Isolation, Characterization, and Comparative Analysis of Two Subtypes of Goose Astrovirus in Guangdong Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection, Nucleic Acid Extraction, and GAstV Identification
2.2. Clinical and Pathological Features, and Hematoxylin and Eosin (H and E) Staining
2.3. Isolation of GAstVs
2.4. Goose Embryos and Goslings
2.5. Genome Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.6. Recombination Analysis
2.7. Infection Experiment
2.8. Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
2.9. Comparison of GAstV Capsid Structures
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
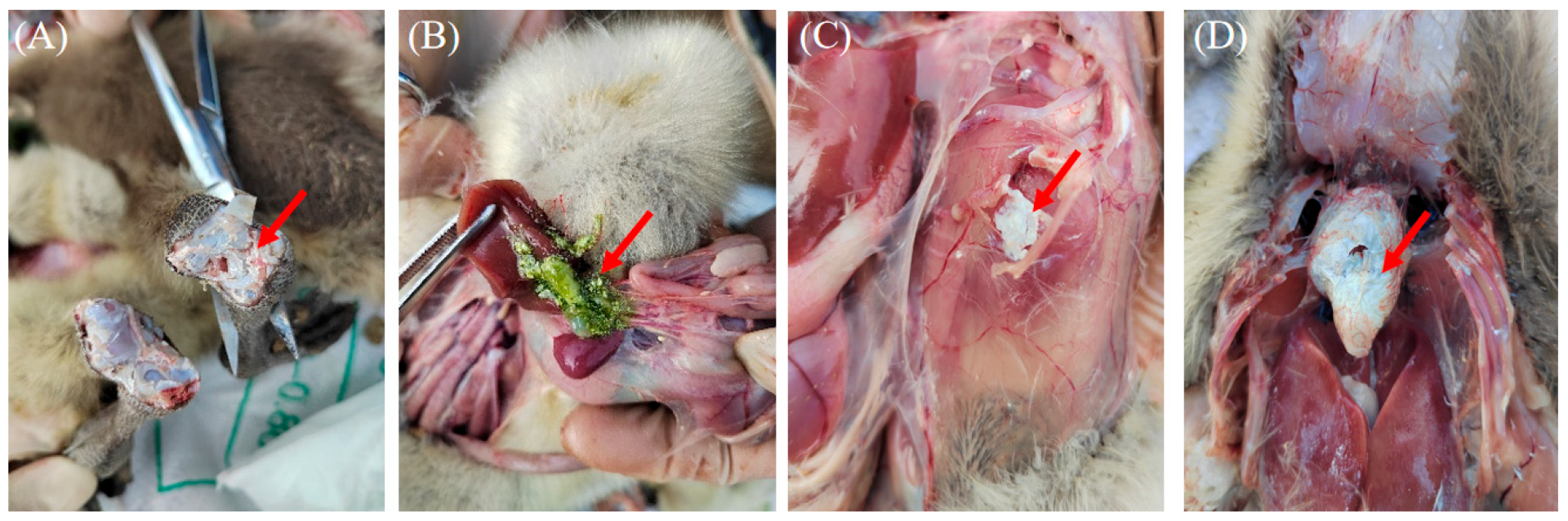
3.1. Clinical Features, Sample Identification and Histopathological Analysis
3.2. Virus Isolation, Whole Genome Sequencing, and Recombination Analysis
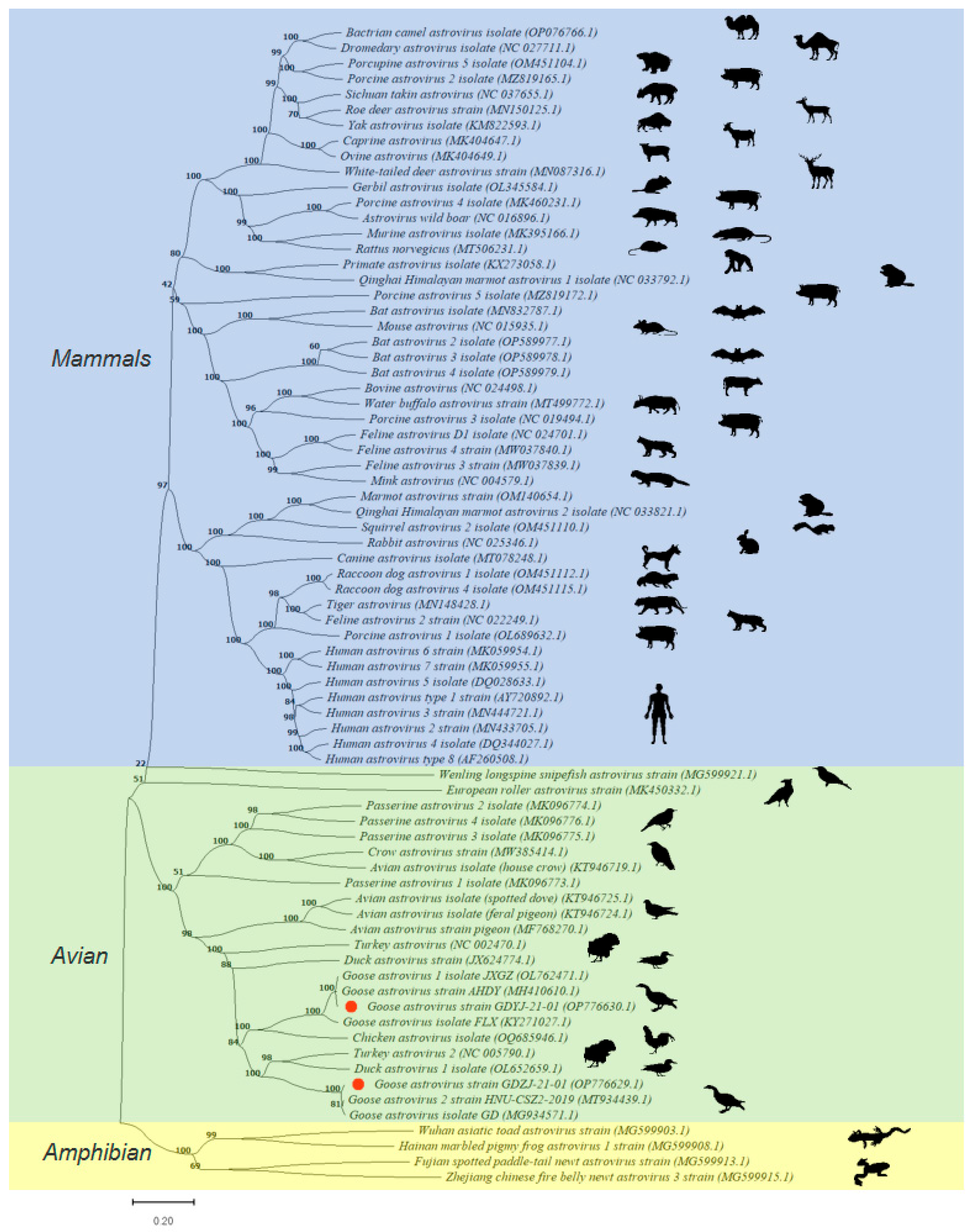
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of GAstVs
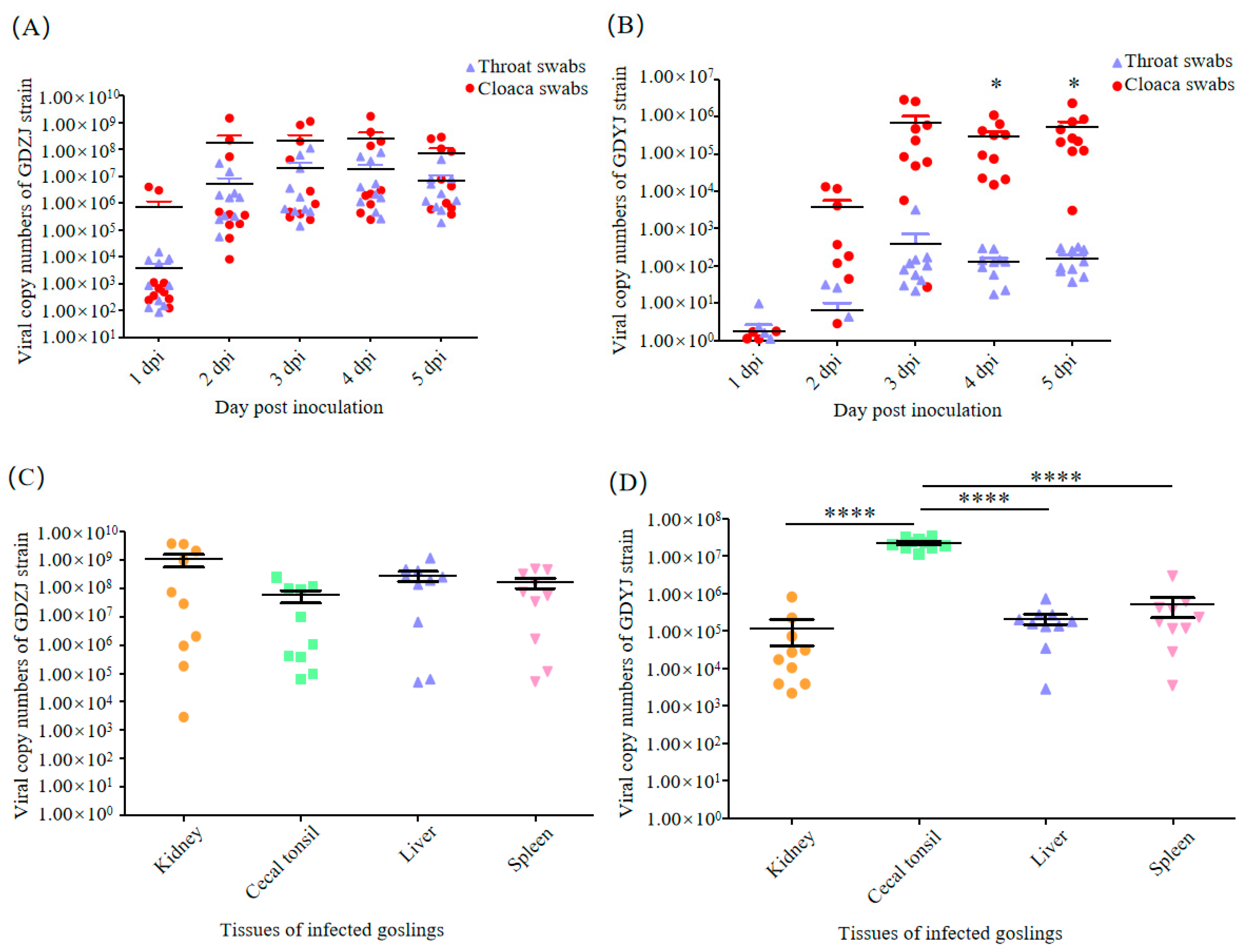
3.4. Difference in the Tissue Tropism of GAstVs
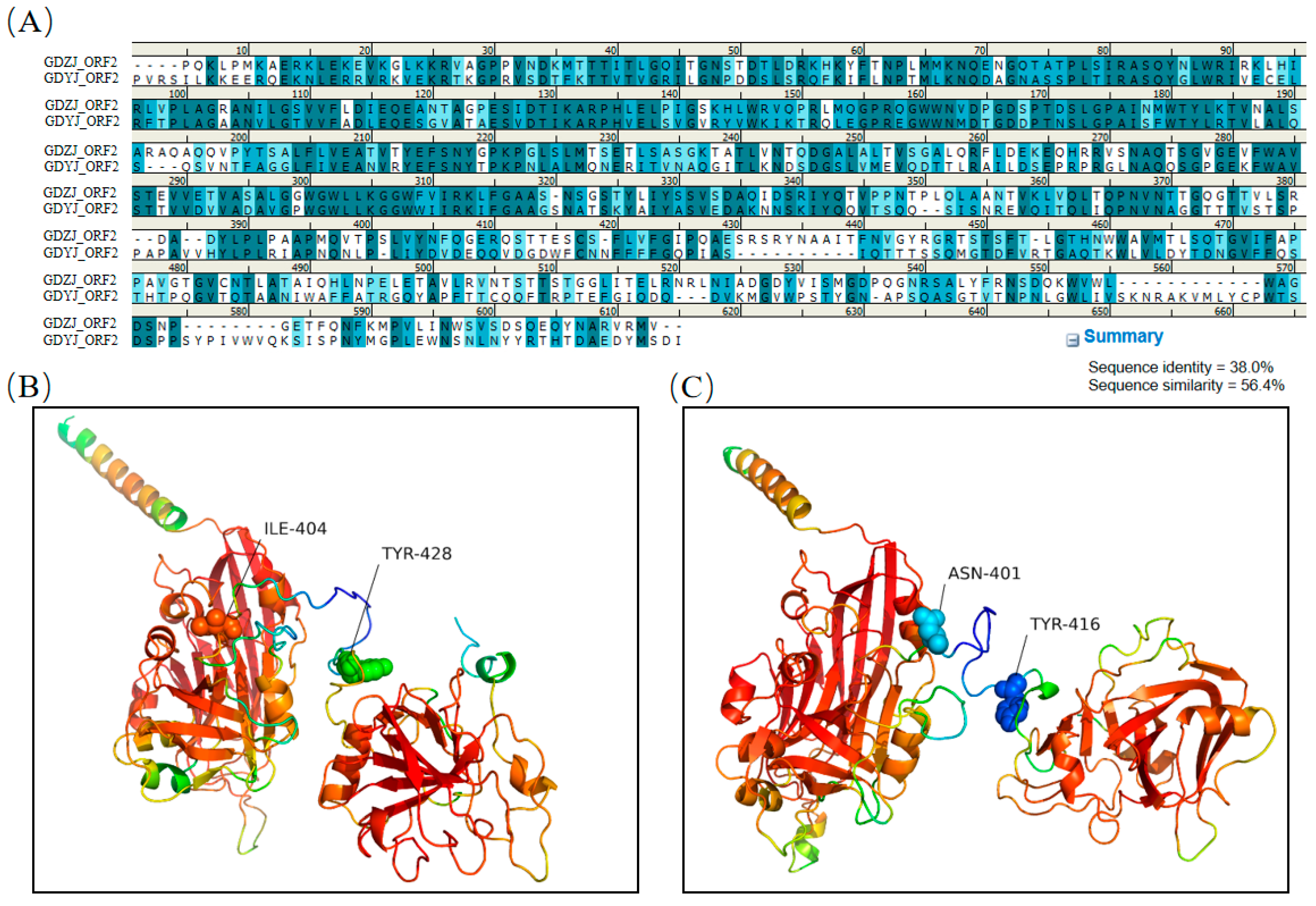
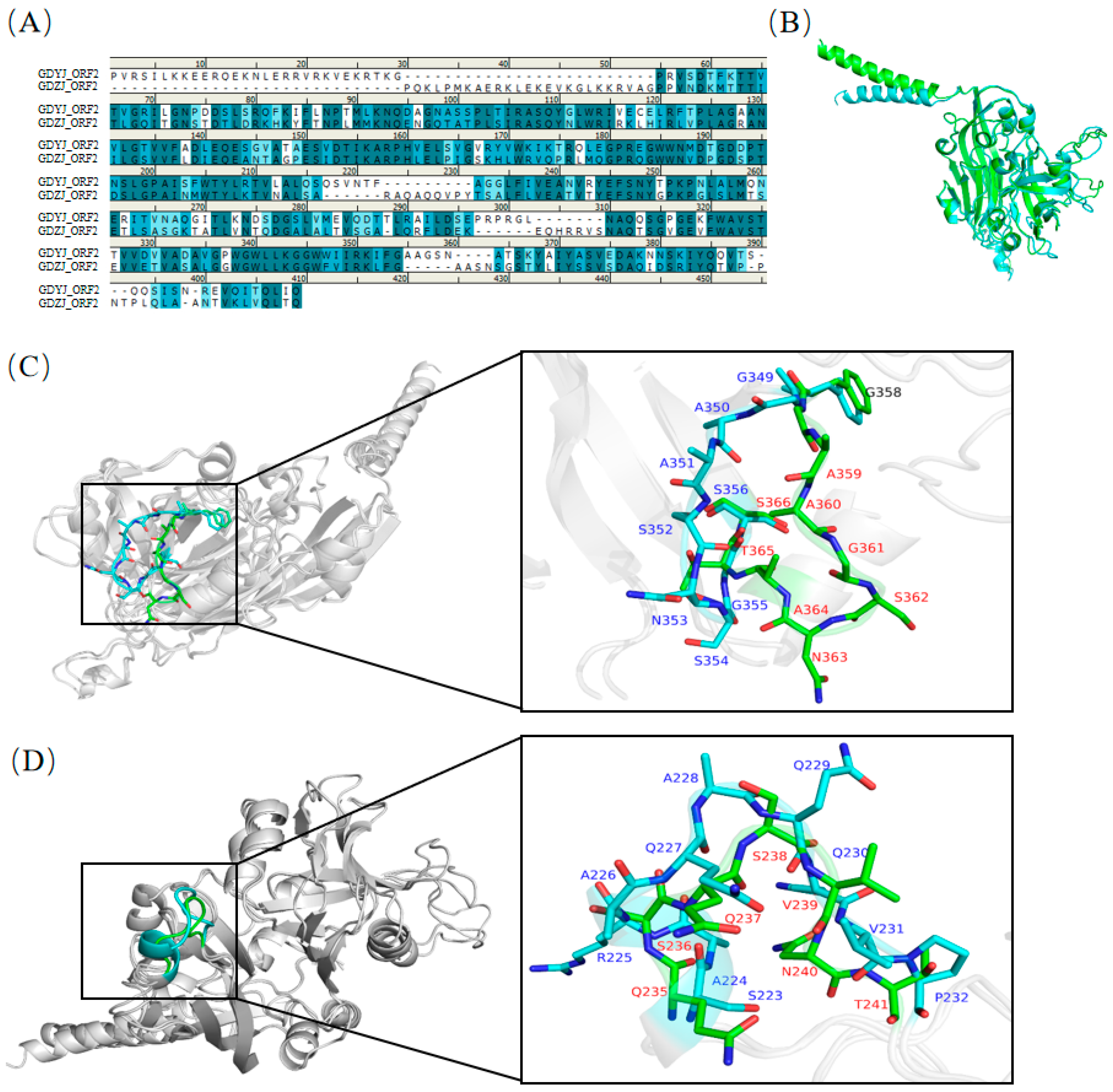
3.5. Structural Comparison of GAstV Capsids
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.; Tian, J.; Tang, Y.; Diao, Y. Isolation and genomic characterization of gosling gout caused by a novel goose astrovirus. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Fu, G.; Sun, M.; Zhang, L.; Meng, L.; Cui, G.; Huang, Y.; Hu, X.; et al. Isolation and characterization of an astrovirus causing fatal visceral gout in domestic goslings. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ren, D.; Li, T.; Zhou, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Lu, H.; Gao, W.; Wang, Y.; Zou, X.; et al. An emerging novel goose astrovirus associated with gosling gout disease, China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gao, L.; Zhu, P.; Chen, S.; Chen, Z.; Yan, Z.; Lin, W.; Yin, L.; Javed, M.T.; Tang, Z.; et al. Isolation, identification, and pathogenicity analysis of newly emerging gosling astrovirus in South China. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1112245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Hua, J.; Ye, W.; Chen, L.; Ni, Z.; Yun, T.; Ma, J.; Yao, H.; Bao, E.; et al. Isolation and Pathogenicity of a Novel Goose Astrovirus from Overfed Adult Landaise Geese in China. Viruses 2022, 14, 2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; He, D.; Wu, B.; Diao, Y.; Tang, Y. Isolation, Identification, and Pathogenicity of a Goose Astrovirus Genotype 1 Strain in Goslings in China. Viruses 2024, 16, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sun, M.; Liao, M. A Review of Emerging Goose Astrovirus Causing Gout. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 1635373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Tian, J.; Yang, J.; Jiang, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Yi, T.; Diao, Y. Novel Goose Astrovirus Associated Gout in Gosling, China. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 220, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Tang, Y.; Diao, Y. Novel goose-origin astrovirus infection in geese: The effect of age at infection. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 4323–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, B.; Yan, M.; Diao, Y.; Tang, Y. First report of a novel goose astrovirus outbreak in Cherry Valley ducklings in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Jiang, X.; Tian, M.; Niu, X.; Wei, F.; Wu, B.; Gao, L.; Tang, Y.; Diao, Y. Pathogenicity of goose astrovirus genotype 2 in chickens. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Yang, J.; He, D.; Diao, Y.; Tang, Y. Evidence of vertical transmission of novel astrovirus virus in goose. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 244, 108657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Jiang, B.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, Z.; He, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; et al. Molecular epidemiology and virulence of goose astroviruses genotype-2 with different internal gene sequences. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1301861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Xu, X.; Yu, Z.; Sui, C.; Zuo, K.; Zhi, G.; Ji, J.; Yao, L.; Kan, Y.; Bi, Y.; et al. Characterization and genomic analysis of emerging astroviruses causing fatal gout in goslings. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Chen, M.; Sun, M.; Dong, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhai, Q.; Liao, M.; Li, L. Isolation, identification, and epidemiological characteristics of goose astrovirus causing acute gout in Guangdong province, China. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Deng, T.; Song, Y.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Peng, Z.; Guo, Y.; Yang, L.; Qiao, H.; Xia, Y.; et al. Identification and genomic characterization of emerging goose astrovirus in central China, 2020. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, D.M.; Qiu, S. Proteolytic processing of the astrovirus capsid. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 1810–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, E.; Fernández-Luna, T.; López, S.; Méndez-Toss, M.; Arias, C.F. Proteolytic processing of a serotype 8 human astrovirus ORF2 polyprotein. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 7996–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, H.; Molleston, J.M.; Hall, P.D.; Bui, D.; Wang, L.; Bhatt, K.D.; Foster, L.; Antia, A.; Ding, S.; Lee, S.; et al. The neonatal Fc receptor is a cellular receptor for human astrovirus. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 3321–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Li, T.; Zhang, X.; Yao, X.; Gao, W.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, J.; Shao, H.; Wan, Z.; Qin, A.; et al. OASL Triggered by Novel Goose Astrovirus via ORF2 Restricts Its Replication. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01767-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricemeyer, L.; Aguilar-Hernández, N.; López, T.; Espinosa, R.; Lanning, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Cuellar, C.; López, S.; Arias, C.F.; DuBois, R.M. Structures of Two Human Astrovirus Capsid/Neutralizing Antibody Complexes Reveal Distinct Epitopes and Inhibition of Virus Attachment to Cells. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0141521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, C.F.; DuBois, R.M. The Astrovirus Capsid: A Review. Viruses 2017, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ykema, M.; Tao, Y.J. Structural Insights into the Human Astrovirus Capsid. Viruses 2021, 13, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, L.; Dong, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhai, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Jin, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, G.; et al. Global analysis of gene expression profiles and gout symptoms in goslings infected with goose astrovirus. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 279, 109677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Jin, S.; Liang, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, D.; Cao, N.; Sun, M.; Tian, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, D.; et al. Apoptosis, inflammatory and innate immune responses induced by infection with a novel goose astrovirus in goose embryonic kidney cells. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1452158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Xie, J.; Wu, Z.; Liu, L.; Wu, S.; Feng, Q.; Dong, H.; Zhu, S. Pathogenicity of a goose astrovirus 2 strain causing fatal gout in goslings. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 184, 106341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Ji, L.; Dong, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Lei, B.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, W.; et al. Comparative transcriptomic analysis of goose astrovirus genotype 1 and 2 in goose embryonic fibroblasts. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.P.; Zhang, S.; Xie, J.; Gu, L.L.; Wu, S.; Wu, Z.; Liu, L.; Feng, Q.; Dong, H.Y.; Zhu, S.Y. Isolation and characterization of a goose astrovirus 1 strain causing fatal gout in goslings, China. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Xiong, H.; Lv, X.; Wei, C.; Liu, M.; Yin, D.; He, C.; Qi, K.; et al. Coinfection of parvovirus and astrovirus in gout-affected goslings. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 2830–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Meng, K.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, L.; Ai, W.; Wang, Y. Establishment and Application of Rapid Diagnosis for Reverse Transcription-Quantitative PCR of Newly Emerging Goose-Origin Nephrotic Astrovirus in China. mSphere 2018, 3, e00380-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Chen, C.; Cheng, L.; Fu, G.; Shi, S.; Liu, R.; Chen, H.; Fu, Q.; Huang, Y. Specific detection of the novel goose astrovirus using a TaqMan real-time RT-PCR technology. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 137, 103766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.K.; Xu, L.; Liang, Y.Q.; Yin, D.D.; Tu, J.; Song, X.J.; Shao, Y.; Liu, H.M.; Qi, K.Z. Simultaneous differentiation and diagnosis of goose parvovirus and astrovirus in clinical samples with duplex SYBR Green I real-time PCR. Mol. Cell Probes 2020, 52, 101561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Ding, R.; Cao, R.; Sun, W.; Sun, M.; Dong, Y.; Rehana, B.; Bao, E.; Lv, Y. Development of a duplex TaqMan real-time RT-PCR assay for simultaneous detection of goose astrovirus genotypes 1 and 2. J. Virol. Methods 2022, 306, 114542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, L.; Dong, J.; Kuang, R.; Liao, M.; Sun, M. First Identification and Genetic Characterization of a Novel Duck Astrovirus in Ducklings in China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 873062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senior, A.W.; Evans, R.; Jumper, J.; Kirkpatrick, J.; Sifre, L.; Green, T.; Qin, C.; Žídek, A.; Nelson, A.W.R.; Bridgland, A.; et al. Improved protein structure prediction using potentials from deep learning. Nature 2020, 577, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeliger, D.; de Groot, B.L. Ligand docking and binding site analysis with PyMOL and Autodock/Vina. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2010, 24, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Xie, J.; Feng, Q.; Dong, H.; Cheng, Y.; Jia, W.; et al. Isolation, identification, and pathogenicity of a goose astrovirus 1 strain from goslings in Jiangsu province, China. Microb. Pathog. 2025, 200, 107324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Cui, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, H.; Xiong, H.; Qi, K.; Liu, H. Characterisation of natural co-infection with Goose astrovirus genotypes I and II in gout affected goslings. Avian Pathol. 2024, 53, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cui, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J. Epidemiological Investigation of Goose Astrovirus in Hebei Province, China, 2019–2021. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yu, Z.; Xu, X.; Ji, J.; Yao, L.; Kan, Y.; Bi, Y.; Xie, Q. First report of a novel goose astrovirus outbreak in Muscovy ducklings in China. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Hu, W.Q.; Liu, T.N.; Zhang, H.H.; Opriessnig, T.; Xiao, C.T. Isolation and evolutionary analyses of gout-associated goose astrovirus causing disease in experimentally infected chickens. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhu, M.; Li, X.; Xu, H.; Lv, Y. Primary goose kidney tubular epithelial cells for goose astrovirus genotype 2 infection: Establishment and RNA sequencing analysis. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Zhu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Lu, L.; Li, J.; Zhong, S.; Ma, C.; Ouyang, K.; Chen, Y.; et al. Replication of Porcine Astrovirus Type 1-Infected PK-15 Cells In Vitro Affected by RIG-I and MDA5 Signaling Pathways. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0070123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bub, T.; Hargest, V.; Tan, S.; Smith, M.; Vazquez-Pagan, A.; Flerlage, T.; Brigleb, P.; Meliopoulos, V.; Lindenbach, B.; Ramanathan, H.N.; et al. Astrovirus replication is dependent on induction of double-membrane vesicles through a PI3K-dependent, LC3-independent pathway. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0102523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximova, O.A.; Weller, M.L.; Krogmann, T.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Ricklefs, S.; Virtaneva, K.; Martens, C.; Wollenberg, K.; Minai, M.; Moore, I.N.; et al. Pathogenesis and outcome of VA1 astrovirus infection in the human brain are defined by disruption of neural functions and imbalanced host immune responses. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Su, Q.; Fu, D.; Huang, H.; Lu, Z.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Tan, M.; Huang, J.; Kang, Z.; et al. Alteration of gut microbiome in goslings infected with goose astrovirus. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Xu, R.; Lv, Y.; Bao, E. Goose astrovirus infection affects uric acid production and excretion in goslings. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 1967–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Tian, J.; Yang, J.; Tang, Y.; Diao, Y. Pathogenicity of novel goose-origin astrovirus causing gout in goslings. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Miao, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, W.; Yang, X.; Yu, S.; Guo, D.; Sun, D. Isolation, identification, and pathogenicity of a goose astrovirus causing fatal gout in goslings. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 274, 109570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Cunningham, K.; López, T.; Khatib, F.; Arias, C.F.; DuBois, R.M. Structure of the divergent human astrovirus MLB capsid spike. Structure 2022, 30, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Delgado-Cunningham, K.; López, T.; Green, K.; Arias, C.F.; DuBois, R.M. Structure and antigenicity of the divergent human astrovirus VA1 capsid spike. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1012028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, D.; Li, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, J.; Shao, H.; Wan, Z.; Qin, A.; et al. Identification of three novel B cell epitopes in ORF2 protein of the emerging goose astrovirus and their application. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Primer Name | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Product (bp) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAstV-I ORF2-F | AGTGGAGTGTTATGCCTACCAGGAGA | 2314 bp | Amplification of ORF2 gene by RT-PCR |
| GAstV-I ORF2-R | TTTTCCTCCGTAATCAGGAGGTTTTTTGGG | ||
| GAstV-II ORF2-F | GCGAAAATGCACCCAATAGTGTTAGAGAG | 2436 bp | Amplification of ORF2 gene by RT-PCR |
| GAstV-II ORF2-R | CCCCTGACCGGGTTTTTGTTTAAAGAAT | ||
| GAstV-I-F | TCGTTGGGACCTGCAATATC | 94 bp | Detection of viral RNA copies by qRT-PCR |
| GAstV-I-R | TAAAGAGACCACCAGCGAAAG | ||
| GAstV-II-F | GGGTGATCCGCAAGGAAATA | 98 bp | Detection of viral RNA copies by qRT-PCR |
| GAstV-II-R | AAGTTTCGCCAGGGTTAGAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Li, L.; Dong, J.; Jin, J.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhai, Q.; Huang, Y.; Sun, B.; Liao, M.; et al. Isolation, Characterization, and Comparative Analysis of Two Subtypes of Goose Astrovirus in Guangdong Province, China. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051037
Liu C, Li L, Dong J, Jin J, Xiang Y, Zhang J, Zhai Q, Huang Y, Sun B, Liao M, et al. Isolation, Characterization, and Comparative Analysis of Two Subtypes of Goose Astrovirus in Guangdong Province, China. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(5):1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051037
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chenggang, Linlin Li, Jiawen Dong, Jin Jin, Yong Xiang, Junqin Zhang, Qi Zhai, Yunzhen Huang, Binyi Sun, Ming Liao, and et al. 2025. "Isolation, Characterization, and Comparative Analysis of Two Subtypes of Goose Astrovirus in Guangdong Province, China" Microorganisms 13, no. 5: 1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051037
APA StyleLiu, C., Li, L., Dong, J., Jin, J., Xiang, Y., Zhang, J., Zhai, Q., Huang, Y., Sun, B., Liao, M., & Sun, M. (2025). Isolation, Characterization, and Comparative Analysis of Two Subtypes of Goose Astrovirus in Guangdong Province, China. Microorganisms, 13(5), 1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051037






