The Meso- and Bathypelagic Archaeal and Bacterial Communities of the Southern Gulf of Mexico Are Dominated by Nitrifiers and Hydrocarbon Degraders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Sample Characterization
2.2. Total DNA Extraction, V4-16S rRNA Amplification and Sequencing
2.3. Sequencing Data Analyses
2.4. Ecological and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
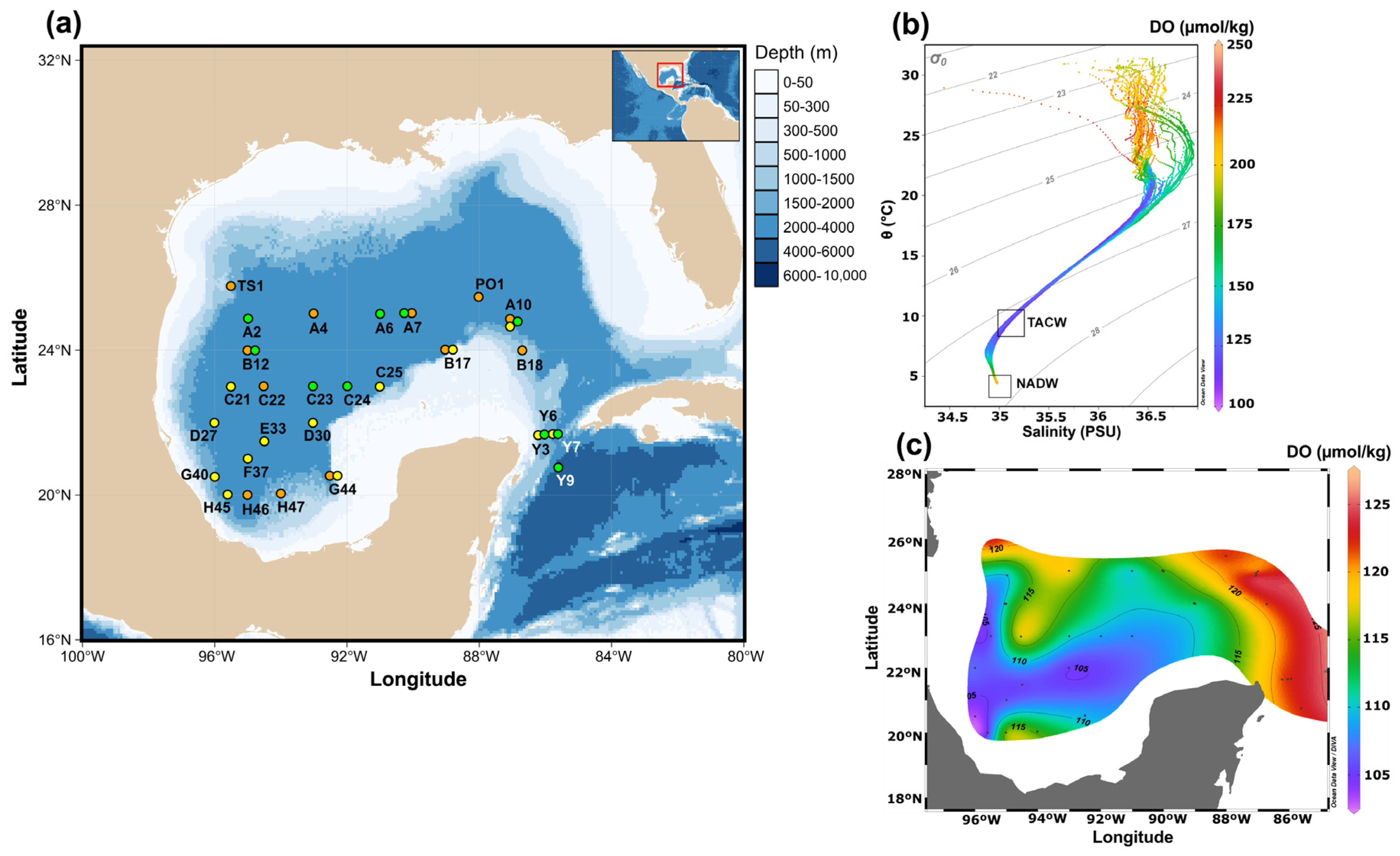
3.1. Environmental Context
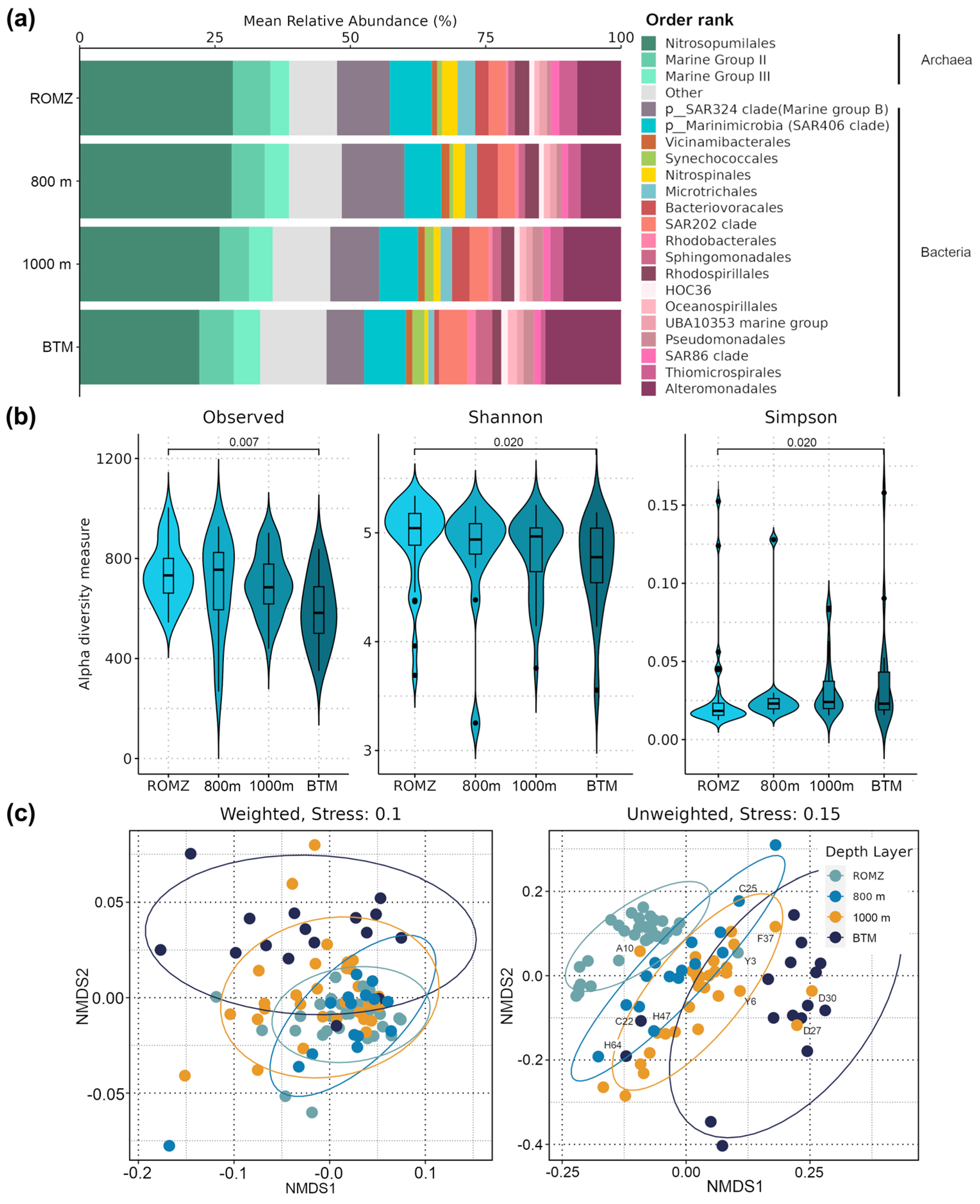
3.2. Structure of Bacterial and Archaeal Communities in the Aphotic Zone of the GoM
3.3. Effect of Environment on the Bacterial and Archaeal Community Structure
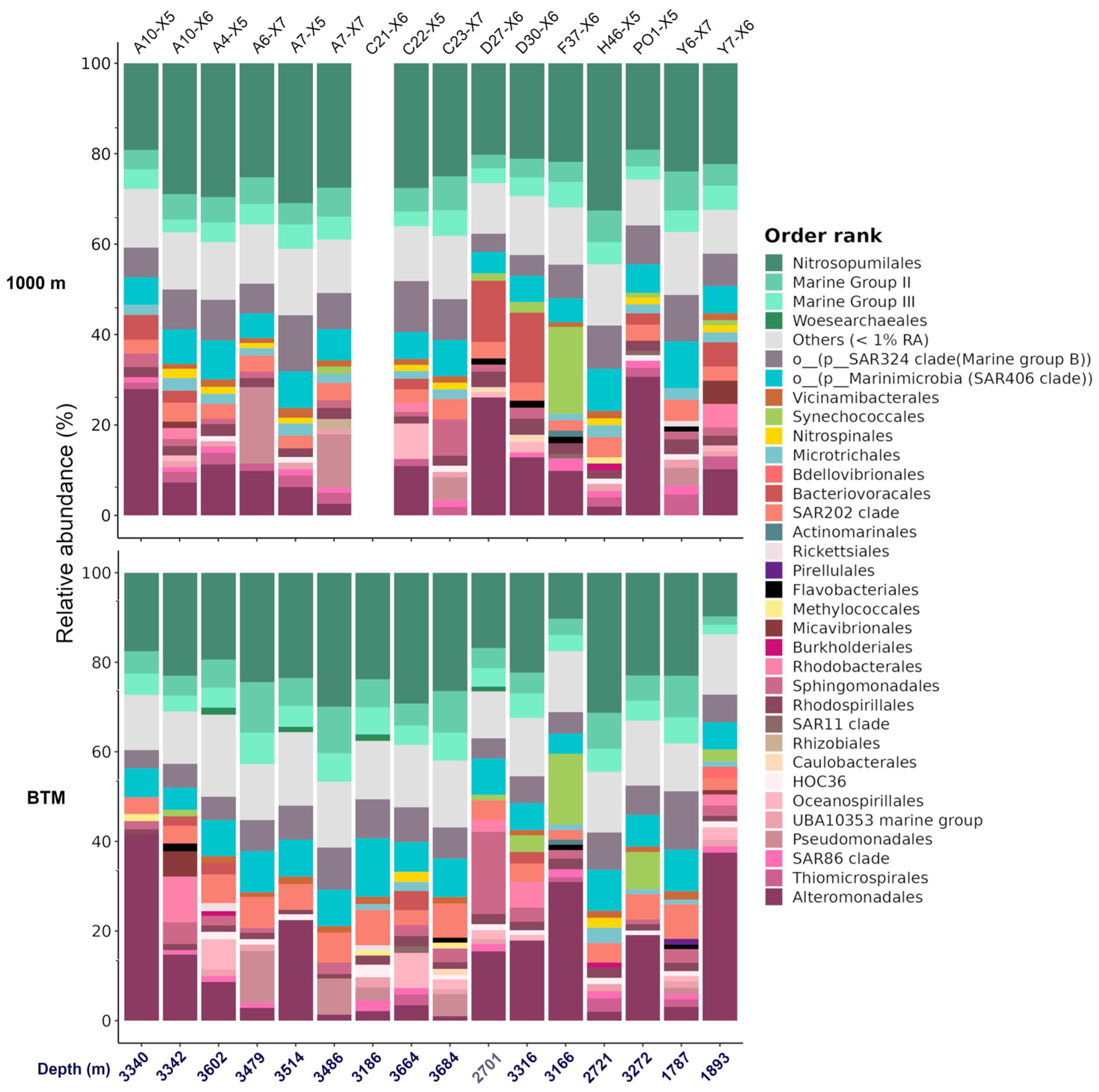
3.4. Analysis of the Prokaryotic Community in the Bathypelagic Zone
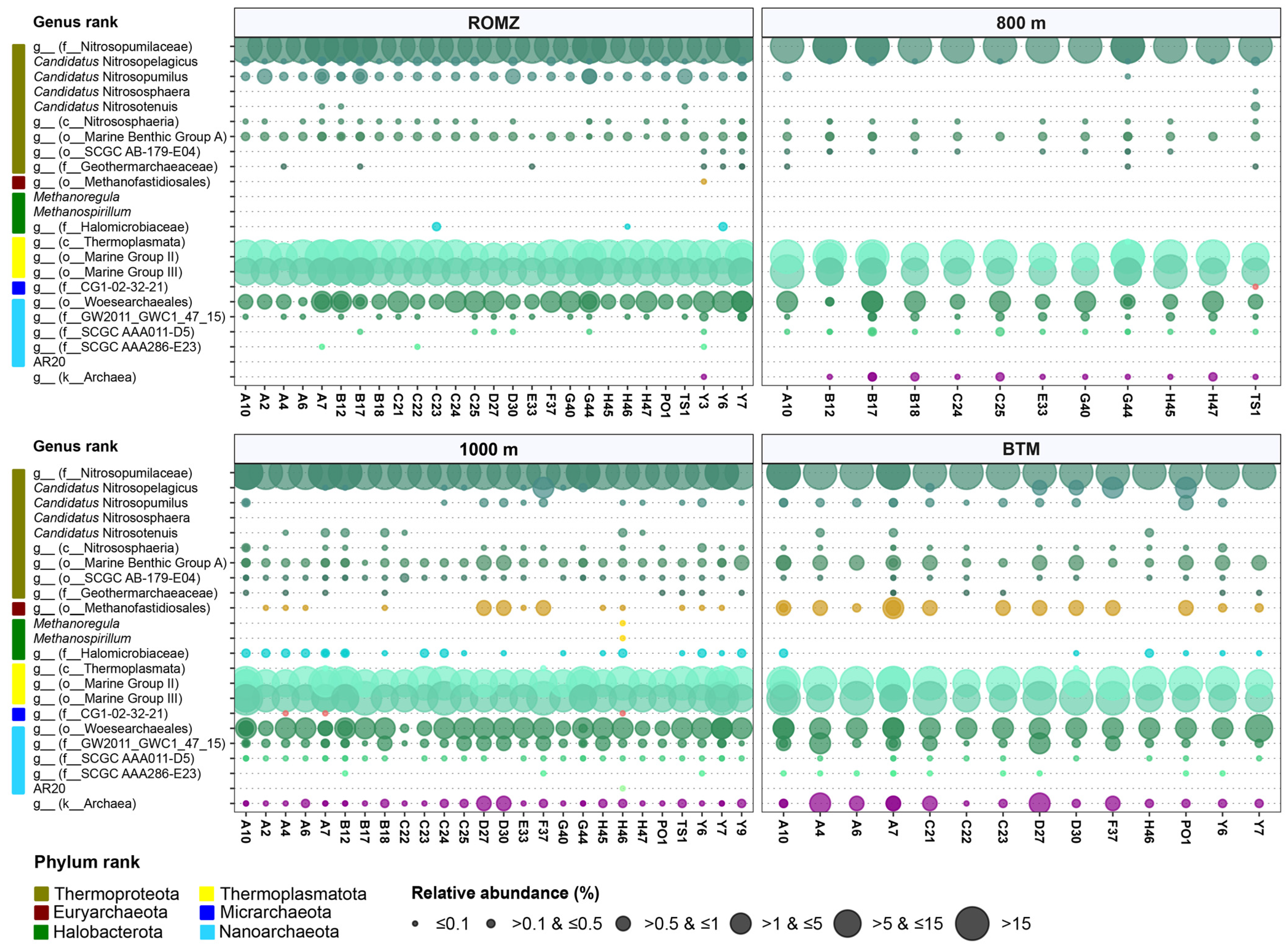
3.5. Diversity and Distribution of Archaea in the Southern GoM
3.6. Metabolic Potential of Bacterial and Archaeal Communities Across Water Column Depths of the GoM
4. Discussion
4.1. Horizontal Distribution of the Microbial Communities in the Mesopelagic Zone Is Shaped by the Oxygen Utilization
4.2. The Large Heterogeneity in the Bathypelagic Zone Is Mainly Explained by Hydrocarbon Degraders
4.3. Unknown Phylotypes of Nitrosopumilales Dominated the Archaeal Community in the Deep Waters of the GoM
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GoM | Gulf of Mexico |
| EEZ | Exclusive Economic Zone |
| AOU | Apparent Oxygen Utilization |
| ROMZ | Relative Oxygen Minimum Zone |
| NADW | North Atlantic Deep Water |
| AAIW | Antarctic Intermediate Water |
| SUW | Subtropical Underwater |
| TACW | Tropical Atlantic Central Water |
| POM | Particulate Organic Matter |
| NPP | Net Primary Production |
| PSU | Practical Salinity Units |
| ASV | Amplicon Sequence Variant |
| NMDS | Non-Metric Multidimensional Scaling |
| PERMANOVA | Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance |
| VIF | Variance Inflation Factor |
| CTD | Conductivity–Temperature–Depth |
References
- Rivas, D.; Badan, A.; Ochoa, J. The Ventilation of the Deep Gulf of Mexico. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2005, 35, 1763–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, W.J.; Biggs, D.C.; Lugo-Fernandez, A.; Oey, L.-Y.; Sturges, W. A Synopsis of the Circulation in the Gulf of Mexico and on Its Continental Margins. In Geophysical Monograph Series; Sturges, W., Lugo-Fernandez, A., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 11–29. ISBN 978-1-118-66616-6. [Google Scholar]
- Portela, E.; Tenreiro, M.; Pallàs-Sanz, E.; Meunier, T.; Ruiz-Angulo, A.; Sosa-Gutiérrez, R.; Cusí, S. Hydrography of the Central and Western Gulf of Mexico. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2018, 123, 5134–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Gasti, J.A.; Camacho-Ibar, V.F.; Herguera, J.C. Water Mass Structure and Mixing Fractions in the Deepwater Region of the Gulf of Mexico. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2022, 127, e2021JC017705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.; Steinberg, D.K.; Anderson, T.R.; Arístegui, J.; Carlson, C.A.; Frost, J.R.; Ghiglione, J.-F.; Hernández-León, S.; Jackson, G.A.; Koppelmann, R.; et al. Mesopelagic Zone Ecology and Biogeochemistry—A Synthesis. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2010, 57, 1504–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavan, E.L.; Laurenceau-Cornec, E.C.; Bressac, M.; Boyd, P.W. Exploring the Ecology of the Mesopelagic Biological Pump. Prog. Oceanogr. 2019, 176, 102125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukel, M.R.; Kelly, T.B.; Landry, M.R.; Selph, K.E.; Swalethorp, R. Sinking Carbon, Nitrogen, and Pigment Flux within and beneath the Euphotic Zone in the Oligotrophic, Open-Ocean Gulf of Mexico. J. Plankton Res. 2022, 44, 711–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, I.R.; Garcia-Pineda, O.; Beet, A.; Daneshgar Asl, S.; Feng, L.; Graettinger, G.; French-McCay, D.; Holmes, J.; Hu, C.; Huffer, F.; et al. Natural and Unnatural Oil Slicks in the Gulf of Mexico. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 8364–8380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe-Martínez, A.; Espinoza-Tenorio, A.; Cruz-Pech, J.B.; Cupido-Santamaría, D.G.; Trujillo-Córdova, J.A.; García-Nava, H.; Flores-Vidal, X.; Gudiño-Elizondo, N.; Herguera, J.C.; Appendini, C.M.; et al. An Affordable Operational Oil Spill Monitoring System in Action: A Diachronic Multiplatform Analysis of Recent Incidents in the Southern Gulf of Mexico. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, I.R.; Guinasso, N.L.; Reilly, J.F.; Brooks, J.M.; Callender, W.R.; Gabrielle, S.G. Gulf of Mexico Hydrocarbon Seep Communities: VI. Patterns in Community Structure and Habitat. Geo-Mar. Lett. 1990, 10, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, C.; Roberts, H.; Cordes, E.; Bernard, B. Cold Seeps and Associated Communities of the Gulf of Mexico. Oceanography 2007, 20, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orcutt, B.N.; Joye, S.B.; Kleindienst, S.; Knittel, K.; Ramette, A.; Reitz, A.; Samarkin, V.; Treude, T.; Boetius, A. Impact of Natural Oil and Higher Hydrocarbons on Microbial Diversity, Distribution, and Activity in Gulf of Mexico Cold-Seep Sediments. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2010, 57, 2008–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agogué, H.; Lamy, D.; Neal, P.R.; Sogin, M.L.; Herndl, G.J. Water Mass-Specificity of Bacterial Communities in the North Atlantic Revealed by Massively Parallel Sequencing. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, H.; Xia, X.; Suzuki, K.; Liu, H. Vertical Profiles of Bacteria in the Tropical and Subarctic Oceans Revealed by Pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, G.; Cornejo-Castillo, F.M.; Benítez-Barrios, V.; Fraile-Nuez, E.; Álvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Duarte, C.M.; Gasol, J.M.; Acinas, S.G. Global Diversity and Biogeography of Deep-Sea Pelagic Prokaryotes. ISME J. 2016, 10, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, C.; Balbín, R.; Reglero, P.; Martín, M.; Santiago, R.; Sintes, E. Dynamic Prokaryotic Communities in the Dark Western Mediterranean Sea. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Sun, D.; Fang, C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, C. Biodiversity and Biogeography of Abundant and Rare Microbial Assemblages in the Western Subtropical Pacific Ocean. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 839562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Letona, M.; Arístegui, J.; Hernández-Hernández, N.; Álvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Álvarez, M.; Delgadillo, E.; Pérez-Lorenzo, M.; Teira, E.; Hernández-León, S.; Sebastián, M. Deep Ocean Prokaryotes and Fluorescent Dissolved Organic Matter Reflect the History of the Water Masses across the Atlantic Ocean. Prog. Ocean. 2022, 205, 102819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastián, M.; Giner, C.R.; Balagué, V.; Gómez-Letona, M.; Massana, R.; Logares, R.; Duarte, C.M.; Gasol, J.M. The Active Free-Living Bathypelagic Microbiome Is Largely Dominated by Rare Surface Taxa. ISME Commun. 2024, 4, ycae015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumas, C.M.J.; Le Moigne, F.A.C.; Garel, M.; Bhairy, N.; Guasco, S.; Riou, V.; Armougom, F.; Grossart, H.-P.; Tamburini, C. Mesopelagic Microbial Carbon Production Correlates with Diversity across Different Marine Particle Fractions. ISME J. 2021, 15, 1695–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltar, F.; Arístegui, J.; Gasol, J.M.; Sintes, E.; Herndl, G.J. Evidence of Prokaryotic Metabolism on Suspended Particulate Organic Matter in the Dark Waters of the Subtropical North Atlantic. Limnol. Ocean. 2009, 54, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.M.; Smith, C.B.; Tolar, B.; Hollibaugh, J.T. Analysis of Composition and Structure of Coastal to Mesopelagic Bacterioplankton Communities in the Northern Gulf of Mexico. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easson, C.G.; Lopez, J.V. Depth-Dependent Environmental Drivers of Microbial Plankton Community Structure in the Northern Gulf of Mexico. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, O.U.; Hazen, T.C.; Borglin, S.; Chain, P.S.G.; Dubinsky, E.A.; Fortney, J.L.; Han, J.; Holman, H.-Y.N.; Hultman, J.; Lamendella, R.; et al. Metagenome, Metatranscriptome and Single-Cell Sequencing Reveal Microbial Response to Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1715–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubinsky, E.A.; Conrad, M.E.; Chakraborty, R.; Bill, M.; Borglin, S.E.; Hollibaugh, J.T.; Mason, O.U.; Piceno, Y.M.; Reid, F.C.; Stringfellow, W.T.; et al. Succession of Hydrocarbon-Degrading Bacteria in the Aftermath of the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill in the Gulf of Mexico. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10860–10867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleindienst, S.; Grim, S.; Sogin, M.; Bracco, A.; Crespo-Medina, M.; Joye, S.B. Diverse, Rare Microbial Taxa Responded to the Deepwater Horizon Deep-Sea Hydrocarbon Plume. ISME J. 2016, 10, 400–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raggi, L.; García-Guevara, F.; Godoy-Lozano, E.E.; Martínez-Santana, A.; Escobar-Zepeda, A.; Gutierrez-Rios, R.M.; Loza, A.; Merino, E.; Sanchez-Flores, A.; Licea-Navarro, A.; et al. Metagenomic Profiling and Microbial Metabolic Potential of Perdido Fold Belt (NW) and Campeche Knolls (SE) in the Gulf of Mexico. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, A.; Licea, A.F.; Lizárraga-Partida, M.L. Metagenomic Analysis among Water Masses and Sediments from the Southern Gulf of Mexico. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1020136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offre, P.; Spang, A.; Schleper, C. Archaea in Biogeochemical Cycles. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 437–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, G.; Laso-Pérez, R.; Orphan, V.J.; Boetius, A. Anaerobic Degradation of Alkanes by Marine Archaea. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 76, 553–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolar, B.B.; King, G.M.; Hollibaugh, J.T. An Analysis of Thaumarchaeota Populations from the Northern Gulf of Mexico. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, L.E.; Thrash, J.C.; deRada, S.; Rabalais, N.N.; Mason, O.U. Archaeal Enrichment in the Hypoxic Zone in the Northern G Ulf of M Exico. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3847–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ye, G.; Wang, F.; Bell, R.; Noakes, J.; Short, T.; Zhang, C.L. Community Structure of Archaea in the Water Column above Gas Hydrates in the Gulf of Mexico. Geomicrobiol. J. 2009, 26, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakowski, C.V.; Magen, C.; Bosman, S.; Rogers, K.L.; Gillies, L.E.; Chanton, J.P.; Mason, O.U. Methane and Microbial Dynamics in the Gulf of Mexico Water Column. Front. Mar. Sci. 2015, 2, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Agami, S.S.; Cerqueda-García, D.; Gamboa-Muñoz, A.M.; Aguirre-Macedo, M.L.; García-Maldonado, J.Q. Structure and Composition of Microbial Communities in the Water Column from Southern Gulf of Mexico and Detection of Putative Hydrocarbon-degrading Microorganisms. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2024, 16, e13264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linacre, L.; Durazo, R.; Camacho-Ibar, V.F.; Selph, K.E.; Lara-Lara, J.R.; Mirabal-Gómez, U.; Bazán-Guzmán, C.; Lago-Lestón, A.; Fernández-Martín, E.M.; Sidón-Ceseña, K. Picoplankton Carbon Biomass Assessments and Distribution of Prochlorococcus Ecotypes Linked to Loop Current Eddies during Summer in the Southern Gulf of Mexico. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2019, 124, 8342–8359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, H.E.; Gordon, L.I. Oxygen Solubility in Seawater: Better Fitting Equations. Limnol. Ocean. 1992, 37, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IOC; SCOR; IAPSO. The International Thermodynamic Equation of Seawater—2010: Calculation and Use of Thermodynamic Properties. 2010. Available online: https://repository.oceanbestpractices.org/handle/11329/286 (accessed on 1 December 2018).
- Wright, J.J.; Lee, S.; Zaikova, E.; Walsh, D.A.; Hallam, S.J. DNA Extraction from 0.22 microM Sterivex Filters and Cesium Chloride Density Gradient Centrifugation. J. Vis. Exp. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a Dual-Index Sequencing Strategy and Curation Pipeline for Analyzing Amplicon Sequence Data on the MiSeq Illumina Sequencing Platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global Patterns of 16S rRNA Diversity at a Depth of Millions of Sequences per Sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108 (Suppl. 1), 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2019. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodenhofer, U.; Bonatesta, E.; Horejš-Kainrath, C.; Hochreiter, S. Msa: An R Package for Multiple Sequence Alignment. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3997–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schliep, K.P. Phangorn: Phylogenetic Analysis in R. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 592–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradis, E.; Schliep, K. Ape 5.0: An Environment for Modern Phylogenetics and Evolutionary Analyses in R. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for Prediction of Metagenome Functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahti, L.; Shetty, L. Microbiome R Package 2017. [CrossRef]
- Mangiafico, S. Rcompanion: Functions to Support Extension Education Program Evaluation. 2016. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rcompanion (accessed on 12 July 2024).
- Lozupone, C.; Lladser, M.E.; Knights, D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R. UniFrac: An Effective Distance Metric for Microbial Community Comparison. ISME J. 2011, 5, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.L.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Szoecs, E.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package 2024. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- Arbizu, P.M. pairwiseAdonis: Pairwise Multilevel Comparison Using Adonis 2020. Available online: https://github.com/pmartinezarbizu/pairwiseAdonis (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Legendre, P.; Oksanen, J.; Ter Braak, C.J.F. Testing the Significance of Canonical Axes in Redundancy Analysis. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2011, 2, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lex, A.; Gehlenborg, N.; Strobelt, H.; Vuillemot, R.; Pfister, H. UpSet: Visualization of Intersecting Sets. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2014, 20, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.D.; Macklaim, J.M.; Linn, T.G.; Reid, G.; Gloor, G.B. ANOVA-like Differential Expression (ALDEx) Analysis for Mixed Population RNA-Seq. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.D.; Reid, J.N.; Macklaim, J.M.; McMurrough, T.A.; Edgell, D.R.; Gloor, G.B. Unifying the Analysis of High-Throughput Sequencing Datasets: Characterizing RNA-Seq, 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and Selective Growth Experiments by Compositional Data Analysis. Microbiome 2014, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloor, G.B.; Macklaim, J.M.; Fernandes, A.D. Displaying Variation in Large Datasets: Plotting a Visual Summary of Effect Sizes. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2016, 25, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beman, J.M.; Carolan, M.T. Deoxygenation Alters Bacterial Diversity and Community Composition in the Ocean’s Largest Oxygen Minimum Zone. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villegas-Mendoza, J.; Gómez-Ocampo, E.; Velásquez-Aristizábal, J.; Rodríguez-Escobar, D. Microbial Metabolic Activity in Two Basins of the Gulf of Mexico Influenced by Mesoscale Structures. J. Mar. Syst. 2022, 234, 103781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanilla, J.G.; Herguera, J.C.; Sheinbaum, J. Oxygenation of the Gulf of Mexico Thermocline Linked to the Detachment of Loop Current Eddies. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1479837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, S.E.; Fawcett, S.E.; Ward, B.B. Depth Distribution of Ammonia Oxidation Rates and Ammonia-oxidizer Community Composition in the Sargasso Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58, 1491–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yingling, N.; Kelly, T.B.; Shropshire, T.A.; Landry, M.R.; Selph, K.E.; Knapp, A.N.; Kranz, S.A.; Stukel, M.R. Taxon-Specific Phytoplankton Growth, Nutrient Utilization and Light Limitation in the Oligotrophic Gulf of Mexico. J. Plankton Res. 2022, 44, 656–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.C.Y.; Raven, J.A.; Aldunate, M.; Silva, S.; Gaitán-Espitia, J.D.; Vargas, C.A.; Ulloa, O.; Von Dassow, P. Do Phytoplankton Require Oxygen to Survive? A Hypothesis and Model Synthesis from Oxygen Minimum Zones. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2023, 68, 1417–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, C.; Reglero, P.; Balbín, R.; Martín, M.; Santiago, R.; Sintes, E. Dynamics of Actively Dividing Prokaryotes in the Western Mediterranean Sea. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabirova, J.S.; Ferrer, M.; Regenhardt, D.; Timmis, K.N.; Golyshin, P.N. Proteomic Insights into Metabolic Adaptations in Alcanivorax Borkumensis Induced by Alkane Utilization. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 3763–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coscolín, C.; Bargiela, R.; Martínez-Martínez, M.; Alonso, S.; Bollinger, A.; Thies, S.; Chernikova, T.N.; Hai, T.; Golyshina, O.V.; Jaeger, K.-E.; et al. Hydrocarbon-Degrading Microbes as Sources of New Biocatalysts. In Taxonomy, Genomics and Ecophysiology of Hydrocarbon-Degrading Microbes; McGenity, T.J., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 353–373. ISBN 978-3-030-14795-2. [Google Scholar]
- Valentine, D.L.; Kessler, J.D.; Redmond, M.C.; Mendes, S.D.; Heintz, M.B.; Farwell, C.; Hu, L.; Kinnaman, F.S.; Yvon-Lewis, S.; Du, M.; et al. Propane Respiration Jump-Starts Microbial Response to a Deep Oil Spill. Science 2010, 330, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerqueda-García, D.; García-Maldonado, J.Q.; Aguirre-Macedo, L.; García-Cruz, U. A Succession of Marine Bacterial Communities in Batch Reactor Experiments during the Degradation of Five Different Petroleum Types. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Zeng, L.; Dong, C.; Shao, Z. The Oxidation of Hydrocarbons by Diverse Heterotrophic and Mixotrophic Bacteria That Inhabit Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Ecosystems. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1994–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-González, C.; Mestre, M.; Estrada, M.; Sebastián, M.; Salazar, G.; Agustí, S.; Moreno-Ostos, E.; Reche, I.; Álvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Morán, X.A.G.; et al. Major Imprint of Surface Plankton on Deep Ocean Prokaryotic Structure and Activity. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 1820–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Long, L.; Huang, S. Quantification of Marine Picocyanobacteria on Water Column Particles and in Sediments Using Real-Time PCR Reveals Their Role in Carbon Export. mSphere 2022, 7, e0049922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrin, R.; Isaji, M.; Obara, Y.; Agostini, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Hiroe, Y.; Ichikawa, T.; Hidaka, K. Distribution of Synechococcus in the Dark Ocean. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 64, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, W.D.; Richardson, M.J.; Mishonov, A.V.; Bean, D.A.; Herguera, J.C. Nepheloid Layers in the Deep Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Geol. 2022, 454, 106950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Beltrán, M.; Vargas-Gastélum, L.; Magdaleno-Moncayo, D.; Riquelme, M.; Herguera-García, J.C.; Prieto-Davó, A.; Lago-Lestón, A. The Metabolic Core of the Prokaryotic Community from Deep-Sea Sediments of the Southern Gulf of Mexico Shows Different Functional Signatures between the Continental Slope and Abyssal Plain. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunagawa, S.; Coelho, L.P.; Chaffron, S.; Kultima, J.R.; Labadie, K.; Salazar, G.; Djahanschiri, B.; Zeller, G.; Mende, D.R.; Alberti, A.; et al. Structure and Function of the Global Ocean Microbiome. Science 2015, 348, 1261359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mende, D.R.; Bryant, J.A.; Aylward, F.O.; Eppley, J.M.; Nielsen, T.; Karl, D.M.; DeLong, E.F. Environmental Drivers of a Microbial Genomic Transition Zone in the Ocean’s Interior. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, N.; Achterberg, E.P.; Carlson, C.A.; Gledhill, M.; Liu, S.; Matheson-Barker, J.R.; Nelson, N.B.; Parsons, R.J. The Role of Heterotrophic Bacteria and Archaea in the Transformation of Lignin in the Open Ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Könneke, M.; Bernhard, A.E.; de la Torre, J.R.; Walker, C.B.; Waterbury, J.B.; Stahl, D.A. Isolation of an Autotrophic Ammonia-Oxidizing Marine Archaeon. Nature 2005, 437, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semedo, M.; Lopes, E.; Baptista, M.S.; Oller-Ruiz, A.; Gilabert, J.; Tomasino, M.P.; Magalhães, C. Depth Profile of Nitrifying Archaeal and Bacterial Communities in the Remote Oligotrophic Waters of the North Pacific. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 624071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steen, A.D.; Crits-Christoph, A.; Carini, P.; DeAngelis, K.M.; Fierer, N.; Lloyd, K.G.; Thrash, J.C. High Proportions of Bacteria and Archaea across Most Biomes Remain Uncultured. ISME J. 2019, 13, 3126–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Cuadrado, A.-B.; Rodriguez-Valera, F.; Moreira, D.; Alba, J.C.; Ivars-Martínez, E.; Henn, M.R.; Talla, E.; López-García, P. Hindsight in the Relative Abundance, Metabolic Potential and Genome Dynamics of Uncultivated Marine Archaea from Comparative Metagenomic Analyses of Bathypelagic Plankton of Different Oceanic Regions. ISME J. 2008, 2, 865–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, H.; Deng, Q.; Cao, L. Actinobacterial Flora in Feces of Healthy Cottontail Rabbits (Sylvilagus auduboni). Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2015, 7, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haro-Moreno, J.M.; Rodriguez-Valera, F.; López-García, P.; Moreira, D.; Martin-Cuadrado, A.-B. New Insights into Marine Group III Euryarchaeota, from Dark to Light. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1102–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, B.J. Metabolic Diversity within the Globally Abundant Marine Group II Euryarchaea Offers Insight into Ecological Patterns. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, F.; Nunoura, T.; Nakagawa, S.; Teske, A.; Lever, M.; Lauer, A.; Suzuki, M.; Takai, K.; Delwiche, M.; Colwell, F.S.; et al. Biogeographical Distribution and Diversity of Microbes in Methane Hydrate-Bearing Deep Marine Sediments on the Pacific Ocean Margin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2815–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teske, A.; Sørensen, K.B. Uncultured Archaea in Deep Marine Subsurface Sediments: Have We Caught Them All? ISME J. 2008, 2, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.; Hedlund, B.P.; Xie, W.; Liu, J.; Phelps, T.J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, P. Impact of Terrestrial Input on Deep-Sea Benthic Archaeal Community Structure in South China Sea Sediments. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 572017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecoeuvre, A.; Ménez, B.; Cannat, M.; Chavagnac, V.; Gérard, E. Microbial Ecology of the Newly Discovered Serpentinite-Hosted Old City Hydrothermal Field (Southwest Indian Ridge). ISME J. 2021, 15, 818–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Gu, L.; Bai, S.; Wang, J.; Su, L.; Wei, B.; Zhang, L.; Fang, J. Characterization of Particle-Associated and Free-Living Bacterial and Archaeal Communities along the Water Columns of the South China Sea. Biogeosciences 2021, 18, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungbluth, S.P.; Amend, J.P.; Rappé, M.S. Metagenome Sequencing and 98 Microbial Genomes from Juan de Fuca Ridge Flank Subsurface Fluids. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170037. [Google Scholar]
- Le Moine Bauer, S.; Lu, G.-S.; Goulaouic, S.; Puzenat, V.; Schouw, A.; Barreyre, T.; Pawlowsky-Glahn, V.; Egozcue, J.J.; Martelat, J.-E.; Escartin, J.; et al. Structure and Metabolic Potential of the Prokaryotic Communities from the Hydrothermal System of Paleochori Bay, Milos, Greece. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1060168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurber, A.R.; Seabrook, S.; Welsh, R.M. Riddles in the Cold: Antarctic Endemism and Microbial Succession Impact Methane Cycling in the Southern Ocean. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2020, 287, 20201134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Teske, A.P.; MacGregor, B.J.; McKay, L.J.; Mendlovitz, H.; Albert, D.; Ma, Z.; Li, J. Thermal Selection of Microbial Communities and Preservation of Microbial Function in Guaymas Basin Hydrothermal Sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e0001823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, T.; Yoshioka, H.; Kaneko, M.; Amo, M.; Fujii, T.; Takahashi, H.A.; Yoshida, S.; Sakata, S. Cultivation and Biogeochemical Analyses Reveal Insights into Methanogenesis in Deep Subseafloor Sediment at a Biogenic Gas Hydrate Site. ISME J 2022, 16, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, H.J.; Hodges, C.; Wilson, K.; Macdonald, I.R.; Sobecky, P.A. Microbial Diversity in Sediments Associated with Surface-Breaching Gas Hydrate Mounds in the Gulf of Mexico. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2003, 46, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGonigle, J.M.; Bernau, J.A.; Bowen, B.B.; Brazelton, W.J. Robust Archaeal and Bacterial Communities Inhabit Shallow Subsurface Sediments of the Bonneville Salt Flats. mSphere 2019, 4, e00378-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Seawater Depth | Conservative Temperature | Absolute Salinity | Dissolved Oxygen | AOU 1 | NO3− + NO2− | PO43− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| –––(°C)––– | ––(g kg−1)–– | –––––––––––––––––––(µmol kg−1)––––––––––––––––––– | ||||
| ROMZ (n = 32) | 10.1 2 ± 0.7 3 a 4 | 35.41 ± 0.10 a | 107 ± 5 d | 166.8 ± 4 a | 26.5 ± 1.7 b | 1.6 ± 0.1 b |
| 800 m (n = 15) | 6.1 ± 0.5 b | 35.09 ± 0.01 b | 139 ± 10 c | 163.8 ± 6 a | 28.5 ± 1.5 a | 1.8 ± 0.1 a |
| 1000 m (n = 32) | 5.1 ± 0.4 c | 35.10 ± 0.01 b | 166 ± 12 b | 145 ± 9 b | 25.6 ± 3.5 b | 1.7 ± 0.1 a |
| BTM (n = 16) | 4.1 ± 0.1 d | 35.15 ± 0.00 c | 203 ± 4 a | 116.8 ± 4 c | 22.4 ± 0.3 c | 1.4 ± 0.1 c |
| F-value | 84.68 | 82.41 | 84.46 | 76.05 | 52.40 | 51.34 |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Weighted UniFrac | Unweighted UniFrac | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ––––––––––––––––––––––––––– | ––––––––––––––––––––––––––– | ||||||
| PERMANOVA 1 | Betadisper 2 | PERMANOVA | Betadisper | ||||
| ––––––––––––– | ––––––––––– | ––––––––––––– | ––––––––––– | ||||
| Factor | Df 3 | R2 | p-Value | p-Value | R2 | p-Value | p-Value |
| Depth 4 | 3 | 13.5 | <0.001 | 0.057 | 17.9 | <0.001 | 0.052 |
| Campaign 5 | 2 | 12.7 | <0.001 | 0.041 | 9.2 | <0.001 | 0.012 |
| Region 6 | 3 | 9.6 | 0.003 | 0.063 | 5.5 | <0.001 | 0.112 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osorio-Pando, L.S.; Hernández-Guzmán, M.; Sidón-Ceseña, K.; Ortega-Saad, Y.; Camacho-Ibar, V.F.; Chong-Robles, J.; Lago-Lestón, A. The Meso- and Bathypelagic Archaeal and Bacterial Communities of the Southern Gulf of Mexico Are Dominated by Nitrifiers and Hydrocarbon Degraders. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051106
Osorio-Pando LS, Hernández-Guzmán M, Sidón-Ceseña K, Ortega-Saad Y, Camacho-Ibar VF, Chong-Robles J, Lago-Lestón A. The Meso- and Bathypelagic Archaeal and Bacterial Communities of the Southern Gulf of Mexico Are Dominated by Nitrifiers and Hydrocarbon Degraders. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(5):1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051106
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsorio-Pando, Lizt Selene, Mario Hernández-Guzmán, Karla Sidón-Ceseña, Yamne Ortega-Saad, Victor F. Camacho-Ibar, Jennyfers Chong-Robles, and Asunción Lago-Lestón. 2025. "The Meso- and Bathypelagic Archaeal and Bacterial Communities of the Southern Gulf of Mexico Are Dominated by Nitrifiers and Hydrocarbon Degraders" Microorganisms 13, no. 5: 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051106
APA StyleOsorio-Pando, L. S., Hernández-Guzmán, M., Sidón-Ceseña, K., Ortega-Saad, Y., Camacho-Ibar, V. F., Chong-Robles, J., & Lago-Lestón, A. (2025). The Meso- and Bathypelagic Archaeal and Bacterial Communities of the Southern Gulf of Mexico Are Dominated by Nitrifiers and Hydrocarbon Degraders. Microorganisms, 13(5), 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051106






