Enhancing Lignocellulose Degradation and Mycotoxin Reduction in Co-Composting with Bacterial Inoculation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Microbial Agents
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Physicochemical Properties
2.5. Degradation of Hemicellulose, Cellulose and Lignin
2.6. Analysis of Mycotoxins
2.7. Microbial Community Structure
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
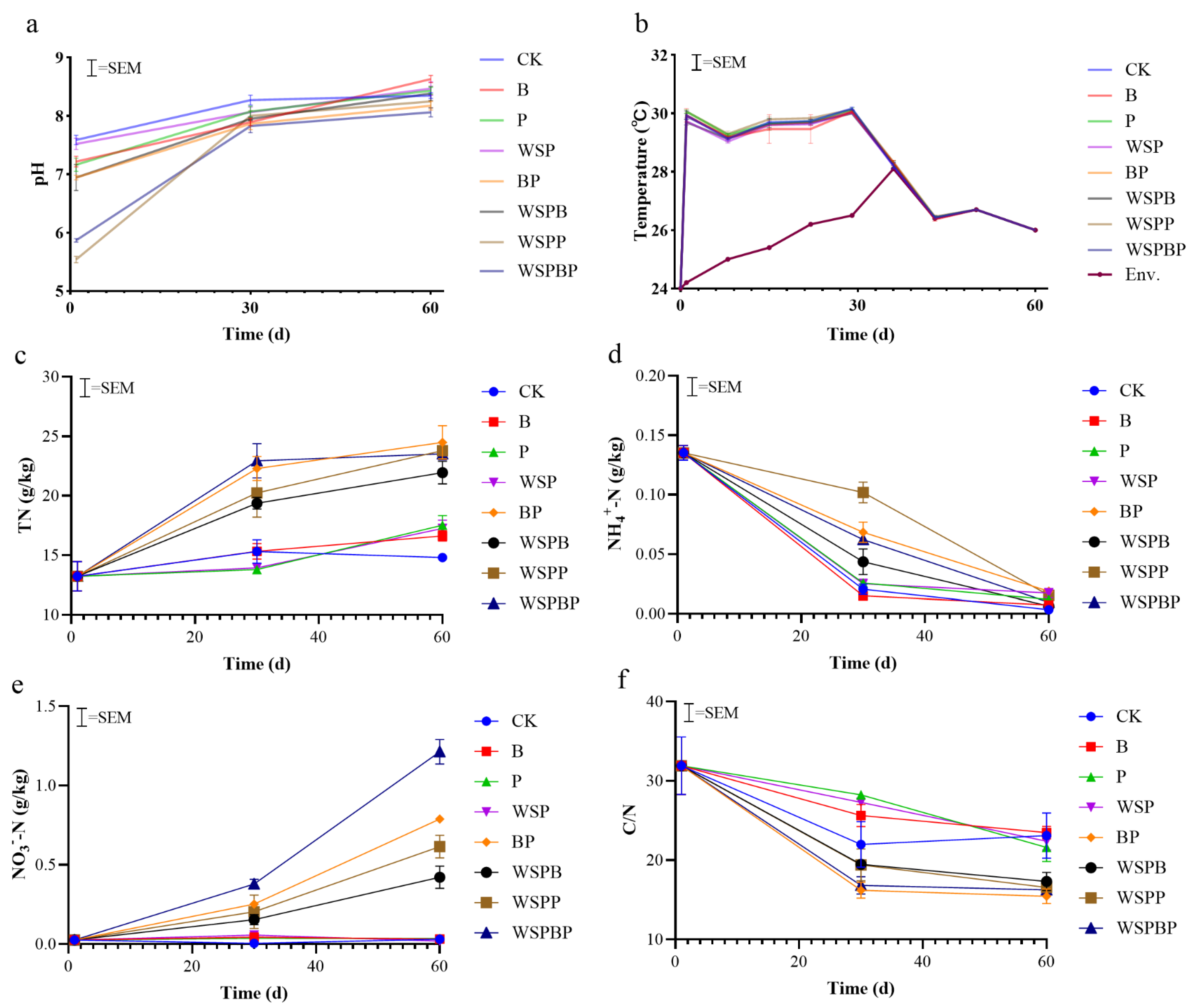
3.1. Physical–Chemical Characterization
3.1.1. pH
3.1.2. Temperature
3.1.3. Nitrogen Conversion and C/N
3.2. Analysis of Lignocellulose
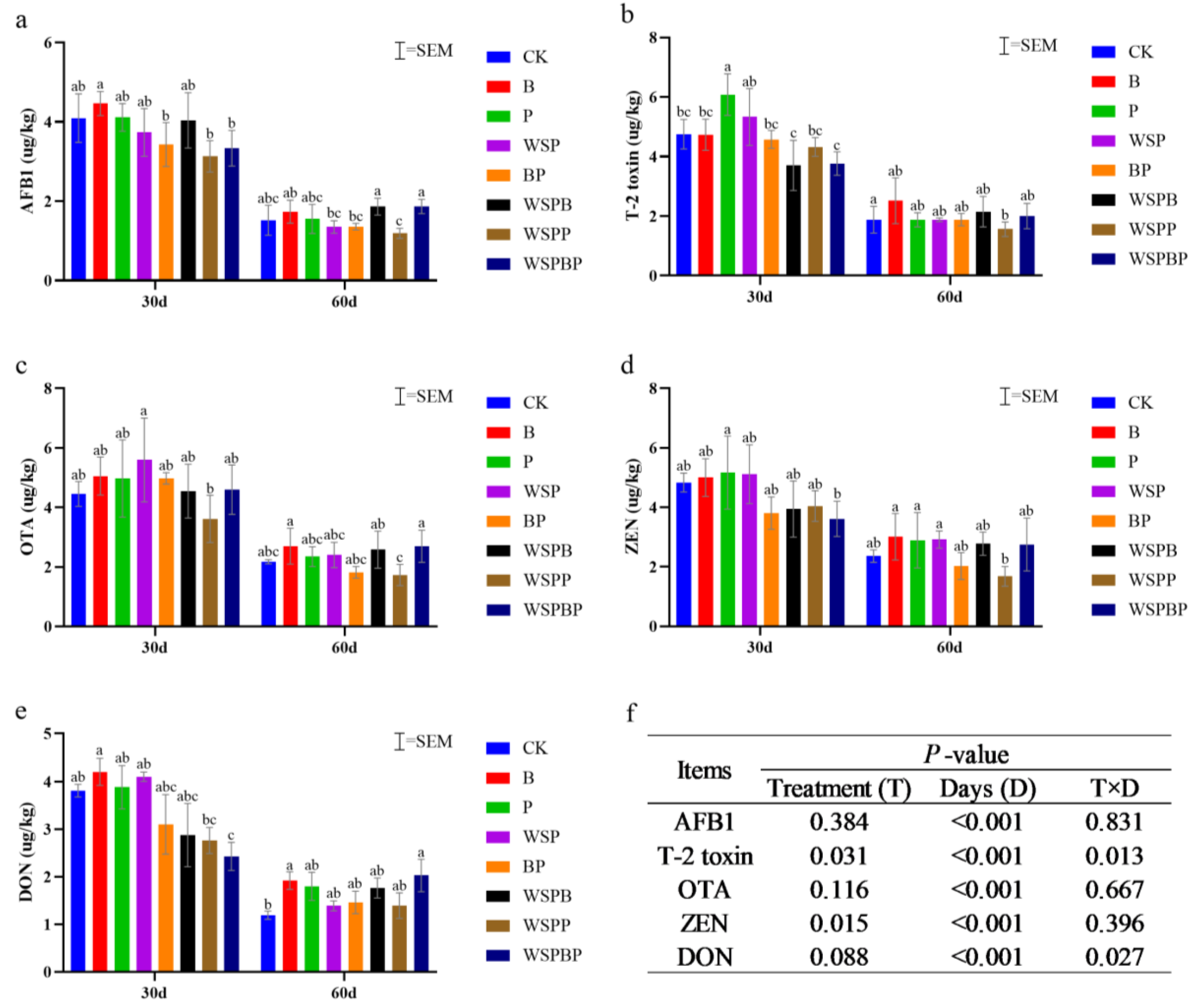
3.3. Content of Mycotoxins Analysis
3.4. Analysis of Micro-Ecological Community in Composting
3.4.1. Analysis of Bacterial Community in Composting
3.4.2. Analysis of Fungal Community in Composting
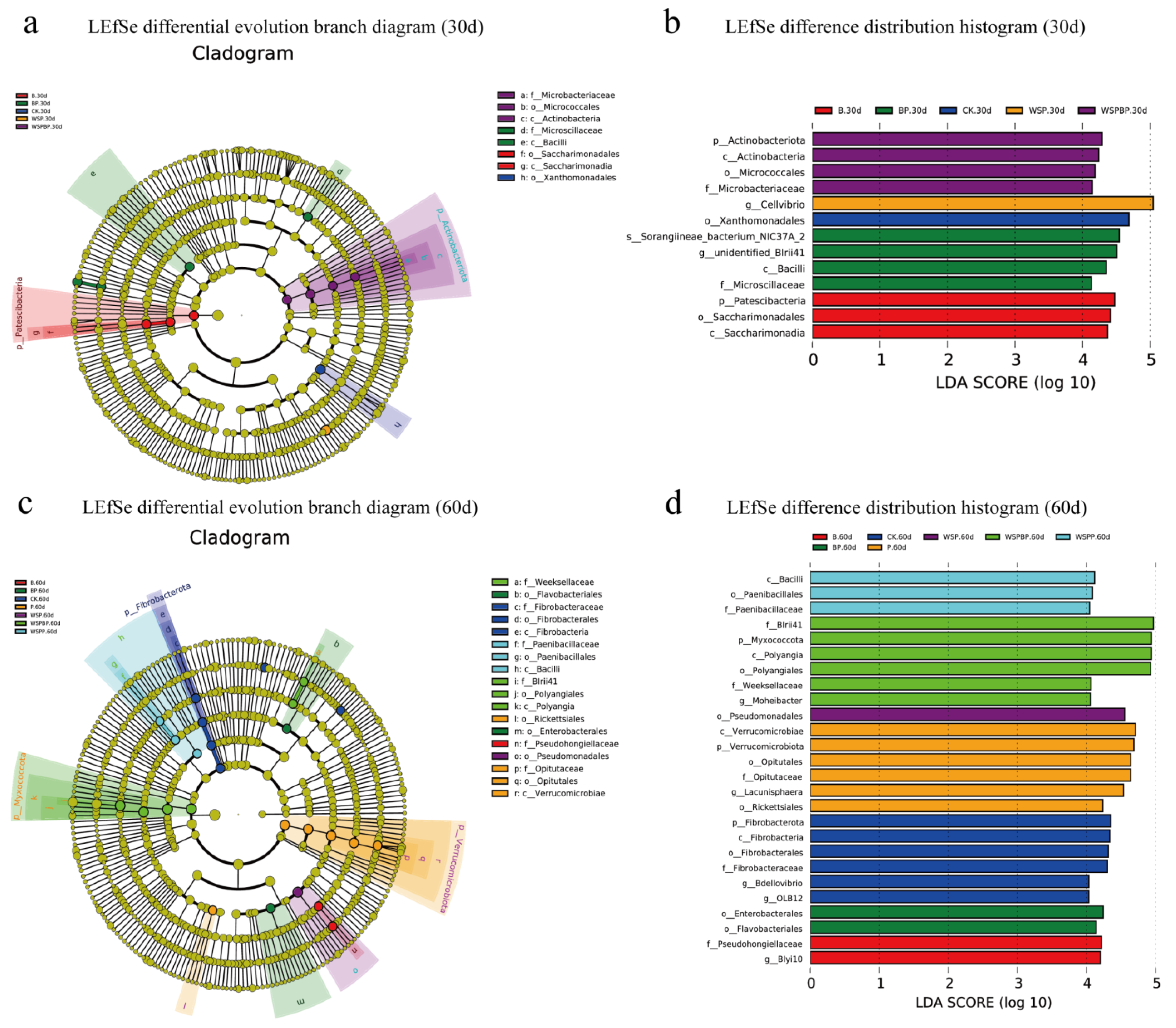
3.5. LEfSe Analysis in Composting
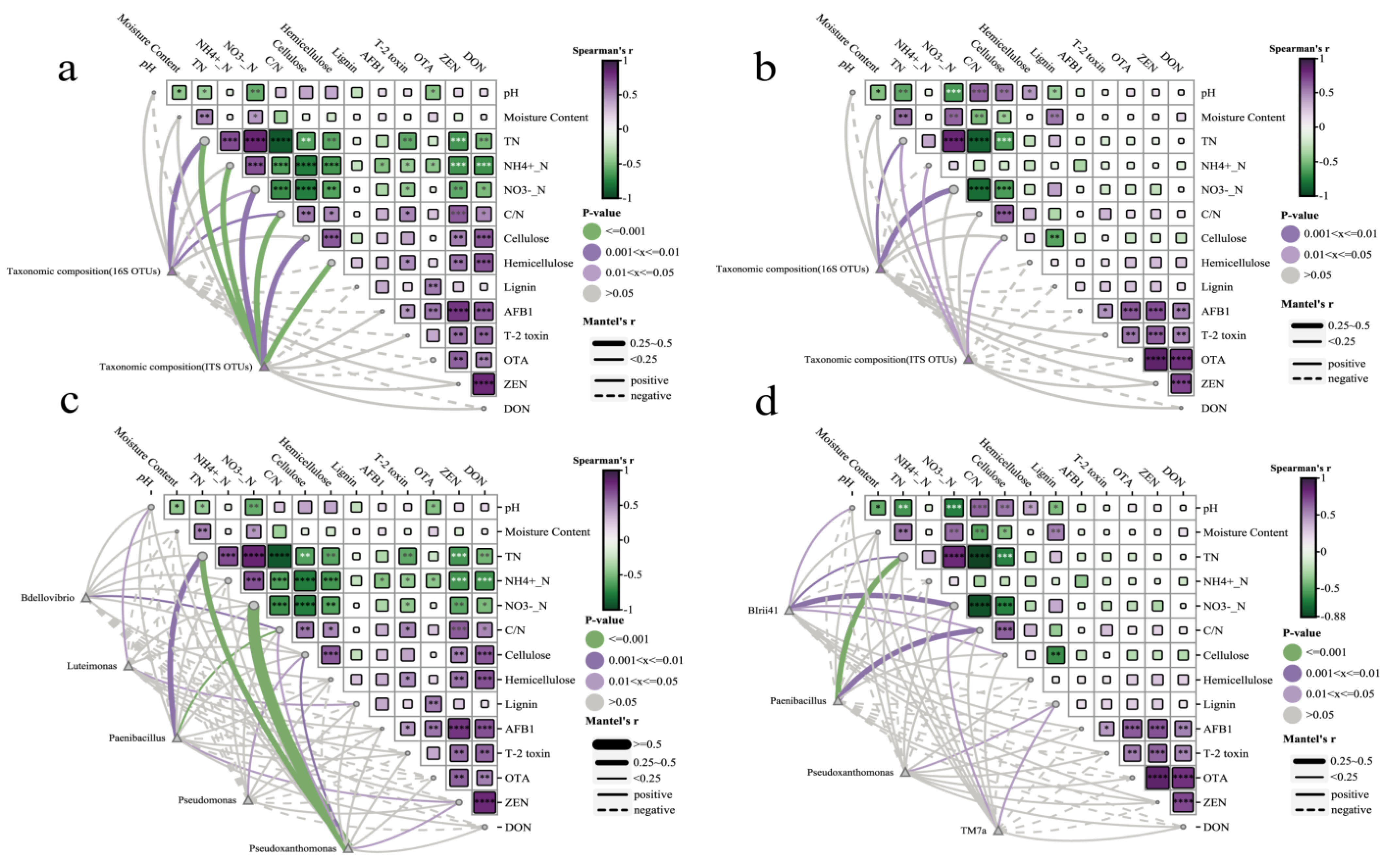
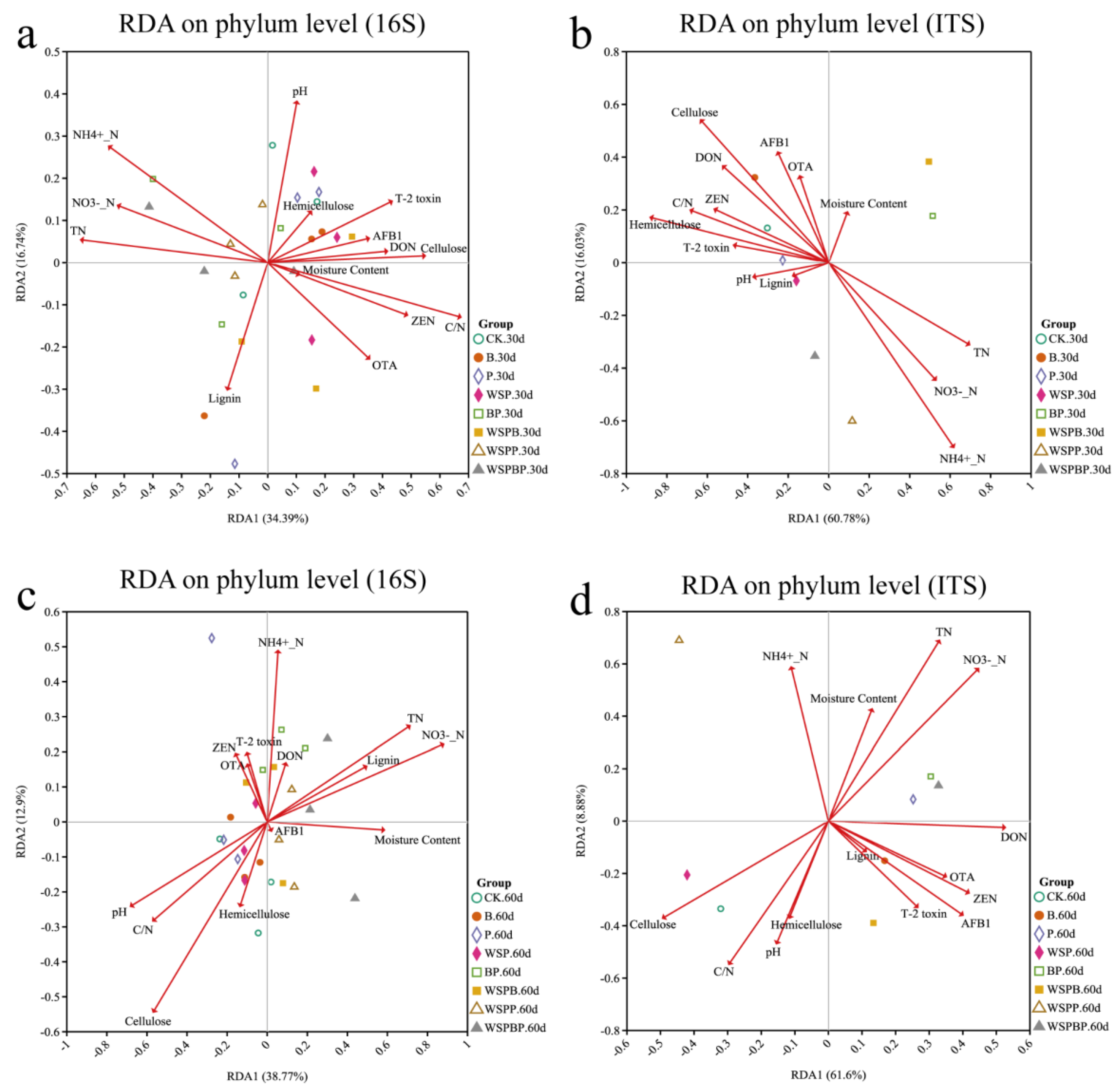
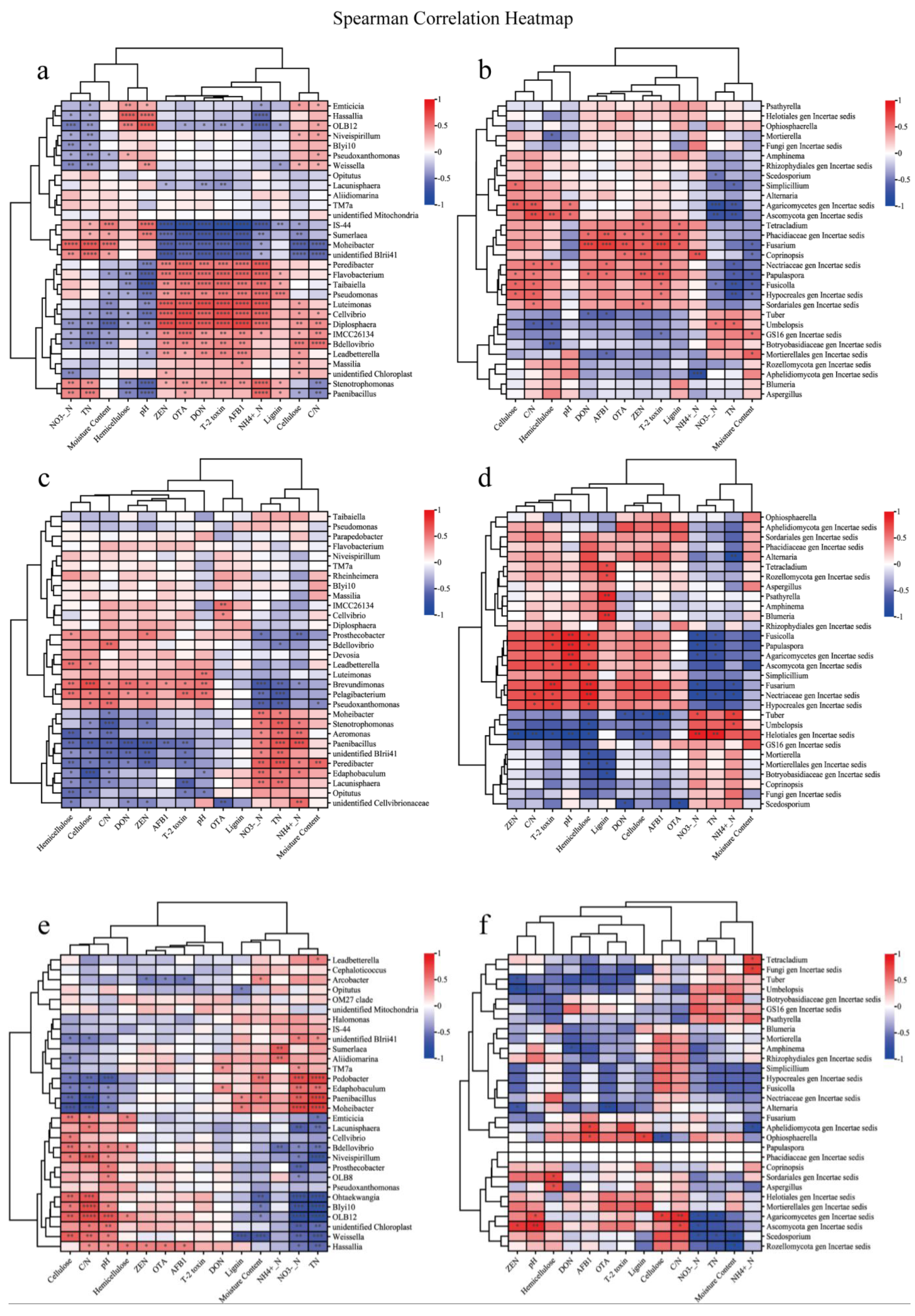
3.6. Correlation Analysis with Environmental Factors
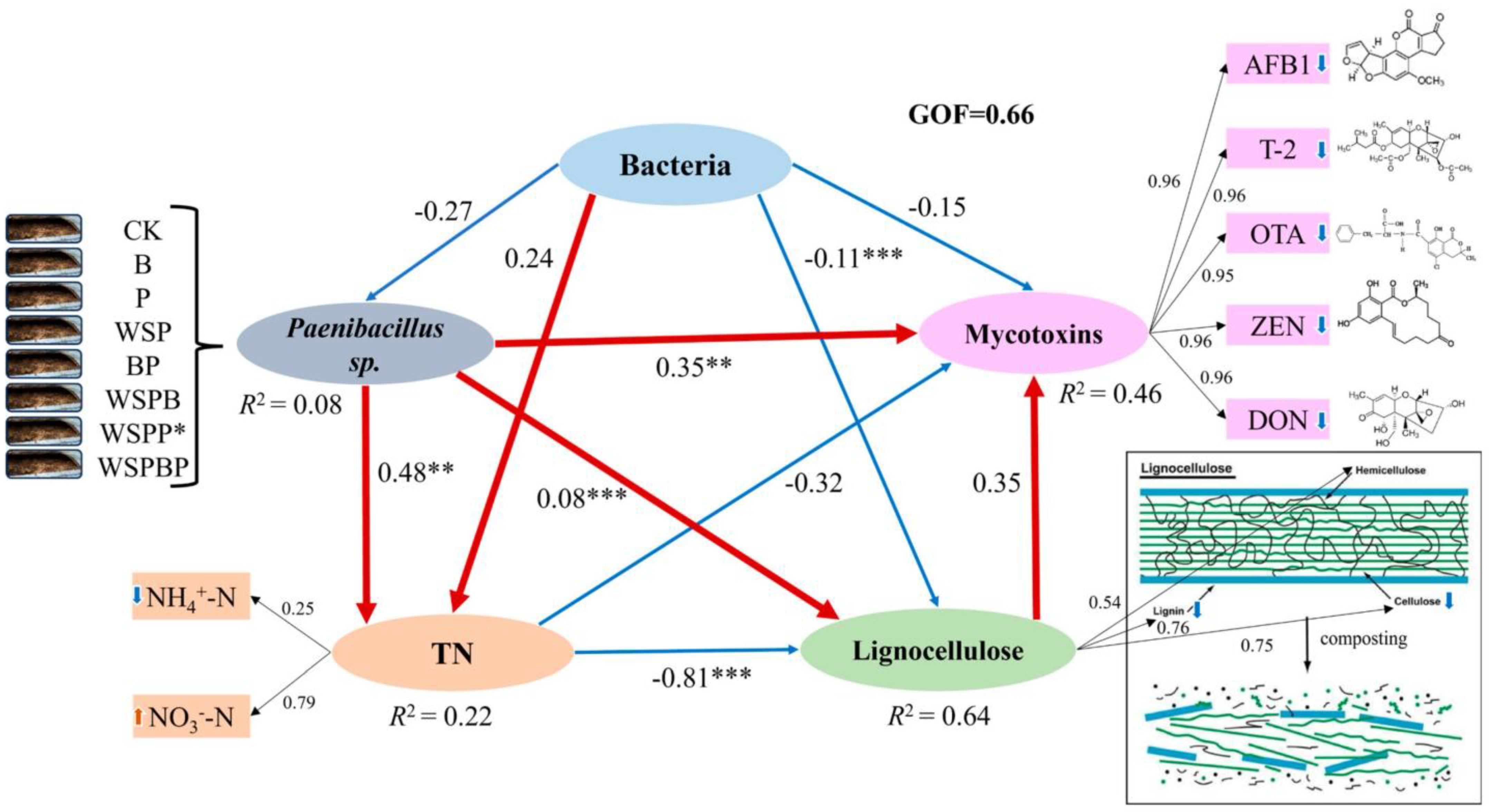
3.7. Relationship Among Bacterial Community, Paenibacillus sp., TN, Mycotoxins, and Lignocellulose
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CK | Control check group. |
| B | Bacillus subtilis group. |
| P | Paenibacillus sp. group. |
| WSP | Weissella paramesenteroides group. |
| BP | Bacillus subtilis and Paenibacillus sp. group. |
| WSPB | Weissella paramesenteroides and Bacillus subtilis group. |
| WSPP | Weissella paramesenteroides and Paenibacillus sp. group. |
| WSPBP | Weissella paramesenteroides, Bacillus subtilis and Paenibacillus sp. group. |
References
- Wang, C.; Jia, Y.; Li, J.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Yan, F.; Wu, M.; Fang, W.; Xu, F.; Qiu, Z. Influence of microbial augmentation on contaminated manure composting: Metal immobilization, matter transformation, and bacterial response. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 441, 129762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Hu, C.; Xu, J.; Ming, J.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, M.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X. Dissolved organic matter derived from rape straw pretreated with selenium in soil improves the inhibition of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum growth. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Fan, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, H.; Li, C.; Zhu, Y. Co-hydrothermal carbonization of rape straw and microalgae: pH-enhanced carbonization process to obtain clean hydrochar. Energy 2022, 257, 124733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.H.; Pourcher, A.M.; Bureau, C.; Peu, P. Cellulose accessibility and microbial community in solid state anaerobic digestion of rape straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 223, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ren, T.; Yang, X.; Zhou, X.; Li, X.; Cong, R.; Lu, J. Biochar return in the rice season and straw mulching in the oilseed rape season achieve high nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency and low greenhouse gas emissions in paddy-upland rotations. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 148, 126869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.H.; Pourcher, A.M.; Bize, A.; Wazeri, A.; Peu, P. Impact of wet aerobic pretreatments on cellulose accessibility and bacterial communities in rape straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 237, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhao, W.; Yan, L.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Gou, W.; You, M.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, C. Inclusion of abandoned rhubarb stalk enhanced anaerobic fermentation of alfalfa on the Qinghai Tibetan Plateau. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunade, I.M.; Martinez-Tuppia, C.; Queiroz, O.C.M.; Jiang, Y.; Drouin, P.; Wu, F.; Vyas, D.; Adesogan, A.T. Silage review: Mycotoxins in silage: Occurrence; effects; prevention; mitigation. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4034–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, A.; Fancello, F.; Ghilardelli, F.; Zara, S.; Froldi, F.; Spanghero, M. Effects of several lactic acid bacteria inoculants on fermentation and mycotoxins in corn silage. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2021, 277, 114962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juraschek, L.M.; Kappenberg, A.; Amelung, W. Mycotoxins in soil and environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tian, L.; Li, Y.; Zhong, C.; Tian, C. Effects of exogenous cellulose-degrading bacteria on humus formation and bacterial community stability during composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 359, 127458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M.; Li, Q. A compost-derived thermophilic microbial consortium enhances the humification process and alters the microbial diversity during composting. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 243, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Z.; Li, M.; Song, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, S.; Yan, Z.; Wang, Y. Study on nitrogen-retaining microbial agent to reduce nitrogen loss during chicken manure composting and nitrogen transformation mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, T.; Zhou, Y. Fungal flora and mycotoxin contamination in tea: Current status, detection methods and dietary risk assessment—A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 127, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu-Rodas, Y.; Calixto-Romo, M.L.A.; Guillen-Navarro, K.; Sanchez, J.E.; Zamora-Briseno, J.A.; Amaya-Delgado, L. Bacillus subtilis with endocellulase and exocellulase activities isolated in the thermophilic phase from composting with coffee residues. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2018, 50, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhan, K.; Patra, R.K.; Sethi, D.; Mohanty, S.; Sahoo, S.K.; Panda, N.; Pattanayak, S.K.; Patra, A.K. Exploitation of cellulose degrading bacteria in bioconversion of agro-wastes. Chemosphere 2024, 347, 140654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Liao, C.; Zhou, S.; Chen, C.; Li, L.; Lu, G.; Huang, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, C.; Li, P. Potential of perennial sorghum for biogas production: Pretreatment with yeast-contained inoculants during anaerobic storage. Fuel 2024, 359, 130365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY/T1116-2014; Determination of Nitrate Nitrogen, Ammonium Nitrogen and Amide Nitrogen Content of Fertilizers. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Zhang, X.-W.; Chen, Z.-G.; Yi, S.-J.; Liu, J.-M. Rapid detection of lignin content in corn straw based on Laplacian Eigenmaps. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 133, 104787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, M.; Peng, C.; Yan, F.; Jia, Y.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Wu, B.; Xu, H.; Qiu, Z. Bacterial dynamics and functions driven by a novel microbial agent to promote kitchen waste composting and reduce environmental burden. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 337, 130491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mohamed, T.A.; Wei, Z. The key bacteria as the “Activator” promotes the rapid degradation of organic compounds during the start-up of low-temperature compost. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 330, 124950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, L.; Hassan, M.; Xie, B. Succession of the functional microbial communities and the metabolic functions in maize straw composting process. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 256, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Huang, D.; Ren, Q.; Hu, S.; Xu, J.; Xu, K.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Su, S.; Xiang, J. Inner-particle reaction mechanism of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin during photo-thermal pyrolysis process: Evolution characteristics of free radicals. Energy 2024, 297, 131201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulier, M.; Maho, T.; Lo, J.; Guillot, P.; Muja, C. Bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) fungal and mycotoxin contamination control enhanced by a dual-frequency cold plasma. Food Control 2024, 163, 110477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo-Ocaña, E.R.; Soto-Paz, J.; Torres, V.S.; Castellanos-Suarez, L.J.; Komilis, D. Effect of the addition of the Bacillus sp. Paenibacillus sp. bacterial strains on the co-composting of green and food waste. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, L.; Zheng, Y.-M.; Ma, L.; Zhao, Q.-B.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.-X. Influence of plants on anammox process in constructed Wetland: Irrelevance, inhibition or enhancement. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 460, 141619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Xi, B.; Huang, C.; Tan, W.; Xia, X.; Yang, T.; Yu, M.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, W. Linking phytoavailability of heavy metals with microbial community dynamics during municipal sludge composting. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 130, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Li, S.; Qv, M.; Wang, W.; Wu, Q.; Nugroho, Y.K.; Huang, L.; Zhu, L. Urea addition as an enhanced strategy for degradation of petroleum contaminants during co-composting of straw and pig manure: Evidences from microbial community and enzyme activity evaluation. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 393, 130135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zheng, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Dong, S.; Hu, X. The impact of microbial inoculants on large-scale composting of straw and manure under natural low-temperature conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 400, 130696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Abdellah, Y.A.Y.; Miao, L.; Wu, B.; Ma, T.; Wang, Y.; Zang, H.; Zhao, X.; Li, C. Impact of microbial inoculants combined with humic acid on the fate of estrogens during pig manure composting under low-temperature conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yang, X.; Liang, X.; Song, Y.; Zhu, L.; Xing, S.; Yang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Borriss, R.; Dong, S.; et al. Fusaricidin produced by the rhizobacterium Paenibacillus polymyxa NX20 is involved in the biocontrol of postharvest plant-pathogenic oomycete Phytophthora capsica. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 205, 112545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Gu, J.; Wang, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, J.; Lei, L.; Dai, X.; Zhao, W. Effects of inoculation with lignocellulose-degrading microorganisms on nitrogen conversion and denitrifying bacterial community during aerobic composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 313, 123664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, P.; Cai, F.; Kubicek, C.P.; Jiang, S.; Grujic, M.; Rahimi, M.J.; Sheteiwy, M.S.; Giles, R.; Riaz, A.; de Vries, R.P.; et al. From lignocellulose to plastics: Knowledge transfer on the degradation approaches by fungi. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 50, 107770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakra, A.K.; Domdi, L.; Hanjon, G.; Tilwani, Y.M.; Arul, V. Some probiotic potential of Weissella confusa MD1 and Weissella cibaria MD2 isolated from fermented batter. LWT 2020, 125, 109261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Tian, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, X.; Lei, Y.; Tang, F. Mycobiome mediates the interaction between environmental factors and mycotoxin contamination in wheat grains. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 928, 172494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfliegler, W.P.; Pocsi, I.; Gyori, Z.; Pusztahelyi, T. The Aspergilli and Their Mycotoxins: Metabolic Interactions With Plants and the Soil Biota. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Z.U.; Al Thani, R.; Alsafran, M.; Migheli, Q.; Jaoua, S. Selection of Bacillus spp. with decontamination potential on multiple Fusarium mycotoxins. Food Control 2021, 127, 108119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.; Yang, C.; Ma, T.; Osei, R.; Jin, M.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. An endophytic Paenibacillus polymyxa hg18 and its biocontrol potential against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cucumerinum. Biol. Control 2024, 188, 105380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schierstaedt, J.; Grosch, R.; Schikora, A. Agricultural production systems can serve as reservoir for human pathogens. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnaa016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, N.; Zhang, J.; Hu, R.; Liu, S.; Liu, F.; Fan, Y.; Yang, H.; Huang, J.; Ding, J.; Chen, R.; et al. Hidden pathogen risk in mature compost: Low optimal growth temperature confers pathogen survival and activity during manure composting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fickers, P.; Guez, J.S.; Damblon, C.; Leclere, V.; Bechet, M.; Jacques, P.; Joris, B. High-level biosynthesis of the anteiso-C(17) isoform of the antibiotic mycosubtilin in Bacillus subtilis and characterization of its candidacidal activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 4636–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Cai, P.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, Z.; Li, Y.X. Metabolic engineering of “last-line antibiotic” colistin in Paenibacillus polymyxa. Metab. Eng. 2024, 85, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; van Kleunen, M.; Becks, L.; Thakur, M.P. Towards a General Understanding of Bacterial Interactions. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 783–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gallagher, L.A.; Andrade, P.A.; Liu, A.; Humphreys, I.R.; Turkarslan, S.; Cutler, K.J.; Arrieta-Ortiz, M.L.; Li, Y.; Radey, M.C.; et al. Genetic manipulation of Patescibacteria provides mechanistic insights into microbial dark matter and the epibiotic lifestyle. Cell 2023, 186, 4803–4817.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Revathi, K.; Khanna, S. Biodegradation of cellulosic and lignocellulosic waste by Pseudoxanthomonas sp R-28. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 134, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, E.N.; MacDonald, J.; Liu, L.; Richman, A.; Yuan, Z.C. Current knowledge and perspectives of Paenibacillus: A review. Microb. Cell Factories 2016, 15, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Chhatpar, H.S. Purification and characterization of chitinase from Paenibacillus sp. D1. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 164, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Li, J.; Li, Q.X.; Chen, S.F. Paenibacillus beijingensis sp. nov., a nitrogen-fixing species isolated from wheat rhizosphere soil. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2013, 104, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, K.Y.; Woo, H.M.; Lee, S.M.; Um, Y. Aerobic and anaerobic cellulose utilization by Paenibacillus sp. CAA11 and enhancement of its cellulolytic ability by expressing a heterologous endoglucanase. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 268, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorentz, R.H.; Artico, S.; da Silveira, A.B.; Einsfeld, A.; Corcao, G. Evaluation of antimicrobial activity in Paenibacillus spp. strains isolated from natural environment. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Du, G.; Fang, F. Synergistic fermentation with functional bacteria for production of salt-reduced soy sauce with enhanced aroma and saltiness. Food Biosci. 2024, 57, 103459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Su, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Shen, G.; Yuan, Y.; Yan, L.; Tang, H.; Song, F.; Wang, W. Characteristics and functional bacteria in a microbial consortium for rice straw lignin-degrading. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 331, 125066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Index | Composting Period | Treatment (T) | SEM | p-Value | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | B | P | WSP | BP | WSPB | WSPP | WSPBP | T | D | T × D | |||
| OTUs | Day 1 | 638 Ca | 554 Bab | 553 Cab | 596 Ca | 533 Cab | 449 Cb | 531 Cab | 563 Bab | 31.889 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.170 |
| Day 30 | 906 Bc | 1155 Aab | 909 Bc | 920 Bc | 943 Bbc | 732 Bc | 953 Bbc | 1198 Aa | |||||
| Day 60 | 1017 A | 1254 A | 1076 A | 1051 A | 1165 A | 1012 A | 1034 A | 1166 A | |||||
| Chao1 | Day 1 | 766.36 Ca | 673.20 Bab | 697.61 Cab | 705.09 Cab | 660.90 Cabc | 505.19 Cc | 577.38 Cbc | 674.26 Bab | 40.147 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.295 |
| Day 30 | 1087.01 Bbc | 1503.41 Aa | 1024.59 Bc | 1115.23 Bbc | 1138.34 Bbc | 877.27 Bc | 1112.50 Bbc | 1401.07 Aab | |||||
| Day 60 | 1226.58 A | 1590.83 A | 1304.99 A | 1292.61 A | 1494.61 A | 1187.32 A | 1205.31 A | 1423.85 A | |||||
| Coverage | Day 1 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.0001 | 0.002 | <0.001 | 0.786 |
| Day 30 | 0.997 | 0.996 | 0.998 | 0.997 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.997 | |||||
| Day 60 | 0.997 | 0.996 | 0.997 | 0.997 | 0.996 | 0.997 | 0.997 | 0.996 | |||||
| Shannon | Day 1 | 6.33 Ba | 5.56 Bab | 5.45 Bab | 5.63 Cab | 5.98 Cab | 5.08 Cb | 5.52 Bab | 5.96 Cab | 0.112 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.005 |
| Day 30 | 7.30 Ab | 7.72 Aab | 7.07 Abc | 6.54 Bcd | 7.07 Bbc | 6.23 Bd | 7.73 Aab | 8.14 Aa | |||||
| Day 60 | 7.22 Aab | 7.90 Aa | 7.12 Ab | 7.48 Aab | 7.60 Aab | 7.29 Aab | 7.23 Aab | 7.04 Bb | |||||
| Index | Composting Period | Treatment (T) | SEM | p-Value | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | B | P | WSP | BP | WSPB | WSPP | WSPBP | T | D | T × D | |||
| OTUs | Day 1 | 348 Ca | 293 Bb | 87 Cf | 101 Cef | 10 Cg | 168 Ac | 112 Be | 129 Bd | 23.906 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.124 |
| Day 30 | 477 Bd | 365 Ae | 532 Ac | 824 Aa | 131 Bf | 167 Af | 144 Af | 618 Ab | |||||
| Day 60 | 512 Aa | 118 Cd | 119 Bd | 385 Bb | 159 Ac | 141 Bcd | 118 Bd | 137 Bcd | |||||
| Chao1 | Day 1 | 367.83 Ca | 314.14 Bb | 92.50 Cf | 102.43 Cef | 10.00 Cg | 171.21 Bc | 112.00 Be | 131.33 Bd | 26.686 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.237 |
| Day 30 | 488.54 Bd | 419.81 Ae | 553.50 Ac | 951.10 Aa | 148.27 Bh | 190.00 Af | 153.23 Ag | 665.19 Ab | |||||
| Day 60 | 568.95 Aa | 123.14 Cf | 130.25 Be | 419.17 Bb | 167.57 Ac | 144.88 Cd | 120.33 Bg | 145.67 Bd | |||||
| Coverage | Day 1 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.0001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.115 |
| Day 30 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.999 | 0.997 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 1.000 | 0.998 | |||||
| Day 60 | 0.998 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.999 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | |||||
| Shannon | Day 1 | 5.77 Bb | 6.15 Aa | 3.48 Bg | 4.61 Cd | 0.88 Ch | 3.77 Af | 5.20 Ac | 4.50 Be | 0.190 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.005 |
| Day 30 | 6.37 Aa | 3.24 BCc | 6.52 Aa | 7.03 Aa | 3.10 Ac | 3.20 Bc | 4.96 Ab | 6.70 Aa | |||||
| Day 60 | 5.94 Ba | 3.73 Bb | 2.90 Cc | 5.78 Ba | 2.82 Bc | 3.06 Bc | 4.12 Bb | 2.72 Cc | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.; Tang, X.; Liao, C.; Huang, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Yang, S.; Li, P.; Chen, C. Enhancing Lignocellulose Degradation and Mycotoxin Reduction in Co-Composting with Bacterial Inoculation. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030677
Chen C, Tang X, Liao C, Huang X, Zhang M, Zhang Y, Wang P, Yang S, Li P, Chen C. Enhancing Lignocellulose Degradation and Mycotoxin Reduction in Co-Composting with Bacterial Inoculation. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(3):677. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030677
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Cheng, Xiaolong Tang, Chaosheng Liao, Xiaokang Huang, Mingjie Zhang, Yubo Zhang, Pan Wang, Siqi Yang, Ping Li, and Chao Chen. 2025. "Enhancing Lignocellulose Degradation and Mycotoxin Reduction in Co-Composting with Bacterial Inoculation" Microorganisms 13, no. 3: 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030677
APA StyleChen, C., Tang, X., Liao, C., Huang, X., Zhang, M., Zhang, Y., Wang, P., Yang, S., Li, P., & Chen, C. (2025). Enhancing Lignocellulose Degradation and Mycotoxin Reduction in Co-Composting with Bacterial Inoculation. Microorganisms, 13(3), 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030677





