Abstract
The presence of Salmonella in rivers, lakes, or beaches in South America represents a challenge to public health and aquatic ecosystems. This review explores the distribution, prevalence, and the main factors contributing to the survival and spread of Salmonella, including wastewater discharge, agricultural runoff, and climatic variables such as high temperatures and precipitation. These factors also facilitate the distribution of multidrug-resistant strains in water. The review is based on bibliographic searches in various databases, focusing on Salmonella species, South American countries, and types of water bodies. Predominant serovars include S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium, with S. Typhi and S. Panama frequently detected in Chile, S. Enteritidis in Argentina, and S. Typhimurium in Brazil. Less common serovars, including S. Dublin and S. Paratyphi B, were identified, along with subspecies such as diarizonae and houtenae. These findings highlight the role of environmental, physicochemical, and anthropogenic factors influencing Salmonella dynamics. The review identifies research gaps, advocating for further studies to better understand the interactions between Salmonella, climate change, and human activity. Strengthening surveillance and mitigation strategies is crucial to protect water resources and public health in South America.
1. Introduction
Water bodies are essential resources, playing a critical role in sustaining human communities and natural ecosystems [1,2]. These water bodies support essential activities such as drinking water supply, agriculture, hydropower, recreation, and aquatic biodiversity [3,4,5,6]. However, rapid urbanization, intensive agriculture, and the lack of efficient waste management systems have placed growing pressure on water quality in the region [7,8]. Pathogen contamination of water bodies poses a major threat, affecting both human health and ecosystems [9,10].
To address these challenges, South American countries have implemented various monitoring and mitigation strategies. These include microbiological and physicochemical monitoring, remote sensing, and hydrological modeling to predict pathogen dispersion [11]. Mitigation efforts focus on improving wastewater treatment, promoting sustainable agriculture, and restoring aquatic ecosystems. However, the lack of standardized methods, real-time data, and effective enforcement limits their impact [11]. Strengthening monitoring frameworks and targeted strategies is essential to controlling waterborne pathogens [11].
Among microbiological contaminants, Salmonella stands out as one of the most significant pathogens due to its public health and environmental impact [12,13]. This bacterial genus, widespread in terrestrial and aquatic environments, causes salmonellosis and typhoid fever, affecting millions worldwide each year [14]. Salmonella enters water bodies through multiple pathways, including untreated wastewater, agricultural runoff carrying fertilizers and manure, and improper disposal of industrial waste [15], with risks exacerbated in regions with limited sanitation infrastructure and poor waste management [16,17].
Beyond its direct impact on public health, Salmonella can disrupt aquatic ecosystems [18] by altering local microbial communities and reducing biodiversity [19,20]. In aquatic environments, Salmonella can persist and proliferate under various environmental conditions, including elevated temperatures and high levels of organic matter [12,21]. Additionally, antibiotic use in agriculture and aquaculture promotes the growth of Salmonella and the emergence of multidrug-resistant strains, compounding the issue [10].
Climate factors, such as precipitation and elevated temperatures, are key variables in the distribution and incidence of Salmonella in water bodies [12,22]. Precipitation can transport contaminants from terrestrial areas into water bodies, increasing bacterial loads, while higher temperatures prolong Salmonella survival in the environment, enhancing its capacity for dissemination [23,24,25]. These dynamics are particularly relevant in the context of climate change, which is altering precipitation and temperature patterns across many regions of South America, further complicating control efforts [26,27].
Understanding how climatic factors and local contamination dynamics influence the incidence and distribution of Salmonella in water bodies is essential for developing more effective monitoring and mitigation strategies. Assessing the prevalence of Salmonella in different water bodies across South America will help identify incidence patterns and areas of higher vulnerability and inform the design of policies aimed at reducing health risks and protecting aquatic ecosystems.
2. Materials and Methods
This bibliographic review was conducted using a combination of search terms applied across PubMed, Web of Science, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar to identify studies on Salmonella in water bodies across South America. The search strategy was informed by previous reviews to ensure comprehensive literature coverage.
The search strategy was divided into three search components (SC): SC1 Salmonella species, including search terms specifically targeting the genus and species level to ensure the review captured the largest number of studies. SC2 country of origin, including search terms for South American countries (Argentina, Bolivia, Brasil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Perú, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela), aiming to refine the search to studies conducted in these regions to gather specific data. SC3 water body types, including an extensive list of water-related terms in both English and Spanish, such as Bay (Bahía), Beach (Playa), Brook (Riachuelo), Drainage basin (Cuenca hidrográfica), Estuary (Estuario), Glacier (Glaciar), Gulf (Golfo), Lagoon (Laguna), Lake (Lago), Ocean (Océano), Port (Puerto), Puddle (Charco), Reservoir (Embalse), Ria (Ría), River (Río), River delta (Delta fluvial), River mouth (Desembocadura), Sea (Mar), Ship canal (Canal de navegación), Strait (Estrecho), Stream (Arroyo), Swamp (Pantano), Tidal marsh (Marisma), Well (Pozo), and Wetland (Humedal), to capture studies across diverse aquatic environments.
Given the large number of articles identified under SC1, SC2 and SC3 were applied to article titles and abstracts to refine results. The specific search terms and criteria for each component are detailed in Figure 1. A manual review of the selected articles was conducted to ensure relevance and a manageable dataset. The selection covered publications from 1970 to 2024. Additionally, manual searches were performed by reviewing the reference lists of the initially selected articles. This step helped to identify any further studies that met the inclusion criteria but may not have been captured in the database search.
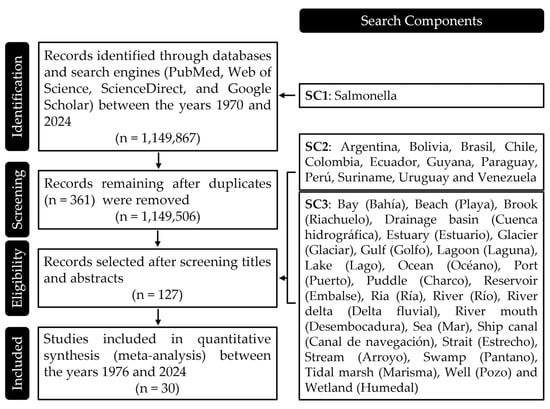
Figure 1.
Search Components Used in the Review Process. This figure provides a detailed breakdown of the search components employed during the literature review. Each component was carefully crafted to capture a comprehensive range of studies relevant to the presence of Salmonella in water bodies across South America. The components are categorized by species identification, geographical focus, and types of water bodies, ensuring a thorough and targeted search strategy that covers the essential aspects of the research topic.
A total of 30 studies were included: 1 study from Venezuela, 2 from Colombia and Perú, 3 from Bolivia, 6 from Chile, 7 from Brazil, and 10 from Argentina (Brazil and Chile shared one study).
The variability in the methodologies used to detect the presence of Salmonella prevented the application of comparative statistical analyses. For this reason, the review focused solely on the presence or absence of Salmonella in water bodies, without assessing relative abundance or other quantitative factors. This limitation arose because the selected studies employed different detection approaches, making their results not directly comparable. Additionally, many articles analyzed various types of water bodies within the same country, further complicating the identification of general patterns.
To ensure transparency and rigor in the review process, the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines were followed [28]. This framework helped standardize the selection and reporting of studies, ensuring a structured and comprehensive bibliographic review.
3. Results
3.1. Subsection: Diversity and Clinical Relevance of Salmonella Serovars in Aquatic Environments Across South America
Salmonella is a genus of gram-negative bacteria belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae, widely distributed in terrestrial and aquatic environments [12]. This genus includes two main species: Salmonella enterica and Salmonella bongori, with the former being responsible for most clinically significant infections [29]. Within S. enterica, six subspecies have been identified: enterica (I), salamae (II), arizonae (IIIa), diarizonae (IIIb), houtenae (IV), and indica (VI), which together comprise more than 2600 serovars [30]. These serovars differ in their specific combinations of somatic (O) and flagellar (H) antigens [31]. The subsp. enterica includes the majority of clinically and environmentally relevant serovars, being the most frequently isolated in human and animal infections [32]. Among the serovars, S. Typhi and S. Paratyphi B are associated with systemic diseases such as typhoid and paratyphoid fever, whose transmission is often linked to the consumption of contaminated water [33]. In contrast, serovars like S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium have been detected in water but are also widely associated with zoonotic and foodborne infections, affecting both humans and animals [33]. Additionally, these studies have reported less common serovars, such as Dublin, which primarily affect cattle [34]. Moreover, within the subsp. diarizonae, the serovar 16:z10:e,n,x,z15 has been identified, primarily infecting frogs and snakes [35]. These findings highlight the diversity of Salmonella in aquatic environments and its potential role in bacterial transmission.
Table 1 provides a summary of the serovars of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica identified in various water bodies across South America, along with their respective hosts and associated diseases. These serovars have been isolated from a variety of aquatic environments, such as streams, lakes, and rivers. The primarily affected hosts include humans, swine, cattle, and poultry, causing diseases such as gastroenteritis, one of the most common clinical manifestations. Among the most relevant serovars of S. enterica subsp. enterica identified are:
Enteritidis: One of the most frequent serovars, associated with infections in both humans and poultry [36]. In humans, it primarily causes gastroenteritis accompanied by fever, and in severe cases, it can progress to septicemia [13]. In poultry, it generally presents asymptomatically, although it can affect egg quality, making poultry an important reservoir and a source of transmission to humans through contaminated food [37].
Dublin: This serovar primarily affects swine and cattle. It is known to cause gastroenteritis, fever, and septicemia, as well as abortions in infected cows [34]. In humans, although infections are less common, they tend to be severe, particularly in immunocompromised individuals, highlighting their importance as a zoonotic pathogen [34].
Typhimurium: This serovar infects a wide range of hosts, including humans, pigs, cattle, and horses [38]. It is one of the leading causes of salmonellosis in humans, manifesting symptoms such as gastroenteritis, fever, and, in severe cases, septicemia [39]. In animals, it can cause intestinal and systemic infections that compromise their health and productivity, particularly in intensive agricultural systems [40,41].
Paratyphi B: This serovar has been isolated from humans and is associated with gastritis and paratyphoid fever [42]. Although this systemic disease is less severe than typhoid fever, it represents a significant risk, particularly in areas with poor water quality, where transmission through contaminated water is more likely [43].
In addition to the serovars of the subsp. enterica identified in surface waters (rivers, canals, streams, ponds, and reservoirs, among others), several serovars belonging to other subspecies were also found. Within the subsp. diarizonae, the serovars 35:r:z, 38:(k):z35, 50:r:z, 61:l,v:z, P:k:z35, 18:i:z, 18:k:z, 18:z10:e,n,x,z15, 48:i:z, 58:k:z, 61:i:z, 65:(k):z, and 16:z10:e,n,x,z15 were identified; the latter primarily infects frogs and snakes [35]. Meanwhile, in the subsp. houtenae, the serovars 40:z4,z24:-, 43:z4,z23:-, R:z4,z24:-, and 16:z4,z32:- were found, with the latter associated with humans as its main host [44]. Additionally, a representative of the subsp. salamae was identified, corresponding to the serovar 42:r:-.


Table 1.
Serovars of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica isolated from water bodies in South America, their main hosts, and associated diseases.
Table 1.
Serovars of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica isolated from water bodies in South America, their main hosts, and associated diseases.
| Host * | Diseases | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serovar |  |  |  |  | Other | GE | Other | Ref. |
| Agona | [45] | |||||||
| Anatum | Birds | [46] | ||||||
| Bareilly | [47] | |||||||
| Braenderup | [47] | |||||||
| Corvallis | [48] | |||||||
| Derby | Birds | Septicemia | [33] | |||||
| Dublin | Sheep | Abortion, Fever, Septicemia | [33] | |||||
| Enteritidis | Wild rodents | Fever, Septicemia | [33] | |||||
| Give | Ruminants | Splenic abscess | [49] | |||||
| Heidelberg | [50] | |||||||
| Infantis | [51] | |||||||
| Javiana | Various animals | [52] | ||||||
| Kentucky | [53] | |||||||
| London | [53] | |||||||
| Manhattan | [54] | |||||||
| Mbandaka | [55] | |||||||
| Meleagridis | [56] | |||||||
| Montevideo | [57] | |||||||
| Newport | [56] | |||||||
| Ohio | Bone abscess | [58] | ||||||
| Oranienburg | Various animals | [59] | ||||||
| Paratyphi B | Fever, Septicemia | [33] | ||||||
| Rissen | [60] | |||||||
| Typhi | Fever, Septicemia | [33] | ||||||
| Typhimurium | Horses | Fever, Septicemia | [33] | |||||
* The silhouettes shown in the table represent the categories Humans ( ), Swine (
), Swine ( ), Poultry (
), Poultry ( ), and Cattle (
), and Cattle ( ), while the abbreviation GE stands for gastroenteritis, a disease affecting the gastrointestinal tract.
), while the abbreviation GE stands for gastroenteritis, a disease affecting the gastrointestinal tract.
 ), Swine (
), Swine ( ), Poultry (
), Poultry ( ), and Cattle (
), and Cattle ( ), while the abbreviation GE stands for gastroenteritis, a disease affecting the gastrointestinal tract.
), while the abbreviation GE stands for gastroenteritis, a disease affecting the gastrointestinal tract.3.2. Distribution of Salmonella in South American Bodies of Water
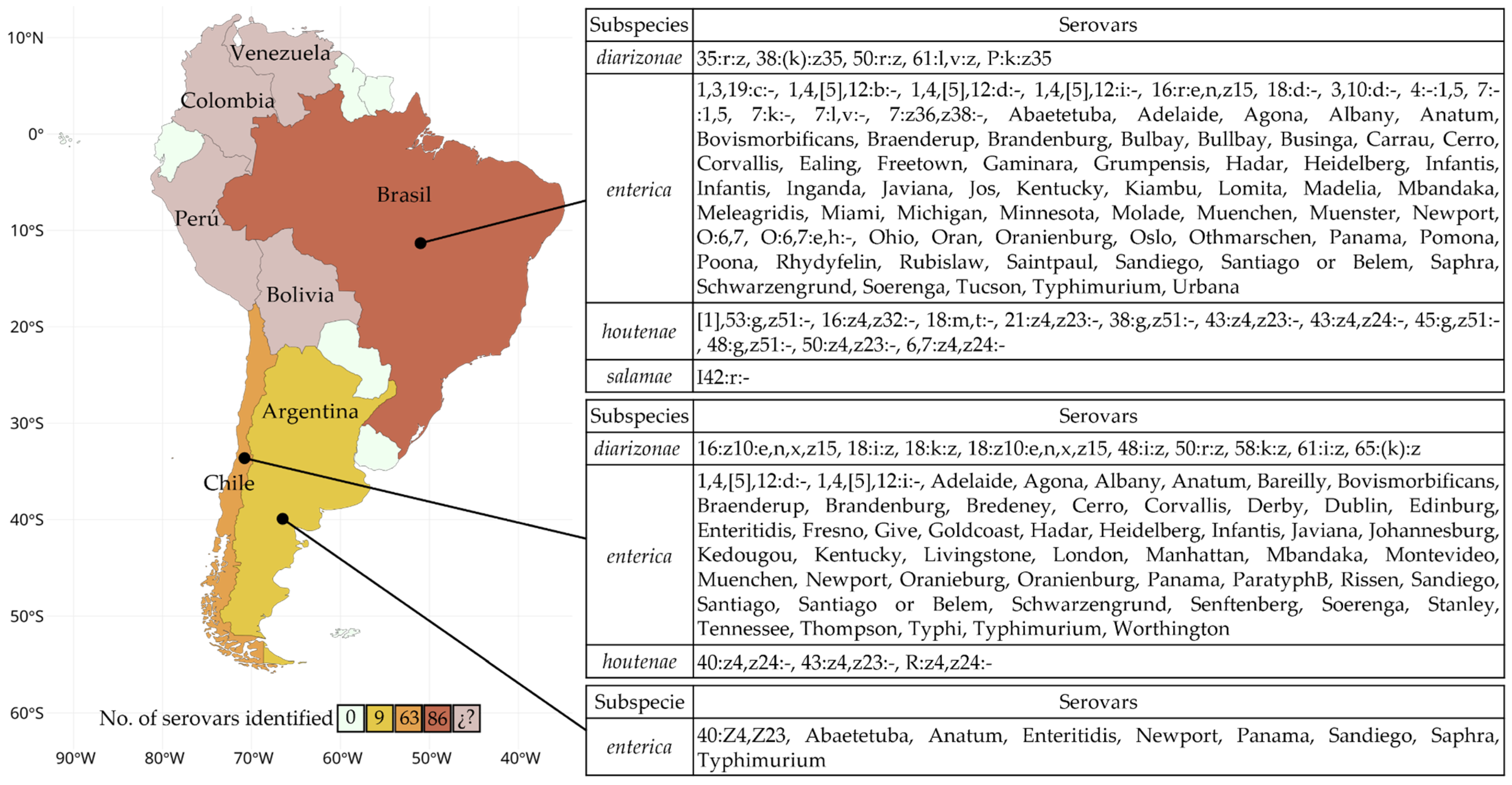
The contamination of water bodies by Salmonella represents a critical issue in South America. This pathogen is widely detected in rivers, lakes, and estuaries, which are essential for human activities such as drinking water, recreation, and agriculture. Its presence degrades water quality, threatens food security, and disrupts aquatic ecosystems. The diversity of Salmonella serovars recorded in different countries (Figure 2, Table S1), reflects the variety of contamination factors and the need for continuous monitoring.
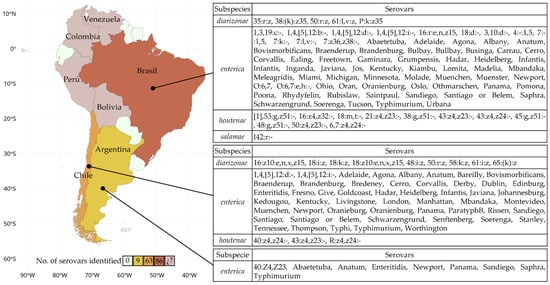
Figure 2.
Map of South America representing the number of Salmonella serovars identified in water bodies by country. The colors indicate the number of reported serovars. In the case of Bolivia, Colombia, Perú, and Venezuela, (¿?) Salmonella was detected, but only at the genus level.
In Argentina, Salmonella has been detected in major hydrological systems, including the Luján, San Luis, Negro, and de la Plata rivers. The latter, used for consumption, recreation, and fishing [61], is contaminated by direct wastewater discharge and the transport of pollutants during precipitation events [6,62,63]. It presents high levels of bacteria resistant to multiple drugs, posing a significant risk to public health and local ecosystems [6]. In the Luján River, S. Enteritidis [64] was predominant, commonly associated with poultry farming and transmission through contaminated food [65]. Multiple serovars were detected in the San Luis River, including Enteritidis, Newport, Panama, Sandiego, and Typhimurium [66]. Their presence could be linked to the discharge of domestic wastewater and agro-industrial effluents, which contribute organic matter and nutrients, favoring their survival and dispersion [18]. In addition to these large river systems, the presence of Salmonella has also been identified in other water bodies across the country, such as the Maldonado Canal [67], Lake Argüello [68], Napostá Stream [67], and La Choza [63] (Table 2).
In Bolivia, the La Paz River exhibits heavy pollution from untreated urban wastewater discharges, particularly from densely populated areas and hospitals [69,70]. Salmonella has been identified in 83–92% of water samples collected from impacted sites, highlighting its high prevalence in specific areas of the basin [69]. The Holguín site, located 17.4 km downstream from Incachaca, is situated in a densely populated urban area, right next to a hospital compound, making it a critical contamination point. Mecapaca, located 40 km from Incachaca in the agricultural lowlands, is another area impacted by wastewater discharges, as is the Jillusaya River, an urban lateral tributary of the La Paz River [69]. In these areas, Salmonella is among the most prevalent enteric pathogens in surface waters. Isolated strains exhibit resistance to multiple antibiotics, including ampicillin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, nalidixic acid, cefoxitin, and tetracycline [69,71], suggesting the possible dissemination of resistance genes from urban and hospital sources [69]. Moreover, the presence of genes associated with extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (blaCTX-M) could indicate the potential horizontal transfer of resistance genes among different bacterial species in the aquatic environment [71] (Table 2 and Table S1).
In Brazil, studies have primarily focused on rivers, where S. Typhimurium has been primarily identified in the Arrudas and Onça rivers [72], along with the serovars Madelia, Panama, and Saintpaul in the Jaguaribe River [16]. These serovars are associated with aquaculture environments, such as shrimp farms, and the discharge of untreated wastewater. In particular, S. Typhimurium can tolerate a wide range of physicochemical conditions in effluent water [73], contributing to its persistence in these environments. Additionally, along with the serovar Panama, it is one of the most prevalent serotypes isolated from swine in Brazil [74,75,76,77] (Table 2).
In Rio de Janeiro and Paraíba, various subspecies of Salmonella have been identified, each with distinct characteristics and specific serovars. The subsp. diarizonae, naturally found in reptiles, includes serovars such as 35:r:z, 38:(k):z35, 50:r:z, 61:l,v:z, and P:k:z35 [78]. Meanwhile, the subsp. houtenae, which inhabits the intestinal tract of reptiles and establishes an endophytic relationship with the natural environment [44,79], is represented by serovars such as [1], 53:g,z51:-, 16:z4,z32:-, 18:m,t:-, 21:z4,z23:-, 38:g,z51:-, 43:z4,z23:-, 43:z4,z24:-, 45:g,z51:-, 48:g,z51:-, 50:z4,z23:-, and 6,7:z4,z24:- [78]. Finally, the subsp. salamae, with a more restricted distribution and less frequently associated with virulence in humans or animals [80], includes the serovar 42:r:- [78].
In Chile, contamination by Salmonella is widespread across various regions and areas with different land uses, including rural, peri-urban, and urban zones. In the Metropolitan Region, the Zanjón de la Aguada and the Mapocho and Maipo rivers have been identified as significant sources of Salmonella contamination, including serovars Panama [14], Typhi [81], and Typhimurium [81]. In the Zanjón de la Aguada, which is highly polluted with industrial waste and untreated wastewater [82], concerning levels of S. Typhi were detected in water used for irrigation in nearby agricultural areas [81,83]. This pattern is also observed in the Maipo River, which supplies approximately 90% of the irrigation needs of the Metropolitan Region, and in the Mapocho River [84], where agricultural activities and septic systems significantly contribute to microbiological contamination [83,85]. Studies have identified the prevalence of Salmonella spp. in 50% of irrigation water samples collected from rivers and canals in these areas [81,83] (Table 2). In rural areas such as Calera de Tango and Isla de Maipo, serovars such as Mbandaka, Montevideo, Heidelberg, Infantis, and Panama were detected [85], along with specific groups like C2 and C3 [85]. In peri-urban areas, such as Melipilla and Talagante, serovars like Agona, Corvallis, Newport, Enteritidis, and Livingstone were identified, highlighting the diversity of serotypes in these locations [83,85] (Table 2). In rural and peri-urban zones such as Paine, Peñaflor, and María Pinto, serovars Brandenburg, Santiago, and Anatum were identified [85], along with others like Infantis and Senftenberg, showing a high prevalence in agricultural and livestock systems. In the Maule and Metropolitan regions, subspecies such as diarizonae and houtenae have been documented [78,85], as well as an extensive variety of serovars from subsp. enterica, including Adelaide, Agona, Albany, Anatum, Bovismorbificans, Braenderup, Brandenburg, Derby, Dublin, Enteritidis, Infantis, Kentucky, Montevideo, Newport, Panama, Paratyphi B, Schwarzengrund, Senftenberg, and Typhimurium [83,85]. These findings reflect a relationship between human activities, such as waste management and the use of wastewater in agriculture, and the spread of Salmonella, posing a significant risk to public health and food safety [81,83] (Table 2).
In Colombia, Salmonella has been documented in both freshwater and coastal environments. In the Bogotá River, which receives untreated wastewater from Bogotá and other localities [86], high concentrations of Salmonella were found, ranging between 105.3 and 108.4 CFU/L by direct isolation [86]. On the Atlantic coast beaches, such as Palmarito, Puerto Colombia, Salgar, and Santa Verónica, Salmonella spp. was detected in 14% of water samples [87], mainly in areas near channels and streams discharging untreated wastewater. Urban beaches like Salgar and Puerto Colombia showed higher prevalence, attributed to poor waste management and intense human activity in these areas [87] (Table 2).
In Perú, studies in the Huatanay River revealed the presence of Salmonella associated with high levels of antibiotic residues, such as amoxicillin and ceftriaxone [17]. These substances, originating from livestock practices and domestic and industrial discharges, not only favor the survival of Salmonella in the environment but also increase antimicrobial resistance in the detected strains [17] (Table 2 and Table S1).


Table 2.
Summary of Salmonella presence in South American water bodies: this table highlights the diversity of species and serovars, as well as their geographical distribution.
Table 2.
Summary of Salmonella presence in South American water bodies: this table highlights the diversity of species and serovars, as well as their geographical distribution.
| Country | Body of Water | Geographical Location | Species | Subspecies | Serovar | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Argentina | Canal | Maldonado | Salmonella spp. | [67] | ||
| Downstream | Merlo | Salmonella spp. | [63] | |||
| Lake | Argüello | Salmonella spp. | [68] | |||
| River | Club de Regatas Beach | Salmonella spp. | [68] | |||
| River | Río de la Plata | Salmonella spp. | [6] | |||
| River | Luján | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Enteritidis | [64] | |
| River | Luján | Salmonella spp. | [88] | |||
| River | Negro | Salmonella spp. | [68] | |||
| River | San Luis | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Enteritidis, Newport, Panama, Sandiego, Typhimurium | [66,89] | |
| Stream | La choza | Salmonella spp. | [63] | |||
| Stream | Napostá | Salmonella spp. | [67] | |||
| Stream | Zaimán | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Abaetetuba, Saphra, Anatum, Newport, Saphra | [90] | |
| Bolivia | River | Choqueyapu | Salmonella enterica | enterica | [71] | |
| River | Jillusaya | Salmonella spp. | [69] | |||
| River | La Paz | Salmonella enterica | enterica | O:4 | [91] | |
| River | La Paz (Holguín) | Salmonella spp. | [69] | |||
| River | La Paz (Mecapaca) | Salmonella spp. | [69] | |||
| Brazil | Estuary | Ubicado en São Francisco do Conde | Salmonella spp. | [10] | ||
| Estuary | Ubicado en Valença | Salmonella spp. | [10] | |||
| Lake | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Ealing, Infantis, O:6,7, O:6,7:e,h:- | [92] | ||
| River | Arrudas | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Typhimurium | [72] | |
| River | Camboa Grande | Salmonella spp. | [93] | |||
| River | Jaguaribe | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Madelia, Panama, Saintpaul | [16] | |
| River | Jaguaribe | Salmonella enterica | houtenae | [16] | ||
| River | Onça | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Typhimurium | [72] | |
| River | São João | Salmonella spp. | [23] | |||
| Surface water * | Rio de Janeiro and Paraíba | Salmonella enterica | diarizonae | 35:r:z, 38:(k):z35, 50:r:z, 61:l,v:z, P:k:z35 | [78] | |
| Surface water * | Rio de Janeiro and Paraíba | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Abaetetuba, Adelaide, Agona, Albany, Anatum, Bovismorbificans, Braenderup, Brandenburg, Bulbay, Bullbay, Businga, Carrau, Cerro, Corvallis, Freetown, Gaminara, Grumpensis, Hadar, Heidelberg, Infantis, Inganda, Javiana, Jos, Kentucky, Kiambu, Lomita, Madelia, Mbandaka, Meleagridis, Miami, Michigan, Minnesota, Molade, Muenchen, Muenster, Newport, Ohio, Oran, Oranienburg, Oslo, Othmarschen, Panama, Pomona, Poona, Rhydyfelin, Rubislaw, Saintpaul, Sandiego, Santiago or Belem, Saphra, Schwarzengrund, Soerenga, Tucson, Typhimurium, Urbana | [78] | |
| Surface water * | Rio de Janeiro and Paraíba | Salmonella enterica | houtenae | [1],53:g,z51:-, 16:z4,z32:-, 18:m,t:-, 21:z4,z23:-, 38:g,z51:-, 43:z4,z23:-, 43:z4,z24:-, 45:g,z51:-, 48:g,z51:-, 50:z4,z23:-, 6,7:z4,z24:- | [78] | |
| Surface water * | Rio de Janeiro and Paraíba | Salmonella enterica | salamae | 42:r:- | [78] | |
| Chile | Channel | Zanjon de la Aguada | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Typhi | [81] |
| Municipality | Calera de Tango (rural) | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Mbandaka | [85] | |
| Municipality | Colina (urban) | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Montevideo | [85] | |
| Municipality | Isla Maipo (rural) | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Heidelberg, Infantis, Panama | [85] | |
| Municipality | Isla Maipo (rural) | Salmonella sp. Group C2 | [85] | |||
| Municipality | Isla Maipo (rural) | Salmonella sp. Group C3 | [85] | |||
| Municipality | La Florida (urban) | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Enteritidis | [85] | |
| Municipality | La Pintana (urban) | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Typhimurium | [85] | |
| Municipality | Maria Pinto (rural) | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Anatum, Mbandaka, Typhimurium | [85] | |
| Municipality | Melipilla (peri-urban) | Salmonella enterica | diarizonae | [85] | ||
| Municipality | Melipilla (peri-urban) | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Agona, Corvallis, Newport | [85] | |
| Municipality | Melipilla (rural) | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Corvallis, Enteritidis, Typhimurium | [85] | |
| Municipality | Paine (rural) | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Brandenburg, Santiago, Typhimurium | [85] | |
| Municipality | Paine (rural) | Salmonella sp. Group C4 | [85] | |||
| Municipality | Peñaflor (peri-urban) | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Infantis, Panama | [85] | |
| Municipality | Talagante (rural) | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Brandenburg, Senftenberg | [85] | |
| Municipality | Talagante (peri-urban) | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Enteritidis, Give, Livingstone, Typhimurium | [85] | |
| Municipality | Talagante (peri-urban) | Salmonella sp. Group C1 | [85] | |||
| River | Claro | Salmonella spp. | [83] | |||
| River | Lontue | Salmonella spp. | [83] | |||
| River | Maipo | Salmonella spp. | [83] | |||
| River | Mapocho | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Panama, Typhi | [14,81] | |
| River | Mapocho | Salmonella spp. | [83] | |||
| River | Mataquito | Salmonella spp. | [83] | |||
| River | Santiago | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Agona, Anatum, Bareilly, Bredeney, Derby, Enteritidis, Infantis, Livingstone, London, Oranieburg, Paratyphi B, Senftenberg, Thompson, Typhimurium | [9] | |
| River | Santiago | Salmonella sp. Group K | [9] | |||
| Surface water * | Maule and MR * | Salmonella enterica | diarizonae | 16:z10:e,n,x,z15, 18:i:z, 18:k:z, 18:z10:e,n,x,z15, 48:i:z, 50:r:z, 58:k:z, 61:i:z, 65:(k):z | [78] | |
| Surface water * | Maule and MR * | Salmonella enterica | enterica | Adelaide, Agona, Albany, Anatum, Bovismorbificans, Braenderup, Brandenburg, Cerro, Corvallis, Derby, Dublin, Edinburg, Enteritidis, Fresno, Give, Goldcoast, Hadar, Infantis, Javiana, Johannesburg, Kedougou, Kentucky, Livingstone, Manhattan, Mbandaka, Montevideo, Muenchen, Newport, Oranienburg, Panama, Paratyphi B, Rissen, Sandiego, Santiago or Belem, Schwarzengrund, Senftenberg, Soerenga, Stanley, Tennessee, Thompson, Typhimurium, Worthington | [78] | |
| Surface water * | Maule and MR * | Salmonella enterica | houtenae | 40:z4,z24:-, 43:z4,z23:-, R:z4,z24:- | [78] | |
| Colombia | Beach | Palmarito | Salmonella spp. | [87] | ||
| Beach | Puerto Colombia | Salmonella spp. | [87] | |||
| Beach | Salgar | Salmonella spp. | [87] | |||
| Beach | Santa Veronica | Salmonella spp. | [87] | |||
| River | Bogota | Salmonella spp. | [86] | |||
| Peru | Beach | La Chira | Salmonella spp. | [94] | ||
| River | Huatanay | Salmonella spp. | [17] | |||
| River | Surco | Salmonella spp. | [94] | |||
| Venezuela | Lagoon | Grande del Obispo | Salmonella spp. | [95] |
* Surface water refers to rivers, canals, streams, ponds, dams, and other similar bodies of water, as the specific type of water body was not precisely defined in the study. The abbreviation MR stands for Metropolitan Region.
3.3. Factors Influencing the Development of Salmonella in Water Bodies
Salmonella is a widely distributed pathogen in the environment, capable of proliferating in rivers, lakes, beaches, and other water bodies due to multiple factors. Key factors include climatic and environmental conditions, such as temperature and precipitation, along with the physicochemical properties of water, which can support bacterial survival. Human activities, particularly agricultural and urban practices, contribute contaminants through runoff, fecal waste, and untreated wastewater. Understanding how these factors influence the persistence and spread of Salmonella in aquatic environments is essential for developing effective monitoring and mitigation strategies to reduce public health risks.
3.3.1. Influence of Temperature on Salmonella Survival and Growth
Temperature is a critical factor for the proliferation of Salmonella in water bodies. Studies show a marked increase in Salmonella during warmer seasons, such as summer, when higher temperatures favor the survival and multiplication of pathogenic bacteria in surface waters [81,83]. Most Salmonella serotypes can grow within a temperature range of 5 °C to 47 °C, with an optimal range between 35 °C and 37 °C. However, growth is significantly reduced below 15 °C and is completely inhibited at temperatures below 7 °C [96]. Some strains can survive extreme temperatures, growing at as low as 2 °C and up to 54 °C [97,98,99].
Climate change is an additional factor contributing to the emergence of infectious diseases, including salmonellosis. Rising ambient temperatures correlate positively with the rise in gastrointestinal infections caused by Salmonella [100], as higher temperatures accelerate its reproduction and dissemination [12]. A linear relationship between salmonellosis rates and average temperatures over the previous week or month, with peaks occurring in summer [22]. An example of Salmonella growth capacity is observed in S. Typhimurium, whose generation time at 25 °C in enteral diets varies between 21 and 34.8 min, with a maximum growth rate (µmax) of 1.28 to 1.95 h−1 [101]. Under optimal conditions, the bacterial population can increase by 5 to 6 logarithmic cycles within 14 to 24 h [101].
3.3.2. Precipitation and Its Impact on Salmonella Dispersal
Precipitation plays a crucial role in the contamination of water bodies with Salmonella [102]. Heavy rainfall generates runoff that transports fecal matter and contaminated sediments from agricultural and urban areas into rivers, lakes, and beaches, increasing microbial loads in the water [103]. Studies have found that the influence of extreme weather events on the incidence of salmonellosis is not immediate [22]; instead, there is typically a delay of 2 to 4 weeks between a high precipitation event and an increase in reported cases [22,104,105].
Drought conditions can also favor Salmonella persistence in water bodies. Reduced flow and evaporation concentrate contaminants in stagnant waters, increasing exposure risks [106]. In temperate regions, variations in water temperature influence the hydrodynamic distribution of microorganisms [107]. During summer, lakes generally stratify, with warmer water at the surface, but heavy rainfall events can disrupt this stratification (destratification) and redistribute pathogens in the water [108,109].
3.3.3. Physicochemical Properties of Water and Salmonella Persistence
The physicochemical properties of water, such as pH, nutrient concentration, and dissolved oxygen levels, are key determinants in Salmonella survival [110,111,112]. This bacterium can grow within a pH range of 4 to 9, with an optimal pH between 6.5 and 7.5 [96]. Growth is favored in waters with moderate to high nutrient levels and warm temperatures [12]. Dissolved oxygen levels also influence Salmonella presence [110,111,112]. As a facultative anaerobe, Salmonella can survive in low-oxygen environments [113] and in waters with high organic matter content [114], where contaminated waste and sediments can act as reservoirs for the pathogen. In recreational water bodies such as beaches and lagoons, water quality can be compromised by factors like salinity and seasonal temperature variations [18].
3.3.4. Human Activities and Salmonella Contamination in Water
Agricultural, urban, and livestock practices are key sources of Salmonella contamination in water bodies [115]. The use of manure as fertilizer in agricultural areas and runoff from contaminated fields introduce pathogens into surface water. Additionally, Salmonella in manure can survive for up to 231 days [116], posing a significant risk to agricultural production if carried by rainwater.
In urban areas, untreated or inadequately treated wastewater discharge is a major source of contamination [117]. The presence of Salmonella has been reported in treated effluents, with concentrations reaching up to 2.7 × 102 CFU/100 mL [118,119]. Although modern wastewater treatment methods reduce bacterial loads, they do not completely eliminate Salmonella, posing a risk if treated water is reused for irrigation or discharged into surface waters [18].
Recreational activities also increase the risk of Salmonella transmission, as contact with contaminated water in beaches, lagoons, and rivers can be a source of infection [120]. Outbreaks of salmonellosis have been linked to the use of contaminated water in food production, such as papaya and cantaloupe [22], highlighting the importance of monitoring water quality in the food supply chain.
3.4. Isolation, Identification, and Serotyping of Salmonella
The isolation of Salmonella spp. from water samples was carried out using selective culture methodologies, enrichment, and biochemical and serological confirmation. In most of the studies analyzed, water samples were filtered using 0.45 µm membranes [23,66,67,68,69,87], although some studies employed alternative methods such as ultrafiltration or centrifugation at 4500 rpm [86], allowing for the concentration of the microorganism before the cultivation process.
For selective enrichment, specific broths such as Selenite-F [14,81], Rappaport-Vassiliadis (RV) [16,68,83], and Müller-Kauffmann Tetrathionate were used [16,66,83], incubated at temperatures between 35 and 42 °C [68,69,81,90] for 18–24 h [16,23,68,69,90]. Subsequently, the samples were plated on selective and differential media, with Xylose Lysine Deoxycholate (XLD) agar [17,85], Salmonella-Shigella (SS) [66,68,81,85,87], Brilliant Green [66,88,90,121], Bismuth Sulfite [67,88,90,121], and Hektoen Enteric [16,17,67,83] being the most used. Salmonella suspect colonies were characterized by black centers on differential media due to hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) production.
For the confirmation of isolates, standard biochemical tests were performed, including Triple Sugar Iron (TSI) [16,66,83,93] agar, Lysine Iron (LIA) [16,83,93], motility and indole test (SIM) [16,83], and the Indole, Methyl Red, Voges-Proskauer, and Citrate (IMViC) [67,93] series is commonly used for the identification of Enterobacteriaceae. Additionally, some studies implemented PCR for the invA gene as a complementary method for molecular identification [6,69,78,87].
Confirmed isolates were serotyped using the Kauffmann-White-Le Minor scheme [71,85] through agglutination tests with O and H antisera, enabling the identification of various serovars of public health importance, such as S. Typhimurium, S. Enteritidis, S. Panama, S. Anatum, and S. Newport. In some studies, serotyping was complemented with genotyping techniques such as Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis (PEFG) or Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) [78].
3.5. Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Salmonella
In addition to the identification of Salmonella serotype for understanding its epidemiological role, host specificity, and potential impact on public health, evaluating its antimicrobial susceptibility is critical, as water bodies can serve as reservoirs for antibiotic-resistant strains. The increasing prevalence of antimicrobial resistance among Salmonella isolates raises concerns about the role of contaminated water in the dissemination of resistant bacteria, which could compromise treatment options for both human and animal infections.
In the reviewed articles, antimicrobial resistance was primarily assessed using the disk diffusion method (Kirby-Bauer) [17,69], following the guidelines of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) [6,10,16,68,69,71,85,92]. The tested antibiotics covered multiple classes, including beta-lactams (ampicillin, ceftriaxone, cefotaxime) [6,10,14,16,17,67,68,69,71,83,85,92], quinolones (ciprofloxacin, nalidixic acid) [6,10,14,16,17,68,69,71,83,85,92], sulfonamides (trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole) [6,14,68,69,71,78,92], phenicols (chloramphenicol, florfenicol) [10,14,16,68,69,83], tetracyclines (tetracycline) [6,10,68,69,71,78,83,85], aminoglycosides (gentamicin) [14,16,83,92], nitrofuran derivatives (nitrofurantoin) [14,83], and polymyxins (colistin) [6,68,71]. Several of these antibiotics are used to treat both human and animal infections, such as chloramphenicol, florfenicol, gentamicin, ampicillin, and tetracycline [122,123], as well as colistin, an antibiotic of last resort for multi-resistant organisms (MDR) in humans [124], and florfenicol, which is used in aquaculture [125].
Results show that MDR isolates, defined as resistant to three or more antibiotic classes, are commonly found. Resistance to ampicillin, ceftriaxone, ciprofloxacin, chloramphenicol [6,10,14,16,17,67,68,69,71,83,85,92], and tetracycline [6,10,68,69,71,78,83,85] was the most frequently reported. However, resistance patterns varied across the reviewed studies, with some reporting higher resistance to beta-lactams and tetracyclines, while others described predominant resistance to quinolones and third-generation cephalosporins (Table S1).
4. Conclusions
The presence of Salmonella in water bodies across South America represents a significant challenge for both public health and the integrity of aquatic ecosystems. This pathogen is widely found in aquatic environments; its survival and proliferation are influenced by pollution, climate variability, and the physicochemical characteristics of water. Key contributing factors include the discharge of untreated wastewater, agricultural runoff, and elevated temperatures, which prolong Salmonella survival and facilitate its dissemination. Moreover, the rising incidence of multidrug-resistant strains underscores the urgency of addressing this issue from a comprehensive perspective.
The analysis of geographical distribution and predominant serovars in various countries highlights the diversity and complexity of contamination sources. Countries such as Argentina, Brazil, Chile, and Colombia exhibit specific patterns that reflect the interactions between anthropogenic activities, environmental conditions, and water management systems.
Among the most frequent serovars are S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium, which are widely associated with human and animal infections. In Argentina, S. Enteritidis predominates in irrigation systems and agricultural areas, while in Brazil, S. Typhimurium is prominent in aquaculture environments and wastewater. In Chile, S. Typhi and S. Panama have been identified in rivers used for irrigation and consumption, whereas in Colombia, contamination by Salmonella spp. in the Bogotá River and Atlantic beaches reflects the impact of untreated wastewater. Notably, the presence of less common serovars, such as Dublin, Paratyphi B, and those belonging to subspecies such as diarizonae and houtenae, demonstrates the influence of specific environmental and biological factors on the dynamics of this pathogen. This diversity of serovars, along with their adaptive capacity, emphasizes the need to implement more effective and continuous monitoring and control strategies.
The control of Salmonella in water bodies requires a comprehensive approach that combines prevention, monitoring, and mitigation strategies. At the preventive level, it is essential to improve wastewater treatment through advanced disinfection, regulate the use of antibiotics in livestock and aquaculture, and reduce agricultural runoff that can introduce resistant bacteria into water sources. The implementation of best practices in manure and fertilizer management, along with the protection of ecosystems such as wetlands and riparian forests, can also help limit the spread of Salmonella in the environment.
On the other hand, epidemiological surveillance and microbiological monitoring are key tools for early detection and rapid response to Salmonella outbreaks in water. The use of techniques such as real-time PCR and genomic sequencing allows for more precise identification of pathogenic strains and their antimicrobial resistance profiles. Additionally, public policies focused on water quality regulation, the application of the One Health approach, and improving access to sanitation in rural communities can significantly contribute to reducing the impact of Salmonella on public health and aquatic ecosystems.
Despite advances in understanding Salmonella contamination in South America, research and policy gaps remain. Long-term surveillance programs integrating climatic, hydrological, and microbiological data are needed to improve contamination predictions. At the policy level, stricter water quality regulations and enhanced transnational cooperation are essential for unified monitoring frameworks. The development of national groundwater monitoring networks in Argentina, Brazil, and Colombia provides a foundation for expanding standardized surveillance and contamination control. Strengthening policies on wastewater treatment and agricultural runoff management can further reduce Salmonella introduction into water systems.
Emerging technologies offer promising solutions for improving surveillance and outbreak detection. Early warning systems using remote sensing and machine learning could enhance real-time monitoring of water bodies, enabling faster responses. Additionally, whole genome sequencing (WGS) and metagenomics can provide valuable insights into Salmonella’s adaptability and resistance. Digital tools, such as web-based monitoring platforms and automated data processing systems, can improve data accessibility and analysis, ensuring a more proactive approach to contamination control.
Community-driven mitigation is also crucial. Public education on sanitation, food safety, and water conservation can help prevent infections, while citizen science programs involving local communities in water quality monitoring can enhance surveillance efforts. Strengthening clean water infrastructure, particularly in rural areas, is key to reducing waterborne disease risks.
Combining scientific research, policy development, and community action will be key to managing Salmonella contamination sustainably and protecting public health and aquatic ecosystems.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms13030489/s1, Table S1: Summary of Salmonella presence in South American water bodies. This table highlights the diversity of species and serovars, as well as their geographical distribution, including the number of confirmed Salmonella samples and the date of collection.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.S.A.P.; methodology, R.S.A.P. and M.S.G.R.; software, M.S.G.R.; writing—original draft preparation, R.S.A.P. and M.S.G.R.; writing—review and editing, R.S.A.P., M.S.G.R., F.F.M., S.A. and E.A.U.; visualization, M.S.G.R.; project administration, R.S.A.P. and E.A.U.; funding acquisition, R.S.A.P. and S.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Inter-American Institute for Global Change Research (IAI) Climate, Environment, and Health for the Americas. This work was supported by Agencia Nacional de Investigación y Desarrollo ANID/FONDAP CIGIDEN [Grant 1522A0005] and FONDECYT [Grant 1242022].
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| SC1 | Search Component 1 |
| SC2 | Search Component 2 |
| SC3 | Search Component 3 |
| RM | Metropolitan Region |
| MDR | multi-resistant organisms |
References
- Bănăduc, D.; Simić, V.; Cianfaglione, K.; Barinova, S.; Afanasyev, S.; Öktener, A.; McCall, G.; Simić, S.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A. Freshwater as a Sustainable Resource and Generator of Secondary Resources in the 21st Century: Stressors, Threats, Risks, Management and Protection Strategies, and Conservation Approaches. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musie, W.; Gonfa, G. Fresh Water Resource, Scarcity, Water Salinity Challenges and Possible Remedies: A Review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, J.G.; Mace, A.C., Jr. Effects of Recreation on Water Quality. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1974, 46, 2453–2459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boutraa, T. Improvement of Water Use Efficiency in Irrigated Agriculture: A Review. J. Agron. 2009, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, G.; Ennaanay, D.; Conte, M.; Walter, M.T.; Freyberg, D.; Wolny, S.; Hay, L.; White, S.; Nelson, E.; Solorzano, L. Water Supply as an Ecosystem Service for Hydropower and Irrigation. In Natural Capital; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 52–72. ISBN 9780199588992. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, S.M.; Barrios, M.E.; Galli, L.; Cammarata, R.V.; Torres, C.; Fortunato, M.S.; García López, G.; Costa, M.; Sanguino Jorquera, D.G.; Oderiz, S.; et al. Microbiological Hazard Identification in River Waters Used for Recreational Activities. Environ. Res. 2024, 247, 118161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Sarkar, A.; Hou, M.; Liu, W.; Guo, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhao, M. The Impacts of Urbanization to Improve Agriculture Water Use Efficiency—An Empirical Analysis Based on Spatial Perspective of Panel Data of 30 Provinces of China. Land 2022, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, N.; Yang, H.; Li, Y. Exploring the Relationship between Urbanization and Water Environment Based on Coupling Analysis in Nanjing, East China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 4654–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordano, A.M.; Virgilio, R. Relaciones Ecológicas de Salmonella En Chile. Bol. Oficina Sanit. Panam. 1976, 81, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Silveira, C.S.D.A.; Sousa, O.V.D.E.; Evangelista-Barreto, N.S. PROPAGATION OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANT Salmonella spp. IN BIVALVE MOLLUSKS FROM ESTUARY AREAS OF BAHIA, BRAZIL. Rev. Caatinga 2016, 29, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyedotun, T.D.T.; Ally, N. Environmental Issues and Challenges Confronting Surface Waters in South America: A Review. Environ. Chall. 2021, 3, 100049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billah, M.M.; Rahman, M.S. Salmonella in the Environment: A Review on Ecology, Antimicrobial Resistance, Seafood Contaminations, and Human Health Implications. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 13, 100407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, B.; Mawad, A.M.M.; Saleh, M.; Kelley, W.G.; Harrington, P.J., 2nd; Lovestad, C.W.; Amezcua, J.; Sarhan, M.M.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Ramadan, H.; et al. Salmonellosis: An Overview of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Innovative Approaches to Mitigate the Antimicrobial Resistant Infections. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordano, A.M.; Virgilio, R. Evolution of Drug Resistance in Salmonella Panama Isolates in Chile. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1996, 40, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Xiang, L.; Sze-Yin Leung, K.; Elsner, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Pan, B.; Sun, H.; An, T.; Ying, G.; et al. Emerging Contaminants: A One Health Perspective. Innovation 2024, 5, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, F.C.T.; Sousa, O.V.; Carvalho, E.M.R.; Hofer, E.; Vieira, R.H.S.F. Antibiotic Resistance of Salmonella spp. Isolated from Shrimp Farming Freshwater Environment in Northeast Region of Brazil. J. Pathog. 2013, 2013, 685193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo De Loayza, D.; Maldonado, T.; Vilca, I. Identification and Quantification of Antibiotic Residues and Evaluation of Microbial Resistance to Antibiotics in Huatanay River Waters in Peru. Pollution 2023, 9, 1236–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Whitehouse, C.A.; Li, B. Presence and Persistence of Salmonella in Water: The Impact on Microbial Quality of Water and Food Safety. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jewett, C.; Gilley, J.; Bartelt-Hunt, S.L.; Snow, D.D.; Hodges, L.; Li, X. Microbial Communities in the Rhizosphere and the Root of Lettuce as Affected by Salmonella-Contaminated Irrigation Water. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Guragain, M.; Chitlapilly Dass, S.; Palanisamy, V.; Bosilevac, J.M. Impact of Intense Sanitization on Environmental Biofilm Communities and the Survival of Salmonella Enterica at a Beef Processing Plant. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1338600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, S.; Nadal, L.; Álvarez, I.; Mañas, P.; Cebrián, G. Impact of the Resistance Responses to Stress Conditions Encountered in Food and Food Processing Environments on the Virulence and Growth Fitness of Non-Typhoidal Salmonellae. Foods 2021, 10, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, D.M.; Barnett, A.G. Effect of Temperature and Precipitation on Salmonellosis Cases in South-East Queensland, Australia: An Observational Study. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, A.-S. São João River’s Microbiological Profile, Region of the Iguaçu National Park—Preliminary Analysis. 2015. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/276293648_Sao_Joao_River’s_microbiological_profile_region_of_the_Iguacu_National_Park_-_Preliminary_analysis (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Ahmed, W.; Hamilton, K.; Toze, S.; Cook, S.; Page, D. A Review on Microbial Contaminants in Stormwater Runoff and Outfalls: Potential Health Risks and Mitigation Strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 1304–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alegbeleye, O.O.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Manure-Borne Pathogens as an Important Source of Water Contamination: An Update on the Dynamics of Pathogen Survival/transport as Well as Practical Risk Mitigation Strategies. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 227, 113524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, J.C.; Herbst, S.; Rechenburg, A.; Suk, J.E.; Höser, C.; Schreiber, C.; Kistemann, T. Climate Change Impact Assessment of Food- and Waterborne Diseases. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 857–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, C.; McKenzie, T.; Gaw, I.M.; Dean, J.M.; von Hammerstein, H.; Knudson, T.A.; Setter, R.O.; Smith, C.Z.; Webster, K.M.; Patz, J.A.; et al. Over Half of Known Human Pathogenic Diseases Can Be Aggravated by Climate Change. Nat. Clim. Change 2022, 12, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teklemariam, A.D.; Al-Hindi, R.R.; Albiheyri, R.S.; Alharbi, M.G.; Alghamdi, M.A.; Filimban, A.A.R.; Al Mutiri, A.S.; Al-Alyani, A.M.; Alseghayer, M.S.; Almaneea, A.M.; et al. Human Salmonellosis: A Continuous Global Threat in the Farm-to-Fork Food Safety Continuum. Foods 2023, 12, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, G.; Xia, P.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, C.; Meng, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhu, G. Fimbriae and Related Receptors for Salmonella Enteritidis. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 126, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessiani, A.; La Bella, G.; Donatiello, A.; Occhiochiuso, G.; Faleo, S.; Didonna, A.; D’Attoli, L.; Selicato, P.; Pedarra, C.; La Salandra, G.; et al. Occurrence of a New Variant of Salmonella Infantis Lacking Somatic Antigen. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fàbrega, A.; Vila, J. Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium Skills to Succeed in the Host: Virulence and Regulation. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 308–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-M.; Wang, Y.; Su, L.-H.; Chiu, C.-H. Nontyphoid Salmonella Infection: Microbiology, Clinical Features, and Antimicrobial Therapy. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2013, 54, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonough, P.L.; Fogelman, D.; Shin, S.J.; Brunner, M.A.; Lein, D.H. Salmonella Enterica Serotype Dublin Infection: An Emerging Infectious Disease for the Northeastern United States. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 2418–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorski, L.; Jay-Russell, M.T.; Liang, A.S.; Walker, S.; Bengson, Y.; Govoni, J.; Mandrell, R.E. Diversity of Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Pulsotypes, Serovars, and Antibiotic Resistance among Salmonella Isolates from Wild Amphibians and Reptiles in the California Central Coast. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, R.G.; Rosario, D.K.A.; Cunha-Neto, A.; Mano, S.B.; Figueiredo, E.E.S.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Worldwide Epidemiology of Salmonella Serovars in Animal-Based Foods: A Meta-Analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e00591-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omwandho, C.O.A.; Kubota, T. Salmonella Enterica Serovar Enteritidis: A Mini-Review of Contamination Routes and Limitations to Effective Control. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2010, 44, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabsch, W.; Andrews, H.L.; Kingsley, R.A.; Prager, R.; Tschäpe, H.; Adams, L.G.; Bäumler, A.J. Salmonella Enterica Serotype Typhimurium and Its Host-Adapted Variants. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 2249–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, L.; Garrett, S.; Sun, J. Salmonella Infection in Chronic Inflammation and Gastrointestinal Cancer. Diseases 2019, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbrugghe, E.; Van Parys, A.; Leyman, B.; Boyen, F.; Haesebrouck, F.; Pasmans, F. HtpG Contributes to Salmonella Typhimurium Intestinal Persistence in Pigs. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.T.; Gerner, R.R.; Nuccio, S.-P.; Raffatellu, M. Murine Models of Salmonella Infection. Curr. Protoc. 2023, 3, e824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, F.; Rajib, N.H.; Tonks, S.; Khalequzzaman, M.; Pollard, A.J.; Clemens, J.D.; Qadri, F.; STRATAA study team. Case Report: Salmonella Enterica Serovar Paratyphi B Infection in a Febrile Ill Child during Enhanced Passive Surveillance in an Urban Slum in Mirpur, Dhaka. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, J.A.; Sjölund-Karlsson, M.; Gordon, M.A.; Parry, C.M. Epidemiology, Clinical Presentation, Laboratory Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Antimicrobial Management of Invasive Salmonella Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 901–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, H.-L.; Wang, C.; Tang, L.; Wang, X.; Yu, K.-J.; Liu, S.-L. Non-Contiguous Finished Genome Sequence and Description of Salmonella Enterica Subsp. Houtenae Str. RKS3027. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2013, 8, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; McCann, A.; Litrup, E.; Murphy, R.; Cormican, M.; Fanning, S.; Brown, D.; Guttman, D.S.; Brisse, S.; Achtman, M. Neutral Genomic Microevolution of a Recently Emerged Pathogen, Salmonella Enterica Serovar Agona. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunn, L.; Finn, S.; Hurley, D.; Bai, L.; Wall, E.; Iversen, C.; Threlfall, J.E.; Fanning, S. Molecular Characterization of Salmonella Serovars Anatum and Ealing Associated with Two Historical Outbreaks, Linked to Contaminated Powdered Infant Formula. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, C.-S.; Lin, J.-M.; Chiu, C.-H.; Chu, C.-H.; Chen, S.-W.; Chang, Y.-F.; Weng, B.-C.; Tsay, J.-G.; Chen, C.-L.; Liu, C.-H.; et al. Clonal Dissemination of the Multi-Drug Resistant Salmonella Enterica Serovar Braenderup, but Not the Serovar Bareilly, of Prevalent Serogroup C1 Salmonella from Taiwan. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Aissa, R.; Al-Gallas, N. Molecular Typing of Salmonella Enterica Serovars Enteritidis, Corvallis, Anatum and Typhimurium from Food and Human Stool Samples in Tunisia, 2001–2004. Epidemiol. Infect. 2008, 136, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardin, F.; Mezger, N.; Hächler, H.; Bovier, P.A. Salmonella Serovar Give: An Unusual Pathogen Causing Splenic Abscess. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2006, 25, 272–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravena, C.; Valencia, B.; Villegas, A.; Ortega, M.; Fernández, R.A.; Araya, R.P.; Saavedra, A.; Del Campo, R. Caracterización de Cepas Clínicas Y Ambientales de Salmonella Enterica Subsp. Enterica Serovar Heidelberg Aisladas En Chile. Rev. Med. Chil. 2019, 147, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviv, G.; Cornelius, A.; Davidovich, M.; Cohen, H.; Suwandi, A.; Galeev, A.; Steck, N.; Azriel, S.; Rokney, A.; Valinsky, L.; et al. Differences in the Expression of SPI-1 Genes Pathogenicity and Epidemiology between the Emerging Salmonella Enterica Serovar Infantis and the Model Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, N.; Nolan, V.G.; Dunn, J.R.; Banerjee, P. Sources of Human Infection by Salmonella Enterica Serotype Javiana: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Lin, G.; Li, Y.; Lin, Q.; Lou, H.; Lin, M.; Hu, Y.; Xie, A.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; et al. Genomic Characterization of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Kentucky and London Recovered from Food and Human Salmonellosis in Zhejiang Province, China (2016-2021). Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 961739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canvas, M. Salmonella Manhattan (Salmonella enterica subsp. Enterica Serovar Manhattan). Available online: https://microbe-canvas.com/Bacteria/gram-negative-rods/facultative-anaerobic-3/catalase-negative-7/colistin-susceptible-2/salmonella-manhattan.html (accessed on 2 January 2025).
- Benevides, V.P.; Saraiva, M.M.S.; Nascimento, C.F.; Delgado-Suárez, E.J.; Oliveira, C.J.B.; Silva, S.R.; Miranda, V.F.O.; Christensen, H.; Olsen, J.E.; Berchieri Junior, A. Genomic Features and Phylogenetic Analysis of Antimicrobial-Resistant Salmonella Mbandaka ST413 Strains. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Li, C.; Hsu, C.-H.; Tyson, G.H.; Strain, E.; Tate, H.; Tran, T.-T.; Abbott, J.; McDermott, P.F. Comparative Genomic Analysis of 450 Strains of Salmonella Enterica Isolated from Diseased Animals. Genes 2020, 11, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugarel, M.; Cook, P.W.; den Bakker, H.C.; Harhay, D.; Nightingale, K.K.; Loneragan, G.H. Complete Genome Sequences of Four Salmonella Enterica Strains (including Those of Serotypes Montevideo, Mbandaka, and Lubbock) Isolated from Peripheral Lymph Nodes of Healthy Cattle. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e01450-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Ueda, A.; Tsukiji, J.; Sano, K.; Yamada, M.; Ishigatsubo, Y. Salmonella Enterica Serovar Ohio Septic Arthritis and Bone Abscess in an Immunocompetent Patient: A Case Report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2012, 6, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, H.; Watarai, M.; Shirahata, T.; Makino, S.-I. Viable but Nonculturable Salmonella Species Recovery and Systemic Infection in Morphine-Treated Mice. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 186, 1526–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Ni, J.; Guo, J.; Yao, Y.-F.; Wu, W. Whole-Genome Comparative and Pathogenicity Analysis of Salmonella Enterica Subsp. Enterica Serovar Rissen. G3 2020, 10, 2159–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Alonso, J.; Lercari, D.; Defeo, O. Río de La Plata: A Neotropical Estuarine System. In Coasts and Estuaries; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 45–56. ISBN 9780128140031. [Google Scholar]
- Basualdo, J.; Pezzani, B.; De Luca, M.; Córdoba, A.; Apezteguía, M. Screening of the Municipal Water System of La Plata, Argentina, for Human Intestinal Parasites. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2000, 203, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, O.C.F.; Duverne, L.B.; Mazieres, J.O.; Salibián, A. Microbiological Pollution of Surface Water in the Upper-Middle Basin of the Reconquista River (Argentina): 2010-2011 Monitoring. Int. J. Environ. Health 2013, 6, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmo, R.J.; Barrios, H.A. Nuevos Perfiles Genéticos de Salmonella Enteritidis Identificados En Luján, Argentina. CIT Inform. Tecnol. 2012, 23, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fegan, N.; McAuley, C.M.; Gray, J.A.; Duffy, L.L.; Namvar, A.; Warriner, K. Current Trends in Zoonoses and Foodborne Pathogens Linked to the Consumption of Meat. In New Aspects of Meat Quality; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 717–754. ISBN 9780323858793. [Google Scholar]
- Pastor, A.; Varela, P.; Bianchi, V.; Durando, P. CALIDAD BACTERIOLÓGICA DEL AGUA DEL RÍO SAN JUAN EN ZONAS ALEDAÑAS A LA DESEMBOCADURA DEL ARROYO LOS TAPONES (SAN JUAN, ARGENTINA). Nat. Neotrop. 2015, 1, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Streitenberger, M.E.; Baldini, M.D. APORTE DE LOS AFLUENTES A LA CONTAMINACIÓN FECAL DEL ESTUARIO DE BAHÍA BLANCA, ARGENTINA. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2016, 32, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, L.A.; Tracogna, M.F.; Lösch, L.S.; Alonso, J.M. Detection and Characterization of Salmonella spp. in Recreational Aquatic Environments in the Northeast of Argentina. Ambiente Agua—Interdiscip. J. Appl. Sci. 2013, 8, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Poma, V.; Mamani, N.; Iñiguez, V. Impact of Urban Contamination of the La Paz River Basin on Thermotolerant Coliform Density and Occurrence of Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens in River Water, Irrigated Soil and Fresh Vegetables. Springerplus 2016, 5, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginn, O.; Nichols, D.; Rocha-Melogno, L.; Bivins, A.; Berendes, D.; Soria, F.; Andrade, M.; Deshusses, M.A.; Bergin, M.; Brown, J. Antimicrobial Resistance Genes Are Enriched in Aerosols near Impacted Urban Surface Waters in La Paz, Bolivia. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman-Otazo, J.; Gonzales-Siles, L.; Poma, V.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Thorell, K.; Flach, C.-F.; Iñiguez, V.; Sjöling, Å. Diarrheal Bacterial Pathogens and Multi-Resistant Enterobacteria in the Choqueyapu River in La Paz, Bolivia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, Y.X.; Souza, E.; Ferreira, M.D.D. Drug Resistance and Colicinogeny of Salmonella Typhimurium Strains Isolated from Sewage-Contamined Surface Water and Humans in Belo Horizonte. Brazil. Rev. Microbiol. 1989, 20, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Mahagamage, M.G.Y.L.; Pathirage, M.V.S.C.; Manage, P.M. Contamination Status of Salmonella spp., Shigella spp. and Campylobacter spp. in Surface and Groundwater of the Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka. Water 2020, 12, 2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kich, J.D.; Schwarz, P.; Eduardo Silva, L.; Coldebella, A.; Piffer, I.A.; Vizzoto, R.; Ribeiro de Itapema Cardoso, M. Development and Application of an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay to Detect Antibodies against Prevalent Salmonella Serovars in Swine in Southern Brazil. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2007, 19, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.S.; Medeiros, L.M.; Costa, R.G.; Festivo, M.L.; dos Reis, E.M.F.; Seki, L.M.; Rodrigues, D. Phage Typing and Multidrug Resistance Profile in S. Typhimurium Isolated from Different Sources in Brazil from 1999 to 2004. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2007, 38, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kich, J.D.; Coldebella, A.; Morés, N.; Nogueira, M.G.; Cardoso, M.; Fratamico, P.M.; Call, J.E.; Fedorka-Cray, P.; Luchansky, J.B. Prevalence, Distribution, and Molecular Characterization of Salmonella Recovered from Swine Finishing Herds and a Slaughter Facility in Santa Catarina, Brazil. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 151, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palhares, J.C.P.; Kich, J.D.; Bessa, M.C.; Biesus, L.L.; Berno, L.G.; Triques, N.J. Salmonella and Antimicrobial Resistance in an Animal-Based Agriculture River System. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Moreno-Switt, A.I.; Reyes-Jara, A.; Delgado Suarez, E.; Adell, A.D.; Oliveira, C.J.B.; Bonelli, R.R.; Huang, X.; Brown, E.; Allard, M.; et al. A Multicenter Genomic Epidemiological Investigation in Brazil, Chile, and Mexico Reveals the Diversity and Persistence of Salmonella Populations in Surface Waters. MBio 2024, 15, e0077724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda-Ruelas, G.M.; Burgeño-Román, A.; Jiménez-Edeza, M. Genetics and Physiology of Salmonella Houtenae Isolated from a River in Mexico Provides Insight into the Aquatic Habitat Influence on Its Adaptation and Pathogenesis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 83, 104326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandry, P.S.; Gladman, S.; Moore, S.C.; Seemann, T.; Crandall, K.A.; Fegan, N. A Genomic Island in Salmonella Enterica Ssp. Salamae Provides New Insights on the Genealogy of the Locus of Enterocyte Effacement. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, S.D.; Ferreccio, C.; Levine, M.M.; Cordano, A.M.; Monreal, J.; Black, R.E.; D’Ottone, K.; Rowe, B. The Use of Moore Swabs for Isolation of Salmonella Typhi from Irrigation Water in Santiago, Chile. J. Infect. Dis. 1984, 149, 640–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa Garza, J.A.; Gómez Urquijo, M.; Paredes Figueroa, M.G. The Integral Management of the Wastewater Treatment Sector in Mexico Using a Circular Economy Approach. Recycling 2024, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, M.; Weller, D.; Ramos, R.; Diaz, L.; Alvarez, F.P.; Reyes-Jara, A.; Moreno-Switt, A.I.; Meng, J.; Adell, A.D. Environmental and Anthropogenic Factors Associated with the Likelihood of Detecting Salmonella in Agricultural Watersheds. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgias, S.; Bauer, C.J. Trajectory of a Divided River Basin: Law, Conflict, and Cooperation along Chile’s Maipo River. Water Policy 2018, 20, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.C.; Retamal, P.; Rojas-Aedo, J.F.; Fernández, J.; Fernández, A.; Lapierre, L. Multidrug-Resistant Outbreak-Associated Salmonella Strains in Irrigation Water from the Metropolitan Region, Chile. Zoonoses Public Health 2017, 64, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao-Herreño, L.X.; López-Tamayo, A.M.; Ramos-Bonilla, J.P.; Haas, C.N.; Husserl, J. Risk of Illness with Salmonella due to Consumption of Raw Unwashed Vegetables Irrigated with Water from the Bogotá River. Risk Anal. 2017, 37, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Varela, Z.E.; Rosado-Porto, D.; Bolívar-Anillo, H.J.; Pichón González, C.; Granados Pantoja, B.; Estrada Alvarado, D.; Anfuso, G. Preliminary Microbiological Coastal Water Quality Determination along the Department of Atlántico (Colombia): Relationships with Beach Characteristics. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmo, R.J.; Viora, S.; Barrios, H.; Terragno, R.; Alcaín, A.; Caffer, M.I. Serotypes of Salmonella isolated from the Luján river, Argentina. Rev. Latinoam. Microbiol. 1999, 41, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cortínez, I.D.; Velázquez, L.D.; Escudero, M.E.; Caffer, M.I.; Cobo, M.F.; Guzmán, A.D. Salmonella serotypes from surface waters in san luis, Argentina. Rev. Microbiol. 1995, 26, 180–185. [Google Scholar]
- Benassi, F.O.; Vázquez, M.; Eiguer, F. Salmonella: Su Incidencia En Aguas Del Arroyo Zaimán [Salmonella: Its Incidence in Waters of the Zaimán Arroyo. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 1983, 15, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohno, A.; Marui, A.; Castro, E.S.; Reyes, A.A.; Elio-Calvo, D.; Kasitani, H.; Ishii, Y.; Yamaguchi, K. Enteropathogenic Bacteria in the La Paz River of Bolivia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 57, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, F.E.L.; da Silva Dantas, F.G.; Grisolia, A.B.; Crispim, B.d.A.; Oliveira, K.M.P. Identification of Class 1 and 2 Integrons from Clinical and Environmental Salmonella Isolates. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2014, 8, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima Grisi, T.C.S.; Gorlach-Lira, K. The Abundance of Some Pathogenic Bacteria in Mangrove Habitats of Paraiba Do Norte Estuary and Crabmeat Contamination of Mangrove Crab Ucides Cordatus. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2010, 53, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plenge, O.; Fernando, R.; Reyes, J.; Carlos, R. Presencia de Bacterias Patógenas En Las Aguas de La Desembocadura Del Río Surco Y La Playa La Chira; Junio: Lima, Perú, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- González, M.; Crucita, B.; Vásquez-Suárez, A. Calidad Microbiológica de La Ostra Crassostrea Rhizophorae Y Aguas de Extracción, Estado Sucre, Venezuela. Rev. Científica 2009, 19, 659–666. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez Pedraza, J.; Pereira Sanandres, N.; Soto Varela, Z.; Hernández Aguirre, E.; Villarreal Camacho, J. Aislamiento Microbiológico de Salmonella spp. Y Herramientas Moleculares Para Su Detección. Salud Uninorte 2014, 30, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychlik, I.; Barrow, P.A. Salmonella Stress Management and Its Relevance to Behaviour during Intestinal Colonisation and Infection. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 1021–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andino, A.; Hanning, I. Salmonella Enterica: Survival, Colonization, and Virulence Differences among Serovars. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 520179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elpers, L.; Deiwick, J.; Hensel, M. Effect of Environmental Temperatures on Proteome Composition of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2022, 21, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akil, L.; Ahmad, H.A.; Reddy, R.S. Effects of Climate Change on Salmonella Infections. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2014, 11, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.R.; Moraes, C.A.; Bessan, J.; Vanetti, M.C.D. Validation of a Predictive Model Describing Growth of Salmonella in Enteral Feeds. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2009, 40, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.L.; Kase, J.A.; Harrison, L.M.; Balan, K.V.; Babu, U.; Chen, Y.; Macarisin, D.; Kwon, H.J.; Zheng, J.; Stevens, E.L.; et al. The Persistence of Bacterial Pathogens in Surface Water and Its Impact on Global Food Safety. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aström, J.; Petterson, S.; Bergstedt, O.; Pettersson, T.J.R.; Stenström, T.A. Evaluation of the Microbial Risk Reduction due to Selective Closure of the Raw Water Intake before Drinking Water Treatment. J. Water Health 2007, 5 (Suppl. S1), 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, R.M.; Becker, N.G.; Hall, G.; Moodie, K.B.A. Does Ambient Temperature Affect Foodborne Disease? Epidemiology 2004, 15, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Bi, P.; Hiller, J.E. Climate Variations and Salmonella Infection in Australian Subtropical and Tropical Regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, D.A.; Masoud, H.A.; Hamad, A. Climate Changes and Food-Borne Pathogens: The Impact on Human Health and Mitigation Strategy. Clim. Change 2024, 177, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, A.-V.; Le Cann, P.; Roig, B.; Thomas, O.; Baurès, E.; Thomas, M.-F. Microbial Contamination Detection in Water Resources: Interest of Current Optical Methods, Trends and Needs in the Context of Climate Change. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 4292–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brookes, J.D.; Hipsey, M.R.; Burch, M.D.; Regel, R.H.; Linden, L.G.; Ferguson, C.M.; Antenucci, J.P. Relative Value of Surrogate Indicators for Detecting Pathogens in Lakes and Reservoirs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8614–8621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyer, M.D.; Kay, D.; Watkins, J.; Davies, C.; Kay, C.; Thomas, R.; Porter, J.; Stapleton, C.M.; Moore, H. Evaluating Short-Term Changes in Recreational Water Quality during a Hydrograph Event Using a Combination of Microbial Tracers, Environmental Microbiology, Microbial Source Tracking and Hydrological Techniques: A Case Study in Southwest Wales, UK. Water Res. 2010, 44, 4783–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, M.; Odumeru, J. Irrigation Water as Source of Foodborne Pathogens on Fruit and Vegetables. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 2839–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, G.; Edge, T.A.; Gannon, V.P.J.; Jokinen, C.; Lyautey, E.; Neumann, N.F.; Ruecker, N.; Scott, A.; Sunohara, M.; Topp, E.; et al. Associations among Pathogenic Bacteria, Parasites, and Environmental and Land Use Factors in Multiple Mixed-Use Watersheds. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5807–5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanjugi, P.; Harwood, V.J. The Influence of Predation and Competition on the Survival of Commensal and Pathogenic Fecal Bacteria in Aquatic Habitats: Biotic Stressors Affect FIB and Pathogen Survival. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzymajło, K.; Dutkiewicz, A.; Czajkowska, J.; Carolak, E.; Aleksandrowicz, A.; Waszczuk, W. Salmonella Adhesion Is Decreased by Hypoxia due to Adhesion and Motility Structure Crosstalk. Vet. Res. 2023, 54, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.O.; Cavalcante, C.B.; Nunes, N.B.; Neto, A.C.; Machado, M.A.M.; Porto, Y.D.; Castro, V.S.; Figueiredo, E.E.d.S. Influence of Organic Matter from Native Fish on the Antimicrobial Efficacy of Sodium Hypochlorite (NaClO) in Reducing Salmonella spp. Population. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 15, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, T.A.; Topp, E. Role of Livestock in Microbiological Contamination of Water: Commonly the Blame, but Not Always the Source. Anim. Front. 2012, 2, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Morgan, J.; Doyle, M.P.; Phatak, S.C.; Millner, P.; Jiang, X. Fate of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium on Carrots and Radishes Grown in Fields Treated with Contaminated Manure Composts or Irrigation Water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 2497–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Poonia, T.; Siwal, S.S.; Srivastav, A.L.; Sharma, H.K.; Mittal, S.K. Challenges of Water Contamination in Urban Areas. In Urban Water Crisis and Management—Strategies for Sustainable Development; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 173–202. ISBN 9780323918381. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, J.B.; Huffman, D.E.; Riley, K.; Farrah, S.R.; Lukasik, J.O.; Hamann, C.L. Reduction of Enteric Microorganisms at the Upper Occoquan Sewage Authority Water Reclamation Plant. Water Environ. Res. 2001, 73, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, I.; Espigares, E.; Lardelli, P.; Martín, J.L.; Espigares, M. Evaluation of Microbiological and Physicochemical Indicators for Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Toxicol. 2004, 19, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stec, J.; Kosikowska, U.; Mendrycka, M.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Niedźwiedzka-Rystwej, P.; Bębnowska, D.; Hrynkiewicz, R.; Ziętara-Wysocka, J.; Grywalska, E. Opportunistic Pathogens of Recreational Waters with Emphasis on Antimicrobial Resistance-A Possible Subject of Human Health Concern. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benassi, F.O.; Martínez Vázquez, F.; Eiguer, T.; Bendersky, S.; Martos, M.A. Isolation of new serovars of Salmonella in streams of water. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 1985, 17, 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- Schmerold, I.; van Geijlswijk, I.; Gehring, R. European Regulations on the Use of Antibiotics in Veterinary Medicine. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 189, 106473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, R.; Mochel, J.P.; Schmerold, I. Understanding the Background and Clinical Significance of the WHO, WOAH, and EMA Classifications of Antimicrobials to Mitigate Antimicrobial Resistance. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1153048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Zeng, X.; Li, Y.; Dong, N. Valnemulin Restores Colistin Sensitivity against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Pathogens. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chen, H.; Tong, Y.; Wu, X.; Tang, C.; Qin, X.; Guo, J.; Li, P.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; et al. A Review on the Antibiotic Florfenicol: Occurrence, Environmental Fate, Effects, and Health Risks. Environ. Res. 2024, 244, 117934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).