The Improved Remediation Effect of the Combined Use of Earthworms with Bacillus subtilis-Loaded Biochar in Ameliorating Soda Saline–Alkali Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
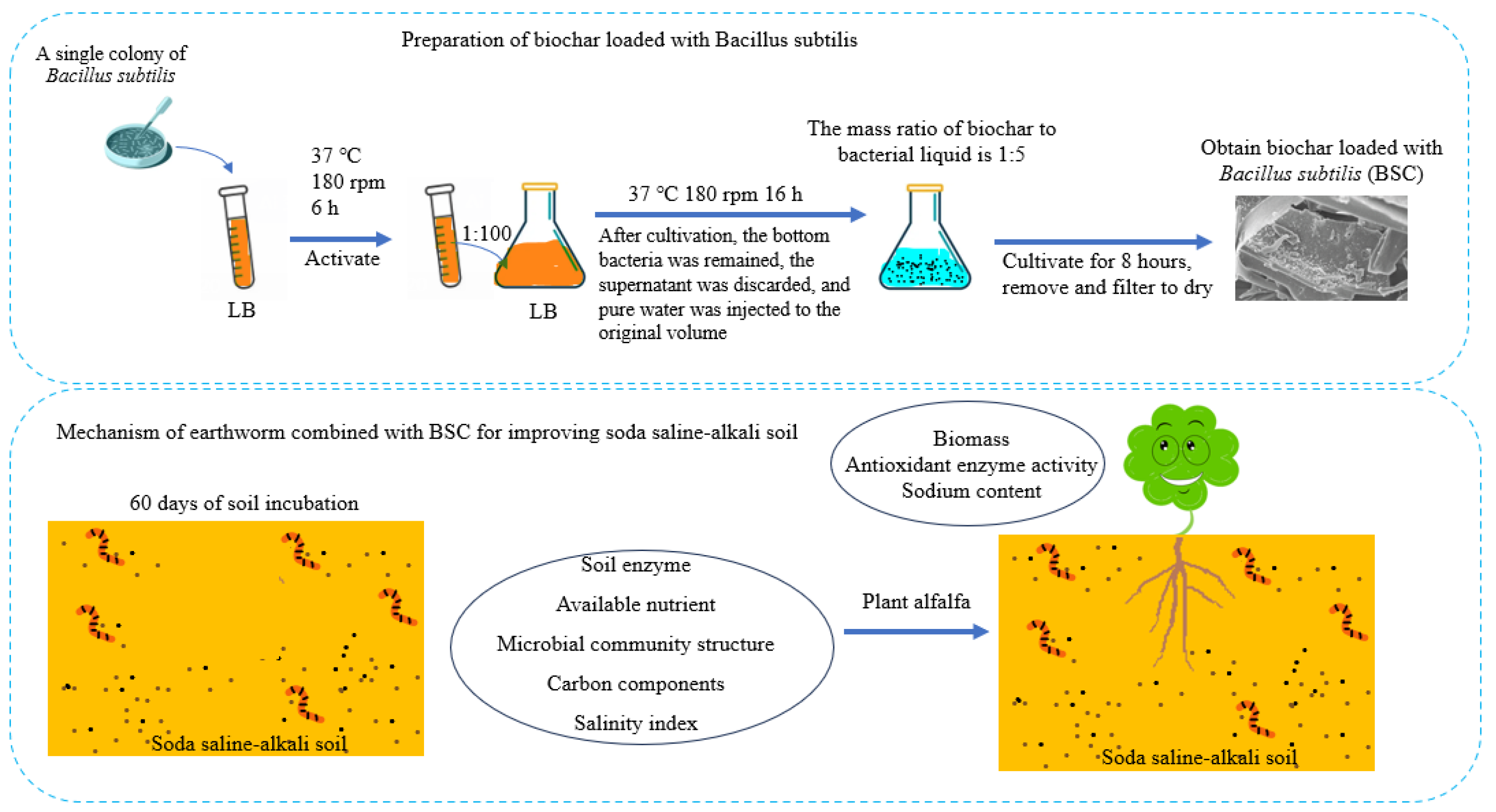
2.2. Preparation of B. subtilis-Loaded Biochar, and Salt–Alkali Tolerance of B. subtilis
2.3. Experimental Design, Materials, and Sample Collection
2.4. Physical and Chemical Analyses
2.5. Microbial Community Structure Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
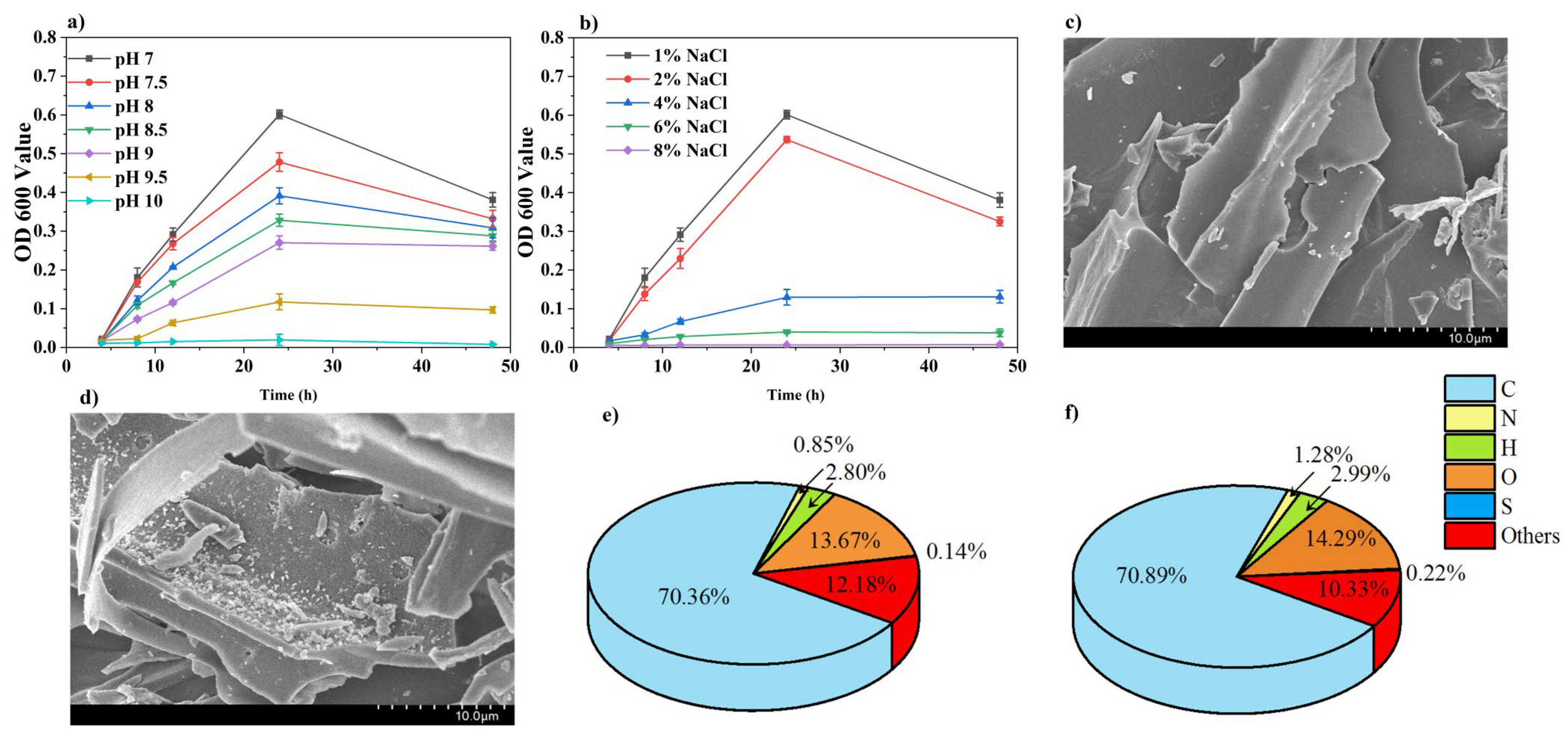
3.1. Growth Status of Free B. subtilis and Characterization of BSC
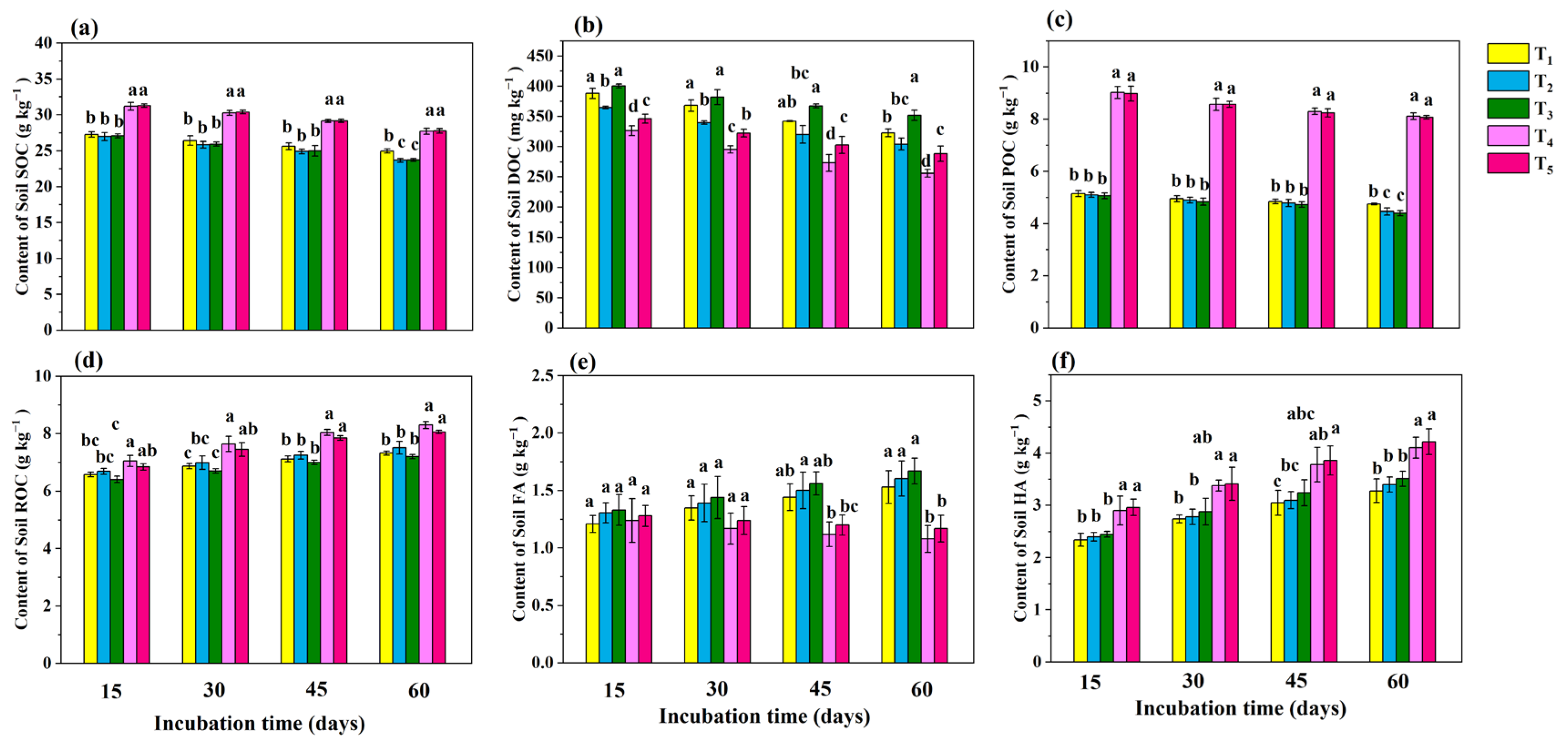
3.2. Soil Carbon Fractions
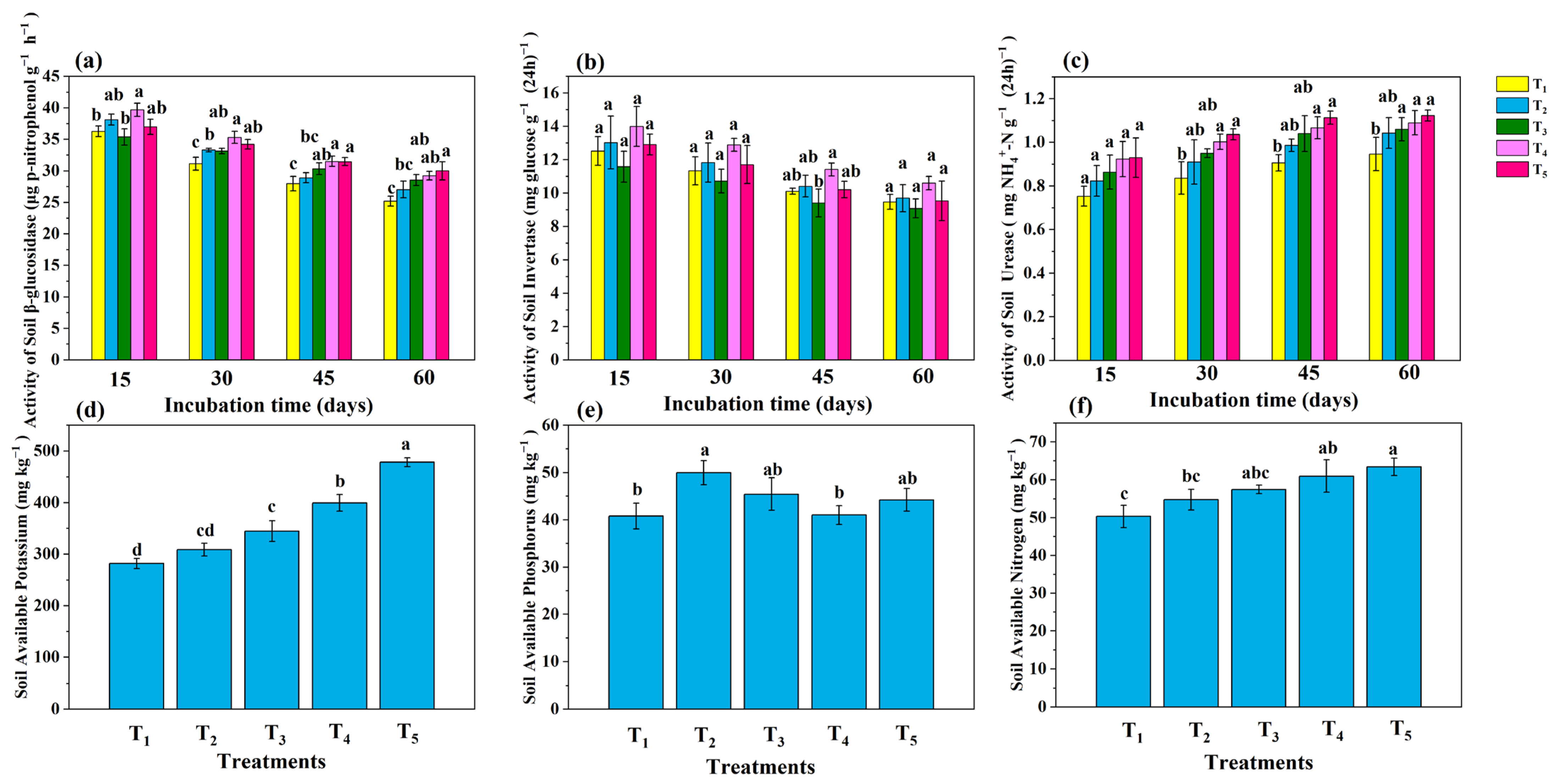
3.3. Key Soil Enzyme Activities
3.4. Available Nutrients and Elimination of Saline–Alkali Barriers
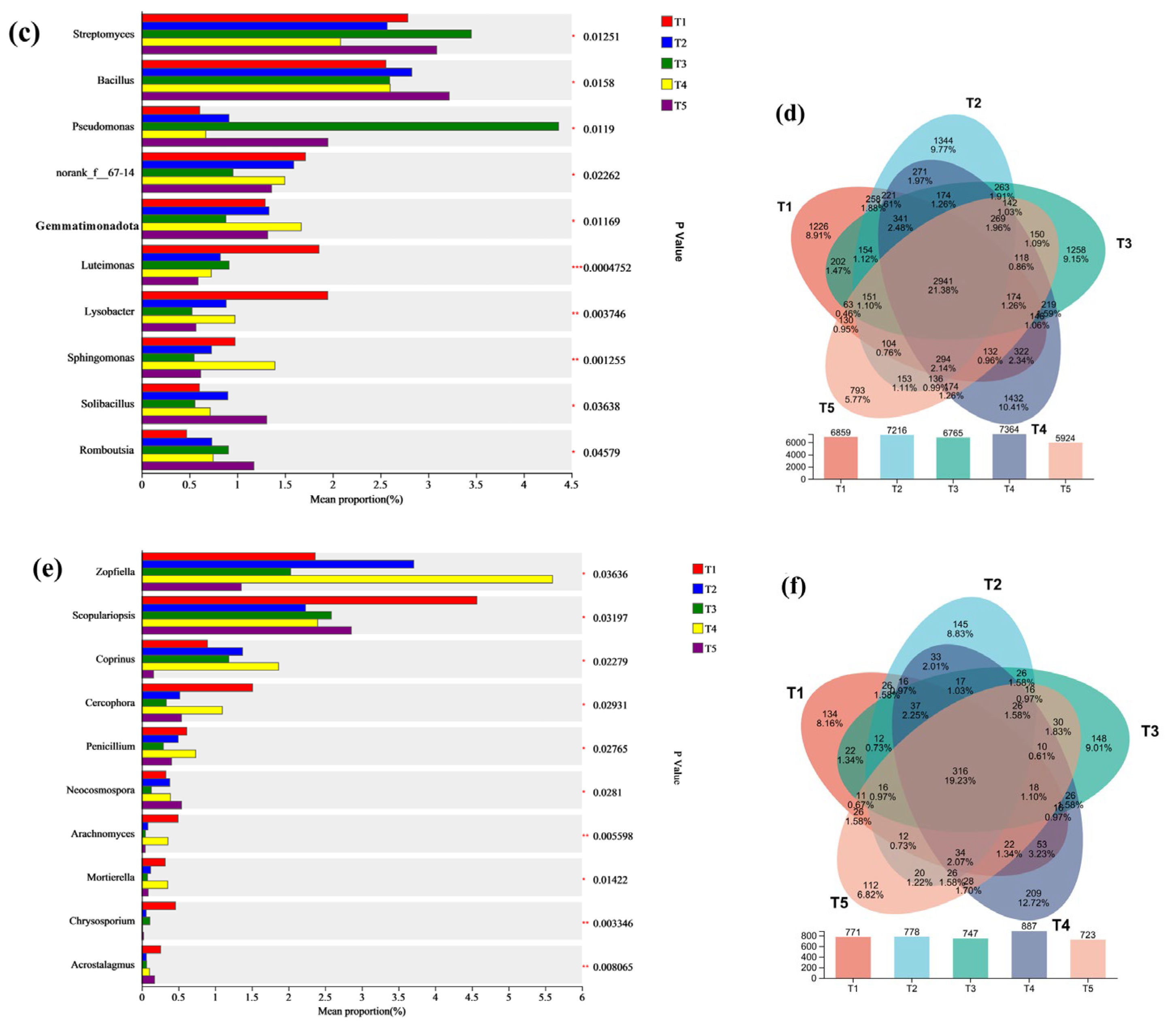
3.5. Microbial Composition and Analysis of Differences
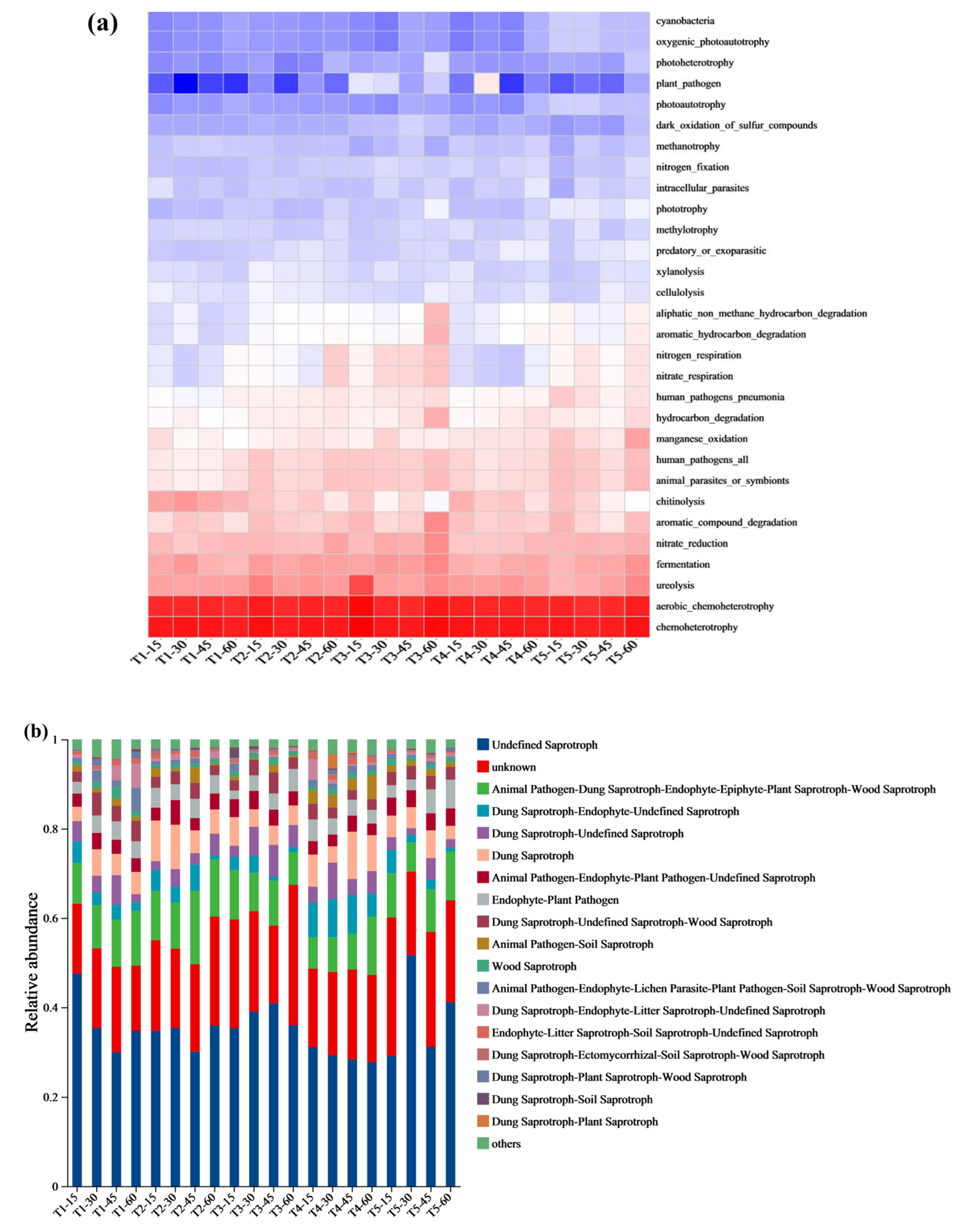
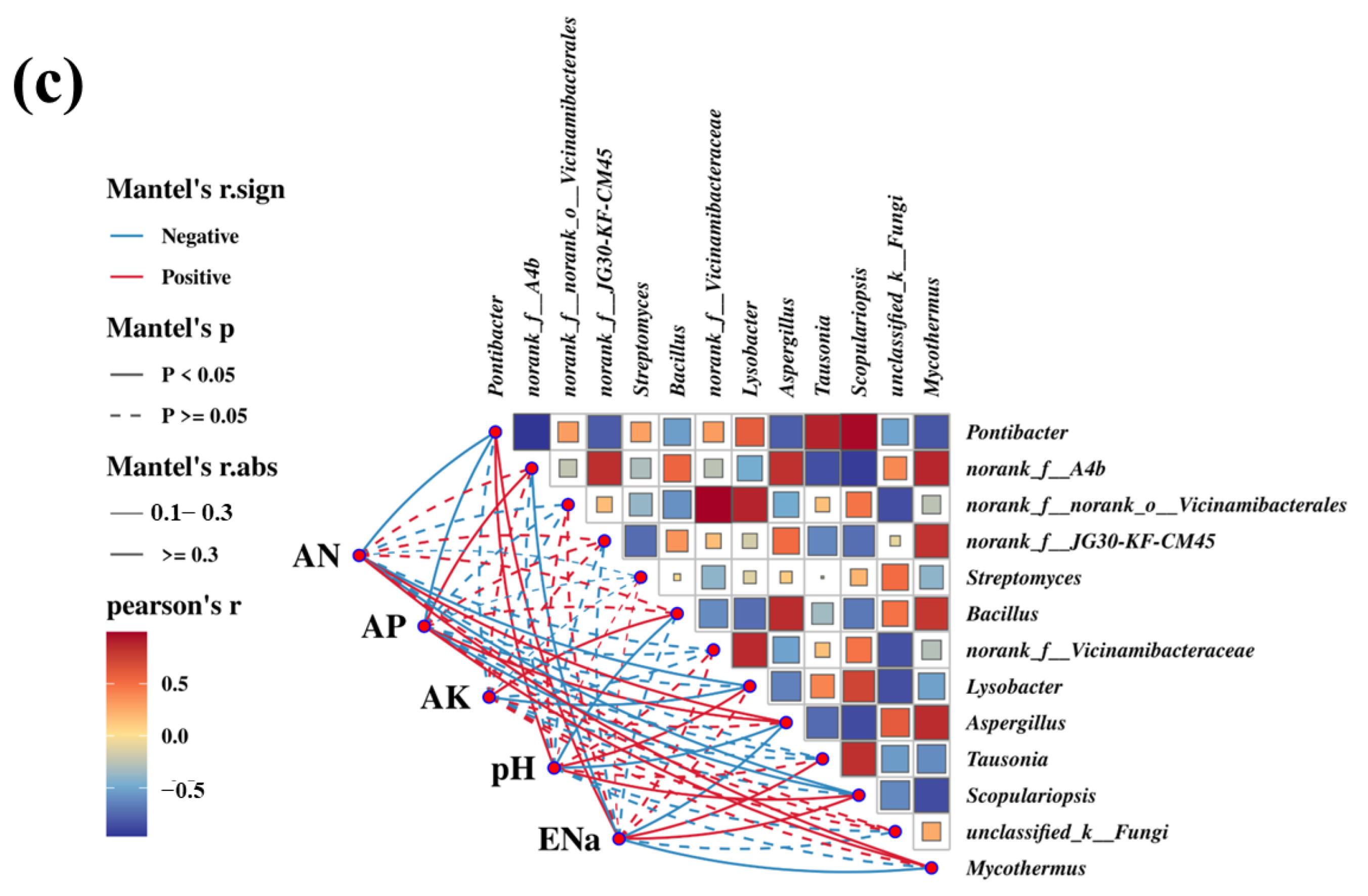
3.6. Microbial Composition Prediction and Correlation Analysis of Microbial Community Function
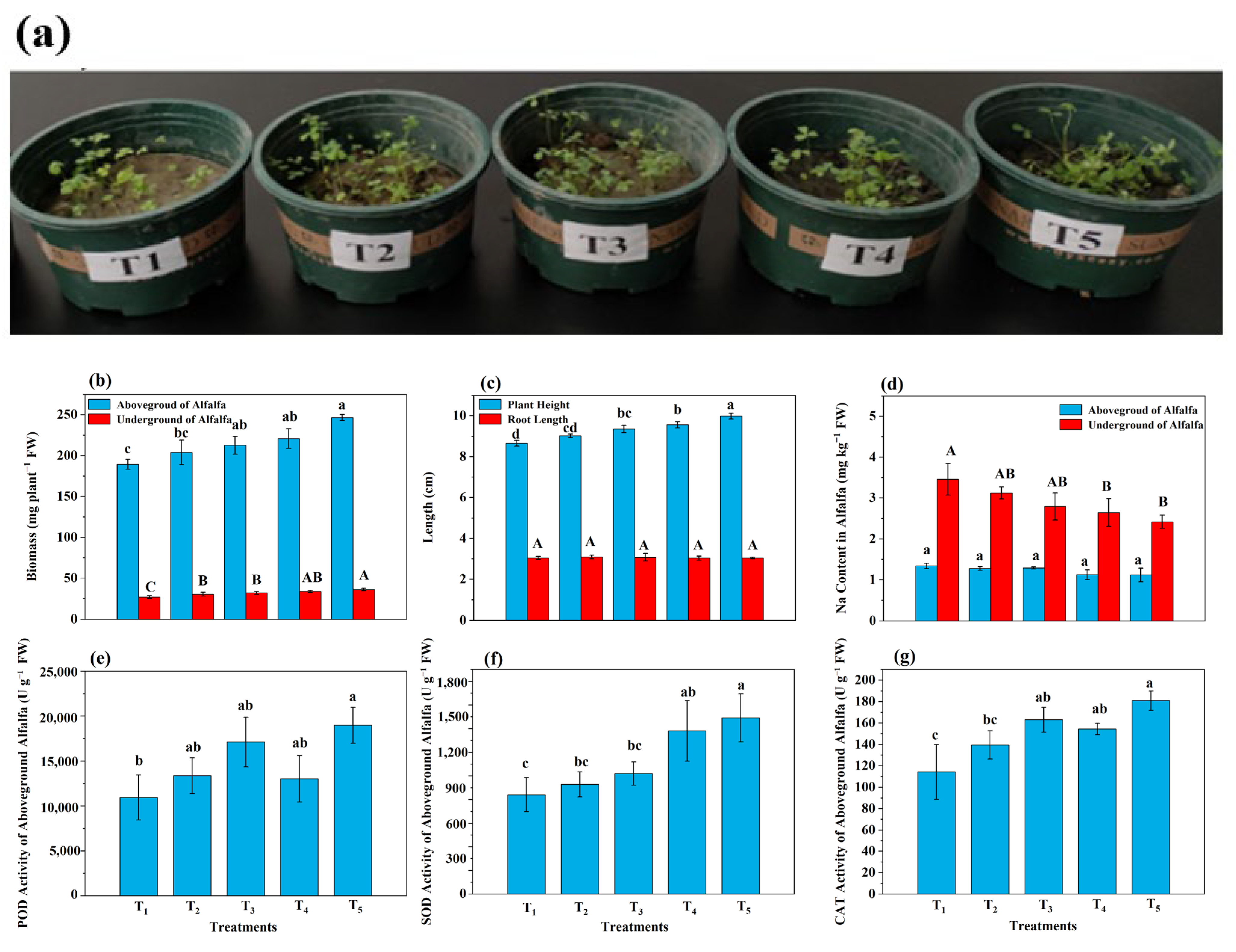
3.7. Growth and Resistance of Alfalfa
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Salt Alkali Tolerance of Free B. subtilis and Characterization of BSC
4.2. Analysis of Dynamic Changes in Soil Carbon Fractions
4.3. Analysis of Key Soil Enzymes, Available Nutrients, and Elimination of Salt–Alkali Barriers
4.4. The Analysis of the Diversity, Composition, and Functional Prediction of the Microbial Community
4.5. Analysis of Alfalfa Growth
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SOC | soil organic carbon |
| ROC | readily oxidizable organic carb |
| DOC | dissolved organic carbon |
| HA | humic acid |
| FA | fulvic acid |
| ESP | Exchangeable sodium saturation percentage |
| ENa | Exchange sodium s |
| POC | particulate organic carbon |
| CEC | cation exchange capacity |
| POD | peroxidase |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| CAT | catalase |
| BC | biochar |
| BS | Bacillus subtilis |
| E | earthworm |
| BSC | Bacillus subtilis-loaded biochar |
| AN | available nitrogen |
| AP | available phosphorus |
| AK | available potassium |
References
- Amundson, R.; Berhe, A.A.; Hopmans, J.W.; Olsen, C.; Sztein, E.A.; Sparks, D.L. Soil and human security in the 21st century. Science 2022, 348, 1261071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Xie, R.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z. Comparative study on the abilities of different crack parameters to estimate the salinity of soda saline-alkali soil in Songnen Plain, China. Catena 2022, 213, 106221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhdar, A.; Rabhi, M.; Ghnaya, T.; Montemurro, F.; Jedidi, N.; Abdelly, C. Effectiveness of compost use in salt-affected soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, W.; Liang, G.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; He, P. Distribution of soil nutrients, extracellular enzyme activities and microbial communities across particle-size fractions in a long-term fertilizer experiment. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 94, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, M.; Wu, Y.; Delgado, A.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Peng, Q.; Lin, S.; Hu, R. Enzyme activities and organic matter mineralization in response to application of gypsum, manure and rice straw in saline and sodic soils. Environ. Res. 2023, 224, 115393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, J.; Cong, Y.; Lu, Y.; Guo, M. Fine-crush straw returning enhances dry matter accumulation rate of maize seedlings in Northeast China. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouni, Y.; Ghnaya, T.; Montemurro, F.; Lakhdar, A. The role of humic substances in mitigating the harmful effects of soil salinity and improve plant productivity. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2014, 8, 353–374. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zhu, M.; Guo, X.; Wang, H.; Sui, B.; Zhao, L. Organic carbon content and humus composition after application aluminum sulfate and rice straw to soda saline-alkaline soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 13746–13754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Chu, S.; Wei, Q.; Tian, C.; Fang, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, S. Prediction of Salt-Tolerant Earthworms’ Cultivation Conditions Based on the Robust Artificial Intelligence Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, Y.; Sun, Z. Responses of Saline Soil Properties and Cotton Growth to Different Organic Amendments. Pedosphere 2018, 28, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cao, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C. Effect of earthworms and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the microbial community and maize growth under salt stress. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 107, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ma, K.; Xia, X.; Gao, K.; Lu, Y. Biochar and magnetite promote methanogenesis during anaerobic decomposition of rice straw. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 43, 107740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhou, W.; Sun, J.; Liang, G.; Liu, G.; Sun, G.; Yuan, F. Effects of different straw-decomposition inoculants on increasing the activities of extracellular enzymes and decomposition of rice straw buried into soil. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2020, 26, 2070–2080. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Z.; Paungfoo, L.C.; Ye, J.; Garcia, A.G.; Petersen, I.; Di, B.L.; Hobbs, R.; Ibanez, M.; Heenan, M.; Wang, W.; et al. Biofertilizers can enhance nitrogen use efficiency of sugarcane. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 3655–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivan, S.; Ebrahem, M.; Mostafa, A.; Mohamed, H.; Hanan, E.; Pankaj, K.; Bashir, A.; Sami, A.; Boro, M.; Madhumita, G.; et al. Combined Use of Spent Mushroom Substrate Biochar and PGPR Improves Growth, Yield, and Biochemical Response of Cauliflower (Brassica oleracea var. botrytis): A Preliminary Study on Greenhouse Cultivation. Horticulture 2022, 8, 830. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Wang, W.; Penuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Martinez, M.; Su, C.; Xu, X.; Singh, B.; Fang, Y. Combined slag and biochar amendments to subtropical paddy soils lead to a short-term change of bacteria community structure and rise of soil organic carbon. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 179, 104593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, L.; Sanaullah, M.; Mahmood, F.; Hussain, S.; Siddique, M.H.; Anwar, F.; Shahzad, F. Unlocking the potential of co-applied biochar and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) for sustainable agriculture under stress conditions. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2022, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tan, W.; Yang, D.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, L.; Xie, Z.; Xu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Pan, X.; et al. Mitigation of soil salinization and alkalization by bacterium-induced inhibition of evaporation and salt crystallization. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Yu, K.; Liu, H.; Sheng, Q.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on Rose Growth Promotion and Rhizosphere Microbial Community Changes Under Saline–Alkaline Stress. Agronomy 2024, 14, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Cao, M.; Lai, K.; Sun, K.; Zhang, L.; Gao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, B.; Guo, L. Unveiling key metabolic pathways in Bacillus subtilis-mediated salt tolerance enhancement in Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. through multi-omics analysis. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2024, 219, 105631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhi, D.; Yao, B.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Immobilization of microbes on biochar for water and soil remediation: A review. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Tan, X.; Zheng, M.; Yu, D.; Lin, A.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Gao, Z.; Cui, J. Modified biochar/humic substance/fertiliser compound soil conditioner for highly efficient improvement of soil fertility and heavy metals remediation in acidic soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, W.; Sun, Y.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Niu, Y. Bacillus halophilus BH-8 Combined with Coal Gangue as a Composite Microbial Agent for the Rehabilitation of Saline-Alkali Land. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Guo, H.; Han, S.; Chang, J.-S.; Lee, D.-J. Enhanced Remediation of Salt-Affected Petroleum-Contaminated Soil by Modified Biochar Loaded with Acinetobacter Bacteria. SSRN, 2023. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4605927 (accessed on 4 March 2025). [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Tang, F.; Chen, H.; Zhao, C.; Li, L. A novel chitosan-biochar immobilized microorganism strategy to enhance bioremediation of crude oil in soil. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Hu, C.; Tan, Q.; Yu, M.; Shabala, S.; Yang, L.; Sun, X. Highly efficient removal of cadmium from aqueous solution by ammonium polyphosphate-modified biochar. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Riaz, M.; Babar, S.; Eldesouki, Z.; Liu, B.; Xia, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Xia, X.; Jiang, C. Alterations in the composition and metabolite profiles of the saline-alkali soil microbial community through biochar application. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 352, 120033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhou, Q.; Tian, Z.; Cui, Y.; Liang, Y.; Wang, H. Apply biochar to ameliorate soda saline-alkali land, improve soil function and increase corn nutrient availability in the Songnen Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Kim, K.-R.; Yang, J.E.; Ok, Y.S.; Owens, G.; Nehls, T.; Wessolek, G.; Kim, K.-H. Effect of biochar on reclaimed tidal land soil properties and maize (Zea mays L.) response. Chemosphere 2016, 142, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkash, V.; Singh, S. Potential of biochar application to mitigate salinity stress in eggplant. Hortscience 2020, 55, 1946–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Si, G.; Chen, G.; Feng, T.; Liu, C.; Chen, J. Bacteria-loaded biochar for the immobilization of cadmium in an alkaline-polluted soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 31, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Gou, J.; Chen, X.; Xiao, S.; Ali, I.; Shang, R.; Wang, D.; Wu, Y.; Han, M.; Luo, X. Application of mixed bacteria-loaded biochar to enhance uranium and cadmium immobilization in a co-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chang, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, H. Characterization of microbial community succession during vermicomposting of medicinal herbal residues. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schacht, K.; Marschner, B. Treated wastewater irrigation effects on soil hydraulic conductivity and aggregate stability of loamy soils in Israel. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2015, 62, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, W.; Wang, M.; Chai, H. Quantitatively estimating main soil water-soluble salt ions content based on Visible-near infrared wavelength selected using GC, SR and VIP. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Hu, C.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, W.; Sun, X.; Elyamine, A.; Zhao, H. Selenium induces changes of rhizosphere bacterial characteristics and enzyme activities affecting chromium/selenium uptake by pak choi (Brassica campestris L. ssp. Chinensis Makino) in chromium contaminated soil. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 716–727. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, J.; Chadha, B.; Kumar, B.; Saini, H. Purification and characterization of β-glucosidase from Melanocarpus sp. MTCC 3922. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 10, 260–270. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, S.M.; Hou, J.Q.; Zhao, J.S.; Clarke, N.; Kempenaar, C.; Chen, X.L. Predicting Soil Organic Matter, Available Nitrogen, Available Phosphorus and Available Potassium in a Black Soil Using a Nearby Hyperspectral Sensor System. Sensors 2024, 24, 2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramandi, A.; Seifi, A. Cupriavidus metallidurans bacteria enhance sodium uptake by plants. Rhizosphere 2023, 27, 100767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Tao, Y.; Yang, X.Z.; Liu, Y.N.; Shen, R.F.; Zhu, X.F. Gibberellic acid alleviates cadmium toxicity in rice by regulating NO accumulation and cell wall fixation capacity of cadmium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Yang, H.; Ai, S.; Sheng, M.; Tian, X.; Teng, J.; Wang, Y.; Ai, Y. Effects of different restoration methods on soil organic carbon and its fractions of cut slopes in mountainous areas of southwestern China. J. Soil Sediments 2024, 24, 1933–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Song, Z.; Bates, T.S.; Branco, S.; Tedersoo, L.; Menke, J.; Schillinge, J.; Kennedy, P. FUNGuild: An open annotation tool for parsing fungal community datasets by ecological guild. Fungal Ecol. 2016, 20, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, P. Improvement in nitrogen removal and changes in community structure in a sequencing batch reactor bioaugmented with P. stutzeri strain XL-2. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 317, 123976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partric, D.S.; Sarah, L.W.; Thomas, R.; Justine, R.H.; Martin, H.; Emily, B.H.; Ryan, A.L.; Brain, B.O.; Donovan, H.P.; Countney, J.R.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537. [Google Scholar]
- Kai, M. Diversity and Distribution of Volatile Secondary Metabolites Throughout Bacillus subtilis Isolates. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Shen, J.; Riaz, M.; Jiang, C.; Zu, C.; Jiang, C.; Liu, B. Effects of Biochar and Straw Amendment on Soil Fertility and Microbial Communities in Paddy Soils. Plants 2024, 13, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Gao, X.; Hu, K.; Guo, N.; Wei, X.; Meng, R.; Zhu, C.; et al. Dissolved Mn2+ promotes microbially-catalyzed protodolomite precipitation in brackish oxidized water. Chem. Geol. 2024, 650, 121986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chi, F.; Wei, D.; Zhou, B.; Cai, S.; Li, Y.; Kuang, E.; Sun, L.; Li, L. Impacts of Long-term Fertilization on the Molecular Structure of Humic Acid and Organic Carbon Content in Soil Aggregates in Black Soil. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananbeh, H.; Stojanović, M.; Pompeiano, A.; Voběrková, S.; Trasar-Cepeda, C. Use of soil enzyme activities to assess the recovery of soil functions in abandoned coppice forest systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ye, Y.; Liu, Y.; Da, B.; Zhao, Y. Short-term effects of nitrogen deposition on soil enzyme activities in Tibet grasslands. Anim. Husb. Feed Sci. 2018, 10, 206–212. [Google Scholar]
- Bandick, A.; Dick, R. Field management effects on soil enzyme activities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Kang, J.; Han, C.; Gu, Y.; Siddique, K.; Li, F. Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Resorption Responses of Alfalfa to Increasing Soil Water and P Availability in a Semi-Arid Environment. Agronomy 2020, 10, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wan, J.; Wu, S.; Wong, M. Effects of earthworms and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on availability of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in soil. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2012, 175, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Li, M.; Li, R.; Rasul, F.; Shahzad, S.; Wu, C.; Shao, J.; Huang, G.; Li, R.; Almari, S.; et al. Soil acidification and salinity: The importance of biochar application to agricultural soils. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1206820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, E.; Ibrahim, M. Effect of vermicompost and its mixtures with water treatment residuals on soil chemical properties and barley growth. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2012, 12, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Xiong, H.; Jiang, X. Role of cationic polarization in humus-increased soil aggregate stability. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2016, 67, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, S.; Ghadiri, H.; Chen, C.; Marschner, P. Salt-affected soils, reclamation, carbon dynamics, and biochar: A review. J. Soil Sediments 2016, 16, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wei, W.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Ding, X. Fertilization effects on microbial community composition and aggregate formation in saline-alkaline soil. Plant Soil 2021, 463, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, L.; Wang, C.; Huang, H.; Zhang, M. Synergistic improvement of carbon sequestration and crop yield by organic material addition in saline soil: A global meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 891, 164530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, K.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, M.; Li, H.; Yu, F. Vermicompost Application Enhances Halophyte Suaeda salsa Performance and Improves Coastal Saline Soil Quality. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 22, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yu, F.; Zhai, C.; Zhong, R.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Meng, Q. Long-term effects of cattle manure application on the soil aggregate stability of salt-affected soil on the Songnen Plain of North-Eastern China. J. Soil Sediments 2023, 23, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Peng, H.; Bai, L.; Ye, B.; Qiu, W.; Song, Z. Response of wheat (Triticum aestivum L. cv.) to the coexistence of micro-/nanoplastics and phthalate esters alter its growth environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Cai, Z. The families Ruminococcaceae, Lachnospiraceae, and Clostridiaceae are the dominant bacterial groups during reductive soil disinfestation with incorporated plant residues. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 135, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manici, L.M.; Caputo, F.; Fornasier, F.; Paletto, A.; Ceotto, E.; Meo, I.D. Ascomycota and Basidiomycota fungal phyla as indicators of land use efficiency for soil organic carbon accrual with woody plantations. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouyia, F.; Ventorino, V.; Pepe, O. Diversity, mechanisms and beneficial features of phosphate-solubilizing Streptomyces in sustainable agriculture: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1035358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ren, X.; Ibrahim, E.; Kong, H.; Wang, M.; Xia, J.; Wang, H.; Shou, L.; Zhou, T.; Li, B.; et al. Response of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa subsp. pekinensis) to bacterial soft rot infection by change of soil microbial community in root zone. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1401896. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, R.; Wang, X.; Paolina, G.; Etienne, Y. The nitrification inhibitor nitrapyrin has non-target effects on the soil microbial community structure, composition, and functions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 71, 104350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Xu, C.; Li, C.; Deng, L.; Dong, L.; Wang, C.; Huhe, T.; Niu, D. Effects of Adding Thermally Treated Penicillin Mycelial Dreg on the Lignocellulose Degradation, Fungal Diversity, and Fertilizer Efficiency of Compost. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 14, 1879–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, L.; Brewer, M. Detection of azole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus in the environment from air, plant debris, compost, and soil. PLoS ONE 2023, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Nikitin, D.; Sadykova, V.; Kuvarina, A.; Dakh, A.; Biryukov, M. Enzymatic and Antimicrobial Activities in Polar Strains of Microscopic Soil Fungi. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2022, 507, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Yang, C.; Tao, W.; Li, S. Polysaccharides Produced by Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria Strain Burkholderia sp. BK01 Enhance Salt Stress Tolerance to Arabidopsis thaliana. Polymers 2024, 16, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
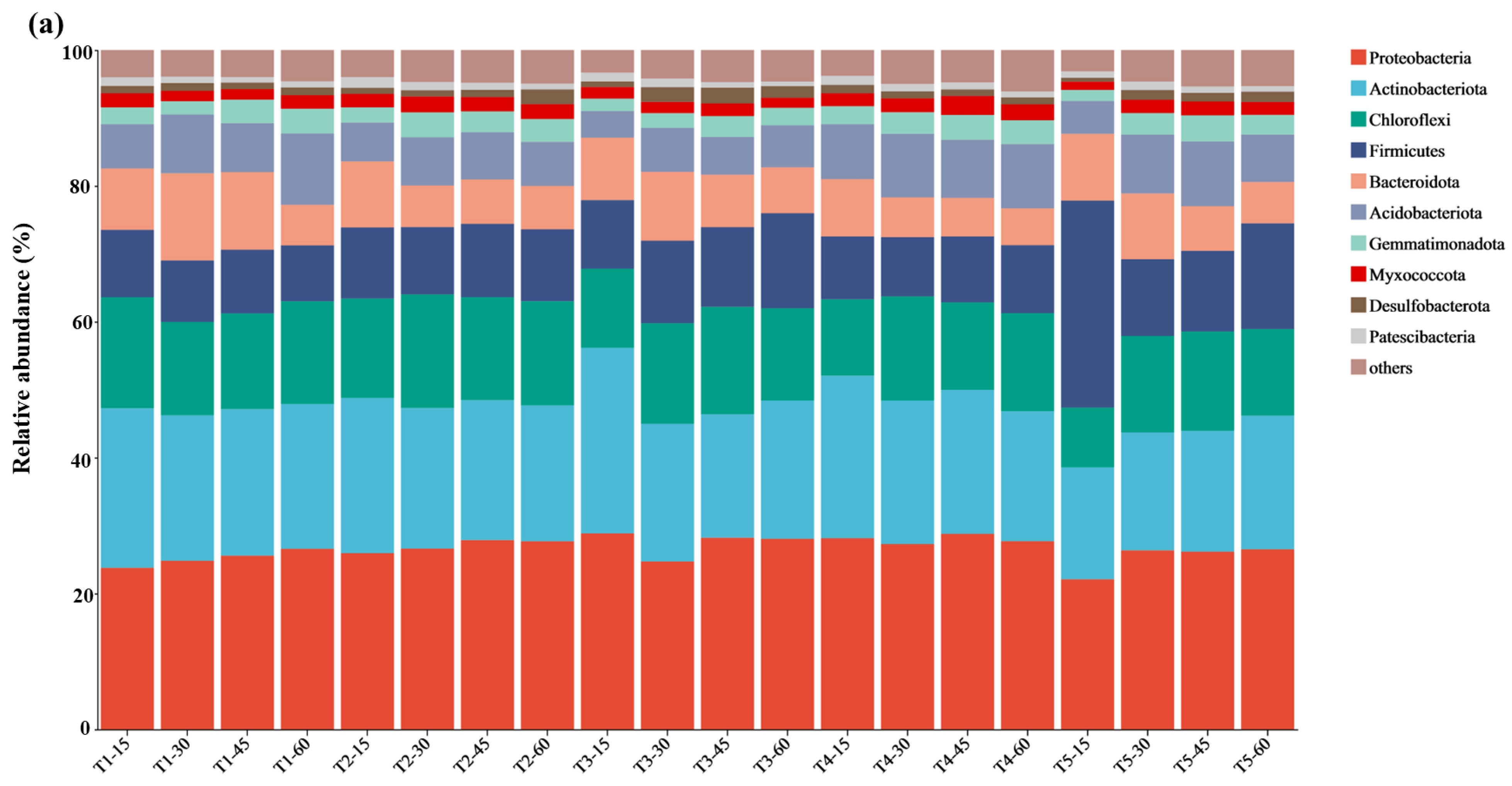
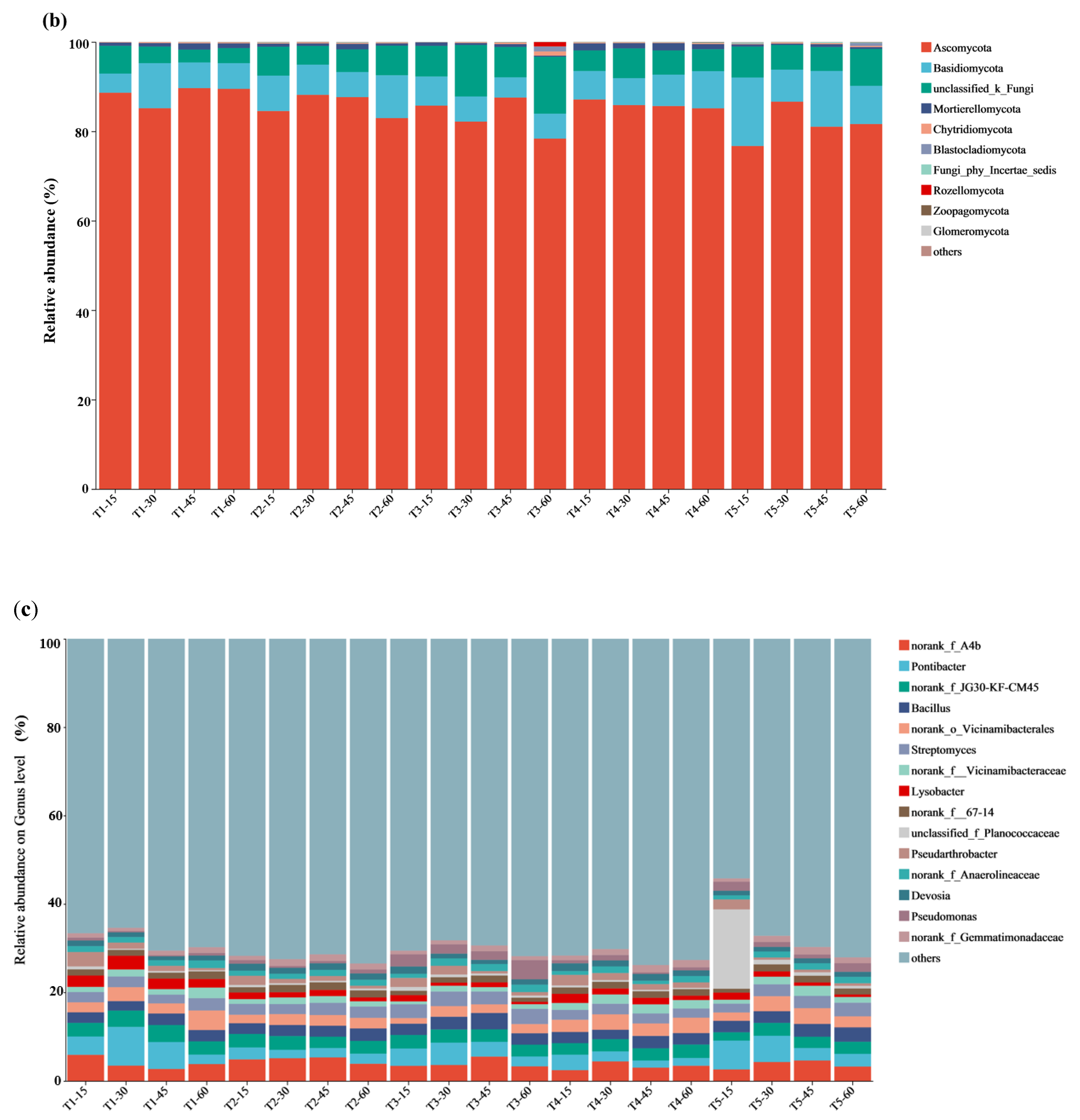
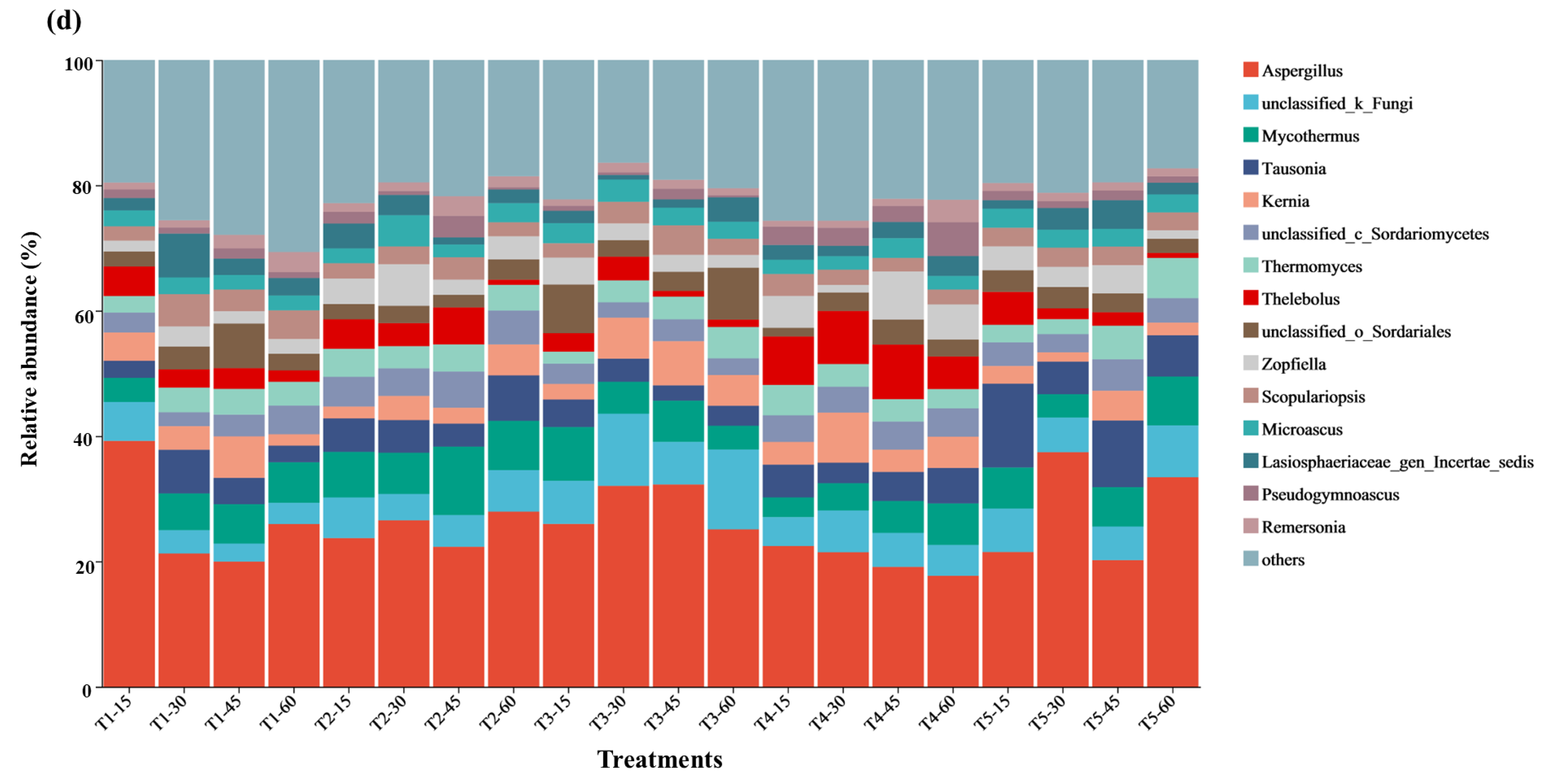
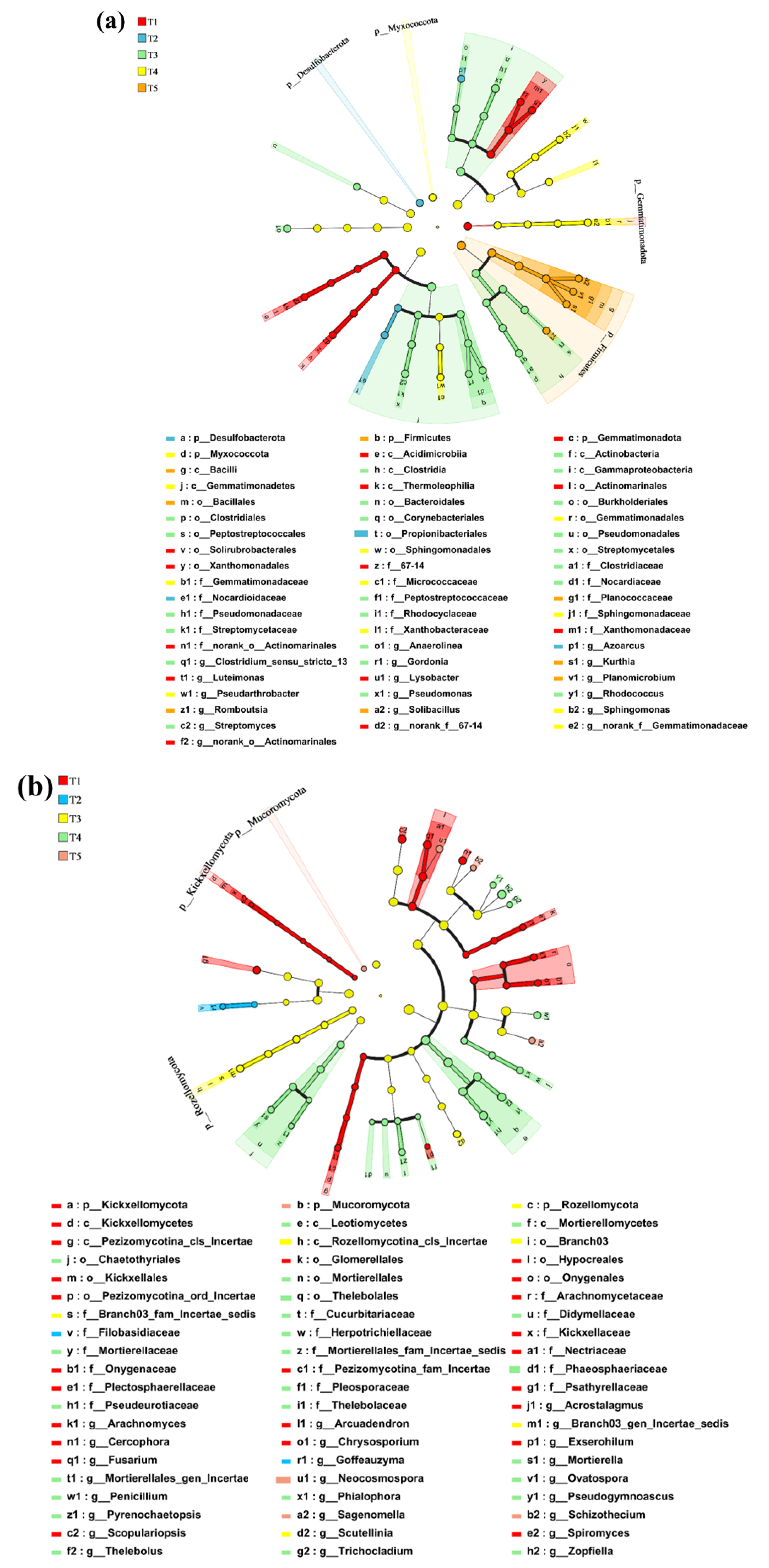
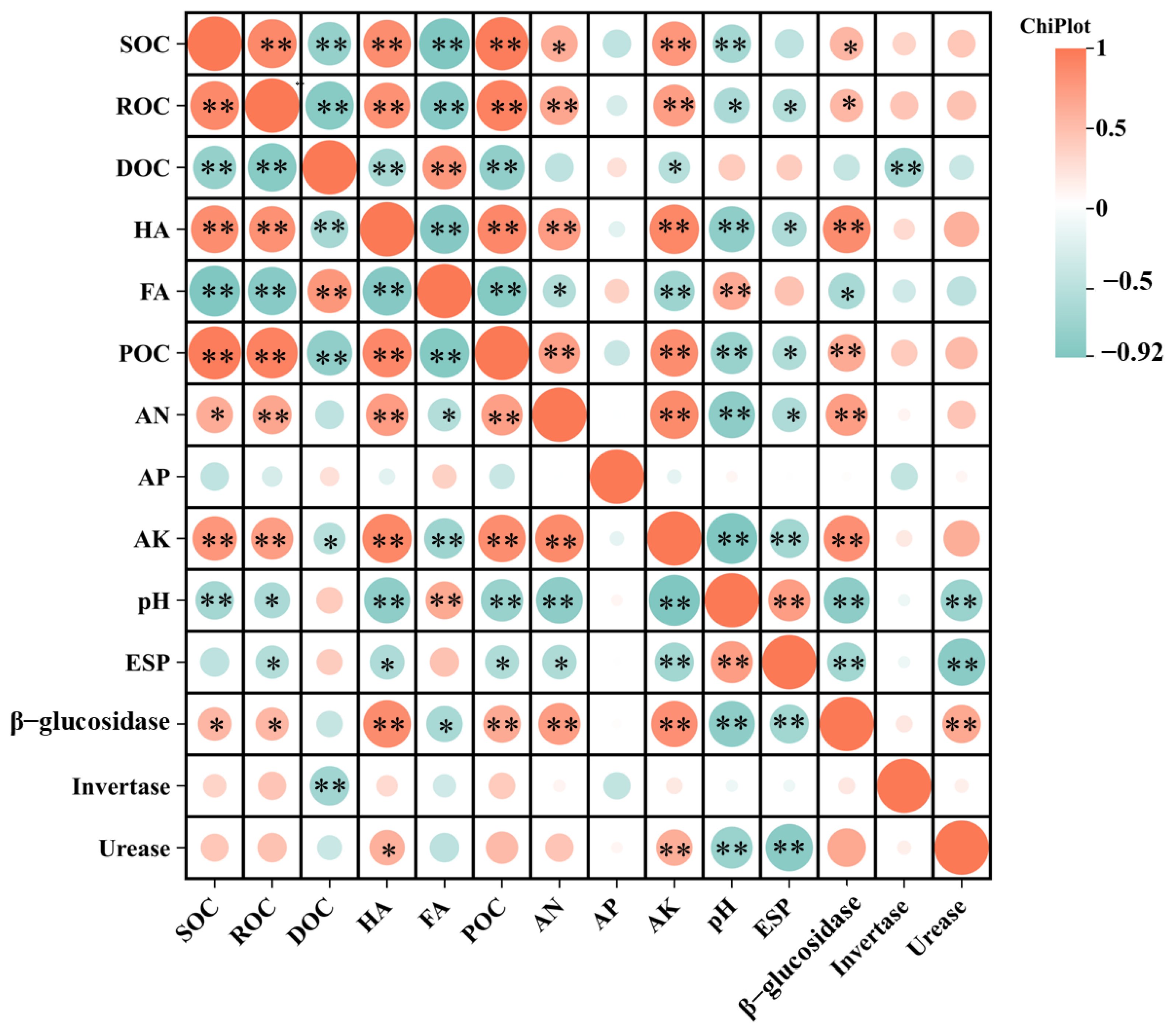
| Treatments | pH | EC (μs cm−1) | ) (mg kg−1) | ENa (mmol kg−1) | CEC (mmol kg−1) | ESP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 9.32 ± 0.04 a | 651 ± 12.1 b | 1088 ± 13.4 a | 2.43 ± 0.08 a | 18.7 ± 1.93 c | 13.1 ± 1.66 a |
| T2 | 9.27 ± 0.03 ab | 466 ± 22.0 d | 1042 ± 17.6 b | 2.18 ± 0.06 c | 19.2 ± 2.01 c | 11.6 ± 1.55 ab |
| T3 | 9.20 ± 0.03 bc | 424 ± 15.6 d | 1003 ± 17.0 bc | 2.20 ± 0.07 c | 20.6 ± 1.28 ab | 10.6 ± 0.43 ab |
| T4 | 9.17 ± 0.03 c | 824 ± 26.1 a | 980 ± 11.0 c | 2.30 ± 0.04 ab | 23.0 ± 1.39 ab | 10.0 ± 0.43 b |
| T5 | 9.08 ± 0.03 d | 539 ± 15.1 c | 968 ± 13.0 c | 2.32 ± 0.07 ab | 24.1 ± 2.15 a | 9.77 ± 0.88 b |
| Groups | Bacterial | Fungal | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ace | Chao1 | Shannon | Ace | Chao1 | Shannon | |
| T1-15 | 4783 ± 107 a | 4602 ± 111 a | 6.84 ± 0.08 a | 552 ± 54.8 a | 550 ± 42.5 a | 3.48 ± 0.46 a |
| T2-15 | 4819 ± 149 a | 4600 ± 160 a | 6.82 ± 0.05 a | 591 ± 39.0 a | 592 ± 33.3 a | 3.71 ± 0.14 a |
| T3-15 | 4413 ± 209 a | 4224 ± 186 ab | 6.47 ± 0.34 ab | 551 ± 28.3 a | 535 ± 25.3 a | 3.71 ± 0.11 a |
| T4-15 | 4818 ± 183 a | 4596 ± 197 a | 6.86 ± 0.03 a | 514 ± 17.3 a | 502 ± 20.3 a | 3.75 ± 0.10 a |
| T5-15 | 4071 ± 231 a | 3843 ± 224 b | 5.66 ± 0.22 b | 527 ± 8.38 a | 527 ± 10.3 a | 3.75 ± 0.31 a |
| T1-30 | 4584 ± 178 a | 4408 ± 229 a | 6.60 ± 0.09 b | 518 ± 64.2 a | 518 ± 68.3 a | 3.80 ± 0.16 a |
| T2-30 | 4762 ± 235 a | 4574 ± 193 a | 6.91 ± 0.10 a | 488 ± 41.1 a | 485 ± 38.3 a | 3.63 ± 0.39 a |
| T3-30 | 4614 ± 100 a | 4453 ± 73.0 a | 6.75 ± 0.07 ab | 480 ± 37.7 a | 480 ± 35.6 a | 3.38 ± 0.23 a |
| T4-30 | 5024 ± 264 a | 4835 ± 305 a | 6.90 ± 0.13 a | 537 ± 25.3 a | 545 ± 20.3 a | 3.72 ± 0.11 a |
| T5-30 | 4584 ± 64.5 a | 4403 ± 79.8 a | 6.78 ± 0.05 ab | 493 ± 19.4 a | 494 ± 21.0 a | 3.51 ± 0.40 a |
| T1-45 | 4743 ± 224 b | 4557 ± 172 b | 6.77 ± 0.09 b | 512 ± 56.6 a | 518 ± 60.8 a | 3.88 ± 0.15 a |
| T2-45 | 4891 ± 73.5 ab | 4707 ± 129 ab | 6.86 ± 0.05 ab | 487 ± 37.7 a | 497 ± 41.8 a | 3.70 ± 0.18 a |
| T3-45 | 4727 ± 75.3 b | 4549 ± 136 b | 6.81 ± 0.05 b | 464 ± 46.1 a | 461 ± 48.2 a | 3.52 ± 0.32 a |
| T4-45 | 5101 ± 266 a | 4899 ± 240 a | 6.94 ± 0.03 a | 509 ± 36.0 a | 512 ± 36.3 a | 3.83 ± 0.26 a |
| T5-45 | 4990 ± 106 ab | 4810 ± 119 ab | 6.86 ± 0.03 ab | 526 ± 47.8 a | 529 ± 46.7 a | 3.79 ± 0.21 a |
| T1-60 | 4969 ± 208 a | 4796 ± 185 a | 6.85 ± 0.04 abc | 454 ± 65.9 a | 449 ± 67.4 a | 3.58 ± 0.30 a |
| T2-60 | 5163 ± 81.3 a | 4986 ± 20.4 a | 6.96 ± 0.04 ab | 460 ± 59.1 a | 461 ± 49.9 a | 3.58 ± 0.40 a |
| T3-60 | 4803 ± 196 a | 4623 ± 185 a | 6.72 ± 0.16 c | 441 ± 13.0 a | 445 ± 18.8 a | 3.57 ± 0.23 a |
| T4-60 | 5224 ± 146 a | 5025 ± 181 a | 7.01 ± 0.04 a | 510 ± 33.0 a | 509 ± 35.8 a | 3.80 ± 0.15 a |
| T5-60 | 4828 ± 185 a | 4611 ± 139 a | 6.77 ± 0.08 bc | 518 ± 69.4 a | 516 ± 56.5 a | 3.54 ± 0.24 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y. The Improved Remediation Effect of the Combined Use of Earthworms with Bacillus subtilis-Loaded Biochar in Ameliorating Soda Saline–Alkali Soil. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061243
Liu Z, Huang Y, Li Q, Zhang L, Liu Z, Zhang Z, Chen Y. The Improved Remediation Effect of the Combined Use of Earthworms with Bacillus subtilis-Loaded Biochar in Ameliorating Soda Saline–Alkali Soil. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061243
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhichen, Yingxin Huang, Qibiao Li, Luwen Zhang, Zhenke Liu, Zunhao Zhang, and Yuxiang Chen. 2025. "The Improved Remediation Effect of the Combined Use of Earthworms with Bacillus subtilis-Loaded Biochar in Ameliorating Soda Saline–Alkali Soil" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061243
APA StyleLiu, Z., Huang, Y., Li, Q., Zhang, L., Liu, Z., Zhang, Z., & Chen, Y. (2025). The Improved Remediation Effect of the Combined Use of Earthworms with Bacillus subtilis-Loaded Biochar in Ameliorating Soda Saline–Alkali Soil. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061243





