reddy, K.S. Hydraulic properties of soil under warming climate. In Climate Change and Soil Interactions; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 473–508. [Google Scholar]
- AghaKouchak, A.; Farahmand, A.; Melton, F.S.; Teixeira, J.; Anderson, M.C.; Wardlow, B.D.; Hain, C.R. Remote sensing of drought: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 452–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Peng, C.; Kim, D.G.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Hai, X.; Liu, Q.; Huang, C.; Shangguan, Z.; Kuzyakov, Y. Drought effects on soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics in global natural ecosystems. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 214, 103501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Yang, J.; Ruan, H. Meta-analysis shows non-uniform responses of above-and belowground productivity to drought. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Estiarte, M.; Bengtson, P.; Li, J.; Asensio, D.; Wallander, H.; Peñuelas, J. Drought legacies on soil respiration and microbial community in a Mediterranean forest soil under different soil moisture and carbon inputs. Geoderma 2022, 405, 115425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, Z.; Táncsics, A.; Kriszt, B.; Kröel-Dulay, G.; Ónodi, G.; Hornung, E. Extreme effects of drought on composition of the soil bacterial community and decomposition of plant tissue. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 68, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homyak, P.M.; Allison, S.D.; Huxman, T.E.; Goulden, M.L.; Treseder, K.K. Effects of drought manipulation on soil nitrogen cycling: A meta-analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2017, 122, 3260–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.A.; Barnard, R.L.; Marhan, S.; Niklaus, P.A. Effects of drought and N-fertilization on N cycling in two grassland soils. Oecologia 2013, 171, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossiord, C.; Gessler, A.; Reed, S.C.; Borrego, I.; Collins, A.D.; Dickman, L.T.; Ryan, M.; Schönbeck, L.; Sevanto, S.; Vilagrosa, A. Reductions in tree performance during hotter droughts are mitigated by shifts in nitrogen cycling. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 2627–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, S.; Schimel, J.P.; Porporato, A. Responses of soil microbial communities to water stress: Results from a meta-analysis. Ecology 2012, 93, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L. Climate change impacts on soil salinity in agricultural areas. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 72, 842–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chytrý, M.; Danihelka, J.; Ermakov, N.; Hájek, M.; Hájková, P.; Kočí, M.; Kubešová, S.; Lustyk, P.; Otýpková, Z. Plant species richness in continental southern Siberia: Effects of pH and climate in the context of the species pool hypothesis. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2007, 16, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Han, X.; Zhu, X.; Herbert, S.J. Response to water stress of soil enzymes and root exudates from drought and non-drought tolerant corn hybrids at different growth stages. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2012, 92, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DesRochers, A.; Van Den Driessche, R.; Thomas, B.R. The interaction between nitrogen source, soil pH, and drought in the growth and physiology of three poplar clones. Botany 2007, 85, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, D.; DeGraaf, S.; Purdom, E.; Coleman-Derr, D. Drought and host selection influence bacterial community dynamics in the grass root microbiome. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2691–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hueso, S.; García, C.; Hernández, T. Severe drought conditions modify the microbial community structure, size and activity in amended and unamended soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 50, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, J.; Balser, T.C.; Wallenstein, M. Microbial stress-response physiology and its implications for ecosystem function. Ecology 2007, 88, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lareen, A.; Burton, F.; Schäfer, P. Plant root-microbe communication in shaping root microbiomes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 90, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jentsch, A.; White, P. A theory of pulse dynamics and disturbance in ecology. Ecology 2019, 100, e02734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, D.L.; Duniway, M.C.; Belnap, J. Pulse-drought atop press-drought: Unexpected plant responses and implications for dryland ecosystems. Oecologia 2015, 179, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, D.L.; Knapp, A.K.; Smith, M.D. Resistance and resilience of a grassland ecosystem to climate extremes. Ecology 2014, 95, 2646–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meeteren, M.J.M.; Tietema, A.; Van Loon, E.E.; Verstraten, J.M. Microbial dynamics and litter decomposition under a changed climate in a Dutch heathland. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 38, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.A. Response of microbial communities to water stress in irrigated and drought-prone tallgrass prairie soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2750–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.A.; Rice, C.W. Seven years of enhanced water availability influences the physiological, structural, and functional attributes of a soil microbial community. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2007, 35, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenovsky, R.E.; Vo, D.; Graham, K.J.; Scow, K.M. Soil water content and organic carbon availability are major determinants of soil microbial community composition. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 48, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söderberg, K.H.; Probanza, A.; Jumpponen, A.; Baath, E. The microbial community in the rhizosphere determined by community-level physiological profiles (CLPP) and direct soil- and cfu PLFA techniques. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2004, 25, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Andreu, L.; Gómez, I.; Parrado, J.; García, C.; Hernández, T.; Tejada, M. Soil biology changes as a consequence of organic amendments subjected to a severe drought. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebielec, G.; Siebielec, S.; Lipski, D. Long-term impact of sewage sludge, digestate and mineral fertilizers on plant yield and soil biological activity. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebielec, S.; Siebielec, G.; Klimkowicz-Pawlas, A.; Gałązka, A.; Grządziel, J.; Stuczyński, T. Impact of water stress on microbial community and activity in sandy and loamy soils. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueso, S.; Hernández, T.; García, C. Resistance and resilience of the soil microbial biomass to severe drought in semiarid soils: The importance of organic amendments. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2011, 50, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida, F.; Torres, I.F.; Andrés-Abellán, M.; Baldrian, P.; López-Mondéjar, R.; Větrovský, T.; Richnow, H.H.; Starke, R.; Ondoño, S.; García, C. Differential sensitivity of total and active soil microbial communities to drought and forest management. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 4185–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, S.L.; Warnock, D.D.; Litvak, M.E.; Porras-Alfaro, A.; Sinsabaugh, R. Root-associated fungal community response to drought-associated changes in vegetation community. Mycologia 2015, 107, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, N.W.; Slessarev, E.; Marschmann, G.L.; Nicolas, A.; Blazewicz, S.J.; Brodie, E.L.; Firestone, M.K.; Foley, M.M.; Hestrin, R.; Hungate, B.A. Life and death in the soil microbiome: How ecological processes influence biogeochemistry. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nessner Kavamura, V.; Taketani, R.G.; Lançoni, M.D.; Andreote, F.D.; Mendes, R.; Soares de Melo, I. Water regime influences bulk soil and rhizosphere of Cereus jamacaru bacterial communities in the Brazilian Caatinga biome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouskill, N.J.; Lim, H.C.; Borglin, S.; Salve, R.; Wood, T.E.; Silver, W.L.; Brodie, E.L. Pre-exposure to drought increases the resistance of tropical forest soil bacterial communities to extended drought. ISME J. 2013, 7, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, J.; Caravaca, F.; Azcón, R.; Díaz, G.; Roldán, A. Suitability of the microbial community composition and function in a semiarid mine soil for assessing phytomanagement practices based on mycorrhizal inoculation and amendment addition. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 169, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitkreuz, C.; Herzig, L.; Buscot, F.; Reitz, T.; Tarkka, M. Interactions between soil properties, agricultural management and cultivar type drive structural and functional adaptations of the wheat rhizosphere microbiome to drought. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 5866–5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida, F.; Torres, I.F.; Hernández, T.; García, C. The impacts of organic amendments: Do they confer stability against drought on the soil microbial community? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 113, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, R.L.; Osborne, C.A.; Firestone, M.K. Changing precipitation pattern alters soil microbial community response to wet-up under a Mediterranean-type climate. ISME J. 2015, 9, 946–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, E.A.; Coleman, D.C. Litter placement effects on microbial and organic matter dynamics in an agroecosystem. Ecology 1987, 68, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, F.T.; Griffiths, R.I.; Bailey, M.; Craig, H.; Girlanda, M.; Gweon, H.S.; Bardgett, R.D. Soil bacterial networks are less stable under drought than fungal networks. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3033. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-018-05516-7 (accessed on 15 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Treseder, K.K.; Lennon, J.T. Fungal traits that drive ecosystem dynamics on land. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2015, 79, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, F.; Lau, J.; Hawkes, C.; Semchenko, M. Plant–soil feedback under drought: Does history shape the future? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2023, 38, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaisermann, A.; Maron, P.A.; Beaumelle, L.; Lata, J.C. Fungal communities are more sensitive indicators to non-extreme soil moisture variations than bacterial communities. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 86, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannenberg, S.A.; Novick, K.A.; Phillips, R.P. Coarse roots prevent declines in whole-tree non-structural carbohydrate pools during drought in an isohydric and an anisohydric species. Tree Physiol. 2018, 38, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroca, R.; Ruiz-Lozano, J.M. Induction of plant tolerance to semi-arid environments by beneficial soil microorganisms—A review. In Climate Change, Intercropping, Pest Control and Beneficial Microorganisms: Climate Change, Intercropping, Pest Control and Beneficial Microorganisms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 121–135. [Google Scholar]
- Hemkemeyer, M.; Schwalb, S.A.; Heinze, S.; Joergensen, R.G.; Wichern, F. Functions of elements in soil microorganisms. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 252, 126832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, G.; Varma, A. (Eds.) Soil Enzymology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 22, pp. 1–392. [Google Scholar]
- Chernysheva, E.; Korobov, D.; Khomutova, T.; Fornasier, F.; Borisov, A. Soil microbiological properties in livestock corrals: An additional new line of evidence to identify livestock dung. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2021, 37, 103012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompała-Bąba, A.; Bierza, W.; Sierka, E.; Błońska, A.; Besenyei, L.; Woźniak, G. The role of plants and soil properties in the enzyme activities of substrates on hard coal mine spoil heaps. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrian, P.; Merhautová, V.; Petránková, M.; Cajthaml, T.; Šnajdr, J. Distribution of microbial biomass and activity of extracellular enzymes in a hardwood forest soil reflect soil moisture content. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 46, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J. Drought decreases soil enzyme activity in a Mediterranean Quercus ilex L. forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criquet, S.; Ferre, E.; Farnet, A.M. Annual dynamics of phosphatase activities in an evergreen oak litter: Influence of biotic and abiotic factors. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criquet, S.; Farnet, A.M.; Tagger, S.; Le Petit, J. Annual variations of phenoloxidase activities in an evergreen oak litter: Influence of certain biotic and abiotic factors. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Fonseca, C.; Bossolani, M.D.; de Oliveira, J.W.; Moretti, S.L.; Portugal, L.G.; Scudeletti, J.R.; de Oliveira, D.; Cruscio, E.F.; Costa, C.A. Bacillus Subtilis Inoculation Improves Nutrient Uptake and Physiological Activity in Sugarcane under Drought Stress. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.R.; Bottos, J.-Y.; Brislawn, E.M.; White, C.J., III; Bramer, R.A.; Brown, L.M.; Zucker, J.; Kim, J.D.; Jumponen, Y.-M.; Rice, A.; et al. Metaphenomic Responses of a Native Prairie Soil Microbiome to Moisture Perturbations. Msystems 2019, 4, e00061-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.M.; Jones, D.L.; Chadwick, D.R.; Qi, X.; Cotta, S.R.; Araújo, V.L.P.; Matteoli, F.P.; Lacerda-Júnior, G.V.; Pereira, A.P.A.; Fernandes-Júnior, P.I. Can arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobacteria facilitate P uptake in maize plants under water stress. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 271, 127350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, A.; Batool, A.; Nasir, F.; Jiang, S.; Mingsen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, H. Mechanistic Insights into Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi-Mediated Drought Stress Tolerance in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Freitas, V.F.; Cerezini, P.; Hungria, M.; Nogueira, M.A. Strategies to deal with drought-stress in biological nitrogen fixation with soybean. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 172, 104352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipper, S.C.; Qiu, J.; Kucharik, C.J. Drought effects on us maize and soybean production: Spatiotemporal patterns and historical changes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 094021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, D.; Burkhardt, J.; Goemans, C.; Maas, A. An Analysis of the Impact of Drought on Agriculture, Local Economies, Public Health, and Crime Across the Western United States. 2021. Available online: https://www.drought.gov/documents/analysis-impact-drought-agriculture-local-economies-public-health-and-crime-across (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2014: Impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. In Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects; Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sultan, B.; Defrance, D.; Iizumi, T. Evidence of crop production losses in West Africa due to historical global warming in two crop models. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saud, S.; Wang, D.; Fahad, S.; Alharby, H.F.; Bamagoos, A.A.; Mjrashi, A.; Alabdallah, N.M.; AlZahrani, S.S.; AbdElgawad, H.; Adnan, M.; et al. Comprehensive Impacts of Climate Change on Rice Production and Adaptive Strategies in China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 926059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, S.M.; Yan, D.H.; Zhang, T.X.; Weng, B.S.; Zhang, Z.B.; Gang, W. Effects of extreme drought on agriculture soil and sustainability of different drought soil. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2014, 11, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Shew, A.M. Geospatial Analysis of Droughts, Rice and Wheat Production, and Agrarian Vulnerability: A District-Level Study of the Self-Calibrated Palmer Drought Severity Index in India. 2016. Available online: https://scholarworks.uark.edu/etd/1458 (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Daryanto, S.; Wang, L.; Jacinthe, P.A. Global Synthesis of Drought Effects on Maize and Wheat Production. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Al-Suhaibani, N.; Ali, N.; Akmal, M.; Alotaibi, M.; Refay, Y.; Dindaroglu, T.; Abdul-Wajid, H.H.; Battaglia, M.L. Drought stress impacts on plants and different approaches to alleviate its adverse effects. Plants 2021, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veresoglou, S.D.; Li, G.C.; Chen, J.; Johnson, D. Direction of plant–soil feedback determines plant responses to drought. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yao, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, E.; Tian, C.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, C.; Tian, L. Current studies of the effects of drought stress on root exudates and rhizosphere microbiomes of crop plant species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solh, M.; van Ginkel, M. Drought preparedness and drought mitigation in the developing world’s drylands. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2014, 3, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, S.; Khan, T.; Farooq, I.; Shah, L.R.; Sharma, V.; Sonne, C.; Rinklebe, J.; Ahmad, P. Drought and global hunger: Biotechnological interventions in sustainability and management. Planta 2022, 256, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Silva, S.; Kariyawasam Hetti Gamage, L.; Thapa, V.R. Impact of Drought on Soil Microbial Communities. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071625
De Silva S, Kariyawasam Hetti Gamage L, Thapa VR. Impact of Drought on Soil Microbial Communities. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071625
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Silva, Sujani, Lithma Kariyawasam Hetti Gamage, and Vesh R. Thapa. 2025. "Impact of Drought on Soil Microbial Communities" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071625
APA StyleDe Silva, S., Kariyawasam Hetti Gamage, L., & Thapa, V. R. (2025). Impact of Drought on Soil Microbial Communities. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071625





