Pseudorabies Virus IE180 Inhibits Virus Replication by Activating the Type I Interferon Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Viruses
2.2. Antibodies, Reagents, and Plasmids
2.3. Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR, qPCR
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Virus Infection and Titer Determination
2.7. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
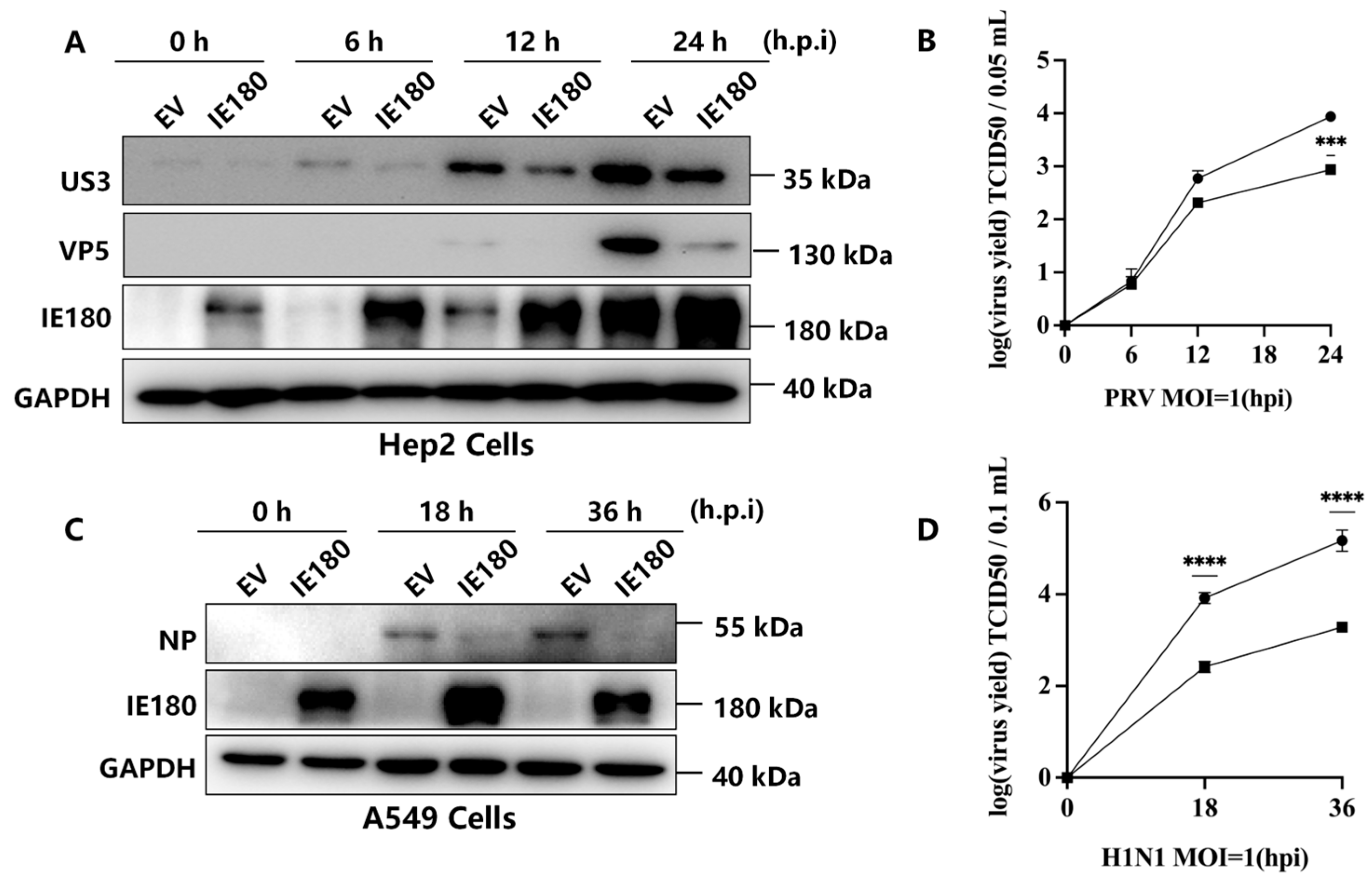
3.1. IE180 Suppresses PRV and H1N1 Replication
3.2. IE180 Activates IFN-I Signaling Pathways
3.3. IE180’s Antiviral Function Requires Intact IFN-I Signaling
3.4. The ICP4-Like2 Domain of IE180 Mediates IFN-β Activation and Antiviral Activity
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ChIP | Chromatin Immunoprecipitation |
| CPE | Cytopathic Effect |
| DTT | Dithiothreitol |
| ECL | Enhanced Chemiluminescence |
| EV | Empty Vector |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| HA | Hemagglutinin tag |
| HIF1α | Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 alpha |
| HSV-1 | Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 |
| IFN-I | Type I Interferon |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| IRF9 | Interferon Regulatory Factor 9 |
| ISG | Interferon-Stimulated Gene |
| ISRE | Interferon-Stimulated Response Element |
| MBT1 | Also known as L3MBTL3, histone methyl-lysine binding protein 3 |
| MOI | Multiplicity of Infection |
| NP | Nucleoprotein |
| PRV | Pseudorabies Virus |
| qPCR | Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| SG | Stress Granule |
| STAT | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription |
| TCID50 | 50% Tissue Culture Infective Dose |
References
- Chen, Y.; Gao, J.; Hua, R.; Zhang, G. Pseudorabies virus as a zoonosis: Scientific and public health implications. Virus Genes 2024, 61, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, T.Q.; Peng, J.M.; Tian, Z.J.; Zhao, H.Y.; Li, N.; Liu, Y.M.; Chen, J.Z.; Leng, C.L.; Sun, Y.; Chang, D.; et al. Pseudorabies virus variant in Bartha-K61-vaccinated pigs, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerma, L.; Munoz, A.L.; Garcia Utrilla, R.; Sainz, B., Jr.; Lim, F.; Tabares, E.; Gomez-Sebastian, S. Partial complementation between the immediate early proteins ICP4 of herpes simplex virus type 1 and IE180 of pseudorabies virus. Virus Res. 2020, 279, 197896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeranz, L.E.; Reynolds, A.E.; Hengartner, C.J. Molecular biology of pseudorabies virus: Impact on neurovirology and veterinary medicine. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 69, 462–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.W.; Engel, E.A.; Enquist, L.W. Characterization of a replication-incompetent pseudorabies virus mutant lacking the sole immediate early gene IE180. mBio 2014, 5, e01850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, E.; Taharaguchi, S.; Watanabe, S.; Nikami, H.; Shimizu, Y.; Kida, H. Suppression of pseudorabies virus replication by a mutant form of immediate-early protein IE180 repressing the viral gene transcription. Vet. Microbial. 1998, 60, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Sebastian, S.; Tabares, E. Negative regulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP4 promoter by IE180 protein of pseudorabies virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 2125–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Opdenbosch, N.; Van den Broeke, C.; De Regge, N.; Tabares, E.; Favoreel, H.W. The IE180 protein of pseudorabies virus suppresses phosphorylation of translation initiation factor eIF2alpha. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 7235–7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerma, L.; Alcala, S.; Pinero, C.; Torres, M.; Martin, B.; Lim, F.; Sainz, B., Jr.; Tabares, E. Expression of the immediate early IE180 protein under the control of the hTERT and CEA tumor-specific promoters in recombinant pseudorabies viruses: Effects of IE180 protein on promoter activity and apoptosis induction. Virology 2015, 488, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, W.; Wen, W.; Zhang, Z.; Favoreel, H.W.; Li, X. Pseudorabies virus IE180 protein hijacks G3BPs into the nucleus to inhibit stress granule formation. J. Virol. 2025, 99, e0208824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, C.E. Antiviral actions of interferons. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 778–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katze, M.G.; He, Y.; Gale, M., Jr. Viruses and interferon: A fight for supremacy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, C.; Levy, D.E.; Decker, T. JAK-STAT signaling: From interferons to cytokines. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 20059–20063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, W.M.; Chevillotte, M.D.; Rice, C.M. Interferon-stimulated genes: A complex web of host defenses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 513–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tang, J. Evasion of I Interferon-Mediated Innate Immunity by Pseudorabies Virus. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 801257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular Cloning, a Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Cidoncha, M.; Killip, M.J.; Asensio, V.J.; Fernandez, Y.; Bengoechea, J.A.; Randall, R.E.; Ortin, J. Generation of replication-proficient influenza virus NS1 point mutants with interferon-hyperinducer phenotype. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, M.; Kato, N.; Otsuka, M.; Shao, R.X.; Taniguchi, H.; Kawabe, T.; Omata, M. Interferon-beta is activated by hepatitis C virus NS5B and inhibited by NS4A, NS4B, and NS5A. Hepatol. Int. 2007, 1, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahoor, M.A.; Xue, G.; Sato, H.; Murakami, T.; Takeshima, S.N.; Aida, Y. HIV-1 Vpr induces interferon-stimulated genes in human monocyte-derived macrophages. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, W.B.; Loo, Y.M.; Gale, M., Jr.; Hartman, A.L.; Kimberlin, C.R.; Martinez-Sobrido, L.; Saphire, E.O.; Basler, C.F. Ebola virus VP35 protein binds double-stranded RNA and inhibits alpha/beta interferon production induced by RIG-I signaling. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5168–5178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basler, C.F.; Wang, X.; Muhlberger, E.; Volchkov, V.; Paragas, J.; Klenk, H.D.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Palese, P. The Ebola virus VP35 protein functions as a type I IFN antagonist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12289–12294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, L.W.; Park, M.S.; Martinez, O.; Valmas, C.; Lopez, C.B.; Basler, C.F. Ebolavirus VP35 suppresses IFN production from conventional but not plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2011, 89, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luthra, P.; Ramanan, P.; Mire, C.E.; Weisend, C.; Tsuda, Y.; Yen, B.; Liu, G.; Leung, D.W.; Geisbert, T.W.; Ebihara, H.; et al. Mutual antagonism between the Ebola virus VP35 protein and the RIG-I activator PACT determines infection outcome. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gantke, T.; Boussouf, S.; Janzen, J.; Morrice, N.A.; Howell, S.; Muhlberger, E.; Ley, S.C. Ebola virus VP35 induces high-level production of recombinant TPL-2-ABIN-2-NF-kappaB1 p105 complex in co-transfected HEK-293 cells. Biochem. J. 2013, 452, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, F.; Song, J.; Chen, X.; Xing, D.; Bai, R.; Cheng, C.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, R. Pseudorabies Virus IE180 Inhibits Virus Replication by Activating the Type I Interferon Pathway. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061397
Zheng F, Song J, Chen X, Xing D, Bai R, Cheng C, Yuan J, Zhang R. Pseudorabies Virus IE180 Inhibits Virus Replication by Activating the Type I Interferon Pathway. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061397
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Feiyang, Jingjing Song, Xuan Chen, Dongyue Xing, Rulan Bai, Changyong Cheng, Jin Yuan, and Rui Zhang. 2025. "Pseudorabies Virus IE180 Inhibits Virus Replication by Activating the Type I Interferon Pathway" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061397
APA StyleZheng, F., Song, J., Chen, X., Xing, D., Bai, R., Cheng, C., Yuan, J., & Zhang, R. (2025). Pseudorabies Virus IE180 Inhibits Virus Replication by Activating the Type I Interferon Pathway. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061397





