Development of a TaqMan One-Step Quantitative PCR Assay for the Simultaneous Detection of Novel Goose Parvovirus and Novel Duck Reovirus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Cheng, X.; Xiao, S.; Zhu, X.; Lin, F.; Wu, N.; Wang, J.; Huang, M.; Zheng, M.; et al. Isolation and characterization of a distinct duck-origin goose parvovirus causing an outbreak of duckling short beak and dwarfism syndrome in China. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 2407–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Ma, X.; Sheng, Z.; Qi, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, D.; Huang, B.; Li, F.; Song, M. Identification of Goose-Origin Parvovirus as a Cause of Newly Emerging Beak Atrophy and Dwarfism Syndrome in Ducklings. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1999–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Afumba, R.; Pang, F.; Yuan, R.; Dong, H. Advances in Research on Genetic Relationships of Waterfowl Parvoviruses. J. Vet. Res. 2021, 65, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y. Evolution, genetic recombination, and phylogeography of goose parvovirus. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 102, 102079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, N.T.; Hieu, D.V.; Bich, N.T.; Khanh, T.V.; Ba, N.T.; Xuan, C.T.N.; Hien, Q.T.M.; Thai, T.H.; Huong, C.T.T. Isolation and genetic characterization of waterfowl parvovirus in ducks in Northern Vietnam. Vet. World 2024, 17, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matczuk, A.K.; Chmielewska-Władyka, M.; Siedlecka, M.; Bednarek, K.J.; Wieliczko, A. Short Beak and Dwarfism Syndrome in Ducks in Poland Caused by Novel Goose Parvovirus. Animals 2020, 10, 2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, J.K.; Sterner, F.J.; Botts, S.; Lee, K.P.; Margolin, A. In vitro and in vivo characterization of avian reoviruses. I. Pathogenicity and antigenic relatedness of several avian reovirus isolates. Avian Dis. 1989, 33, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Shao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xie, Z.; Feng, K.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Q. Molecular characterization, complete genome sequencing, and pathogenicity of Novel Duck Reovirus from South Coastal Area in China. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Hong, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, K.; Cai, Y.; Liu, S.; Wei, L.; Chai, T. The pathogenicity of novel duck reovirus in Cherry Valley ducks. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 192, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Diao, Y.; Tang, Y. Pathogenicity of a variant duck orthoreovirus strain in Cherry Valley Ducklings. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 242, 108546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, N.E.; Roldán, J.S.; Castillo, D.S. Novel competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of the high-risk Human Papillomavirus 18 E6 oncoprotein. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, G.; Shi, M.; Qiao, Y.; Huang, T.; Wei, T.; Mo, M.; He, X.; et al. Rapid and visual detection of the emerging novel duck reovirus by using a specific and sensitive reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification method. J. Virol. Methods 2021, 291, 114098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Yu, X.; Niu, X.; Tang, Y.; Diao, Y. Development of a Quantitative Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for the Rapid Detection of Novel Goose Parvovirus. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.; Hua, J.; Ye, W.; Chen, L.; Ni, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, C. Development and Evaluation of a Monoclonal Antibody-Based Blocking Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for the Detection of Antibodies against Novel Duck Reovirus in Waterfowl Species. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0258122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Easley, C.J. Isothermal DNA amplification in bioanalysis: Strategies and applications. Bioanalysis 2011, 3, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Yang, Y.T.; Du, S.M.; Yi, H.D.; Xu, D.N.; Cao, N.; Jiang, D.L.; Huang, Y.M.; Tian, Y.B. Rapid and sensitive detection of goose parvovirus and duck-origin novel goose parvovirus by recombinase polymerase amplification combined with a vertical flow visualization strip. J. Virol. Methods 2019, 266, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, G.; Ding, X.; Zhang, K.; Sun, W.; Li, Q.; Yi, Y.; Wang, J.; Pang, X.; Chen, L. A rapid simultaneous detection of duck hepatitis A virus 3 and novel duck reovirus based on RPA CRISPR Cas12a/Cas13a. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 274, 133246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Chen, H.; Yang, J.; Yu, X.; Ti, J.; Wang, A.; Diao, Y. Development of a TaqMan-based real-time PCR assay for the detection of Novel GPV. J. Virol. Methods 2016, 237, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Cui, Y.; Nan, H.; Yuan, W. Development of a TaqMan-based real-time PCR assay for the rapid and specific detection of novel duck- origin goose parvovirus. Mol. Cell. Probes 2017, 34, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Gao, B.; Diao, Y.; Tang, Y. A TaqMan-based real-time PCR assay for specific detection of novel duck reovirus in China. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bi, Z.; Liu, Y.; Meng, C.; Zhu, J.; Liu, G.; Li, C. Simultaneous detection of novel goose parvovirus and novel duck reovirus by SYBR Green I-based duplex real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. 3 Biotech 2024, 14, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
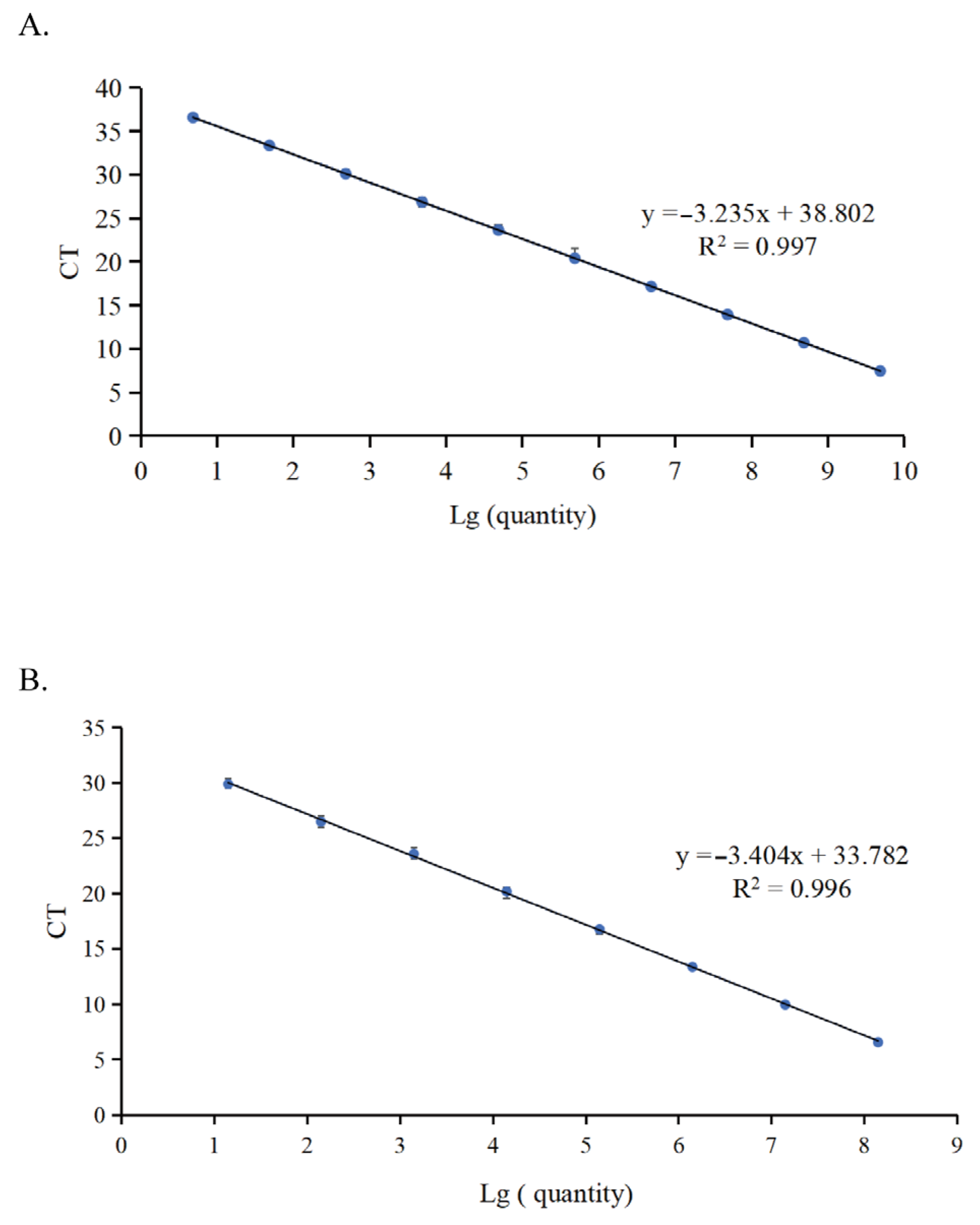
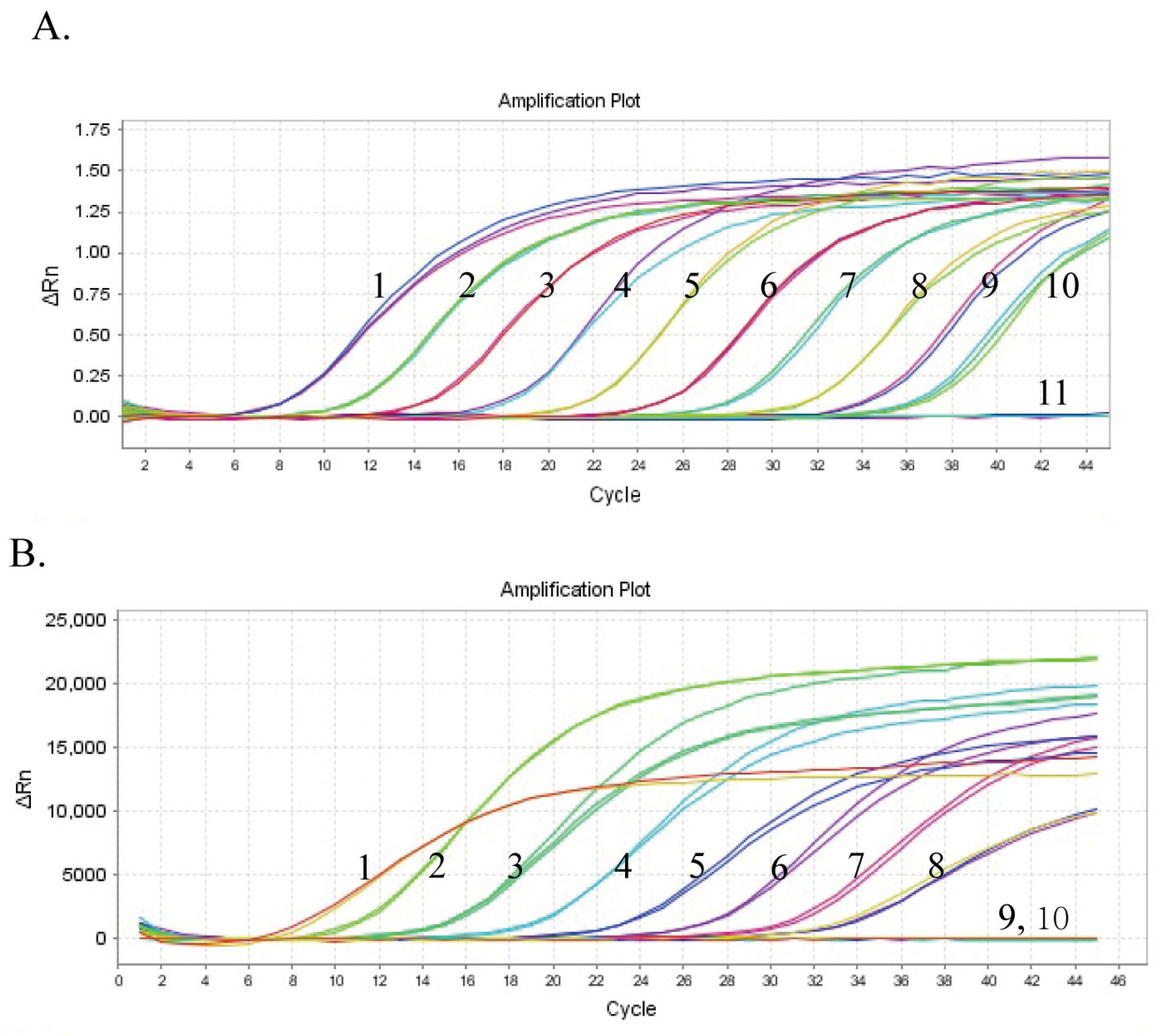
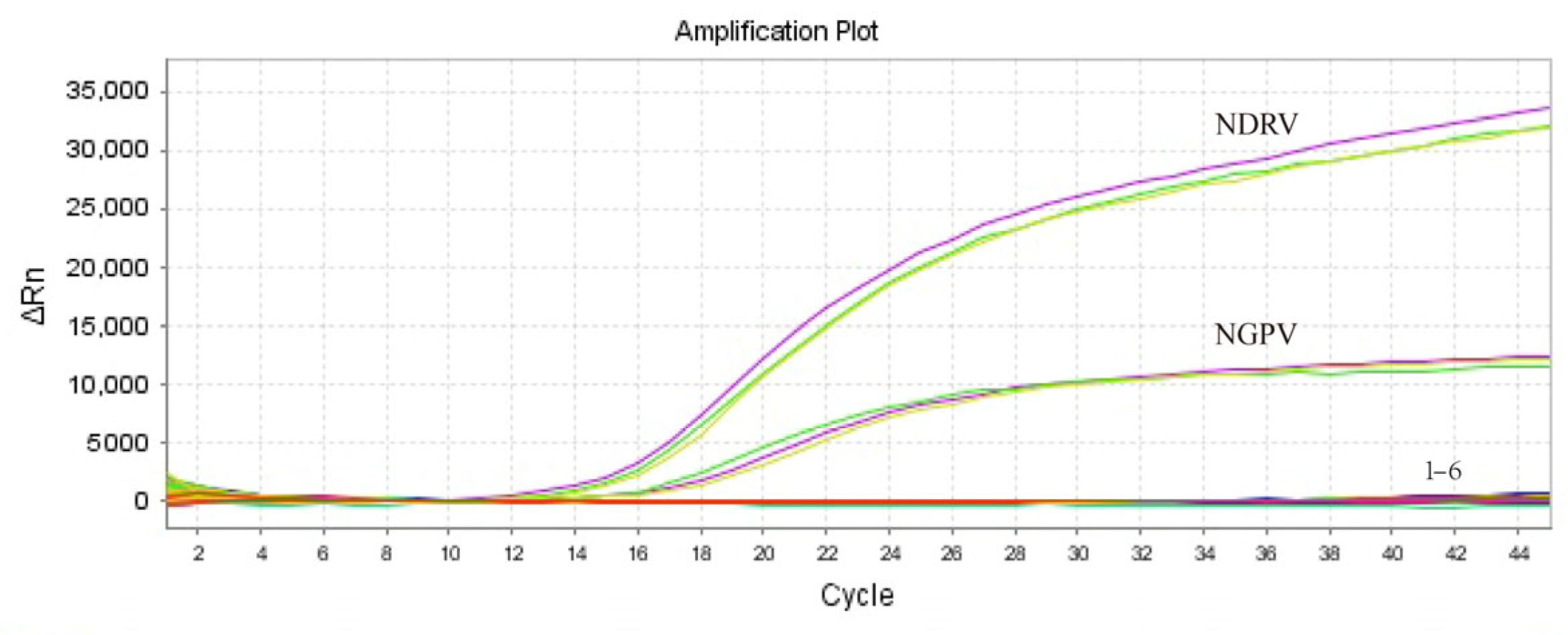
| Category | Concentration (Copies/μL) | Mean Ct | SD | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-assay | 104 | 24.130 | 0.074 | 0.32 |
| 105 | 20.919 | 0.052 | 0.26 | |
| 106 | 17.116 | 0.024 | 0.14 | |
| Inter-assay | 104 | 24.863 | 0.043 | 0.17 |
| 105 | 20.981 | 0.055 | 0.26 | |
| 106 | 17.319 | 0.108 | 0.62 |
| Category | Concentration (Copies/μL) | Mean Ct | SD | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-assay | 104 | 20.510 | 0.057 | 0.27 |
| 105 | 16.847 | 0.144 | 0.85 | |
| 106 | 13.060 | 0.072 | 0.55 | |
| Inter-assay | 104 | 20.110 | 0.160 | 0.79 |
| 105 | 16.391 | 0.073 | 0.44 | |
| 106 | 12.840 | 0.136 | 1.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bi, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Ru, X.; Meng, C.; Zhu, J.; Liu, G.; Li, C. Development of a TaqMan One-Step Quantitative PCR Assay for the Simultaneous Detection of Novel Goose Parvovirus and Novel Duck Reovirus. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071582
Wang Y, Wang Y, Bi Z, Wang J, Wang G, Ru X, Meng C, Zhu J, Liu G, Li C. Development of a TaqMan One-Step Quantitative PCR Assay for the Simultaneous Detection of Novel Goose Parvovirus and Novel Duck Reovirus. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071582
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yimin, Yong Wang, Zhuangli Bi, Jinbin Wang, Gang Wang, Xin Ru, Chunchun Meng, Jie Zhu, Guangqing Liu, and Chuanfeng Li. 2025. "Development of a TaqMan One-Step Quantitative PCR Assay for the Simultaneous Detection of Novel Goose Parvovirus and Novel Duck Reovirus" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071582
APA StyleWang, Y., Wang, Y., Bi, Z., Wang, J., Wang, G., Ru, X., Meng, C., Zhu, J., Liu, G., & Li, C. (2025). Development of a TaqMan One-Step Quantitative PCR Assay for the Simultaneous Detection of Novel Goose Parvovirus and Novel Duck Reovirus. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071582






